Uremic Toxins and Atrial Fibrillation: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Epidemiology of AF
3. Pathophysiological Mechanisms of AF
3.1. Triggers and Substrate of AF
3.2. Cardiac Autonomic Nervous System and Triggered Spontaneous Pulmonary Vein Firing
4. Treatment of AF
4.1. Stabilization of Underlying and Accompanying Cardiovascular Conditions
4.2. Stroke Risk Assessment and Oral Anticoagulation for Stroke Prevention
4.3. Rate and Rhythm Control Therapy
5. AF and CKD
6. Uremic Toxins and Cardiovascular Diseases
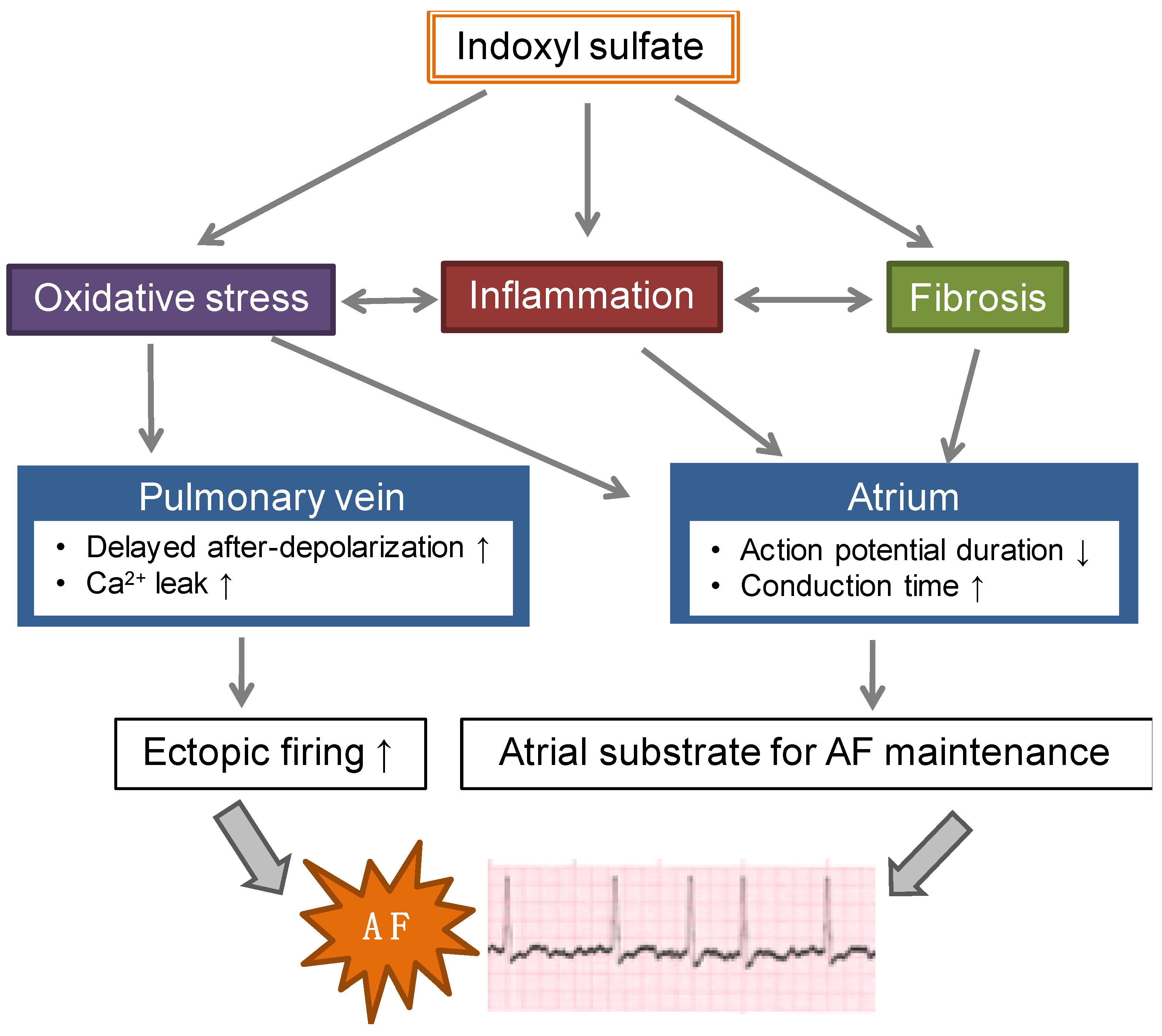
7. IS and AF
7.1. Experimental Studies in Animal Models
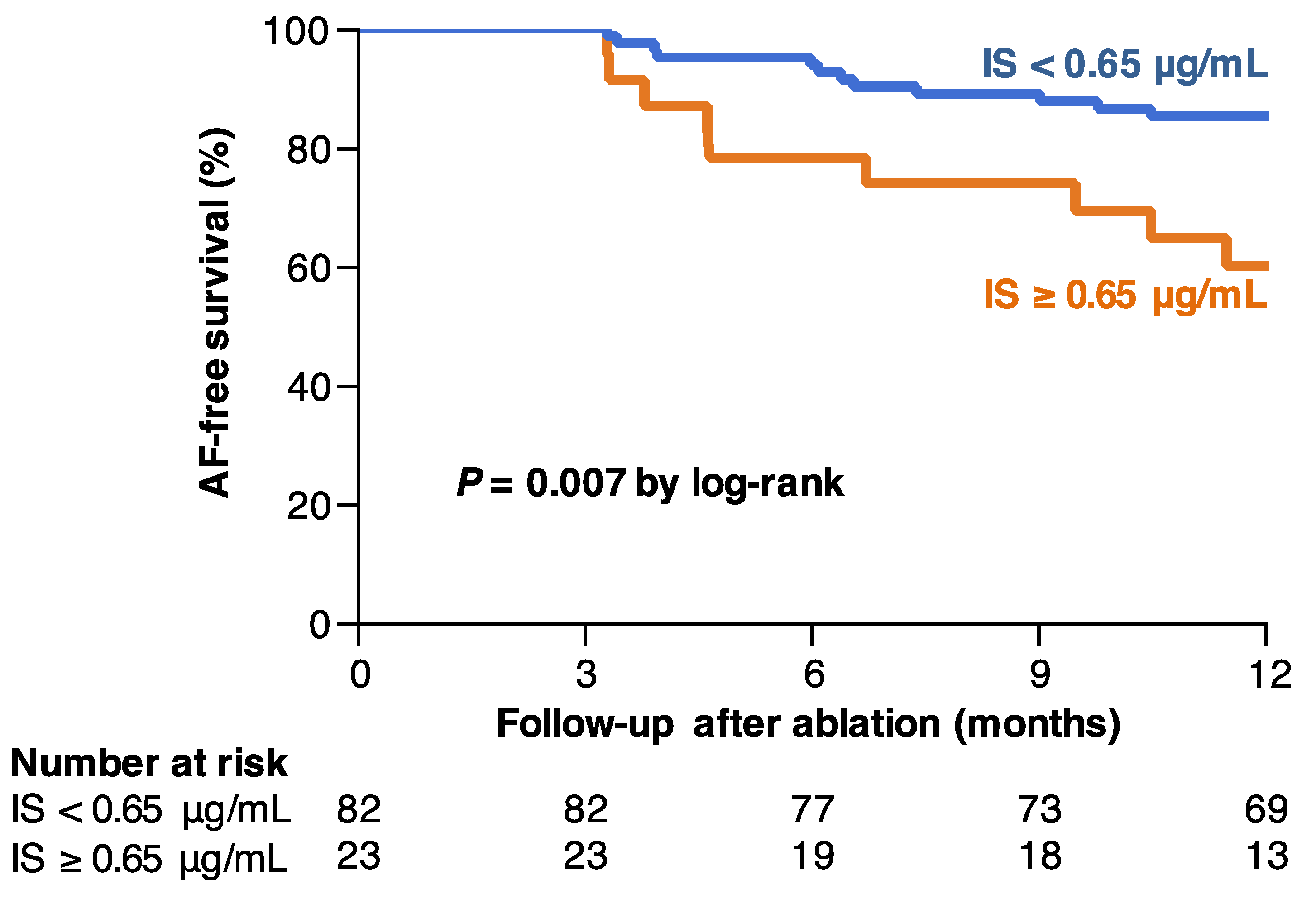
7.2. IS and AF Recurrence after Catheter Ablation
8. Therapeutic Potential of AST-120 for AF
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fuster, V.; Rydén, L.E.; Cannom, D.S.; Crijns, H.J.; Curtis, A.B.; Ellenbogen, K.A.; Halperin, J.L.; Kay, G.N.; Le Huezey, J.-Y.; Lowe, J.E.; et al. 2011 ACCF/AHA/HRS Focused Updates Incorporated Into the ACC/AHA/ESC 2006 Guidelines for the Management of Patients With Atrial Fibrillation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2011, 57, e101–e198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olesen, J.B.; Lip, G.Y.H.; Kamper, A.-L.; Hommel, K.; Køber, L.; Lane, D.A.; Lindhardsen, J.; Gislason, G.H.; Torp-Pedersen, C. Stroke and Bleeding in Atrial Fibrillation with Chronic Kidney Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 625–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greene, S.J.; Fonarow, G.C.; Solomon, S.D.; Subacius, H.P.; Ambrosy, A.P.; Vaduganathan, M.; Maggioni, A.P.; Böhm, M.; Lewis, E.F.; Zannad, F.; et al. Influence of atrial fibrillation on post-discharge natriuretic peptide trajectory and clinical outcomes among patients hospitalized for heart failure: insights from the ASTRONAUT trial. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2017, 19, 552–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jabre, P.; Roger, V.L.; Murad, M.H.; Chamberlain, A.M.; Prokop, L.; Adnet, F.; Jouven, X. Mortality Associated With Atrial Fibrillation in Patients With Myocardial Infarction. Circulation 2011, 123, 1587–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Wang, Y.-L.; Shantsila, A.; Lip, G.Y.H. The Global Burden of Atrial Fibrillation and Stroke: A Systematic Review of the Clinical Epidemiology of Atrial Fibrillation in Asia. Chest 2017, 152, 810–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chugh, S.S.; Havmoeller, R.; Narayanan, K.; Singh, D.; Rienstra, M.; Benjamin, E.J.; Gillum, R.F.; Kim, Y.-H.; McAnulty, J.H.; Zheng, Z.-J.; et al. Worldwide epidemiology of atrial fibrillation: a Global Burden of Disease 2010 Study. Circulation 2014, 129, 837–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.-A.; Hsieh, M.-H.; Tai, C.-T.; Tsai, C.-F.; Prakash, V.S.; Yu, W.-C.; Hsu, T.-L.; Ding, Y.-A.; Chang, M.-S. Initiation of Atrial Fibrillation by Ectopic Beats Originating From the Pulmonary Veins. Circulation 1999, 100, 1879–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calkins, H.; Kuck, K.H.; Cappato, R.; Brugada, J.; Camm, A.J.; Chen, S.-A.; Crijns, H.J.G.; Damiano, R.J.; Davies, D.W.; DiMarco, J.; et al. 2012 HRS/EHRA/ECAS Expert Consensus Statement on Catheter and Surgical Ablation of Atrial Fibrillation: Recommendations for Patient Selection, Procedural Techniques, Patient Management and Follow-up, Definitions, Endpoints, and Research Trial Design. Hear. Rhythm 2012, 9, 632–696.e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchhof, P. The future of atrial fibrillation management: integrated care and stratified therapy. Lancet (London, England) 2017, 390, 1873–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, R.; Bertini, M.; Blomstrom-Lundqvist, C.; Dobrev, D.; Kirchhof, P.; Pappone, C.; Ravens, U.; Tamargo, J.; Tavazzi, L.; Vicedomini, G.G. An update on atrial fibrillation in 2014: From pathophysiology to treatment. Int. J. Cardiol. 2016, 203, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lip, G.Y.; Tse, H.F.; Lane, D.A. Atrial fibrillation. Lancet 2012, 379, 648–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knecht, S.; O’Neill, M.D.; Verbeet, T. Rhythm Control versus Rate Control for Atrial Fibrillation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 1522. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wazni, O.M.; Marrouche, N.F.; Martin, D.O.; Verma, A.; Bhargava, M.; Saliba, W.; Bash, D.; Schweikert, R.; Brachmann, J.; Gunther, J.; et al. Radiofrequency Ablation vs Antiarrhythmic Drugs as First-line Treatment of Symptomatic Atrial Fibrillation. JAMA 2005, 293, 2634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morillo, C.A.; Verma, A.; Connolly, S.J.; Kuck, K.H.; Nair, G.M.; Champagne, J.; Sterns, L.D.; Beresh, H.; Healey, J.S.; Natale, A.; et al. Radiofrequency ablation vs antiarrhythmic drugs as first-line treatment of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation (RAAFT-2): a randomized trial. JAMA 2014, 311, 692–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosedis Nielsen, J.; Johannessen, A.; Raatikainen, P.; Hindricks, G.; Walfridsson, H.; Kongstad, O.; Pehrson, S.; Englund, A.; Hartikainen, J.; Mortensen, L.S.; et al. Radiofrequency Ablation as Initial Therapy in Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 1587–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuster, V.; Rydén, L.E.; Cannom, D.S.; Crijns, H.J.; Curtis, A.B.; Ellenbogen, K.A.; Halperin, J.L.; Le Heuzey, J.-Y.; Kay, G.N.; Lowe, J.E.; et al. ACC/AHA/ESC 2006 guidelines for the management of patients with atrial fibrillation–executive summary. Eur. Heart J. 2006, 27, 1979–2030. [Google Scholar]
- January, C.T.; Wann, L.S.; Alpert, J.S.; Calkins, H.; Cigarroa, J.E.; Cleveland, J.C.; Conti, J.B.; Ellinor, P.T.; Ezekowitz, M.D.; Field, M.E.; et al. 2014 AHA/ACC/HRS Guideline for the Management of Patients With Atrial Fibrillation: Executive Summary: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines and the Heart Rhythm Society. Circulation 2014, 130, 2071–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.N.; Jaïs, P.; Cummings, J.; Di Biase, L.; Sanders, P.; Martin, D.O.; Kautzner, J.; Hao, S.; Themistoclakis, S.; Fanelli, R.; et al. Pulmonary-vein isolation for atrial fibrillation in patients with heart failure. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 1778–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, M.R.; Connelly, D.T.; Hawkins, N.M.; Steedman, T.; Payne, J.; Shaw, M.; Denvir, M.; Bhagra, S.; Small, S.; Martin, W.; et al. Radiofrequency ablation for persistent atrial fibrillation in patients with advanced heart failure and severe left ventricular systolic dysfunction: a randomised controlled trial. Heart 2011, 97, 740–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.G.; Haldar, S.K.; Hussain, W.; Sharma, R.; Francis, D.P.; Rahman-Haley, S.L.; McDonagh, T.A.; Underwood, S.R.; Markides, V.; Wong, T. A randomized trial to assess catheter ablation versus rate control in the management of persistent atrial fibrillation in heart failure. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2013, 61, 1894–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.S.; Marrouche, N.F.; Khaykin, Y.; Gillinov, A.M.; Wazni, O.; Martin, D.O.; Rossillo, A.; Verma, A.; Cummings, J.; Erciyes, D.; et al. Pulmonary vein isolation for the treatment of atrial fibrillation in patients with impaired systolic function. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2004, 43, 1004–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Biase, L.; Mohanty, P.; Mohanty, S.; Santangeli, P.; Trivedi, C.; Lakkireddy, D.; Reddy, M.; Jais, P.; Themistoclakis, S.; Dello Russo, A.; et al. Ablation Versus Amiodarone for Treatment of Persistent Atrial Fibrillation in Patients With Congestive Heart Failure and an Implanted Device. Circulation 2016, 133, 1637–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marrouche, N.F.; Brachmann, J.; Andresen, D.; Siebels, J.; Boersma, L.; Jordaens, L.; Merkely, B.; Pokushalov, E.; Sanders, P.; Proff, J.; et al. Catheter Ablation for Atrial Fibrillation with Heart Failure. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 417–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Virk, S.A.; Bennett, R.G.; Chow, C.; Sanders, P.; Kalman, J.M.; Thomas, S.; Kumar, S. Catheter Ablation Versus Medical Therapy for Atrial Fibrillation in Patients With Heart Failure: A Meta-Analysis of Randomised Controlled Trials. Hear. Lung Circ. 2019, 28, 707–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blomström-Lundqvist, C.; Gizurarson, S.; Schwieler, J.; Jensen, S.M.; Bergfeldt, L.; Kennebäck, G.; Rubulis, A.; Malmborg, H.; Raatikainen, P.; Lönnerholm, S.; et al. Effect of Catheter Ablation vs Antiarrhythmic Medication on Quality of Life in Patients With Atrial Fibrillation: The CAPTAF Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2019, 321, 1059–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgendy, A.Y.; Mahmoud, A.N.; Khan, M.S.; Sheikh, M.R.; Mojadidi, M.K.; Omer, M.; Elgendy, I.Y.; Bavry, A.A.; Ellenbogen, K.A.; Miles, W.M.; et al. Meta-Analysis Comparing Catheter-Guided Ablation Versus Conventional Medical Therapy for Patients With Atrial Fibrillation and Heart Failure With Reduced Ejection Fraction. Am. J. Cardiol. 2018, 122, 806–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirchhof, P.; Benussi, S.; Kotecha, D.; Ahlsson, A.; Atar, D.; Casadei, B.; Castella, M.; Diener, H.-C.; Heidbuchel, H.; Hendriks, J.; et al. 2016 ESC Guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with EACTS. Eur. Heart J. 2016, 37, 2893–2962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kornej, J.; Hindricks, G.; Kosiuk, J.; Arya, A.; Sommer, P.; Husser, D.; Rolf, S.; Richter, S.; Huo, Y.; Piorkowski, C.; et al. Comparison of CHADS2, R2CHADS2, and CHA2DS2-VASc scores for the prediction of rhythm outcomes after catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation: the Leipzig Heart Center AF Ablation Registry. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 2014, 7, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, H.; Watanabe, T.; Sasaki, S.; Nagai, K.; Roden, D.M.; Aizawa, Y. Close bidirectional relationship between chronic kidney disease and atrial fibrillation: the Niigata preventive medicine study. Am. Heart J. 2009, 158, 629–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, A.; Lopez, F.L.; Matsushita, K.; Loehr, L.R.; Agarwal, S.K.; Chen, L.Y.; Soliman, E.Z.; Astor, B.C.; Coresh, J. Chronic Kidney Disease Is Associated With the Incidence of Atrial Fibrillation: The Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) Study. Circulation 2011, 123, 2946–2953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, N.; Fan, D.; Hsu, C.-Y.; Ordonez, J.D.; Marcus, G.M.; Go, A.S. Incident Atrial Fibrillation and Risk of End-Stage Renal Disease in Adults With Chronic Kidney Disease. Circulation 2013, 127, 569–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, Y.C.; Proietti, M.; Guiducci, E.; Blann, A.D.; Lip, G.Y.H. Atrial Fibrillation and Thromboembolism in Patients With Chronic Kidney Disease. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2016, 68, 1452–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wetmore, J.B.; Mahnken, J.D.; Rigler, S.K.; Ellerbeck, E.F.; Mukhopadhyay, P.; Spertus, J.A.; Hou, Q.; Shireman, T.I. The prevalence of and factors associated with chronic atrial fibrillation in Medicare/Medicaid-eligible dialysis patients. Kidney Int. 2012, 81, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzog, C.A.; Asinger, R.W.; Berger, A.K.; Charytan, D.M.; Díez, J.; Hart, R.G.; Eckardt, K.-U.; Kasiske, B.L.; McCullough, P.A.; Passman, R.S.; et al. Cardiovascular disease in chronic kidney disease. A clinical update from Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO). Kidney Int. 2011, 80, 572–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wizemann, V.; Tong, L.; Satayathum, S.; Disney, A.; Akiba, T.; Fissell, R.B.; Kerr, P.G.; Young, E.W.; Robinson, B.M. Atrial fibrillation in hemodialysis patients: clinical features and associations with anticoagulant therapy. Kidney Int. 2010, 77, 1098–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genovesi, S.; Pogliani, D.; Faini, A.; Valsecchi, M.G.; Riva, A.; Stefani, F.; Acquistapace, I.; Stella, A.; Bonforte, G.; DeVecchi, A.; et al. Prevalence of atrial fibrillation and associated factors in a population of long-term hemodialysis patients. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2005, 46, 897–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujii, H.; Kim, J.-I.; Yoshiya, K.; Nishi, S.; Fukagawa, M. Clinical Characteristics and Cardiovascular Outcomes of Hemodialysis Patients with Atrial Fibrillation: A Prospective Follow-Up Study. Am. J. Nephrol. 2011, 34, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkelmayer, W.C.; Patrick, A.R.; Liu, J.; Brookhart, M.A.; Setoguchi, S. The Increasing Prevalence of Atrial Fibrillation among Hemodialysis Patients. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 22, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.-T.; Lai, L.-P.; Lin, J.-L.; Chiang, F.-T.; Hwang, J.-J.; Ritchie, M.D.; Moore, J.H.; Hsu, K.-L.; Tseng, C.-D.; Liau, C.-S.; et al. Renin-angiotensin system gene polymorphisms and atrial fibrillation. Circulation 2004, 109, 1640–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.-L.; Chen, Y.-C.; Yeh, Y.-H.; Lai, Y.-J.; Yeh, H.-I.; Lin, C.-I.; Lin, Y.-K.; Lin, Y.-J.; Wu, T.-J.; Huang, Y.-K.; et al. Heart failure enhances arrhythmogenesis in pulmonary veins. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2011, 38, 666–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.-C.; Chang, J.-M.; Liu, W.-C.; Huang, J.-C.; Tsai, J.-C.; Lin, M.-Y.; Su, H.-M.; Hwang, S.-J.; Chen, H.-C. Echocardiographic parameters are independently associated with increased cardiovascular events in patients with chronic kidney disease. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant 2012, 27, 1064–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naruse, Y.; Tada, H.; Sekiguchi, Y.; Machino, T.; Ozawa, M.; Yamasaki, H.; Igarashi, M.; Kuroki, K.; Itoh, Y.; Murakoshi, N.; et al. Concomitant chronic kidney disease increases the recurrence of atrial fibrillation after catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation: a mid-term follow-up. Hear. Rhythm 2011, 8, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokuda, M.; Yamane, T.; Matsuo, S.; Ito, K.; Narui, R.; Hioki, M.; Tanigawa, S. -i.; Nakane, T.; Yamashita, S.; Inada, K.; et al. Relationship between renal function and the risk of recurrent atrial fibrillation following catheter ablation. Heart 2011, 97, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanagisawa, S.; Inden, Y.; Kato, H.; Fujii, A.; Mizutani, Y.; Ito, T.; Kamikubo, Y.; Kanzaki, Y.; Ando, M.; Hirai, M.; et al. Impaired renal function is associated with recurrence after cryoballoon catheter ablation for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation: A potential effect of non-pulmonary vein foci. J. Cardiol. 2017, 69, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raff, A.C.; Meyer, T.W.; Hostetter, T.H. New insights into uremic toxicity. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2008, 17, 560–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.-Y.; Chang, S.-C.; Wu, M.-S. Uremic toxins induce kidney fibrosis by activating intrarenal renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system associated epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. PLoS One 2012, 7, e34026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lekawanvijit, S.; Adrahtas, A.; Kelly, D.J.; Kompa, A.R.; Wang, B.H.; Krum, H. Does indoxyl sulfate, a uraemic toxin, have direct effects on cardiac fibroblasts and myocytes? Eur. Heart J. 2010, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.-S.; Lin, Y.-T.; Wang, S.-D.; Hung, K.-Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, S.-M. P-cresol induces disruption of cardiomyocyte adherens junctions. Toxicology 2013, 306, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lekawanvijit, S.; Kompa, A.R.; Manabe, M.; Wang, B.H.; Langham, R.G.; Nishijima, F.; Kelly, D.J.; Krum, H. Chronic kidney disease-induced cardiac fibrosis is ameliorated by reducing circulating levels of a non-dialysable uremic toxin, indoxyl sulfate. PLoS One 2012, 7, e41281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, T.; Ise, M.; Hirata, M.; Endo, K.; Ito, Y.; Seo, H.; Niwa, T. Indoxyl sulfate stimulates renal synthesis of transforming growth factor-beta 1 and progression of renal failure. Kidney Int. Suppl. 1997, 63, S211–S214. [Google Scholar]
- Ito, S.; Yoshida, M. Protein-Bound Uremic Toxins: New Culprits of Cardiovascular Events in Chronic Kidney Disease Patients. Toxins (Basel) 2014, 6, 665–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lekawanvijit, S.; Kompa, A.R.; Wang, B.H.; Kelly, D.J.; Krum, H. Cardiorenal syndrome: the emerging role of protein-bound uremic toxins. Circ. Res. 2012, 111, 1470–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dou, L.; Sallée, M.; Cerini, C.; Poitevin, S.; Gondouin, B.; Jourde-Chiche, N.; Fallague, K.; Brunet, P.; Calaf, R.; Dussol, B.; et al. The cardiovascular effect of the uremic solute indole-3 acetic acid. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 26, 876–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lekawanvijit, S. Cardiotoxicity of Uremic Toxins: A Driver of Cardiorenal Syndrome. Toxins (Basel) 2018, 10, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreto, F.C.; Barreto, D.V.; Liabeuf, S.; Meert, N.; Glorieux, G.; Temmar, M.; Choukroun, G.; Vanholder, R.; Massy, Z.A. European Uremic Toxin Work Group (EUTox) Serum Indoxyl Sulfate Is Associated with Vascular Disease and Mortality in Chronic Kidney Disease Patients. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 4, 1551–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-J.; Liu, H.-L.; Pan, C.-F.; Chuang, C.-K.; Jayakumar, T.; Wang, T.-J.; Chen, H.-H.; Wu, C.-J. Indoxyl sulfate predicts cardiovascular disease and renal function deterioration in advanced chronic kidney disease. Arch. Med. Res. 2012, 43, 451–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimazu, S.; Hirashiki, A.; Okumura, T.; Yamada, T.; Okamoto, R.; Shinoda, N.; Takeshita, K.; Kondo, T.; Niwa, T.; Murohara, T. Association between indoxyl sulfate and cardiac dysfunction and prognosis in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy. Circ. J. 2013, 77, 390–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, B.; Yoshikawa, D.; Ishii, H.; Suzuki, S.; Inoue, Y.; Takeshita, K.; Tanaka, M.; Kumagai, S.; Matsumoto, M.; Okumura, S.; et al. Relation of plasma indoxyl sulfate levels and estimated glomerular filtration rate to left ventricular diastolic dysfunction. Am. J. Cardiol. 2013, 111, 712–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, R.R.G.; Tan, G.H.J.; Liu, W.; Ti, L.K.; Chew, S.T.H. The Association of Acute Kidney Injury and Atrial Fibrillation after Cardiac Surgery in an Asian Prospective Cohort Study. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016, 95, e3005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Hao, G.; Pan, Y.; Ma, S.; Yang, T.; Shi, P.; Zhu, Q.; Xie, Y.; Ma, S.; Zhang, Q.; et al. Serum indoxyl sulfate is associated with mortality in hospital-acquired acute kidney injury: a prospective cohort study. BMC Nephrol. 2019, 20, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Harty, G.J.; Zheng, Y.; Iyer, S.R.; Sugihara, S.; Sangaralingham, S.J.; Ichiki, T.; Grande, J.P.; Lee, H.-C.; Wang, X.; et al. CRRL269. Circ. Res. 2019, 124, 1462–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoki, K.; Teshima, Y.; Kondo, H.; Saito, S.; Fukui, A.; Fukunaga, N.; Nawata, T.; Shimada, T.; Takahashi, N.; Shibata, H. Role of Indoxyl Sulfate as a Predisposing Factor for Atrial Fibrillation in Renal Dysfunction. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2015, 4, e002023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CHEN, W.-T.; CHEN, Y.-C.; HSIEH, M.-H.; HUANG, S.-Y.; KAO, Y.-H.; CHEN, Y.-A.; LIN, Y.-K.; CHEN, S.-A.; CHEN, Y.-J. The Uremic Toxin Indoxyl Sulfate Increases Pulmonary Vein and Atrial Arrhythmogenesis. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2015, 26, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamagami, F.; Tajiri, K.; Doki, K.; Hattori, M.; Honda, J.; Aita, S.; Harunari, T.; Yamasaki, H.; Murakoshi, N.; Sekiguchi, Y.; et al. Indoxyl Sulphate is Associated with Atrial Fibrillation Recurrence after Catheter Ablation. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 17276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Za’abi, M.; Ali, B.; Al Toubi, M. HPLC-fluorescence method for measurement of the uremic toxin indoxyl sulfate in plasma. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2013, 51, 40–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asai, M.; Kumakura, S.; Kikuchi, M. Review of the efficacy of AST-120 (KREMEZIN®) on renal function in chronic kidney disease patients. Ren. Fail. 2019, 41, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, T.; Aoyama, I.; Ise, M.; Seo, H.; Niwa, T. An oral sorbent reduces overload of indoxyl sulphate and gene expression of TGF-β1 in uraemic rat kidneys. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2000, 15, 1773–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoyama, I.; Shimokata, K.; Niwa, T. An oral adsorbent downregulates renal expression of genes that promote interstitial inflammation and fibrosis in diabetic rats. Nephron 2002, 92, 635–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulman, G.; Agarwal, R.; Acharya, M.; Berl, T.; Blumenthal, S.; Kopyt, N. A multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-ranging study of AST-120 (Kremezin) in patients with moderate to severe CKD. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2006, 47, 565–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoyama, I.; Niwa, T. An oral adsorbent ameliorates renal overload of indoxyl sulfate and progression of renal failure in diabetic rats. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2001, 37, S7–S12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konishi, K.; Nakano, S.; Tsuda, S.; Nakagawa, A.; Kigoshi, T.; Koya, D. AST-120 (Kremezin®) initiated in early stage chronic kidney disease stunts the progression of renal dysfunction in type 2 diabetic subjects. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2008, 81, 310–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, T.; Kawagoe, Y.; Matsuda, T.; Ueda, Y.; Shimada, N.; Ebihara, I.; Koide, H. Oral ADSORBENT AST-120 decreases carotid intima-media thickness and arterial stiffness in patients with chronic renal failure. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2004, 27, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoji, T.; Wada, A.; Inoue, K.; Hayashi, D.; Tomida, K.; Furumatsu, Y.; Kaneko, T.; Okada, N.; Fukuhara, Y.; Imai, E.; et al. Prospective randomized study evaluating the efficacy of the spherical adsorptive carbon AST-120 in chronic kidney disease patients with moderate decrease in renal function. Nephron. Clin. Pract. 2007, 105, c99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akizawa, T.; Asano, Y.; Morita, S.; Wakita, T.; Onishi, Y.; Fukuhara, S.; Gejyo, F.; Matsuo, S.; Yorioka, N.; Kurokawa, K.; et al. Effect of a carbonaceous oral adsorbent on the progression of CKD: a multicenter, randomized, controlled trial. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2009, 54, 459–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulman, G.; Berl, T.; Beck, G.J.; Remuzzi, G.; Ritz, E.; Arita, K.; Kato, A.; Shimizu, M. Randomized Placebo-Controlled EPPIC Trials of AST-120 in CKD. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 26, 1732–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, R.-H.; Kang, S.W.; Park, C.W.; Cha, D.R.; Na, K.Y.; Kim, S.G.; Yoon, S.A.; Han, S.Y.; Chang, J.H.; Park, S.K.; et al. A Randomized, Controlled Trial of Oral Intestinal Sorbent AST-120 on Renal Function Deterioration in Patients with Advanced Renal Dysfunction. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2016, 11, 559–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogas, S.M.; Voroneanu, L.; Serban, D.N.; Segall, L.; Hogas, M.M.; Serban, I.L.; Covic, A. Methods and potential biomarkers for the evaluation of endothelial dysfunction in chronic kidney disease: a critical approach. J. Am. Soc. Hypertens. 2010, 4, 116–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namikoshi, T.; Tomita, N.; Satoh, M.; Sakuta, T.; Kuwabara, A.; Kobayashi, S.; Higuchi, Y.; Nishijima, F.; Kashihara, N. Oral adsorbent AST-120 ameliorates endothelial dysfunction independent of renal function in rats with subtotal nephrectomy. Hypertens. Res. 2009, 32, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, S.; Zuo, Y.; Ma, J.; Yancey, P.G.; Hunley, T.E.; Motojima, M.; Fogo, A.B.; Linton, M.F.; Fazio, S.; Ichikawa, I.; et al. Oral activated charcoal adsorbent (AST-120) ameliorates extent and instability of atherosclerosis accelerated by kidney disease in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant 2011, 26, 2491–2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niwayama, J.; Sanaka, T. Development of a new method for monitoring blood purification: the blood flow analysis of the head and foot by laser Doppler blood flowmeter during hemodialysis. Hemodial. Int. 2005, 9, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, J.-H.; Yu, M.; Lee, S.; Ryu, D.-R.; Kim, S.-J.; Kang, D.-H.; Choi, K.B. AST-120 Improves Microvascular Endothelial Dysfunction in End-Stage Renal Disease Patients Receiving Hemodialysis. Yonsei Med. J. 2016, 57, 942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujii, H.; Nishijima, F.; Goto, S.; Sugano, M.; Yamato, H.; Kitazawa, R.; Kitazawa, S.; Fukagawa, M. Oral charcoal adsorbent (AST-120) prevents progression of cardiac damage in chronic kidney disease through suppression of oxidative stress. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2009, 24, 2089–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuwahara, M.; Bannai, K.; Segawa, H.; Miyamoto, K.; Yamato, H. Cardiac remodeling associated with protein increase and lipid accumulation in early-stage chronic kidney disease in rats. Biochim. Biophys. Acta - Mol. Basis Dis. 2014, 1842, 1433–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakai, K.; Fujii, H.; Kono, K.; Goto, S.; Fukagawa, M.; Nishi, S. Effects of AST-120 on left ventricular mass in predialysis patients. Am. J. Nephrol. 2011, 33, 218–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asanuma, H.; Chung, H.; Ito, S.; Min, K.-D.; Ihara, M.; Takahama, H.; Funayama, M.; Imazu, M.; Fukuda, H.; Ogai, A.; et al. AST-120, an Adsorbent of Uremic Toxins, Improves the Pathophysiology of Heart Failure in Conscious Dogs. Cardiovasc. Drugs Ther. 2019, 33, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yamagami, F.; Tajiri, K.; Yumino, D.; Ieda, M. Uremic Toxins and Atrial Fibrillation: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implications. Toxins 2019, 11, 597. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11100597
Yamagami F, Tajiri K, Yumino D, Ieda M. Uremic Toxins and Atrial Fibrillation: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implications. Toxins. 2019; 11(10):597. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11100597
Chicago/Turabian StyleYamagami, Fumi, Kazuko Tajiri, Dai Yumino, and Masaki Ieda. 2019. "Uremic Toxins and Atrial Fibrillation: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implications" Toxins 11, no. 10: 597. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11100597
APA StyleYamagami, F., Tajiri, K., Yumino, D., & Ieda, M. (2019). Uremic Toxins and Atrial Fibrillation: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implications. Toxins, 11(10), 597. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11100597




