Abstract
Studies on Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli (STEC) typically examine and classify the virulence gene profiles based on genomic analyses. Among the screened strains, a subgroup of STEC which lacks the locus of enterocyte effacement (LEE) has frequently been identified. This raises the question about the level of pathogenicity of such strains. This review focuses on the advantages and disadvantages of the standard screening procedures in virulence profiling and summarizes the current knowledge concerning the function and regulation of toxins encoded by LEE-negative STEC. Although LEE-negative STEC usually come across as food isolates, which rarely cause infections in humans, some serotypes have been implicated in human diseases. In particular, the LEE-negative E. coli O104:H4 German outbreak strain from 2011 and the Australian O113:H21 strain isolated from a HUS patient attracted attention. Moreover, the LEE-negative STEC O113:H21 strain TS18/08 that was isolated from minced meat is remarkable in that it not only encodes multiple toxins, but in fact expresses three different toxins simultaneously. Their characterization contributes to understanding the virulence of the LEE-negative STEC.
Keywords:
LEE-negative STEC; Shiga toxin; Subtilase Cytotoxin; Cytolethal distending toxin; EHEC-Hly; profiling studies; O104:H4; O113:H21; TS18/08 Key Contribution:
This review describes the current knowledge about the function and regulation of toxins of LEE-negative Shiga toxin producing E. coli.
1. Introduction
Escherichia coli strains that produce Shiga toxins (Stx) occur widely in the gastrointestinal tract of animals and humans. In most animals, the presence of Shiga toxin-producing E. coli (STEC) does not cause any disease (reviewed in [1]). In humans however, a STEC subgroup, the enterohemorrhagic E. coli (EHEC) can cause serious, life-threatening diseases such as hemorrhagic colitis or the hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS) [2]. Clinically relevant EHEC strains produce one or more Stx which are considered to be crucial for the development of HUS [3]. Many EHEC strains also express additional virulence factors required to cause disease. The majority of these are encoded by phages, plasmids, and pathogenicity islands (PAIs) (reviewed in [4,5,6]). Amongst them, the locus of enterocyte effacement (LEE) is frequently detected in EHEC strains [7,8,9]. This 35.6 kb large pathogenicity island contains genes encoding a type III secretion system and several translocated effector proteins, including the translocated intimin receptor (tir), as well as the adhering intimin (encoded by eae) [10,11,12,13,14,15]. The LEE is responsible for the formation of attaching and effacing (AE) lesions in intestinal epithelial cells. They are caused by changes in the cytoskeleton and the accumulation of actin at the attachment site [16,17]. The interactions between bacterial and epithelial cells are mediated by the bacterial outer membrane protein intimin and the binding of its receptor, Tir, which is translocated into the epithelial cell via the type III secretion system [15]. Furthermore, the LEE is a mobile genetic element that can be transmitted by horizontal gene transfer [18]. Due to its causality for sequelae and its rate of detection in STEC, samples that are analyzed for STEC properties and found to encode Stx are by default screened for the eae gene, as it is a marker for the occurrence of the LEE [19,20]. Particular EHEC serogroups such as O157, O26, O103, O145, and O111 are associated with human infections and as such are sometimes called the big five serogroups [21]. Following the recommendation of the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA), beside these five serogroups, EHEC belonging to the serogroup O104 are considered to be potentially highly virulent and together, these six are the most important serogroups that should be screened for in stool samples from patients [22].
Besides these typical EHEC, a growing number of LEE-negative EHEC have been isolated from stool samples. This showed on the one hand that the LEE is not mandatory for infections and on the other hand raised the question whether they are as pathogenic as the LEE-positive ones [9,23,24]. In addition, numerous STEC isolates from animals, food, and the environment were shown to be LEE-negative [25,26,27]. For instance, of all isolates originating from infections in Switzerland during the periods between 2000 to 2009 and 2010 to 2014, about 30% did not contain the LEE [7,9]. This leads to the question: why do these strains not contain the LEE? Until today, several studies have shown that the LEE-negative STEC are not a clonal group but evolved independently by acquiring comparable virulence features in parallel [27,28]. In their study on the location of the insertion sites of LEE, Bertin et al. [19] identified three different tRNA genes—selC, pheU, and pheV—which were used for chromosomal insertion. They suggested that these sites could additionally be used for the insertion of other foreign DNA. Based on a comparative study of mainly LEE-negative food isolates and 12 strains of the HUSEC strain collection, Hauser et al. [29] showed in a study in 1996, that in the majority of the food isolates—96% of the characterized strains—the three integration sites for LEE were occupied by different DNA insertions, which could be the cause of the missing LEE [23]. Still, the analyzed strains clustered together with pathogenic strains based on multi-locus sequence typing (MLST), which allowed for them to be classified as a potential cause of infections in humans [29]. Current theories state that these STEC harbor alternative factors such as the saa (STEC autoagglutinating adhesin), sab (for STEC autotransporter (AT) mediating biofilm formation), iha (Irg A homologue adhesion), and/or tia (toxigenic invasion loci A) gene, probably to cope for the functional loss of LEE and convey pathogenicity on a different path [30,31].
Two of these alternative adhesins—Saa and Sab—were identified within an LEE-negative EHEC of the serotype O113:H13, which caused a HUS-associated outbreak in Australia [32,33,34]. Saa is a plasmid-encoded adhesin which showed minor similarities with the adhesin YadA from Yersinia enterocolitica (about 25% amino acid identity) and the phage-encoded immunoglobulin binding protein EibD of E. coli [32,35,36]. Initial analyses indicated that the functionality depends on the length of C-terminal 3′ repeats of the Saa protein [32]. So far, however, these findings could not be verified in follow-up studies. The capacity of Saa to allow E. coli laboratory strains to adhere to HEp-2 cells (Human Epithelial type 2 cells) was not significantly dependent on the length of the 3′ repeats and/or the expression level of Saa [37,38].
The sab gene encodes a large protein of about 160 kD that resembles features of the AT protein family. This family covers the entirety of surface proteins which are either linked to the outer membrane or released by proteolysis of Gram-negative bacteria. [33]. Each AT protein reveals a characteristic layout of three different domains. Beginning at the N-terminal signal peptide domain, the proteins compose a passenger domain of various functions (α-domain), and end with a conserved pore-forming domain at the C-terminus [33,39]. Sab is located on the surface and was found to contribute to the adhesion to HEp-2 cells and biofilm formation on polystyrene surfaces of the pathogen E. coli O113:H21 and laboratory strain E. coli JM109 by Herold et al. [33].
Tarr et al. [40] described the iha gene which mediates adherence in an E. coli O157:H7 strain and non-adherent E. coli laboratory strains. It encodes a protein of 78 kDa which is homologous to the adhesive protein IrgA (iron regulated gene A) of Vibrio cholerae [40,41,42]. In contrast to saa and sab, iha can be found in LEE-negative and LEE-positive STEC as well as other pathogenic E. coli [38,43]. Based on these genetic profiling studies, it is assumed that iha is an adhesion-associated gene which seems to be preserved throughout STEC serotypes. This indicates a probable importance for human infections [38,40,43]. However, deletion of neither saa nor iha showed a non-adhering phenotype, which is why it is assumed that there are multiple factors involved in the adherence of LEE-negative STEC [32,40].
The tia gene was originally described for enterotoxigenic E. coli (ETEC) in the form of an invasion factor for several intestinal cell lines [30,31]. Nevertheless, tia can also be found in LEE-negative STEC, where it is encoded within a pathogenic island termed SE-PAI [44]. In their in vivo study involving two different LEE-negative STEC, Bondì et al. [45] showed that tia is needed to mediate the invasion into Caco-2 (human colon adenocarcinoma cells/Cancer coli-2) and HEp-2 cells. The transformation of a tia-carrying expression vector to an E. coli laboratory strain did not lead to a comparable effect on cell invasion, though. This indicates that the presence of Tia is not sufficient to transfer the invasive property of an STEC strain [45].
Including all HUS cases, there were 1885 EHEC infections registered in Germany in 2016 [46]. Since only the detection of Stx or the stx gene is crucial for a therapeutic decision, isolations of STEC from stool samples and subsequent enrichment cultures were only infrequently performed [47]. As a consequence, there were only 348 STEC isolates serotyped in 2016 [46]. Within these more thoroughly characterized strains, the majority belonged either to serogroup O157 (48 isolates) or O91 (47 isolates). This is of great interest for two main reasons. First, O157 strains are typically LEE-positive and cause severe infection processes in humans [48]. Second, O91 strains predominantly belong to the group of LEE-negative STEC and are typically classified as less infectious/dangerous [22,49], although an O91 strain that caused HUS and was shown to produce a variant of Stx2 has been described [50]. In addition, O91 strains have been regularly isolated from patient samples and could be found in different foods [7,27,49,51,52]. Recent studies showed that O91 isolates of various origin (food, environment, and humans) share similar genotypic profiles, are phylogenetically related, could be mainly attributed to cattle as a reservoir for human infections, and, thus, could potentially lead to severe human infections [53,54]. Comparing the infection numbers and distribution in detected serotypes of 2016 to the three previous years, there is an increase in the number of cases, but the overall distribution of LEE-positive and LEE-negative pathogens remained steady throughout those years [46,55,56,57]. With respect to the large STEC outbreak in Germany in 2011 which was caused by an E. coli O104:H4 strain that carried stx2a and lacked the eae gene, these data show that the impact of LEE-negative STEC on human health has to be taken seriously. In this context, it is noteworthy that this particular strain originates from enteroaggregative E. coli, which most likely evolved to an STEC by acquiring a bacteriophage that encodes stx2a [58,59,60]. Finally, there is a demand to understand the complexity of the virulence factor profiles of this subgroup of STEC.
The goal of this review is to enlighten the variety of the pathogenicity factors of LEE-negative STEC targeting especially actively secreted proteins that have a toxic effect on host cells. Based on examples of recent studies on the virulence profiles in LEE-negative STEC, the general procedure and results of such studies are presented. In the following, the functionality and regulation of the toxins that are found in LEE-negative STEC are described.
2. Toxins of LEE-Negative STEC
More than 80 studies on the genotyping und virulence profiling of STEC and EHEC were published in the past 10 years, examples of which are given in several studies [23,61,62,63]. In general, all of these screening studies aimed to elucidate the serotypes and virulence properties of STEC including Stx-variants, LEE, further toxins, and other adhesion factors such as the ones mentioned above. As the sources of EHEC infections are manifold, the origin of the examined strains varied from environmental and animal isolates to food isolates to clinical isolates [64,65,66]. Among them, cattle are one of the main reservoirs for STEC. Hence, isolates originating from bovine meat and dairy products, as well as the production plants of bovine products and workers in this field were often examined [26,65,67,68,69,70,71,72]. Furthermore, animal products originating from sheep, goat, deer, or wild boar are of particular interest for screening STEC virulence profiles because these animals harbor a large amount of potential EHEC strains [73,74,75,76,77,78]. In addition to the investigation of animal products, fresh products such as lettuce and spinach are also typically examined in such screening studies [51,79].
Each study followed an essentially similar track of identification. When starting from a sample pool, the first step was to detect stx genes and particularly the eae gene by polymerase chain reaction (PCR). A stx-positive PCR was then usually followed by an isolation of the strain that harbored the stx gene [23,70,80]. Subsequently, the serotypes and genetic profiles regarding further toxins and pathogenicity factors were examined. Among these studies, subtyping of the stx variants and the detection of enterohemolysin (EHEC-Hly) were the most common targets of investigation [81,82,83]. Besides these, the presence of other toxin genes, such as the cytholethal distending toxin V (Cdt-V) and the subtilase cytotoxin (SubAB), was often determined [62,67,84,85,86]. Furthermore, the identification of adhesion factors, which are present in addition to or alternatively to the LEE, were of great interest. Here, especially iha and saa, and less often sab, were targets for screening [26,87,88].
Slanec et al. [23] isolated 34 STEC strains out of 504 food samples to identify their specific virulence profiles. The stx subtype (stx1 and stx2, and their variants) and the virulence genes eae, ehxA, espP, as well as the type III effectors nleA and cif, the adhesins iha and efa1, and the toxin genes subAB and cdt-V were investigated. The authors showed that the majority of the strains (88%) carried stx2 variants. Among these, 18% harbored a second toxin gene, while 4% carried even two additional toxin genes that were different from stx. Two stx variants, independent of the combination of stx1 with stx2, or two different stx2 alleles were found in 29% of all isolates. Of those, 38% carried subAB in addition to two stx genes. Ignoring the differentiation into stx1 and stx2 subtypes, this study identified as many as 33 different virulence types [23]. In contrast to the results of Slanec et al. [23], Martins et al. [89] identified 45 virulence profiles when ignoring the stx type in 65 isolates originating from sheep. Here, 56% carried just one stx gene, 33% two stx genes, and 11% three. Furthermore, the toxin genes subAB and cdt-V were analyzed. These genes were carried by 2% and 3% of the analyzed strains, respectively. In addition to the aforementioned genes, the author also investigated eae, ehxA, saa, and iha. The studies by Slanec et al. [23] and Martins et al. [89] had already conclusively demonstrated the complexity and intricacy of virulence gene profiling in STEC. In addition, the distribution of percentages of the quantity of stx genes and all other tested genes reveal that even the statistical distribution of virulence genes is highly variable in different strain sets.
The study by Slanec et al. [23] highlights a major drawback of all virulence screening studies. Typically, all screenings are conducted on a genetic level and do not determine if the encoded toxins and virulence genes were actually expressed. Only a few studies performed biochemical and microbiological tests to show the presence of the toxin that was identified on a genetic level. Often, Vero cell assays were performed to characterize the phenotypic features of isolates and show the presence of Stx in the corresponding culture supernatant [89]. As an alternative method, quantitative real-time polymerase chain reactions (qRT-PCR) could also be conducted to identify expression levels of different stx genes within one strain. The limitation lies in the differentiation between two variants of one Stx class [90]. The expression of enterohemolysin is typically proved with hemolysis assays on special blood agar plates [86].
Nevertheless, all screening studies revealed a great variation in virulence profiles which often encode multiple toxins. This leads to the question how these multiple toxin systems could work. Following the assumption that the information located in the bacterial chromosome is essential, it is likely that each of the toxins encoded is expressed. To our knowledge, there are almost no data or studies available that target the question of multi-toxin expression and their regulation. Still, there has been data obtained on the regulation of some of the toxins found within the repository of LEE-negative STEC. In the following, the currently known characteristics, functions, and regulations of the virulence factors Stx, SubAB, EHEC-Hly, and Cdt are summarized to allow for a glimpse into the complexity of a regulation system that has to manage multiple toxins. Table 1 gives an overview of the toxins that are described in detail in the following sections and highlights their function, strain of origin, and alternative species in which they could be found. A schematic overview of the transport and target sites of Stx, SubAB, Cdt, and EHEC-Hly are presented in Figure 1. These toxins are frequently found in LEE-negative STEC and sparked great interest to understand their potential virulence [23,85,87,88,89].

Table 1.
Summary of toxins identified within STEC. Besides their biological/biochemical functions, the strain of origin and other organisms, which could encode the toxin too, are depicted.
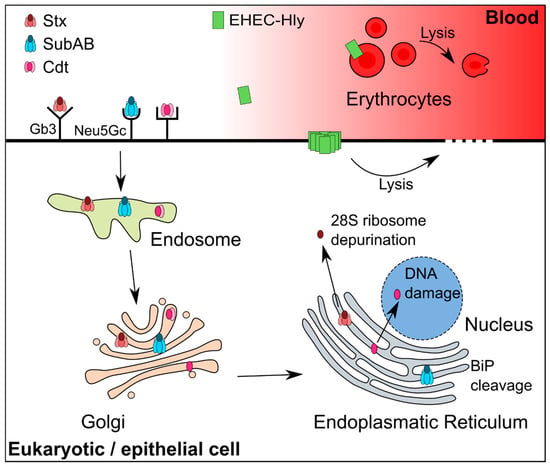
Figure 1.
Schematic view of the transport and target sites of the toxins Stx, SubAB, Cdt, and EHEC-Hly. Gb3 and Neu5Gc stand for globotriaosylceramide and N-glycolylneuraminic acid and are the binding partners of Stx and SubAB on the cell surface, respectively. The cell membrane receptor for Cdt is not known and thus not indicated here. SubAB cleaves its natural substrate, the endoplasmatic chaperone BiP (binding immunoglobulin protein) in the endoplasmatic reticulum. Stx depurinates the 28S subunit of the ribosome in the cytosol. Cdt leads to DNA damage in the nucleus and EHEC-Hly causes lysis of erythrocytes and epithelial cells. The effect of EHEC-Hly on target cells mediated by the OMV associated form is not depicted. Modified according to Beddoe et al. [95] and Jinadasa et al. [96].
2.1. Stx
As main pathogenicity factors of EHEC, the Stx family is currently one of the best described toxin families. In 1983, O’Brien et al. [91] identified a verotoxin, produced by an E. coli O157:H7 strain, to be similar to the previously reported Stx that is encoded by Shigella dysenteriae type 1. Following this recognition, the molecular characterization of Stx in pathogenic E. coli revealed that there are two main groups of Stx, namely Stx1 and Stx2. Based on genetic variations and the resulting differences in toxicity, toxin receptors, and amino acid compositions, the two main variants were further subtyped into Stx1a to Stx1d, and Stx2a to Stx2f [61,97,98,99,100]. In both cases, the a-form is considered to be the prototype for the respective main variant. Among the variants, Stx1a shows the highest cytotoxicity in Vero cell cytotoxicity assays [101]. Nevertheless, the severe and life-threatening HUS is frequently associated with the production of Stx2a and Stx2c [102].
Stx belong to the class of AB5 toxins. They are composed of one enzymatic active A-subunit and a pentamer of B-subunits, which mediates the uptake of the holotoxin via endosomes into target cells [103,104,105,106]. The cytotoxic effect of Stx is based on the irreversible removal of an adenine of the 28S ribosomal subunit, which prohibits the interaction of the elongation factor 1 [107,108,109]. This inhibits the protein synthesis and finally leads to apoptosis of the affected cell [109].
The expression of the members of the Stx family is regulated by many different environmental effects, such as temperature, growth phase, oxidative stress, quorum sensing, and antibiotics [110,111,112,113,114,115,116]. A common regulatory mechanism for Stx expression is the inclusion in regulatory processes of the phage replication cycle, because Stx1 and Stx2 are encoded in the genome of lambdoid prophages.
Its specific location between the genes encoding the late anti-terminator Q and the lysis enzymes allows Stx to be co-transcribed with the late phage genes [117,118]. Basically, this happens when the prophages are induced. Phage induction is connected with the bacterial SOS response, which mediates one of the main regulation pathways for the Stx production. Several antibiotics and hydrogen peroxide also activate the SOS response, thereby likewise increasing Stx production [116,119]. This connection is one of the main reasons why the treatment of an EHEC infection with antibiotics is not recommended, because the increased Stx production can lead to a more severe infection process [120]. In contrast, a negative effect on the Stx expression mediated by the SOS response is induced by nitric oxide. This negative response is caused by the downregulation of RecA, the global initiator of the SOS response [121,122]. In addition, the expression of Stx1 is sensitive to the concentration of iron due to the fact that the stx1AB promotor is iron dependent. Specifically, decreased levels of iron lead to an increase in Stx1 production and vice versa [123].
Although only limited effectors are known for the regulation of Stx1, there are several affecting conditions that were analyzed for the regulation of Stx2. For instance, the global regulator protein H-NS (histone-like nucleoid structuring protein) affects the expression of Stx2 by changing the activity of the specific promoter and the modulation of the phage induction. This effect was shown to depend on temperature, but remain unaltered upon changes in pH, osmolarity, oxygen tension, iron levels, or carbon sources [111,124]. The latest reported global regulator that is involved in the modulation of Stx2 production is the RNA chaperone Hfq. Kendall et al. [125] showed that the production of Stx2 is increased in hfq deletion mutants, which leads to the assumption that Hfq itself or small RNAs (sRNA) regulated by Hfq reduce the Stx2 amount in wild-type strains. Furthermore, Stx2 expression appears to be influenced by stress signals and inter-kingdom signaling [126]. Finally, EHEC are able to react to the mammalian stress response by recognizing adrenaline and noradrenaline, which also leads to an increase of its pathogenicity factors including Stx [127].
2.2. SubAB
The subtilase cytotoxin (SubAB) was initially described in STEC by Paton et al. [92] in 2001 in the context of a HUS outbreak with E. coli O113:H21 98 NK2 in Australia. SubAB is an AB5 toxin and has since then been commonly detected in eae-negative STEC. Similar to other AB5 toxins, SubAB is composed of two subunits. The enzymatically active A-subunit has a subtilase-like serine protease activity, while the pentamer of B-subunits mediates the transport into the target cells in an clathrin-dependent way [128,129]. However, SubAB shows a narrow target spectrum. It only cleaves the endoplasmatic heat shock protein 70 (Hsp70), also named binding immonoglubulin protein (BiP), or 78 kDa glucose-regulated protein (GRP78). The cleavage occurs between its two functional domains, the nucleotide-binding domain (NBD) and the substrate-binding domain (SBD) [130].
Internalization occurs after the B-subunit is bound to its eukaryotic receptor N-glycolyl neuraminic acid (Neu5Gc), a glycan side chain that is not synthesized by human cells. Rather, it can be incorporated in the glycan matrix when dairy products and red meat are consumed [95]. Furthermore, experiments by Funk et al. [131] implied a translocation mechanism of the A-subunit (SubA) on its own which is independent of the B-subunit, since in Vero cell-based assays, SubA exhibited cytotoxic effects when applied to the cells in the absence of the B-subunit.
So far, two different encoding locations in the genome of STEC are known for SubAB. SubAB1 was the first identified variant and is located on the virulence plasmid pO113 [92]. During the last eight years, further variants of SubAB were described which are all encoded on the bacterial chromosome, thus named SubAB2-1 to SubAB2-3 [132,133,134].
Despite analyses of several aspects of the biochemical processes involved in the functionality of SubAB and its consequences on the target cells, aspects of the regulation of SubAB expression itself are still unvetted [135,136]. One hypothesis is that the expression is triggered based on the position in the genome. Given that SubAB1 is encoded within a virulence plasmid pO113, it is possible that its regulation is related to the activation of other pathogenicity factors on the same plasmid. Also, the location within the pathogenicity island SE-PAI in close proximity to the tia gene of SubAB2-1 or the OEP-locus of SubAB2-2 hints at a regulation that is linked to the genetic surrounding. One exclusive study performed by Hauser et al. [114] gives first insights into the regulation of SubAB1. Based on qRT-PCR data, they reported that the expression of SubAB1 was at its maximum in the late exponential growth phase within an STEC which was isolated from minced meat. This indicates that the expression of the plasmid-encoded SubAB1 depends on the bacterial life cycle [114].
Still, conditions and environmental factors which induce or repress the expression of the SubAB variants are not yet characterized and have to be investigated further to allow for an overall assessment of their pathogenic potentials.
2.3. EHEC-Hly
The enterohemolysin or EHEC hemolysin (EHEC-Hly) that has been analyzed in detail is a heat labile toxin which belongs to the repeats-in-toxin (RFX) family [137,138,139]. Therefore, it is characterized by repeats of glycine-rich nonapeptides that are located in proximity to its carboxy-terminus [140,141].
EHEC-Hly is encoded in most EHEC serotypes, which are regularly associated with the development of HUS, the most severe course of an EHEC infection [138]. The actual involvement of the toxin in this infection process was proven by the detection of EHEC-Hly specific antibodies in patients who were suffering from HUS [138,142]. Moreover, it can be found in eae-negative STEC, which cause diarrhea in humans, in isolates from livestock such as cattle and sheep, and isolates from foodstuff [23,143,144,145].
After secretion by the type I secretion system, the nonapeptide repeats bind Ca2+ ions. In turn, this leads to the activation of the toxin via a conformational switch and the stabilization of the terminal domains [146,147]. Finally, this concludes with the exposure of a hydrophobic domain which is located at the N-terminus region and required for the toxic effect itself. It therefore mediates pore formation in the target cells [138]. Whether pore formation occurs in an oligomeric form, such as that described for the Staphylococcus aureus’ α-hemolysis, or in a monomeric way is still unknown. The same is true for the mechanism which is needed to form the first contact with the membrane of erythrocytes and eukaryotic cells, both of which are the typical target cells of EHEC-Hly [148,149]. In addition, and as something that is similar to all toxins of the RFX family, EHEC-Hly requires post-transformational activation by fatty acylation of specific lysine residues [150]. Because it is highly conserved throughout the STEC family and is present in most EHEC isolates, it has been proposed as a detection marker for EHEC [151].
EHEC-Hly occurs in two different forms. On the one hand as a free form and on the other hand as an outer membrane vesicle (OMV)-associated form. Both forms are cytotoxic but show differences regarding their mechanism towards different cell types such as microvascular endothelial and intestinal epithelial cells [86,152]. OMV-associated EHEC-Hly does not lyse the target cells directly, while the free version does. By binding to the OMV, EHEC-Hly is shuffled into the target cells, separated from the vesicle by lysozymes, and—after translocation to the mitochondria—it activates caspase-9-mediated apoptosis [152].
Similar to the aforementioned Stx, several regulatory pathways are known for EHEC-Hly. In a study by Li et al. [124], the authors showed that the expression of EHEC-Hly is regulated by the sigma factor RpoS, H-NS, and the sRNA DsrA. Mutations in the RpoS—the mediator of the general stress response—inhibited the expression of EHEC-Hly. For H-NS and DsrA, Li et al. [124] described that the different regulation pathways depended on the temperature. For instance, H-NS inhibit the expression of EHEC-Hly more efficiently when the temperature is higher (37 °C vs. 30 °C). In contrast, the effect of DsrA could either be direct or indirect. Again, this depended on temperature. At a lower temperature (30 °C) H-NS was involved in the DrsA-triggered regulation, while at higher temperatures (37 °C) DsrA interacted directly. In contrast to the effect of H-NS, DsrA increased the expression of EHEC-Hly by inhibiting H-NS or direct transcription activation [124].
2.4. Cdt-V
In 1987, Johnson and Lior [153] described another cytotoxin which they named cytolethal distending toxin (Cdt) in accordance with its effect on CHO (Chinese hamster ovary) cells. One of their colleagues, Anderson, reported only a few months later that Cdt is an important virulence factor in an E. coli isolate, which originated from a young patient with a severe course of gastroenteritis infection [144]. During the following years, many variants of the Cdt were identified in multiple genera including E. coli, Campylobacter sp., Salmonella Typhi, Helicobacter sp., and several others [43,154,155,156].
Cdts are known to form a large subfamily of AB2 toxins and spread throughout a variety of Gram-negative bacteria (reviewed in [157]). Amongst this extensive toxin family, there are five different Cdt variants known at the present day which are only found in E. coli. Cdt-I and Cdt-II are encoded by enteropathogenic E. coli (EPEC) and were not found in STEC [145,158,159], whereas Cdt-V is the variant which is typically encoded by STEC. Besides Cdt-V, Cdt-III can also be found in STEC, but at a much lower rate [159]. Bielaszewska et al. [159] purified Cdt-III and Cdt-V of eae-negative patients isolates and verified the expression of these toxins during the infection process by CHO cell culture tests.
Cdt-V—as with all Cdt variants—consists of the three distinct subunits CdtA, CdtB, and CdtC, which assemble in an AB2 formation. In Cdt, the enzymatically active A-subunit is composed of the CdtB chain which itself is highly conserved among the different bacteria [160]. The B-subunit is required for the interaction of the holotoxin with the target cell and is assembled by the CdtA and CdtC chain [161,162]. Cdt-V shows DNaseI activity and, as a response to DNA damage, arrests the cell cycle in the G1- or G2-phase depending on the target cells. Hereby, the cell morphology is distended, which can lead to cell death [160,163].
Multiple pathways and interaction partners which are affected by the Cdts are known [160,163,164,165,166,167]. Nevertheless, there are only few studies that target the regulation of the toxins. Oogai et al. [168] published a prediction of regulated genes by sRNAs in the human oral pathogen Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans amongst which Cdt was one of those reported. This concept of regulation was previously described for other toxins, e.g., the alpha-toxin of Staphylococcus aureus and could be one possibility for the regulation of Cdt in STEC [168,169].
All of the toxins described above are frequently detected within the virulence profiles of STEC isolates from food, environment, livestock, and in EHEC isolates of patients. In addition, they are often found in combination, forming complex multiple toxin networks. The last part of this review will focus on three particular LEE-negative STEC strains whose characterization could count as novel assessments in the understanding of the virulence of this subgroup of STEC.
3. The Lee-Negative O113:H21 Strains 98 NK2 and TS18/08, and the E. coli O104:H4 Outbreak Strain
LEE-negative STEC strains are frequently detected within human, animal, food, and environmental isolates. However, these strains were rated as less virulent than STEC carrying the LEE. The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) classifies LEE-negative STEC as less dangerous for human health and states that the serogroups O157, O26, O103, O145, O111, and O104 in combination with the stx2 and eae genes are associated with a higher risk of developing severe infections [22]. However, there are examples which do not fit into this simplified scheme of assessing the pathogenicity of STEC. In 1999, Paton et al. [34] published a study on an E. coli O113:H21 which lacked the LEE but was responsible for a HUS outbreak in Australia. Comparative multi-locus sequence typing (MLST) studies on E. coli O113:H21 isolates from all over the world revealed that especially strains originating from Australia comprised sequence type ST-820 rather than ST-223, which was predominantly found for strains of serotype O113:H21. These results also pertain to the strain described by Paton et al. [34] and indicate either the association with virulence or regional clustering of this sequence type [88]. Subsequent studies by Paton et al. [92] on the E. coli O113:H21 strain 98 NK2 revealed that it also produces a second AB5 toxin, the SubAB, which caused cytotoxic effects in cell culture experiments when the Stx was depleted from the supernatant by adding a recombinant E. coli strain which specifically binds Stx. This finding was a novelty as such genetic equipment for any other STEC or EHEC had not been described before. Furthermore, a new field of toxin research was opened which led to the identification of several other variants of SubAB within STEC [76,133,134]. Currently, the evolutional origin of SubAB is not known. Paton et al. [92] hypothesized that it arose from genetic rearrangements of harmless genes that become dangerous when encoded and expressed in parallel, and, as shown by many virulence profiling studies, appear to be encoded exclusively in LEE-negative STEC [23,28,44,134]. E. coli O113:H21 strain 98 NK2 in particular contains the genes for Stx2, SubAB1, EHEC-Hly, Saa, and Sab [34].
In contrast to the LEE-negative EHEC studied by Paton et al. [34,92] the LEE-negative strain of the 2011 outbreak in Germany does not share the genetic composition attributed to EHEC. As discussed above, this strain is described as an enteroaggregative E. coli strain with a stx2a prophage, which in addition carries a plasmid encoding an extended-spectrum beta-lactamase [60]. This E. coli O104:H4 revealed a unique pathogenicity, 22% of all documented cases developed HUS. This rate is significantly higher than the number of HUS cases of other EHEC strains, which usually lies between 1–5% [46,55,56,57]. Furthermore, the patients who developed HUS were of uncharacteristic age. Typically, children are more prone to develop HUS upon EHEC infection with the highest rate of incidence among the group of children younger than five years. In 2011, however, the median age of HUS patients was 42 (reviewed in [170]).
Besides these two strains, which have been isolated from human feces, there are also LEE-negative STEC which have not caused any infection so far, but are of scientific interest concerning their genetic virulence equipment. One of these strains is the E. coli O113:H21 TS18/08. This strain was originally isolated during the study of Slanec et al. [23] from mixed minced meat and characterized as an STEC of serotype O113:H21. Its virulence profile is determined by the presence of the stx2a genes as well as the genes for the toxins SubAB1 and Cdt-V. Furthermore, it encodes EHEC-Hly and Iha [23,114]. To our knowledge, this strain/virulence profile is not linked to any infection, but represents an example for the research field of multiple toxin expression in STEC.
The characterization of TS18/08 on the genetic level and the finding that it encodes three different toxins motivated the researchers to investigate whether the transcription of all toxins occur at the same time and whether SubAB contributes to the overall cytotoxicity of the strain itself [23,114]. By using quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR), the transcription levels at different time points within a batch growth were detected. The mRNA levels for subA1 and cdt-V peaked after 3 h of cultivation in the late exponential growth phase. In contrast, stx2 revealed the highest mRNA-level within the stationary phase after 6 h. The overall highest transcription level of all three toxins was achieved by cdt-V at its transcription maximum, most likely caused by the induction of the cdt-V encoding prophage within this strain. The second largest amount of transcripts was allocated to subAB1 and the smallest amount to stx2. Analysis on the cytotoxicity to Vero cells revealed that SubAB contributes to the toxicity of this strain. This study showed that each toxin of E. coli O113:H21 strain TS18/08 was transcribed and that changes on mRNA levels of the three different toxins corresponded to the growth phase of a discontinuous culture [114]. The transcription maxima at different time points showed different expression profiles, which may indicate alternative regulation patterns for each toxin.
Based on the capacity to code for a second AB5 toxin, to cause untypical and high pathogenicity, and to encode and express three toxins of different toxin families—imprinted by the strains E. coli O113:H21 98 KN2, E. coli O104:H4, and E. coli O113:H21 TS18/08, respectively—LEE-negative strains should not be underestimated with respect to their risk for virulence.
4. Conclusions
This short review showed the complexity and variability of virulence factors of LEE-negative STEC focusing on the toxins. The typically conducted virulence profiling studies only reveal information concerning the genetic state of an STEC/EHEC. Even if the amount of such data is enormous, there is an increased demand for the analyses of these toxins on the protein level.
The outbreak strains from Australia in 1999 and Germany in 2011 exemplify the potentially severe virulence of LEE-negative STEC. As described above, little is known about the regulation of the expression of the different virulence factors, especially toxins, when represented in one single STEC. Concerning this, it is necessary to further explore the expression and regulation mechanisms of different STEC toxins. In this context, whole genome sequencing could be one major technique upon which these studies could be based. Analyses on the genetic location of regulatory proteins, virulence factors in general, and regulatory binding sites within the genome would allow for an elucidation of possible regulatory networks. In addition, it is indispensable to analyze synergistic effects within multiple toxin networks. Knowing specific regulation mechanisms which are linked to respective metabolic and infectious states of the STEC will likely allow for the exploration of their pathogenicity in general and will lead to an improved assessment of their threat to human health.
Author Contributions
Writing—Original Draft Preparation, M.K.; Writing—Review & Editing, M.K., H.B., and H.S.
Funding
This work was funded by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft, grants Schm 1360/11-1 and Ba 2087/6-1.
Acknowledgments
We thank Nicolai S. Waniek for comments on the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Persad, A.K.; LeJeune, J.T. Animal reservoirs of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli. Microbiol. Spectr. 2014, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorpe, C.M. Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli infection. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2004, 38, 1298–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eklund, M.; Leino, K.; Siitonen, A. Clinical Escherichia coli strains carrying stx genes: Stx variants and stx-positive virulence profiles. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2002, 40, 4585–4593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, H.; Hensel, M. Pathogenicity islands in bacterial pathogenesis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2004, 17, 14–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abedon, S.T.; Lejeune, J.T. Why bacteriophage encode exotoxins and other virulence factors. Evol. Bioinform. Online 2005, 1, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, T.J.; Nolan, L.K. Pathogenomics of the virulence plasmids of Escherichia coli. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2009, 73, 750–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Käppeli, U.; Hächler, H.; Giezendanner, N.; Beutin, L.; Stephan, R. Human Infections with Non-O157 Shiga Toxin–producing Escherichia coli, Switzerland, 2000–2009. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Käppeli, U.; Hächler, H.; Giezendanner, N.; Cheasty, T.; Stephan, R. Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli O157 associated with human infections in Switzerland, 2000–2009. Epidemiol. Infect. 2011, 139, 1097–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fierz, L.; Cernela, N.; Hauser, E.; Nüesch-Inderbinen, M.; Stephan, R. Characteristics of Shigatoxin-producing Escherichia coli strains isolated during 2010–2014 from human infections in Switzerland. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarvis, K.G.; Giron, J.A.; Jerse, A.E.; McDaniel, T.K.; Donnenberg, M.S.; Kaper, J.B. Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli contains a putative type III secretion system necessary for the export of proteins involved in attaching and effacing lesion formation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 7996–8000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDaniel, T.K.; Jarvis, K.G.; Donnenberg, M.S.; Kaper, J.B. A genetic locus of enterocyte effacement conserved among diverse enterobacterial pathogens. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 1664–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jerse, A.E.; Yu, J.; Tall, B.D.; Kaper, J.B. A genetic locus of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli necessary for the production of attaching and effacing lesions on tissue culture cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 7839–7843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarvis, K.G.; Kaper, J.B. Secretion of extracellular proteins by enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli via a putative type III secretion system. Infect. Immun. 1996, 64, 4826–4829. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Perna, N.T.; Mayhew, G.F.; Pósfai, G.; Elliott, S.; Donnenberg, M.S.; Kaper, J.B.; Blattner, F.R. Molecular evolution of a pathogenicity island from enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7. Infect. Immun. 1998, 66, 3810–3817. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kenny, B.; DeVinney, R.; Stein, M.; Reinscheid, D.J.; Frey, E.A.; Finlay, B.B. Enteropathogenic E. coli (EPEC) transfers its receptor for intimate adherence into mammalian cells. Cell 1997, 91, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnenberg, M.S.; Yu, J.; Kaper, J.B. A second chromosomal gene necessary for intimate attachment of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli to epithelial cells. J. Bacteriol. 1993, 175, 4670–4680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donnenberg, M.S.; Tzipori, S.; McKee, M.L.; O’Brien, A.D.; Alroy, J.; Kaper, J.B. The role of the eae gene of enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli in intimate attachment in vitro and in a porcine model. J. Clin. Investig. 1993, 92, 1418–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, W.; Li, Y.; Vallance, B.A.; Finlay, B.B. Locus of enterocyte effacement from Citrobacter rodentium: Sequence analysis and evidence for horizontal transfer among attaching and effacing pathogens. Infect. Immun. 2001, 69, 6323–6335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertin, Y.; Boukhors, K.; Livrelli, V.; Martin, C. Localization of the insertion site and pathotype determination of the locus of enterocyte effacement of shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli strains. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kagkli, D.M.; Weber, T.P.; Van den Bulcke, M.; Folloni, S.; Tozzoli, R.; Morabito, S.; Ermolli, M.; Gribaldo, L.; Van den Eede, G. Application of the modular approach to an in-house validation study of real-time PCR methods for the detection and serogroup determination of verocytotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 6954–6963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eichhorn, I.; Heidemanns, K.; Semmler, T.; Kinnemann, B.; Mellmann, A.; Harmsen, D.; Anjum, M.F.; Schmidt, H.; Fruth, A.; Valentin-Weigand, P.; et al. Highly virulent non-O157 enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli (EHEC) serotypes reflect similar phylogenetic lineages, providing new insights into the evolution of EHEC. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 7041–7047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EFSA Panel on Biological Hazards Scientific Opinion on VTEC-seropathotype and scientific criteria regarding pathogenicity assessment. EFSA J. 2013, 11. [CrossRef]
- Slanec, T.; Fruth, A.; Creuzburg, K.; Schmidt, H. Molecular analysis of virulence profiles and Shiga toxin genes in food-borne Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 6187–6197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bettelheim, K.A. The non-O157 Shiga-toxigenic (verocytotoxigenic) Escherichia coli; Under-Rated Pathogens. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2007, 33, 67–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, H.-J.; Lee, S.; Kim, W.; An, J.-U.; Kim, J.; Kim, D.; Cho, S. Prevalence, virulence potential, and pulsed-field gel electrophoresis profiling of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli strains from cattle. Gut Pathog. 2017, 9, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chui, L.; Li, V.; Fach, P.; Delannoy, S.; Malejczyk, K.; Patterson-Fortin, L.; Poon, A.; King, R.; Simmonds, K.; Scott, A.N.; et al. Molecular profiling of Escherichia coli O157:H7 and non-O157 strains isolated from humans and cattle in Alberta, Canada. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 986–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galli, L.; Miliwebsky, E.; Irino, K.; Leotta, G.; Rivas, M. Virulence profile comparison between LEE-negative Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli (STEC) strains isolated from cattle and humans. Vet. Microbiol. 2010, 143, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newton, H.J.; Sloan, J.; Bulach, D.M.; Seemann, T.; Allison, C.C.; Tauschek, M.; Robins-Browne, R.M.; Paton, J.C.; Whittam, T.S.; Paton, A.W.; et al. Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli strains negative for locus of enterocyte effacement. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2009, 15, 372–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauser, E.; Mellmann, A.; Semmler, T.; Stoeber, H.; Wieler, L.H.; Karch, H.; Kuebler, N.; Fruth, A.; Harmsen, D.; Weniger, T.; et al. Phylogenetic and molecular analysis of food-borne Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 2731–2740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsinghorst, E.A.; Kopecko, D.J. Molecular cloning of epithelial cell invasion determinants from enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect. Immun. 1992, 60, 2409–2417. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fleckenstein, J.M.; Kopecko, D.J.; Warren, R.L.; Elsinghorst, E.A. Molecular characterization of the tia invasion locus from enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect. Immun. 1996, 64, 2256–2265. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Paton, A.W.; Srimanote, P.; Woodrow, M.C.; Paton, J.C. Characterization of Saa, a novel autoagglutinating adhesin produced by locus of enterocyte effacement-negative Shiga-toxigenic Escherichia coli strains that are virulent for humans. Infect. Immun. 2001, 69, 6999–7009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herold, S.; Paton, J.C.; Paton, A.W. Sab, a novel autotransporter of locus of enterocyte effacement-negative shiga-toxigenic Escherichia coli O113:H21, contributes to adherence and biofilm formation. Infect. Immun. 2009, 77, 3234–3243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paton, A.W.; Woodrow, M.C.; Doyle, R.M.; Lanser, J.A.; Paton, J.C. Molecular characterization of a Shiga toxigenic Escherichia coli O113:H21 strain lacking eae responsible for a cluster of cases of hemolytic-uremic syndrome. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1999, 37, 3357–3361. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sandt, C.H.; Hill, C.W. Four different genes responsible for nonimmune immunoglobulin-binding activities within a single strain of Escherichia coli. Infect. Immun. 2000, 68, 2205–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandt, C.H.; Hopper, J.E.; Hill, C.W. Activation of prophage eib genes for immunoglobulin-binding proteins by genes from the IbrAB genetic island of Escherichia coli ECOR-9. J. Bacteriol. 2002, 184, 3640–3648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucchesi, P.M.A.; Krüger, A.; Parma, A.E. Distribution of saa gene variants in verocytotoxigenic Escherichia coli isolated from cattle and food. Res. Microbiol. 2006, 157, 263–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toma, C.; Nakasone, N.; Miliwebsky, E.; Higa, N.; Rivas, M.; Suzuki, T. Differential adherence of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli harboring saa to epithelial cells. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2008, 298, 571–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jose, J.; Jähnig, F.; Meyer, T.F. Common structural features of IgA1 protease-like outer membrane protein autotransporters. Mol. Microbiol. 1995, 18, 378–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarr, P.I.; Bilge, S.S.; Vary, J.C.; Jelacic, S.; Habeeb, R.L.; Ward, T.R.; Baylor, M.R.; Besser, T.E. Iha: A novel Escherichia coli O157:H7 adherence-conferring molecule encoded on a recently acquired chromosomal island of conserved structure. Infect. Immun. 2000, 68, 1400–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldberg, M.B.; Boyko, S.A.; Butterton, J.R.; Stoebner, J.A.; Payne, S.M.; Calderwood, S.B. Characterization of a Vibrio cholerae virulence factor homologous to the family of TonB-dependent proteins. Mol. Microbiol. 1992, 6, 2407–2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rashid, R.A.; Tarr, P.I.; Moseley, S.L. Expression of the Escherichia coli IrgA homolog adhesin is regulated by the ferric uptake regulation protein. Microb. Pathog. 2006, 41, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, J.R.; Russo, T.A.; Tarr, P.I.; Carlino, U.; Bilge, S.S.; Vary, J.C.; Stell, A.L. Molecular epidemiological and phylogenetic associations of two novel putative virulence genes, iha and iroN (E. coli), among Escherichia coli isolates from patients with urosepsis. Infect. Immun. 2000, 68, 3040–3047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tozzoli, R.; Caprioli, A.; Cappannella, S.; Michelacci, V.; Marziano, M.L.; Morabito, S. Production of the subtilase AB5 cytotoxin by Shiga toxin-negative Escherichia coli. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 178–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bondì, R.; Chiani, P.; Michelacci, V.; Minelli, F.; Caprioli, A.; Morabito, S. The gene tia, harbored by the subtilase-encoding pathogenicity island, is involved in the ability of locus of enterocyte effacement-negative Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli strains to invade monolayers of epithelial cells. Infect. Immun. 2017, 85, e00613–e00617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anonymous. Infektionsepidemiologisches Jahrbuch meldepflichtiger Krankheiten für 2016; Robert-Koch-Institut: Berlin, Germany, 2017; ISBN 9783896062635. [Google Scholar]
- Fruth, A.; Prager, R.; Tietze, E.; Rabsch, W.; Flieger, A. Molecular epidemiological view on Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli causing human disease in Germany: Diversity, prevalence, and outbreaks. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2015, 305, 697–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karmali, M.A.; Mascarenhas, M.; Shen, S.; Ziebell, K.; Johnson, S.; Reid-Smith, R.; Isaac-Renton, J.; Clark, C.; Rahn, K.; Kaper, J.B. Association of genomic O island 122 of Escherichia coli EDL 933 with verocytotoxin-producing Escherichia coli seropathotypes that are linked to epidemic and/or serious disease. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 4930–4940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mellmann, A.; Fruth, A.; Friedrich, A.W.; Wieler, L.H.; Harmsen, D.; Werber, D.; Middendorf, B.; Bielaszewska, M.; Karch, H. Phylogeny and disease association of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli O91. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2009, 15, 1474–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melton-Celsa, A.R.; Darnell, S.C.; O’Brien, A.D. Activation of Shiga-like toxins by mouse and human intestinal mucus correlates with virulence of enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O91:H21 isolates in orally infected, streptomycin-treated mice. Infect. Immun. 1996, 64, 1569–1576. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Feng, P.C.H.; Reddy, S. Prevalences of Shiga toxin subtypes and selected other virulence factors among Shiga-toxigenic Escherichia coli isolated from fresh produce. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 6917–6923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bielaszewska, M.; Stoewe, F.; Fruth, A.; Zhang, W.; Prager, R.; Brockmeyer, J.; Mellmann, A.; Karch, H.; Friedrich, A.W. Shiga toxin, cytolethal distending toxin, and hemolysin repertoires in clinical Escherichia coli O91 isolates. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2009, 47, 2061–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mughini-Gras, L.; van Pelt, W.; van der Voort, M.; Heck, M.; Friesema, I.; Franz, E. Attribution of human infections with Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli (STEC) to livestock sources and identification of source-specific risk factors, The Netherlands (2010–2014). Zoonoses Public Health 2018, 65, e8–e22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, P.C.H.; Delannoy, S.; Lacher, D.W.; Bosilevac, J.M.; Fach, P.; Beutin, L. Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli strains of O91 serogroup isolated from food and environmental samples. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anonymous. Infektionsepidemiologisches Jahrbuch meldepflichtiger Krankheiten für 2015; Robert-Koch-Institut: Berlin, Germany, 2016; ISBN 9783896062505. [Google Scholar]
- Anonymous. Infektionsepidemiologisches Jahrbuch meldepflichtiger Krankheiten für 2014; Robert-Koch-Institut: Berlin, Germany, 2015; ISBN 9783896062635. [Google Scholar]
- Anonymous. Infektionsepidemiologisches Jahrbuch meldepflichtiger Krankheiten für 2013; Robert-Koch-Institut: Berlin, Germany, 2014; ISBN 9783896062505. [Google Scholar]
- Scheutz, F.; Nielsen, E.M.; Frimodt-Møller, J.; Boisen, N.; Morabito, S.; Tozzoli, R.; Nataro, J.P.; Caprioli, A. Characteristics of the enteroaggregative Shiga toxin/verotoxin-producing Escherichia coli O104:H4 strain causing the outbreak of haemolytic uraemic syndrome in Germany, may to june 2011. Eurosurveillance 2011, 16, 19889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasko, D.A.; Webster, D.R.; Sahl, J.W.; Bashir, A.; Boisen, N.; Scheutz, F.; Paxinos, E.E.; Sebra, R.; Chin, C.-S.; Iliopoulos, D.; et al. Origins of the E. coli strain causing an outbreak of hemolytic–uremic syndrome in Germany. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 709–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brzuszkiewicz, E.; Thürmer, A.; Schuldes, J.; Leimbach, A.; Liesegang, H.; Meyer, F.-D.; Boelter, J.; Petersen, H.; Gottschalk, G.; Daniel, R. Genome sequence analyses of two isolates from the recent Escherichia coli outbreak in Germany reveal the emergence of a new pathotype: Entero-Aggregative-Haemorrhagic Escherichia coli (EAHEC). Arch. Microbiol. 2011, 193, 883–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beutin, L.; Miko, A.; Krause, G.; Pries, K.; Haby, S.; Steege, K.; Albrecht, N. Identification of human-pathogenic strains of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli from food by a combination of serotyping and molecular typing of Shiga toxin genes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 4769–4775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cadona, J.S.; Bustamante, A.V.; Parma, A.E.; Lucchesi, P.M.A.; Sanso, A.M. Distribution of additional virulence factors related to adhesion and toxicity in Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli isolated from raw products in Argentina. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2013, 56, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zweifel, C.; Fierz, L.; Cernela, N.; Laaksonen, S.; Fredriksson-Ahomaa, M.; Stephan, R. Characteristics of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli O157 in slaughtered reindeer from Northern Finland. J. Food Prot. 2017, 454–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monaghan, A.M.; Byrne, B.; McDowell, D.; Carroll, A.M.; McNamara, E.B.; Bolton, D.J. Characterization of farm, food, and clinical Shiga toxin–producing Escherichia coli (STEC) O113. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2012, 9, 1088–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cergole-Novella, M.C.; Nishimura, L.S.; dos Santos, L.F.; Irino, K.; Vaz, T.M.I.; Bergamini, A.M.M.; Guth, B.E.C. Distribution of virulence profiles related to new toxins and putative adhesins in Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli isolated from diverse sources in Brazil. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2007, 274, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buvens, G.; Lauwers, S.; Piérard, D. Prevalence of subtilase cytotoxin in verocytotoxin-producing Escherichia coli isolated from humans and raw meats in Belgium. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2010, 29, 1395–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosilevac, J.M.; Koohmaraie, M. Prevalence and characterization of non-O157 Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli isolates from commercial ground beef in the United States. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 2103–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dehkordi, F.; Yazdani, F.; Mozafari, J.; Valizadeh, Y. Virulence factors, serogroups and antimicrobial resistance properties of Escherichia coli strains in fermented dairy products. BMC Res. Notes 2014, 7, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, T.; Schellhorn, H.E. Global effect of RpoS on gene expression in pathogenic Escherichia coli O157:H7 strain EDL933. BMC Genom. 2009, 10, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pigatto, C.P.; Schocken-Iturrino, R.P.; Souza, E.M.; Pedrosa, F.O.; Comarella, L.; Irino, K.; Kato, M.A.M.F.; Farah, S.M.S.S.; Warth, J.F.; Fadel-Picheth, C.M.T. Virulence properties and antimicrobial susceptibility of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli strains isolated from healthy cattle from Paraná State, Brazil. Can. J. Microbiol. 2008, 54, 588–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polifroni, R.; Etcheverría, A.I.; Sanz, M.E.; Cepeda, R.E.; Krüger, A.; Lucchesi, P.M.A.; Fernández, D.; Parma, A.E.; Padola, N.L. Molecular characterization of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli isolated from the environment of a dairy farm. Curr. Microbiol. 2012, 65, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pradel, N.; Bertin, Y.; Martin, C.; Livrelli, V. Molecular analysis of shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli strains isolated from hemolytic-uremic syndrome patients and dairy samples in France. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 2118–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz-Sánchez, S.; Sánchez, S.; Sánchez, M.; Herrera-León, S.; Hanning, I.; Vidal, D. Detection and characterization of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli in game meat and ready-to-eat meat products. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2012, 160, 179–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miko, A.; Rivas, M.; Bentancor, A.; Delannoy, S.; Fach, P.; Beutin, L. Emerging types of Shiga toxin-producing E. coli (STEC) O178 present in cattle, deer, and humans from Argentina and Germany. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2014, 4, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miko, A.; Pries, K.; Haby, S.; Steege, K.; Albrecht, N.; Krause, G.; Beutin, L. Assessment of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli isolates from wildlife meat as potential pathogens for humans. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 6462–6470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nüesch-Inderbinen, M.T.; Funk, J.; Cernela, N.; Tasara, T.; Klumpp, J.; Schmidt, H.; Stephan, R. Prevalence of subtilase cytotoxin-encoding subAB variants among Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli strains isolated from wild ruminants and sheep differs from that of cattle and pigs and is predominated by the new allelic variant subAB2-2. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2015, 305, 124–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orden, J.A.; Horcajo, P.; de la Fuente, R.; Ruiz-Santa-Quiteria, J.A.; Domínguez-Bernal, G.; Carrión, J. Subtilase cytotoxin-coding genes in verotoxin-producing Escherichia coli strains from sheep and goats differ from those from Cattle. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 8259–8264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez, S.; Beristain, X.; Martínez, R.; García, A.; Martín, C.; Vidal, D.; Díaz-Sánchez, S.; Rey, J.; Alonso, J.M.; Herrera-León, S. Subtilase cytotoxin encoding genes are present in human, sheep and deer intimin-negative, Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli O128:H2. Vet. Microbiol. 2012, 159, 531–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, P.C.H.; Councell, T.; Keys, C.; Monday, S.R. Virulence characterization of Shiga-toxigenic Escherichia coli isolates from wholesale produce. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 343–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irino, K.; Kato, M.A.M.F.; Vaz, T.M.I.; Ramos, I.I.; Souza, M.A.C.; Cruz, A.S.; Gomes, T.A.T.; Vieira, M.A.M.; Guth, B.E.C. Serotypes and virulence markers of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli (STEC) isolated from dairy cattle in São Paulo State, Brazil. Vet. Microbiol. 2005, 105, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso, M.Z.; Krüger, A.; Sanz, M.E.; Padola, N.L.; Lucchesi, P.M.A. Serotypes, virulence profiles and stx subtypes of Shigatoxigenic Escherichia coli isolated from chicken derived products. Rev. Argent. Microbiol. 2016, 48, 325–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balière, C.; Rincé, A.; Delannoy, S.; Fach, P.; Gourmelon, M. Molecular profiling of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli and enteropathogenic E. coli strains isolated from French coastal environments. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 3913–3927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baranzoni, G.M.; Fratamico, P.M.; Gangiredla, J.; Patel, I.; Bagi, L.K.; Delannoy, S.; Fach, P.; Boccia, F.; Anastasio, A.; Pepe, T. Characterization of Shiga toxin subtypes and virulence genes in porcine Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amézquita-López, B.A.; Quiñones, B.; Lee, B.G.; Chaidez, C. Virulence profiling of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli recovered from domestic farm animals in Northwestern Mexico. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2014, 4, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cáceres, M.E.; Etcheverría, A.I.; Fernández, D.; Rodríguez, E.M.; Padola, N.L. Variation in the distribution of putative virulence and colonization factors in Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli isolated from different categories of cattle. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aldick, T.; Bielaszewska, M.; Uhlin, B.E.; Humpf, H.-U.; Wai, S.N.; Karch, H. Vesicular stabilization and activity augmentation of enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli haemolysin. Mol. Microbiol. 2009, 71, 1496–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akiyama, Y.; Futai, H.; Saito, E.; Ogita, K.; Sakae, H.; Fukunaga, M.; Tsuji, H.; Chikahira, M.; Iguchi, A. Shiga toxin subtypes and virulence genes in Escherichia coli isolated from cattle. Jpn. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 70, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, P.C.H.; Delannoy, S.; Lacher, D.W.; dos Santos, L.F.; Beutin, L.; Fach, P.; Rivas, M.; Hartland, E.L.; Paton, A.W.; Guth, B.E.C. Genetic diversity and virulence potential of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli O113:H21 strains isolated from clinical, environmental, and food sources. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 4757–4763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, F.H.; Guth, B.E.C.; Piazza, R.M.; Leão, S.C.; Ludovico, A.; Ludovico, M.S.; Dahbi, G.; Marzoa, J.; Mora, A.; Blanco, J.; et al. Diversity of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli in sheep flocks of Paraná State, southern Brazil. Vet. Microbiol. 2015, 175, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steyert, S.R.; Sahl, J.W.; Fraser, C.M.; Teel, L.D.; Scheutz, F.; Rasko, D.A. Comparative genomics and stx phage characterization of LEE-negative Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2012, 2, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Brien, A.D.; LaVeck, G.D.; Thompson, M.R.; Formal, S.B. Production of Shigella dysenteriae type 1-like cytotoxin by Escherichia coli. J. Infect. Dis. 1982, 146, 763–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paton, A.W.; Srimanote, P.; Talbot, U.M.; Wang, H.; Paton, J.C. A new family of potent AB(5) cytotoxins produced by Shiga toxigenic Escherichia coli. J. Exp. Med. 2004, 200, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, H.; Karch, H.; Beutin, L. The large-sized plasmids of enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157 strains encode hemolysins which are presumably members of the E. coli alpha-hemolysin family. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1994, 117, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, W.M.; Lior, H. Response of Chinese hamster ovary cells to a cytolethal distending toxin (CDT) of Escherichia coli and possible misinterpretation as heat-labile (LT) enterotoxin. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1987, 43, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beddoe, T.; Paton, A.W.; Rô Me Le Nours, J.; Rossjohn, J.; Paton, J.C. Structure, biological functions and applications of the AB 5 toxins. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2015, 35, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jinadasa, R.N.; Bloom, S.E.; Weiss, R.S.; Duhamel, G.E. Cytolethal distending toxin: A conserved bacterial genotoxin that blocks cell cycle progression, leading to apoptosis of a broad range of mammalian cell lineages. Microbiology 2011, 157, 1851–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheutz, F.; Teel, L.D.; Beutin, L.; Pierard, D.; Buvens, G.; Karch, H.; Mellmann, A.; Caprioli, A.; Tozzoli, R.; Morabito, S.; et al. Multicenter evaluation of a sequence-based protocol for subtyping Shiga toxins and standardizing Stx nomenclature. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 2951–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishikawa, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Hase, A.; Ogasawara, J.; Cheasty, T.; Haruki, K. Relationship of genetic type of Shiga toxin to manifestation of bloody diarrhea due to enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli serogroup O157 isolates in Osaka City, Japan. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2000, 38, 2440–2442. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fraser, M.E.; Fujinaga, M.; Cherney, M.M.; Melton-Celsa, A.R.; Twiddy, E.M.; O’Brien, A.D.; James, M.N.G. Structure of Shiga Toxin Type 2 (Stx2) from Escherichia coli O157:H7. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 27511–27517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müthing, J.; Schweppe, C.H.; Karch, H.; Friedrich, A.W. Shiga toxins, glycosphingolipid diversity, and endothelial cell injury. Thromb. Haemost. 2009, 101, 252–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, M.J.; Teel, L.D.; Carvalho, H.M.; Melton-Celsa, A.R.; O’Brien, A.D. Development of a hybrid Shiga holotoxoid vaccine to elicit heterologous protection against Shiga toxins types 1 and 2. Vaccine 2006, 24, 4122–4129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boerlin, P.; McEwen, S.A.; Boerlin-Petzold, F.; Wilson, J.B.; Johnson, R.P.; Gyles, C.L. Associations between virulence factors of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli and disease in humans. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1999, 37, 497–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindberg, A.A.; Brown, J.E.; Strömberg, N.; Westling-Ryd, M.; Schultz, J.E.; Karlsson, K.A. Identification of the carbohydrate receptor for Shiga toxin produced by Shigella dysenteriae type 1. J. Biol. Chem. 1987, 262, 1779–1785. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fraser, M.E.; Chernaia, M.M.; Kozlov, Y.V.; James, M.N.G. Crystal structure of the holotoxin from Shigella dysenteriae at 2.5 Å resolution. Nat. Struct. Biol. 1994, 1, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein, P.E.; Boodhoo, A.; Tyrrell, G.J.; Brunton, J.L.; Read, R.J. Crystal structure of the cell-binding B oligomer of verotoxin-1 from E. coli. Nature 1992, 355, 748–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandvig, K.; Garred, Ø.; Prydz, K.; Kozlov, J.V.; Hansen, S.H.; van Deurs, B. Retrograde transport of endocytosed Shiga toxin to the endoplasmic reticulum. Nature 1992, 358, 510–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Endo, Y.; Tsurugi, K.; Yutsudo, T.; Takeda, Y.; Ogasawara, T.; Igarashi, K. Site of action of a Vero toxin (VT2) from Escherichia coli O157:H7 and of Shiga toxin on eukaryotic ribosomes: RNA N-glycosidase activity of the toxins. Eur. J. Biochem. 1988, 171, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obrig, T.G.; Moran, T.P.; Brown, J.E. The mode of action of Shiga toxin on peptide elongation of eukaryotic protein synthesis. Biochem. J. 1987, 244, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furutani, M.; Kashiwagi, K.; Ito, K.; Endo, Y.; Igarashi, K. Comparison of the modes of action of a vero toxin (a Shiga-like toxin) from Escherichia coli, of ricin, and of α-sarcin. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1992, 293, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperandio, V.; Torres, A.G.; Jarvis, B.; Nataro, J.P.; Kaper, J.B. Bacteria-host communication: The language of hormones. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 8951–8956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mühldorfer, I.; Hacker, J.; Keusch, G.T.; Acheson, D.W.; Tschäpe, H.; Kane, A.V.; Ritter, A.; Ölschläger, T.; Donohue-Rolfe, A. Regulation of the Shiga-like toxin II operon in Escherichia coli. Infect. Immun. 1996, 64, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- McGannon, C.M.; Fuller, C.A.; Weiss, A.A. Different classes of antibiotics differentially influence Shiga toxin production. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 3790–3798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, D.T.; Clarke, M.B.; Yamamoto, K.; Rasko, D.A.; Sperandio, V. The QseC adrenergic signaling cascade in enterohemorrhagic E. coli (EHEC). PLoS Pathog. 2009, 5, e1000553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauser, E.; Bruederle, M.; Reich, C.; Bruckbauer, A.; Funk, J.; Schmidt, H. Subtilase contributes to the cytotoxicity of a Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli strain encoding three different toxins. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2015, 217, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergholz, T.M.; Wick, L.M.; Qi, W.; Riordan, J.T.; Ouellette, L.M.; Whittam, T.S. Global transcriptional response of Escherichia coli O157:H7 to growth transitions in glucose minimal medium. BMC Microbiol. 2007, 7, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imlay, J.A.; Linn, S. Mutagenesis and stress responses induced in Escherichia coli by hydrogen peroxide. J. Bacteriol. 1987, 169, 2967–2976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, P.L.; Livny, J.; Neely, M.N.; Acheson, D.W.K.; Friedman, D.I.; Waldor, M.K. Bacteriophage control of Shiga toxin 1 production and release by Escherichia coli. Mol. Microbiol. 2002, 44, 957–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyler, J.S.; Mills, M.J.; Friedman, D.I. The operator and early promoter region of the Shiga toxin type 2-encoding bacteriophage 933W and control of toxin expression. J. Bacteriol. 2004, 186, 7670–7679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; McDaniel, A.D.; Wolf, L.E.; Keusch, G.T.; Waldor, M.K.; Acheson, D.W.K. Quinolone antibiotics induce Shiga toxin–encoding bacteriophages, toxin production, and death in mice. J. Infect. Dis. 2000, 181, 664–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, C.S.; Jelacic, S.; Habeeb, R.L.; Watkins, S.L.; Tarr, P.I. The risk of the hemolytic–uremic syndrome after antibiotic treatment of Escherichia coli O157:H7 infections. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 342, 1930–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vareille, M.; de Sablet, T.; Hindré, T.; Martin, C.; Gobert, A.P. Nitric oxide inhibits Shiga-toxin synthesis by enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 10199–10204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selbitschka, W.; Arnold, W.; Priefer, U.B.; Rottschäfer, T.; Schmidt, M.; Simon, R.; Pühler, A. Characterization of recA genes and recA mutants of Rhizobium meliloti and Rhizobium leguminosarum biovar viciae. Mol. Gen. Genet. 1991, 229, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinstein, D.L.; Holmes, R.K.; O’Brien, A.D. Effects of iron and temperature on shiga-like toxin I production by Escherichia coli. Infect. Immun. 1988, 56, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Granat, A.; Stewart, V.; Gillespie, J.R. RpoS, H-NS, and DsrA influence EHEC hemolysin operon (ehxCABD) transcription in Escherichia coli O157:H7 strain EDL933. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2008, 285, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kendall, M.M.; Gruber, C.C.; Rasko, D.A.; Hughes, D.T.; Sperandio, V. Hfq virulence regulation in enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7 strain 86-24. J. Bacteriol. 2011, 193, 6843–6851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacheco, A.R.; Sperandio, V. Inter-kingdom signaling: Chemical language between bacteria and host. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2009, 12, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sperandio, V.; Torres, A.G.; Girón, J.A.; Kaper, J.B. Quorum sensing is a global regulatory mechanism in enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7. J. Bacteriol. 2001, 183, 5187–5197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furukawa, T.; Yahiro, K.; Tsuji, A.B.; Terasaki, Y.; Morinaga, N.; Miyazaki, M.; Fukuda, Y.; Saga, T.; Moss, J.; Noda, M. Fatal hemorrhage induced by subtilase cytotoxin from Shiga-toxigenic Escherichia coli. Microb. Pathog. 2011, 50, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, D.C.; Paton, J.C.; Thorpe, C.M.; Paton, A.W. Clathrin-dependent trafficking of subtilase cytotoxin, a novel AB5 toxin that targets the endoplasmic reticulum chaperone BiP. Cell. Microbiol. 2008, 10, 795–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paton, A.W.; Beddoe, T.; Thorpe, C.M.; Whisstock, J.C.; Wilce, M.C.J.; Rossjohn, J.; Talbot, U.M.; Paton, J.C. AB5 subtilase cytotoxin inactivates the endoplasmic reticulum chaperone BiP. Nature 2006, 443, 548–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Funk, J.; Biber, N.; Schneider, M.; Hauser, E.; Enzenmuller, S.; Fortsch, C.; Barth, H.; Schmidt, H. Cytotoxic and apoptotic effects of recombinant subtilase cytotoxin variants of shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli. Infect. Immun. 2015, 83, 2338–2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marquez, L.B.; Velazquez, N.; Repetto, H.A.; Paton, A.W.; Paton, J.C.; Ibarra, C.; Silberstein, C. Effects of Escherichia coli subtilase cytotoxin and Shiga toxin 2 on primary cultures of human renal tubular epithelial cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e87022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michelacci, V.; Tozzoli, R.; Caprioli, A.; Martínez, R.; Scheutz, F.; Grande, L.; Sánchez, S.; Morabito, S. A new pathogenicity island carrying an allelic variant of the subtilase cytotoxin is common among Shiga toxin producing Escherichia coli of human and ovine origin. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2013, 19, E149–E156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Funk, J.; Stoeber, H.; Hauser, E.; Schmidt, H. Molecular analysis of subtilase cytotoxin genes of food-borne Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli reveals a new allelic subAB variant. BMC Microbiol. 2013, 13, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yahiro, K.; Tsutsuki, H.; Ogura, K.; Nagasawa, S.; Moss, J.; Noda, M. DAP1, a negative regulator of autophagy, controls SubAB-mediated apoptosis and autophagy. Infect. Immun. 2014, 82, 4899–4908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- May, K.L.; Paton, J.C.; Paton, A.W. Escherichia coli subtilase cytotoxin induces apoptosis regulated by host Bcl-2 family proteins Bax/Bak. Infect. Immun. 2010, 78, 4691–4696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, M.E.; Welch, R.A. Characterization of an RTX toxin from enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7. Infect. Immun. 1996, 64, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, H.; Beutin, L.; Karch, H. Molecular analysis of the plasmid-encoded hemolysin of Escherichia coli O157:H7 strain EDL 933. Infect. Immun. 1995, 63, 1055–1061. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bielaszewska, M.; Aldick, T.; Bauwens, A.; Karch, H. Hemolysin of enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli: Structure, transport, biological activity and putative role in virulence. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2014, 304, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumann, U.; Wu, S.; Flaherty, K.M.; McKay, D.B. Three-dimensional structure of the alkaline protease of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: A two-domain protein with a calcium binding parallel beta roll motif. EMBO J. 1993, 12, 3357–3364. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ostolaza, H.; Soloaga, A.; Goni, F.M. The binding of divalent cations to Escherichia coli alpha-haemolysin. Eur. J. Biochem. 1995, 228, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Cheng, B.; Feng, L.; Jing, H.; Yang, J.; Zhao, G.; Wang, H.; Li, H. Serological investigations on patients with hemolytic uremic syndromes due to enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7 infection. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi 2002, 23, 114–118. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Alvarez, R.S.; Sacerdoti, F.; Jancic, C.; Paton, A.W.; Paton, J.C.; Ibarra, C.; Amaral, M.M. Comparative characterization of Shiga toxin type 2 and subtilase cytotoxin effects on human renal epithelial and endothelial cells grown in monolayer and bilayer conditions. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0158180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, J.D.; MacNab, A.J.; Gransden, W.R.; Damm, S.M.; Johnson, W.M.; Lior, H. Gastroenteritis and encephalopathy associated with a strain of Escherichia coli 055:K59:H4 that produced a cytolethal distending toxin. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 1987, 6, 1135–1136. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ansaruzzaman, M.; Kühn, I.; Byun, R.; Möllby, R.; Albwert, M.J.; Nahar, S.; Katouli, M. Clonal groups of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli isolated in case-control studies of diarrhoea in Bangladesh. J. Med. Microbiol. 2000, 49, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Magraner, L.; Cortajarena, A.L.; García-Pacios, M.; Arrondo, J.-L.R.; Agirre, J.; Guérin, D.M.A.; Goñi, F.M.; Ostolaza, H. Interdomain Ca2+ effects in Escherichia coli α-haemolysin: Ca2+ binding to the C-terminal domain stabilizes both C- and N-terminal domains. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2010, 1798, 1225–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Magraner, L.; Viguera, A.R.; García-Pacios, M.; Garcillán, M.P.; Arrondo, J.-L.R.; de la Cruz, F.; Goñi, F.M.; Ostolaza, H. The calcium-binding C-terminal domain of Escherichia coli α-hemolysin is a major determinant in the surface-active properties of the protein. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 11827–11835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figueirêdo, P.M.S.; Catani, C.F.; Yano, T. Thiol-independent activity of a cholesterol-binding enterohemolysin produced by enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2003, 36, 1495–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jürgens, D.; Özel, M.; Takaisi-Kikuni, N.B. Production and characterization of Escherichia coli enterohemolysin and its effects on the structure of erythrocyte membranes. Cell Biol. Int. 2002, 26, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pellett, S.; Welch, R.A. Escherichia coli hemolysin mutants with altered target cell specificity. Infect. Immun. 1996, 64, 3081–3087. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Beutin, L.; Zimmermann, S.; Gleier, K. Rapid detection and isolation of Shiga-like toxin (Verocytotoxin)-producing Escherichia coli by direct testing of individual enterohemolytic colonies from washed sheep blood agar plates in the VTEC-RPLA assay. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1996, 34, 2812–2814. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bielaszewska, M.; Rüter, C.; Kunsmann, L.; Greune, L.; Bauwens, A.; Zhang, W.; Kuczius, T.; Kim, K.S.; Mellmann, A.; Schmidt, M.A.; et al. Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli hemolysin employs outer membrane vesicles to target mitochondria and cause endothelial and epithelial apoptosis. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, W.M.; Lior, H. A new heat-labile cytolethal distending toxin (CLDT) produced by Campylobacter spp. Microb. Pathog. 1988, 4, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Gao, X.; Galán, J.E. Structure and function of the Salmonella Typhi chimaeric A2B5 typhoid toxin. Nature 2013, 499, 350–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, Z.; Rogers, A.B.; Feng, Y.; Lee, A.; Xu, S.; Taylor, N.S.; Fox, J.G. Bacterial cytolethal distending toxin promotes the development of dysplasia in a model of microbially induced hepatocarcinogenesis. Cell. Microbiol. 2007, 9, 2070–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aragon, V.; Chao, K.; Dreyfus, L.A. Effect of cytolethal distending toxin on F-actin assembly and cell division in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Infect. Immun. 1997, 65, 3774–3780. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- DiRienzo, J.M. Cytolethal distending toxin: A unique variation on the AB toxin paradigm. New J. Sci. 2014, 2014, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrich, A.W.; Lu, S.; Bielaszewska, M.; Prager, R.; Bruns, P.; Xu, J.-G.; Tschäpe, H.; Karch, H. Cytolethal distending toxin in Escherichia coli O157:H7: Spectrum of conservation, structure, and endothelial toxicity. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 1844–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bielaszewska, M.; Fell, M.; Greune, L.; Prager, R.; Fruth, A.; Tschape, H.; Schmidt, M.A.; Karch, H.; Tscha, H. Characterization of cytolethal distending toxin genes and expression in shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli strains of non-O157 serogroups. Infect. Immun. 2004, 72, 1812–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elwell, C.A.; Dreyfus, L.A. DNase I homologous residues in CdtB are critical for cytolethal distending toxin-mediated cell cycle arrest. Mol. Microbiol. 2000, 37, 952–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pickett, C.L.; Cottle, D.L.; Pesci, E.C.; Bikah, G. Cloning, sequencing, and expression of the Escherichia coli cytolethal distending toxin genes. Infect. Immun. 1994, 62, 1046–1051. [Google Scholar]
- Scott, D.A.; Kaper, J.B. Cloning and sequencing of the genes encoding Escherichia coli cytolethal distending toxin. Infect. Immun. 1994, 62, 244–251. [Google Scholar]
- Lara-Tejero, M.; Galán, J.E. A bacterial toxin that controls cell cycle progression as a deoxyribonuclease I-like protein. Science 2000, 290, 354–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Méndez-Olvera, E.T.; Bustos-Martínez, J.A.; López-Vidal, Y.; Verdugo-Rodríguez, A.; Martínez-Gómez, D. Cytolethal distending toxin from Campylobacter jejuni requires the cytoskeleton for toxic activity. Jundishapur J. Microbiol. 2016, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nešić, D.; Hsu, Y.; Stebbins, C.E. Assembly and function of a bacterial genotoxin. Nature 2004, 429, 429–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shenker, B.J.; Hoffmaster, R.H.; Zekavat, A.; Yamaguchi, N.; Lally, E.T.; Demuth, D.R. Induction of apoptosis in human T cells by Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans cytolethal distending toxin is a consequence of G2 arrest of the cell cycle. J. Immunol. 2001, 167, 435–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haghjoo, E.; Galan, J.E. Salmonella typhi encodes a functional cytolethal distending toxin that is delivered into host cells by a bacterial-internalization pathway. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 4614–4619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oogai, Y.; Gotoh, Y.; Ogura, Y.; Kawada-Matsuo, M.; Hayashi, T.; Komatsuzawa, H. Small RNA repertoires and their intraspecies variation in Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans. DNA Res. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morfeldt, E.; Taylor, D.; von Gabain, A.; Arvidson, S. Activation of alpha-toxin translation in Staphylococcus aureus by the trans-encoded antisense RNA, RNAIII. EMBO J. 1995, 14, 4569–4577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarro-Garcia, F. Escherichia coli O104:H4 Pathogenesis: An Enteroaggregative E. coli/Shiga toxin-producing E. coli explosive cocktail of high virulence. Microbiol. Spectr. 2014, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).