Structure and Activity of a Cytosolic Ribosome-Inactivating Protein from Rice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
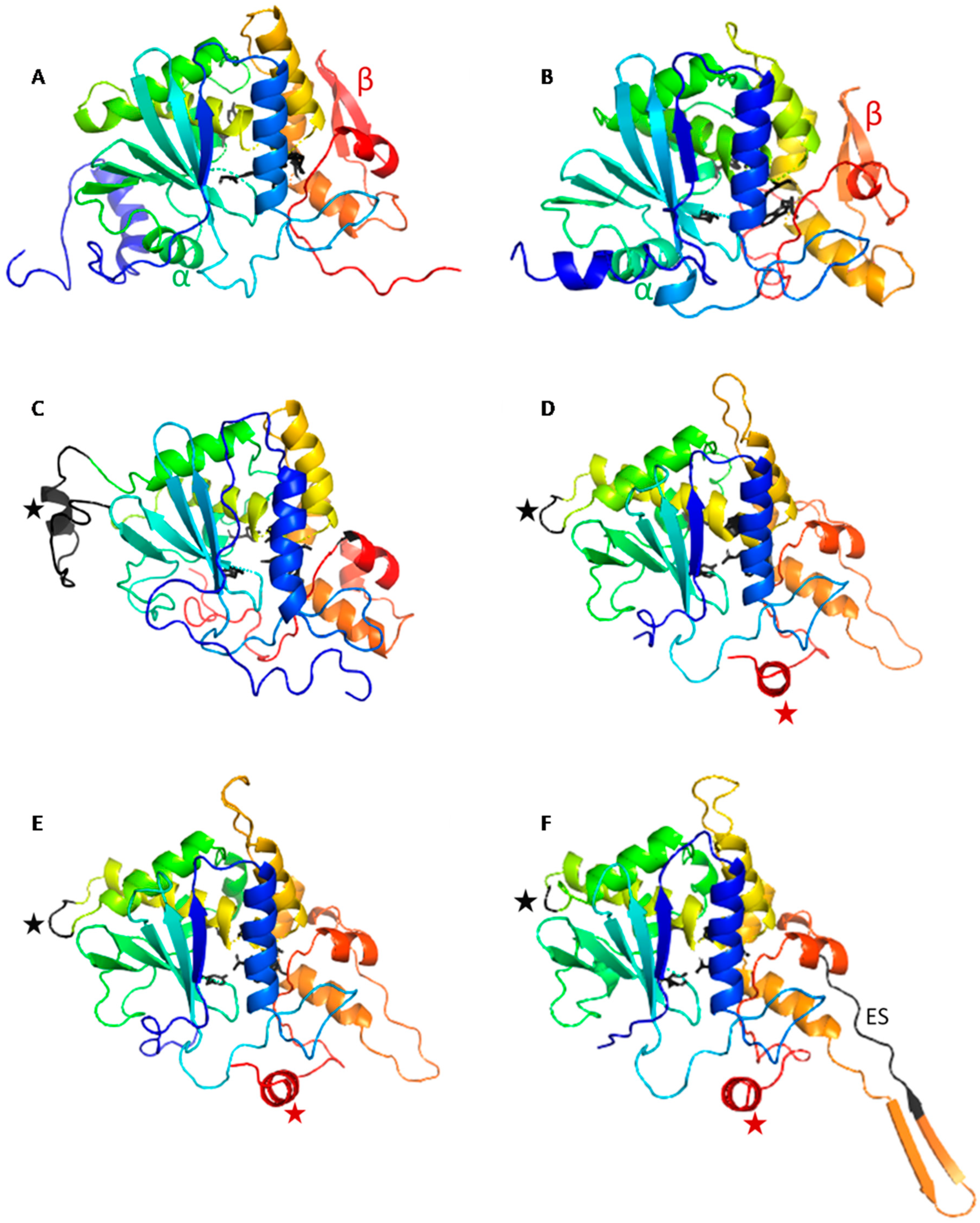
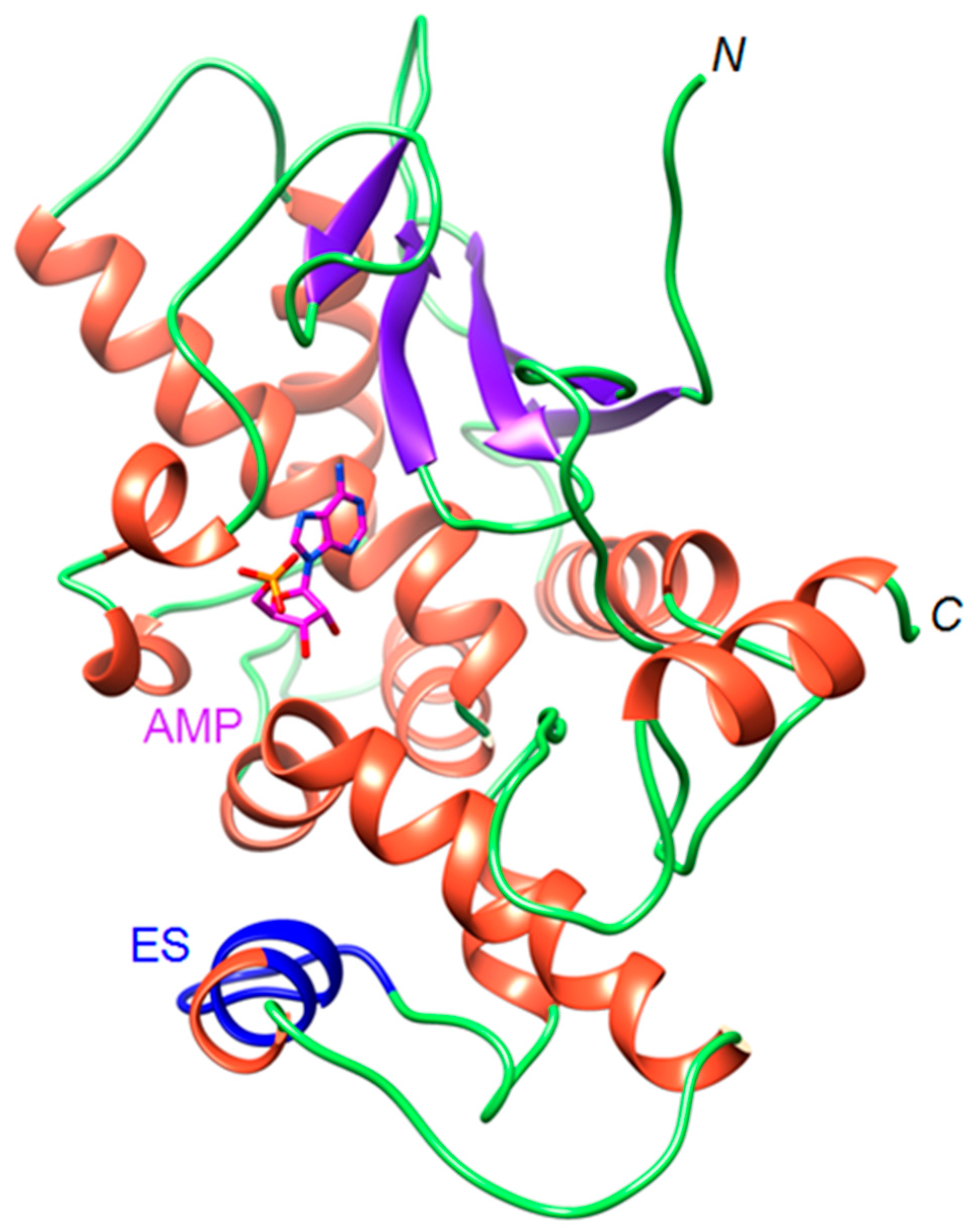
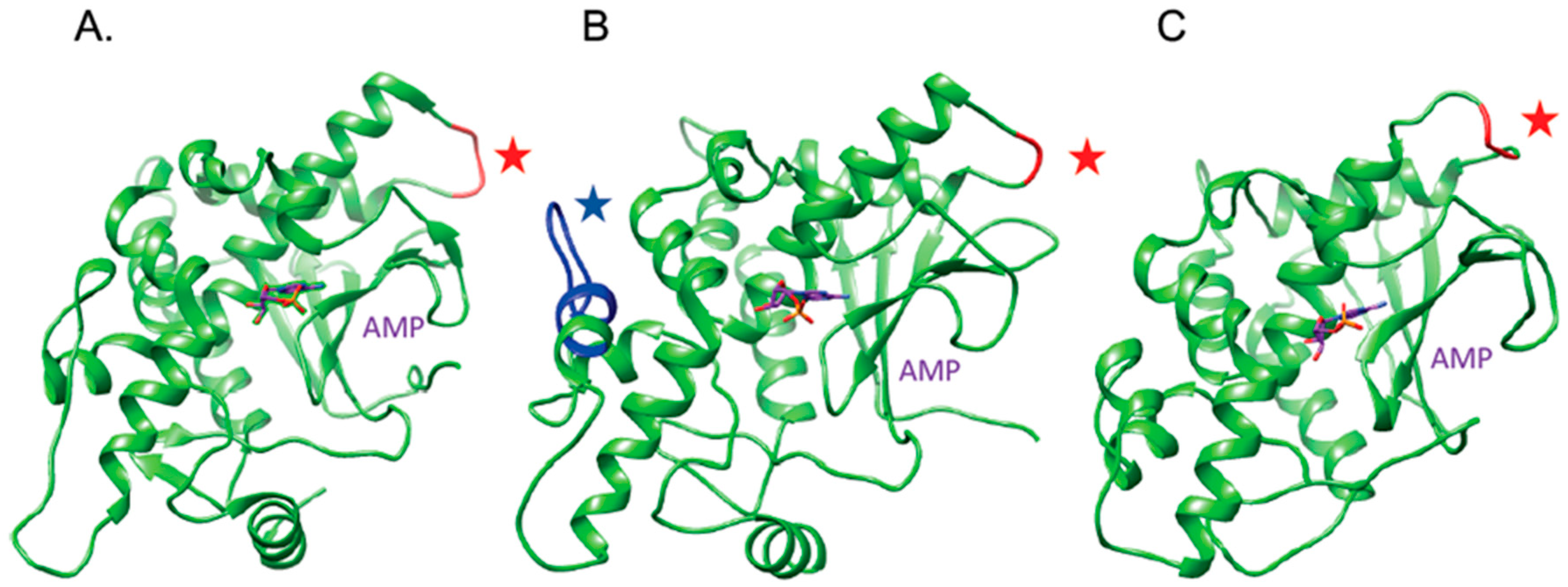
2.1. The OsRIP1 Structure Resembles Other Cereal RIPs and Suggests OsRIP1 Is a Functional Ribosome-Inactivating Protein
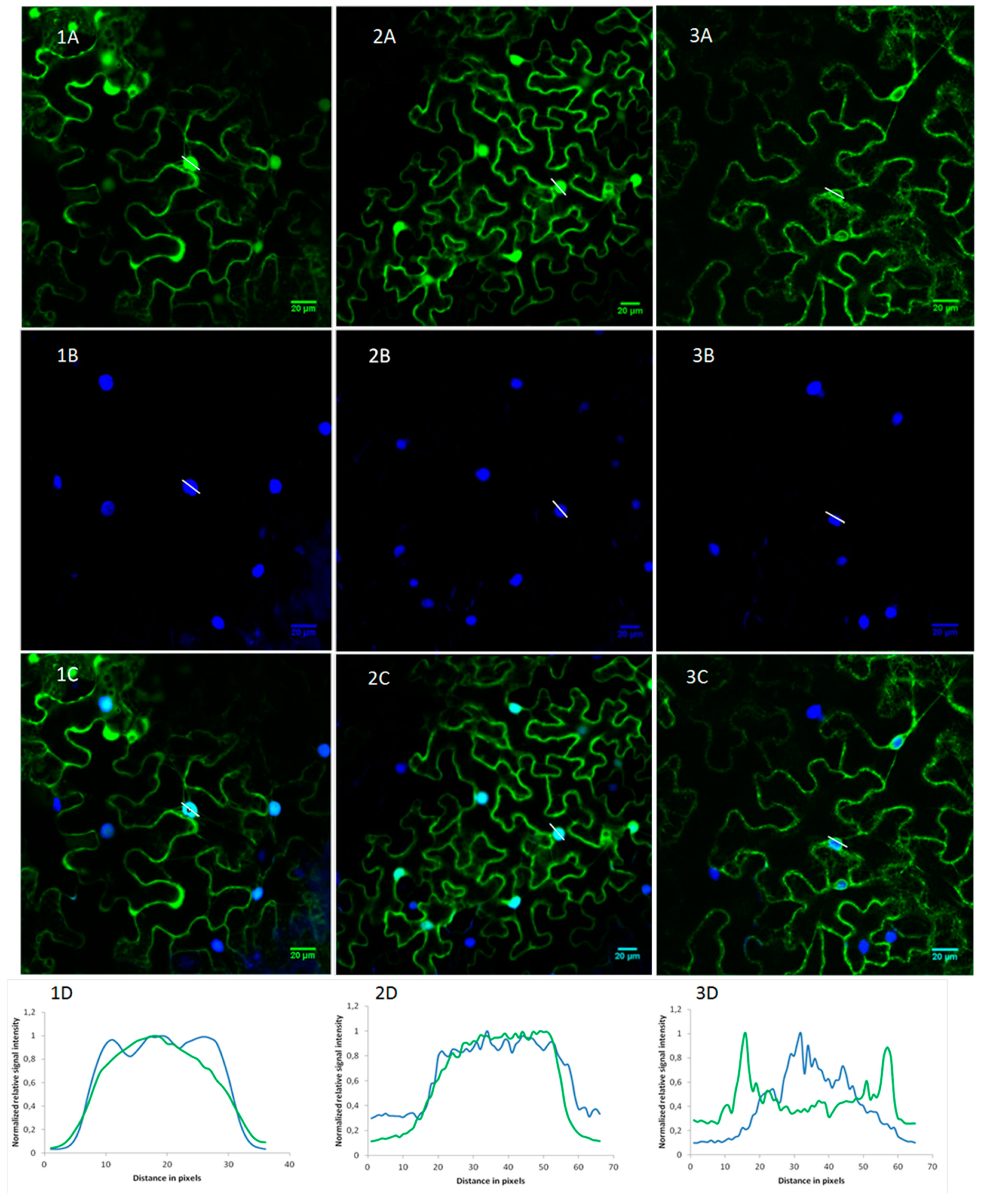
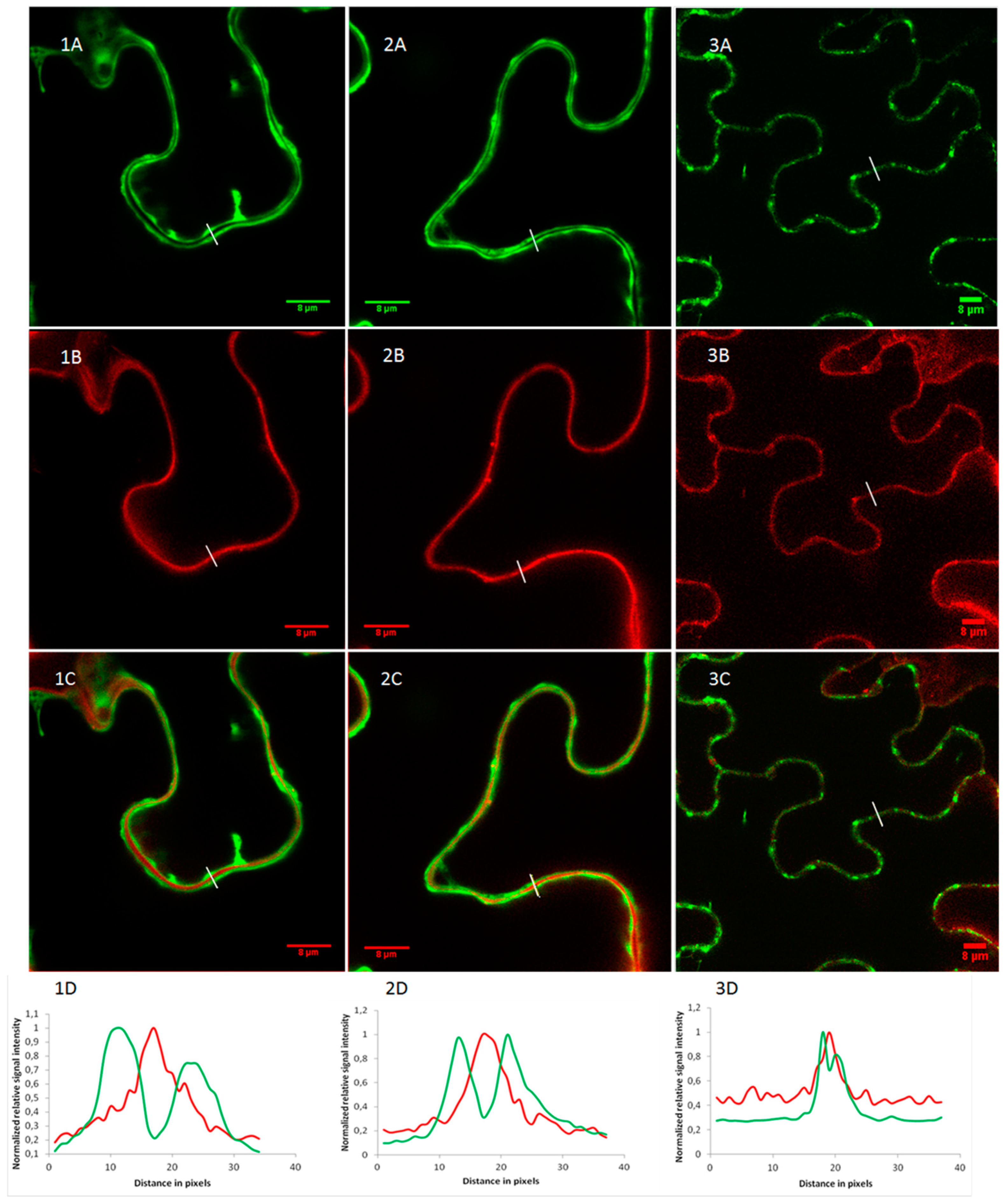
2.2. OsRIP1 Locates to the Nucleocytoplasmic Space
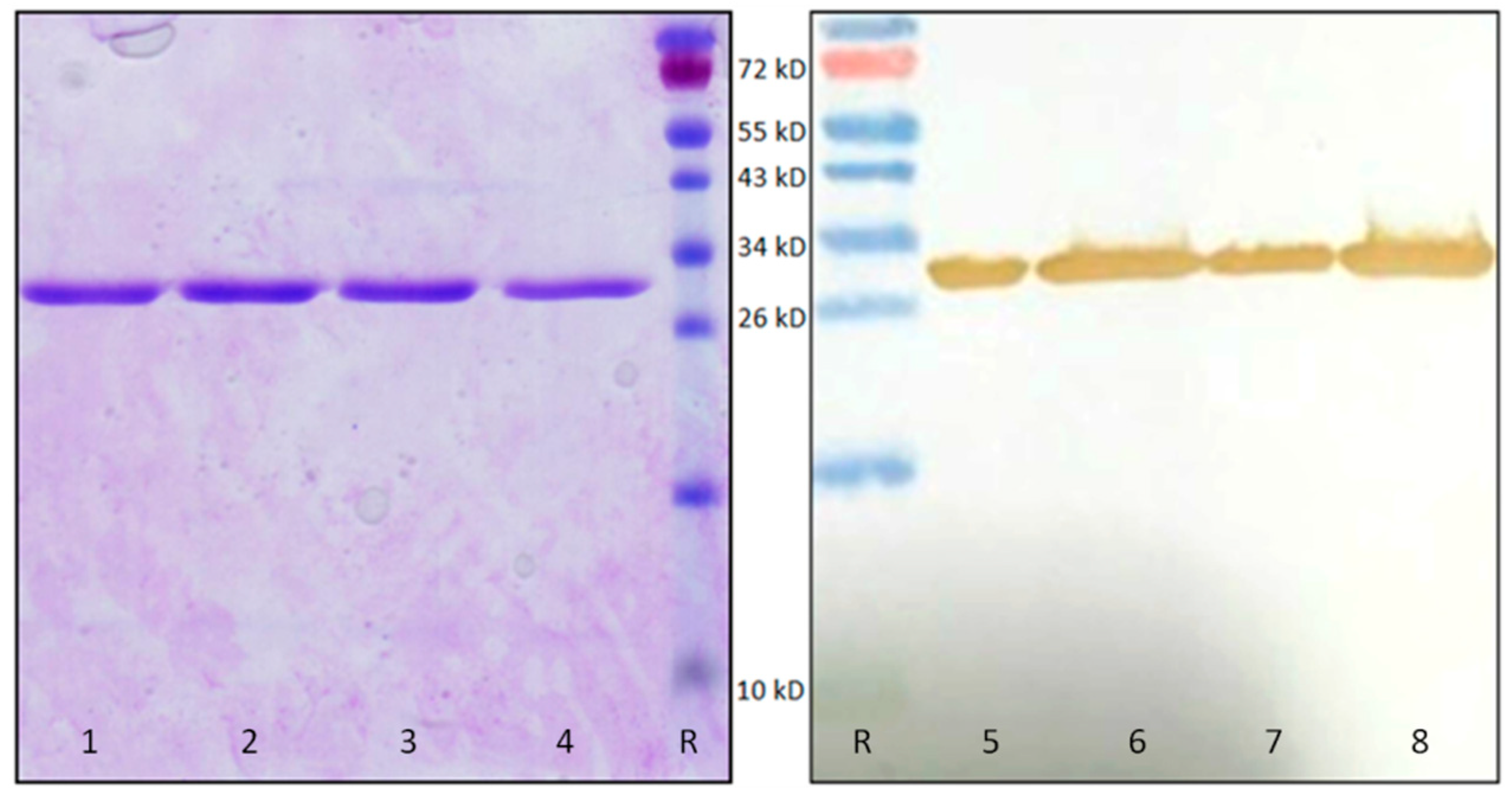
2.3. Recombinant OsRIP1 Inhibits Protein Translation and Shows Selectivity Towards Non-Plant Ribosomes
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials
4.2. Construction of Expression Vectors
4.3. Localization Constructs
4.4. Construct for Recombinant Protein Production
4.5. Transient Transformation of N.benthamiana
4.6. Stable Transformation of A. thaliana PSB-D Cells
4.7. OsRIP1 Protein Production
4.8. OsRIP1 Protein Purification
4.9. SDS-PAGE and Western Blot
4.10. Protein Synthesis Inhibition Assay
4.11. Confocal Microscopy and Image Analysis
4.12. In Silico Analyses
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barbieri, L.; Ferreras, J.M.; Barraco, A.; Ricci, P.; Stirpe, F. Some ribosome-inactivating proteins depurinate ribosomal RNA at multiple sites. Biochem. J. 1992, 286, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbieri, L.; Valbonesi, P.; Bonora, E.; Gorini, P.; Bolognesi, A.; Stirpe, F. Polynucleotide:adenosine glycosidase activity of ribosome-inactivating proteins: Effect on DNA, RNA and poly(A). Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 518–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbieri, L.; Valbonesi, P.; Righi, F.; Zuccheri, G.; Monti, F.; Gorini, P.; Samori, B.; Stirpe, F. Polynucleotide:adenosine glycosidase is the sole activity of ribosome-inactivating proteins on DNA. J. Biochem. 2000, 128, 883–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peumans, W.J.; Van Damme, E.J.M. Evolution of plant ribosome-inactivating proteins. In Toxic Plant Proteins; Lord, J.M., Hartley, M.R., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; Volume 18, pp. 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Peumans, W.; Shang, C.; Van Damme, E.J.M. Updated model of the molecular evolution of RIP genes. In Ribosome-Inactivating Proteins: Ricin and Related Proteins; Stirpe, F., Lappi, D., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 134–150. [Google Scholar]
- Giansanti, F.; Di Leandro, L.; Koutris, I.; Cialfi, A.; Benedetti, E.; Laurenti, G.; Pitari, G.; Ippoliti, R. Ricin and saporin: Plant enzymes for the research and the clinics. Curr. Chem. Biol. 2012, 4, 99–107. [Google Scholar]
- Giansanti, F.; Flavell, D.J.; Angelucci, F.; Fabbrini, M.S.; Ippoliti, R. Strategies to improve the clinical utility of saporin-based targeted toxins. Toxins 2018, 10, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, F.; Zhou, Y.-K.; Ji, Z.-L.; Chen, X.-R. The plant ribosome-inactivating proteins play important roles in defense against pathogens and insect pest attacks. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartley, M.R.; Chacidock, J.A.; Bonness, M.S. The structure and function of ribosome-inactivating proteins. Trends Plant Sci. 1996, 1, 254–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prestle, J.; Schönfelder, M.; Adam, G.; Mundry, K.W. Type 1 ribosome-inactivating proteins depurinate plant 25S rRNA without species specificity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992, 20, 3179–3182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartley, M.R.; Lord, J.M. Structure, function and applications of ricin and related cytotoxic proteins. In Biosynthesis and Manipulation of Plant Products; Grierson, D., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1993; pp. 210–239. [Google Scholar]
- Neuhaus, J.M.; Rogers, J.C. Sorting of proteins to vacuoles in plant cells. In Protein Trafficking in Plant Cells; Soll, J., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1998; pp. 127–144. [Google Scholar]
- Vitale, A.; Raikhel, N.V. What do proteins need to reach different vacuoles? Trends Plant Sci. 1999, 4, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.H.; Chow, L.P.; Lin, J.Y. Sechiumin, a ribosome-inactivating protein from the edible gourd, Sechium edule Swartz: Purification, characterization, molecular cloning and expression. Eur. J. Biochem. 1998, 255, 400–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ready, M.P.; Brown, D.T.; Robertus, J.D. Extracellular localization of pokeweed antiviral protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1986, 83, 5053–5056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kataoka, J.; Habuka, N.; Miyano, M.; Masuta, C.; Koiwai, A. Adenine depurination and inactivation of plant ribosomes by an antiviral protein of Mirabilis jalapa (MAP). Plant Mol. Biol. 1992, 20, 1111–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Virgilio, M.; Lombardi, A.; Caliandro, R.; Fabbrini, M.S. Ribosome-inactivating proteins: From plant defense to tumor attack. Toxins 2010, 2, 2699–2737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, T.A.; Morgan, A.E.; Hey, T.D. Characterization and molecular cloning of a proenzyme form of a ribosome-inactivating protein from maize: Novel mechanism of proenzyme activation by proteolytic removal of a 2.8-kilodalton internal peptide segment. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 23422–23427. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chaudhry, B.; Müller-Uri, F.; Cameron-Mills, V.; Gough, S.; Simpson, D.; Skriver, K.; Mundy, J. The barley 60 kDa jasmonate-induced protein (JIP60) is a novel ribosome-inactivating protein. Plant J. 1994, 6, 815–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leah, R.; Tommerup, H.; Svendsen, I.; Mundy, J. Biochemical and molecular characterization of three barley seed proteins with antifungal properties. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 1564–1573. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Habuka, N.; Kataoka, J.; Miyano, M.; Tsuge, H.; Ago, H.; Noma, M. Nucleotide sequence of a genomic gene encoding tritin, a ribosome-inactivating protein from Triticum aestivum. Plant Mol. Biol. 1993, 22, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Zaeytijd, J.; Van Damme, E.J.M. Extensive evolution of cereal ribosome-inactivating proteins translates into unique structural features, activation mechanisms, and physiological roles. Toxins 2017, 9, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hey, T.D.; Hartley, M.; Walsh, T.A. Maize ribosome-inactivating protein (b-32). Homologs in related species, effects on maize ribosomes, and modulation of activity by pro-peptide deletions. Plant Physiol. 1995, 107, 1323–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massiah, A.J.; Hartley, M.R. Wheat ribosome-inactivating proteins: Seed and leaf forms with different specificities and cofactor requirements. Planta 1995, 197, 633–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinbothe, S.; Reinbothe, C.; Lehmann, J.; Becker, W.; Apel, K.; Parthier, B. JIP60, a methyl jasmonate-induced ribosome-inactivating protein involved in plant stress reactions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 7012–7016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rustgi, S.; Pollmann, S.; Buhr, F.; Springer, A.; Reinbothe, C.; von Wettstein, D.; Reinbothe, S. JIP60-mediated, jasmonate- and senescence-induced molecular switch in translation toward stress and defense protein synthesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 14181–14186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krause, C.; Richter, S.; Knöll, C.; Jürgens, G. Plant secretome—From cellular process to biological activity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1834, 2429–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wytynck, P.; Rougé, P.; Van Damme, E.J.M. Genome-wide screening of Oryza sativa ssp. japonica and indica reveals a complex family of proteins with ribosome-inactivating protein domains. Phytochemistry 2017, 143, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bendtsen, J.D.; Nielsen, H.; Von Heijne, G.; Brunak, S. Improved prediction of signal peptides: SignalP 3.0. J. Mol. Biol. 2004, 340, 783–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, B.G.; Kim, M.K.; Kim, B.W.; Suh, S.W.; Song, H.K. Structures of the ribosome-inactivating protein from barley seeds reveal a unique activation mechanism. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2012, 68, 1488–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelley, L.A.; Mezulis, S.; Yates, C.M.; Wass, M.N.; Sternberg, M.J.E. The Phyre2 web portal for protein modeling, prediction and analysis. Nat. Protoc. 2015, 10, 845–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Lukasik, E.; Gawehns, F.; Takken, F.L.W. The use of agroinfiltration for transient expression of plant resistance and fungal effector proteins in Nicotiana benthamiana leaves. Methods Mol. Biol. 2012, 835, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jiang, S.Y.; Ramamoorthy, R.; Bhalla, R.; Luan, H.F.; Venkatesh, P.N.; Cai, M.; Ramachandran, S. Genome-wide survey of the RIP domain family in Oryza sativa and their expression profiles under various abiotic and biotic stresses. Plant Mol. Biol. 2008, 67, 603–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertus, J.D.; Monzingo, A.F. The structure of ribosome inactivating proteins. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2004, 4, 477–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Robertus, J.D. Analysis of several key active site residues of ricin a chain by mutagenesis and X-ray crystallography. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 1992, 5, 775–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, M.-C.; Sturm, M.B.; Almo, S.C.; Schramm, V.L. Transition state analogues in structures of ricin and saporin ribosome-inactivating proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 20276–20281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Z.; Chen, A.; Chen, W.; Liao, Q.; Zhang, H.; Bao, Y.; Roossinck, M.J.; Carr, J.P. Nuclear-cytoplasmic partitioning of cucumber mosaic virus protein 2b determines the balance between its roles as a virulence determinant and an RNA-silencing suppressor. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 5228–5241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Ren, Y.; Sun, S.; Wang, D.; Zhang, F.; Li, D.; Li, S.; Zhou, X. Identification of the potential virulence factors and RNA silencing suppressors of mulberry mosaic dwarf-associated geminivirus. Viruses 2018, 10, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Brattain, M.G. The maximal size of protein to diffuse through the nuclear pore is larger than 60 kDa. FEBS Lett. 2007, 581, 3164–3170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabbrini, M.S.; Rappocciolo, E.; Carpani, D.; Solinas, M.; Valsasina, B.; Breme, U.; Cavallaro, U.; Nykjaer, A.; Rovida, E.; Legname, G.; et al. Characterization of a saporin isoform with lower ribosome-inhibiting activity. Biochem. J. 2015, 322, 719–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, S.L.; An, C.C.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J.Y.; Che, N.Y.; Gao, Y.; Chen, Z.L. Trichomislin, a novel ribosome-inactivating protein, induces apoptosis that involves mitochondria and caspase-3. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2005, 434, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honjo, E.; Dong, D.; Motoshima, H.; Watanabe, K. Genomic clones encoding two isoforms of pokeweed antiviral protein in seeds (PAP-S1 and S2) and the N-glycosidase activities of their recombinant proteins on ribosomes and DNA in comparison with other isoforms. J. Biochem. 2002, 131, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.K.; Choi, Y.; Moon, Y.H.; Kim, S.G.; Do Choi, Y.; Lee, J.S. Systemic induction of a Phytolacca insularis antiviral protein gene by mechanical wounding, jasmonic acid, and abscisic acid. Plant Mol. Biol. 2000, 43, 439–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bass, H.W.; Krawetz, J.E.; Obrian, G.R.; Zinselmeier, C.; Habben, J.E.; Boston, R.S. Maize ribosome-inactivating proteins (RIPs) with distinct expression patterns have similar requirements for proenzyme activation. J. Exp. Bot. 2004, 55, 2219–2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.J.; Lee, S.J.; Kim, S.; Kim, B.D. Isolation and characterization of cDNAs encoding ribosome inactivating protein from Dianthus sinensis L. Mol. Cells 2000, 10, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Halaweish, F.T. Isolation and characterization of ribosome-inactivating proteins from Cucurbitaceae. Chem. Biodivers. 2007, 4, 431–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tse, P.M.F.; Ng, T.B.; Fong, W.P.; Wong, R.N.S.; Wan, C.C.; Mak, N.K.; Yeung, H.W. New ribosome-inactivating proteins from seeds and fruits of the bitter gourd Momordica charantia. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 1999, 31, 895–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivieri, F.; Prasad, V.; Valbonesi, P.; Srivastava, S.; Ghosal-Chowdhury, P.; Barbieri, L.; Bolognesi, A.; Stirpe, F. A systemic antiviral resistance-inducing protein isolated from Clerodendrum inerme Gaertn. is a polynucleotide: Adenosine glycosidase (ribosome-inactivating protein). FEBS Lett. 1996, 396, 132–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, C.; Rougé, P.; Van Damme, E.J.M. Ribosome inactivating proteins from Rosaceae. Molecules 2016, 21, 1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moin, M.; Bakshi, A.; Saha, A.; Dutta, M.; Madhav, S.M.; Kirti, P.B. Rice ribosomal protein large subunit genes and their spatio-temporal and stress regulation. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Leene, J.; Stals, H.; Eeckhout, D.; Persiau, G.; Van De Slijke, E.; Van Isterdael, G.; De Clercq, A.; Bonnet, E.; Laukens, K.; Remmerie, N.; et al. A tandem affinity purification-based technology platform to study the cell cycle interactome in Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2007, 6, 1226–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schindelin, J.; Arganda-Carreras, I.; Frise, E.; Kaynig, V.; Longair, M.; Pietzsch, T.; Preibisch, S.; Rueden, C.; Saalfeld, S.; Schmid, B.; et al. Fiji: An open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emanuelsson, O.; Nielsen, H.; Brunak, S.; Von Heijne, G. Predicting subcellular localization of proteins based on their N-terminal amino acid sequence. J. Mol. Biol. 2000, 300, 1005–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldberg, T.; Hecht, M.; Hamp, T.; Karl, T.; Yachdav, G.; Ahmed, N.; Altermann, U.; Angerer, P.; Ansorge, S.; Balasz, K.; et al. LocTree3 prediction of localization. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, W350–W355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, K.C.; Shen, H. Bin Plant-mPLoc: A top-down strategy to augment the power for predicting plant protein subcellular localization. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sperschneider, J.; Catanzariti, A.M.; Deboer, K.; Petre, B.; Gardiner, D.M.; Singh, K.B.; Dodds, P.N.; Taylor, J.M. LOCALIZER: Subcellular localization prediction of both plant and effector proteins in the plant cell. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhasin, M.; Raghava, G.P.S. ESLpred: SVM-based method for subcellular localization of eukaryotic proteins using dipeptide composition and PSI-BLAST. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, W414–W419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sievers, F.; Wilm, A.; Dineen, D.; Gibson, T.J.; Karplus, K.; Li, W.; Lopez, R.; McWilliam, H.; Remmert, M.; Söding, J.; et al. Fast, scalable generation of high-quality protein multiple sequence alignments using Clustal Omega. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2011, 7, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krieger, E.; Koraimann, G.; Vriend, G. Increasing the precision of comparative models with YASARA NOVA—A self-parameterizing force field. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2002, 47, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laskowski, R.A.; MacArthur, M.W.; Thornton, J.M. PROCHECK: A program to check the stereochemical quality of protein structures. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1993, 26, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, F.; Feytmans, E. Assessing protein structures with a non-local atomic interaction energy. J. Mol. Biol. 1998, 277, 1141–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benkert, P.; Biasini, M.; Schwede, T. Toward the estimation of the absolute quality of individual protein structure models. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, K.; Bordoli, L.; Kopp, J.; Schwede, T. The SWISS-MODEL workspace: A web-based environment for protein structure homology modelling. Bioinformatics 2006, 22, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grosdidier, A.; Zoete, V.; Michielin, O. SwissDock, a protein-small molecule docking web service based on EADock DSS. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, W270–W277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosdidier, A.; Zoete, V.; Michielin, O. Fast docking using the CHARMM force field with EADock DSS. J. Comput. Chem. 2011, 32, 2149–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pettersen, E.F.; Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Couch, G.S.; Greenblatt, D.M.; Meng, E.C.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF Chimera—A visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1605–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
De Zaeytijd, J.; Rougé, P.; Smagghe, G.; Van Damme, E.J.M. Structure and Activity of a Cytosolic Ribosome-Inactivating Protein from Rice. Toxins 2019, 11, 325. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11060325
De Zaeytijd J, Rougé P, Smagghe G, Van Damme EJM. Structure and Activity of a Cytosolic Ribosome-Inactivating Protein from Rice. Toxins. 2019; 11(6):325. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11060325
Chicago/Turabian StyleDe Zaeytijd, Jeroen, Pierre Rougé, Guy Smagghe, and Els J.M. Van Damme. 2019. "Structure and Activity of a Cytosolic Ribosome-Inactivating Protein from Rice" Toxins 11, no. 6: 325. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11060325
APA StyleDe Zaeytijd, J., Rougé, P., Smagghe, G., & Van Damme, E. J. M. (2019). Structure and Activity of a Cytosolic Ribosome-Inactivating Protein from Rice. Toxins, 11(6), 325. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11060325







