Uptake, Growth, and Pigment Changes in Lemna minor L. Exposed to Environmental Concentrations of Cylindrospermopsin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
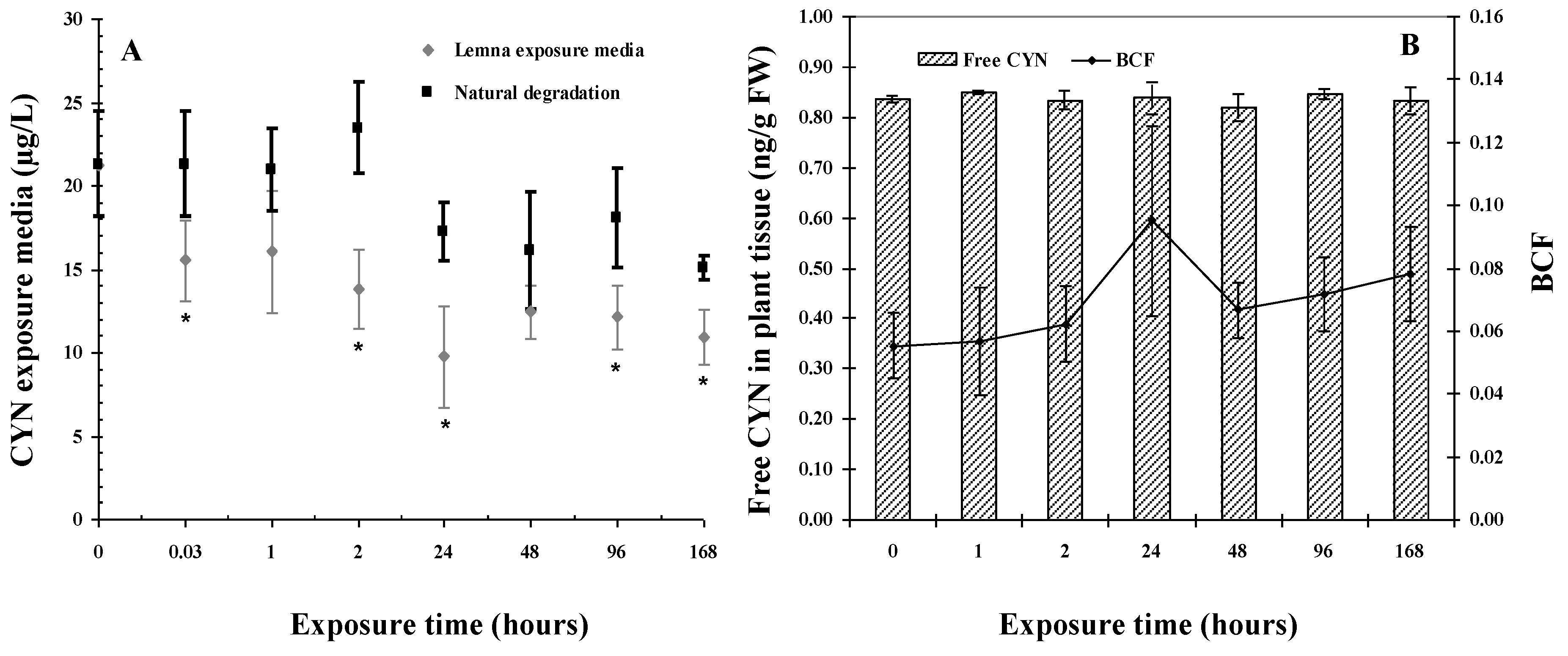
2.1. CYN Uptake
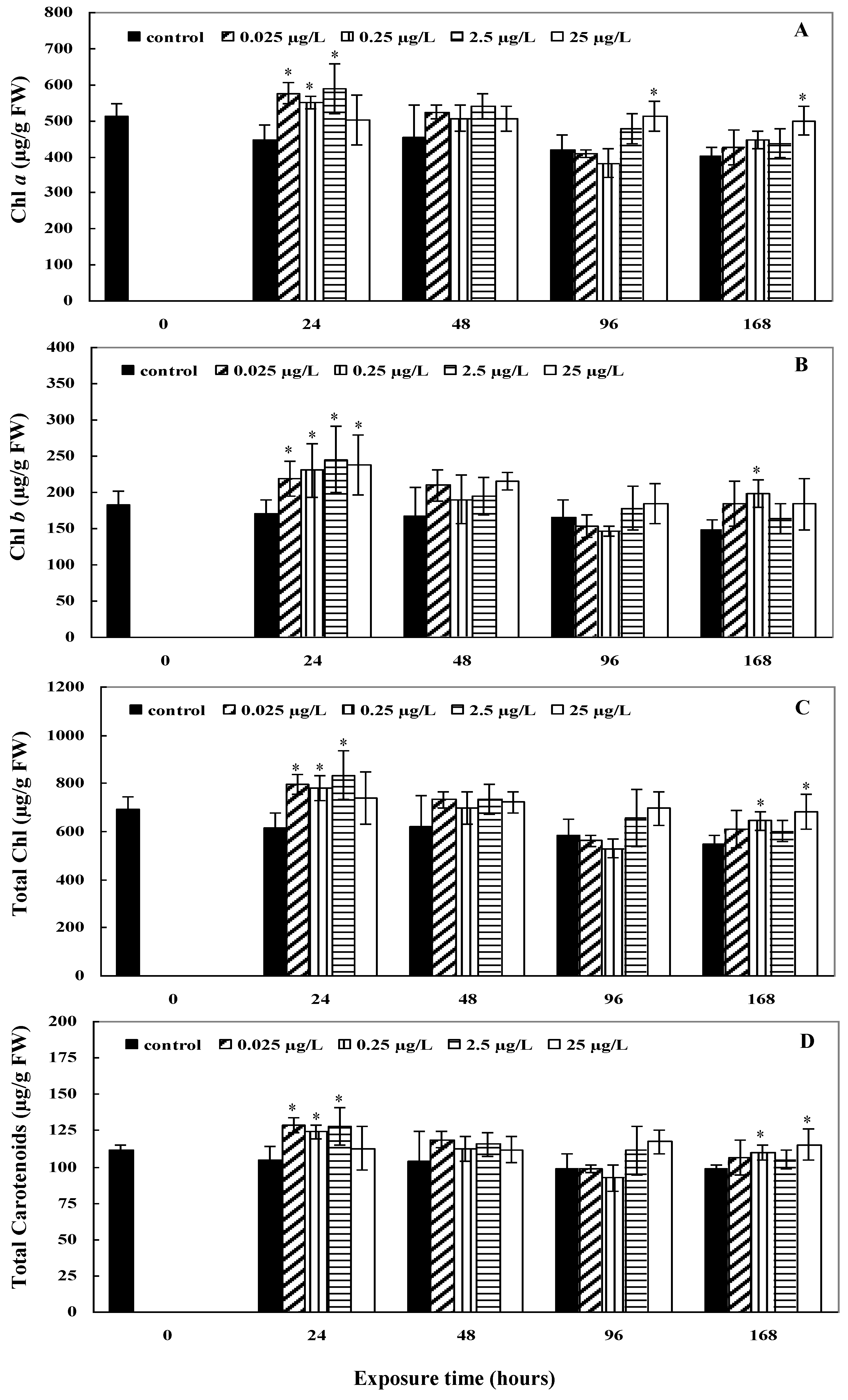
2.2. Photosynthetic Pigment Contents
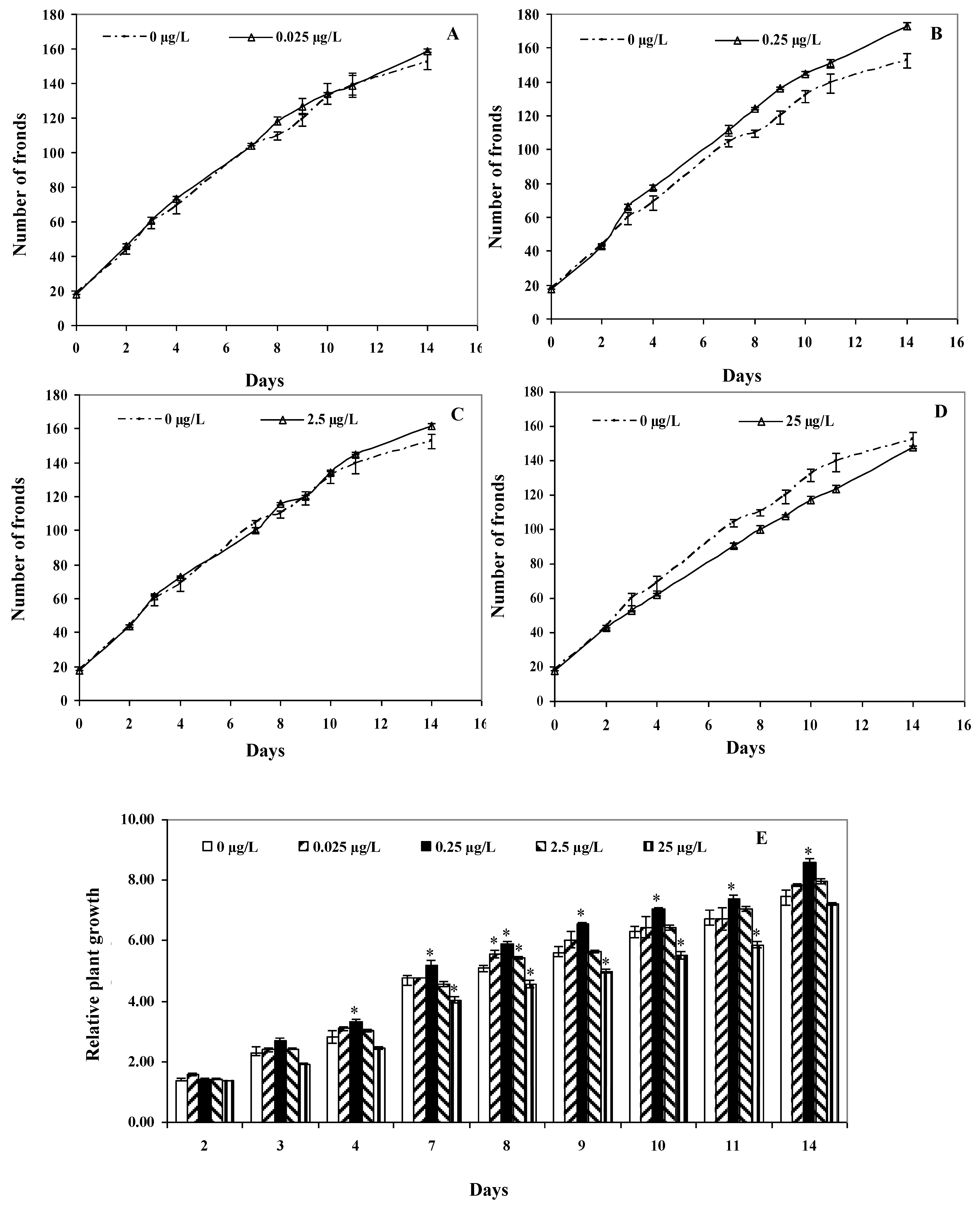
2.3. Plant Growth
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Material
4.2. Chemicals
4.3. CYN Treatments
4.4. Analysis of CYN
4.5. Photosynthetic Pigment Contents
4.6. Plant Growth Determination
4.7. Statistics
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ohtani, I.; Moore, R.E.; Runnegar, M.T.C. Cylindrospermopsin: A potent hepatotoxin from the blue-green alga. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1992, 114, 7941–7942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norris, R.L.; Eaglesham, G.; Pierens, G.; Shaw, G.; Smith, M.J.; Chiswell, R.K.; Seawright, A.A.; Moore, M.R. Deoxycylindrospermopsin, an analog of cylindrospermopsin from Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii. Environ. Toxicol. 1999, 14, 163–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banker, R.; Carmeli, S.; Teltsch, B.; Sukenik, A. 7-Epicylindrospermopsin, a toxic minor metabolite of the cyanobacterium Aphanizomenon ovalisporum from Lake Kinneret, Israel. J. Nat. Prod. 2000, 63, 387–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De la Cruz, A.; Hiskia, A.; Kaulodis, T.; Chernoff, N.; Hill, D.; Antoniou, M.; He, X.; Loftin, K.; O’Shea, K.; Zhao, C.; et al. A review on cylindrospermopsin: The global occurrence, detection, toxicity and degradation of a potent cyanotoxin. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2013, 15, 1979–2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinnear, S. Cylindrospermopsin: A decade of progress on bioaccumulation research. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 542–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, C.; Azevedo, J.; Antunes, A.; Vasconcelos, V. Cylindrospermopsin: Occurrence, methods of detection and toxicology. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2012, 114, 605–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiswell, R.K.; Shaw, G.R.; Eaglesham, G.; Smith, M.J.; Norris, R.L.; Seawright, A.A.; Moore, M.R. Stability of cylindrospermopsin, the toxin from the cyanobacterium, Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii: Effect of pH, temperature, and sunlight on decomposition. Environ. Toxicol. 1999, 14, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomaz, S.M.; da Cunha, E.R. The role of macrophytes in habitat structuring in aquatic ecosystems: Methods of measurement, causes and consequences on animal assemblages’ composition and biodiversity. Acta Limnol. Bras. 2010, 22, 218–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, S.H.; Duivenvoorden, L.J.; Fabbro, L.D. Absence of free-cylindrospermopsin bioconcentration in Water Thyme (Hydrilla verticillata). Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2005, 75, 574–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinnear, S.H.W.; Duivenvoorden, L.J.; Fabbro, L.D. Growth and bioconcentration in Spirodella oligorrhiza following exposure to Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii whole cell extracts. Australas. J. Ecotoxicol. 2007, 13, 19–31. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, C.; Azevedo, J.; Campos, A.; Vasconcelos, V.; Pereira, A. Biochemical and growth performance of the aquatic macrophyte Azolla filiculoides to sub-chronic exposure to cylindrospermopsin. Ecotoxicology 2015, 24, 1848–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jámbrik, K.; Máthé, C.; Vasas, G.; Bácsi, I.; Surányi, G.; Gonda, S.; Borbély, G.; M-Hamvas, M. Cylindrospermopsin inhibits growth and modulates protease activity in the aquatic plants Lemna minor L. and Wolffia arrhiza (L.) Horkel. Acta Biol. Hung. 2010, 61, 77–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinnear, S.H.W.; Fabbro, L.D.; Duivenvoorden, L.J. Variable growth responses of water thyme (Hydrilla verticillata) to whole-cell extracts of Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2008, 54, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prieto, A.; Campos, A.; Camea, A.; Vasconcelos, V. Effects on growth and oxidative stress status of rice plants (Oryza sativa) exposed to two extracts of toxin-producing cyanobacteria (Aphanizomenon ovalisporum and Microcystis aeruginosa). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2011, 74, 1973–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flores-Rojas, N.C.; Esterhuizen-Londt, M.; Pflugmacher, S. Antioxidative stress responses in the floating macrophyte Lemna minor L. with cylindrospermopsin exposure. Aquat. Toxicol. 2015, 169, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pflugmacher, S.; Kühn, S.; Lee, S.-H.; Choi, J.-W.; Baik, S.; Kwon, K.-S.; Contardo-Jara, V. Green Liver Systems® for water purification: Using the phytoremediation potential of aquatic macrophytes for the removal of different cyanobacterial toxins from water. Am. J. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 1607–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kováts, N.; Ács, A.; Paulovits, G.; Vasas, G. Response of Lemna minor clones to Microcystis toxicity. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2011, 9, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piotrowska, A.; Bajguz, A.; Godlewska-Żyłkiewicz, B.; Zambrzycka, E. Changes in growth, biochemical components, and antioxidant activity in aquatic plant Wolffia arrhiza (Lemnaceae) exposed to cadmium and lead. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2010, 58, 594–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rücker, J.; Stüken, A.; Nixdorf, B.; Fastner, J.; Chorus, I.; Wiedner, C. Concentrations of particulate and dissolved cylindrospermopsin in 21 Aphanizomenon-dominated temperate lakes. Toxicon 2007, 50, 800–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbel, S.; Mougin, C.; Bouaïcha, N. Cyanobacterial toxins: Modes of actions, fate in aquatic and soil ecosystems, phytotoxicity and bioaccumulation in agricultural crops. Chemosphere 2014, 96, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wörmer, L.; Huerta-Fontela, M.; Cirés, S.; Quesada, A. Natural photodegradation of the cyanobacterial toxins microcystin and cylindrospermopsin. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 3002–3007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wörmer, L.; Cirés, S.; Carrasco, D.; Quesada, A. Cylindrospermopsin is not degraded by co-occurring natural bacterial communities during a 40-day study. Harmful Algae 2008, 7, 206–213. [Google Scholar]
- Klitzke, S.; Fastner, J. Cylindrospermopsin degradation in sediments—The role of temperature, redox conditions, and dissolved organic carbon. Water Res. 2012, 46, 1549–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esterhuizen-Londt, M.; Pflugmacher, S. Inability to detect free cylindrospermopsin in spiked aquatic organism extracts plausibly suggests protein binding. Toxicon 2016, 122, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contardo-Jara, V.; Funke, M.S.; Peuthert, A.; Pflugmacher, S. β-N-Methylamino-L-alanine exposure alters defense against oxidative stress in aquatic plants Lomariopsis lineata, Fontinalis antipyretica, Riccia fluitans and Taxiphyllum barbieri. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2013, 88, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimptsch, J.; Wiegand, C.; Pflugmacher, S. Cyanobacterial toxin elimination via bioaccumulation of MC-LR in aquatic macrophytes: An application of the “Green Liver Concept”. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 8552–8557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esterhuizen-Londt, M.; Pflugmacher, S.; Downing, T. ß-N-Methylamino-l-alanine (BMAA) uptake by the aquatic macrophyte Ceratophyllum demersum. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2011, 74, 74–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, M.-H.; Contardo-Jara, V.; Pflugmacher, S. Uptake of the cyanobacterial neurotoxin, anatoxin-a, and alterations in oxidative stress in the submerged aquatic plant Ceratophyllum demersum. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2014, 101, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esterhuizen-Londt, M.; Kühn, S.; Pflugmacher, S. Development and validation of an in-house quantitative analysis method for cylindrospermopsin using hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry: Quantification demonstrated in 4 aquatic organisms. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2015, 34, 2878–2883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuluaga, M.; Gueguen, V.; Pavon-Djavid, G.; Letourneur, D. Carotenoids from microalgae to block oxidative stress. Bioimpacts 2017, 7, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.J.; Zhou, Y.H.; Shi, K.; Zhou, J.; Foyer, C.H.; Yu, J.Q. Interplay between reactive oxygen species and hormones in the control of plant development and stress tolerance. J. Exp. Bot. 2015, 66, 2839–2856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cedergreen, N.; Streibig, J.C.; Kudsk, P.; Mathiassen, S.K.; Duke, S.O. The occurrence of hormesis in plants and algae. Dose Response 2007, 5, 150–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cazzonelli, C.I.; Pogson, B.J. Source to sink: Regulation of carotenoid biosynthesis in plants. Trends Plant Sci. 2010, 15, 266–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothmaler, W. Exkursionsflora von Deutschland; 10 Aufl; Elsevier: Berlin, Germany, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Botanical Society of Britain & Ireland. Available online: https://bsbi.org/ (accessed on 10 September 2019).
- Walker, C.H.; Hopkin, S.P.; Sibly, R.M.; Peakall, D.B. Principles of Ecotoxicology, 2nd ed.; Taylor & Francis: London, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Inskeep, W.P.; Bloom, P.R. Extinction coefficients of chlorophyll a and b in N, N-Dimethylformamide and 80% acetone. Plant Physiol. 1985, 77, 483–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wellburn, A.R. The spectral determination of chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b, as well as total carotenoids, using various solvents with spectrophotometers of different resolution. J. Plant Physiol. 1994, 144, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ensley, H.E.; Barber, J.T.; Polito, M.A.; Oliver, A.I. Toxicity and metabolism of 2,4-dichlorophenol by the aquatic angiosperm Lemna gibba. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1994, 13, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Flores-Rojas, N.C.; Esterhuizen-Londt, M.; Pflugmacher, S. Uptake, Growth, and Pigment Changes in Lemna minor L. Exposed to Environmental Concentrations of Cylindrospermopsin. Toxins 2019, 11, 650. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11110650
Flores-Rojas NC, Esterhuizen-Londt M, Pflugmacher S. Uptake, Growth, and Pigment Changes in Lemna minor L. Exposed to Environmental Concentrations of Cylindrospermopsin. Toxins. 2019; 11(11):650. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11110650
Chicago/Turabian StyleFlores-Rojas, Nelida Cecilia, Maranda Esterhuizen-Londt, and Stephan Pflugmacher. 2019. "Uptake, Growth, and Pigment Changes in Lemna minor L. Exposed to Environmental Concentrations of Cylindrospermopsin" Toxins 11, no. 11: 650. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11110650
APA StyleFlores-Rojas, N. C., Esterhuizen-Londt, M., & Pflugmacher, S. (2019). Uptake, Growth, and Pigment Changes in Lemna minor L. Exposed to Environmental Concentrations of Cylindrospermopsin. Toxins, 11(11), 650. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11110650




