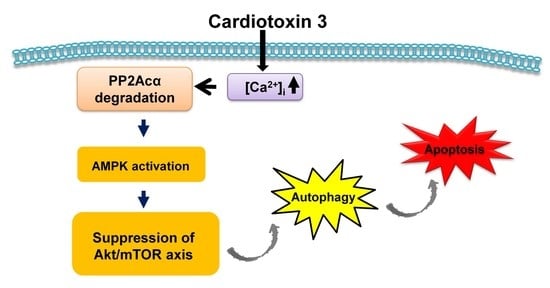
Naja atra Cardiotoxin 3 Elicits Autophagy and Apoptosis in U937 Human Leukemia Cells through the Ca2+/PP2A/AMPK Axis
Abstract
1. Introduction
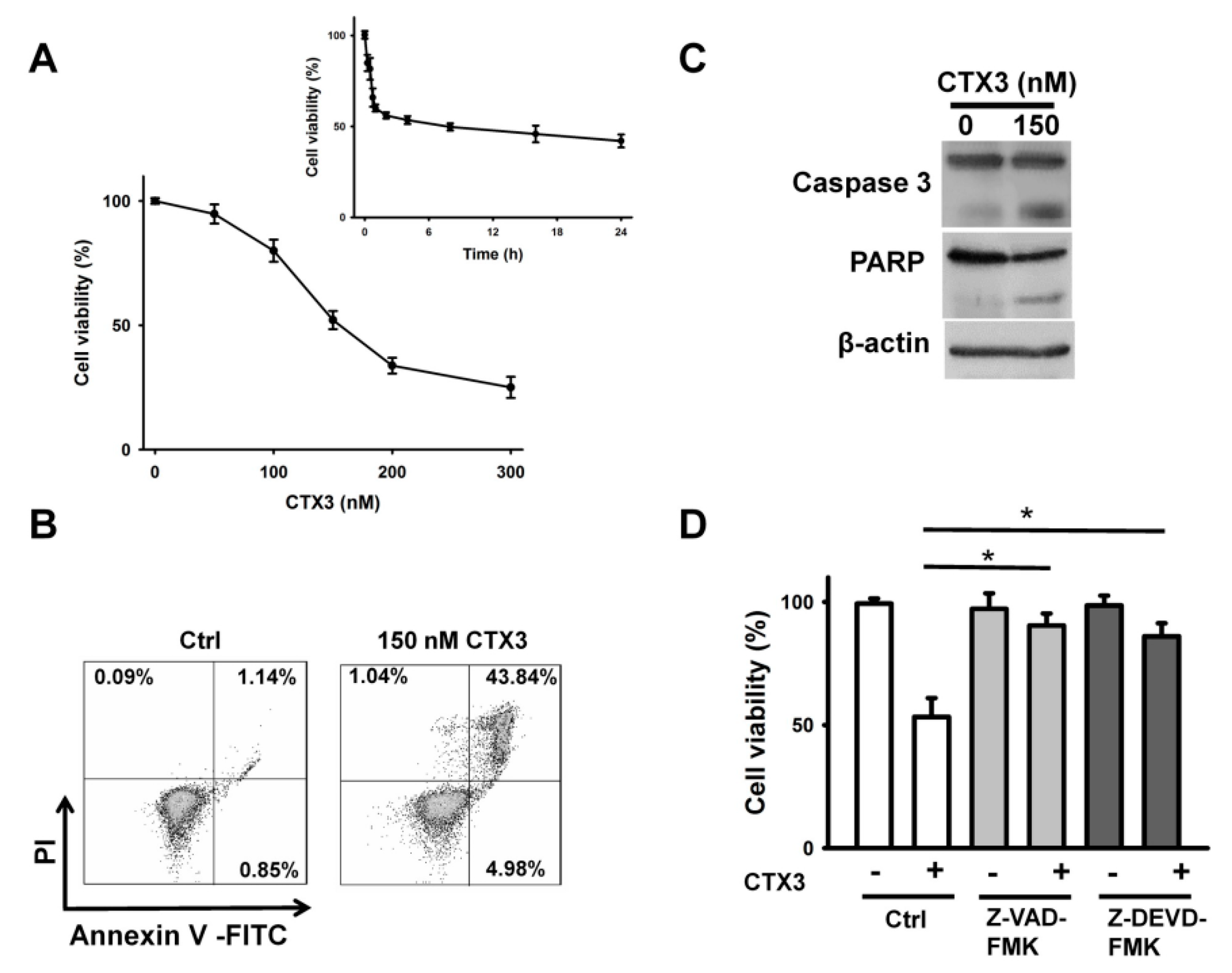
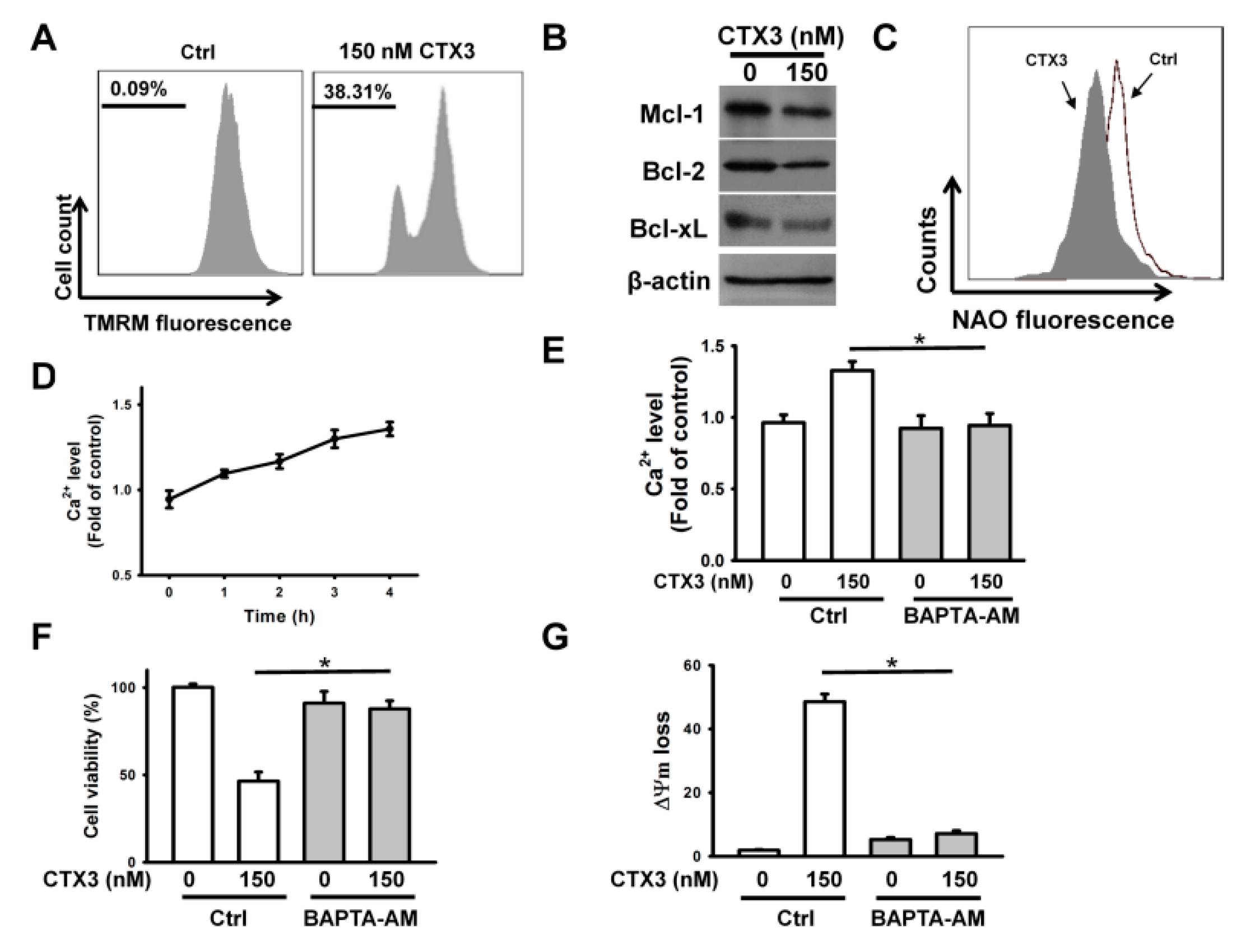
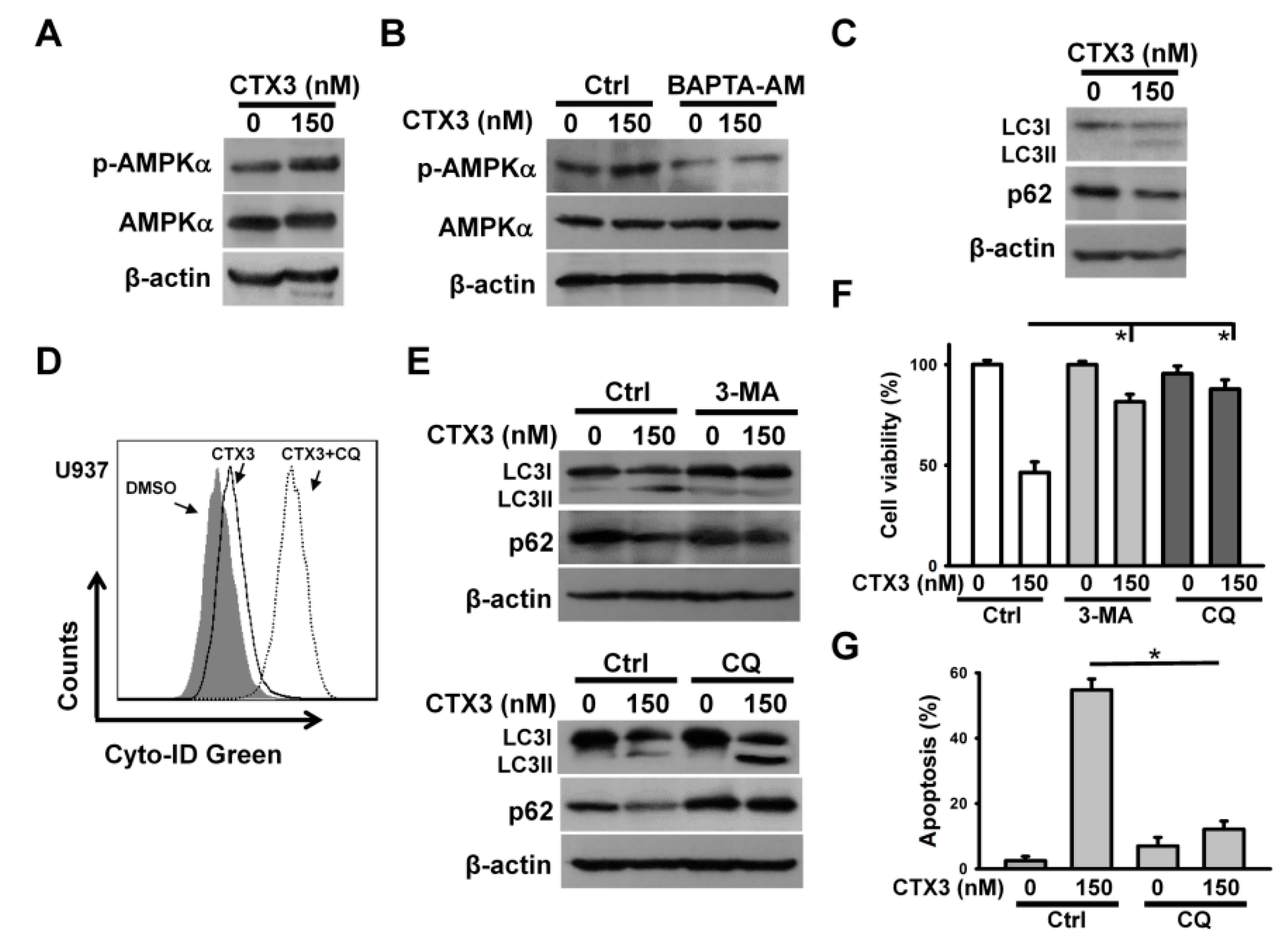
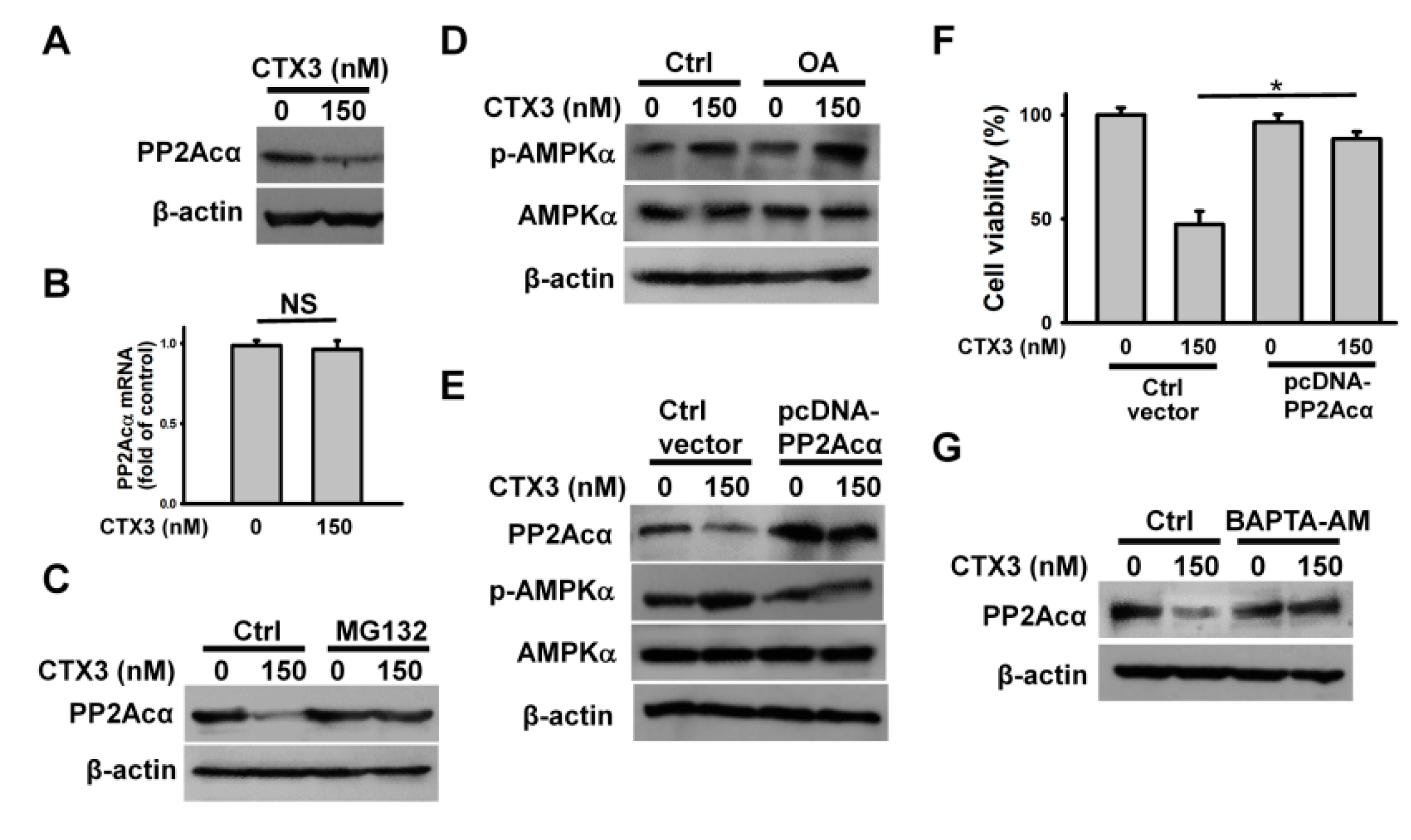
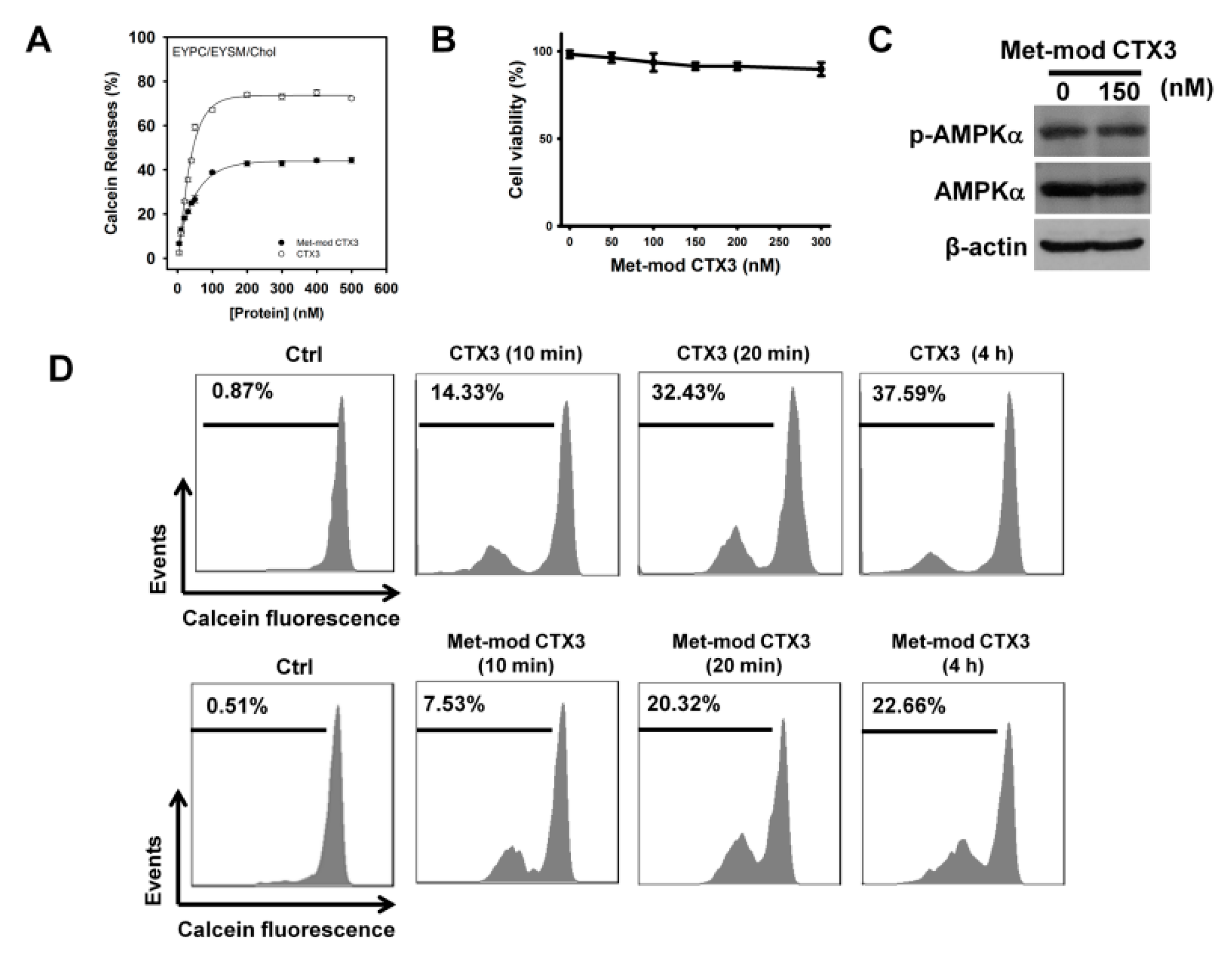
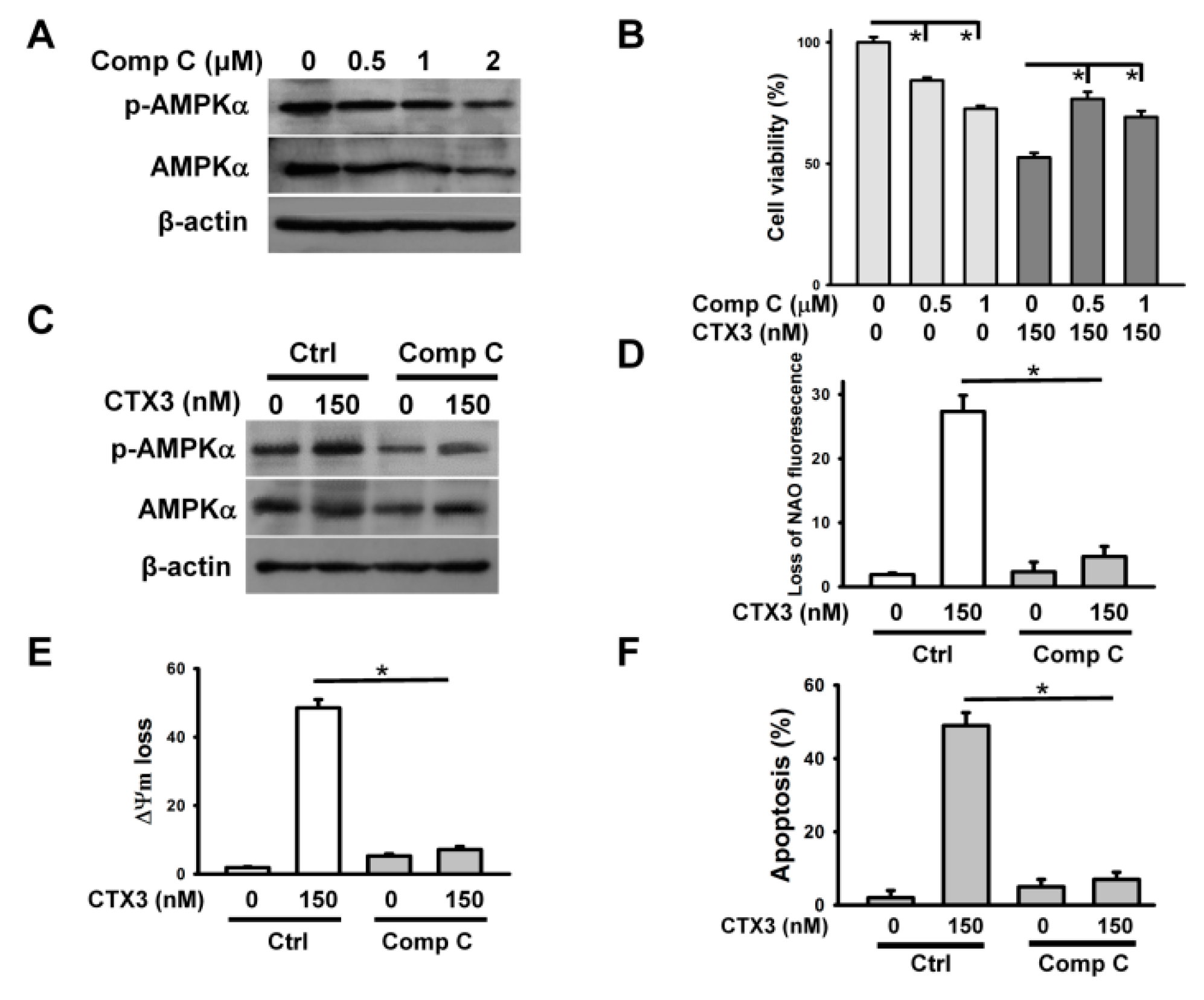
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Chemicals and Reagents
5.2. Cell Culture
5.3. Measurement of Mitochondrial Depolarization
5.4. Measurement of Intracellular Ca2+ Concentration ([Ca2+]i)
5.5. Measurement of Mitochondrial Mass
5.6. Quantitative RT-PCR
5.7. Transfection of DNA
5.8. Membrane Permeability Assay
5.9. Leakage of Calcein-Loaded Cells
5.10. Other Tests
5.11. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dufton, M.J.; Hider, R.C. The structure and pharmacology of Elapid cytotoxins. In Snake Toxins; Harvey, A.L., Ed.; Pergamon Press: New York, NY, USA, 1999; pp. 259–302. [Google Scholar]
- Konshina, A.G.; Dubovskii, P.V.; Efremov, R.G. Structure and dynamics of cardiotoxins. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2012, 13, 570–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogasawara, S.; Cheng, X.W.; Inoue, A.; Hu, L.; Piao, L.; Yu, C.; Goto, H.; Xu, W.; Zhao, G.; Lei, Y.; et al. Cathepsin K activity controls cardiotoxin-induced skeletal muscle repair in mice. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2018, 9, 160–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feofanov, A.V.; Sharonov, G.V.; Astapova, M.V.; Rodionov, D.I.; Utkin, Y.N.; Arseniev, A.S. Cancer cell injury by cytotoxins from cobra venom is mediated through lysosomal damage. Biochem. J. 2005, 390, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chien, C.M.; Yang, S.H.; Yang, C.C.; Chang, L.S.; Lin, S.R. Cardiotoxin III induces c-jun N-terminal kinase-dependent apoptosis in HL-60 human leukaemia cells. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2008, 26, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vyas, V.K.; Brahmbhatt, K.; Bhatt, H.; Parmar, U. Therapeutic potential of snake venom in cancer therapy: Current perspectives. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2013, 3, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Ming, W.; Tang, Y.; Zhou, S.; Kong, T.; Dong, W. The anticancer effect of cytotoxin 1 from Naja atra Cantor venom is mediated by a lysosomal cell death pathway involving lysosomal membrane permeabilization and cathepsin B release. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2013, 41, 643–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaisakul, J.; Hodgson, W.C.; Kuruppu, S.; Prasongsook, N. Effects of animal venoms and toxins on hallmarks of cancer. J. Cancer 2016, 7, 1571–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.G.; Tjong, S.C.; Wu, P.L.; Kuo, J.H.; Wu, K. Role of heparan sulfates and glycosphingolipids in the pore formation of basic polypeptides of cobra cardiotoxin. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2010, 677, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.H.; Wu, W.G. Amphiphilic β-sheet cobra cardiotoxin targets mitochondria and disrupts its network. FEBS Lett. 2005, 579, 3169–3174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Li, F.; Chen, Z.; Shrivastava, I.H.; Gasanoff, E.S.; Dagda, R.K. Naja mossambica mossambica cobra cardiotoxin targets mitochondria to disrupt mitochondrial membrane structure and function. Toxins 2019, 11, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langone, F.; Cannata, S.; Fuoco, C.; Lettieri Barbato, D.; Testa, S.; Nardozza, A.P.; Ciriolo, M.R.; Castagnoli, L.; Gargioli, C.; Cesareni, G. Metformin protects skeletal muscle from cardiotoxin induced degeneration. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e114018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marin, T.L.; Gongol, B.; Zhang, F.; Martin, M.; Johnson, D.A.; Xiao, H.; Wang, Y.; Subramaniam, S.; Chien, S.; Shyy, J.Y. AMPK promotes mitochondrial biogenesis and function by phosphorylating the epigenetic factors DNMT1, RBBP7, and HAT1. Sci. Signal 2017, 10, eaaf7478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herzig, S.; Shaw, R.J. AMPK: Guardian of metabolism and mitochondrial homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2018, 19, 121–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichner, L.J.; Brun, S.N.; Herzig, S.; Young, N.P.; Curtis, S.D.; Shackelford, D.B.; Shokhirev, M.N.; Leblanc, M.; Vera, L.I.; Hutchins, A.; et al. Genetic analysis reveals AMPK is required to support tumor growth in murine Kras-dependent lung cancer models. Cell Metab. 2019, 29, 285–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, J.; Mills, G.B. AMPK: A contextual oncogene or tumor suppressor? Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 2929–2935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mihaylova, M.M.; Shaw, R.J. The AMPK signalling pathway coordinates cell growth, autophagy and metabolism. Nat. Cell Biol. 2011, 13, 1016–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiou, S.H.; Raynor, R.L.; Zheng, B.; Chambars, T.C.; Kuo, J.F. Cobra venom cardiotoxin (cytotoxin) isoforms and neurotoxin: Comparative potency of protein kinase C inhibition and cancer cell cytotoxicity and model of enzyme inhibition. Biochemistry 1993, 32, 2062–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morciano, G.; Giorgi, C.; Balestra, D.; Marchi, S.; Perrone, D.; Pinotti, M.; Pinton, P. Mcl-1 involvement in mitochondrial dynamics is associated with apoptotic cell death. Mol. Biol. Cell 2016, 27, 20–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Scheffler, T.L.; Rossie, S.S.; Gerrard, D.E. AMPK activity is regulated by calcium-mediated protein phosphatase 2A activity. Cell Calcium 2013, 53, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, B.K.; Liu, H.Y.; Francisco, J.; Pandya, D.; Donigan, M.; Gallo-Ebert, C.; Giordano, C.; Bata, A.; Nickels, J.T., Jr. Inhibition of AMP kinase by the protein phosphatase 2A heterotrimer, PP2APpp2r2d. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 10588–10598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Chen, C.; Ji, F.; Mao, L.; Xie, Y. PP2A catalytic subunit silence by microRNA-429 activates AMPK and protects osteoblastic cells from dexamethasone. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 487, 660–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kao, P.H.; Lin, S.R.; Chang, L.S. Differential binding to phospholipid bilayers modulates membrane-damaging activity of Naja naja atra cardiotoxins. Toxicon 2009, 54, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.C.; Kao, P.H.; Lin, S.R.; Chang, L.S. The mechanism of cytotoxicity by Naja naja atra cardiotoxin 3 is physically distant from its membrane-damaging effect. Toxicon 2007, 50, 816–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, S.H.; Su, S.J.; Lin, S.R.; Chang, K.L. Cardiotoxin-III selectively enhances activation-induced apoptosis of human CD8+ T lymphocytes. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2003, 193, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.H.; Monette, R.; Lee, S.C.; Morley, P.; Wu, W.G. Cobra cardiotoxin-induced cell death in fetal rat cardiomyocytes and cortical neurons: Different pathway but similar cell surface target. Toxicon 2005, 46, 430–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.H.; Chang, L.S. Reactive oxygen species and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase induce apoptotic death of U937 cells in response to Naja nigricollis toxin-γ. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2009, 13, 1695–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyama, E.Q.; Herzig, S.; Courchet, J.; Lewis, T.L., Jr.; Losón, O.C.; Hellberg, K.; Young, N.P.; Chen, H.; Polleux, F.; Chan, D.C.; et al. AMP-activated protein kinase mediates mitochondrial fission in response to energy stress. Science 2016, 351, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekar, P.; Huang, D.Y.; Hsieh, S.L.; Chang, S.F.; Lin, W.W. AMPK-dependent and independent actions of P2X7 in regulation of mitochondrial and lysosomal functions in microglia. Cell Commun. Signal. 2018, 16, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trockenbacher, A.; Suckow, V.; Foerster, J.; Winter, J.; Krauss, S.; Ropers, H.H.; Schneider, R.; Schweiger, S. MID1, mutated in Opitz syndrome, encodes an ubiquitin ligase that targets phosphatase 2A for degradation. Nat. Genet. 2001, 29, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, M.; Ditsworth, D.; Lindsten, T.; Thompson, C.B. α4 is an essential regulator of PP2A phosphatase activity. Mol. Cell 2009, 36, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Stanevich, V.; Satyshur, K.A.; Kong, M.; Watkins, G.R.; Wadzinski, B.E.; Sengupta, R.; Xing, Y. Structural basis of protein phosphatase 2A stable latency. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.J.; Huang, C.H.; Lee, Y.C.; Wang, L.J.; Chiou, J.T.; Chang, L.S. Naja atra cardiotoxins enhance the protease activity of chymotrypsin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 136, 512–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.H.; Chou, W.M.; Chang, L.S. p38 MAPK/PP2Acα/TTP pathway on the connection of TNF-α and caspases activation on hydroquinone-induced apoptosis. Carcinogenesis 2013, 34, 818–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.C.; Chen, Y.J.; Huang, C.H.; Chang, L.S. Amsacrine-induced apoptosis of human leukemia U937 cells is mediated by the inhibition of AKT- and ERK-induced stabilization of MCL1. Apoptosis 2017, 22, 406–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.C.; Wang, L.J.; Huang, C.H.; Shi, Y.J.; Chang, L.S. ABT-263-induced MCL1 upregulation depends on autophagy-mediated 4EBP1 downregulation in human leukemia cells. Cancer Lett. 2018, 432, 191–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chiou, J.-T.; Shi, Y.-J.; Wang, L.-J.; Huang, C.-H.; Lee, Y.-C.; Chang, L.-S. Naja atra Cardiotoxin 3 Elicits Autophagy and Apoptosis in U937 Human Leukemia Cells through the Ca2+/PP2A/AMPK Axis. Toxins 2019, 11, 527. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11090527
Chiou J-T, Shi Y-J, Wang L-J, Huang C-H, Lee Y-C, Chang L-S. Naja atra Cardiotoxin 3 Elicits Autophagy and Apoptosis in U937 Human Leukemia Cells through the Ca2+/PP2A/AMPK Axis. Toxins. 2019; 11(9):527. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11090527
Chicago/Turabian StyleChiou, Jing-Ting, Yi-Jun Shi, Liang-Jun Wang, Chia-Hui Huang, Yuan-Chin Lee, and Long-Sen Chang. 2019. "Naja atra Cardiotoxin 3 Elicits Autophagy and Apoptosis in U937 Human Leukemia Cells through the Ca2+/PP2A/AMPK Axis" Toxins 11, no. 9: 527. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11090527
APA StyleChiou, J.-T., Shi, Y.-J., Wang, L.-J., Huang, C.-H., Lee, Y.-C., & Chang, L.-S. (2019). Naja atra Cardiotoxin 3 Elicits Autophagy and Apoptosis in U937 Human Leukemia Cells through the Ca2+/PP2A/AMPK Axis. Toxins, 11(9), 527. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11090527