The Novel Clostridial Neurotoxin Produced by Strain IBCA10-7060 Is Immunologically Equivalent to BoNT/HA
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. BoNT/H LC-HN Fragment Expression and Mouse Immunization
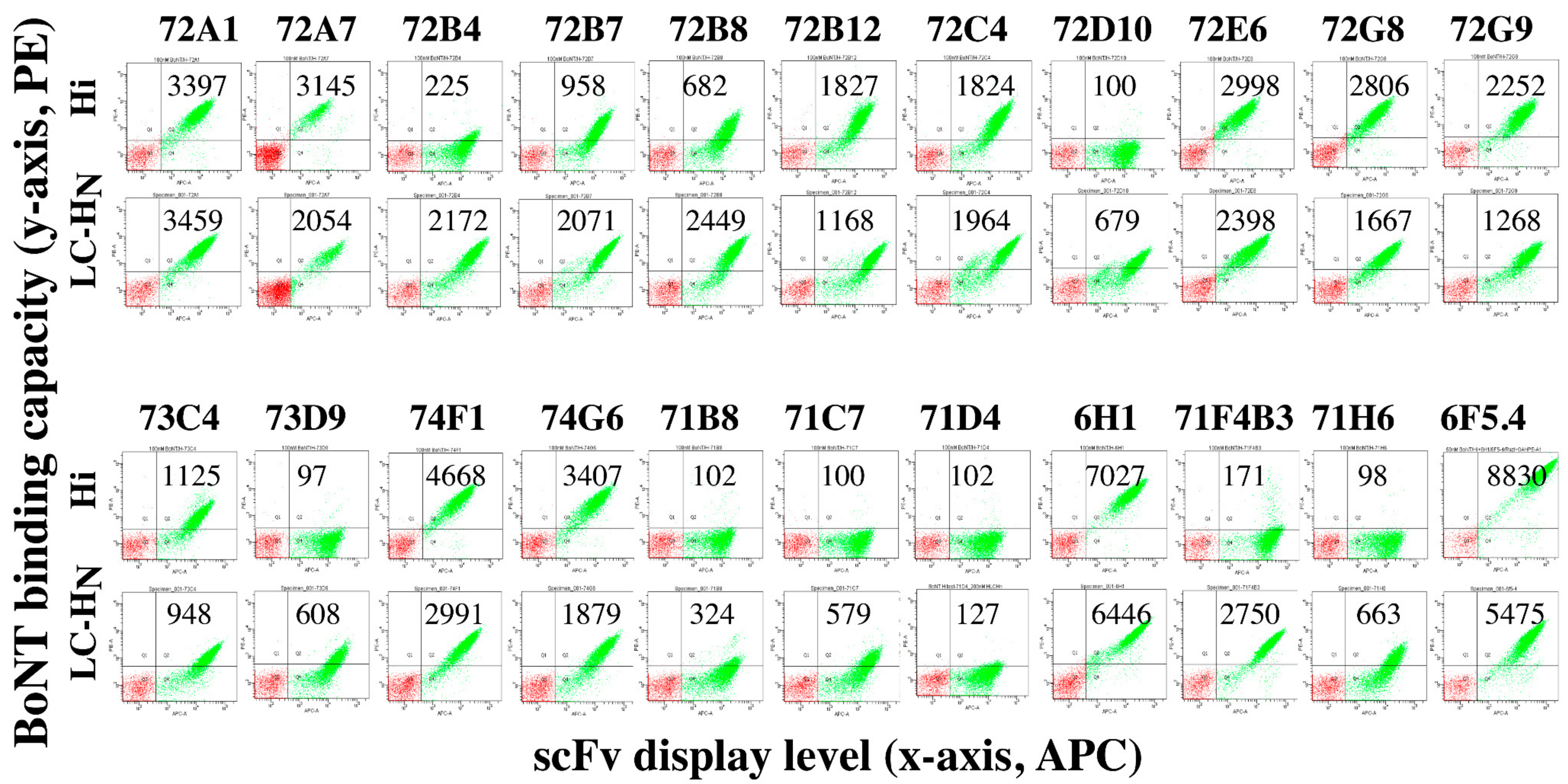
2.2. Isolation and Initial Characterization of mAbs from Mice Immunized with BoNT/H LC-HN
2.3. Isolation and Initial Characterization of mAbs from Mice Immunized with BoNT/F LC-HN
2.4. The BoNT/H LC-HN scFv mAbs Bind Nine Non-Overlapping Epitopes
2.5. mAbs Binding BoNT/H LC-HN do not Bind BoNT Serotypes A–G
2.6. Some mAbs can Bind both BoNT/A HC and BoNT/H
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Materials
5.2. Protein Expression and Purification
5.3. Ethics Statement
5.4. Mouse Immunization, Spleen Harvest, and Antiserum Titer
5.5. scFv library Construction and FACS Sorting
5.6. scFv binding Confirmation and Affinity Determination
5.7. Epitope Overlap Determination
5.8. MAb Affinity Maturation
5.9. Measurement of Solution Phase Affinity at Equilibrium
6. Patents
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gill, M.D. Bacterial toxins: A table of lethal amounts. Microbiol. Rev. 1982, 46, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lacy, D.B.; Tepp, W.; Cohen, A.C.; DasGupta, B.R.; Stevens, R.C. Crystal structure of botulinum neurotoxin type A and implications for toxicity. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 1998, 5, 898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacy, D.B.; Stevens, R.C. Sequence homology and structural analysis of the Clostridial neurotxins. J. Mol. Biol. 1999, 291, 1091–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, K.K.; Smith, T.J. Genetic diversity within Clostridium botulinum serotypes, botulinum neurotoxin gene clusters and toxin subtypes. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2013, 364, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Masuyer, G.; Zhang, J.; Shen, Y.; Lundin, D.; Henriksson, L.; Miyashita, S.-I.; Martínez-Carranza, M.; Dong, M.; Stenmark, P. Identification and characterization of a novel botulinum neurotoxin. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunt, J.; Carter, A.T.; Stringer, S.C.; Peck, M.W. Identification of a novel botulinum neurotoxin gene cluster in Enterococcus. FEBS Lett. 2018, 592, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barash, J.R.; Arnon, S.S. A novel strain of Clostridium botulinum that produces type B and type H botulinum toxins. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 209, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dover, N.; Barash, J.R.; Hill, K.K.; Xie, G.; Arnon, S.S. Molecular characterization of a novel botulinum neurotoxin type H gene. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 209, 192–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maslanka, S.E.; Luquez, C.; Dykes, J.K.; Tepp, W.H.; Pier, C.L.; Pellett, S.; Raphael, B.H.; Kalb, S.R.; Barr, J.R.; Rao, A.; et al. A novel botulinum neurotoxin, previously reported as serotype H, has a hybrid-like structure with regions of similarity to the structures of serotypes A and F and is neutralized with serotype A antitoxin. J. Infect. Dis. 2016, 213, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellett, S.; Tepp, W.H.; Bradshaw, M.; Kalb, S.R.; Dykes, J.K.; Lin, G.; Nawrocki, E.M.; Pier, C.L.; Barr, J.R.; Maslanka, S.E.; et al. Purification and characterization of botulinum neurotoxin FA from a genetically modified Clostridium botulinum strain. mSphere 2016, 1, e00100–e00115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Escalona, N.; Thirunavukkarasu, N.; Singh, A.; Toro, M.; Brown, E.W.; Zink, D.; Rummel, A.; Sharma, S.K. Draft genome sequence of bivalent Clostridium botulinum strain IBCA10-7060, encoding botulinum neurotoxin B and a new FA mosaic type. Genome Announc. 2014, 2, e01275–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Barash, J.R.; Lou, J.; Conrad, F.; Marks, J.D.; Arnon, S.S. Immunological characterization and neutralizing ability of monoclonal antibodies directed against botulinum neurotoxin type H. J. Infect. Dis. 2016, 213, 1606–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, G.; Zhang, S.; Mahrhold, S.; Lam, K.-H.; Stern, D.; Bagramyan, K.; Perry, K.; Kalkum, M.; Rummel, A.; Dong, M. N-linked glycosylation of SV2 is required for binding and uptake of botulinum neurotoxin A. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2016, 23, 656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, G.; Lam, K.-H.; Perry, K.; Weisemann, J.; Rummel, A.; Jin, R. Crystal structure of the receptor-binding domain of botulinum neurotoxin type HA, also known as type FA or H. Toxins 2017, 9, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, R.; Forsyth, C.; LaPorte, S.; Geren, I.; Smith, L.; Marks, J. Fine and domain-level epitope mapping of botulinum neurotoxin type A neutralizing antibodies by yeast surface display. J. Mol. Biol. 2007, 365, 196–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, C.; Levy, R.; Arndt, J.; Forsyth, C.; Razai, A.; Lou, J.; Geren, I.; Stevens, R.; Marks, J. Molecular evolution of antibody specificity and cross reactivity for type A botulinum neurotoxins. Nat. Biotech 2007, 25, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Rodriguez, C.; Geren, I.N.; Lou, J.; Conrad, F.; Forsyth, C.; Wen, W.; Chakraborti, S.; Zao, H.; Manzanarez, G.; Smith, T.J.; et al. Neutralizing human monoclonal antibodies binding multiple serotypes of botulinum neurotoxin. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. Peds 2011, 24, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Garcia-Rodriguez, C.; Lou, J.; Wen, W.; Conrad, F.; Zhai, W.; Smith, T.J.; Smith, L.A.; Marks, J.D. A three monoclonal antibody combination potently neutralizes multiple botulinum neurotoxin serotype F subtypes. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0174187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfenninger, W. Toxico Immunologic and Serologic Relationship of B. botulinus, Type C, and B. parabotulinus,” Seddon.” XXII. J. Infect. Dis. 1924, 35, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriishi, K.; Koura, M.; Fujii, N.; Fujinaga, Y.; Inoue, K.; Syuto, B.; Oguma, K. Molecular cloning of the gene encoding the mosaic neurotoxin, composed of parts of botulinum neurotoxin types C1 and D, and PCR detection of this gene from Clostridium botulinum type C organisms. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1996, 62, 662–667. [Google Scholar]
- Moriishi, K.; Koura, M.; Abe, N.; Fujii, N.; Fujinaga, Y.; Inoue, K.; Ogumad, K. Mosaic structures of neurotoxins produced from Clostridium botulinum types C and D organisms. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gene Struct. Expr. 1996, 1307, 123–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botulism Antitoxin Heptavalent (A, B, C, D, E, F, G)—(Equine). Package Insert. Cangene Corp. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/vaccines-blood-biologics/approved-blood-products/bat-botulism-antitoxin-heptavalent-b-c-d-e-f-g-equine (accessed on 29 April 2019).
- Hill, K.K.; Xie, G.; Foley, B.T.; Smith, T.J. Genetic diversity within the botulinum neurotoxin-producing bacteria and their neurotoxins. Toxicon 2015, 107, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, K.-H.; Sikorra, S.; Weisemann, J.; Maatsch, H.; Perry, K.; Rummel, A.; Binz, T.; Jin, R. Structural and biochemical characterization of the protease domain of the mosaic botulinum neurotoxin type HA. Pathog. Dis. 2018, 76, fty044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatheway, C.H.; Snyder, J.D.; Seals, J.E.; Edell, T.A.; Lewis, G.E., Jr. Antitoxin levels in botulism patients treated with trivalent equine botulism antitoxin to toxin types A, B, and E. J. Infect. Dis. 1984, 150, 407–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheth, A.N.; Wiersma, P.; Atrubin, D.; Dubey, V.; Zink, D.; Skinner, G.; Doerr, F.; Juliao, P.; Gonzalez, G.; Burnett, C. International outbreak of severe botulism with prolonged toxemia caused by commercial carrot juice. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2008, 47, 1245–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagan, R.P.; McLaughlin, J.B.; Middaugh, J.P. Persistence of botulinum toxin in patients’ serum: Alaska, 1959–2007. J. Infect. Dis. 2009, 199, 1029–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagan, R.P.; Neil, K.P.; Sasich, R.; Luquez, C.; Asaad, H.; Maslanka, S.; Khalil, W. Initial recovery and rebound of type F intestinal colonization botulism after administration of investigational heptavalent botulinum antitoxin. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2011, 53, e125–e128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, S.U.; Griffiss, J.M.; McKenzie, R.; Fuchs, E.J.; Jurao, R.A.; An, A.T.; Ahene, A.; Tomic, M.; Hendrix, C.W.; Zenilman, J.M. Safety and pharmacokinetics of XOMA 3AB, a novel mixture of three monoclonal antibodies against botulinum toxin A. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 5047–5053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowakowski, A.; Wang, C.; Powers, D.B.; Amersdorfer, P.; Smith, T.J.; Montgomery, V.A.; Sheridan, R.; Blake, R.; Smith, L.A.; Marks, J.D. Potent neutralization of botulinum neurotoxin by recombinant oligoclonal antibody. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 11346–11350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Geren, I.N.; Dong, J.; Lou, J.; Wen, W.; Conrad, F.; Smith, T.J.; Smith, L.A.; Ho, M.; Pires-Alves, M.; et al. Monoclonal antibodies targeting the alpha-exosite of botulinum neurotoxin serotype/A inhibit catalytic activity. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0135306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Library Name | Immunogens | Library Size |
|---|---|---|
| BoNT/F libraries | BoNT/F1HC and F1 holotoxin BoNT/F3 LC-HN BoNT/F5 LC-HN BoNT/F6 LC-HN BoNT/F7 LC-HN | 2 × 108 |
| BoNT/H library | BoNT/H LC-HN | 5 × 107 |
| Domain Specificity | BoNT/F Binding1 | KD on Yeast (nM) | Epitope Group | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H LC-HN | BoNT/Hi | ||||
| MAbs from BoNT/H Library | |||||
| 72A1 | H LC | No | 3.08 | 2.41 | II |
| 72A7 | H LC-HN | No | 0.78 | 1.79 | IX |
| 72B4 | H LC-HN | No | 12.5 | >200 | VI |
| 72B7 | H LC-HN | No | 25.1 | 32.85 | V/IX |
| 72B8 | H LC-HN | No | 14.2 | 52.4 | IX |
| 72B12 | H LC-HN | No | 29.4 | 19.5 | IX/IV |
| 72C4 | H LC-HN | No | 17.1 | 43.5 | VII |
| 72D10 | H LC-HN | No | 40.8 | No Binding | IX |
| 72E6 | H LC-HN | No | 0.99 | 0.88 | IX |
| 72G8 | H LC-HN | No | 5.00 | 2.4 | VIII |
| 72G9 | H LC | No | 6.62 | 53.9 | I/II |
| 73C4 | H LC-HN | No | 182 | >100 | V |
| 73D9 | H LC-HN | No | 30.0 | No Binding | VII/IX |
| 74F1 | H HN | No | 1.77 | 2.18 | II |
| 74G6 | H HN | No | 4.05 | 5.50 | III |
| MAbs from BoNT/F Libraries | |||||
| 71B8 | H LC-HN | No | 1490 | No Binding | VIII/IX |
| 71C7 | H LC-HN | No | 38.8 | No Binding | IV |
| 71D4 | H LC-HN | No | 184.8 | No Binding | III |
| 71E4 | H LC | F5 LC-HN | 70.65 (3984) | 68.8 | I |
| 6H12 | 2.89 (13.24) | 3.07 | |||
| 71F4 | H LC | No | 124.4 | No Binding | II |
| 71F4B3 | 34.6 | >200 | |||
| 71H6 | H LC-HN | No | 20.5 | No Binding | VII/IX |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fan, Y.; Barash, J.R.; Conrad, F.; Lou, J.; Tam, C.; Cheng, L.W.; Arnon, S.S.; Marks, J.D. The Novel Clostridial Neurotoxin Produced by Strain IBCA10-7060 Is Immunologically Equivalent to BoNT/HA. Toxins 2020, 12, 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12010009
Fan Y, Barash JR, Conrad F, Lou J, Tam C, Cheng LW, Arnon SS, Marks JD. The Novel Clostridial Neurotoxin Produced by Strain IBCA10-7060 Is Immunologically Equivalent to BoNT/HA. Toxins. 2020; 12(1):9. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12010009
Chicago/Turabian StyleFan, Yongfeng, Jason R. Barash, Fraser Conrad, Jianlong Lou, Christina Tam, Luisa W. Cheng, Stephen S. Arnon, and James D. Marks. 2020. "The Novel Clostridial Neurotoxin Produced by Strain IBCA10-7060 Is Immunologically Equivalent to BoNT/HA" Toxins 12, no. 1: 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12010009
APA StyleFan, Y., Barash, J. R., Conrad, F., Lou, J., Tam, C., Cheng, L. W., Arnon, S. S., & Marks, J. D. (2020). The Novel Clostridial Neurotoxin Produced by Strain IBCA10-7060 Is Immunologically Equivalent to BoNT/HA. Toxins, 12(1), 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12010009








