Pre-Harvest Survival and Post-Harvest Chlorine Tolerance of Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli on Lettuce
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Effect of RH on EHEC Survival is Dependent on the Seasonal Conditions
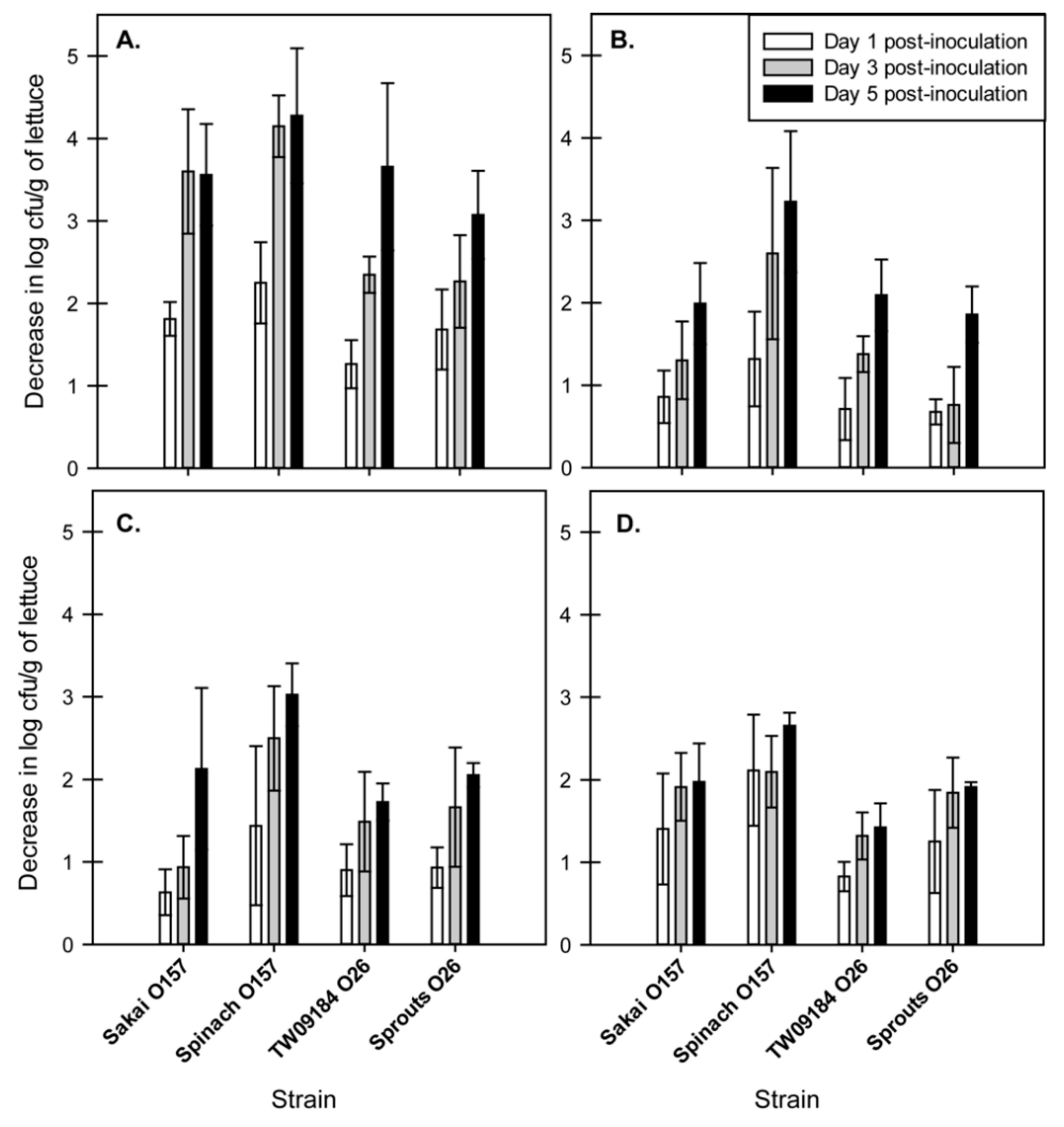
2.2. EHEC Strains Demonstrated Changes in Tolerance to Chlorine over Time
2.3. Changes in EHEC Transcriptomes During Incubation on Lettuce Plants
2.3.1. Changes in O157 Sakai Gene Expression During Incubation on Lettuce Plants
2.3.2. Changes in O26 Sprouts Strain Gene Expression During Incubation on Lettuce Plants
3. Discussion
3.1. Pathogen Survival on Pre-Harvest Lettuce under Different RH is Dependent on Seasonal Conditions
3.2. Association of EHEC with Pre-Harvest Lettuce Impacts Chlorine Tolerance
3.3. Upregulation of Virulence Genes in O157 Sakai During Association with Pre-Harvest Lettuce
3.4. Gene Expression Changes Indicate Activation of Stress Responses During Association with Pre-Harvest Lettuce
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Bacterial Isolates and Growth Conditions
5.2. Lettuce Cultivation Conditions
5.3. Preparation of Inoculum and Lettuce Inoculation
5.4. Incubation Conditions for Inoculated Lettuce
5.5. Incubation and Collection of Lettuce for RNA Isolation
5.6. RNA Sequencing
5.7. Genome Sequencing
5.8. Incubation and Harvest of Lettuce for the Chlorine Survival Assay
5.9. Chlorine Survival Assay
5.10. Bacterial Enumeration
5.11. Statistical Analysis
5.12. RNA-seq Data Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Scallan, E.; Hoekstra, R.M.; Angulo, F.J.; Tauxe, R.V.; Widdowson, M.A.; Roy, S.L.; Jones, J.L.; Griffin, P.M. Foodborne illness acquired in the United States—Major pathogens. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeni, F.; Yavas, S.; Alpas, H.; Soyer, Y. Most Common Foodborne Pathogens and Mycotoxins on Fresh Produce: A Review of Recent Outbreaks. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2016, 56, 1532–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rangel, J.M.; Sparling, P.H.; Crowe, C.; Griffin, P.M.; Swerdlow, D.L. Epidemiology of Escherichia coli O157: H7 Outbreaks, United States, 1982–2002. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2005, 11, 603–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breuer, T.; Benkel, D.H.; Shapiro, R.L.; Hall, W.N.; Winnett, M.M.; Linn, M.J.; Neimann, J.; Barrett, T.J.; Dietrich, S.; Downes, F.P.; et al. A multistate outbreak of Escherichia coli O157: H7 infections linked to alfalfa sprouts grown from contaminated seeds. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2001, 7, 977–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CDC. Multistate Outbreak of Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia Coli O121 Infections Linked to Raw Clover Sprouts (Final Update). Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/ecoli/2014/o121-05-14/index.html (accessed on 12 September 2019).
- Painter, J.A.; Hoekstra, R.M.; Ayers, T.; Tauxe, R.V.; Braden, C.R.; Angulo, F.J.; Griffin, P.M. Attribution of Foodborne Illnesses, Hospitalizations, and Deaths to Food Commodities by using Outbreak Data, United States, 1998–2008. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2013, 19, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ackers, M.; Mahon, B.E.; Leahy, E.; Goode, B.; Damrow, T.; Hayes, P.S.; Bibb, W.F.; Rice, D.H.; Barrett, T.J.; Hutwagner, L.; et al. An outbreak of Escherichia coli O157: H7 infections associated with leaf lettuce consumption. J. Infect. Dis. 1998, 177, 1588–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilborn, E.D.; Mermin, J.H.; Mshar, P.A.; Hadler, J.L.; Voetsch, A.; Wojtkunski, C.; Swartz, M.; Mshar, R.; Lambert-Fair, M.A.; Farrar, J.A.; et al. A multistate outbreak of Escherichia coli O157: H7 infections associated with consumption of mesclun lettuce. Arch. Intern. Med. 1999, 159, 1758–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharapov, U.; Grant, J.; Monson, T.; Koschmann, C.; Wendel, A.M.; Johnson, D.H.; Archer, J.R.; Davis, J.P. Multistate Outbreak of Escherichia coli O157: H7 Infection Associated with Consumption of Packaged Spinach, August–September 2006: The Wisconsin Investigation. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2009, 48, 1079–1086. [Google Scholar]
- Grant, J.; Wendelboe, A.M.; Wendel, A.; Jepson, B.; Torres, P.; Smelser, C.; Rolfs, R.T. Spinach-associated Escherichia coli O157: H7 outbreak, Utah and New Mexico 2006. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2008, 14, 1633–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharapov, U.M.; Wendel, A.M.; Davis, J.P.; Keene, W.E.; Farrar, J.; Sodha, S.; Hyytia-Trees, E.; Leeper, M.; Gerner-Smidt, P.; Griffin, P.M.; et al. Multistate Outbreak of Escherichia coli O157: H7 Infections Associated with Consumption of Fresh Spinach: United States 2006. J. Food Prot. 2016, 79, 2024–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slayton, R.B.; Turabelidze, G.; Bennett, S.D.; Schwensohn, C.A.; Yaffee, A.Q.; Khan, F.; Butler, C.; Trees, E.; Ayers, T.L.; Davis, M.L.; et al. Outbreak of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli (STEC) O157: H7 associated with romaine lettuce consumption 2011. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e55300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandl, M.T. Fitness of Human Enteric Pathogens on Plants and Implications for Food Safety. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2006, 44, 367–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erickson, M.C.; Webb, C.C.; Diaz-Perez, J.C.; Phatak, S.C.; Silvoy, J.J.; Davey, L.; Payton, A.S.; Liao, J.; Ma, L.; Doyle, M.P. Surface and Internalized Escherichia coli O157: H7 on Field-Grown Spinach and Lettuce Treated with Spray-Contaminated Irrigation Water. J. Food Prot. 2010, 73, 1023–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, M.; Morgan, J.; Doyle, M.P.; Phatak, S.C.; Millner, P.; Jiang, X. Persistence of Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium on Lettuce and Parsley and in Soils on Which They Were Grown in Fields Treated with Contaminated Manure Composts or Irrigation Water. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2004, 1, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markland, S.M.; Shortlidge, K.L.; Hoover, D.G.; Yaron, S.; Patel, J.; Singh, A.; Sharma, M.; Kniel, K.E. Survival of pathogenic Escherichia coli on basil, lettuce, and spinach. Zoonoses Public Health 2013, 60, 563–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moyne, A.L.; Sudarshana, M.R.; Blessington, T.; Koike, S.T.; Cahn, M.D.; Harris, L.J. Fate of Escherichia coli O157: H7 in field-inoculated lettuce. Food Microbiol. 2011, 28, 1417–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stine, S.W.; Song, I.; Choi, C.Y.; Gerba, C.P. Effect of Relative Humidity on Preharvest Survival of Bacterial and Viral Pathogens on the Surface of Cantaloupe, Lettuce, and Bell Peppers. J. Food Prot. 2005, 68, 1352–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Linden, I.; Cottyn, B.; Uyttendaele, M.; Vlaemynck, G.; Heyndrickx, M.; Maes, M. Survival of Enteric Pathogens During Butterhead Lettuce Growth: Crop Stage, Leaf Age, and Irrigation. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2013, 10, 485–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandl, M.T.; Amundson, R. Leaf Age as a Risk Factor in Contamination of Lettuce with Escherichia coli O157: H7 and Salmonella enterica. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 2298–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Gálvez, F.; Gil, M.I.; Truchado, P.; Selma, M.V.; Allende, A. Cross-contamination of fresh-cut lettuce after a short-term exposure during pre-washing cannot be controlled after subsequent washing with chlorine dioxide or sodium hypochlorite. Food Microbiol. 2010, 27, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Ma, L.; Phelan, V.H.; Doyle, M.P. Efficacy of Antimicrobial Agents in Lettuce Leaf Processing Water for Control of Escherichia coli O157: H7. J. Food Prot. 2009, 72, 1392–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, M.M.; Harris, L.J.; Beuchat, L.R. Survival and Recovery of Escherichia coli O157: H7, Salmonella, and Listeria monocytogenes on Lettuce and Parsley as Affected by Method of Inoculation, Time between Inoculation and Analysis, and Treatment with Chlorinated Water. J. Food Prot. 2004, 67, 1092–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Nou, X.; Millner, P.; Zhou, B.; Shen, C.; Yang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Feng, H.; Shelton, D. A pilot plant scale evaluation of a new process aid for enhancing chlorine efficacy against pathogen survival and cross-contamination during produce wash. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2012, 158, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmoud, B.; Linton, R. Inactivation kinetics of inoculated Escherichia coli O157: H7 and Salmonella enterica on lettuce by chlorine dioxide gas. Food Microbiol. 2008, 25, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidson, G.R.; Buchholz, A.L.; Ryser, E.T. Efficacy of Commercial Produce Sanitizers against Nontoxigenic Escherichia coli O157: H7 during Processing of Iceberg Lettuce in a Pilot-Scale Leafy Green Processing Line. J. Food Prot. 2013, 76, 1838–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindow, S.E.; Brandl, M.T. Microbiology of the phyllosphere. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 1875–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomás-Callejas, A.; López-Velasco, G.; Camacho, A.B.; Artés, F.; Artés-Hernández, F.; Suslow, T.V. Survival and distribution of Escherichia coli on diverse fresh-cut baby leafy greens under preharvest through postharvest conditions. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2011, 151, 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinu, L.D.; Delaquis, P.; Bach, S. Nonculturable Response of Animal Enteropathogens in the Agricultural Environment and Implications for Food Safety. J. Food Prot. 2009, 72, 1342–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, J.D. The viable but nonculturable state in bacteria. J. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 93–100. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, C.; Tyrrell, G.; Li, X.F. Production of Shiga-like toxins in viable but nonculturable Escherichia coli O157: H7. Water Res. 2010, 44, 711–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDougald, D.; Rice, S.A.; Weichart, D.; Kjelleberg, S. Nonculturability: Adaptation or debilitation? FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 1998, 25, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinu, L.D.; Bach, S. Induction of Viable but Nonculturable Escherichia coli O157: H7 in the Phyllosphere of Lettuce: A Food Safety Risk Factor. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 8295–8302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moyne, A.L.; Harris, L.J.; Marco, M.L. Assessments of Total and Viable Escherichia coli O157: H7 on Field and Laboratory Grown Lettuce. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gil, M.I.; Selma, M.V.; López-Gálvez, F.; Allende, A. Fresh-cut product sanitation and wash water disinfection: Problems and solutions. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2009, 134, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keskinen, L.A.; Burke, A.; Annous, B.A. Efficacy of chlorine, acidic electrolyzed water and aqueous chlorine dioxide solutions to decontaminate Escherichia coli O157: H7 from lettuce leaves. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2009, 132, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Gálvez, F.; Allende, A.; Selma, M.V.; Gil, M.I. Prevention of Escherichia coli cross-contamination by different commercial sanitizers during washing of fresh-cut lettuce. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2009, 133, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, K.; Wang, X.; Yen, L.H.; Ding, H.; Tortorello, M.L. Behavior of Shiga Toxigenic Escherichia coli Relevant to Lettuce Washing Processes and Consideration of Factors for Evaluating Washing Process Surrogates. J. Food Prot. 2014, 77, 1860–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Luo, Y.; Nou, X.; Wang, Q.; Millner, P. Dynamic Effects of Free Chlorine Concentration, Organic Load, and Exposure Time on the Inactivation of Salmonella, Escherichia coli O157: H7, and Non-O157 Shiga Toxin–Producing E. coli. J. Food Prot. 2013, 76, 386–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prado-Silva, L.; Cadavez, V.; Gonzales-Barron, U.; Rezende, A.C.B.; Sant’Ana, A.S. Meta-analysis of the Effects of Sanitizing Treatments on Salmonella, Escherichia coli O157: H7, and Listeria monocytogenes Inactivation in Fresh Produce. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 8008–8021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, K.H.; Frank, J.F. Attachment of Escherichia coli O157: H7 to lettuce leaf surface and bacterial viability in response to chlorine treatment as demonstrated by using confocal scanning laser microscopy. J. Food Prot. 1999, 62, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, K.; Frank, J.F. Quantitative determination of the role of lettuce leaf structures in protecting Escherichia coli O157: H7 from chlorine disinfection. J. Food Prot. 2001, 64, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyle, J.L.; Parker, C.T.; Goudeau, D.; Brandl, M.T. Transcriptome Analysis of Escherichia coli O157: H7 Exposed to Lysates of Lettuce Leaves. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 1375–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Linden, I.; Cottyn, B.; Uyttendaele, M.; Vlaemynck, G.; Heyndrickx, M.; Maes, M.; Holden, N. Microarray-Based Screening of Differentially Expressed Genes of E. coli O157: H7 Sakai during Preharvest Survival on Butterhead Lettuce. Agriculture 2016, 6, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocharunchitt, C.; King, T.; Gobius, K.; Bowman, J.P.; Ross, T. Global Genome Response of Escherichia coli O157: H7 Sakai during Dynamic Changes in Growth Kinetics Induced by an Abrupt Downshift in Water Activity. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e90422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fink, R.C.; Black, E.P.; Hou, Z.; Sugawara, M.; Sadowsky, M.J.; Diez-Gonzalez, F. Transcriptional Responses of Escherichia coli K-12 and O157: H7 Associated with Lettuce Leaves. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 1752–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landstorfer, R.; Simon, S.; Schober, S.; Keim, D.; Scherer, S.; Neuhaus, K. Comparison of strand-specific transcriptomes of enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157: H7 EDL933 (EHEC) under eleven different environmental conditions including radish sprouts and cattle feces. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, T.; Schellhorn, H.E. Global effect of RpoS on gene expression in pathogenic Escherichia coli O157: H7 strain EDL933. BMC Genom. 2009, 10, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, B.; Yao, J.; Wood, T.K.; Wang, X. Tail-Anchored Inner Membrane Protein ElaB Increases Resistance to Stress While Reducing Persistence in Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 2017, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, S.M.; Schellhorn, H.E. Regulators of oxidative stress response genes in Escherichia coli and their functional conservation in bacteria. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2012, 525, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunasekera, T.S.; Csonka, L.N.; Paliy, O. Genome-Wide Transcriptional Responses of Escherichia coli K-12 to Continuous Osmotic and Heat Stresses. J. Bacteriol. 2008, 190, 3712–3720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.S.; García-Contreras, R.; Wood, T.K. YcfR (BhsA) Influences Escherichia coli Biofilm Formation through Stress Response and Surface Hydrophobicity. J. Bacteriol. 2007, 189, 3051–3062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyagi, D.; Kraft, A.L.; Bergholz, T.M. Isolation of Bacterial RNA from Foods Inoculated with Pathogens. Methods Mol. Biol. 2019, 1918, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Nabulsi, A.A.; Osaili, T.M.; Obaidat, H.M.; Shaker, R.R.; Awaisheh, S.S.; Holley, R.A. Inactivation of Stressed Escherichia coli O157: H7 Cells on the Surfaces of Rocket Salad Leaves by Chlorine and Peroxyacetic Acid. J. Food Prot. 2014, 77, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H. Aligning sequence reads, clone sequences and assembly contigs with BWA-MEM. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1303.3997v1302. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Handsaker, B.; Wysoker, A.; Fennell, T.; Ruan, J.; Homer, N.; Marth, G.; Abecasis, G.; Durbin, R.; 1000 Genome Project Data Processing Subgroup. The Sequence Alignment/Map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 2078–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardcastle, T.J.; Kelly, K.A. baySeq: Empirical Bayesian methods for identifying differential expression in sequence count data. BMC Bioinform. 2010, 11, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Isolate | Pathogen | Serotype | Source | Year of Isolation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TW08264 | EHEC | O157:H7 | Japan sprouts outbreak (Sakai) | 1996 |
| TW014359 | EHEC | O157:H7 | US Spinach outbreak | 2006 |
| TW09184 | EHEC | O26:H11 | Human sporadic | 2003 |
| TW016501 | EHEC | O26:H11 | US Sprouts outbreak | 2012 |
| Season | RH (%) | Day | Average Log CFU/g Lettuce | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sakai O157 | Spinach O157 | TW09184 O26 | Sprouts O26 | |||
| March | 45 | 0 | 7.0 ± 0.4 | 6.6 ± 0.1 | 7.0 ± 0.4 | 7.2 ± 0.2 |
| 1 | 5.6 ± 0.2 | 4.5 ± 0.6 | 6.1 ± 0.3 | 6.0 ± 0.4 | ||
| 3 | 5.1 ± 0.8 | 4.5 ± 0.4 | 5.6 ± 0.2 | 5.4 ± 0.4 | ||
| 5 | 5.0 ± 0.5 | 4.0 ± 0.2 | 5.5 ± 0.4 | 5.3 ± 0.2 | ||
| 75 | 0 | 6.7 ± 0.1 | 6.7 ± 0.6 | 7.2 ± 0.1 | 7.1 ± 0.1 | |
| 1 | 6.1 ± 0.3 | 5.3 ± 0.5 | 6.3 ± 0.3 | 6.2 ± 0.2 | ||
| 3 | 5.8 ± 0.4 | 4.2 ± 0.5 | 5.7 ± 0.6 | 5.5 ± 0.7 | ||
| 5 | 4.6 ± 0.9 | 3.7 ± 0.6 | 5.4 ± 0.2 | 5.1 ± 0.2 | ||
| June | 45 | 0 | 6.8 ± 0.4 | 6.8 ± 0.4 | 7.1 ± 0.1 | 7.0 ± 0.3 |
| 1 | 6.0 ± 0.2 | 5.5 ± 0.1 | 6.4 ± 0.3 | 6.3 ± 0.4 | ||
| 3 | 5.5 ± 0.1 | 4.2 ± 0.7 | 5.7 ± 0.3 | 6.2 ± 0.3 | ||
| 5 | 4.8 ± 0.2 | 3.6 ± 0.5 | 5.0 ± 0.5 | 5.1 ± 0.3 | ||
| 75 | 0 | 8.5 ± 0.2 | 8.1 ± 0.1 | 8.2 ± 0.5 | 8.3 ± 0.1 | |
| 1 | 6.7 ± 0.1 | 5.9 ± 0.6 | 7.0 ± 0.3 | 6.7 ± 0.5 | ||
| 3 | 4.9 ± 0.9 | 4.0 ± 0.3 | 5.9 ± 0.4 | 6.1 ± 0.6 | ||
| 5 | 4.9 ± 0.6 | 3.8 ± 0.8 | 4.6 ± 0.7 | 5.3 ± 0.5 | ||
| Strain | Log Difference in CFU/g Lettuce between Buffered Water Wash and Chlorine Wash | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Day 0 * | Day 1 | Day 3 | Day 5 | |
| Sakai O157 | 0.94 ± 0.14 AB z | 1.03 ± 0.29 A z | 0.36 ± 0.17 A y | 0.34 ± 0.20 A y |
| Spinach O157 | 0.67 ± 0.10 B z | 0.66 ± 0.28 A z | 0.17 ± 0.13 A y | 0.33 ± 0.19 A y |
| TW09184 O26 | 1.13 ± 0.06 A z | 0.79 ± 0.25 A z | 0.35 ± 0.25 A y | 0.81 ± 0.25 A z |
| Sprouts O26 | 0.64 ± 0.26 B z | 1.02 ± 0.30 A z | 0.09 ± 0.03 A y | 0.51 ± 0.30 A z |
| ORF ID | Gene | Function | Significant Differential Gene Expression (Fold Change) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| d1/d3 | d3/d1 | d3/d5 | d5/d1 | d5/d3 | |||
| ECs0025 | espX | T3SS effector-like protein EspX | 1.9 | 5.6 | 3.0 | ||
| ECs0472 | espY3 | T3SS effector-like protein EspY | 1.7 | 4.2 | 2.5 | ||
| ECs0865 | ybhM | BAX Inhibitor-1 family inner membrane protein | 4.6 | 5.1 | |||
| ECs1274 | grvA | Transcriptional regulator | 1.8 | 3.9 | 2.1 | ||
| ECs1388 | pchD | Putative transcriptional regulator | 3.7 | 3.9 | |||
| ECs1417 | csgD | Transcriptional regulator CsgD | 4.5 | 3.3 | |||
| ECs1438 | bssS | biofilm regulator | 3.4 | 4.2 | |||
| ECs1490 | bhsA | multiple stress resistance protein (YcfR) | 3.5 | 4.2 | |||
| ECs1926 | zntB | Zinc transport protein ZntB | 1.8 | 1.8 | |||
| ECs2062 | ybfL | type IV secretion protein Rhs | 3.9 | 3.0 | |||
| ECs2155 | nleG6-2 | T3SS secreted effector NleG | 4.0 | 3.3 | |||
| ECs2291 | ynfC | Hypothetical UPF0257 lipoprotein ynfC precursor | 2.4 | 2.7 | |||
| ECs2333 | blr | beta-lactam resistance membrane protein | 1.8 | 11.6 | 6.3 | ||
| ECs2672 | espR3 | T3SS effector-like protein EspR | 5.3 | 3.9 | |||
| ECs2765 | dicC | cell division control protein | 4.9 | 4.1 | |||
| ECs2844 | wzy | O antigen polymerase | 1.5 | 5.6 | 3.6 | ||
| ECs3124 | glpQ | Glycerophosphoryl diester phosphodiesterase | 2.2 | 2.4 | |||
| ECs3155 | elaA | acetyltransferase | 2.0 | 2.2 | |||
| ECs3241 | lacY | galactosidase permease | 2.4 | 2.6 | |||
| ECs3728 | eivJ1 | type III secretion system protein EivJ1 | 1.7 | 5.4 | 3.2 | ||
| ECs3729 | eivI | type III secretion apparatus protein EivI | 1.5 | 5.7 | 3.8 | ||
| ECs3855 | espL2 | T3SS secreted effector EspL | 3.7 | 2.7 | |||
| ECs3858 | nleE | T3SS secreted effector NleE | 5.2 | 4.9 | |||
| ECs3907 | qseB | Two-component system response regulator QseB | 1.9 | 2.1 | |||
| ECs4188 | hopD | Leader peptidase (Prepilin peptidase) | 2.4 | 2.7 | |||
| ECs4366 | uspB | Universal stress protein B | 3.8 | 4.1 | |||
| ECs4392 | gadE | Transcriptional activator GadE | 1.9 | 4.3 | 8.2 | ||
| ECs4502 | waaR | UDP-galactose:(galactosyl) galactosyltransferase | 1.8 | 9.7 | 5.5 | ||
| ECs4574 | sepD | type III secretion system protein SepD | 1.7 | 10.5 | 6.1 | ||
| ECs4578 | grlR | negative regulator GrlR | 6.5 | 4.8 | |||
| ECs4580 | escU | Type III secretion inner membrane protein | 6.6 | 5.9 | |||
| ECs4584 | Orf5—T3SS component | 1.9 | 11.3 | 5.9 | |||
| ECs4586 | Orf3—T3SS component | 5.0 | 4.4 | ||||
| ECs5048 | espX5 | T3SS effector-like protein EspX | 1.9 | 3.6 | 1.9 | ||
| Homologous ORF in Sakai | Gene | Function | Significant Differential Gene Expression (Fold Change) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| d3/d1 | d5/d1 | |||
| ECs_0014 | dnaK | chaperone Hsp70 | 2.3 | 1.7 |
| ECs_0439 | yaiA | OxyR-regulated protein | 2.7 | 2.2 |
| ECs_0466 | nrdR | transcriptional regulator NrdR | 1.8 | 1.5 |
| ECs_0489 | bolA | transcriptional regulator BolA | 2.1 | 2.0 |
| ECs_0662 | cspE | cold-shock protein CspE | 4.2 | 1.9 |
| ECs_0966 | cspD | cold-shock protein CspD | 1.6 | |
| ECs_1041 | ompA | outer membrane protein A | 2.4 | 1.7 |
| ECs_1154 | cbpM | chaperone modulatory protein CbpM | 1.8 | 1.8 |
| ECs_1387 | ybdM | transcriptional regulator | 2.1 | 1.7 |
| ECs_1438 | bssS | transcriptional regulator biofilm | 2.5 | 1.6 |
| ECs_1683 | ycgB | SpoVR family stationary phase protein | 1.7 | 1.6 |
| ECs_1883 | pspC | envelope stress response membrane protein PspC | 4.0 | 2.5 |
| ECs_1885 | pspE | thiosulfate sulfurtransferase PspE | 5.5 | 2.8 |
| ECs_1915 | fnr | transcriptional regulator FNR | 1.6 | 1.6 |
| ECs_2084 | sra | stationary-phase-induced ribosome-associated protein | 3.1 | 2.4 |
| ECs_2086 | osmC | peroxiredoxin OsmC | 2.8 | 1.9 |
| ECs_2145 | ydeI | hydrogen peroxide resistance OB fold protein | 2.2 | 1.7 |
| ECs_2355 | sodC | superoxide dismutase [Cu-Zn] SodC2 | 3.4 | 2.9 |
| ECs_2504 | yeaQ | stress response membrane protein | 2.7 | 2.7 |
| ECs_2558 | yebG | damage-inducible protein YebG | 2.3 | 1.8 |
| ECs_3271 | mntH | manganese/divalent cation transporter | 1.5 | |
| ECs_3476 | grpE | molecular chaperone GrpE | 1.8 | |
| ECs_3553 | csrA | carbon storage regulator | 2.4 | 1.4 |
| ECs_3556 | recA | DNA recombination/repair protein RecA | 1.7 | 1.6 |
| ECs_3595 | rpoS | RNA polymerase sigma factor RpoS | 3.2 | 1.9 |
| ECs_3887 | yghA | NAD(P)-dependent oxidoreductase | 1.9 | 1.7 |
| ECs_4050 | nusA | transcription elongation factor NusA | 1.7 | 1.5 |
| ECs_4390 | hdeA | acid-resistance protein HdeA | 2.6 | 2.0 |
| ECs_4396 | gadX | GAD regulon transcriptional activator | 1.8 | |
| ECs_4778 | hemG | protoporphyrinogen oxidase | 1.6 | 1.4 |
| ECs_4789 | hemN | coproporphyrinogen III oxidase | 1.5 | |
| ECs_4923 | hupA | transcriptional regulator HU subunit alpha | 2.3 | 1.9 |
| ECs_5029 | zur | transcriptional regulator Zur | 2.3 | 2.0 |
| ECs_5039 | yjbR | MmcQ/YjbR family DNA-binding protein | 1.5 | |
| ECs_5123 | groES | co-chaperonin GroES | 2.5 | 2.2 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tyagi, D.; Kraft, A.L.; Levadney Smith, S.; Roof, S.E.; Sherwood, J.S.; Wiedmann, M.; Bergholz, T.M. Pre-Harvest Survival and Post-Harvest Chlorine Tolerance of Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli on Lettuce. Toxins 2019, 11, 675. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11110675
Tyagi D, Kraft AL, Levadney Smith S, Roof SE, Sherwood JS, Wiedmann M, Bergholz TM. Pre-Harvest Survival and Post-Harvest Chlorine Tolerance of Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli on Lettuce. Toxins. 2019; 11(11):675. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11110675
Chicago/Turabian StyleTyagi, Deepti, Autumn L. Kraft, Sara Levadney Smith, Sherry E. Roof, Julie S. Sherwood, Martin Wiedmann, and Teresa M. Bergholz. 2019. "Pre-Harvest Survival and Post-Harvest Chlorine Tolerance of Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli on Lettuce" Toxins 11, no. 11: 675. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11110675
APA StyleTyagi, D., Kraft, A. L., Levadney Smith, S., Roof, S. E., Sherwood, J. S., Wiedmann, M., & Bergholz, T. M. (2019). Pre-Harvest Survival and Post-Harvest Chlorine Tolerance of Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli on Lettuce. Toxins, 11(11), 675. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11110675






