Proteomic Characterization of High-Density Lipoprotein Particles from Non-Diabetic Hemodialysis Patients
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Proteome Characteristics
2.2. HD-Associated Protein Expression Correlations in HD Patients
3. Discussion
Limitations of the Study
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Recruitment and Sample Collection
5.2. Mass Spectrometry
5.3. Gene Ontology and Protein Network
5.4. Statistical Analysis
5.5. Associated Data
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Go, A.S.; Chertow, G.M.; Fan, D.; McCulloch, C.E.; Hsu, C.-Y. Chronic kidney disease and the risks of death, cardiovascular events, and hospitalization. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 1296–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wanner, C.; Krane, V.; März, W.; Olschewski, M.; Mann, J.F.; Ruf, G.; Ritz, E. Atorvastatin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus undergoing hemodialysis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 353, 238–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fellström, B.C.; Jardine, A.G.; Schmieder, R.E.; Holdaas, H.; Bannister, K.; Beutler, J.; Chae, D.-W.; Chevaile, A.; Cobbe, S.M.; Grönhagen-Riska, C.; et al. Rosuvastatin and cardiovascular events in patients undergoing hemodialysis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 1395–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navab, M.; Reddy, S.T.; Van Lenten, B.J.; Fogelman, A.M. HDL and cardiovascular disease: Atherogenic and atheroprotective mechanisms. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2011, 8, 222–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holzer, M.; Schilcher, G.; Curcic, S.; Trieb, M.; Ljubojevic, S.; Stojakovic, T.; Scharnagl, H.; Kopecky, C.M.; Rosenkranz, A.R.; Heinemann, A.; et al. Dialysis modalities and HDL composition and function. J. Am. Chem. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 26, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shroff, R.; Speer, T.; Colin, S.; Charakida, M.; Zewinger, S.; Staels, B.; Chinetti-Gbaguidi, G.; Hettrich, I.; Rohrer, L.; O’Neill, F.; et al. HDL in children with CKD promotes endothelial dysfunction and an abnormal vascular phenotype. J. Am. Chem. Soc. Nephrol. 2014, 25, 2658–2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, S.; Yancey, P.G.; Ikizler, T.A.; Jerome, W.G.; Kaseda, R.; Cox, B.; Bian, A.; Shintani, A.; Fogo, A.B.; Linton, M.F.; et al. Dysfunctional high-density lipoprotein in patients on chronic hemodialysis. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2012, 60, 2372–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holzer, M.; Birner-Gruenberger, R.; Stojakovic, T.; El-Gamal, D.; Binder, V.; Wadsack, C.; Heinemann, A.; Marsche, G. Uremia alters HDL composition and function. J. Am. Chem. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 22, 1631–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Florens, N.; Calzada, C.; Lyasko, E.; Juillard, L.; Soulage, C. Modified lipids and lipoproteins in chronic kidney disease: A new class uremic toxins. Toxins 2016, 8, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaziri, N.D. Causes of dysregulation of lipid metabolism in chronic renal failure. Semin. Dial. 2009, 22, 644–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinecke, J.W. The HDL proteome: A marker—and perhaps mediator—of coronary artery disease. J. Lipid Res. 2009, 50 (Suppl. S1), 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, B.; Heinecke, J.W. Quantifying HDL proteins by mass spectrometry: How many proteins are there and what are their functions? Expert Rev. Proteomics 2017, 15, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, B.; de Boer, I.; Tang, C.; Mayer, P.S.; Zelnick, L.; Afkarian, M.; Heinecke, J.W.; Himmelfarb, J. A cluster of proteins implicated in kidney disease is increased in high-density lipoprotein isolated from hemodialysis subjects. J. Proteome Res. 2015, 14, 2792–2806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangé, A.; Goux, A.; Badiou, S.; Patrier, L.; Canaud, B.; Maudelonde, T.; Cristol, J.-P.; Solassol, J. HDL proteome in hemodialysis patients: A quantitative nanoflow liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry approach. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e34107-9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oberbach, A.; Adams, V.; Schlichting, N.; Heinrich, M.; Kullnick, Y.; Lehmann, S.; Lehmann, S.; Feder, S.; Correia, J.C.; Mohr, F.-W.; et al. Proteome profiles of HDL particles of patients with chronic heart failure are associated with immune response and also include bacteria proteins. Clin. Chim. Acta 2016, 453, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Craenenbroeck, A.H.; Bragfors-Helin, A.-C.; Qureshi, A.R.; Lindholm, B.; Sjöberg, B.; Anderstam, B.; Heimburger, O.; Stenvinkel, P.; Bárány, P. Plasma beta-trace protein as a marker of residual renal function: The effect of different hemodialysis modalities and intra-individual variability over time. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2017, 42, 877–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gertow, J.; Ng, C.Z.; Mamede Branca, R.M.; Werngren, O.; Du, L.; Kjellqvist, S.; Hemmingsson, P.; Bruchfeld, A.; MacLaughlin, H.; Eriksson, P.; et al. Altered Protein Composition of Subcutaneous Adipose Tissue in Chronic Kidney Disease. Kidney Int. Rep. 2017, 2, 1208–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Havel, R.J.; Eder, H.A.; Bragdon, J.H. The distribution and chemical composition of ultracentrifugally separated lipoproteins in human serum. J. Clin. Investig. 1955, 34, 1345–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
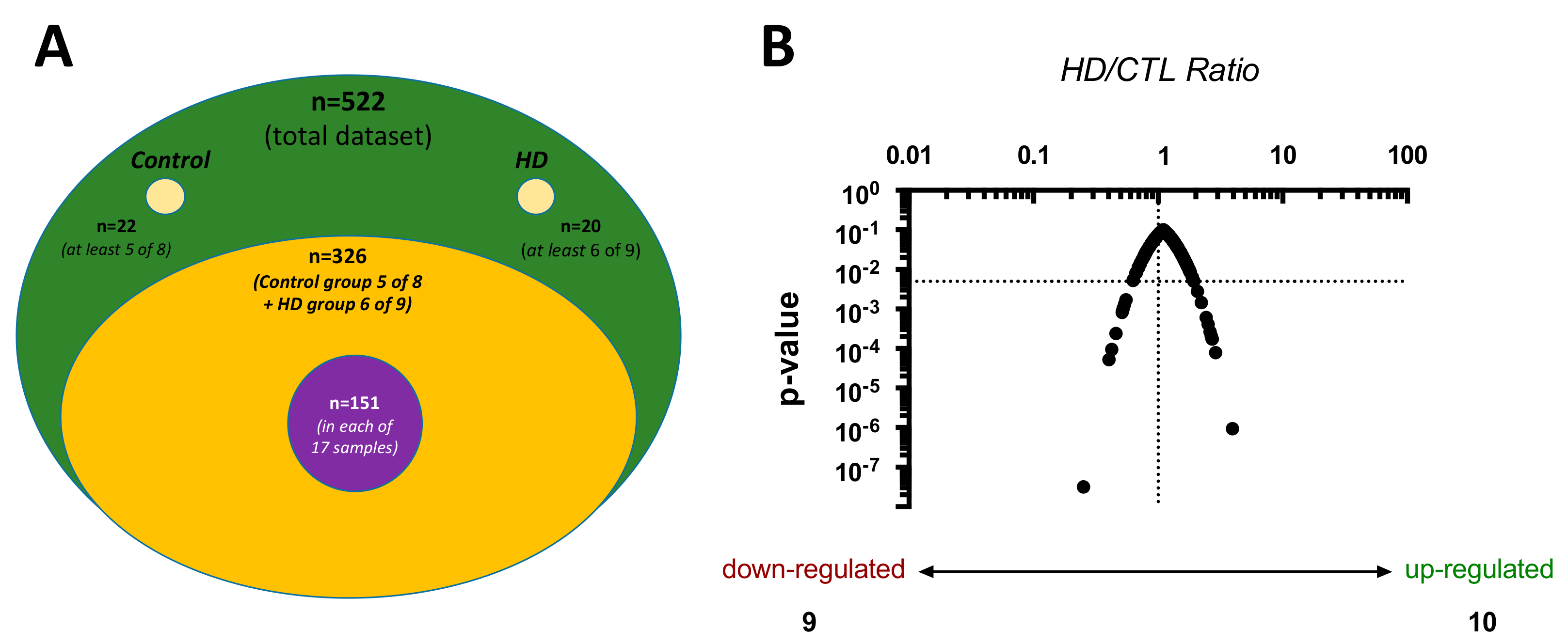

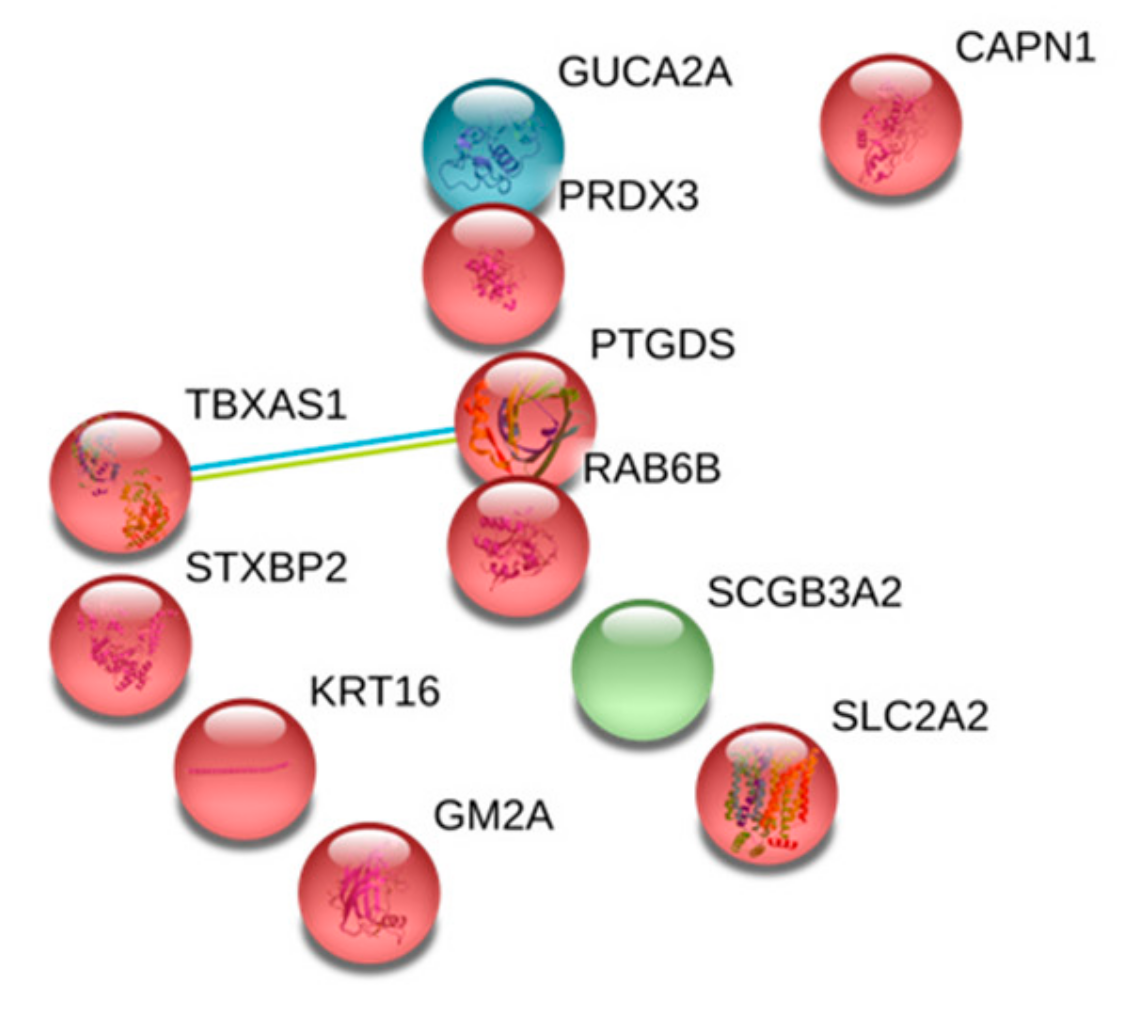
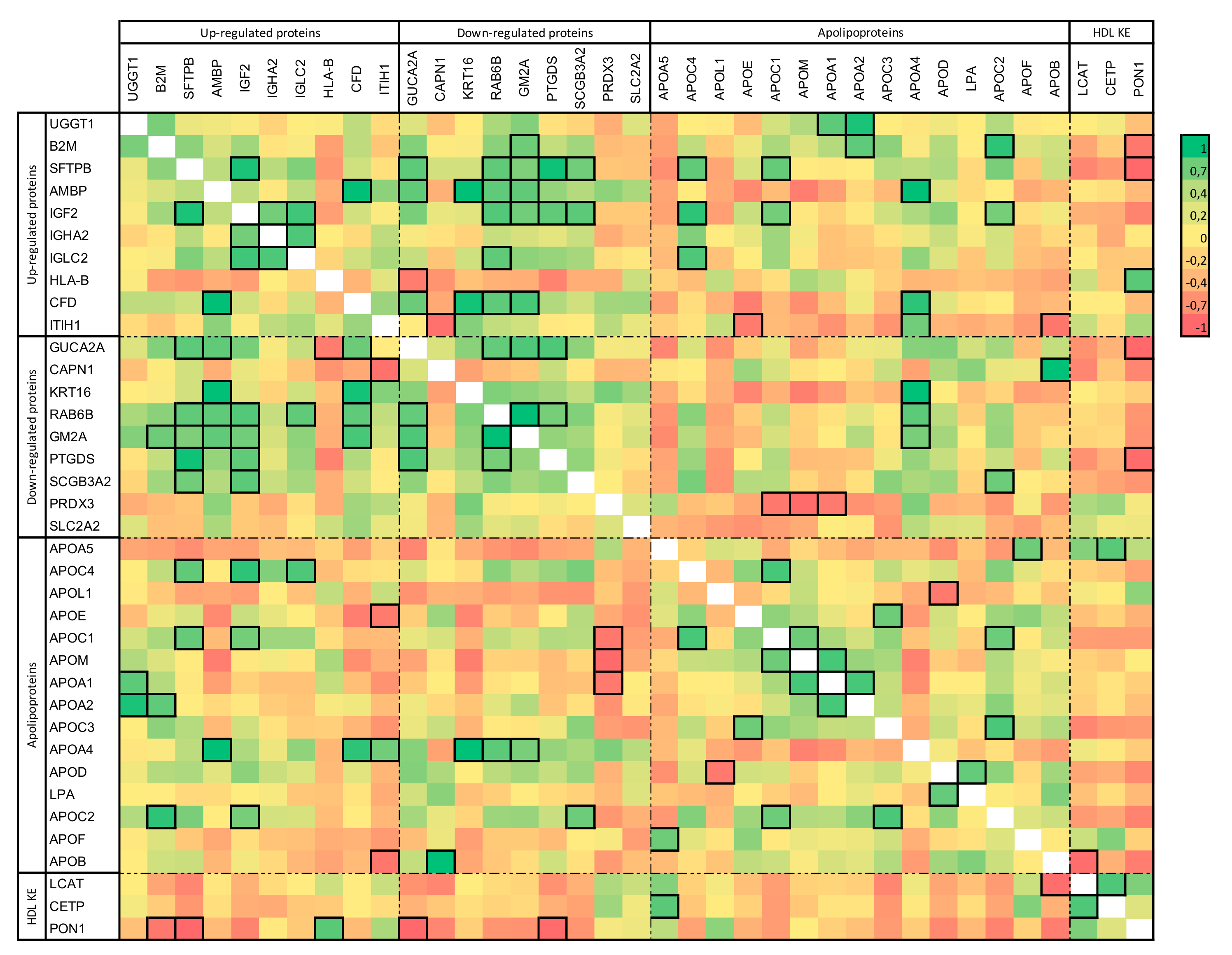
| N | Control (CTL) | Hemodialysis (HD) | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 8 | 9 | ||
| General characteristics | |||
| Age, years | 39 (31–50) | 57 (46–74) | 0.045 |
| Gender, n male/n female | 5/3 | 5/4 | 0.653 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 22 (19–26) | 26 (25–28) | 0.060 |
| Comorbidities | |||
| HT, n | 2 | 8 | |
| Stroke, n | 0 | 0 | |
| CHD, n | 0 | 2 | |
| Cardiopathy, n | 0 | 4 | |
| PVD, n | 0 | 1 | |
| Therapies | |||
| Statins, n | 0 | 6 | |
| PI, n | 0 | 5 | |
| RASi, n | 1 | 3 | |
| ß-blockers, n | 1 | 5 | |
| CCB, n | 1 | 1 | |
| Biological parameters | |||
| Urea, mmol/L | 6.5 (5.3–7.8) | 13.0 (10.9–19.8) | <0.0001 |
| Creatinine, µmol/L | 77.5 (5.3–7.8) | 583 (458.0–798.0) | <0.0001 |
| mGFR, mL/min/1.73 m2 | 94 (84–96) | - | |
| Total cholesterol, mg/dL | 217 (187–238) | 153 (104–191) | 0.021 |
| LDL cholesterol, mg/dL | 141 (104–157) | 71 (43–124) | 0.029 |
| HDL cholesterol, mg/dL | 58 (52–62) | 46 (38–48) | 0.016 |
| Triacylglycerols, mg/dL | 99 (86–133) | 93 (87–138) | 0.999 |
| CRP, mg/L | 1.7 (0.2–4.6) | 2.5 (1.5–24.8) | 0.145 |
| Protein Name | Protein Label | Ratio | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| UDP-glucose: glycoprotein glucosyltransferase 1 | UGGT1 | 3.948 | 9.34 × 10−6 |
| Beta-2-microglobulin | B2M | 2.895 | 7.90 × 10−4 |
| Pulmonary surfactant-associated protein B | SFTPB | 2.716 | 1.72 × 10−3 |
| Protein AMBP | AMBP | 2.711 | 1.75 × 10−3 |
| Insulin-like growth factor II | IGF2 | 2.672 | 2.07 × 10−3 |
| Immunoglobulin heavy constant alpha 2 | IGHA2 | 2.615 | 2.66 × 10−3 |
| Immunoglobulin lambda constant 2 | IGLC2 | 2.514 | 4.13 × 10−3 |
| HLA class I histocompatibility antigen, B-58 alpha chain | HLA-B | 2.427 | 6.05 × 10−3 |
| Complement factor D | CFD | 2.224 | 1.46 × 10−2 |
| Inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor heavy chain H1 | ITIH1 | 2.073 | 2.79 × 10−2 |
| Protein Name | Protein Label | Ratio | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Guanylin | GUCA2A | 0.553 | 1.71 × 10−2 |
| Calpain-1 catalytic subunit | CAPN1 | 0.538 | 1.32 × 10−2 |
| Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 16 | KRT16 | 0.526 | 1.05 × 10−2 |
| Ras-related protein Rab-6B | RAB6B | 0.519 | 9.23 × 10−3 |
| Ganglioside GM2 activator | GM2A | 0.513 | 8.19 × 10−3 |
| Prostaglandin-H2 D-isomerase | PTGDS | 0.458 | 2.40 × 10−3 |
| Secretoglobin family 3A member 2 | SCGB3A2 | 0.424 | 9.51 × 10−4 |
| Thioredoxin-dependent peroxide reductase, mitochondrial | PRDX3 | 0.404 | 5.22 × 10−4 |
| Solute carrier family 2, facilitated glucose transporter member 2 | SLC2A2 | 0.251 | 3.16 × 10−7 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Florens, N.; Calzada, C.; Delolme, F.; Page, A.; Guebre Egziabher, F.; Juillard, L.; Soulage, C.O. Proteomic Characterization of High-Density Lipoprotein Particles from Non-Diabetic Hemodialysis Patients. Toxins 2019, 11, 671. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11110671
Florens N, Calzada C, Delolme F, Page A, Guebre Egziabher F, Juillard L, Soulage CO. Proteomic Characterization of High-Density Lipoprotein Particles from Non-Diabetic Hemodialysis Patients. Toxins. 2019; 11(11):671. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11110671
Chicago/Turabian StyleFlorens, Nans, Catherine Calzada, Frédéric Delolme, Adeline Page, Fitsum Guebre Egziabher, Laurent Juillard, and Christophe O. Soulage. 2019. "Proteomic Characterization of High-Density Lipoprotein Particles from Non-Diabetic Hemodialysis Patients" Toxins 11, no. 11: 671. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11110671
APA StyleFlorens, N., Calzada, C., Delolme, F., Page, A., Guebre Egziabher, F., Juillard, L., & Soulage, C. O. (2019). Proteomic Characterization of High-Density Lipoprotein Particles from Non-Diabetic Hemodialysis Patients. Toxins, 11(11), 671. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11110671





