Cytotoxic Properties of HT-2 Toxin in Human Chondrocytes: Could T3 Inhibit Toxicity of HT-2?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
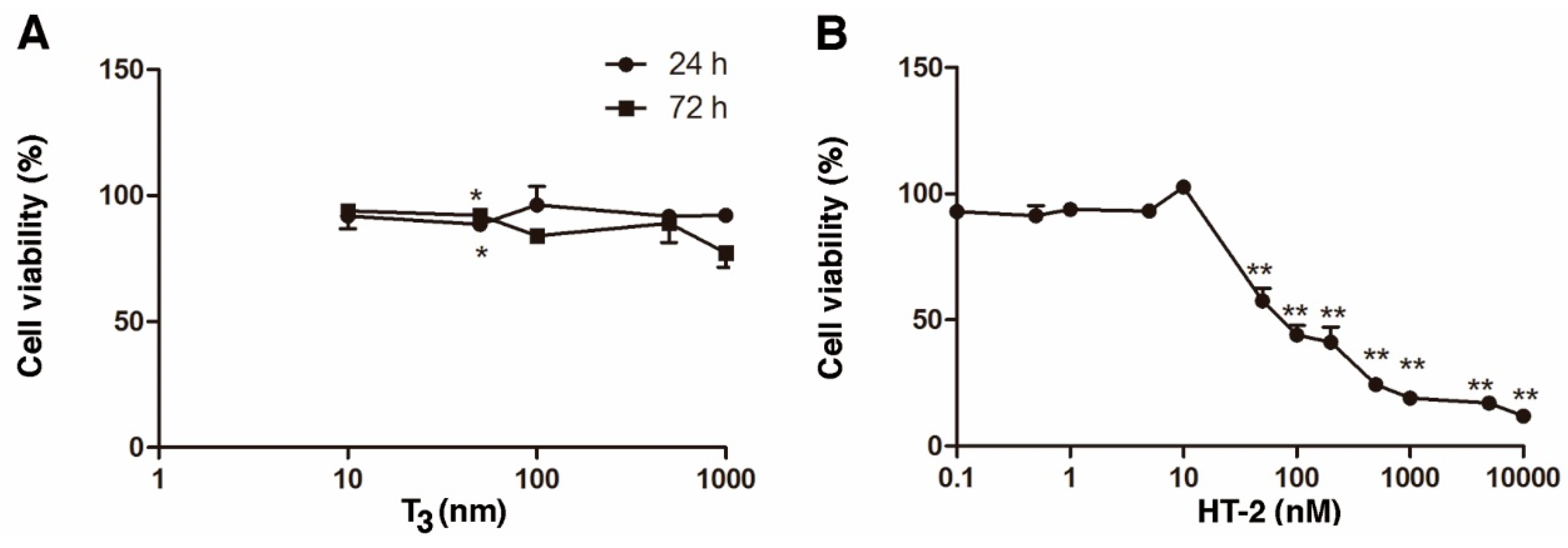
2.1. Individual Cytotoxicity of T3 and HT-2 Toxin in Human C-28/I2 Chondrocytes
2.2. T3 Protects against HT-2 Toxin-Induced Toxicity
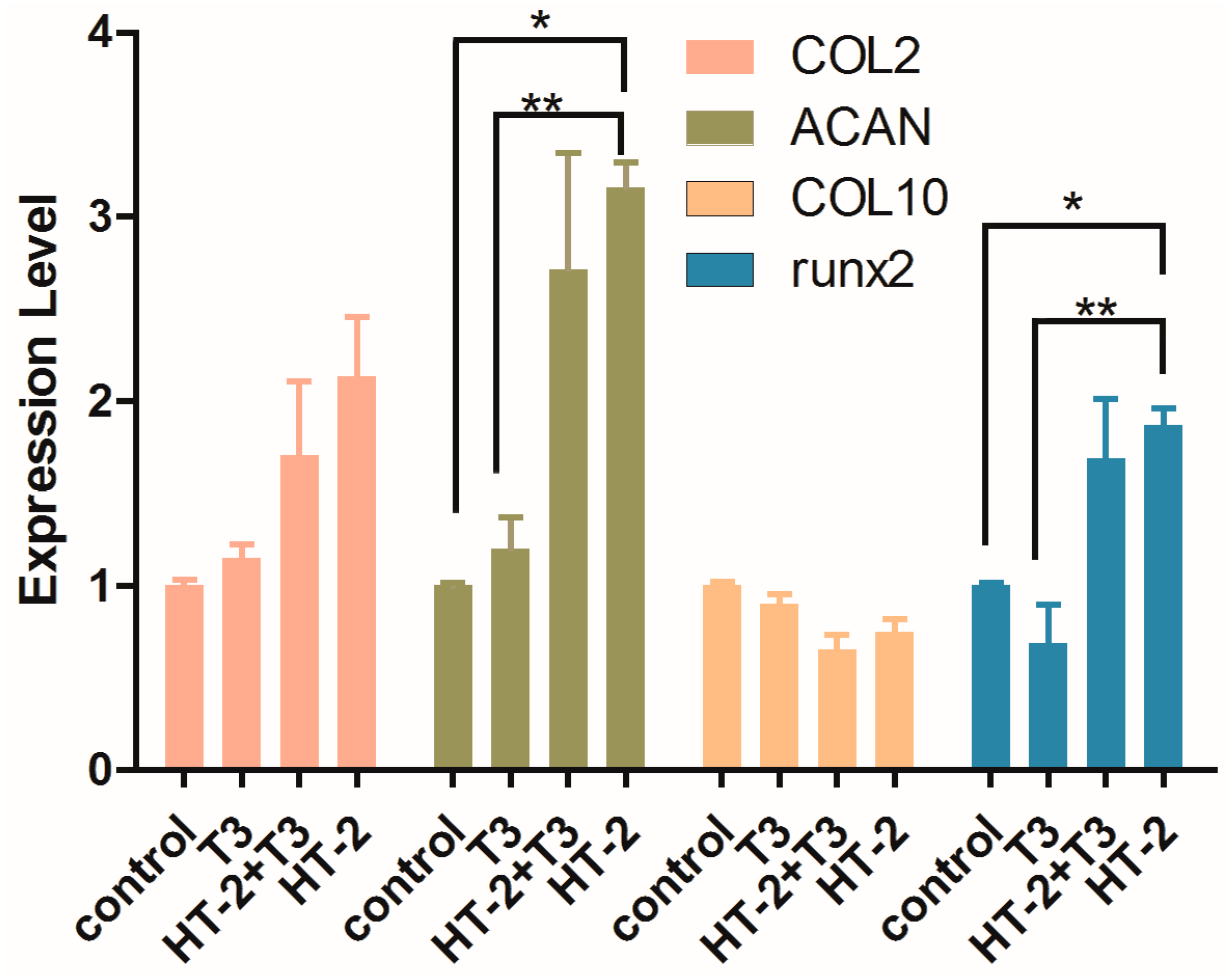
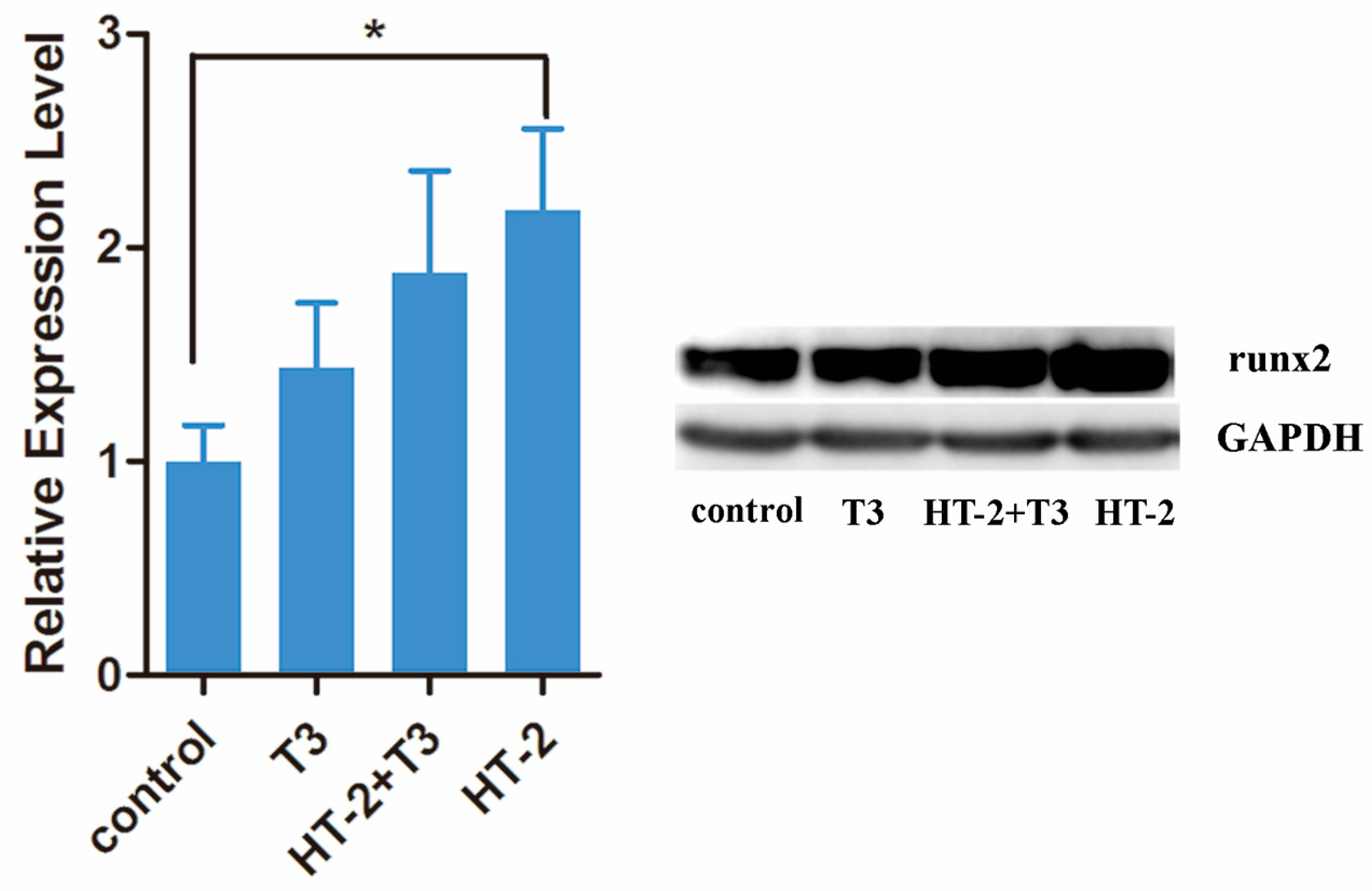
2.3. Expressions of Extracellular Matrix and Hypertrophy Related-Genes in Chondrocyte Cultures Treated with T3 and/or HT-2 Toxin
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Chondrocyte Culture
5.2. MTT Cytotoxicity Assay
5.3. RNA Isolation and Quantitative Real-Time RT-PCR
5.4. Immunoblot Analysis
5.5. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Robson, H.; Siebler, T.; Stevens, D.A.; Shalet, S.M.; Williams, G.R. Thyroid hormone acts directly on growth plate chondrocytes to promote hypertrophic differentiation and inhibit clonal expansion and cell proliferation. Endocrinology 2000, 141, 3887–3897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassett, J.H.D.; Williams, G.R. The molecular actions of thyroid hormone in bone. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 14, 356–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.K.; Gegg, C.A.; Hu, J.C.; Reddi, A.H.; Athanasiou, K.A. Thyroid hormone enhance the biomechanical functionality of scaffold-free neocartilage. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2015, 17, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez-Pernas, P.; Fafian-Labora, J.; Lesende-Rodriguez, I.; Mateos, J.; de la Fuente, A.; Fuentes, I.; de Toro Santos, J.; Blanco Garcia, F.; Arufe, M.C. 3,3′,5-triiodo-L-thyronine increases in vitro chondrogenesis of mesenchymal stem cells from umbilical cord stroma through SRC2. J. Cell. Biochem. 2016, 117, 2097–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Shao, Y.Y.; Ballock, R.T. Thyroid hormone interacts with the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in the terminal differentiation of growth plate chondrocytes. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2007, 22, 1988–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ray, R.D.; Asling, C.W.; Walker, D.G.; Simpson, M.E.; Li, C.H.; Evans, H.M. Growth and differentiation of the skeleton in thyreoidectomized-hypophysectomized rats treated with thyroxin, growth hormone, and combination. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 1954, 36, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagase, H.; Nagasawa, Y.; Tachida, Y.; Sakakibara, S.; Okutsu, J.; Suematsu, N.; Arita, S.; Shimada, K. Deiodinase 2 upregulation demonstrated in osteoarthritis patients cartilage causes cartilage destruction in tissue-specific transgenic rats. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2013, 21, 514–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.M.; Song, R.X.; Jiao, X.H.; Du, X.L.; Liu, J.F.; Liu, X.; Chen, Q. PMS13-Study on mechanism of type 2 deiodinase gene and Erk signal transduction in Kashin-Beck disease. Value Health 2014, 17, A43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Zhang, F.; Li, C.; He, S.; Tan, W.; Lei, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Yu, H.; Zheng, J.; Guo, X. Gene expression analysis suggests bone development-related genes GDF5 and DIO2 are involved in the development of Kashin-Beck disease in children rather than adults. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e103618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Fels-Klerx, H.J. Occurrence data of trichothecene mycotoxins T-2 toxin and HT-2 toxin in food and feed. EFSA Support. Publ. 2010, 7, 1–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.F.; Lin, X.L.; Yang, L.; Liu, H.; Wang, X.; Fang, H.; Lammi, M.J.; Guo, X. Comparison of T-2 toxin and HT-2 toxin distributed in the skeletal system with that in other tissues of rats by acute toxicity test. Biomed. Environ. Sci 2017, 30, 851–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, F.F.; Lin, X.L.; Liu, H.; Yang, L.; Goldring, M.B.; Lammi, M.J.; Guo, X. Selenium promotes metabolic conversion of T-2 toxin to HT-2 toxin in cultured human chondrocytes. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2017, 44, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Beier, R.C.; Shen, J.; de Smet, D.; de Saeger, S.; Zhang, S. T-2 toxin, a trichothecene mycotoxin: Review of toxicity, metabolism, and analytical methods. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 3441–3453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, F.F.; Lin, X.L.; Wang, X.; Ping, Z.G.; Guo, X. Comparison of apoptosis and autophagy in human chondrocytes induced by the T-2 and HT-2 toxins. Toxins 2019, 11, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Wang, L.; Guo, X.; Pang, Q.; Wu, S.; Wu, C.; Xu, P.; Bai, Y. The role of mitochondria in T-2 toxin-induced human chondrocytes apoptosis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e108394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Wang, X.; Sun, Z.; Jin, Z.; Chen, M.; Wang, X.; Lammi, M.J.; Guo, X. Inflammatory cytokine of IL-1β is involved in T-2 toxin-triggered chondrocyte injury and metabolism imbalance by the activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Mol. Immunol. 2017, 91, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Han, J.; Guo, X.; Qu, C.; Yu, F.; Wu, X. The effects of T-2 toxin on the prevalence and development of Kashin-Beck disease in China: A meta-analysis and systematic review. Toxicol. Res. 2016, 5, 731–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruderer, M.; Richards, R.G.; Alini, M.; Stoddart, M.J. Role and regulation of RUNX2 in osteogenesis. Eur. Cell Mater. 2014, 28, 269–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desjardin, C.; Charles, C.; Benoist-Lasselin, C.; Riviere, J.; Gilles, M.; Chassande, O.; Morgenthaler, C.; Laloe, D.; Lecardonnel, J.; Flamant, F.; et al. Chondrocytes play a major role in the stimulation of bone growth by thyroid hormone. Endocrinology 2014, 155, 3123–3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Ma, W.J.; Zhang, F.; Ren, F.L.; Qu, C.J.; Lammi, M.J. Recent advances in the research of an endemic osteochondropathy in China: Kashin-Beck disease. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2014, 22, 1774–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, L.B.; Belanger, J.M.; Oberbauer, A.M. Fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 effects on proliferation and telomerase activity in sheep growth plate chondrocytes. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2012, 3, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karl, A.; Olbrich, N.; Pfeifer, C.; Berner, A.; Zellner, J.; Kujat, R.; Angele, P.; Nerlich, M.; Mueller, M.B. Thyroid hormone-induced hypertrophy in mesenchymal stem cell chondrogenesis is mediated by bone morphogenetic protein-4. Tissue Eng. A 2014, 20, 178–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von der Mark, K.; Kirsch, T.; Nerlich, A.; Kuss, A.; Weseloh, G.; Glückert, K.; Stöss, H. Type X collagen synthesis in human osteoarthritic cartilage. Indication of chondrocyte hypertrophy. Arthritis Rheumatol. 1992, 35, 806–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitney, G.A.; Kean, T.J.; Fernandes, R.J.; Waldman, S.; Tse, M.Y.; Pang, S.C.; Mansour, J.M.; Dennis, J.E. Thyroxine increases collagen type II expression and accumulation in scaffold-free tissue-engineered articular cartilage. Tissue Eng. A 2018, 24, 369–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, P.T.; Zhang, X.L.; Zuo, H.N.; Lu, X.; Gai, P.Z. A study on role of triiodothyronine (T3) hormone on the improvement of articular cartilage surface architecture. Exp. Toxicol. Pathol. 2017, 69, 625–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Chu, Y.; Cao, J.; Wang, W.; Liu, J.; Wang, J. Effects of T-2 toxin and selenium on chondrocyte expression of matrix metalloproteinases (MMP-1, MMP-13), α2-macroglobulin (α2M) and TIMPs. Toxicol. Vitro 2011, 25, 492–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zou, N.; Wang, J.; Wang, K.W.; Li, F.Y.; Chen, F.X.; Sun, B.Y.; Sun, D.J. TGF-β1/Smad3 signaling pathway mediates T-2 toxin-induced decrease of type II collagen in cultured rat chondrocytes. Toxins 2017, 9, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.Y.; Cao, J.L.; Shi, Z.L.; Chen, J.H.; Zhang, Z.T.; Hughes, C.E.; Caterson, B. Promotion of the articular cartilage proteoglycan degradation by T-2 toxin and selenium protective effect. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2008, 9, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Yan, J.; Wang, W.; Zhong, N.; Tian, L.; Sun, J.; Min, Z.; Ma, J.; Lu, S. T-2 toxin enhances catabolic activity of hypertrophic chondrocytes through ROS-NF-κB-HIF-2α pathway. Toxicol. Vitro 2012, 26, 1106–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldring, M.B. Immortalization of human articular chondrocytes for generation of stable, differentiated cell lines. Methods Mol. Med. 2004, 100, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-delta delta C(T)) method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Ratios | Components | Concentrations (nM) |
|---|---|---|
| 1:1 | HT-2 | 1, 5, 10, 50, 100, 200, 500 |
| T3 | 1, 5, 10, 50, 100, 200, 500 | |
| HT-2:T3 | 1:1, 5:5, 10:10, 50:50, 100:100, 200:200, 500:500 | |
| 1:10 | HT-2 | 1, 5, 10, 50, 100 |
| T3 | 10, 50, 100, 500, 1000 | |
| HT-2:T3 | 1:10, 5:50, 10:100, 50:500, 100:1000 | |
| 1:100 | HT-2 | 1, 5, 10, 50, 100 |
| T3 | 100, 500, 10, 50, 100, 200, 500 | |
| HT-2:T3 | 1:100, 5:500, 10:1000, 50:5000, 100:10,000 | |
| 1:1000 | HT-2 | 0.1, 0.5, 1, 5, 10 |
| T3 | 100, 500, 1000, 5000, 10,000 | |
| HT-2:T3 | 0.1:100, 0.5:500, 1:1000, 5:5000, 10:10,000 | |
| 10:1 | HT-2 | 10, 50, 100, 500, 1000 |
| T3 | 1, 5, 10, 50, 100 | |
| HT-2:T3 | 10:1, 50:5, 100:10, 500:50, 1000:100 | |
| 100:1 | HT-2 | 10, 5,0 100, 500, 1000 |
| T3 | 0.1, 0.5, 1, 5, 10 | |
| HT-2:T3 | 10:0.1, 50:0.5, 100:1, 500:5, 1000:10 | |
| 1000:1 | HT-2 | 100, 500, 1000, 5000, 10,000 |
| T3 | 0.1, 0.5, 1, 5, 10 | |
| HT-2:T3 | 100:0.1, 500:0.5, 1000:1, 5000:5, 10,000:10 |
| Genes | Forward Primer | Reverse Primer |
|---|---|---|
| COL2A1 | AGACTGGCGAGACTTGCGTCTA | ATCTCGGACGTTGGCAGTGTTG |
| ACAN | CTGAACGACAGGACCATCGAA | CGTGCCAGATCATCACCACA |
| COL10A1 | GACTCATGTTTGGGTAGGCCTGTA | CCCTGAAGCCTGATCCAGGTA |
| Runx2 | AGCTTCTGTCTGTGCCTTCTGG | GGAGTGGACGAGGCAAGAGTTT |
| GAPDH | GCACCGTCAAGGCTGAGAAC | TGGTGAAGACGCCAGTGGA |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, F.; Lammi, M.J.; Shao, W.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, H.; Guo, X. Cytotoxic Properties of HT-2 Toxin in Human Chondrocytes: Could T3 Inhibit Toxicity of HT-2? Toxins 2019, 11, 667. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11110667
Zhang F, Lammi MJ, Shao W, Zhang P, Zhang Y, Wei H, Guo X. Cytotoxic Properties of HT-2 Toxin in Human Chondrocytes: Could T3 Inhibit Toxicity of HT-2? Toxins. 2019; 11(11):667. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11110667
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Feng’e, Mikko Juhani Lammi, Wanzhen Shao, Pan Zhang, Yanan Zhang, Haiyan Wei, and Xiong Guo. 2019. "Cytotoxic Properties of HT-2 Toxin in Human Chondrocytes: Could T3 Inhibit Toxicity of HT-2?" Toxins 11, no. 11: 667. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11110667
APA StyleZhang, F., Lammi, M. J., Shao, W., Zhang, P., Zhang, Y., Wei, H., & Guo, X. (2019). Cytotoxic Properties of HT-2 Toxin in Human Chondrocytes: Could T3 Inhibit Toxicity of HT-2? Toxins, 11(11), 667. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11110667






