Enzyme Degradation Reagents Effectively Remove Mycotoxins Deoxynivalenol and Zearalenone from Pig and Poultry Artificial Digestive Juices
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
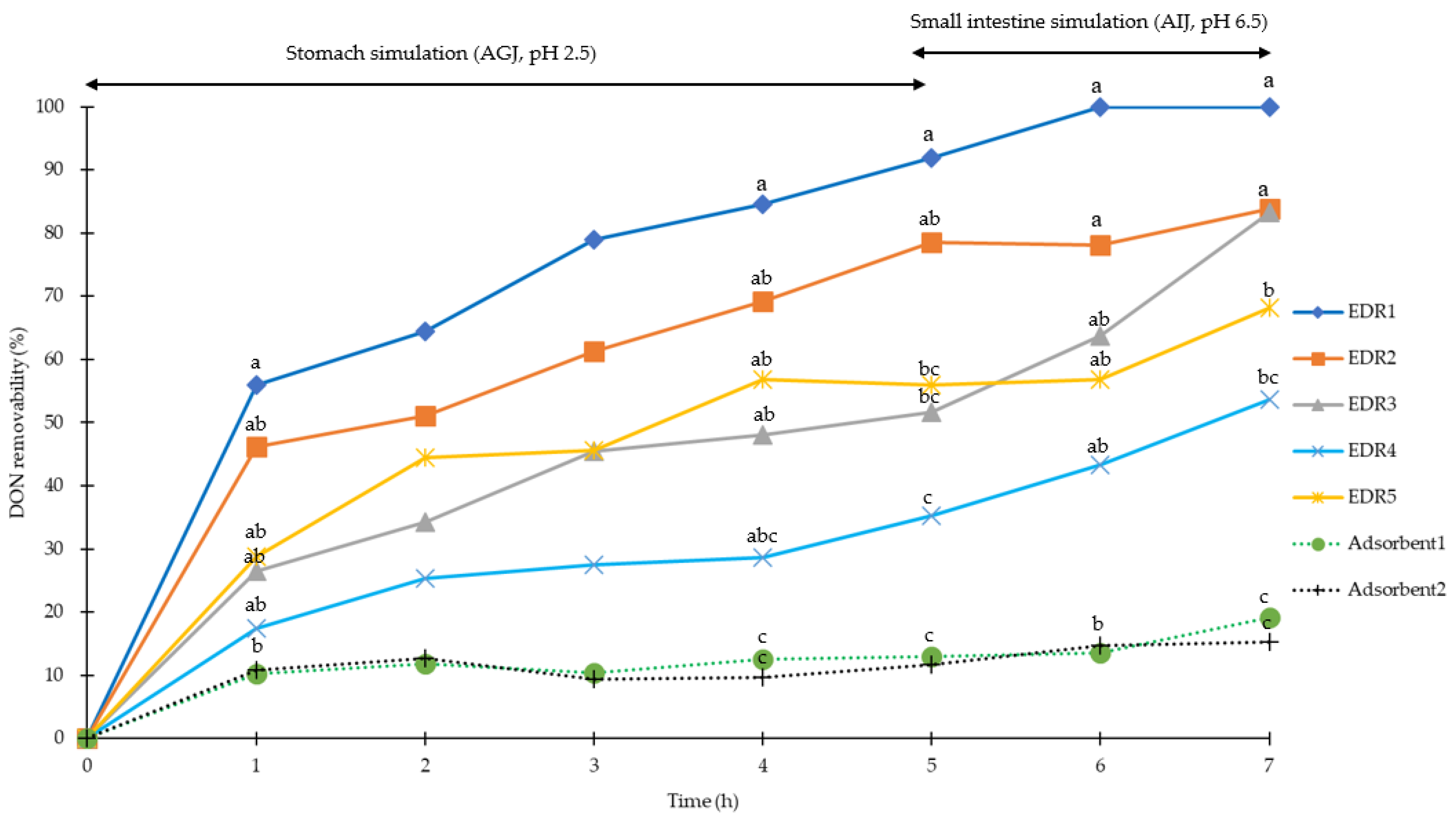
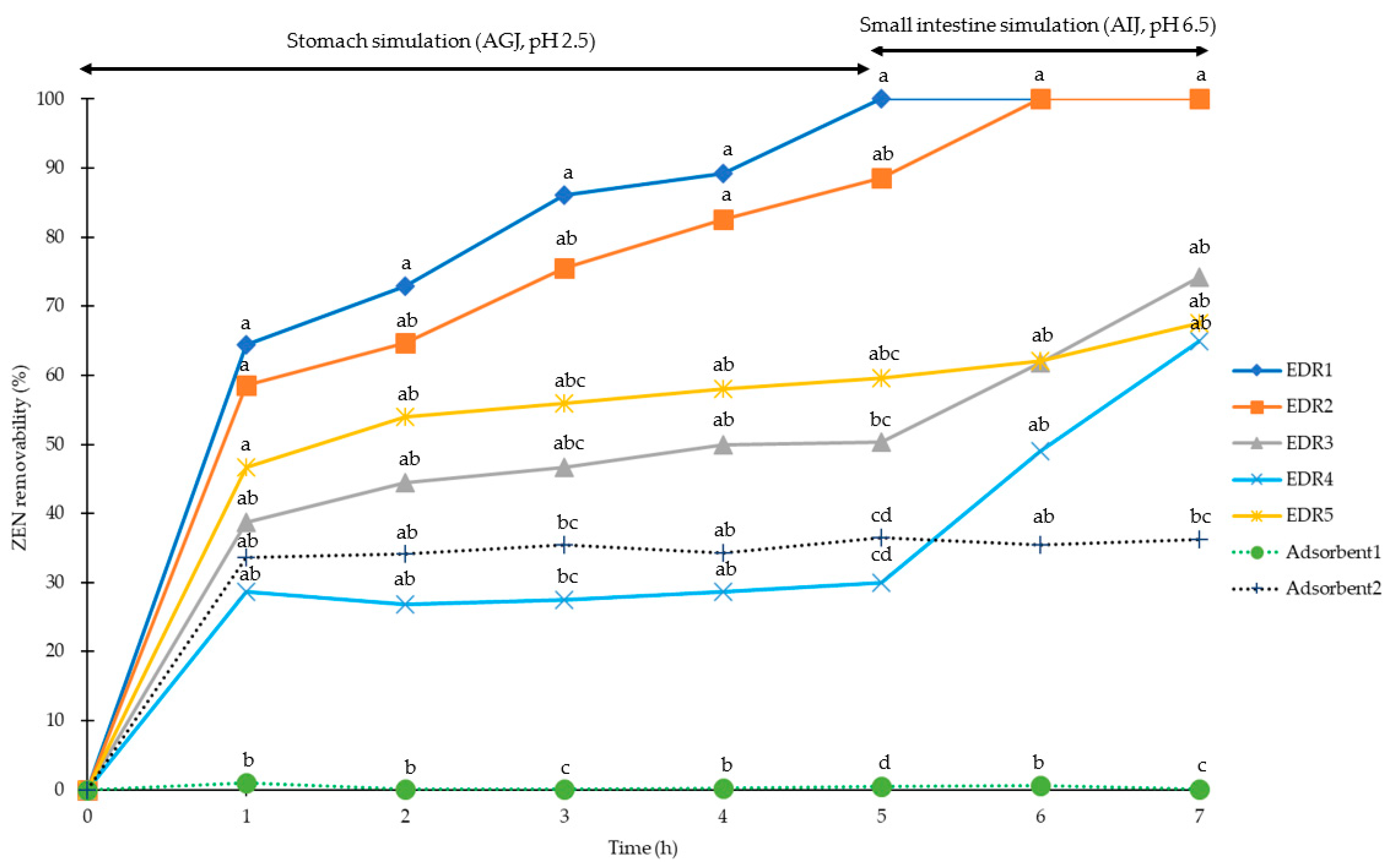
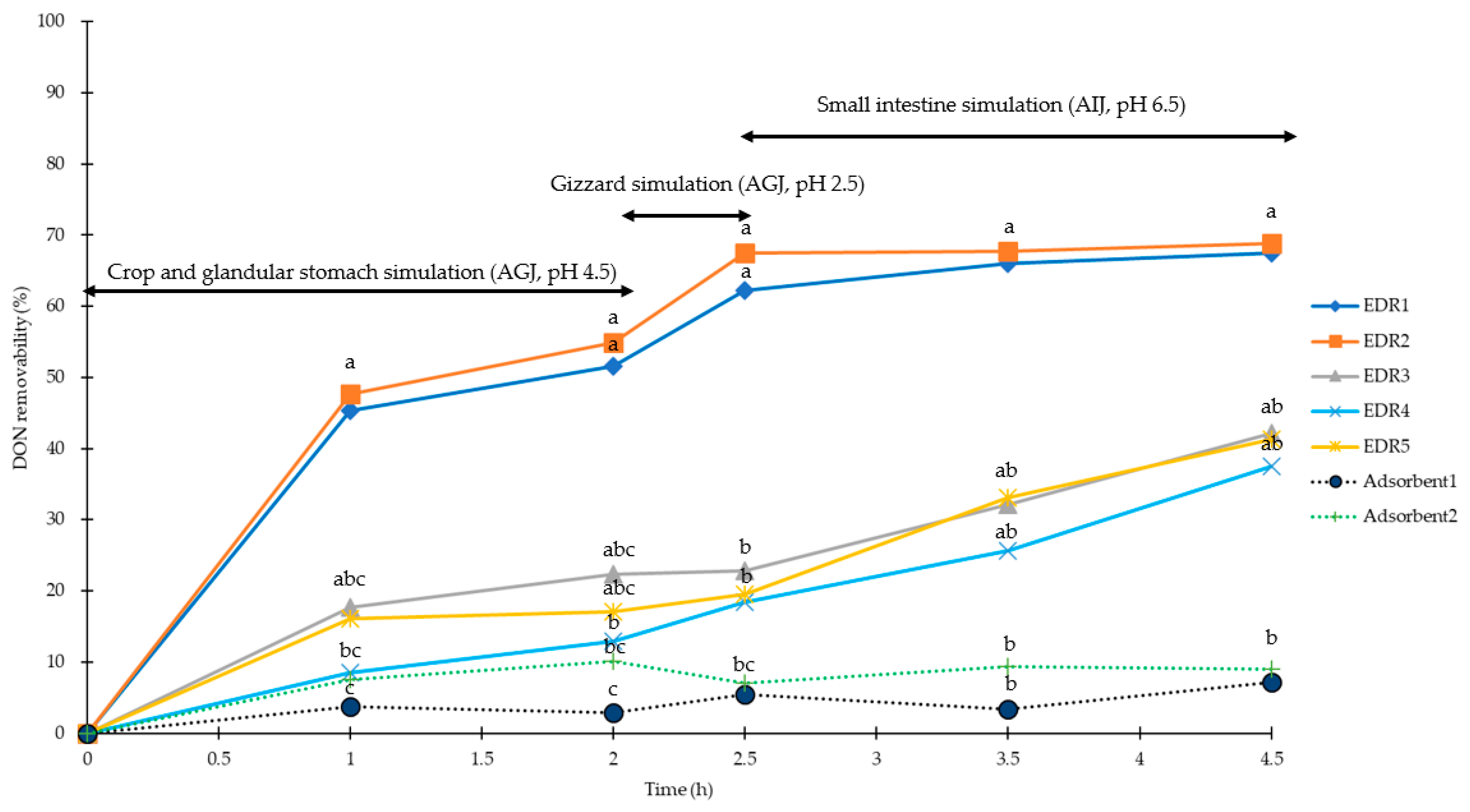
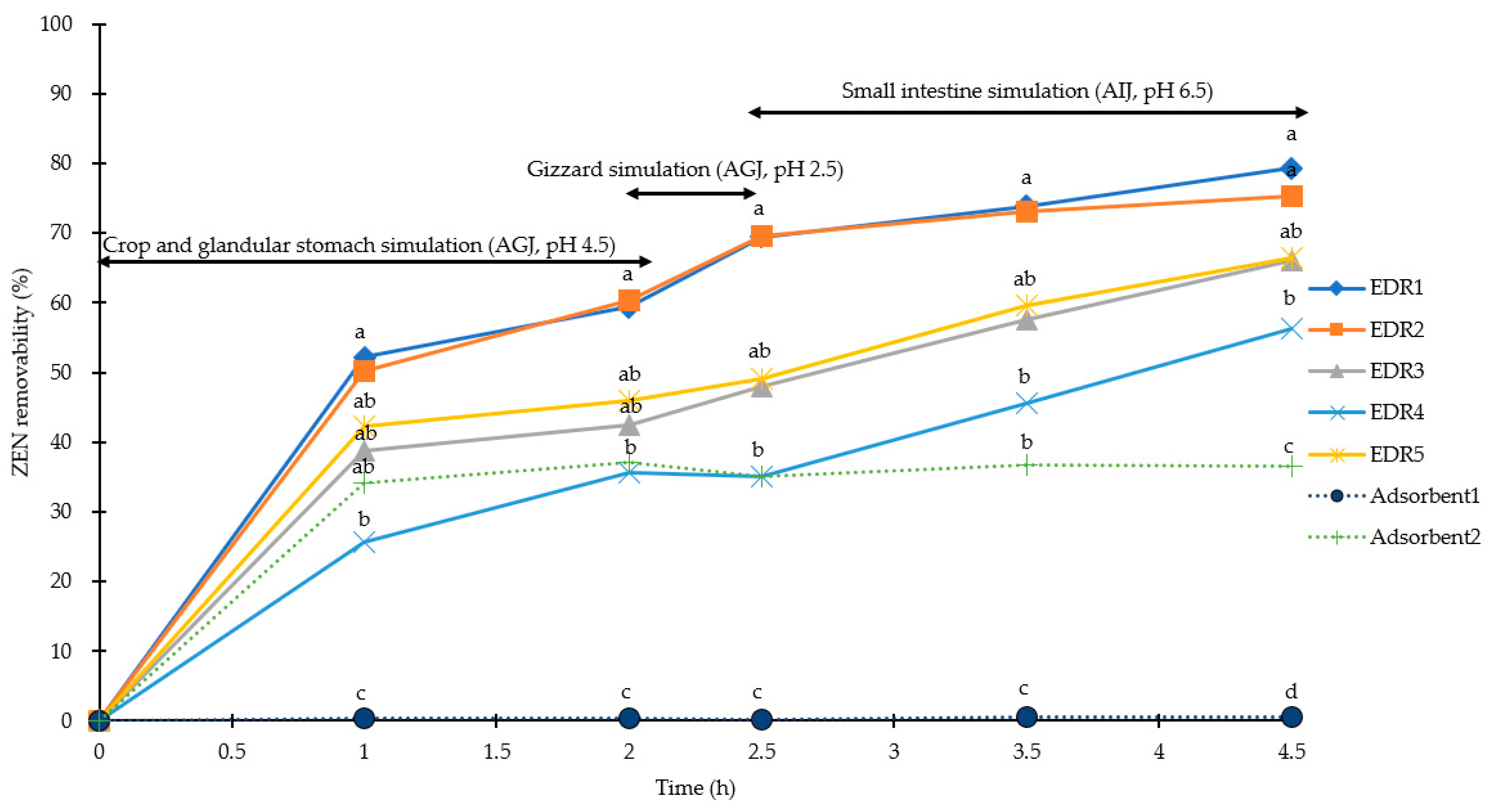
2.1. Simulation of Pig Gastrointestinal Tracts
2.2. Simulation of Poultry Gastrointestinal Tracts
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
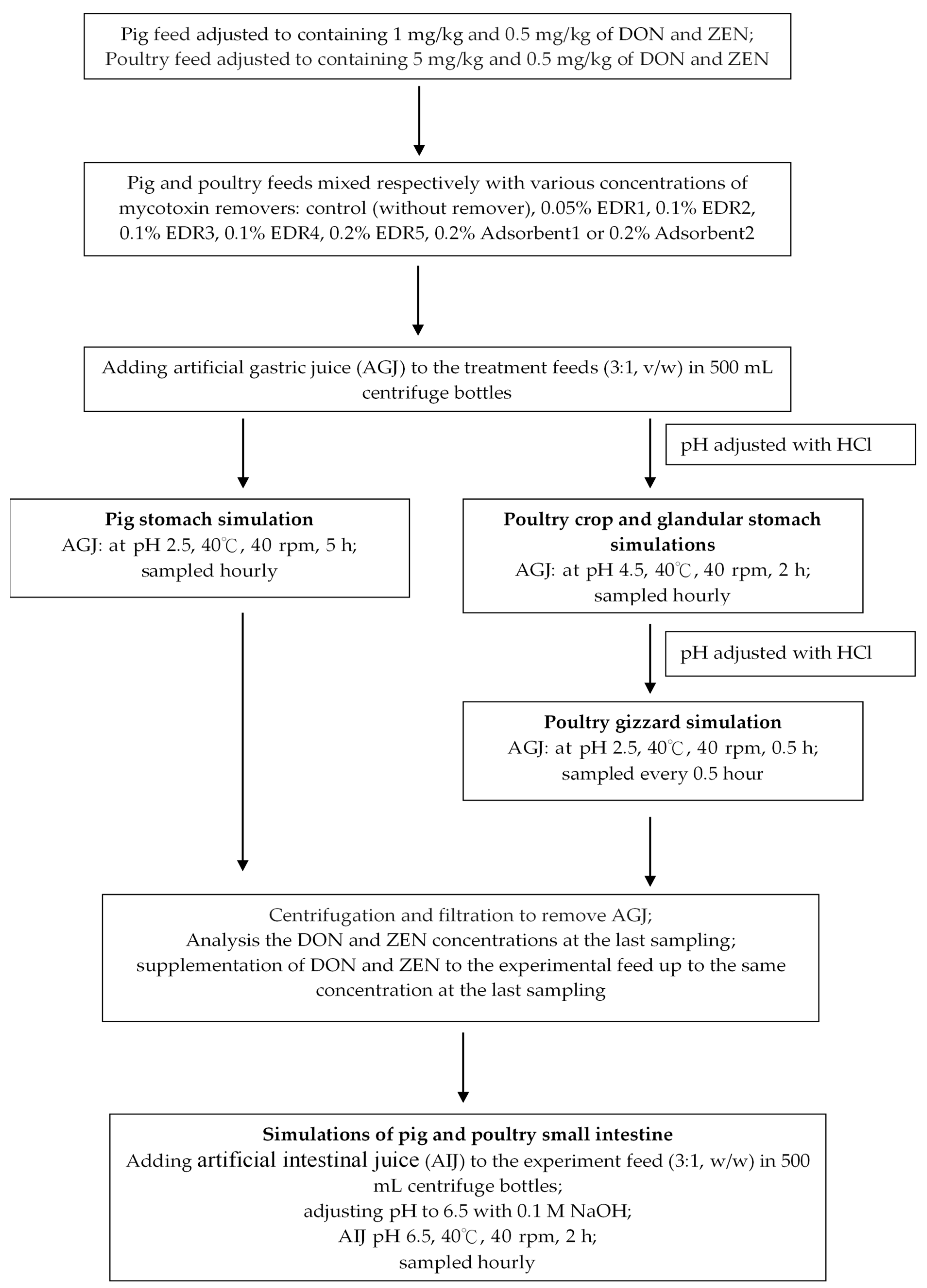
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Reagents
5.2. Solution Preparation
5.2.1. Standards Preparation of DON and ZEN
5.2.2. Preparation of AGJ and AIJ
5.3. In Vitro Procedure
5.3.1. Simulation of Pig Gastrointestinal Tracts
5.3.2. Simulation of Poultry Gastrointestinal Tracts
5.3.3. Extraction and Chromatographic Conditions of DON
5.3.4. Extraction and Chromatographic Conditions of ZEN
5.4. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pierron, A.; Alassane-Kpembi, I.; Oswald, I.P. Impact of two mycotoxins deoxynivalenol and fumonisin on pig intestinal health. Porc. Health Manag. 2016, 2, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Yang, J.; Zhang, B.; Wu, K.; Yang, A.; Li, C.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, C.; Rajput, S.A.; Zhang, N.; et al. Deoxynivalenol impairs porcine intestinal host defense peptide expression in weaned piglets and IPEC-J2 Cells. Toxins 2018, 10, 541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Zhoua, T.; Christopher, Y.J.; Greg, B.J.; Scott, P.M. Chemical and biological transformations for detoxification of trichothecene mycotoxins in human and animal food chains: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 21, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyer, M.; Ferse, I.; Mulac, D.; Wurthwein, E.U.; Humpf, H.U. Structural elucidation of T-2 toxin thermal degradation products and investigations toward their occurrence in retail food. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 1867–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bretz, M.; Beyer, M.; Cramer, B.; Knecht, A.; Humpf, H.U. Thermal degradation of the Fusarium mycotoxin deoxynivalenol. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 6445–6451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FAO (Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations). On-Farm Mycotoxin Control in Food and Feed Grain. Training Manual. Application in Rome. 2007. Available online: http://www.fao.org/3/a1416e/a1416e00.htm (accessed on 9 September 2019).
- Yuan, Q.S.; Yang, P.; Wu, A.B.; Zuo, D.Y.; He, W.J.; Guo, M.W.; Huang, T.; Li, H.P.; Liao, Y.C. Variation in the Microbiome, Trichothecenes, and Aflatoxins in Stored Wheat Grains in Wuhan, China. Toxins 2018, 10, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galvano, F.; Piva, A.; Ritieni, A.; Galvano, G. Dietary strategies to counteract the effects of mycotoxins: A review. J. Food Prot. 2001, 64, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedeljkovic-Trailovic, J.; Trailovic, S.; Resanovic, R.; Milicevic, D.; Jovanovic, M.; Vasiljevic, M. Comparative investigation of the efficacy of three different adsorbents against OTA-induced toxicity in broiler chickens. Toxins 2015, 7, 1174–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saminathan, M.; Selamat, J.; Abbasi Pirouz, A.; Abdullah, N.; Zulkifli, I. Effects of Nano-composite adsorbents on the growth performance, serum biochemistry, and organ weights of broilers fed with aflatoxin-contaminated feed. Toxins 2018, 10, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabak, B.; Dobson, A.D.; Var, I. Strategies to prevent mycotoxin contamination of food and animal feed: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2006, 46, 593–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Lian, C.; Xi, Y.; Sun, Z.; Zheng, S. Evaluation of nonionic surfactant modified montmorillonite as mycotoxins adsorbent for aflatoxin B1 and zearalenone. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 518, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huwig, A.; Freimund, S.; Kappeli, O.; Dutler, H. Mycotoxin detoxication of animal feed by different adsorbents. Toxicol Lett. 2001, 122, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, T.D.; Kubena, L.F.; Harvey, R.B.; Taylor, D.R.; Heidelbaugh, N.D. Hydrated sodium calcium aluminosilicate: A high affinity sorbent for aflatoxin. Poult. Sci. 1988, 67, 243–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doll, S.; Danicke, S. In vivo detoxification of Fusarium toxins. Arch. Anim. Nutr. 2004, 58, 419–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monbaliu, S.; Van Poucke, C.; Van Peteghem, C.; Van Poucke, K.; Heungens, K.; De Saeger, S. Development of a multi-mycotoxin liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry method for sweet pepper analysis. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2009, 23, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, A.; Giuberti, G.; Frisvad, J.C.; Bertuzzi, T.; Nielsen, K.F. Review on mycotoxin issues in ruminants: Occurrence in forages, effects of mycotoxin ingestion on health status and animal performance and practical strategies to counteract their negative effects. Toxins 2015, 7, 3057–3111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuiper-Goodman, T.; Scott, P.M.; Watanabe, H. Risk assessment of the mycotoxin zearalenone. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 1987, 7, 253–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binder, S.B.; Schwartz-Zimmermann, H.E.; Varga, E.; Bichl, G.; Michlmayr, H.; Adam, G.; Berthiller, F. Metabolism of zearalenone and its major modified forms in pigs. Toxins 2017, 9, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doll, S.; Schrickx, J.A.; Valenta, H.; Danicke, S.; Fink-Gremmels, J. Interactions of deoxynivalenol and lipopolysaccharides on cytotoxicity protein synthesis and metabolism of DON in porcine hepatocytes and Kupffer cell enriched hepatocyte cultures. Toxicol. Lett. 2009, 189, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlovsky, P.; Suman, M.; Berthiller, F.; De Meester, J.; Eisenbrand, G.; Perrin, I.; Oswald, I.P.; Speijers, G.; Chiodini, A.; Recker, T.; et al. Impact of food processing and detoxification treatments on mycotoxin contamination. Mycotoxin Res. 2016, 32, 179–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.; Hu, Y.; He, J.; Wu, L.; Liao, F.; Luo, B.; He, Y.; Zuo, Z.; Ren, Z.; Zhong, Z.; et al. Zearalenone degradation by two Pseudomonas strains from soil. Mycotoxin Res. 2014, 30, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahn, I.; Kunz-Vekiru, E.; Twaruzek, M.; Grajewski, J.; Krska, R.; Berthiller, F. Aerobic and anaerobic in vitro testing of feed additives claiming to detoxify deoxynivalenol and zearalenone. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2015, 32, 922–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marroquin-Cardona, A.; Deng, Y.; Taylor, J.F.; Hallmark, C.T.; Johnson, N.M.; Phillips, T.D. In vitro and in vivo characterization of mycotoxin-binding additives used for animal feeds in Mexico. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2009, 26, 733–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zyla, K.; Ledoux, D.R.; Garcia, A.; Veum, T.L. An in vitro procedure for studying enzymic dephosphorylation of phytate in maize-soyabean feeds for turkey poults. Br. J. Nutr. 1995, 74, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.G.; Su, X.O.; Fan, X.; Wang, P.L.; Gao, Z.W.; Zhang, Y. Liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry for determination of aflaoxin B1, deoxynivalenol and zearalenone in artificial porcine gastrointestinal digestive Juice. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2015, 43, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avantaggiato, G.; Havenaar, R.; Visconti, A. Assessment of the multi-mycotoxin-binding efficacy of a carbon/aluminosilicate-based product in an in vitro gastrointestinal model. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 4810–4819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avantaggiato, G.; Havenaar, R.; Visconti, A. Assessing the zearalenone-binding activity of adsorbent materials during passage through a dynamic in vitro gastrointestinal model. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2003, 41, 1283–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grenier, B.; Applegate, T.J. Modulation of intestinal functions following mycotoxin ingestion: Meta-analysis of published experiments in animals. Toxins 2013, 5, 396–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledoux, D.R.; Broomhead, J.N.; Bermudez, A.J.; Rottinghaus, G.E. Individual and combined effects of the Fusarium mycotoxins fumonisin B1 and moniliformin in broiler chicks. Avian Dis. 2003, 47, 1368–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.L.; Troxell, T.C. US Perspective on mycotoxin regulatory issues. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2002, 504, 277–285. [Google Scholar]
- Kolosova, A.; Stroka, J. Evaluation of the effect of mycotoxin binders in animal feed on the analytical performance of standardised methods for the determination of mycotoxins in feed. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2012, 29, 1959–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz, D.E.; Hagler, W.M., Jr.; Hopkins, B.A.; Whitlow, L.W. Aflatoxin binders I: In vitro binding assay for aflatoxin B1 by several potential sequestering agents. Mycopathologia 2002, 156, 223–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millan Trujillo, F.R.; Martinez Yepez, A.J. Efficacy and stability of ammoniation process as aflatoxin B1 decontamination technology in rice. Arch. Latinoam. Nutr. 2003, 53, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brydl, E.; Ványi, A.; Glávits, R.; Könyves, L.; Rafai, P. Reduction of the oestrogenic effect of zearalenone in pigs by a feed additive. Acta Vet. Brno 2014, 83, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Danicke, S.; Matthes, S.; Halle, I.; Ueberschar, K.H.; Doll, S.; Valenta, H. Effects of graded levels of Fusarium toxin-contaminated wheat and of a detoxifying agent in broiler diets on performance, nutrient digestibility and blood chemical parameters. Br. Poult. Sci. 2003, 44, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Mil, T.; Devreese, M.; de Baere, S.; van Ranst, E.; Eeckhout, M.; de Backer, P.; Croubels, S. Characterization of 27 mycotoxin binders and the relation with in vitro zearalenone adsorption at a single concentration. Toxins 2015, 7, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- di Gregorio, M.C.; de Neeff, D.V.; Jager, A.V.; Corassin, C.H.; Carão, Á.C.D.P.; Albuquerque, R.D.; Azevedo, A.C.D.; Oliveira, C.A.F. Mineral adsorbents for prevention of mycotoxins in animal feeds. Toxin Rev. 2014, 33, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomasevic-Canovic, M.; Dakovic, A.; Vesna, M.; Jelića, V.; Ana, R.M. Adsorption effects of mineral adsorbents, Part III: Adsorption behaviour in the presence of vitamin B6 and microelements. Acta. Vet. 2000, 50, 23–30. [Google Scholar]
- Alberts, J.F.; Gelderblom, W.C.; Botha, A.; van Zyl, W.H. Degradation of aflatoxin B(1) by fungal laccase enzymes. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2009, 30, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yehia, R.S. Aflatoxin detoxification by manganese peroxidase purified from Pleurotus ostreatus. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2014, 45, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Ma, Q.; Ma, S.; Zhang, J.; Jia, R.; Ji, C.; Zhao, L. Ameliorating effects of Bacillus subtilis ANSB060 on growth performance, antioxidant functions, and aflatoxin residues in ducks fed diets contaminated with aflatoxins. Toxins 2017, 9, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rotter, B.A.; Prelusky, D.B.; Pestka, J.J. Toxicology of deoxynivalenol (vomitoxin). J. Toxicol. Environ. Health 1996, 48, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundstol Eriksen, G.; Pettersson, H.; Lundh, T. Comparative cytotoxicity of deoxynivalenol, nivalenol, their acetylated derivatives and de-epoxy metabolites. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2004, 42, 619–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schatzmayr, G.; Zehner, F.; Taubel, M.; Schatzmayr, D.; Klimitsch, A.; Loibner, A.P.; Binder, E.M. Microbiologicals for deactivating mycotoxins. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2006, 50, 543–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, C.; Fan, Y.; Zhao, L. Review on biological degradation of mycotoxins. Anim. Nutr. 2016, 2, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fruhauf, S.; Novak, B.; Nagl, V.; Hackl, M.; Hartinger, D.; Rainer, V.; Labudova, S.; Adam, G.; Aleschko, M.; Moll, W.D.; et al. Biotransformation of the mycotoxin zearalenone to its metabolites hydrolyzed zearalenone (HZEN) and decarboxylated hydrolyzed zearalenone (DHZEN) diminishes its estrogenicity in vitro and in vivo. Toxins 2019, 11, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vekiru, E.; Hametner, C.; Mitterbauer, R.; Rechthaler, J.; Adam, G.; Schatzmayr, G.; Krska, R.; Schuhmacher, R. Cleavage of zearalenone by Trichosporon mycotoxinivorans to a novel nonestrogenic metabolite. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 2353–2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masching, S.; Naehrer, K.; Schwartz-Zimmermann, H.E.; Sarandan, M.; Schaumberger, S.; Dohnal, I.; Nagl, V.; Schatzmayr, D. Gastrointestinal degradation of Fumonisin B1 by carboxylesterase FumD prevents fumonisin induced alteration of sphingolipid metabolism in turkey and swine. Toxins 2016, 8, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahill, L.M.; Kruger, S.C.; McAlice, B.T.; Ramsey, C.S.; Prioli, R.; Kohn, B. Quantification of deoxynivalenol in wheat using an immunoaffinity column and liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 1999, 859, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arranz, I.; Mischke, C.; Stroka, J.; Sizoo, E.; van Egmond, H.; Neugebauer, M. Liquid chromatographic method for the quantification of zearalenone in baby food and animal feed: Interlaboratory study. J AOAC Int. 2007, 90, 1598–1609. [Google Scholar]
- Janes, W.; Schuster, M. Determination of deoxynivalenol (DON) in blood, bile, urine and excrement samples from swine using immunoaffinity chromatography and LC-UV-detection. Mycotoxin Res 2001, 17, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Mycotoxin Remover | Dosage (%) | Brand/Company | Composition (Patent) |
|---|---|---|---|
| EDR1 | 0.05 | Detoxa Plus® New/Dr. Bata | Yeast cell wall, lactonase (NCAIM (P) Y001470), de-epoxidase (NCAIM (P) Y001469), carboxypeptidase (NCAIM (P) Y001468) and carboxylesterase (NCAIM (P) Y001467) |
| EDR2 | 0.10 | Detoxa Plus®/Dr. Bata | Yeast cell wall, lactonase (NCAIM (P) Y001470), de-epoxidase (NCAIM (P) Y001469), carboxypeptidase (NCAIM (P) Y001468) and carboxylesterase (NCAIM (P) Y001467) |
| EDR3 | 0.10 | Micofix Plus®MTV/Biomin | Bentonite (EC 1060/2013), Eubacterium BBSH797 (EC 1016/2013), FUMzyme® (EC 1115/2014), Trichosporon mycotoxinivorans and plant-origination components |
| EDR4 | 0.10 | Toxi-free®/Liferainbow | HSCAS, zearalenone hydrolase (US 10,221,403 B1), epoxidase and peptidase |
| EDR5 | 0.20 | MLJ®/Henan Yi-Wan Zhong-Yuan | Yeast cell wall, the mixed enzymes were produced by 3 Bacillus subtilis which contained ANSB471 (CN 103,243,047 B), ANSB01G (CN 102,181,376 B) and ANSB060 (CN 101,705,203 B) |
| Adsorbent1 | 0.20 | Calibrin-Z®/Amlan | Activated calcium montmorillonite (US 20160030475 A1) |
| Adsorbent2 | 0.20 | Minazel Plus®/Patent | Clinoptilolite (EP 1,363,854 B1) |
| Mycotoxin | Concentration mg/kg | Pig | Poultry | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AGJ (pH 2.5, 5 h) | AIJ (pH 6.5, 2 h) | AGJ (pH 4.5, 2 h) | AGJ (pH 2.5, 0.5h) | AIJ (pH 6.5, 2 h) | |||||||
| Recovery% | CV% | Recovery% | CV% | Recovery% | CV% | Recovery% | CV% | Recovery% | CV% | ||
| DON | 0.500 | 90.0 | 4.23 | 94.4 | 4.23 | 91.9 | 5.05 | 89.8 | 5.13 | 88.8 | 5.17 |
| 1.000 | 90.8 | 3.30 | 94.5 | 2.23 | 92.9 | 4.81 | 91.3 | 5.15 | 90.5 | 5.32 | |
| 2.000 | 94.0 | 2.13 | 89.8 | 2.64 | 93.1 | 4.92 | 90.8 | 5.72 | 89.7 | 6.12 | |
| 5.000 | 95.3 | 2.44 | 86.4 | 4.75 | 93.2 | 2.80 | 90.8 | 2.82 | 89.6 | 2.83 | |
| ZEN | 0.025 | 92.5 | 4.01 | 85.0 | 4.25 | 92.1 | 3.89 | 90.7 | 3.78 | 90.0 | 3.73 |
| 0.250 | 95.2 | 4.54 | 84.7 | 4.28 | 90.0 | 4.81 | 87.3 | 4.86 | 85.9 | 4.89 | |
| 0.500 | 95.5 | 4.09 | 88.4 | 4.84 | 92.1 | 5.58 | 90.3 | 5.74 | 89.4 | 5.82 | |
| 1.000 | 95.9 | 2.34 | 90.5 | 4.80 | 93.6 | 5.38 | 92.5 | 6.09 | 92.0 | 6.45 | |
| Item | Feed | |
|---|---|---|
| Pig Feed | Poultry Feed | |
| Ingredients, % | ||
| Corn | 667 | 570 |
| Soybean meal, 44% | 200 | 200 |
| Full fat soybean | 60 | 80 |
| Limestone | - | 99 |
| Wheat middling | - | 25 |
| Fish meal, 65% crude protein | 20 | - |
| Monocalcium phosphate | - | 18 |
| Diphosphate | 25 | - |
| Calcium | 20 | - |
| Salt | 4 | 2 |
| Sodium bicarbonate | 3 | |
| Choline chloride | 1 | |
| 1Vitamin premix | 2 | 1 |
| 2Mineral premix | 2 | 1 |
| Calculated values | ||
| ME, kcal/kg | 3250 | 2707 |
| Crude protein, % | 17.50 | 17.14 |
| Crude fate, % | 4.021 | 3.878 |
| Calcium, % | 1.568 | 4.053 |
| Total phosphorus, % | 0.875 | 0.722 |
| Available phosphorus, % | 0.548 | 0.392 |
| Copper, ppm | 56.96 | 33.54 |
| Zinc, ppm | 225.4 | 166.2 |
| Iron, ppm | 359.4 | 224.2 |
| Simulation Model | Simulation Time (h) | DON (mg/kg) | ZEN (mg/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pig | 0 | 1.00 ± 0.008 | 0.50 ± 0.021 |
| 1 | 1.00 ± 0.109 | 0.48 ± 0.080 | |
| 2 | 0.99 ± 0.050 | 0.48 ± 0.058 | |
| 3 | 0.96 ± 0.127 | 0.47 ± 0.027 | |
| 4 | 0.94 ± 0.128 | 0.43 ± 0.069 | |
| 5 | 0.91 ± 0.117 | 0.42 ± 0.002 | |
| 6 | 0.90 ± 0.103 | 0.41 ± 0.009 | |
| 7 | 0.85 ± 0.146 | 0.40 ± 0.043 | |
| Poultry | 0 | 5.00 ± 0.154 | 0.50 ± 0.149 |
| 1 | 4.83 ± 0.607 | 0.50 ± 0.006 | |
| 2 | 4.64 ± 0.420 | 0.50 ± 0.055 | |
| 2.5 | 4.38 ± 0.282 | 0.49 ± 0.004 | |
| 3.5 | 4.17 ± 0.282 | 0.48 ± 0.058 | |
| 4.5 | 3.93 ± 0.165 | 0.47 ± 0.089 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tso, K.-H.; Ju, J.-C.; Fan, Y.-K.; Chiang, H.-I. Enzyme Degradation Reagents Effectively Remove Mycotoxins Deoxynivalenol and Zearalenone from Pig and Poultry Artificial Digestive Juices. Toxins 2019, 11, 599. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11100599
Tso K-H, Ju J-C, Fan Y-K, Chiang H-I. Enzyme Degradation Reagents Effectively Remove Mycotoxins Deoxynivalenol and Zearalenone from Pig and Poultry Artificial Digestive Juices. Toxins. 2019; 11(10):599. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11100599
Chicago/Turabian StyleTso, Ko-Hua, Jyh-Cherng Ju, Yang-Kwang Fan, and Hsin-I Chiang. 2019. "Enzyme Degradation Reagents Effectively Remove Mycotoxins Deoxynivalenol and Zearalenone from Pig and Poultry Artificial Digestive Juices" Toxins 11, no. 10: 599. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11100599
APA StyleTso, K.-H., Ju, J.-C., Fan, Y.-K., & Chiang, H.-I. (2019). Enzyme Degradation Reagents Effectively Remove Mycotoxins Deoxynivalenol and Zearalenone from Pig and Poultry Artificial Digestive Juices. Toxins, 11(10), 599. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11100599






