The Gene-Lifestyle Interaction on Leptin Sensitivity and Lipid Metabolism in Adults: A Population Based Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Design and Study Population
2.2. Anthropometric Measurements
2.3. Lifestyle Analysis
2.4. Blood Collection and Biochemistry Analysis
2.5. Genetic Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
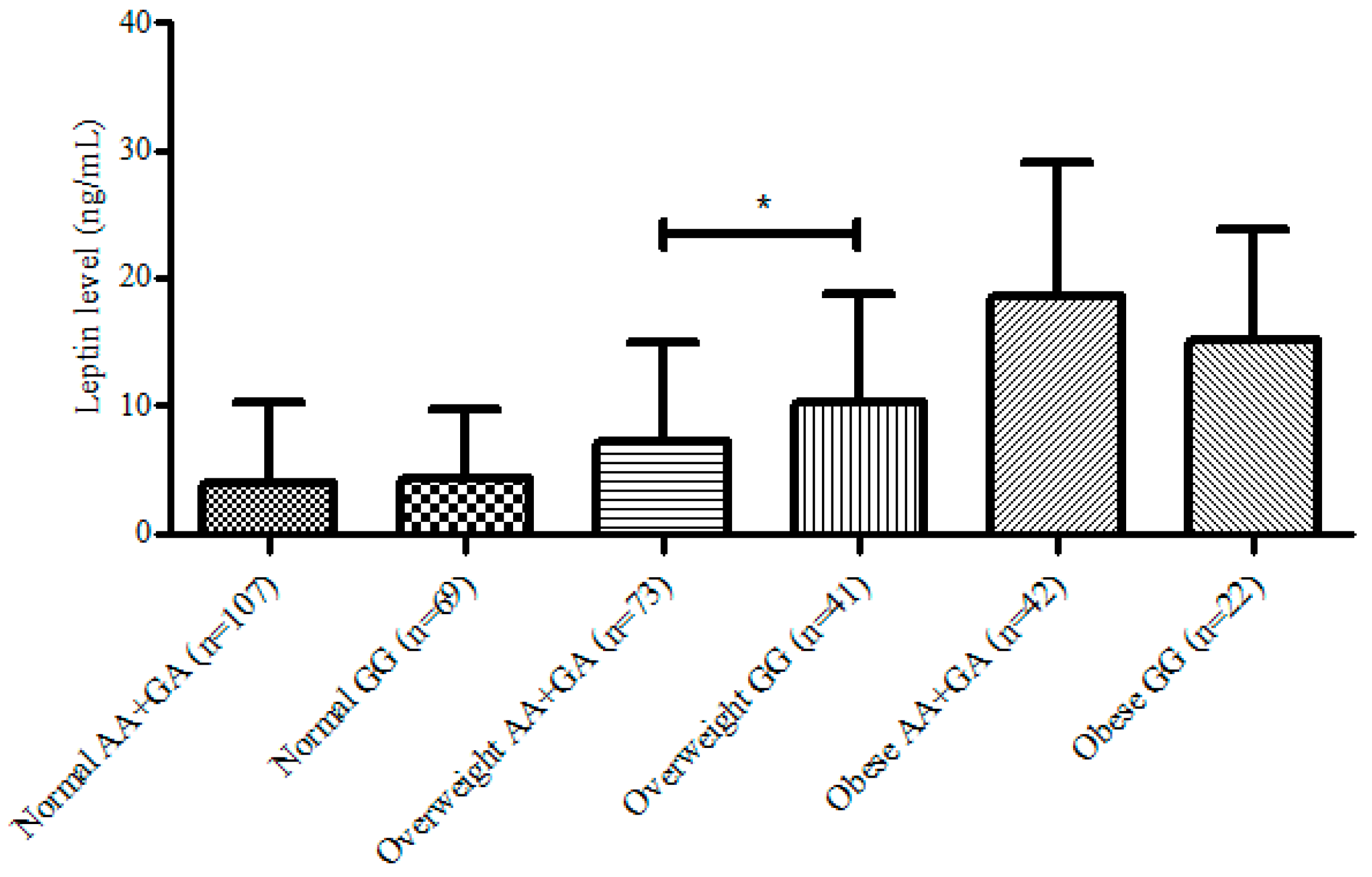
3. Results
4. Discussions
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Popkin, B.M.; Adair, L.S.; Ng, S.W. Global nutrition transition and the pandemic of obesity in developing countries. Nutr. Rev. 2012, 70, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poirier, P.; Giles, T.D.; Bray, G.A.; Hong, Y.; Stern, J.S.; Pi-Sunyer, F.X.; Eckel, R.H. Obesity and Cardiovascular Disease: Pathophysiology, Evaluation, and Effect of Weight Loss: An Update of the 1997 American Heart Association Scientific Statement on Obesity and Heart Disease From the Obesity Committee of the Council on Nutrition, Physical Activity, and Metabolism. Circulation 2006, 113, 898–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, M.W.; Woods, S.C.; Porte, D., Jr.; Seeley, R.J.; Baskin, D.G. Central nervous system control of food intake. Nature 2000, 404, 661–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, S.; Coppack, S.W.; Mohamed-Ali, V.; Landt, M. Adipose Tissue Leptin Production and Plasma Leptin Kinetics in Humans. Diabetes 1996, 45, 984–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Rui, L. Leptin signaling and leptin resistance. Front. Med. 2013, 7, 207–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, S.H.; Say, Y.H. Leptin and leptin receptor gene polymorphisms and their association with plasma leptin levels and obesity in a multi-ethnic Malaysian suburban population. J. Physiol. Anthropol. 2014, 33, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chavarria-Avila, E.; Mercado, M.V.D.; Gomez-Bañuelos, E.; Ruiz-Quezada, S.L.; Castro-Albarran, J.; Sánchez-López, L.; Martín-Marquez, B.T.; Navarro-Hernández, R.E. The Impact of LEP G-2548A and LEPR Gln223Arg Polymorphisms on Adiposity, Leptin, and Leptin-Receptor Serum Levels in a Mexican Mestizo Population. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 539408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahin, D.S.; Tumer, C.; Demir, C.; Celik, M.M.; Celik, M.; Ucar, E.; Gunesacar, R. Association with Leptin Gene c.-2548 G>A Polymorphism, Serum Leptin Levels, and Body Mass Index in Turkish Obese Patients. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2013, 65, 243–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azzu, V.; Brand, M.D. The on-off switches of the mitochondrial uncoupling proteins. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2010, 35, 298–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricquier, D. Respiration uncoupling and metabolism in the control of energy expenditure. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2005, 64, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salopuro, T.; Pulkkinen, L.; Lindström, J.; Kolehmainen, M.; Tolppanen, A.M.; Eriksson, J.G.; Valle, T.T.; Aunola, S.; Ilanne-Parikka, P.; Keinänen-Kiukaanniemi, S.; et al. Variation in the UCP2 and UCP3 genes associates with abdominal obesity and serum lipids: The Finnish Diabetes Prevention Study. BMC Med. Genet. 2009, 10, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jun, H.S.; Kim, I.K.; Lee, H.J.; Lee, H.J.; Kang, J.H.; Kim, J.R.; Shin, H.D.; Song, J. Effects of UCP2 and UCP3 variants on the manifestation of overweight in Korean children. Obesity 2009, 17, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rance, K.A.; Johnstone, A.M.; Murison, A.M.; Duncan, J.S.; Wood, S.G.; Speakman, J.R. Plasma leptin levels are related to body composition, sex, insulin levels and the A55V polymorphism of the UCP2 gene. Int. J. Obes. 2007, 31, 1311–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scarpace, P.J.; Matheny, M.; Moore, R.L.; Kuma, M.V. Modulation of uncoupling protein 2 and uncoupling protein 3: Regulation by denervation, leptin and retinoic acid treatment. J. Endocrinol. 2000, 164, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, P.W.; Liu, H.F.; Ho, J.W.; Zhang, W.Y.; Chu, A.C.; Kwok, K.H.; Ge, X.; Chan, K.H.; Ramsden, D.B.; Ho, S.L. Mitochondrial uncoupling protein-2 (UCP2) mediates leptin protection against MPP+ toxicity in neuronal cells. Neurotox. Res. 2010, 17, 332–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, M.; Zhao, Z.T. Uncoupling protein 2 gene polymorphisms in association with overweight and obesity susceptibility: A meta-analysis. Meta Gene 2014, 2, 143–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esterbauer, H.; Schneitler, C.; Oberkofler, H.; Ebenbichler, C.; Paulweber, B.; Sandhofer, F.; Ladurner, G.; Hell, E.; Strosberg, A.D.; Patsch, J.R.; et al. A common polymorphism in the promoter of UCP2 is associated with decreased risk of obesity in middle-aged humans. Nat. Genet. 2001, 28, 178–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maestrini, S.; Podestà, F.; Di Blasio, A.M.; Savia, G.; Brunani, A.; Tagliaferri, A.; Mencarelli, M.; Chiodini, I.; Liuzzi, A. Lack of association between UCP2 gene polymorphisms and obesity phenotype in Italian Caucasians. J. Endocrinol. Invest. 2003, 26, 985–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, N.; Prakash, J.; Lakhan, R.; Agarwal, C.G.; Pant, D.C.; Mittal, B. A common polymorphism in the promoter of UCP2 is associated with obesity and hyperinsulenemia in northern Indians. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2010, 337, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, J.M. Leptin and the regulation of body weigh. Keio J. Med. 2011, 60, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandit, R.; Beerens, S.; Adan, R.A.H. Role of leptin in energy expenditure: The hypothalamic perspective. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2017, 312, R938–R947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myers, M.G., Jr.; Heymsfield, S.B.; Haft, C.; Kahn, B.B.; Laughlin, M.; Leibel, R.L.; Tschöp, M.H.; Yanovski, J.A. Challenges and opportunities of defining clinical leptin resistance. Cell Metab. 2012, 15, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Reed, D.R.; Price, R.A. Leptin resistance is associated with extreme obesity and aggregates in families. Int. J. Obes. 2001, 25, 1471–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calgani, A.; Delle Monache, S.; Cesare, P.; Vicentini, C.; Bologna, M.; Angelucci, A. Leptin contributes to long-term stabilization of HIF-1α in cancer cells subjected to oxygen limiting conditions. Cancer Lett. 2016, 376, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henry, B.A.; Andrews, Z.B.; Rao, A.; Clarke, I.J. Central leptin activates mitochondrial function and increases heat production in skeletal muscle. Endocrinology 2011, 152, 2609–2618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Myers, L.; Ravussin, E.; Cherry, K.E.; Jazwinski, S.M. Single nucleotide polymorphisms linked to mitochondrial uncoupling protein genes UCP2 and UCP3 affect mitochondrial metabolism and healthy aging in female nonagenarians. Biogerontology 2016, 17, 725–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luglio, H.F.; Eurike, D.; Huriyati, E.; Julia, M.; Susilowati, R. Gene-lifestyle interaction: The role of SNPs in UCP2 −866G/A and UCP3 −55C/T on dietary intake and physical ctivity in Indonesian obese female adolescents. Med. J. Nutr. Metab. 2016, 9, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huriyati, E.; Luglio, H.F.; Ratrikaningtyas, P.D.; Tsani, A.F.A.; Sadewa, A.H.; Juffrie, M. Dyslipidemia, Insulin Resistance and Dietary Fat Intake in Obese and Normal Weight Adolescents: The Role of Uncoupling Protein 2 Gene Polymomrphism. Int. J. Mol. Epidemiol. Genet. 2016, 7, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dagogo-Jack, S. Physiological and Hormonal Factors that Influence Leptin Production. In Leptin, 1st ed.; Dagogo-Jack, S., Ed.; Springer: Basel, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 45–65. [Google Scholar]
| Measurements | Total (n = 380) | AA (n = 54) | GA (n = 184) | GG (n = 142) | pAA + GA vs. GG * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 41.7 ± 11.1 (40.0) | 40.8 ± 10.9 (44.0) | 42.4 ± 9.8 (42.0) | 41.2 ± 12.8 (43.0) | 0.523 |
| Anthropometric measurements | |||||
| Body weight (kg) | 62.3 ± 13.8 (61.4) | 62.1 ± 14.4 (61.5) | 62.8 ± 13.8 (62.2) | 61.7 ± 13.7 (61.2) | 0.518 |
| Height (cm) | 157.3 ± 9.4 (156.9) | 157.2 ± 8.7 (156.2) | 157.4 ± 9.9 (157.0) | 157.1 ± 9.2 (156.8) | 0.748 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 25.2 ± 5.3 (24.6) | 25.2 ± 5.5 (25.5) | 25.3 ± 5.4 (24.6) | 25.0 ± 5.1 (24.5) | 0.724 |
| Waist circumference (cm) | 87.0 ± 13.2 (85.5) | 86.1 ± 13.3 (88.4) | 86.7 ± 12.8 (84.8) | 87.6 ± 13.7 (86.0) | 0.469 |
| Hip circumference (cm) | 94.3 ± 11.7 (94.0) | 94.1 ± 12.3 (94.8) | 94.5 ± 11.7 (93.8) | 94.2 ± 11.4 (93.8) | 0.853 |
| Body fat (%) | 28.3 ± 8.8 (28.3) | 28.0 ± 8.6 (26.6) | 28.2 ± 8.6 (28.0) | 28.5 ± 9.1 (29.7) | 0.651 |
| Plasma lipid profile | |||||
| Triglyceride (mg/dL) | 134.7 ± 68.6 (109.0) | 133.2 ± 72.2 (110.5) | 140.9 ± 77.4 (112.5) | 127.4 ± 53.3 (107.0) | 0.081 |
| HDL cholesterol (mg/dL) | 50.7 ± 44.4 (43.0) | 54.5 ± 59.8 (42.5) | 52.1 ± 51.3 (43.0) | 48.0 ± 23.1 (44.0) | 0.322 |
| Plasma leptin (ng/mL) | 7.4 ± 8.8 (4.0) | 7.1 ± 9.4 (3.5) | 7.4 ± 9.2 (4.0) | 7.5 ± 8.1 (5.0) | 0.871 |
| Dietary intake | |||||
| Total energy (kcal) | 2043.5 ± 775.6 (1884.5) | 2060.1 ± 773.9 (1914.4) | 2005.8 ± 761.1 (1833.9) | 2086.2 ± 797.6 (2000.3) | 0.409 |
| Protein (g) | 60.0 ± 29.3 (55.7) | 60.6 ± 25.2 (56.8) | 57.8 ± 27.3 (54.1) | 62.5 ± 33.1 (59.5) | 0.195 |
| Fat (g) | 53.5 ± 29.7 (47.8) | 52.0 ± 25.6 (43.8) | 52.6 ± 31.4 (47.4) | 55.2 ± 28.9 (48.6) | 0.384 |
| Carbohydrate (g) | 331.8 ± 131.8 (307.4) | 338.0 ± 128.6 (312.9) | 325.5 ± 129.2 (294.1) | 337.7 ± 136.7 (313.2) | 0.502 |
| Physical activity (METS-minute) | 5517.2 ± 5666.4 (3689.0) | 5269.6 ± 6495.8 (3396.7) | 5825.3 ± 5682.6 (4133.8) | 5210.0 ± 5316.5 (3554.5) | 0.417 |
| AA + GA (n = 238) | GG (n = 142) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| r | p | r | p | |
| Age | −0.021 | 0.742 | 0.071 | 0.400 |
| Body weight | 0.415 | <0.0001 | 0.321 | <0.0001 |
| Height | −0.302 | <0.0001 | −0.365 | <0.0001 |
| Body mass index | 0.640 | <0.0001 | 0.567 | <0.0001 |
| Waist circumference | 0.475 | <0.0001 | 0.497 | <0.0001 |
| Hip circumference | 0.629 | <0.0001 | 0.503 | <0.0001 |
| Body fat (%) | 0.709 | <0.0001 | 0.626 | <0.0001 |
| Triglyceride | 0.002 | 0.974 | −0.087 | 0.303 |
| HDL cholesterol | 0.150 | 0.022 | 0.019 | 0.822 |
| AA + GA (n = 238) | GG (n = 142) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| r | p a | p c | r | p a | p c | |
| Energy intake | −0.324 | <0.0001 | 0.004 | −0.111 | 0.188 | 0.148 |
| Protein intake | −0.268 | <0.0001 | 0.001 | −0.065 | 0.439 | 0.104 |
| Fat intake | −0.186 | 0.004 | 0.003 | 0.064 | 0.450 | 0.779 |
| Carbohydrate | −0.323 | <0.0001 | 0.031 | −0.158 | 0.060 | 0.140 |
| Total physical activity | −0.005 | 0.942 | 0.101 | −0.045 | 0.599 | 0.528 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luglio, H.F.; Sulistyoningrum, D.C.; Huriyati, E.; Lee, Y.Y.; Wan Muda, W.A.M. The Gene-Lifestyle Interaction on Leptin Sensitivity and Lipid Metabolism in Adults: A Population Based Study. Nutrients 2017, 9, 716. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9070716
Luglio HF, Sulistyoningrum DC, Huriyati E, Lee YY, Wan Muda WAM. The Gene-Lifestyle Interaction on Leptin Sensitivity and Lipid Metabolism in Adults: A Population Based Study. Nutrients. 2017; 9(7):716. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9070716
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuglio, Harry Freitag, Dian Caturini Sulistyoningrum, Emy Huriyati, Yi Yi Lee, and Wan Abdul Manan Wan Muda. 2017. "The Gene-Lifestyle Interaction on Leptin Sensitivity and Lipid Metabolism in Adults: A Population Based Study" Nutrients 9, no. 7: 716. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9070716
APA StyleLuglio, H. F., Sulistyoningrum, D. C., Huriyati, E., Lee, Y. Y., & Wan Muda, W. A. M. (2017). The Gene-Lifestyle Interaction on Leptin Sensitivity and Lipid Metabolism in Adults: A Population Based Study. Nutrients, 9(7), 716. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9070716





