Sialorrhea in Parkinson’s Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Etiology of Sialorrhea in Parkinson’s Disease (PD)
3. Salivary Glands
4. Conservative Management and Speech Therapy
5. Oral Therapy
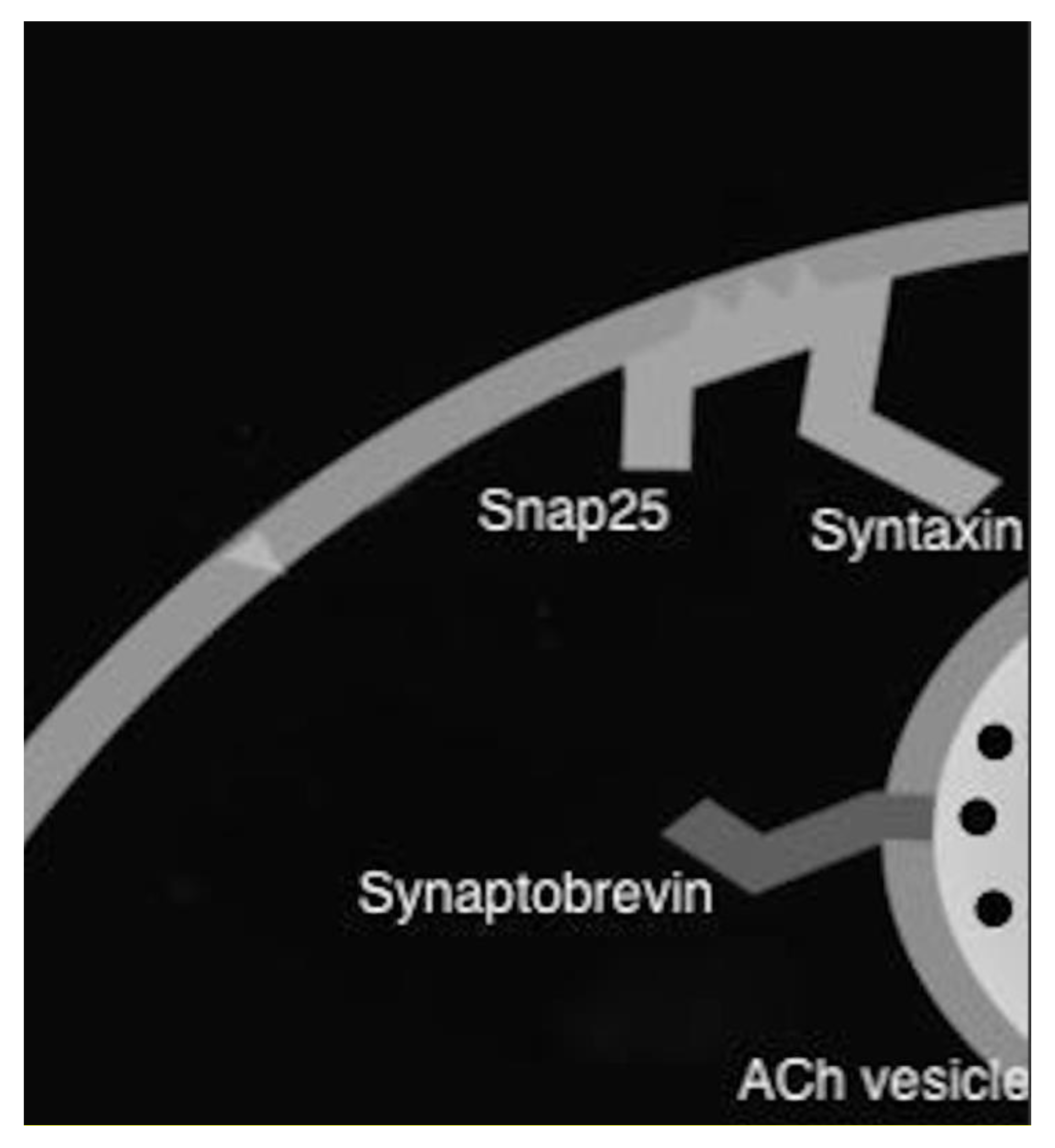
6. Botulinum Toxin
7. Botulinum Toxin in Sialorrhea
8. Techniques
9. IncobotulinumtoxinA
10. RimabotulinumtoxinB
11. OnabotulinumtoxinA
12. AbobotulinumtoxinA
13. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lakraj, A.A.; Moghimi, N.; Jabbari, B. Sialorrhea: Anatomy, Pathophysiology and Treatment with Emphasis on the Role of Botulinum Toxins. Toxins 2013, 5, 1010–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalf, J.G.; De Swart, B.J.M.; Borm, G.F.; Bloem, B.R.; Munneke, M. Prevalence and definition of drooling in Parkinson’s disease: A systematic review. J. Neurol. 2009, 256, 1391–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Politis, M.; Wu, K.; Molloy, S.; Bain, P.G.; Chaudhuri, K.R.; Piccini, P. Parkinson’s disease symptoms: The patient’s perspective. Mov. Disord. 2010, 25, 1646–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scully, C.; Limeres, J.; Gleeson, M.; Tomás, I.; Diz, P. Drooling. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2009, 38, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leopold, N.A.; Kagel, M.C. Pharyngo-Esophageal Dysphagia in Parkinson’s Disease. Dysphagia 1997, 12, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbar, U.; Dham, B.; He, Y.; Hack, N.; Wu, S.; Troche, M.; Tighe, P.; Nelson, E.; Friedman, J.H.; Okun, M.S. Incidence and mortality trends of aspiration pneumonia in Parkinson’s disease in the United States, 1979–2010. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2015, 21, 1082–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagheri, H.; Damase-Michel, C.; Lapeyre-Mestre, M.; Cismondo, S.; O’Connell, D.; Senard, J.-M.; Rascol, O.; Montastruc, J.-L. A study of salivary secretion in Parkinson’s disease. Clin. Neuropharmacol. 1999, 22, 213–215. [Google Scholar]
- Umemoto, G.; Tsuboi, Y.; Kitashima, A.; Furuya, H.; Kikuta, T. Impaired Food Transportation in Parkinson’s Disease Related to Lingual Bradykinesia. Dysphagia 2011, 26, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakoc, M.; Yon, M.I.; Cakmakli, G.Y.; Ulusoy, E.K.; Gulunay, A.; Oztekin, N.; Ak, F. Pathophysiology underlying drooling in Parkinson’s disease: Oropharyngeal bradykinesia. Neurol. Sci. 2016, 37, 1987–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphrey, S.P.; Williamson, R.T. A review of saliva: Normal composition, flow, and function. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2001, 85, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, W.M. Saliva and dental health. Clinical implications of saliva: Report of a consensus meeting. Br. Dent. J. 1990, 169, 96–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marks, L.; Turner, K.; O’Sullivan, J.; Deighton, B.; Lees, A. Drooling in Parkinson’s disease: A novel speech and language therapy intervention. Int. J. Lang. Commun. Disord. 2001, 36, 282–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varley, L.P.; Denieffe, S.; O’Gorman, C.; Murphy, A.; Gooney, M. A systematic review of noninvasive and invasive sialorrhoea management. J. Clin. Nurs. 2019, 28, 4190–4206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGeachan, A.J.; McDermott, C.J. Management of oral secretions in neurological disease. Pract. Neurol. 2017, 17, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts-South, A.; Somers, S.M.; Jog, M.S. Gum chewing improves swallow frequency and latency in Parkinson patients: A preliminary study. Neurology 2010, 74, 1198–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Burg, J.J.W.; Didden, R.; Jongerius, P.H.; Rotteveel, J.J. Behavioral Treatment of Drooling: A methodological critique of the literature with clinical guidelines and suggestions for future research. Behav. Modif. 2007, 31, 573–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirakhur, R.K.; Dundee, J.W. Comparison of the Effects of Atropine and Glycopyrrolate on various End-Organs1. J. R. Soc. Med. 1980, 73, 727–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheife, R.; Takeda, M. Central nervous system safety of anticholinergic drugs for the treatment of overactive bladder in the elderly. Clin. Ther. 2005, 27, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbouw, M.E.L.; Movig, K.L.L.; Koopmann, M.; Poels, P.J.E.; Guchelaar, H.J.; Egberts, T.C.G.; Neef, C.; Van Vugt, J.P.P. Glycopyrrolate for sialorrhea in Parkinson disease: A randomized, double-blind, crossover trial. Neurology 2010, 74, 1203–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lloret, S.P.; Nano, G.; Carrosella, A.; Gamzu, E.; Merello, M. A double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized, crossover pilot study of the safety and efficacy of multiple doses of intra-oral tropicamide films for the short-term relief of sialorrhea symptoms in Parkinson’s disease patients. J. Neurol. Sci. 2011, 310, 248–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dressler, D. Botulinum toxin mechanisms of action. Suppl. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2004, 57, 159–166. [Google Scholar]
- Nigam, P.K.; Nigam, A. Botulinum toxin. Indian J. Dermatol. 2010, 55, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holland, R.; Brown, M.C. Nerve growth in botulinum toxin poisoned muscles. Neuroscience 1981, 6, 1167–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiigimäe-Saar, J.; Tamme, T.; Rosenthal, M.; Kadastik-Eerme, L.; Taba, P. Saliva changes in Parkinson’s disease patients after injection of Botulinum neurotoxin type A. Neurol. Sci. 2018, 39, 871–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, P.K.; Calne, D.B.; Calne, S.; Tsui, J.K. Botulinum Toxin A as treatment for drooling saliva in PD. Neurology 2000, 54, 244–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ondo, W.G.; Hunter, C.; Moore, W. A double-blind placebo-controlled trial of botulinum toxin B for sialorrhea in Parkinson’s disease. Neurology 2004, 62, 37–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentivoglio, A.R.; Del Grande, A.; Petracca, M.; Ialongo, T.; Ricciardi, L. Clinical differences between botulinum neurotoxin type A and B. Toxicon 2015, 107, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jost, W.H.; Firedman, A.; Michel, O.; Oehlwein, C.; Slawek, J.; Bogucki, A.; Ochudlo, S.; Banach, M.; Pagan, F.; Flatau-Baqué, B.; et al. SIAXI: Placebo-controlled, randomized, double-blind study of incobotulinumtoxinA for sialorrhea. Neurology 2019, 92, e1982–e1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaacson, S.H.; Ondo, W.; Jackson, C.E.; Trosch, R.M.; Molho, E.; Pagan, F.; Lew, M.; Dashtipour, K.; Clinch, T.; Espay, A.J.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of RimabotulinumtoxinB for Treatment of Sialorrhea in Adults: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Neurol. 2020, 77, 461–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loens, S.; Brüggemann, N.; Steffen, A.; Bäumer, T. Localization of Salivary Glands for Botulinum Toxin Treatment: Ultrasound Versus Landmark Guidance. Mov. Disord. Clin. Pract. 2019, 7, 194–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- So, J.I.; Song, D.; Park, J.H.; Choi, E.; Yoon, J.Y.; Yoo, Y.J.; Chung, M.E. Accuracy of Ultrasound-Guided and Non-ultrasound-Guided Botulinum Toxin Injection Into Cadaver Salivary Glands. Ann. Rehabil. Med. 2017, 41, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blumel, J.; Frevert, J.; Schwaier, A. Comparative antigenicity of three preparations on botulinum neurotoxin A in the rabbit. Neurotox Res. 2006, 9, 238. [Google Scholar]
- Dashtipour, K.; Bhidayasiri, R.; Chen, J.J.; Jabbari, B.; Lew, M.; Torres-Russotto, D. RimabotulinumtoxinB in sialorrhea: Systematic review of clinical trials. J. Clin. Mov. Disord. 2017, 4, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brin, M.F.; Comella, C.L.; Jankovic, J.; Mmath, F.L.; Naumann, M. Long-term treatment with botulinum toxin type A in cervical dystonia has low immunogenicity by mouse protection assay. Mov. Disord. 2008, 23, 1353–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarenga, A.; Campos, M.; Dias, M.; Melão, L.; Estevão-Costa, J. BOTOX—A injection of salivary glands for drooling. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2017, 52, 1283–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira Filho, A.F.D.; Silva, G.A.D.M.; Almeida, D.M.X. Application of botulinum toxin to treat sialorrhea in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients: A literature review. Einstein 2016, 14, 431–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Petracca, M.; Guidubaldi, A.; Ricciardi, L.; Ialongo, T.; Del Grande, A.; Mulas, D.; Di Stasio, E.; Bentivoglio, A.R. Botulinum Toxin A and B in sialorrhea: Long-term data and literature overview. Toxicon 2015, 107, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgante, F.; Bavikatte, G.; Anwar, F.; Mohamed, B. The burden of sialorrhoea in chronic neurological conditions: Current treatment options and the role of incobotulinumtoxinA (Xeomin®). Ther. Adv. Neurol. Disord. 2019, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Toxins | Brand Name | Indication | Company | Clinical Trial | Dosage | Side-Effect/Cons |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Botulinum toxin A | ||||||
| IncobotulinumtoxinA | Xeomin | FDA-approved for chronic Sialorrhea | Merz Pharmaceuticals (Germany) | SIAXI | 100 U | Dry mouth, dysphagia [28] |
| OnabotulinumtoxinA | Botox | No FDA approval for Sialorrhea | Allergan US | - | Unknown | |
| AbobotulinumtoxinA | Dysport | No FDA approval for Sialorrhea | Ipsen (France) | - | Unknown | |
| Botulinum toxin B | ||||||
| RimabotulinumtoxinB | Myobloc | FDA-approved for chronic Sialorrhea | Myobloc (USA) | Isaacson et al. | 2500 U and 3500 U | Dry mouth, dysphagia, and dental caries [29] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Isaacson, J.; Patel, S.; Torres-Yaghi, Y.; Pagán, F. Sialorrhea in Parkinson’s Disease. Toxins 2020, 12, 691. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12110691
Isaacson J, Patel S, Torres-Yaghi Y, Pagán F. Sialorrhea in Parkinson’s Disease. Toxins. 2020; 12(11):691. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12110691
Chicago/Turabian StyleIsaacson, Jonathan, Sanskruti Patel, Yasar Torres-Yaghi, and Fernando Pagán. 2020. "Sialorrhea in Parkinson’s Disease" Toxins 12, no. 11: 691. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12110691
APA StyleIsaacson, J., Patel, S., Torres-Yaghi, Y., & Pagán, F. (2020). Sialorrhea in Parkinson’s Disease. Toxins, 12(11), 691. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12110691




