Isolation and Characterization of Insecticidal Toxins from the Venom of the North African Scorpion, Buthacus leptochelys
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Characterization of the B. leptochelys Venom
2.2. Purification of Insecticidal Peptides
2.3. Primary Structure of Bl-1
2.4. Sequence Comparison
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Collection of Venom
4.2. Bioassay
4.3. Mass Spectrometric Analysis
4.4. HPLC Purification
4.5. Determination of N-terminal Sequence
4.6. Enzymatic Digestion
4.7. Homology Modeling
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dunlop, J.A. Geological history and phylogeny of Chelicerata. Arthropod. Struct. Dev. 2010, 39, 124–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waddington, J.; Rudkin, D.M.; Dunlop, J.A. A new mid-Silurian aquatic scorpion-one step closer to land? Biol. Lett. 2015, 11, 20140815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santibanez-Lopez, C.E.; Francke, O.F.; Ureta, C.; Possani, L.D. Scorpions from Mexico: From species diversity to venom complexity. Toxins 2015, 8, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Scorpion Files. Available online: https://www.ntnu.no/ub/scorpion-files/intro.php (accessed on 20 March 2019).
- Zlotkin, E. Scorpion venoms. In Comprehensive Molecular Insect Science; Gilbert, L.I., Iatrou, K., Gill, S.S., Eds.; Elsevier B.V.: Oxford, UK, 2005; Volume 5, pp. 173–220. [Google Scholar]
- Santibanez-Lopez, C.E.; Possani, L.D. Overview of the Knottin scorpion toxin-like peptides in scorpion venoms: Insights on their classification and evolution. Toxicon 2015, 107, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almaaytah, A.; Albalas, Q. Scorpion venom peptides with no disulfide bridges: A review. Peptides 2014, 51, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhijian, C.; Feng, L.; Yingliang, W.; Xin, M.; Wenxin, L. Genetic mechanisms of scorpion venom peptide diversification. Toxicon 2006, 47, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Housley, D.M.; Housley, G.D.; Liddell, M.J.; Jennings, E.A. Scorpion toxin peptide action at the ion channel subunit level. Neuropharmacology 2017, 127, 46–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Possani, L.D.; Becerril, B.; Delepierre, M.; Tytgat, J. Scorpion toxins specific for Na+-channels. Eur. J. Biochem. 1999, 264, 287–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez de la Vega, R.C.; Possani, L.D. Overview of scorpion toxins specific for Na+ channels and related peptides: Biodiversity, structure-function relationships and evolution. Toxicon 2005, 46, 831–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.H.; Catterall, W.A. Overview of the voltage-gated sodium channel family. Genome Biol. 2003, 4, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cestele, S.; Catterall, W.A. Molecular mechanisms of neurotoxin action on voltage-gated sodium channels. Biochimie 2000, 82, 883–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cestele, S.; Stankiewicz, M.; Mansuelle, P.; De Waard, M.; Dargent, B.; Gilles, N.; Pelhate, M.; Rochat, H.; Martin-Eauclaire, M.F.; Gordon, D. Scorpion alpha-like toxins, toxic to both mammals and insects, differentially interact with receptor site 3 on voltage-gated sodium channels in mammals and insects. Eur. J. Neurosci. 1999, 11, 975–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergeron, Z.L.; Bingham, J.P. Scorpion toxins specific for potassium (K+) channels: A historical overview of peptide bioengineering. Toxins 2012, 4, 1082–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez de la Vega, R.C.; Possani, L.D. Current views on scorpion toxins specific for K+-channels. Toxicon 2004, 43, 865–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chagot, B.; Pimentel, C.; Dai, L.; Pil, J.; Tytgat, J.; Nakajima, T.; Corzo, G.; Darbon, H.; Ferrat, G. An unusual fold for potassium channel blockers: NMR structure of three toxins from the scorpion Opisthacanthus madagascariensis. Biochem. J. 2005, 388, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Luo, F.; Feng, J.; Yang, W.; Zeng, D.; Zhao, R.; Cao, Z.; Liu, M.; Li, W.; Jiang, L.; et al. Genomic and structural characterization of Kunitz-type peptide LmKTT-1a highlights diversity and evolution of scorpion potassium channel toxins. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e60201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeBin, J.A.; Maggio, J.E.; Strichartz, G.R. Purification and characterization of chlorotoxin, a chloride channel ligand from the venom of the scorpion. Am. J. Physiol. 1993, 264, C361–C369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froy, O.; Sagiv, T.; Poreh, M.; Urbach, D.; Zilberberg, N.; Gurevitz, M. Dynamic diversification from a putative common ancestor of scorpion toxins affecting sodium, potassium, and chloride channels. J. Mol. Evol. 1999, 48, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintero-Hernandez, V.; Jimenez-Vargas, J.M.; Gurrola, G.B.; Valdivia, H.H.; Possani, L.D. Scorpion venom components that affect ion-channels function. Toxicon 2013, 76, 328–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, P.L.; Abdel-Rahman, M.A.; Miller, K.; Strong, P.N. Antimicrobial peptides from scorpion venoms. Toxicon 2014, 88, 115–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scorpiones.pl. Available online: http://scorpiones.pl/maps/#africa (accessed on 20 March 2019).
- Loret, E.P.; Hammock, B.D. Structure and neurotoxicity of venoms. In Scorpion Biology and Research; Brownell, P.H., Polis, G.A., Eds.; Oxford University Press, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2001; pp. 204–233. [Google Scholar]
- Caliskan, F.; Quintero-Hernandez, V.; Restano-Cassulini, R.; Batista, C.V.F.; Zarnudio, F.Z.; Coronas, F.I.; Possani, L.D. Turkish scorpion Buthacus macrocentrus: General characterization of the venom and description of Bu1, a potent mammalian Na+-channel alpha-toxin. Toxicon 2012, 59, 408–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cestele, S.; Kopeyan, C.; Oughideni, R.; Mansuelle, P.; Granier, C.; Rochat, H. Biochemical and pharmacological characterization of a depressant insect toxin from the venom of the scorpion Buthacus arenicola. Eur. J. Biochem. 1997, 243, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyashita, M.; Sakai, A.; Matsushita, N.; Hanai, Y.; Nakagawa, Y.; Miyagawa, H. A novel amphipathic linear peptide with both insect toxicity and antimicrobial activity from the venom of the scorpion Isometrus maculatus. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2010, 74, 364–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzoil-Palma, M.F.; Gobbi, N.; Palma, M.S. Insects as biological models to assay spider and scorpion venom toxicity. Venom. Anim. Toxins incl. Trop. Dis. 2003, 9, 174–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lima, M.E.; Figueiredo, S.G.; Pimenta, A.M.; Santos, D.M.; Borges, M.H.; Cordeiro, M.N.; Richardson, M.; Oliveira, L.C.; Stankiewicz, M.; Pelhate, M. Peptides of arachnid venoms with insecticidal activity targeting sodium channels. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2007, 146, 264–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurevitz, M.; Karbat, I.; Cohen, L.; Ilan, N.; Kahn, R.; Turkov, M.; Stankiewicz, M.; Stuhmer, W.; Dong, K.; Gordon, D. The insecticidal potential of scorpion beta-toxins. Toxicon 2007, 49, 473–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sautiere, P.; Cestele, S.; Kopeyan, C.; Martinage, A.; Drobecq, H.; Doljansky, Y.; Gordon, D. New toxins acting on sodium channels from the scorpion Leiurus quinquestriatus hebraeus suggest a clue to mammalian vs insect selectivity. Toxicon 1998, 36, 1141–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, O.; Martin, M.F.; Rochat, H. Characterization of six toxins from the venom of the Moroccan scorpion Buthus occitanus mardochei. Eur. J. Biochem. 1987, 162, 589–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopeyan, C.; Martinez, G.; Rochat, H. Amino acid sequence of neurotoxin V from scorpion Leiurus quinquestriatus quinquestriatus. FEBS Lett. 1978, 89, 54–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochat, H.; Rochat, C.; Lissitzky, S.; Sampieri, F.; Miranda, F. Amino acid sequence of neurotoxin II of Androctonus australis Hector. Eur. J. Biochem. 1972, 28, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalali, A.; Bosmans, F.; Amininasab, M.; Clynen, E.; Cuypers, E.; Zaremirakabadi, A.; Sarbolouki, M.N.; Schoofs, L.; Vatanpour, H.; Tytgat, J. OD1, the first toxin isolated from the venom of the scorpion Odonthobuthus doriae active on voltage-gated Na(+) channels. FEBS Lett. 2005, 579, 4181–4186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loret, E.P.; Mansuelle, P.; Rochat, H.; Granier, C. Neurotoxins active on insects—Amino acid sequences, chemical modifications, and secondary structure estimation by circular dichroism of toxins from the scorpion Androctonus australis Hector. Biochemistry 1990, 29, 1492–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopeyan, C.; Mansuelle, P.; Sampieri, F.; Brando, T.; Bahraoui, E.M.; Rochat, H.; Granier, C. Primary structure of scorpion antiinsect toxins isolated from the venom of Leiurus quinquestriatus quinquestriatus. FEBS Lett. 1990, 261, 423–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.M.; Ma, Y.B.; He, Y.W.; Di, Z.Y.; Wu, Y.L.; Cao, Z.J.; Li, W.X. Comparative venom gland transcriptome analysis of the scorpion Lychas mucronatus reveals intraspecific toxic gene diversity and new venomous components. BMC Genom. 2010, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.B.; He, Y.W.; Zhao, R.M.; Wu, Y.L.; Li, W.X.; Cao, Z.J. Extreme diversity of scorpion venom peptides and proteins revealed by transcriptomic analysis: Implication for proteome evolution of scorpion venom arsenal. J. Proteom. 2012, 75, 1563–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichiki, Y.; Kawachi, T.; Miyashita, M.; Nakagawa, Y.; Miyagawa, H. Isolation and characterization of a novel non-selective beta-toxin from the venom of the scorpion Isometrus maculatus. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2012, 76, 2089–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kawachi, T.; Miyashita, M.; Nakagawa, Y.; Miyagawa, H. Isolation and characterization of an anti-insect beta-toxin from the venom of the scorpion Isometrus maculatus. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2013, 77, 205–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Karbat, I.; Kahn, R.; Cohen, L.; Ilan, N.; Gilles, N.; Corzo, G.; Froy, O.; Gur, M.; Albrecht, G.; Heinemann, S.H.; et al. The unique pharmacology of the scorpion alpha-like toxin Lqh3 is associated with its flexible C-tail. FEBS J. 2007, 274, 1918–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strohalm, M.; Kavan, D.; Novak, P.; Volny, M.; Havlicek, V. mMass 3: A cross-platform software environment for precise analysis of mass spectrometric data. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 4648–4651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogata, K.; Umeyama, H. An automatic homology modeling method consisting of database searches and simulated annealing. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 2000, 18, 258–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
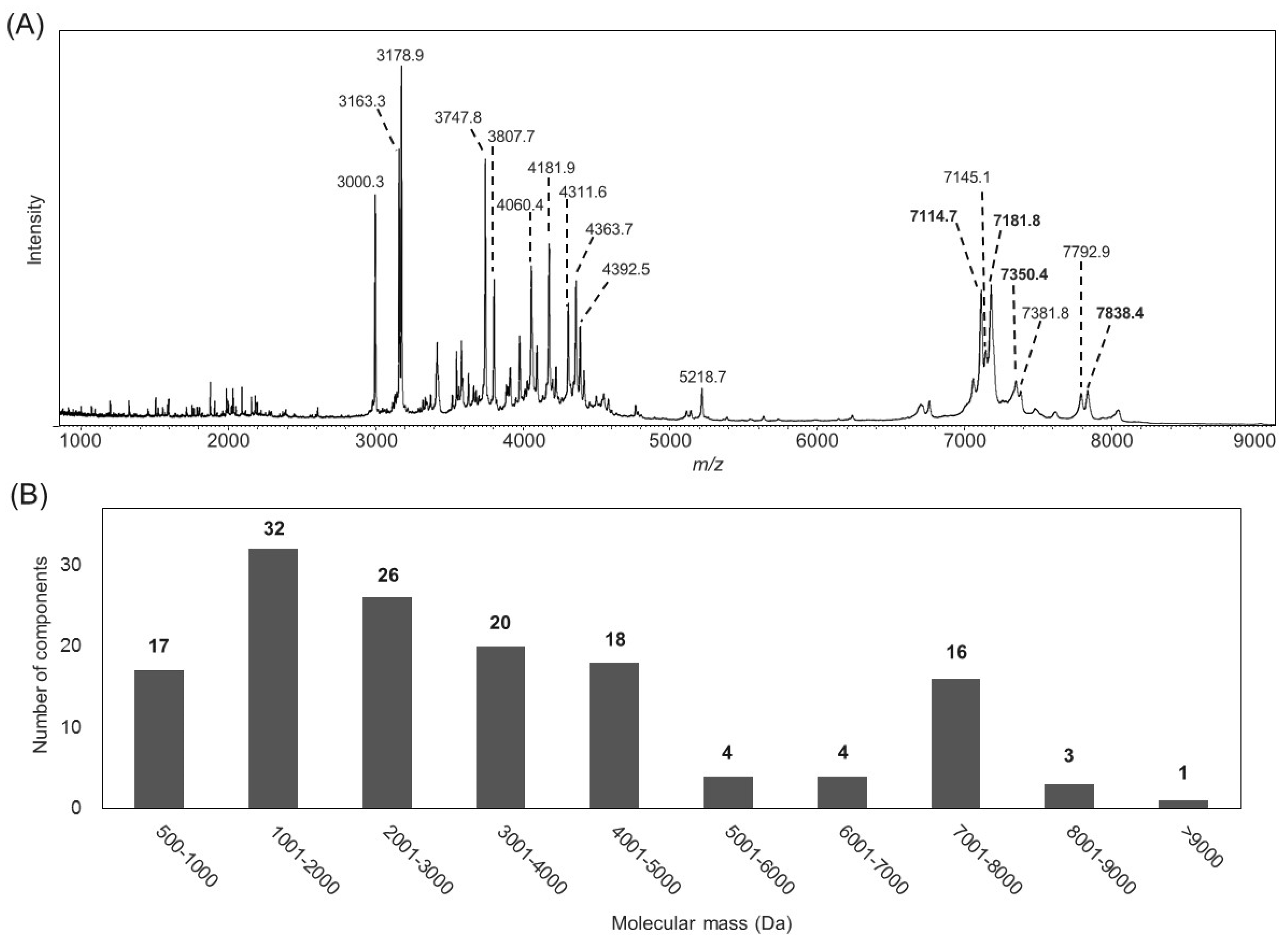
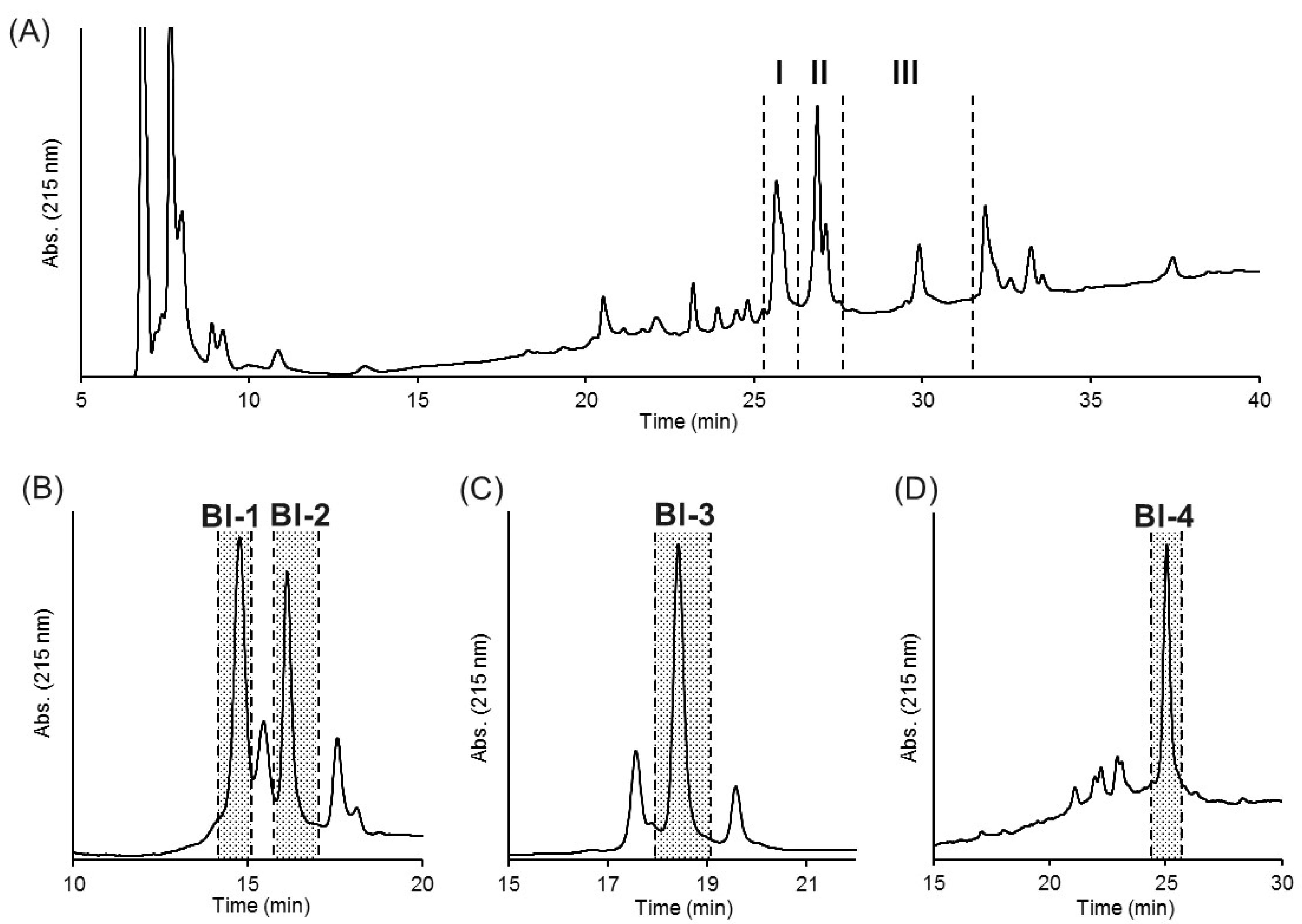

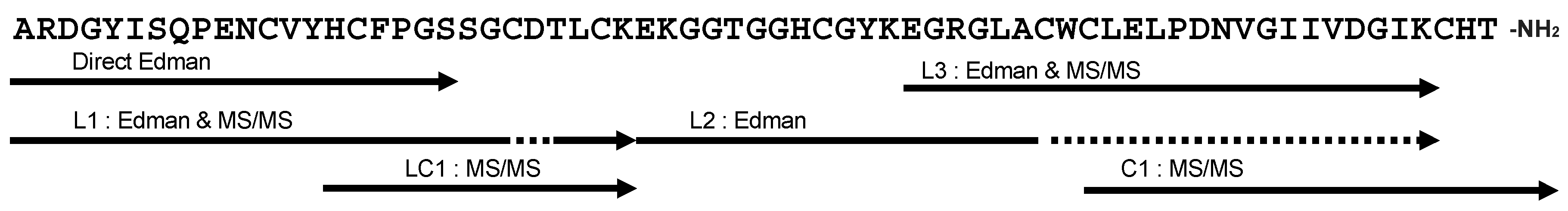
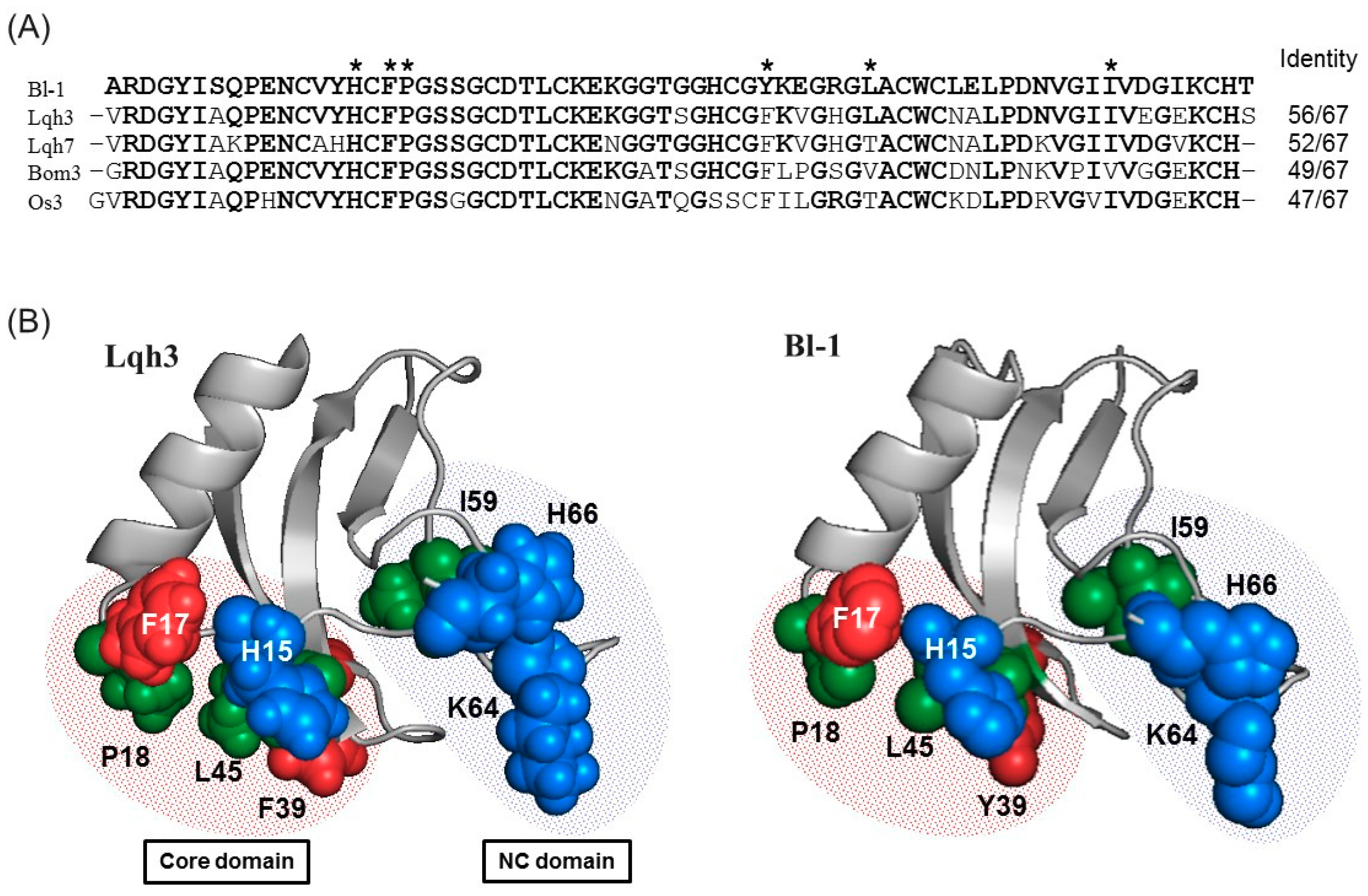
| Name | N-Terminal Sequence (U = Unknown) | Similar Peptides | Toxin Classification |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bl-1 | ARDGYISQPENCVYHCFPGS | Lqh3, Bom3 | α-like insect and mammal toxin |
| Bl-2 | URDGYLVDDUNCTFFCG | Lqh2, AaH2 | α-mammal toxin |
| Bl-3 | UVRDAYIADDKNCVYTCASN | OD1, Bu1 | α-insect and mammal toxin |
| Bl-4 | UKNGYAVDSSGKAPECILSNYCNNECTKV | AaHIT1, LqqIT1 | β-insect toxin |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yoshimoto, Y.; Miyashita, M.; Abdel-Wahab, M.; Sarhan, M.; Nakagawa, Y.; Miyagawa, H. Isolation and Characterization of Insecticidal Toxins from the Venom of the North African Scorpion, Buthacus leptochelys. Toxins 2019, 11, 236. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11040236
Yoshimoto Y, Miyashita M, Abdel-Wahab M, Sarhan M, Nakagawa Y, Miyagawa H. Isolation and Characterization of Insecticidal Toxins from the Venom of the North African Scorpion, Buthacus leptochelys. Toxins. 2019; 11(4):236. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11040236
Chicago/Turabian StyleYoshimoto, Yusuke, Masahiro Miyashita, Mohammed Abdel-Wahab, Moustafa Sarhan, Yoshiaki Nakagawa, and Hisashi Miyagawa. 2019. "Isolation and Characterization of Insecticidal Toxins from the Venom of the North African Scorpion, Buthacus leptochelys" Toxins 11, no. 4: 236. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11040236
APA StyleYoshimoto, Y., Miyashita, M., Abdel-Wahab, M., Sarhan, M., Nakagawa, Y., & Miyagawa, H. (2019). Isolation and Characterization of Insecticidal Toxins from the Venom of the North African Scorpion, Buthacus leptochelys. Toxins, 11(4), 236. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11040236





