Detection and Spatio-Temporal Distribution of Pinnatoxins in Shellfish from the Atlantic and Cantabrian Coasts of Spain
Abstract
1. Introduction
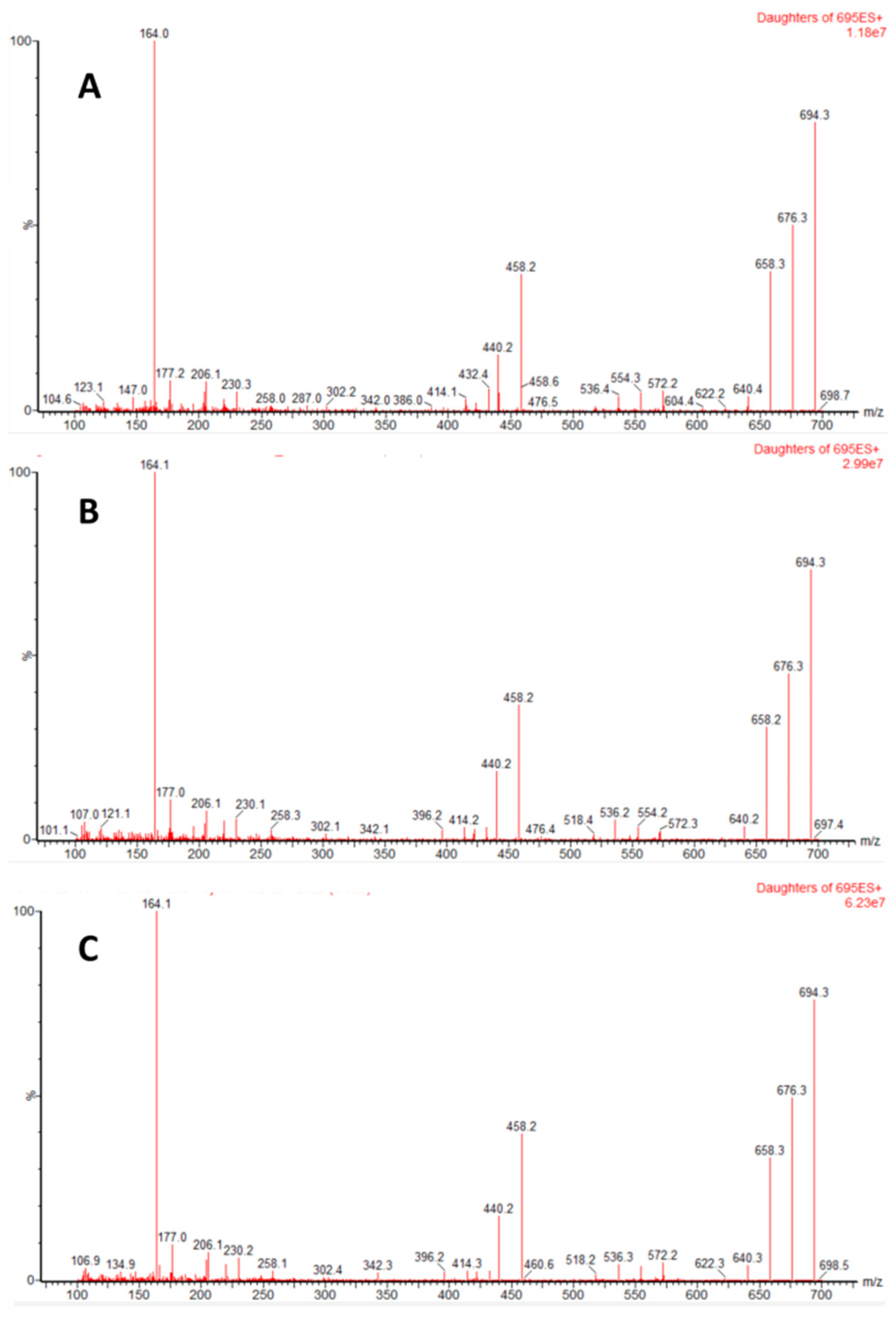
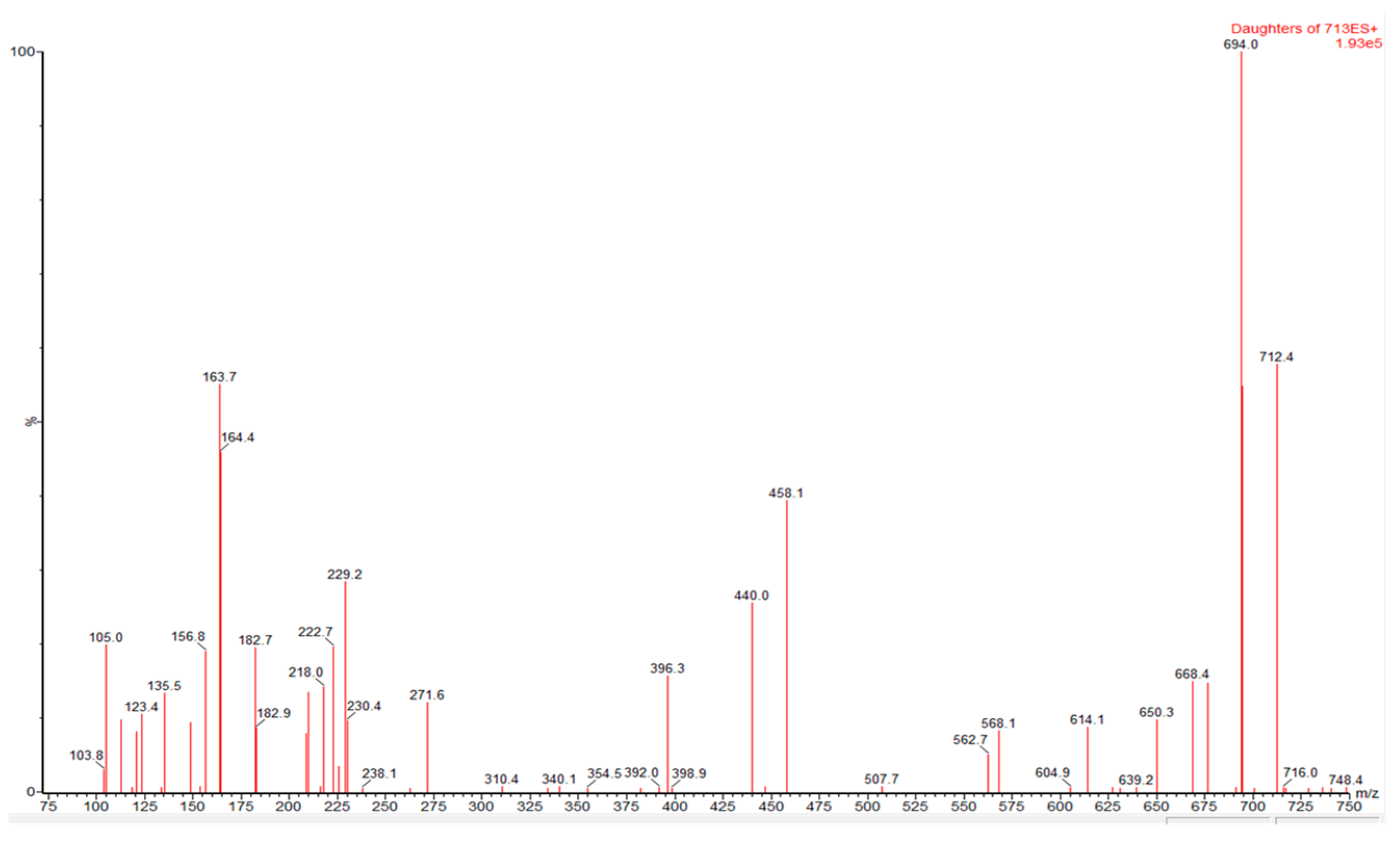
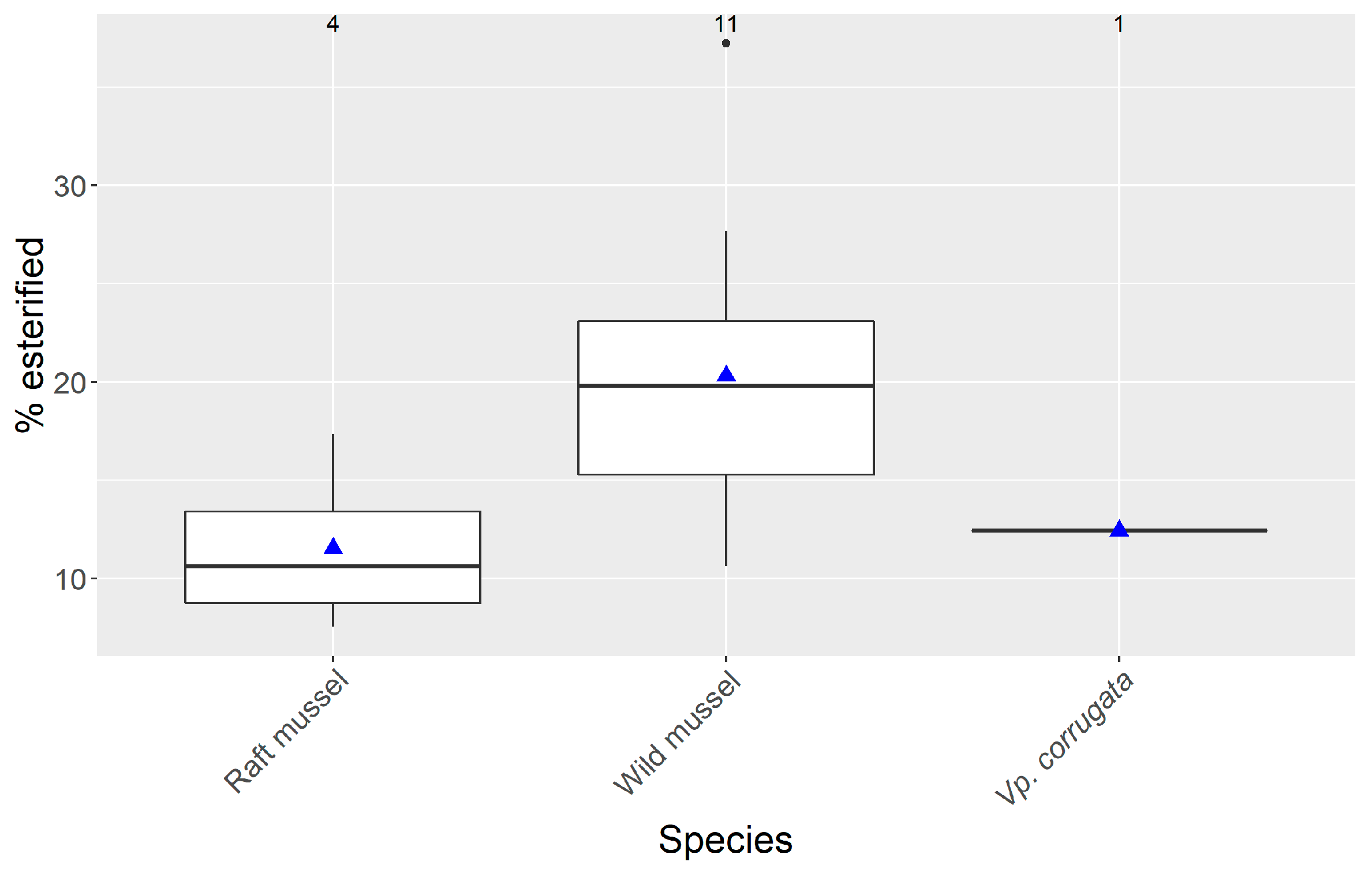
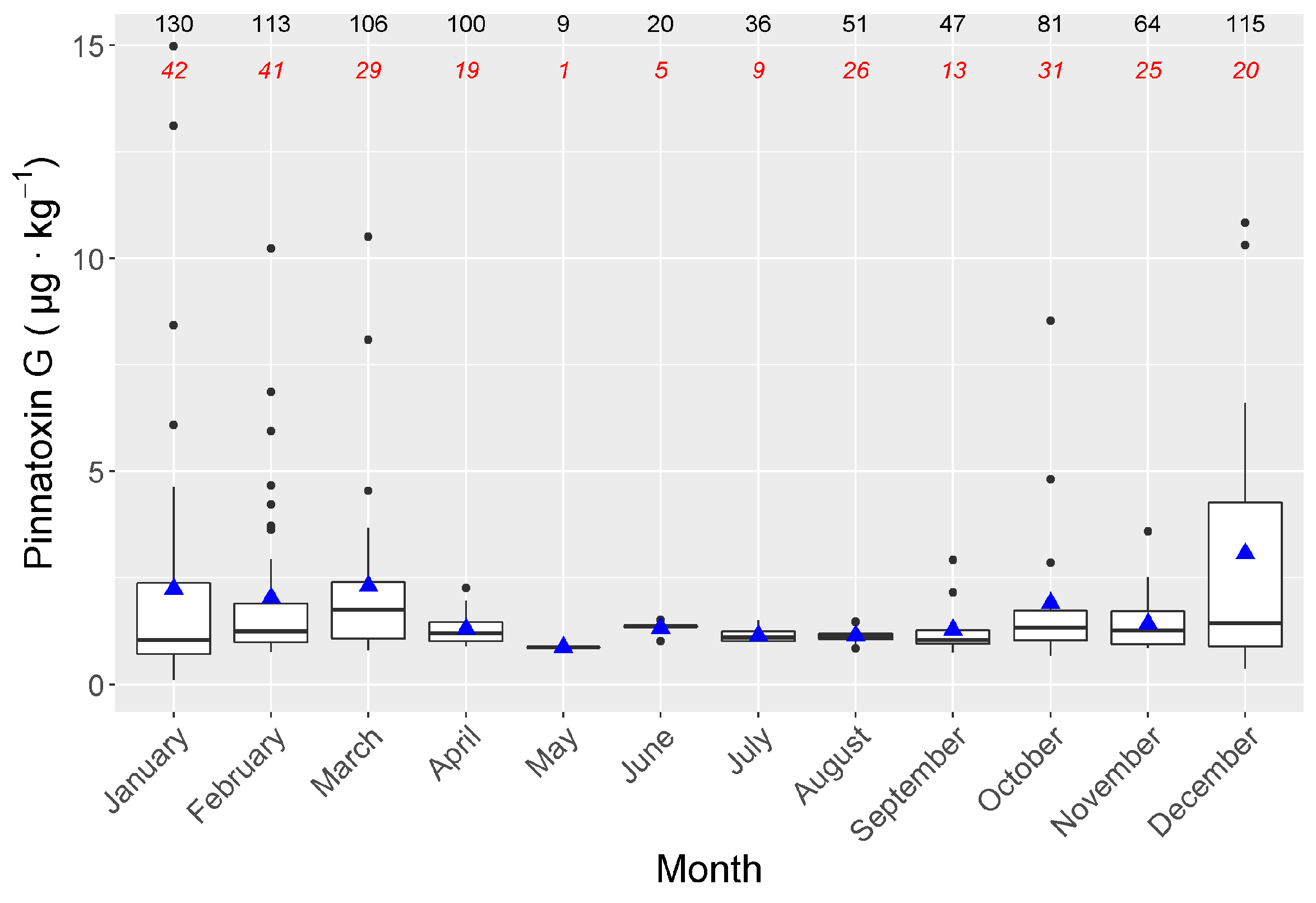
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Material and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Solvents
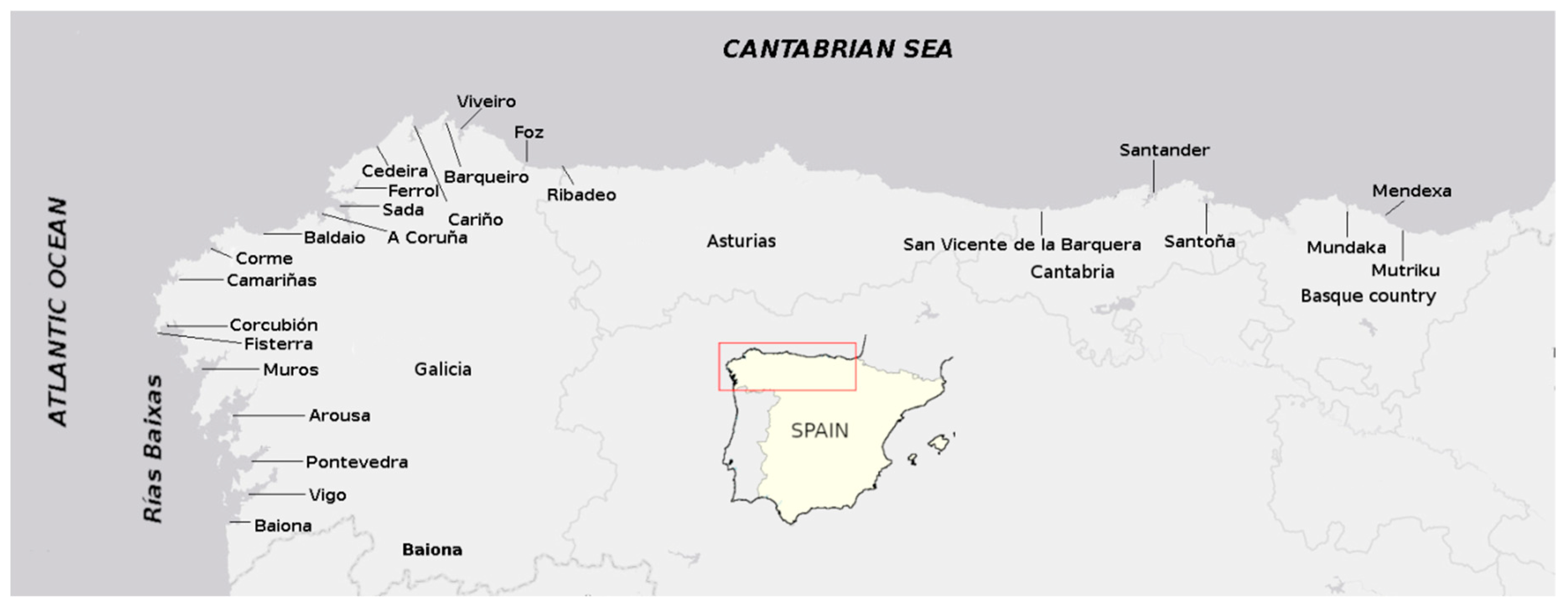
4.2. Sampling
4.3. Extraction and Sample Preparation
4.4. LC-MS/MS Analysis
4.5. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Selwood, A.I.; Miles, C.O.; Wilkins, A.L.; van Ginkel, R.; Munday, R.; Rise, F.; McNabb, P. Isolation, Structural Determination and Acute Toxicity of Pinnatoxins E, F and G. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 6532–6542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munday, R.; Selwood, A.I.; Rhodes, L. Acute toxicity of pinnatoxins E, F and G to mice. Toxicon 2012, 60, 995–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EFSA Panel on Contaminants in the Food Chain. Scientific Opinion on marine biotoxins in shellfish – Cyclic imines (spirolides, gymnodimines, pinnatoxins and pteriatoxins) 1. EFSA J. 2010, 8, 1–39. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, J.J.; Stivala, C.E.; Iorga, B.I.; Molgo, J.; Zakarian, A. Stability of Cyclic Imine Toxins: Interconversion of Pinnatoxin Amino Ketone and Pinnatoxin A in Aqueous Media. J. Org. Chem. 2012, 77, 10435–10440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molgó, J.; Aráoz, R.; Iorga, B.; Benoit, E.; Zakarian, A. Cyclic Imine Neurotoxins Acting on Muscarinic and Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors. In Toxins and Biologically Active Compounds from Microalgae; Rossini, G., Ed.; CRC Press: Modena, Italy, 2014; Volume 2, pp. 116–146. [Google Scholar]
- Hess, P.; Abadie, E.; Herve, F.; Berteaux, T.; Sechet, V.; Araoz, R.; Molgo, J.; Zakarian, A.; Sibat, M.; Rundberget, T.; et al. Pinnatoxin G is responsible for atypical toxicity in mussels (Mytilus galloprovincialis) and clams (Venerupis decussata) from Ingril, a French Mediterranean lagoon. Toxicon 2013, 75, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreira, A.R.; Comas, A.; Valle, A.; Seisdedo, M.; Fernandes, L.F. Bloom of Vulcanodinium rugosum linked to skin lesions in Cienfuegos Bay, Cuba. Harmful Algal News 2016, 55, 10–11. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, S.; Huang, F.; Chen, S.; Tan, X.; Zuo, J.; Peng, J.; Xie, R. The isolation and bioactivities of pinnatoxin. Chin. J. Mar. Drugs 1990, 9, 33–35. [Google Scholar]
- Chou, T.; Haino, T.; Kuramoto, M.; Uemura, D. Isolation and structure of pinnatoxin D, a new shellfish poison from the Okinawan bivalve Pinna muricata. Tetrahedron Lett. 1996, 37, 4027–4030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takada, N.; Umemura, N.; Suenaga, K.; Chou, T.; Nagatsu, A.; Haino, T.; Yamada, K.; Uemura, D. Pinnatoxins B and C, the most toxic components in the pinnatoxin series from the Okinawan bivalve Pinna muricata. Tetrahedron Lett. 2001, 42, 3491–3494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uemura, D.; Chou, T.; Haino, T.; Nagatsu, A.; Fukuzawa, S.; Zheng, S.-Z.; Chen, H.-S. Pinnatoxin A: a toxic amphoteric macrocycle from the Okinawan bivalve Pinna muricata. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1995, 117, 1155–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, L.; Smith, K.; Selwood, A.; McNabb, P.; Molenaar, S.; Munday, R.; Wilkinson, C.; Hallegraeff, G. Production of pinnatoxins E, F and G by scrippsielloid dinoflagellates isolated from Franklin Harbour, South Australia. New Zealand J. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2011, 45, 703–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, L.; Smith, K.; Selwood, A.; McNabb, P.; Munday, R.; Suda, S.; Molenaar, S.; Hallegraeff, G. Dinoflagellate Vulcanodinium rugosum identified as the causative organism of pinnatoxins in Australia, New Zealand and Japan. Phycologia 2011, 50, 624–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, L.; Smith, K.; Selwood, a.; McNabb, P.; van Ginkel, R.; Holland, P.; Munday, R. Production of pinnatoxins by a peridinoid dinoflagellate isolated from Northland, New Zealand. Harmful Algae 2010, 9, 384–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nézan, E.; Chomérat, N. Vulcanodinium rugosum gen. et sp. nov. (Dinophyceae), un Nouveau Dinoflagellé Marin de la Côte Méditerranéenne Française. Cryptogam. Algol. 2011, 32, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, K.F.; Rhodes, L.L.; Suda, S.; Selwood, A.I. A dinoflagellate producer of pinnatoxin G, isolated from sub-tropical Japanese waters. Harmful Algae 2011, 10, 702–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacKenzie, A.L.; Selwood, A.I.; McNabb, P.; Rhodes, L. Benthic dinoflagellate toxins in two warm-temperate estuaries: Rangaunu and Parengarenga Harbours, Northland, New Zealand. Harmful Algae 2011, 10, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNabb, P.S.; McCoubrey, D.J.; Rhodes, L.; Smith, K.; Selwood, A.I.; van Ginkel, R.; MacKenzie, A.L.; Munday, R.; Holland, P.T. New perspectives on biotoxin detection in Rangaunu Harbour, New Zealand arising from the discovery of pinnatoxins. Harmful Algae 2012, 13, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miles, C.O.; Rundberget, T.; Sandvik, M.; Aassen, J.A.B.; Selwood, A.I. The Presence of Pinnatoxins in Norwegian Mussels; Veterinaerinsrituttets Raportserie. Report 07b; National Veterinary Institute: Oslo, Norway, 2010; p. 10.
- Rambla-Alegre, M.; Miles, C.O.; de la Iglesia, P.; Fernandez-Tejedor, M.; Jacobs, S.; Sioen, I.; Verbeke, W.; Samdal, I.A.; Sandvik, M.; Barbosa, V.; et al. Occurrence of cyclic imines in European commercial seafood and consumers risk assessment. Environ. Res. 2018, 161, 392–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rundberget, T.; Aasen, J.A.B.; Selwood, A.I.; Miles, C.O. Pinnatoxins and spirolides in Norwegian blue mussels and seawater. Toxicon 2011, 58, 700–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, M.; Bane, V.; Garcia-Altares, M.; van Pelt, F.N.A.M.; Furey, A.; O’Halloran, J. Assessment of emerging biotoxins (pinnatoxin G and spirolides) at Europe’s first marine reserve: Lough Hyne. Toxicon 2015, 108, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarron, P.; Rourke, W.a.; Hardstaff, W.; Pooley, B.; Quilliam, M.A. Identification of Pinnatoxins and Discovery of Their Fatty Acid Ester Metabolites in Mussels ( Mytilus edulis ) from Eastern Canada. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 1437–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Altares, M.; Casanova, A.; Bane, V.; Diogene, J.; Furey, A.; de la Iglesia, P. Confirmation of Pinnatoxins and Spirolides in Shellfish and Passive Samplers from Catalonia (Spain) by Liquid Chromatography Coupled with Triple Quadrupole and High-Resolution Hybrid Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 3706–3732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlamis, A.; Katikou, P. Human impact in Mediterranean coastal ecosystems and climate change: Emerging toxins. In Climate Change and Marine and Freshwater Toxins; Botana, L., Ed.; Gruyter: Berlin, Germany, 2015; pp. 239–272. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, K.; Rhodes, L.; Selwood, A.; Hallegraeff, G.; Suda, S.; Gu, H. Does the pinnatoxin-producing dinoflagellate, Vulcanodinium rugosum, comprise a species complex? In Harmful Algae 2012, Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Harmful Algae, Changwon, Korea, 29 October–2 November 2012; Kim, H.G., Reguera, B., Hallegraeff, G.M., Lee, C.K., Han, M.S., Choi, J.K., Eds.; International Society for the Study of Harmful Algae: Busan, Korea, 2014; pp. 141–144. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, N.; Gu, H.; Smith, K.; Rhodes, L.; Selwood, A.; Yang, W. The first report of Vulcanodinium rugosum (Dinophyceae) from the South China Sea with a focus on the life cycle. New Zealand J. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2012, 46, 511–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Muftah, A.; Selwood, A.I.; Foss, A.J.; Al-Jabri, H.; Potts, M.; Yilmaz, M. Algal toxins and producers in the marine waters of Qatar, Arabian Gulf. Toxicon 2016, 122, 54–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selwood, A.I.; Wilkins, A.L.; Munday, R.; Gu, H.F.; Smith, K.F.; Rhodes, L.L.; Rise, F. Pinnatoxin H: a new pinnatoxin analogue from a South China Sea Vulcanodinium rugosum isolate. Tetrahedron Lett. 2014, 55, 5508–5510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abadie, E.; Chiantella, C.; Crottier, A.; Rhodes, L.; Masseret, E.; Berteaux, T.; Laabir, M. What are the main environmental factors driving the development of the neurotoxic dinoflagellate Vulcanodinium rugosum in a Mediterranean ecosystem (Ingril lagoon, France)? Harmful Algae 2018, 75, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EURLMB. EU-harmonised Standard Operating Procedure for Determination of Lipophilic Marine Biotoxins in Molluscs by LC-MS/MS. Version 5. Available online: http://aesan.msssi.gob.es/CRLMB/docs/docs/metodos_analiticos_de_desarrollo/EU-Harmonised-SOP-LIPO-LCMSMS_Version5.pdf (accessed on 30 June 2015).
- Regueiro, J.; Rossignoli, A.E.; Alvarez, G.; Blanco, J. Automated on-line solid-phase extraction coupled to liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry for determination of lipophilic marine toxins in shellfish. Food Chem. 2011, 129, 533–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R. Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2014. [Google Scholar]


| Toxin | Ionisation | Parent Ion | MS/MS Transition | CE (eV) | Cone Voltage (V) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PnTX A | ESI+ | [M + H]+ | 712.5> | 164 | 50 | 60 |
| 712.5> | 440.3 | 36 | 60 | |||
| 712.5> | 538.3 | 36 | 60 | |||
| 712.5> | 694.5 | 36 | 60 | |||
| PnTX BC | ESI+ | [M + H]+ | 741.5> | 164 | 50 | 60 |
| 741.5> | 458.3 | 36 | 60 | |||
| 741.5> | 723.5 | 36 | 60 | |||
| PnTX D | ESI+ | [M + H]+ | 782.5> | 164 | 50 | 60 |
| 782.5> | 446.3 | 36 | 60 | |||
| 782.5> | 764.5 | 36 | 60 | |||
| PnTX E | ESI+ | [M + H]+ | 784.5> | 164 | 57 | 60 |
| 784.5> | 446.3 | 41 | 60 | |||
| 784.5> | 766.5 | 57 | 60 | |||
| PnTX F | ESI+ | [M + H]+ | 766.5> | 164 | 50 | 60 |
| 766.5> | 446.3 | 36 | 60 | |||
| 766.5> | 748.5 | 36 | 60 | |||
| PnTX G | ESI+ | [M + H]+ | 694.5> | 164 | 50 | 60 |
| 694.5> | 440.3 | 36 | 60 | |||
| 694.5> | 676.5 | 36 | 60 | |||
| PnTX H | ESI+ | [M + H]+ | 708.5> | 164.2 | 57 | 60 |
| 708.5> | 690.4 | 57 | 60 | |||
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lamas, J.P.; Arévalo, F.; Moroño, Á.; Correa, J.; Muñíz, S.; Blanco, J. Detection and Spatio-Temporal Distribution of Pinnatoxins in Shellfish from the Atlantic and Cantabrian Coasts of Spain. Toxins 2019, 11, 340. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11060340
Lamas JP, Arévalo F, Moroño Á, Correa J, Muñíz S, Blanco J. Detection and Spatio-Temporal Distribution of Pinnatoxins in Shellfish from the Atlantic and Cantabrian Coasts of Spain. Toxins. 2019; 11(6):340. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11060340
Chicago/Turabian StyleLamas, J. Pablo, Fabiola Arévalo, Ángeles Moroño, Jorge Correa, Susana Muñíz, and Juan Blanco. 2019. "Detection and Spatio-Temporal Distribution of Pinnatoxins in Shellfish from the Atlantic and Cantabrian Coasts of Spain" Toxins 11, no. 6: 340. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11060340
APA StyleLamas, J. P., Arévalo, F., Moroño, Á., Correa, J., Muñíz, S., & Blanco, J. (2019). Detection and Spatio-Temporal Distribution of Pinnatoxins in Shellfish from the Atlantic and Cantabrian Coasts of Spain. Toxins, 11(6), 340. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11060340







