Evaluating the Bioactivity of a Novel Broad-Spectrum Antimicrobial Peptide Brevinin-1GHa from the Frog Skin Secretion of Hylarana guentheri and Its Analogues
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. ‘Shotgun’ Cloning of a Novel Peptide Precursor-Encoding cDNA and Bioinformatic Analyses
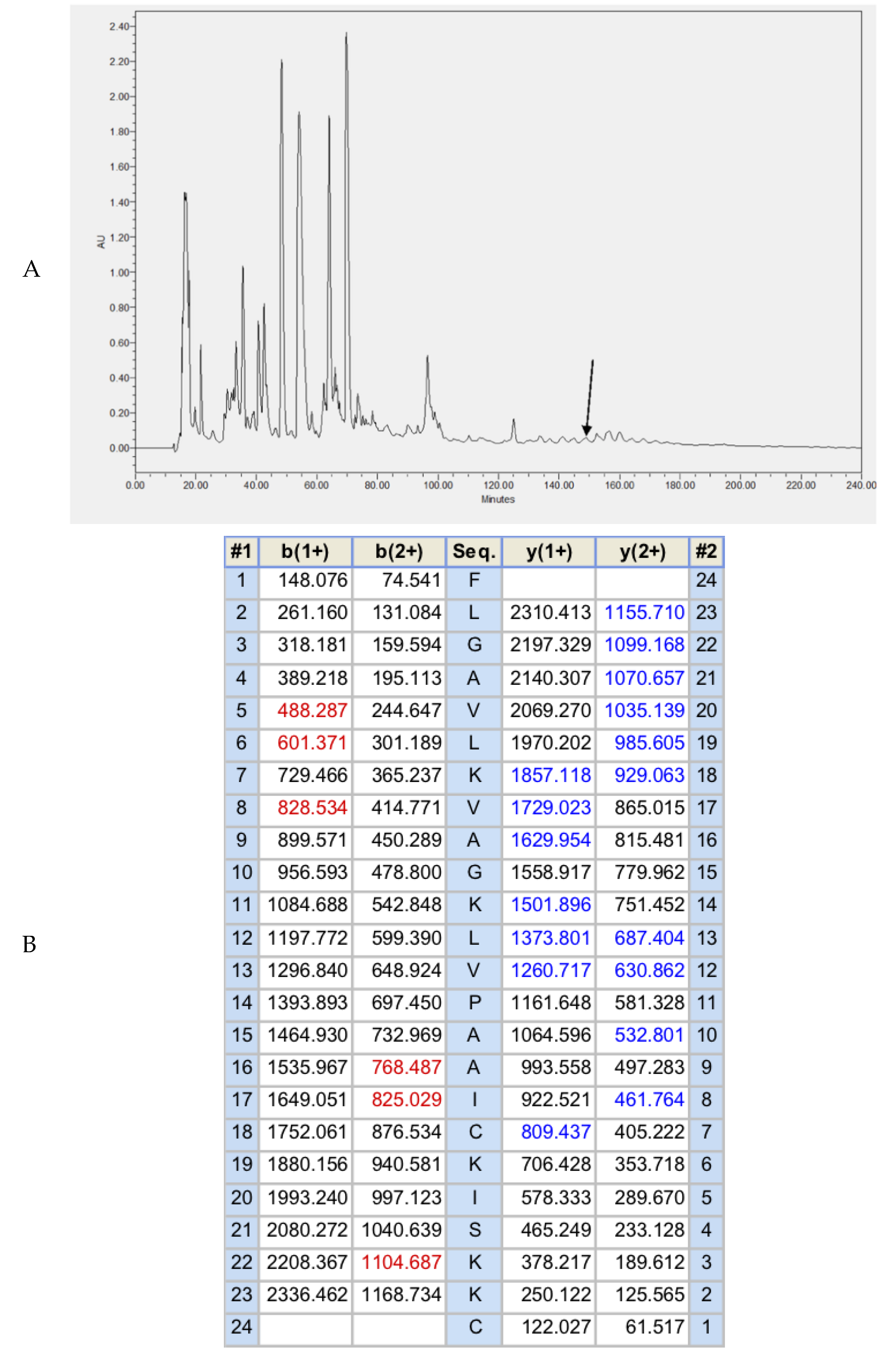
2.2. Fractionation of Skin Secretion, Identification, and Structural Characterisation of Brevinin-1GHa
2.3. Solid Phase Peptide Synthesis (SPPS) of Brevinin-1GHa, Brevinin-1GHb, and Brevinin-1GHc
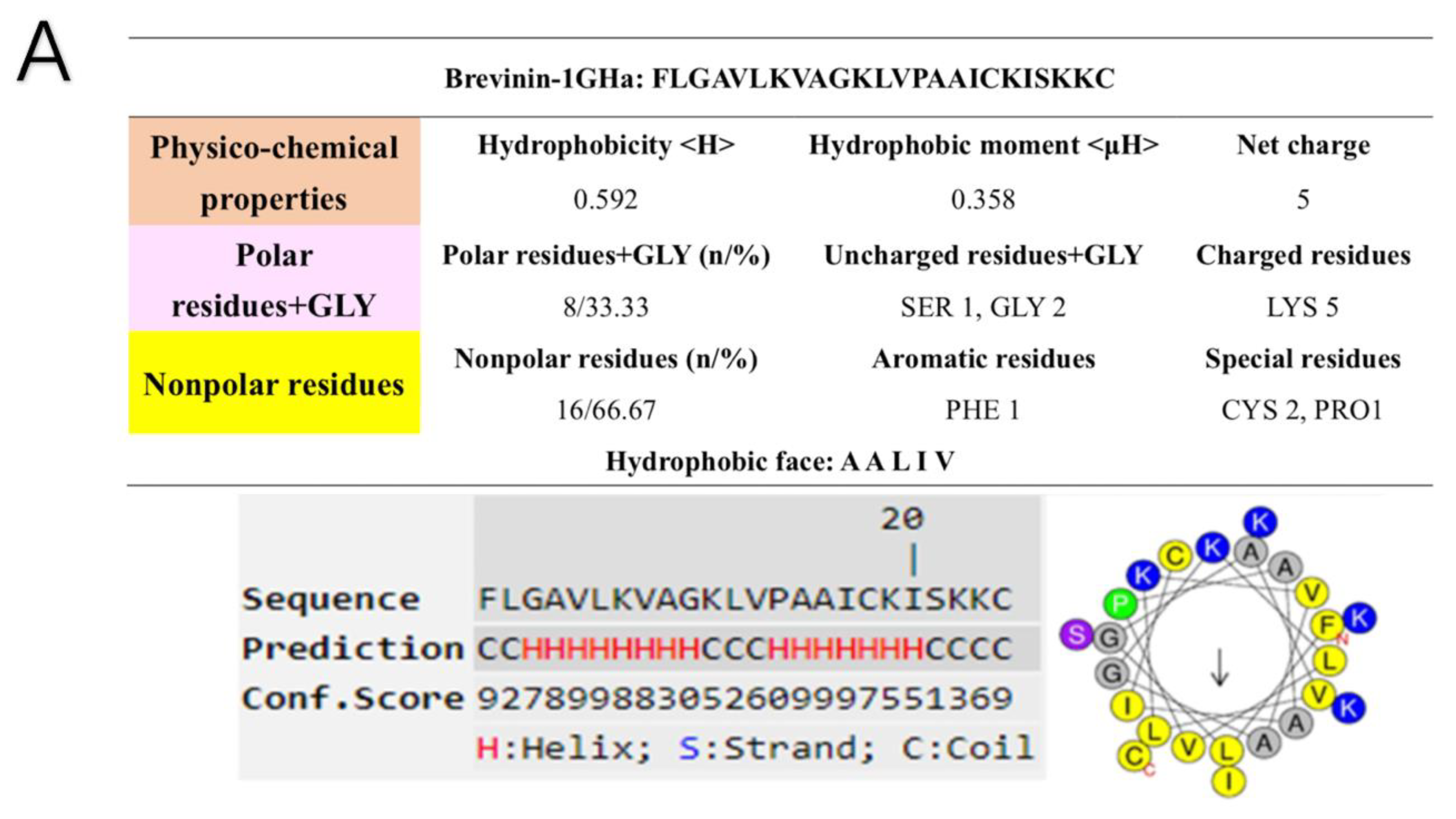
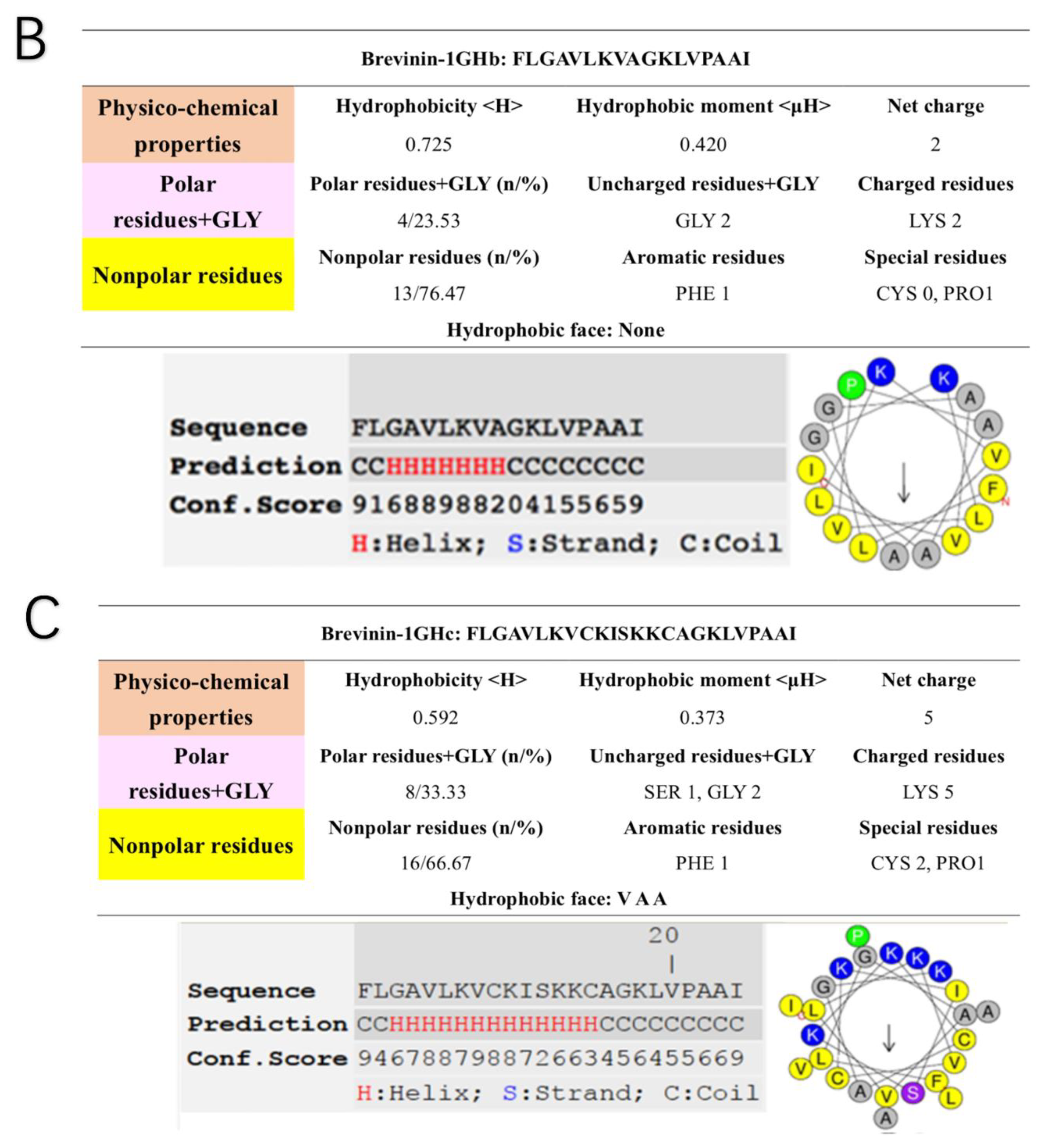
2.4. Secondary Structure Prediction of Brevinin-1GHa, Brevinin-1GHb, and Brevinin-1GHc
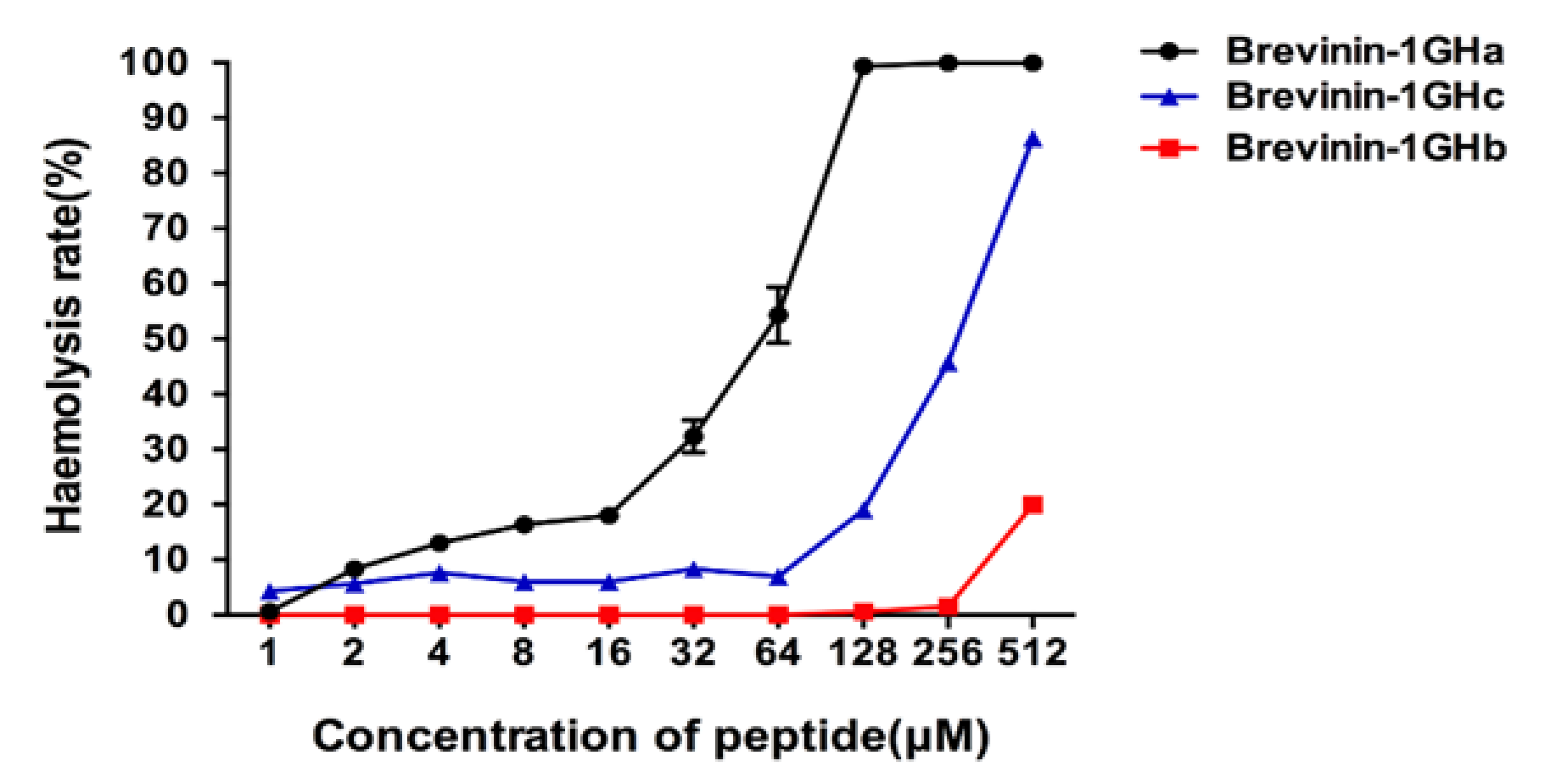
2.5. Antimicrobial and Hemolytic Activities of Brevinin-1GHa, Brevinin-1GHb, and Brevinin-1GHc
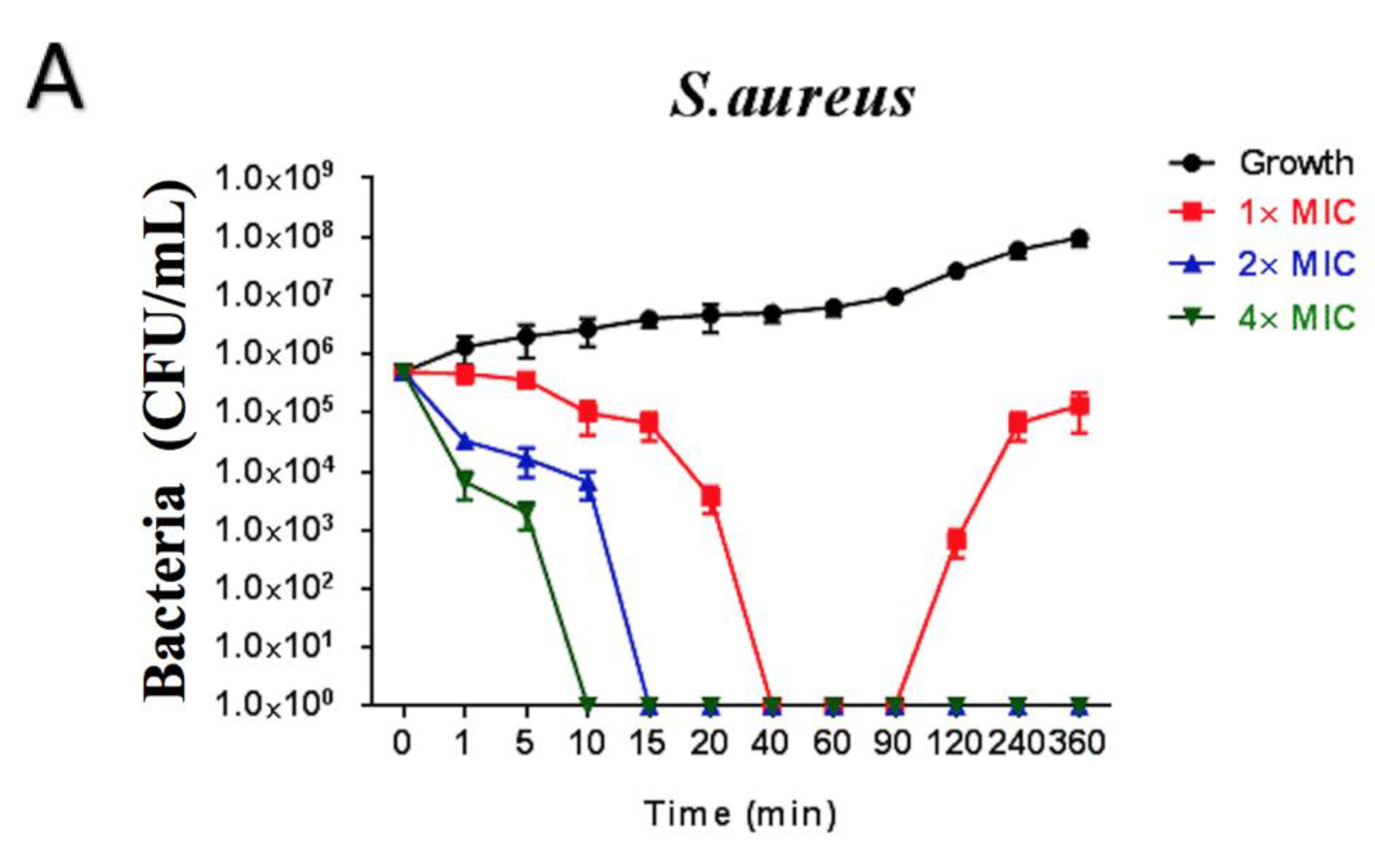
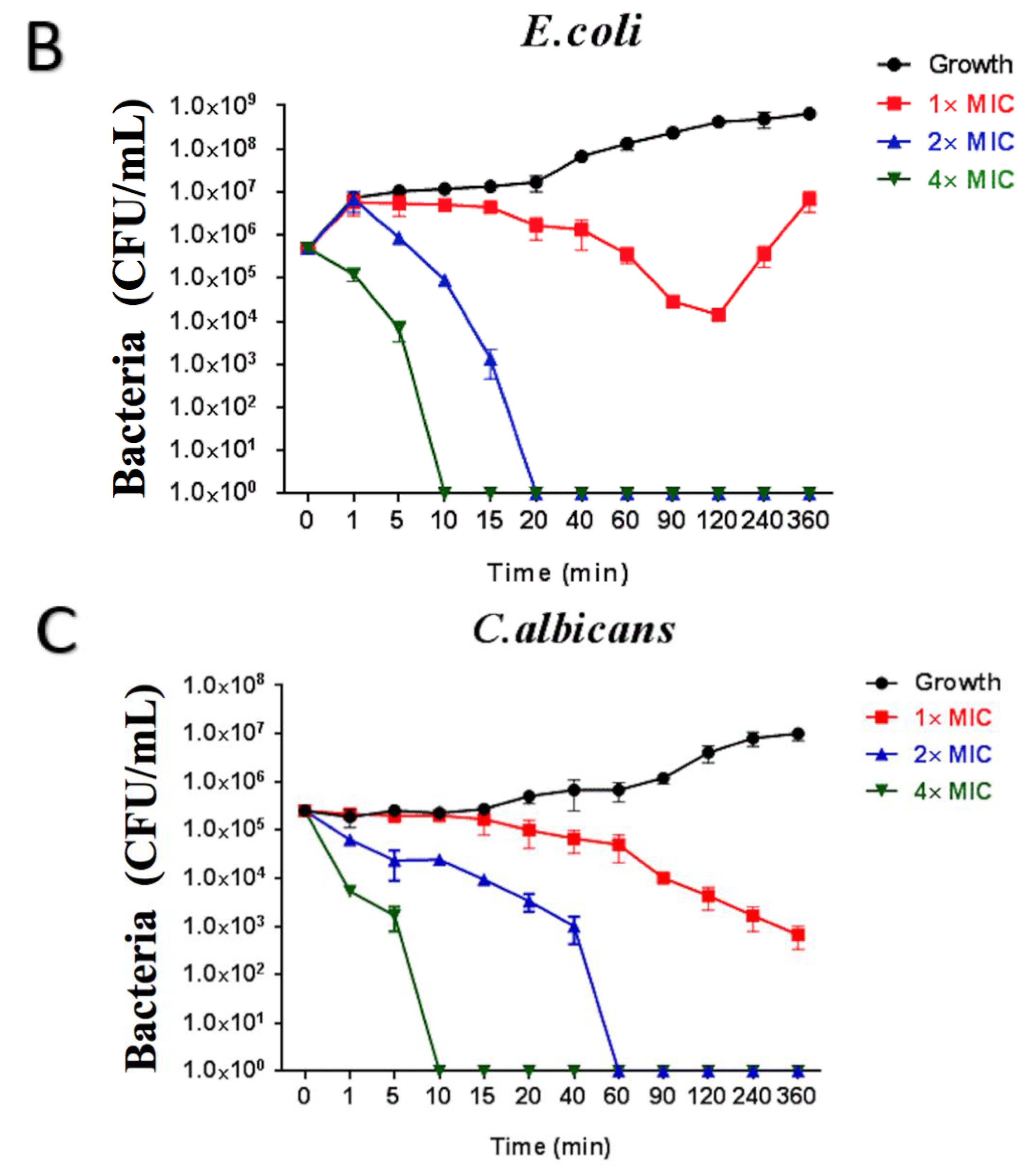
2.6. Time-Killing Assay of Brevinin-1GHa against S. aureus, E. coli, and C. albicans
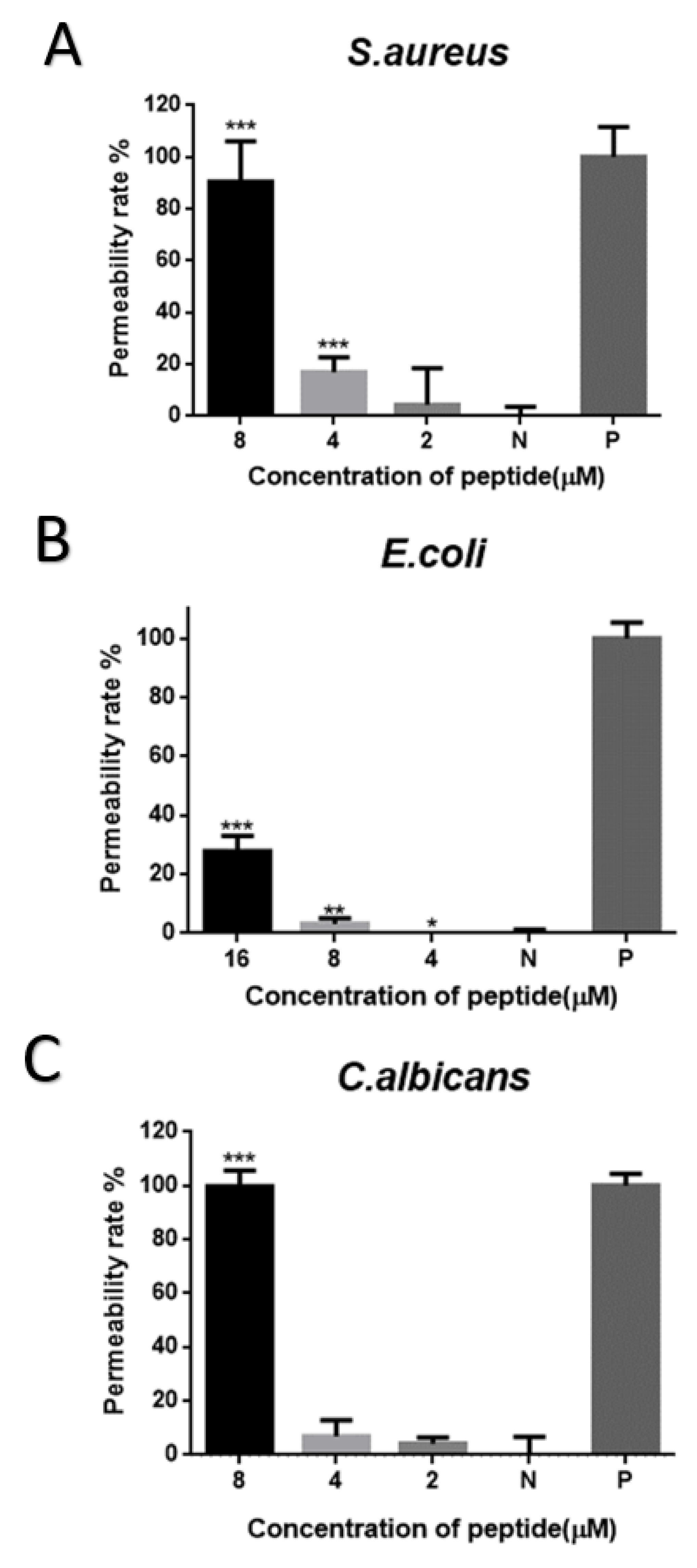
2.7. Cell-Membrane Permeabilization Assay of Brevinin-1GHa against S. aureus, E. coli, and C. albicans
2.8. Anti-Biofilm Assay of Brevinin-1GHa against S. aureus, E. coli, and C. albicans
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Acquisition of Skin Secretions
4.2. Molecular Cloning of an H. guentheri Skin Secretion-Derived cDNA Library
4.3. Identification and Structural Analysis of Brevinin-1GHa
4.4. SPPS of the Novel Peptide and Its Analogues
4.5. Antimicrobial Assay
4.6. Hemolytic Assay
4.7. Time-Killing Assay
4.8. Cell Membrane Permeability Assay
4.9. Anti-Biofilm Assay
4.10. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fridkin, S.K.; Steward, C.D.; Edwards, J.R.; Pryor, E.R.; McGowan, J.E., Jr.; Archibald, L.K.; Gaynes, R.P.; Tenover, F.C. Surveillance of antimicrobial use and antimicrobial resistance in united states hospitals: Project icare phase 2. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1999, 29, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Mouton, R.P.; Hermans, J.; Simoons-Smit, A.M.; Hoogkamp-Korstanje, J.A.; Degener, J.E.; Van, K.B. Correlations between consumption of antibiotics and methicillin resistance in coagulase negative staphylococci. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 1990, 26, 573–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goettsch, W.; Van, P.W.; Nagelkerke, N.; Hendrix, M.G.; Buiting, A.G.; Petit, P.L.; Sabbe, L.J.; van Griethuysen, A.J.; de Neeling, A.J. Increasing resistance to fluoroquinolones in escherichia coli from urinary tract infections in The Netherlands. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2000, 46, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibzadeh, F. Use and misuse of antibiotics in the middle east. Lancet 2013, 382, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, Y.Q.; Hady, W.A.; Deslandes, A.; Rey, A.; Fraisse, L.; Kristensen, H.-H.; Yeaman, M.R.; Bayer, A.S. Efficacy of nz2114, a novel plectasin-derived cationic antimicrobial peptide antibiotic, in experimental endocarditis due to methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 5325–5330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Mcclean, S.; Thompson, A.; Zhang, Y.; Shaw, C.; Rao, P.; Bjourson, A.J. Purification and characterization of novel antimicrobial peptides from the skin secretion of hylarana guentheri. Peptides 2006, 27, 3077–3084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Z.; Luo, W.; Zhong, H.; Wang, M.; Song, Y.; Deng, S.; Zhang, Y. Molecular cloning and characterization of antimicrobial peptides from skin of Hylarana guentheri. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2017, 49, 450–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conlon, J.M.; Power, G.J.; Abdelwahab, Y.H.; Flatt, P.R.; Jiansheng, H.; Coquet, L.; Leprince, J.; Jouenne, T.; Vaudry, H. A potent, non-toxic insulin-releasing peptide isolated from an extract of the skin of the Asian frog, Hylarana guntheri (Anura: Ranidae). Regul. Pept. 2008, 151, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morikawa, N.; Hagiwara, K.; Nakajima, T. Brevinin-1 and -2, unique antimicrobial peptides from the skin of the frog, rana brevipoda porsa. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1992, 189, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, J.Y.; Lee, K.H.; Chi, S.W.; Hong, S.Y.; Choi, B.W.; Moon, H.M.; Choi, B.S. Unusually stable helical kink in the antimicrobial peptide—A derivative of gaegurin. FEBS Lett. 1996, 392, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, D.P.; Durell, S.; Maloy, W.L.; Zasloff, M. Ranalexin. A novel antimicrobial peptide from bullfrog (rana catesbeiana) skin, structurally related to the bacterial antibiotic, polymyxin. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 10849–10855. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kang, S.J.; Ji, H.Y.; Lee, B.J. Anticancer activity of undecapeptide analogues derived from antimicrobial peptide, brevinin-1ema. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2012, 35, 791–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savelyeva, A.; Ghavami, S.; Davoodpour, P.; Asoodeh, A.; Los, M.J. An overview of brevinin superfamily: Structure, function and clinical perspectives. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2014, 818, 197. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kwon, M.Y.; Hong, S.Y.; Lee, K.H. Structure-activity analysis of brevinin 1e amide, an antimicrobial peptide from rana esculenta. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1998, 1387, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conlon, J.M.; Sonnevend, A.; Jouenne, T.; Coquet, L.; Cosquer, D.; Vaudry, H.; Iwamuro, S. A family of acyclic brevinin-1 peptides from the skin of the ryukyu brown frog rana okinavana. Peptides 2005, 26, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumari, V.K.; Nagaraj, R. Structure−function studies on the amphibian peptide brevinin 1e: Translocating the cationic segment from the c-terminal end to a central position favors selective antibacterial activity. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2010, 58, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Lee, W.-H.; Zhang, Y. Extremely abundant antimicrobial peptides existed in the skins of nine kinds of Chinese odorous frogs. J. Proteome Res. 2011, 11, 306–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Hu, Y.; Yu, H.; Liu, J.; Sun, J. The novel antimicrobial peptides from skin of Chinese broad-folded frog, Hylarana latouchii (Anura: Ranidae). Peptides 2009, 30, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zasloff, M. Antimicrobial peptides of multicellular organisms. Nature 2002, 415, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeaman, M.R.; Yount, N.Y. Mechanisms of antimicrobial peptide action and resistance. Pharmacol. Rev. 2003, 55, 27–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sang, M.; Wu, Q.; Xi, X.; Ma, C.; Wang, L.; Zhou, M.; Burrows, J.F.; Chen, T. Identification and target-modifications of temporin-pe: A novel antimicrobial peptide in the defensive skin secretions of the edible frog, Pelophylax kl. Esculentus. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 495, 2539–2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powers, J.P.; Hancock, R.E. The relationship between peptide structure and antibacterial activity. Peptides 2003, 24, 1681–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Guarnieri, M.T.; Vasil, A.I.; Vasil, M.L.; Mant, C.T.; Hodges, R.S. Role of peptide hydrophobicity in the mechanism of action of alpha-helical antimicrobial peptides. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2007, 51, 1398–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreev, K.; Martynowycz, M.W.; Huang, M.L.; Kuzmenko, I.; Bu, W.; Kirshenbaum, K.; Gidalevitz, D. Hydrophobic interactions modulate antimicrobial peptoid selectivity towards anionic lipid membranes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)–Biomembr. 2018, 1860, 1414–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasteiger, E.; Hoogland, C.; Gattiker, A.; Duvaud, S.E.; Wilkins, M.R.; Appel, R.D.; Bairoch, A. Protein Identification and Analysis Tools on the Expasy Server. In Proteomics Protocols Handbook; Walker, J.M., Ed.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2005; p. 531. [Google Scholar]
- Gautier, R.; Douguet, D.; Antonny, B.; Drin, G. Heliquest: A web server to screen sequences with specific alpha-helical properties. Bioinformatics 2008, 24, 2101–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Jiang, J.; Wu, Z.; Xie, F. Antimicrobial peptides from the skin of the asian frog, Odorrana jingdongensis: De novo sequencing and analysis of tandem mass spectrometry data. J. Proteom. 2012, 75, 5807–5821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conlon, J.M.; Kolodziejek, J.N.; Leprince, J.; Vaudry, H.; Coquet, L.; Jouenne, T.; King, J.D. Characterization of antimicrobial peptides from the skin secretions of the Malaysian frogs, odorrana hosii and Hylarana picturata (Anura: Ranidae). Toxicon 2008, 52, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Ran, R.; Yu, H.; Yu, Z.; Hu, Y.; Zheng, H.; Wang, D.; Yang, F.; Liu, R.; Liu, J. Identification and characterization of antimicrobial peptides from skin of Amolops ricketti (Anura: Ranidae). Peptides 2012, 33, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baltzer, S.A.; Brown, M.H. Antimicrobial peptides–promising alternatives to conventional antibiotics. J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 20, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Lee, D.G. Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) with dual mechanisms: Membrane disruption and apoptosis. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 25, 759–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nan, Y.; Lei, L.; Di, W.; Gao, Y.; Xi, X.; Mei, Z.; Lei, W.; Chen, T.; Chris, S. Discovery of novel bacterial cell-penetrating phylloseptins in defensive skin secretions of the South American hylid frogs, Phyllomedusa duellmani and Phyllomedusa coelestis. Toxins 2016, 8, 255. [Google Scholar]
- Hammond, S.M.; Lambert, P.A.; Rycroft, A.N. The Bacterial Cell Surface; CROOM HELM: Kent, UK, 1984; pp. 389–392. [Google Scholar]
- Putker, F.; Bos, M.P.; Tommassen, J. Transport of lipopolysaccharide to the gram-negative bacterial cell surface. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2015, 39, 985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freeman, C.; Lock, M.A. The biofilm polysaccharide matrix: A buffer against changing organic substrate supply? Limnol. Oceanogr. 2003, 40, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mah, T.F.; O’Toole, G.A. Mechanisms of biofilm resistance to antimicrobial agents. Trends Microbiol. 2001, 9, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Peptide Name | Source | Amino Acid Sequence | Alpha Helix | Identities |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brevinin-1GHa | Hylarana guentheri | 1FLGAVLKVAGKLVPAAICKISKKC24 chhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhccc | 83.33% | |
| Brevinin-1HSa | Odorrana hosii | 1FLPAVLRVAAKIVPTVFCAISKKC24 cchhhhhhhhhhccceeeeecccc | 41.67% | 67% |
| Brevinin-1WY7 | Amolops wuyiensis | 47FLGSILGLVGKVVPTLICKISKKC70 cchhhhhhhhhhchheeeeecccc | 50.00% | 67% |
| Brevinin-1WY5 | Amolops wuyiensis | 48FLGSLLGLVGKVVPTLICKISKKC71 chhhhhhhhcccecceeeeeecccc | 29.17% | 67% |
| Brevinin-1JDc | Odorrana jingdongensis | 1FLPAVLRVAAKVVPTVFCLISKKC24 cchhhhhhhhhhccceeeeeeccc | 41.67% | 67% |
| Brevinin-1RTc | Amolops ricketti | 48FLGSLLGLVGKIVPTLICKISKKC71 chhhhhhhhhcecheeeeeecccc | 41.67% | 67% |
| Brevinin-1LTd | Sylvirana latouchii | 48FFGSVLKVAAKVLPAAICQIFKKC71 cchhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhcc | 83.33% | 67% |
| Microorganisms | Brevinin-1GHa | Brevinin-1GHb | Brevinin-1GHc | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIC (µM) | MBC (µM) | MIC (µM) | MBC (µM) | MIC (µM) | MBC (µM) | ||
| Gram-positive | S. aureus | 2 | 2 | 512 | >512 | 32 | 32 |
| E. faecalis | 8 | 16 | >512 | >512 | 128 | 128 | |
| MRSA | 4 | 4 | >512 | >512 | 128 | 128 | |
| Gram-negative | E. coli | 4 | 8 | >512 | >512 | 16 | 32 |
| P. aeruginosa | 32 | 64 | >512 | >512 | 128 | 512 | |
| K. pneumoniae | 8 | 16 | >512 | >512 | 256 | 512 | |
| yeast | C. albicans | 2 | 4 | >512 | >512 | 128 | 128 |
| Microorganisms | S. aureus | E. coli | C. albicans |
|---|---|---|---|
| MBIC (µM) | 4 | 32 | 2 |
| MBEC (µM) | 16 | 64 | 8 |
| Peptide Name | GRAVY | pI | Net Charge | <H> | <𝛍H> | Antimicrobial Activity (MIC 𝛍M) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S. aureus | E. coli | C. albicans | MRSA | ||||||
| Brevinin-1GHa | 1.054 | 9.90 | +5 | 0.592 | 0.358 | 2 | 4 | 2 | 4 |
| Brevinin-1HSa | 1.262 | 9.85 | +4 | 0.728 | 0.377 | 3 | 24 | ND | ND |
| Brevinin-1JDc | 1.333 | 9.85 | +4 | 0.761 | 0.366 | 6 | 49 | 3 | 3 |
| Brevinin-1WY7 | 1.183 | 9.70 | +4 | 0.736 | 0.420 | ND | ND | ND | ND |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Q.; Cheng, P.; Ma, C.; Xi, X.; Wang, L.; Zhou, M.; Bian, H.; Chen, T. Evaluating the Bioactivity of a Novel Broad-Spectrum Antimicrobial Peptide Brevinin-1GHa from the Frog Skin Secretion of Hylarana guentheri and Its Analogues. Toxins 2018, 10, 413. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10100413
Chen Q, Cheng P, Ma C, Xi X, Wang L, Zhou M, Bian H, Chen T. Evaluating the Bioactivity of a Novel Broad-Spectrum Antimicrobial Peptide Brevinin-1GHa from the Frog Skin Secretion of Hylarana guentheri and Its Analogues. Toxins. 2018; 10(10):413. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10100413
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Qi, Peng Cheng, Chengbang Ma, Xinping Xi, Lei Wang, Mei Zhou, Huimin Bian, and Tianbao Chen. 2018. "Evaluating the Bioactivity of a Novel Broad-Spectrum Antimicrobial Peptide Brevinin-1GHa from the Frog Skin Secretion of Hylarana guentheri and Its Analogues" Toxins 10, no. 10: 413. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10100413
APA StyleChen, Q., Cheng, P., Ma, C., Xi, X., Wang, L., Zhou, M., Bian, H., & Chen, T. (2018). Evaluating the Bioactivity of a Novel Broad-Spectrum Antimicrobial Peptide Brevinin-1GHa from the Frog Skin Secretion of Hylarana guentheri and Its Analogues. Toxins, 10(10), 413. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10100413






