Urinary Sodium-to-Potassium Ratio Tracks the Changes in Salt Intake during an Experimental Feeding Study Using Standardized Low-Salt and High-Salt Meals among Healthy Japanese Volunteers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Dietary Protocol
2.3. Urinary Na/K Ratio and Blood Pressure Measurements
2.4. Biochemical Analyses of Urine and Blood
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.5.1. Dietary Intake vs. Urinary Excretion
2.5.2. Daily Na/K ratio Assessment from Multiple Spot Urine Samples for Estimating the 24-h Urine Na/K Ratio
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Parameters of the Participants
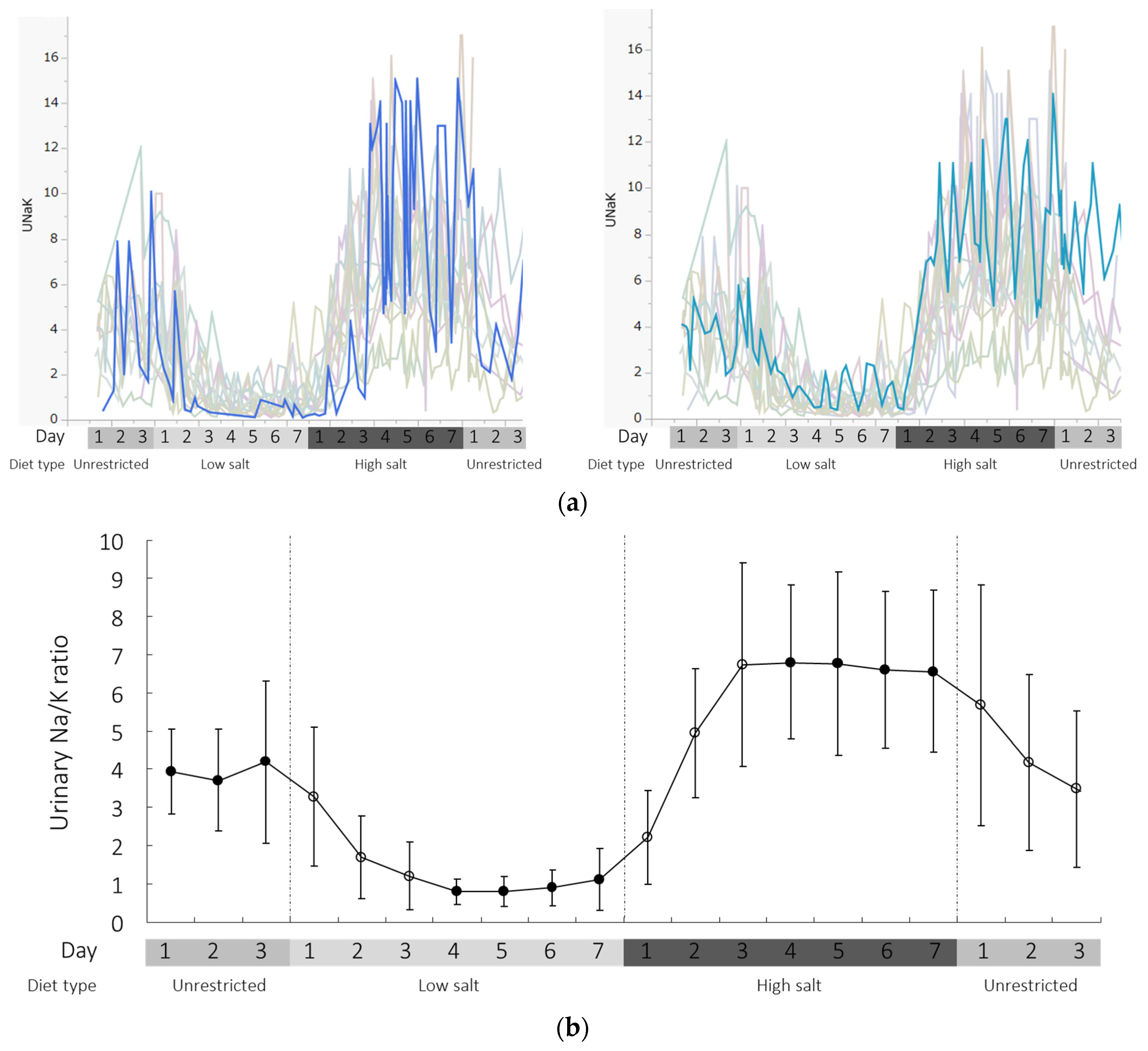
3.2. Changes in 24-h Urinary Na/K Ratio and Basic Parameters During the Study
3.3. Changes in Self-Measured Urinary Na/K Ratio During the Study
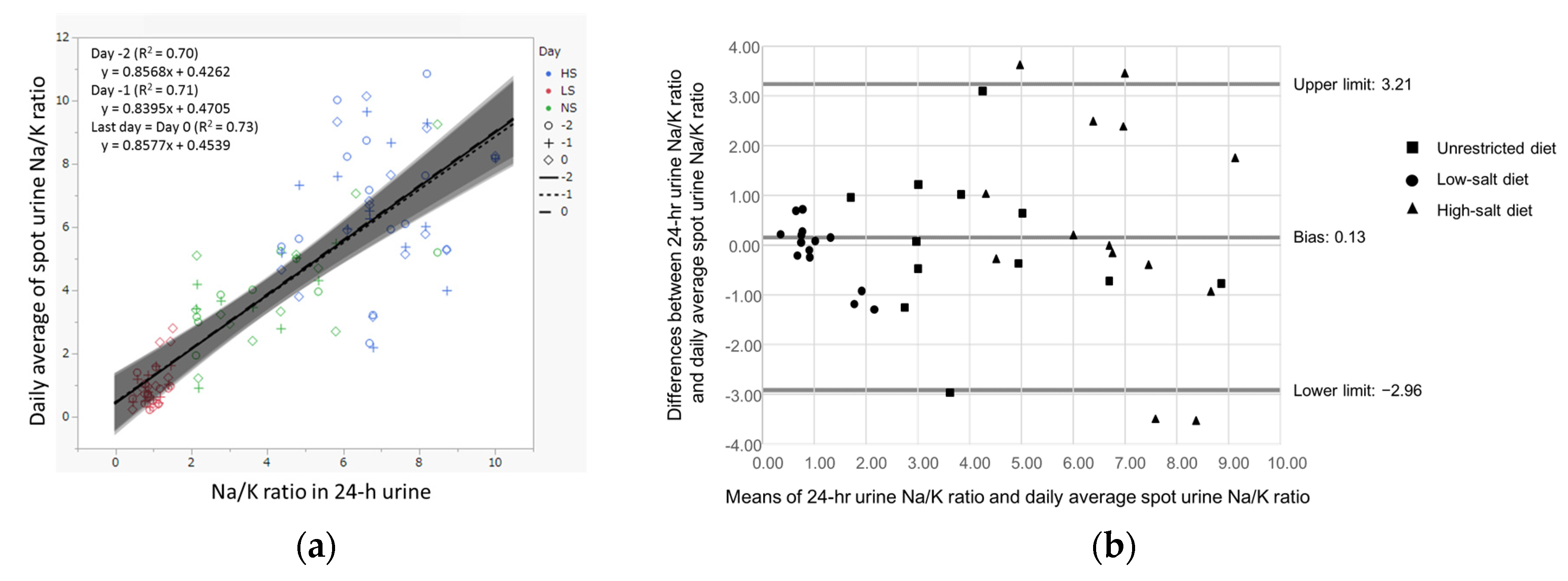
3.4. Validation of Daily Mean Spot Urine Na/K Ratio for Estimating 24-h Urine Na/K Ratio
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Adrogué, H.J.; Madias, N.E. Sodium and potassium in the pathogenesis of hypertension. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 356, 1966–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gay, H.C.; Rao, S.G.; Vaccarino, V.; Ali, M.K. Effects of different dietary interventions on blood pressure: Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Hypertension 2016, 67, 733–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, F.J.; Li, J.; MacGregor, G.A. Effect of longer term modest salt reduction on blood pressure: Cochrane systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized trials. BMJ 2013, 346, f1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aburto, N.J.; Ziolkovska, A.; Hooper, L.; Elliott, P.; Cappuccio, F.P.; Meerpohl, J.J. Effect of lower sodium intake on health: Systematic review and meta-analyses. BMJ 2013, 346, f1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aburto, N.J.; Hanson, S.; Gutierrez, H.; Hooper, L.; Elliott, P.; Cappuccio, F.P. Effect of increased potassium on cardiovascular risk factors and disease: Systematic review and meta-analyses. BMJ 2013, 346, f1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, I.J.; Tzoulaki, I.; Candeias, V.; Elliott, P. Salt intakes around the world: Implications for public health. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2009, 38, 791–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cogswell, M.E.; Zhang, Z.; Carriquiry, A.L.; Gunn, J.P.; Kuklina, E.V.; Saydah, S.H.; Yang, Q.; Moshfegh, A.J. Sodium and potassium intakes among US adults: NHANES 2003–2008. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 96, 647–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernstein, A.M.; Willett, W.C. Trends in 24-h urinary sodium excretion in the United States, 1957–2003: A systematic review. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 92, 1172–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cogswell, M.E.; Mugavero, K.; Bowman, B.A.; Frieden, T.R. Dietary sodium and cardiovascular disease risk-measurement matters. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 580–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cobb, L.K.; Anderson, C.A.; Elliott, P.; Hu, F.B.; Liu, K.; Neaton, J.D.; Whelton, P.K.; Woodward, M.; Appel, L.J. American Heart Association Council on Lifestyle and Metabolic Health. Methodological issues in cohort studies that relate sodium intake to cardiovascular disease outcomes: A science advisory from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2014, 129, 1173–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.; Stamler, J. Assessment of sodium intake in epidemiological studies on blood pressure. Ann. Clin. Res. 1984, 16 (Suppl. 43), 49–54. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lerchl, K.; Rakova, N.; Dahlmann, A.; Rauh, M.; Goller, U.; Basner, M.; Dinges, D.F.; Beck, L.; Agureev, A.; Larina, I.; et al. Agreement between 24-hour salt ingestion and sodium excretion in a controlled environment. Hypertension 2015, 66, 850–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawasaki, T.; Itoh, K.; Uezono, K.; Sasaki, H. A simple method for estimating 24 h urinary sodium and potassium excretion from second morning voiding urine specimen in adults. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 1993, 20, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, T.; Okamura, T.; Miura, K.; Kadowaki, T.; Ueshima, H.; Nakagawa, H.; Hashimoto, T. A simple method to estimate populational 24-h urinary sodium and potassium excretion using a casual urine specimen. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2002, 16, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, I.J.; Dyer, A.R.; Chan, Q.; Cogswell, M.E.; Ueshima, H.; Stamler, J.; Elliott, P.; INTERSALT Co-Operative Research Group. Estimating 24-hour urinary sodium excretion from casual urinary sodium concentrations in Western populations: The INTERSALT study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2013, 177, 1180–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polonia, J.; Lobo, M.F.; Martins, L.; Pinto, F.; Nazare, J. Estimation of populational 24-h urinary sodium and potassium excretion from spot urine samples: Evaluation of four formulas in a large national representative population. J. Hypertens. 2017, 35, 477–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Crino, M.; Wu, J.H.; Woodward, M.; Barzi, F.; Land, M.A.; McLean, R.; Webster, J.; Enkhtungalag, B.; Neal, B. Mean population salt intake estimated from 24-h urine samples and spot urine samples: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2016, 45, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwahori, T.; Miura, K.; Ueshima, H. Time to consider use of the sodium-to-potassium ratio for practical sodium reduction and potassium increase. Nutrients 2017, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- INTERSALT Co-operative Research Group. INTERSALT: An international study of electrolyte excretion and blood pressure. Results for 24-hr urinary sodium and potassium excretion. BMJ 1988, 297, 319–328. [Google Scholar]
- Stamler, J.; Rose, G.; Stamler, R.; Elliott, P.; Dyer, A.; Marmot, M. INTERSALT study findings. Public health and medical care implications. Hypertension 1989, 14, 570–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tzoulaki, I.; Patel, C.J.; Okamura, T.; Chan, Q.; Brown, I.J.; Miura, K.; Ueshima, H.; Zhao, L.; Van Horn, L.; Daviglus, M.L.; et al. A nutrient-wide association study on blood pressure. Circulation 2012, 126, 2456–2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez, V.; Chang, E.T. Sodium-to-potassium ratio and blood pressure, hypertension, and related factors. Adv. Nutr. 2014, 5, 712–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, N.R.; Obarzanek, E.; Cutler, J.A.; Buring, J.E.; Rexrode, K.M.; Kumanyika, S.K.; Appel, L.J.; Whelton, P.K. Trials of Hypertension Prevention Collaborative Research Group. Joint effects of sodium and potassium intake on subsequent cardiovascular disease: The Trials of Hypertension Prevention follow-up study. Arch. Intern. Med. 2009, 169, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, N.R.; Appel, L.J.; Whelton, P.K. Sodium intake and all-cause mortality over 20 years in the Trials of Hypertension Prevention. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2016, 68, 1609–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, N.R.; Cutler, J.A.; Obarzanek, E.; Buring, J.E.; Rexrode, K.M.; Kumanyika, S.K.; Appel, L.J.; Whelton, P.K. Long term effects of dietary sodium reduction on cardiovascular disease outcomes: Observational follow-up of the Trials of Hypertension Prevention (TOHP). BMJ 2007, 334, 885–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwahori, T.; Miura, K.; Ueshima, H.; Chan, Q.; Dyer, A.R.; Elliott, P.; Stamler, J.; INTERSALT Research Group. Estimating 24-hour urinary sodium/potassium ratio from casual (“spot”) urinary sodium/potassium ratio: The INTERSALT Study. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2016, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwahori, T.; Ueshima, H.; Miyagawa, N.; Ohgami, N.; Yamashita, H.; Ohkubo, T.; Murakami, Y.; Shiga, T.; Miura, K. Six random samples of casual urine on different days are sufficient to estimate daily sodium/potassium ratio as compared to 7-day 24-h urine collections. Hypertens. Res. 2014, 37, 765–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwahori, T.; Ueshima, H.; Torii, S.; Saito, Y.; Fujiyoshi, A.; Ohkubo, T.; Miura, K. Four to seven random casual urine specimens are sufficient to estimate 24-h urinary sodium/potassium ratio in individuals with high blood pressure. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2016, 30, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwahori, T.; Ueshima, H.; Ohgami, N.; Yamashita, H.; Miyagawa, N.; Kondo, K.; Torii, S.; Yoshita, K.; Shiga, T.; Ohkubo, T.; et al. Effectiveness of a self-monitoring device for urinary sodium/potassium ratio on dietary improvement in free-living adults: A randomized controlled trial. J. Epidemiol. 2017, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Hunter, D. Biochemical indicators of dietary intake. In Nutritional Epidemiology, 2nd ed.; Willet, W., Ed.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1998; pp. 174–243. [Google Scholar]
- Stamler, J.; Chan, Q.; INTERSALT Co-operative Research Group. INTERMAP appendix tables. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2003, 17, 665–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare. National Nutrition and Health Survey, 2010; Daiichi Shuppan: Tokyo, Japan, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Yatabe, M.S.; Yatabe, J.; Yoneda, M.; Watanabe, T.; Otsuki, M.; Felder, R.A.; Jose, P.A.; Sanada, H. Salt sensitivity is associated with insulin resistance, sympathetic overactivity, and decreased suppression of circulating renin activity in lean patients with essential hypertension. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 92, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bland, J.; Altman, D.G. Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. Lancet 1986, 1, 307–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Liu, T.; Kuklina, E.V.; Flanders, W.D.; Hong, Y.; Gillespie, C.; Chang, M.H.; Gwinn, M.; Dowling, N.; Khoury, M.J.; et al. Sodium and potassium intake and mortality among US adults: Prospective data from the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Arch. Intern. Med. 2011, 171, 1183–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okayama, A.; Okuda, N.; Miura, K.; Okamura, T.; Hayakawa, T.; Akasaka, H.; Ohnishi, H.; Saitoh, S.; Arai, Y.; Kiyohara, Y.; et al. Dietary sodium-to-potassium ratio as a risk factor for stroke, cardiovascular disease and all-cause mortality in Japan: The NIPPON DATA80 cohort study. BMJ Open. 2016, 6, e011632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rakova, N.; Jüttner, K.; Dahlmann, A.; Schröder, A.; Linz, P.; Kopp, C.; Rauh, M.; Goller, U.; Beck, L.; Agureev, A.; et al. Long-term space flight simulation reveals infradian rhythmicity in human Na+ balance. Cell. Metab. 2013, 17, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwahori, T.; Ueshima, H.; Torii, S.; Yoshino, S.; Kondo, K.; Tanaka-Mizuno, S.; Arima, H.; Miura, K. Diurnal variation of urinary sodium-to-potassium ratio in free-living Japanese individuals. Hypertens. Res. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pietinen, P.I.; Findley, T.W.; Clausen, J.D.; Finnerty, F.A.; Altschul, A.M. Studies in community nutrition: Estimation of sodium output. Prev. Med. 1976, 5, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voors, A.W.; Dalferes, E.R., Jr.; Frank, G.C.; Aristimuno, G.G.; Berenson, G.S. Relation between ingested potassium and sodium balance in young blacks and whites. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1983, 37, 583–594. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Clark, A.J.; Mossholder, S. Sodium and potassium intake measurements: Dietary methodology problems. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1986, 43, 470–476. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Holbrook, J.T.; Patterson, K.Y.; Bodner, J.E.; Douglas, L.W.; Veillon, C.; Kelsay, J.L.; Mertz, W.; Smith, J.C., Jr. Sodium and potassium intake and balance in adults consuming self-selected diets. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1984, 40, 786–793. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Palmer, B.F.; Clegg, D.J. Physiology and pathophysiology of potassium homeostasis. Adv. Physiol. Educ. 2016, 40, 480–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, B.F. Regulation of potassium homeostasis. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 10, 1050–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armando, I.; Villar, V.A.; Jose, P.A. Genomics and pharmacogenomics of salt-sensitive hypertension. Curr. Hypertens. Rev. 2015, 11, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. WHO Guideline: Sodium intake for adults and children. In Geneva: World Health Organization (WHO); WHO: Genève, Switzerland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. WHO Guideline: Potassium intake for adults and children. In Geneva: World Health Organization (WHO); WHO: Genève, Switzerland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- The INTERSALT Co-operative Research Group. INTERSALT study: An international co-operative study on the relation of blood pressure to electrolyte excretion in populations, I: Design and methods. J. Hypertens. 1986, 4, 781–787. [Google Scholar]
| Parameter | Unit | Mean ± SD (Range) |
|---|---|---|
| Men/women | 5:9 = 35.7% | |
| Age | Years | 22.5 ± 0.3 (21–26) |
| Weight | kg | 53.3 ± 5.1 (44.9–63.1) |
| BMI | kg/m2 | 20.4 ± 2.0 (17.2–25.6) |
| Fasting serum glucose | mg/dL | 83 ± 7 |
| Insulin | μIU/mL | 7.2 ± 2.6 |
| Morning pulse rate | Beats per min | 66 ± 12 |
| Evening pulse rate | Beats per min | 65 ± 10 |
| Parameter | Unit | Unrestricted | Low Salt | High Salt | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Morning SBP | mmHg | 104 ± 9 | 103 ± 7 | 102 ± 11 | 0.769 |
| Morning DBP | mmHg | 69 ± 7 | 65 ± 8 | 70 ± 7 | 0.102 |
| Morning MBP | mmHg | 76 ± 15 | 78 ± 7 | 81 ± 7 | 0.341 |
| Morning pulse rate | /min | 66 ± 12 | 67 ± 13 | 64 ± 9 | 0.652 |
| Hematocrit | % | 44.3 ± 3.3 | 44.4 ± 3.9 | 42.7 ± 3.0 * | 0.045 |
| PAC | pg/mL | 208 ± 97 | 391 ± 204 $ | 133 ± 63 *,# | 0.001 |
| PRA | ng/mL/h | 1.3 ± 1.1 | 2.9 ± 1.5 $ | 1.0 ± 1.4 * | 0.006 |
| Creatinine | mg/dL | 0.69 ± 0.13 | 0.71 ± 0.14 | 0.65 ± 0.11 *,# | 0.000 |
| Serum Na | mEq/L | 141 ± 2 | 141 ± 1 | 141 ± 2 | 0.220 |
| Serum K | mEq/L | 4.0 ± 0.2 | 4.0 ± 0.2 | 4.1 ± 0.3 | 0.940 |
| Urine volume | mL/day | 926 ± 369 | 978 ± 336 | 1416 ± 495 *,# | 0.016 |
| Urine Na | mmol/day | 128 ± 47 | 30 ± 7 $ | 281 ± 42 *,# | 0.001 |
| Urine K | mmol/day | 32.3 ± 9.4 | 29.5 ± 6.0 | 39.2 ± 7.6 * | 0.032 |
| Urine creatinine | g/day | 1.20 ± 0.25 | 1.14 ± 0.20 | 1.23 ± 0.29 | 0.093 |
| Morning SBP | mmHg | 104 ± 9 | 103 ± 7 | 102 ± 11 | 0.769 |
| Morning DBP | mmHg | 69 ± 7 | 65 ± 8 | 70 ± 7 | 0.102 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yatabe, M.S.; Iwahori, T.; Watanabe, A.; Takano, K.; Sanada, H.; Watanabe, T.; Ichihara, A.; Felder, R.A.; Miura, K.; Ueshima, H.; et al. Urinary Sodium-to-Potassium Ratio Tracks the Changes in Salt Intake during an Experimental Feeding Study Using Standardized Low-Salt and High-Salt Meals among Healthy Japanese Volunteers. Nutrients 2017, 9, 951. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9090951
Yatabe MS, Iwahori T, Watanabe A, Takano K, Sanada H, Watanabe T, Ichihara A, Felder RA, Miura K, Ueshima H, et al. Urinary Sodium-to-Potassium Ratio Tracks the Changes in Salt Intake during an Experimental Feeding Study Using Standardized Low-Salt and High-Salt Meals among Healthy Japanese Volunteers. Nutrients. 2017; 9(9):951. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9090951
Chicago/Turabian StyleYatabe, Midori Sasaki, Toshiyuki Iwahori, Ami Watanabe, Kozue Takano, Hironobu Sanada, Tsuyoshi Watanabe, Atsuhiro Ichihara, Robin A. Felder, Katsuyuki Miura, Hirotsugu Ueshima, and et al. 2017. "Urinary Sodium-to-Potassium Ratio Tracks the Changes in Salt Intake during an Experimental Feeding Study Using Standardized Low-Salt and High-Salt Meals among Healthy Japanese Volunteers" Nutrients 9, no. 9: 951. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9090951
APA StyleYatabe, M. S., Iwahori, T., Watanabe, A., Takano, K., Sanada, H., Watanabe, T., Ichihara, A., Felder, R. A., Miura, K., Ueshima, H., Kimura, J., & Yatabe, J. (2017). Urinary Sodium-to-Potassium Ratio Tracks the Changes in Salt Intake during an Experimental Feeding Study Using Standardized Low-Salt and High-Salt Meals among Healthy Japanese Volunteers. Nutrients, 9(9), 951. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9090951





