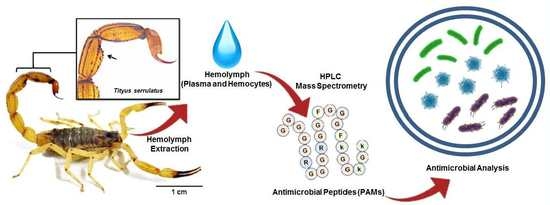
Serrulin: A Glycine-Rich Bioactive Peptide from the Hemolymph of the Yellow Tityus serrulatus Scorpion
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Fractionation of Peptides from the Hemocytes
2.2. Bioassay
2.2.1. Antimicrobial Activity, Minimal Inhibitory Concentration (MIC)
2.2.2. Hemolytic Activity
2.3. Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate-Polyacrylamide Gel (SDS-PAGE)
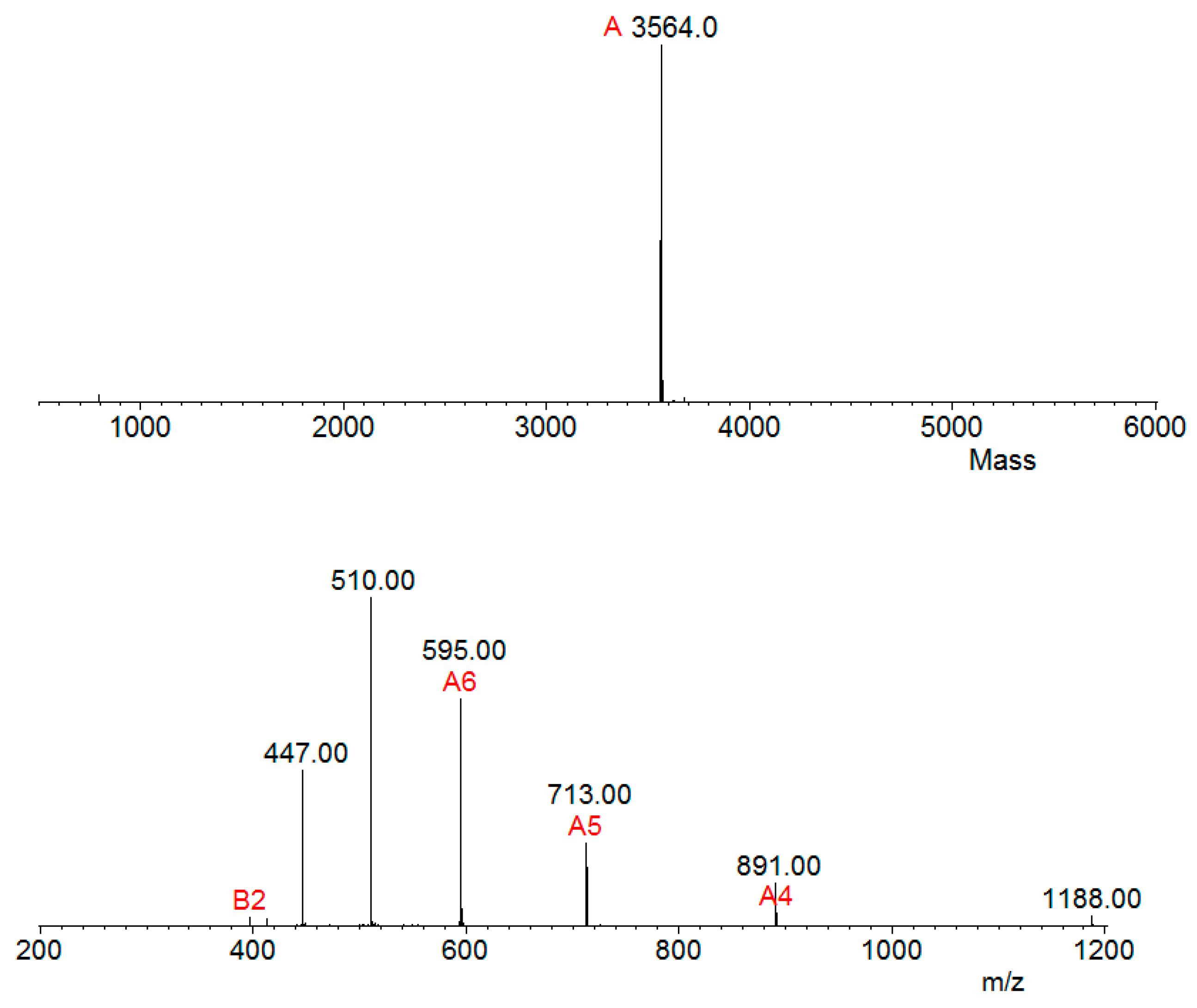
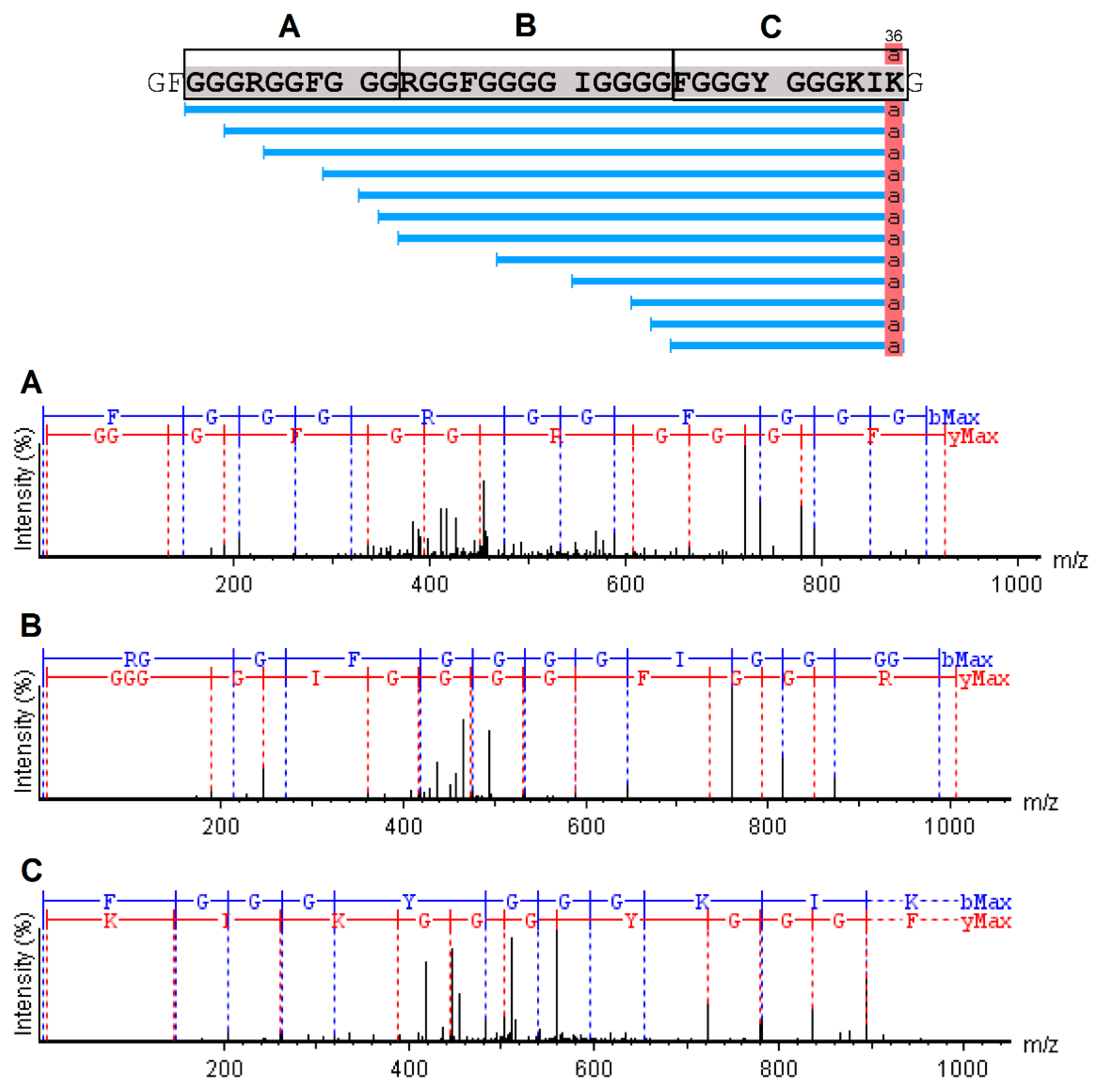
2.4. Mass Spectrometry and Bioinformatics Analyses
3. Conclusions
4. Material and Methods
4.1. Animals and Hemolymph Extraction
4.2. Fractionation of Antimicrobial Peptides
4.3. Bioassays
4.4. Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate-Polyacrylamide Gel (SDS-PAGE)
4.5. Enzymatic “in Gel” Digestion
4.6. Mass Spectrometry and Bioinformatics Analyses
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cologna, C.T.; Marcussi, S.; Giglio, J.R.; Soares, A.M.; Arantes, E.C. Tityus serrulatus scorpion venom and toxins: An overview. Protein Pept. Lett. 2009, 16, 920–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, M.C.; Cella, D.M. Karyotype conservation in 2 populations of the parthenogenetic scorpion Tityus serrulatus (Buthidae): rDNA and its associated heterochromatin are concentrated on only one chromosome. J. Hered. 2010, 101, 491–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Possani, L.D.; Merino, E.; Corona, M.; Bolivar, F.; Becerril, B. Peptides and genes coding for scorpion toxins that affect ion-channels. Biochimie 2000, 82, 861–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Ma, C.; Du, Q.; Wei, R.; Wang, L.; Zhou, M.; Chen, T.; Shaw, C. Two peptides, TsAP-1 and TsAP-2, from the venom of the Brazilian yellow scorpion, Tityus serrulatus: Evaluation of their antimicrobial and anticancer activities. Biochimie 2013, 95, 1784–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahadevappa, R.; Ma, R.; Kwok, H.F. Venom Peptides: Improving Specificity in Cancer Therapy. Trends Cancer 2017, 3, 611–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuzawa, A.H.; Vellutini, B.C.; Lorenzini, D.M.; da Silva Junior, P.I.; Mortara, R.A.; da Silva, J.M.C.; Daffre, S. The roles of hemocytes in the immunity of the spider Acanthoscurria gomesiana. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2008, 32, 716–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nentwing, L.K.; Nentwing, W. The Immune System of Spider. In Spider Ecophysiology; Nentwing, W., Ed.; Springer: Bern, Switzerland, 2013; 82p. [Google Scholar]
- Froy, O.; Gurevitz, M. Arthropod and mollusk defensins-evolution by exon-shuffling. Trends Genet. 2003, 19, 684–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumann, T.; Kuhn-Nentwig, L.; Largiadèr, C.R.; Nentwig, W. Expression of defensins in non-infected araneomorph spiders. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2010, 67, 2643–2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cociancich, S.; Goyffon, M.; Bontems, F.; Bulet, P.; Bouet, F.; Menez, A.; Hoffmann, J. Purification and characterization of a scorpion defensin, a 4kDa antibacterial peptide presenting structural similarities with insect defensins and scorpion toxins. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1993, 194, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehret-Sabatier, L.; Loew, D.; Goyffon, M.; Fehlbaum, P.; Hoffmann, J.A.; van Dorsselaer, A.; Bulet, P. Characterization of novel cysteine-rich antimicrobial peptides from scorpion blood. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 29537–29544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De La Vega, R.R.; Garcia, B.I.; D’Ambrosio, C.; Diego-Garcia, E.; Scaloni, A.; Possani, L.D. Antimicrobial peptide induction in the haemolymph of the Mexican scorpion Centruroides limpidus limpidus in response to septic injury. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2004, 61, 1507–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, P.I., Jr.; Daffre, S.; Bulet, P. Isolation and characterization of gomesin, an 18-residue cysteine-rich defense peptide from the spider Acanthoscurria gomesiana hemocytes with sequence similarities to horseshoe crab antimicrobial peptides of the tachyplesin family. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 33464–33470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenzini, D.M.; da Silva, P.I., Jr.; Fogaça, A.C.; Bulet, P.; Daffre, S. Acanthoscurrin: A novel glycine-rich antimicrobial peptide constitutively expressed in the hemocytes of the spider Acanthoscurria gomesiana. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2003, 7, 781–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann, T.; Kämpfer, U.; Schürch, S.; Schaller, J.; Largiadèr, C.; Nentwig, W.; Kuhn-Nentwig, L. Ctenidins: Antimicrobial glycine-rich peptides from the hemocytes of the spider Cupiennius salei. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2010, 67, 2787–2798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, B.M.; Shirtliff, M.E.; Jabra-Rizk, M.A. Antimicrobial Peptides: Primeval molecules or future drogs? PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1001067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riciluca, K.C.; Sayegh, R.S.; Melo, R.L.; Silva, P.I., Jr. Rondonin an antifungal peptide from spider (Acanthoscurria rondoniae) haemolymph. Results Immunol. 2012, 2, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaparro, E.; da Silva, P.I., Jr. Lacrain: The first antimicrobial peptide from the body extract of the Brazilian centipede Scolopendra viridicornis. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2016, 48, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diniz, L.C.L.; Miranda, A.; da Silva, P.I., Jr. Human Antimicrobial Peptide Isolated from Triatoma infestans Haemolymph, Trypanosoma cruzi-Transmitting Vector. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikonomopoulou, M.P.; Fernandez-Rojo, M.A.; Pineda, S.S.; Cabezas-Sainz, P.; Winnen, B.; Morales, R.A.V.; Brust, A.; Sánchez, L.; Alewood, P.F.; Ramm, G.A.; et al. Gomesin inhibits melanoma growth by manipulating key signaling cascades that control cell death and proliferation. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 11519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulet, P.; Dimarcq, J.L.; Hetru, C.; Lagueux, M.; Charlet, M.; Hegy, G.; Van Dorsselaer, A.; Hoffmann, J.A. A novel inducible antibacterial peptide of Drosophila carries an O-glycosylated substitution. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 14893–14897. [Google Scholar]
- Fuzita, F.J.; Pinkse, M.W.; Patane, J.S.; Juliano, M.A.; Verhaert, P.D.; Lopes, A.R. Biochemical, transcriptomic and proteomic analyses of digestion in the scorpion Tityus serrulatus: Insights into function and evolution of digestion in an ancient arthropod. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0123841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Oliveira, U.C.; Nishiyama, M.Y., Jr.; Dos Santos, M.B.V.; Santos-da-Silva, A.P.; Chalkidis, H.M.; Souza-Imberg, A.; Candido, D.M.; Yamanouye, N.; Dorce, V.A.C.; Junqueira-de-Azevedo, I.L.M. Proteomic endorsed transcriptomic profiles of venom glands from Tityus obscurus and T. serrulatus scorpions. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0193739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhu, S. The defensin gene family expansion in the tick Ixodes scapularis. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2011, 35, 1128–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyoshi, N.; Isogai, E.; Hiramatsu, K.; Sasaki, T. Activity of tick antimicrobial peptide from Ixodes persulcatus (persulcatusin) against cell membranes of drug-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J. Antibiot. 2017, 70, 142–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagel Van Zee, J.; Geraci, N.S.; Guerrero, F.D.; Wikel, S.K.; Stuart, J.J.; Nene, V.M.; Hill, C.A. Tick genomics: The Ixodes genome project and beyond. Int. J. Parasitol. 2007, 37, 1297–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herbinière, J.; Braquart-Varnier, C.; Grève, P.; Strub, J.M.; Frère, J.; Van Dorsselaer, A.; Martin, G. Armadillidin: A novel glycine-rich antibacterial peptide directed against gram-positive bacteria in the woodlouse Armadillidium vulgare (terrestrial isopod, Crustacean). Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2005, 29, 489–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Destoumieux, D.; Bulet, P.; Loew, D.; Van Dorsselaer, A.; Rodriguez, J.; Bachère, E. Penaeidins, a new family of antimicrobial peptides isolated from the shrimp Penaeus vannamei (Decapoda). J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 28398–28406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, T.; Furunaka, H.; Miyata, T.; Tokunaga, F.; Muta, T.; Iwanaga, S.; Niwa, M.; Takao, T.; Shimonishi, Y. Tachyplesin, a class of antimicrobial peptide from the hemocytes of the horseshoe crab (Tachypleus tridentatus): Isolation and chemical structure. J. Biol. Chem. 1988, 263, 16709–16713. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gasteiger, E.; Hoogland, C.; Gattiker, A.; Duvaud, S.; Wilkins, M.R.; Appel, R.D.; Bairoch, A. Protein Identification and Analysis Tools on the ExPASy Server. In The Proteomics Protocols Handbook; John, M.W., Ed.; Humans Press Inc.: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2005; pp. 571–607. [Google Scholar]
- Shrestha, A.; Duwadi, D.; Jukosky, J.; Fiering, S.N. Cecropin-like antimicrobial peptide protects mice from lethal E.coli infection. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0220344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.B.; Kim, M.S.; Kim, S.C. A novel antimicrobial peptide from Bufo bufo gargarizans. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1996, 218, 408–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugiarto, H.; Yu, P.L. Mechanisms of action of ostrich beta-defensins against Escherichia coli. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2007, 270, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Casteels, P.; Ampe, C.; Jacobs, F.; Vaeck, M.; Tempst, P. Apidaecins:antibacterial peptides from honeybees. EMBO J. 1989, 8, 2387–2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Söderhäll, K.; Smith, V.J. Separation of the haemocyte populations of Carcinus maenas and other marine decapods, and prophenoloxidase distribution. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 1983, 7, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, G.; Shi, Y.H.; Tang, Y.L.; Le, G.W. The membrane action mechanism of analogs of the antimicrobial peptide Buforin 2. Peptides 2009, 30, 1421–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanna, S.L.; Sherman, N.E.; Kinter, M.T.; Goldberg, J.B. Comparison of proteins expressed by Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains representing initial and chronic isolates from a cystic fibrosis patient: An analysis by 2-D gel electrophoresis and capillary column liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Microbiology 2000, 146, 2495–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altschul, S.F.; Madden, T.L.; Schäffer, A.A.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Miller, W.; Lipman, D.J. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: A new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 3389–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Marshall, A.G. A Universal Algorithm for Fast and Automated Charge State Deconvolution of Electrospray Mass-to_charge Ratio Spectra. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 1998, 9, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
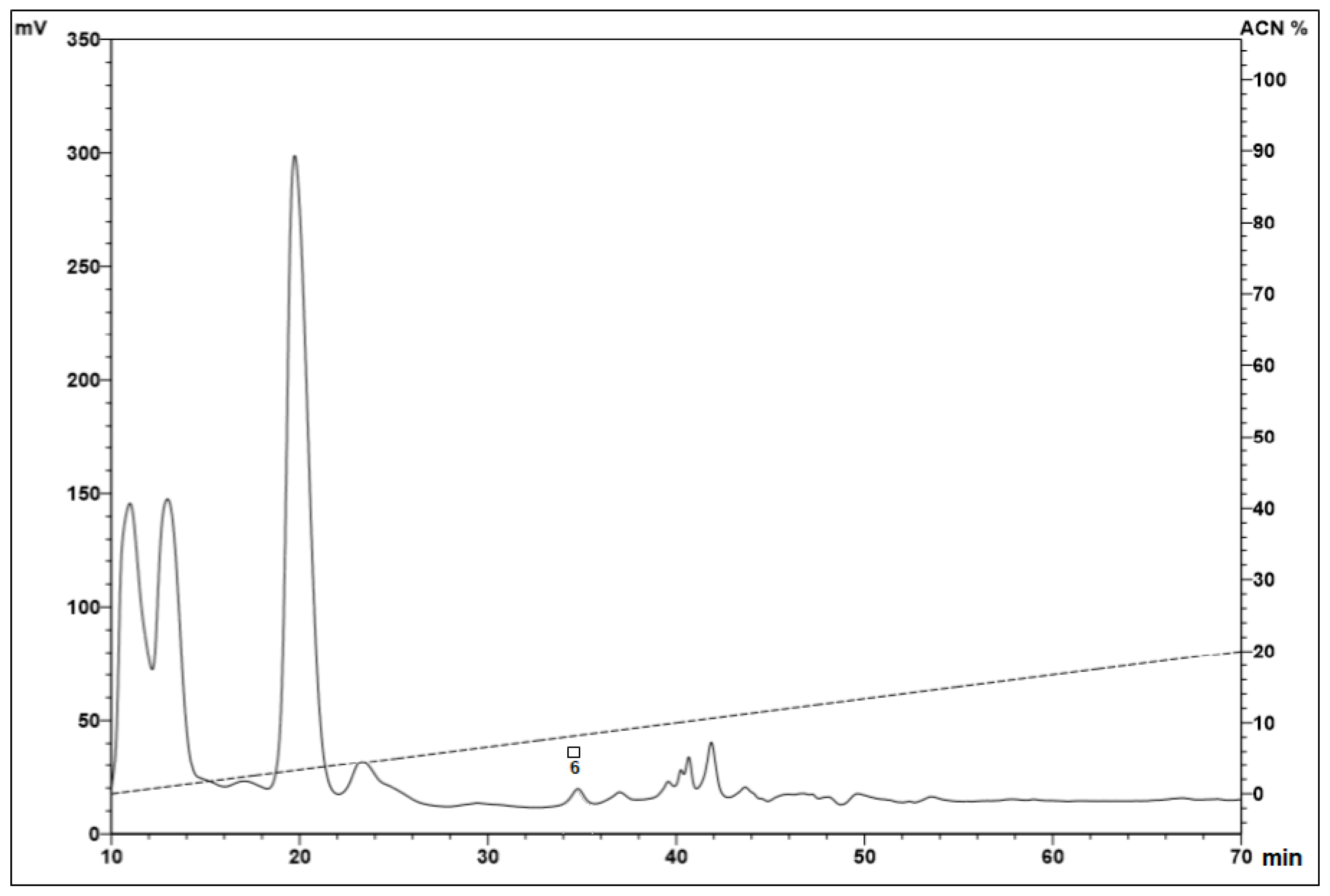
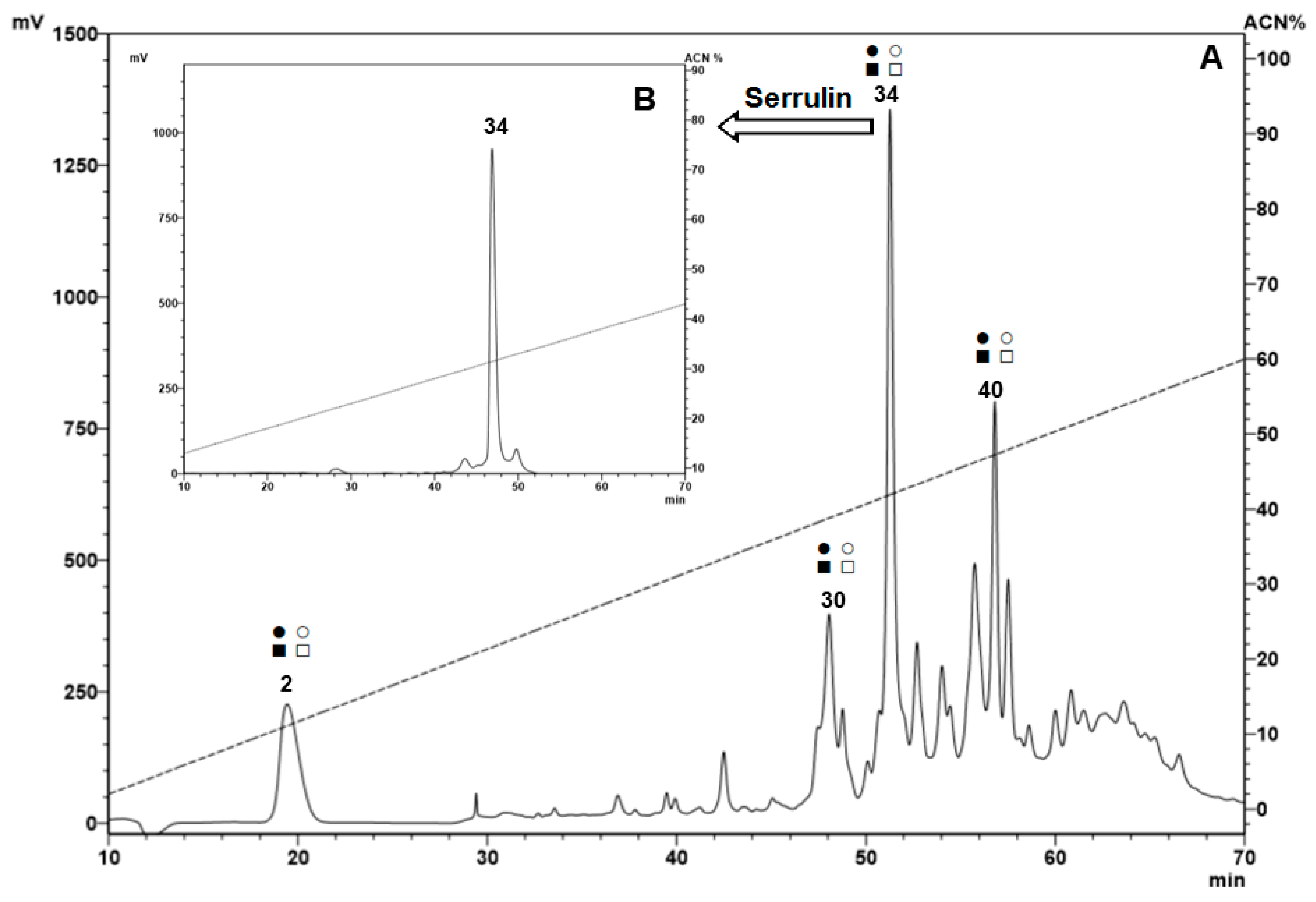
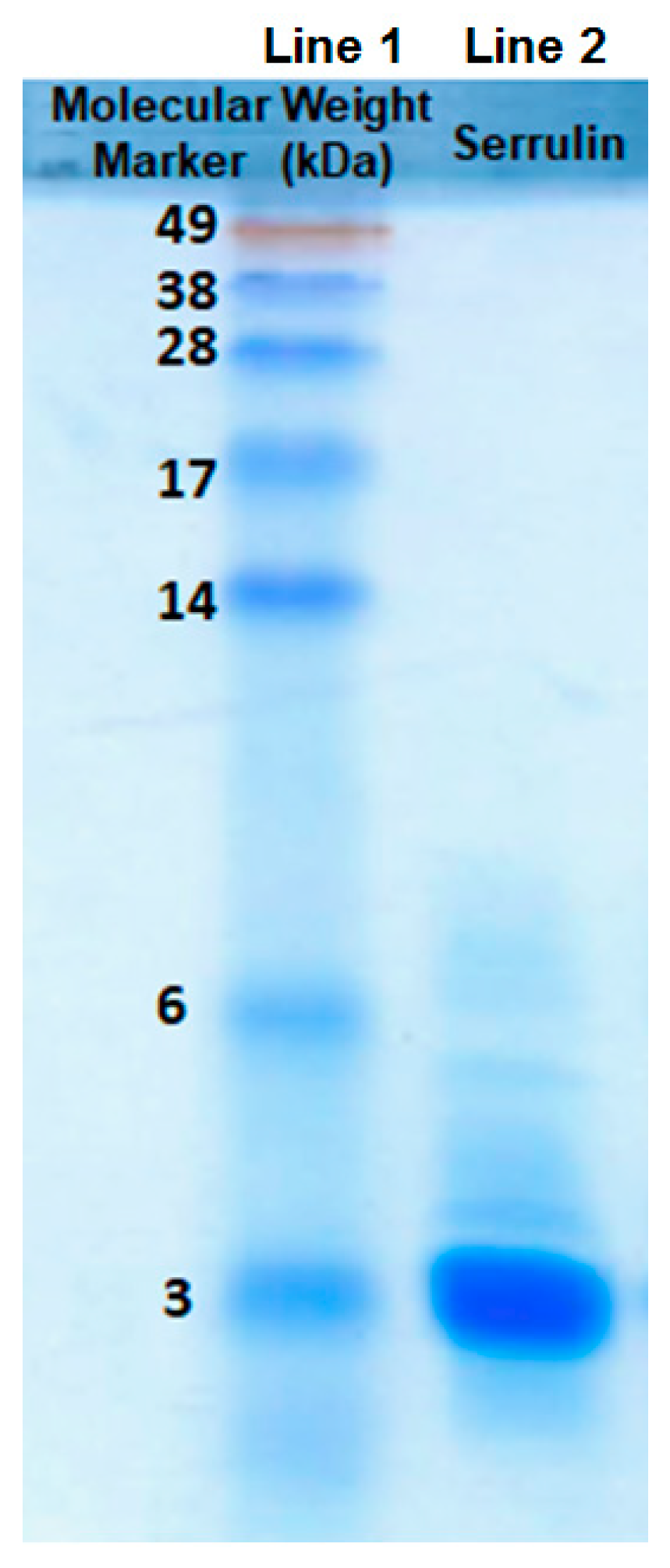

| Microorganism | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hemocytes | Fractions | Escherichia coli SBS363 | Micrococcus luteus A270 | Candida albicans MDM8 | Aspergillus niger |
| 5% | 6 | – | – | – | + |
| 2 | + | + | + | + | |
| 30 | + | + | + | + | |
| 40% | 34 | + | + | + | + |
| 40 | + | + | + | + | |
| Strain | MIC (µg/mL) | µM |
|---|---|---|
| Gram-positive bacteria | ||
| Micrococcus luteus A270 | 1.87–3.75 | (0.5–1) |
| Gram-negative bacteria | ||
| Escherichia coli SBS 363 | 30–60 | (9–16) |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 27853 | 0.05–0.1 | (0.01–0.3) |
| Fungi | ||
| Aspergillus niger | 12–24 | (3–6) |
| Yeast | ||
| Candida albicans MDM8 | 6–12 | (1.5–3) |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
de Jesus Oliveira, T.; Oliveira, U.C.d.; da Silva Junior, P.I. Serrulin: A Glycine-Rich Bioactive Peptide from the Hemolymph of the Yellow Tityus serrulatus Scorpion. Toxins 2019, 11, 517. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11090517
de Jesus Oliveira T, Oliveira UCd, da Silva Junior PI. Serrulin: A Glycine-Rich Bioactive Peptide from the Hemolymph of the Yellow Tityus serrulatus Scorpion. Toxins. 2019; 11(9):517. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11090517
Chicago/Turabian Stylede Jesus Oliveira, Thiago, Ursula Castro de Oliveira, and Pedro Ismael da Silva Junior. 2019. "Serrulin: A Glycine-Rich Bioactive Peptide from the Hemolymph of the Yellow Tityus serrulatus Scorpion" Toxins 11, no. 9: 517. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11090517
APA Stylede Jesus Oliveira, T., Oliveira, U. C. d., & da Silva Junior, P. I. (2019). Serrulin: A Glycine-Rich Bioactive Peptide from the Hemolymph of the Yellow Tityus serrulatus Scorpion. Toxins, 11(9), 517. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11090517