Acute Exposure to Zearalenone Disturbs Intestinal Homeostasis by Modulating the Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Effect of Zearalenone on ER Abundance
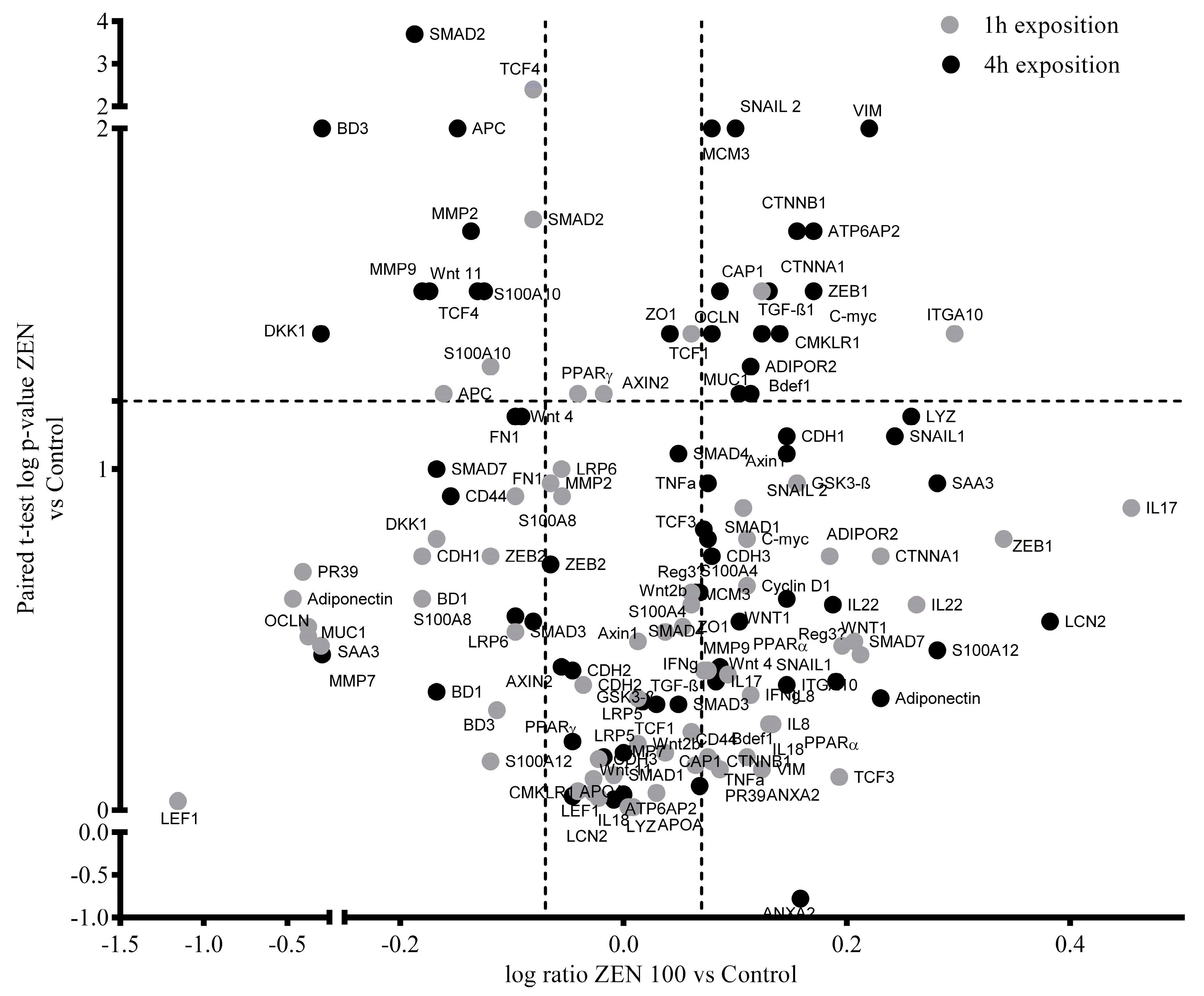
2.2. Effect of ZEN on the Wnt/β-catenin Signaling Pathway
2.3. Effect of ZEN on the TGF-β-catenin Signaling Pathway
2.4. Effect of Zearalenone on Cytokine, Inflammatory Markers, and Adipokine Expression
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Toxin
5.2. Animals and Culture of Pig Jejunal Explants
5.3. RNA Extraction and Real-time Quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR)
5.4. Protein Extraction and Western Blot
5.5. Gelatin Zymography
5.6. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zinedine, A.; Soriano, J.M.; Moltó, J.C.; Mañes, J. Review on the toxicity, occurrence, metabolism, detoxification, regulations and intake of zearalenone: An oestrogenic mycotoxin. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2007, 45, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalska, K.; Habrowska-Górczyńska, D.E.; Piastowska-Ciesielska, A.W. Zearalenone as an endocrine disruptor in humans. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2016, 48, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Wang, B.; Li, X.; Wang, T.; Zou, H.; Gu, J.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, X.; Bai, J.; Bian, J.; et al. Zearalenone promotes cell proliferation or causes cell death? Toxins (Basel) 2018, 10, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazzah, A.C.; El Golli Bennour, E.; Bouaziz, C.; Abid, S.; Ladjimi, M.; Bacha, H. Sequential events of apoptosis induced by zearalenone in cultured hepatocarcinoma cells. Mycotoxin Res. 2010, 26, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.Y.; Zheng, Z.H.; Son, Y.O.; Shi, X.; Jang, Y.O.; Lee, J.C. Mycotoxin zearalenone induces AIF- and ROS-mediated cell death through p53- and MAPK-dependent signaling pathways in RAW264.7 macrophages. Toxicol. In Vitro 2011, 25, 1654–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, W.; Shen, T.; Ding, Q.; Lv, Y.; Li, L.; Huang, K.; Yan, L.; Song, S. Zearalenone induces ROS-mediated mitochondrial damage in porcine IPEC-J2 cells. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2017, 31, e21944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, W.; Huang, Q.; Pan, S.; Fan, W.; Wang, G.; Yuan, Y.; Gu, J.; Liu, X.; Liu, Z.; Bian, J. Regulation of oncogenes and gap junction intercellular communication during the proliferative response of zearalenone in TM3 cells. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2017, 36, 701–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Gao, R.; Meng, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Bi, C.; Shan, A. Toxic effects of maternal zearalenone exposure on intestinal oxidative stress, barrier function, immunological and morphological changes in rats. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e106412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Lv, Y.; Ren, S.; Shao, M.; Shen, T.; Huang, K.; Zhou, J.; Yan, L.; Song, S. Zearalenone (ZEA)-induced intestinal inflammation is mediated by the NLRP3 inflammasome. Chemosphere 2018, 190, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, D.E.; Taranu, I.; Burlacu, R.; Tudor, D.S. Effects of zearalenone and its derivatives on the innate immune response of swine. Toxicon 2010, 56, 956–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, D.E.; Pistol, G.C.; Neagoe, I.V.; Calin, L.; Taranu, I. Effects of zearalenone on oxidative stress and inflammation in weanling piglets. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 58, 408–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braicu, C.; Cojocneanu-Petric, R.; Jurj, A.; Gulei, D.; Taranu, I.; Gras, A.M.; Marin, D.E.; Berindan-Neagoe, I. Microarray based gene expression analysis of Sus Scrofa duodenum exposed to zearalenone: Significance to human health. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metzler, M.; Pfeiffer, E.; Hildebrand, A.A. Zearalenone and its metabolites as endocrine disrupting chemicals. World Mycotoxin J. 2010, 3, 385–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belli, P.; Bellaton, C.; Durand, J.; Balleydier, S.; Milhau, N.; Mure, M.; Mornex, J.-F.; Benahmed, M.; Le Jan, C. Fetal and neonatal exposure to the mycotoxin zearalenone induces phenotypic alterations in adult rat mammary gland. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2010, 48, 2818–2826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuiper, G.G.J.M.; Enmark, E.; Pelto-Huikko, M.; Nilsson, S.; Gustafsson, J.Å. Cloning of a novel estrogen receptor expressed in rat prostate and ovary. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 5925–5930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosselman, S.; Polman, J.; Dijkema, R. ERβ: Identification and characterization of a novel human estrogen receptor. FEBS Lett. 1996, 392, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paech, K.; Webb, P.; Kuiper, G.G.J.M.; Nilsson, S.; Gustafsson, J.Å.; Kushner, P.J.; Scanlan, T.S. Differential ligand activation of estrogen receptors ERα and ERrβ at AP1 sites. Science (80) 1997, 277, 1508–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paterni, I.; Granchi, C.; Katzenellenbogen, J.A.; Minutolo, F. Estrogen receptors alpha (ERα) and beta (ERβ): Subtype-selective ligands and clinical potential. Steroids 2014, 90, 13–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fink-Gremmels, J.; Malekinejad, H. Clinical effects and biochemical mechanisms associated with exposure to the mycoestrogen zearalenone. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2007, 137, 326–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böttner, M.; Thelen, P.; Jarry, H. Estrogen receptor beta: Tissue distribution and the still largely enigmatic physiological function. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2014, 139, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasson, R.M.; Briggs, A.; Carothers, A.M.; Davids, J.S.; Wang, J.; Javid, S.H.; Cho, N.L.; Bertagnolli, M.M. Estrogen receptor α or β loss in the colon of Min/+ mice promotes crypt expansion and impairs TGFβ and HNF3β signaling. Carcinogenesis 2014, 35, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, N.L.; Javid, S.H.; Carothers, A.M.; Redston, M.; Bertagnolli, M.M. Estrogen receptors alpha and beta are inhibitory modifiers of Apc-dependent tumorigenesis in the proximal colon of Min/+ mice. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 2366–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Huang, E.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J.; Wu, N.; Chen, X.; Wang, N.; Wen, S.; Nan, G.; Deng, F.; et al. Crosstalk between Wnt/β-catenin and estrogen receptor signaling synergistically promotes osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal progenitor cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e82436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, T.; Yamamoto, T.; Muraguchi, A.; Saatcioglu, F. Cross-talk between Transforming Growth Factor-β and Estrogen Receptor Signaling through Smad3. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 42908–42914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filardo, E.J.; Quinn, J.A.; Bland, K.I.; Frackelton, J. Estrogen-induced activation of Erk-1 and Erk-2 requires the G protein-coupled receptor homolog, GPR30, and occurs via trans-activation of the epidermal growth factor receptor through release of HB-EGF. Mol. Endocrinol. 2000, 14, 1649–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuiper-Goodman, T.; Scott, P.M.; Watanabe, H. Risk assessment of the mycotoxin zearalenone. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 1987, 7, 253–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binder, S.B.; Schwartz-Zimmermann, H.E.; Varga, E.; Bichl, G.; Michlmayr, H.; Adam, G.; Berthiller, F. Metabolism of zearalenone and its major modified forms in pigs. Toxins (Basel) 2017, 9, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obremski, K.; Gajecka, M.; Zielonka, L.; Jakimiuk, E.; Gajecki, M. Morphology and ultrastructure of small intestine mucosa in gilts with zearalenone mycotoxicosis. Pol. J. Vet. Sci. 2005, 8, 301–307. [Google Scholar]
- Przybylska-Gornowicz, B.; Lewczuk, B.; Prusik, M.; Hanuszewska, M.; Petrusewicz-Kosińska, M.; Gajęcka, M.; Zielonka, Ł.; Gajęcki, M. The effects of deoxynivalenol and zearalenone on the pig large intestine. A light and electron microscopy study. Toxins (Basel) 2018, 10, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taranu, I.; Braicu, C.; Marin, D.E.; Pistol, G.C.; Motiu, M.; Balacescu, L.; Beridan Neagoe, I.; Burlacu, R. Exposure to zearalenone mycotoxin alters in vitro porcine intestinal epithelial cells by differential gene expression. Toxicol. Lett. 2015, 232, 310–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.-J.; Zhou, M.; Huang, L.-B.; Yang, W.-R.; Yang, Z.-B.; Jiang, S.-Z.; Ge, J.-S. Zearalenone-Promoted Follicle Growth through Modulation of Wnt-1/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway and Expression of Estrogen Receptor Genes in Ovaries of Postweaning Piglets. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 7899–7906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalska, K.; Habrowska-Górczyńska, D.E.; Urbanek, K.A.; Domińska, K.; Piastowska-Ciesielska, A.W. Estrogen receptor α is crucial in zearalenone-induced invasion and migration of prostate cancer cells. Toxins (Basel) 2018, 10, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spit, M.; Koo, B.K.; Maurice, M.M. Tales from the crypt: Intestinal niche signals in tissue renewal, plasticity and cancer. Open Biol. 2018, 8, 180120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregorieff, A.; Clevers, H. Wnt signaling in the intestinal epithelium: From endoderm to cancer. Genes Dev. 2005, 19, 877–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sihn, G.; Rousselle, A.; Vilianovitch, L.; Burckle, C.; Bader, M. Physiology of the (pro)renin receptor: Wnt of change. Kidney Int. 2010, 78, 246–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.K.; Kwon, Y.; Jang, M.; Park, M.; Kim, J.; Cho, S.; Jang, D.G.; Lee, W.B.; Jung, S.H.; Choi, H.J.; et al. β-catenin activation down-regulates cell-cell junction-related genes and induces epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in colorectal cancers. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 18440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Es, J.H.; Jay, P.; Gregorieff, A.; van Gijn, M.E.; Jonkheer, S.; Hatzis, P.; Thiele, A.; van den Born, M.; Begthel, H.; Brabletz, T.; et al. Wnt signalling induces maturation of Paneth cells in intestinal crypts. Nat. Cell Biol. 2005, 7, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farin, H.F.; Van Es, J.H.; Clevers, H. Redundant sources of Wnt regulate intestinal stem cells and promote formation of paneth cells. Gastroenterology 2012, 143, 1518–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derynck, R.; Feng, X.H. TGF-β receptor signaling. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 1997, 1333, F105–F150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, B.; Huang, K.; He, X.; Luo, Y.B.; Liang, R.; Luo, H.; Shen, X.L.; Xua, W. Mitochondrial proteomic analysis reveals the molecular mechanisms underlying reproductive toxicity of zearalenone in MLTC-1 cells. Toxicology 2014, 324, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, L.M.; Moeser, A.J.; Blikslager, A.T. Porcine models of digestive disease: The future of large animal translational research. Transl. Res. 2015, 166, 12–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabilloud, T.; Lescuyer, P. Proteomics in mechanistic toxicology: History, concepts, achievements, caveats, and potential. Proteomics 2015, 15, 1051–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennig-Pauka, I.; Koch, F.-J.; Schaumberger, S.; Woechtl, B.; Novak, J.; Sulyok, M.; Nagl, V. Current challenges in the diagnosis of zearalenone toxicosis as illustrated by a field case of hyperestrogenism in suckling piglets. Porcine Health Manag. 2018, 4, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, J.M.; Brummer, R.J.; Derrien, M.; MacDonald, T.T.; Troost, F.; Cani, P.D.; Theodorou, V.; Dekker, J.; Méheust, A.; De Vos, W.M.; et al. Homeostasis of the gut barrier and potential biomarkers. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2017, 312, G171–G193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrckulak, D.; Janeckova, L.; Lanikova, L.; Kriz, V.; Horazna, M.; Babosova, O.; Vojtechova, M.; Galuskova, K.; Sloncova, E.; Korinek, V. Wnt effector TCF4 is dispensable for Wnt signaling in human cancer cells. Genes (Basel) 2018, 9, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.R.; Zhu, L.Q.; Wang, S.H.; Liu, X.A.; Tian, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Q.; Wang, J.Z. 17β-estradiol attenuates glycogen synthase kinase-3β activation and tau hyperphosphorylation in Akt-independent manner. J. Neural Transm. 2008, 115, 879–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.-L.; Song, J.-L.; Ji, C.-L.; Feng, Y.-L.; Yu, J.; Nyachoti, C.M.; Yang, G.-S. Zearalenone Exposure Enhanced the Expression of Tumorigenesis Genes in Donkey Granulosa Cells via the PTEN/PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway. Front. Genet. 2018, 9, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.J.; Zheng, W.L.; Feng, N.N.; Wang, T.; Zou, H.; Gu, J.H.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, X.Z.; Liu, Z.P.; Bian, J.C. The effects of autophagy and PI3K/AKT/m-TOR signaling pathway on the cell-cycle arrest of rats primary sertoli cells induced by zearalenone. Toxins (Basel) 2018, 10, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Wu, W.; Li, L.; He, J.; Huang, S.; Chen, S.; Chen, J.; Long, M.; Yang, S.; Li, P. Analysis of the miRNA Expression Profiles in the Zearalenone-Exposed TM3 Leydig Cell Line. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Railo, A.; Nagy, I.I.; Kilpeläinen, P.; Vainio, S. Wnt-11 signaling leads to down-regulation of the Wnt/β-catenin, JNK/AP-1 and NF-κB pathways and promotes viability in the CHO-K1 cells. Exp. Cell Res. 2008, 314, 2389–2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, L.; Mok, T.S.K.; Tao, Q. 8P Noncanonical Wnt11, a tumor suppressive gene by antagonizing canonical Wnt signaling, represents a putative molecularly therapeutic target in lung cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, S4–S5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankaran-Walters, S.; Hart, R.; Dills, C. Guardians of the gut: Enteric defensins. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, S.K.; McCormick, T.S.; Weinberg, A. Human beta defensins and cancer: Contradictions and common ground. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uraki, S.; Sugimoto, K.; Shiraki, K.; Tameda, M.; Inagaki, Y.; Ogura, S.; Kasai, C.; Nojiri, K.; Yoneda, M.; Yamamoto, N.; et al. Human β-defensin-3 inhibits migration of colon cancer cells via downregulation of metastasis-associated 1 family, member 2 expression. Int. J. Oncol. 2014, 45, 1059–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, L.; Shetty, K.; Tang, Y.; Stuart, A.; Byers, S.W. The role of TGF-β and Wnt signaling in gastrointestinal stem cells and cancer. Oncogene 2005, 24, 5775–5789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massagué, J. TGF-β signaling in development and disease. FEBS Lett. 2012, 586, 1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pistol, G.C.; Braicu, C.; Motiu, M.; Gras, M.A.; Marin, D.E.; Stancu, M.; Calin, L.; Israel-Roming, F.; Berindan-Neagoe, I.; Taranu, I. Zearalenone mycotoxin affects immune mediators, MAPK signalling molecules, nuclear receptors and genome-wide gene expression in pig spleen. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0127503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Liu, T.; Jiang, S.; Yang, Z.; Huang, L.; Liu, F. Effects of purified zearalenone on selected immunological and histopathologic measurements of spleen in post-weanling gilts. Anim. Nutr. 2017, 3, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, D.E.; Motiu, M.; Taranu, I. Food contaminant zearalenone and its metabolites affect cytokine synthesis and intestinal epithelial integrity of porcine cells. Toxins (Basel) 2015, 7, 1979–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vegeto, E.; Cuzzocrea, S.; Crisafulli, C.; Mazzon, E.; Sala, A.; Krust, A.; Maggi, A. Estrogen receptor-α as a drug target candidate for preventing lung inflammation. Endocrinology 2010, 151, 174–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, A.; Rizzi, N.; Vegeto, E.; Ciana, P.; Maggi, A. Estrogen accelerates the resolution of inflammation in macrophagic cells. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saygin, C.; Reizes, O.; Berger, N.A. Adipocytes, Adipocytokines, and Cancer. In Adipocytokines, Energy Balance, and Cancer; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Kwak, S.; Kim, Y.D.; Na, H.G.; Bae, C.H.; Song, S.Y.; Choi, Y.S. Resistin upregulates MUC5AC/B mucin gene expression in human airway epithelial cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 499, 655–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rykaczewska, A.; Gajęcka, M.; Dąbrowski, M.; Wiśniewska, A.; Szcześniewska, J.; Gajęcki, M.T.; Zielonka, Ł. Growth performance, selected blood biochemical parameters and body weights of pre-pubertal gilts fed diets supplemented with different doses of zearalenone (ZEN). Toxicon 2018, 152, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gajęcka, M.; Tarasiuk, M.; Zielonka, Ł.; Dąbrowski, M.; Gajęcki, M. Risk assessment for changes in the metabolic profile and body weights of pre-pubertal gilts during long-term monotonic exposure to low doses of zearalenone (ZEN). Res. Vet. Sci. 2016, 109, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrakis, D.; Vassilopoulou, L.; Mamoulakis, C.; Psycharakis, C.; Anifantaki, A.; Sifakis, S.; Docea, A.O.; Tsiaoussis, J.; Makrigiannakis, A.; Tsatsakis, A.M. Endocrine disruptors leading to obesity and related diseases. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucioli, J.; Pinton, P.; Callu, P.; Laffitte, J.; Grosjean, F.; Kolf-Clauw, M.; Oswald, I.P.; Bracarense, A.P.F.R.L. The food contaminant deoxynivalenol activates the mitogen activated protein kinases in the intestine: Interest of ex vivo models as an alternative to in vivo experiments. Toxicon 2013, 66, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinton, P.; Graziani, F.; Pujol, A.; Nicoletti, C.; Paris, O.; Ernouf, P.; Di Pasquale, E.; Perrier, J.; Oswald, I.P.; Maresca, M. Deoxynivalenol inhibits the expression by goblet cells of intestinal mucins through a PKR and MAP kinase dependent repression of the resistin-like molecule β. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2015, 59, 1076–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, G.R.; Payros, D.; Pinton, P.; Dogi, C.A.; Laffitte, J.; Neves, M.; González Pereyra, M.L.; Cavaglieri, L.R.; Oswald, I.P. Intestinal toxicity of deoxynivalenol is limited by Lactobacillus rhamnosus RC007 in pig jejunum explants. Arch. Toxicol. 2018, 92, 983–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alassane-Kpembi, I.; Puel, O.; Pinton, P.; Cossalter, A.-M.; Chou, T.-C.; Oswald, I.P. Co-exposure to low doses of the food contaminants deoxynivalenol and nivalenol has a synergistic inflammatory effect on intestinal explants. Arch. Toxicol. 2017, 91, 2677–2687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierron, A.; Mimoun, S.; Murate, L.S.; Loiseau, N.; Lippi, Y.; Bracarense, A.-P.F.L.; Schatzmayr, G.; He, J.W.; Zhou, T.; Moll, W.-D.; et al. Microbial biotransformation of DON: Molecular basis for reduced toxicity. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 29105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruijter, J.M.; Ramakers, C.; Hoogaars, W.M.H.; Karlen, Y.; Bakker, O.; van den hoff, M.J.B.; Moorman, A.F.M. Amplification efficiency: Linking baseline and bias in the analysis of quantitative PCR data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, e45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lahjouji, T.; Bertaccini, A.; Neves, M.; Puel, S.; Oswald, I.P.; Soler, L. Acute Exposure to Zearalenone Disturbs Intestinal Homeostasis by Modulating the Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway. Toxins 2020, 12, 113. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12020113
Lahjouji T, Bertaccini A, Neves M, Puel S, Oswald IP, Soler L. Acute Exposure to Zearalenone Disturbs Intestinal Homeostasis by Modulating the Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway. Toxins. 2020; 12(2):113. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12020113
Chicago/Turabian StyleLahjouji, Tarek, Aurora Bertaccini, Manon Neves, Sylvie Puel, Isabelle P. Oswald, and Laura Soler. 2020. "Acute Exposure to Zearalenone Disturbs Intestinal Homeostasis by Modulating the Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway" Toxins 12, no. 2: 113. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12020113
APA StyleLahjouji, T., Bertaccini, A., Neves, M., Puel, S., Oswald, I. P., & Soler, L. (2020). Acute Exposure to Zearalenone Disturbs Intestinal Homeostasis by Modulating the Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway. Toxins, 12(2), 113. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12020113





