Dietary Compound Resveratrol Is a Pan-BET Bromodomain Inhibitor
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Protein Expression
2.1.1. Low Scale Expression
2.1.2. Large Scale Expression
2.2. Protein Purification
2.2.1. Affinity Chromatography with Co2+ Beads
2.2.2. Rebinding with Ni2+ Beads
2.2.3. Size Exclusion Chromatography (SEC)
2.3. Differential Scanning Fluorimetry (DSF)
2.4. Isothermal Titration Calorimetry (ITC)
2.5. Molecular Docking
3. Results
3.1. Differential Scanning Fluorimetry (DSF) and Isothermal Titration Calorimetry (ITC) of RSV against Bromodomains
3.2. Binding Mode of RSV into Kac Binding Site of Bromodomains
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dutra, L.A.; Guanaes, J.F.O.; Johmann, N.; Lopes Pires, M.E.; Chin, C.M.; Marcondes, S.; Dos Santos, J.L. Synthesis, antiplatelet and antithrombotic activities of resveratrol derivatives with NO-donor properties. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 27, 2450–2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferraz da Costa, D.; Fialho, E.; Silva, J. Cancer Chemoprevention by Resveratrol: The p53 Tumor Suppressor Protein as a Promising Molecular Target. Molecules 2017, 22, 1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, Y.; Sumiyoshi, M. Resveratrol Prevents Tumor Growth and Metastasis by Inhibiting Lymphangiogenesis and M2 Macrophage Activation and Differentiation in Tumor-associated Macrophages. Nutr. Cancer 2016, 68, 667–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, C.B.; Hsieh, M.J.; Lin, C.W.; Chiou, H.L.; Lin, P.Y.; Chen, T.Y.; Yang, S.F. The Antimetastatic Effects of Resveratrol on Hepatocellular Carcinoma through the Downregulation of a Metastasis-Associated Protease by SP-1 Modulation. PLoS ONE 2013, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.Y.; Tang, H.Y.; Davis, F.B.; Davis, P.J. Resveratrol and apoptosis. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2011, 1215, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guardi, M.; Frazzi, R. Cellular and Molecular Targets of Resveratrol on Lymphoma and Leukemia Cells. Molecules 2017, 22, 885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feinberg, A.P.; Koldobskiy, M.A.; Göndör, A. Epigenetic modulators, modifiers and mediators in cancer aetiology and progression. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2016, 17, 284–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavan, A.R.; da Silva, G.D.B.; Jornada, D.H.; Chiba, D.E.; Dos Santos Fernandes, G.F.; Chin, C.M.; dos Santos, J.L. Unraveling the anticancer effect of curcumin and resveratrol. Nutrients 2016, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venturelli, S.; Berger, A.; Böcker, A.; Busch, C.; Weiland, T.; Noor, S.; Leischner, C.; Schleicher, S.; Mayer, M.; Weiss, T.S.; et al. Resveratrol as a Pan-HDAC Inhibitor Alters the Acetylation Status of Jistone Proteins in Human-Derived Hepatoblastoma Cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippakopoulos, P.; Knapp, S. Targeting bromodomains: epigenetic readers of lysine acetylation. Nat. Publ. Gr. 2014, 13, 337–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filippakopoulos, P.; Qi, J.; Picaud, S.; Shen, Y.; Smith, W.B.; Fedorov, O.; Morse, E.M.; Keates, T.; Hickman, T.T.; Felletar, I.; et al. Selective inhibition of BET bromodomains. Nature 2010, 468, 1067–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picaud, S.; Wells, C.; Felletar, I.; Brotherton, D.; Martin, S.; Savitsky, P. RVX-208, an inhibitor of BET transcriptional regulators with selectivity for the second bromodomain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 19754–19759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of Structural Proteins during the Assembly of the Head of Bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friesner, R.A.; Banks, J.L.; Murphy, R.B.; Halgren, T.A.; Klicic, J.J.; Mainz, D.T.; Repasky, M.P.; Knoll, E.H.; Shelley, M.; Perry, J.K.; et al. Glide: A New Approach for Rapid, Accurate Docking and Scoring. 1. Method and Assessment of Docking Accuracy. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 1739–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shelley, J.C.; Cholleti, A.; Frye, L.L.; Greenwood, J.R.; Timlin, M.R.; Uchimaya, M. Epik: A software program for pKa prediction and protonation state generation for drug-like molecules. J. Comput. Aided. Mol. Des. 2007, 21, 681–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, P.; Chen, H.; Wold, E.A.; Tian, B.; Brasier, A.R.; Zhou, J. Drug Discovery Targeting Bromodomain-Containing Protein 4. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 4533–4558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bromodomain, C.F.; Chaikuad, A.; Brennan, P.E.; Temperini, C.; Fedorov, O.; Hollander, J.; Nachane, R.; Abell, C.; Mu, S.; Siegal, G.; et al. Structure-Based Identi fi cation of Inhibitory Fragments Targeting the p300/CBP-Associated Factor Bromodomain. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 1648–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewings, D.S.; Wang, M.; Philpott, M.; Fedorov, O.; Uttarkar, S.; Filippakopoulos, P.; Picaud, S.; Vuppusetty, C.; Marsden, B.; Knapp, S.; et al. 5-Dimethylisoxazoles Act As Acetyl-lysine-mimetic Bromodomain Ligands. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 6761–6770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hewitt, M.C.; Leblanc, Y.; Gehling, V.S.; Vaswani, R.G.; Nasveschuk, C.G.; Taylor, A.M.; Harmange, J.C.; Audia, J.E.; Pardo, E.; Cummings, R.; et al. Development of methyl isoxazoleazepines as inhibitors of BET. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 25, 1842–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brand, M.; Measures, A.M.; Wilson, B.G.; Cortopassi, W.A.; Alexander, R.; Ho, M.; Hewings, D.S.; Rooney, T.P.C.; Paton, R.S.; Conway, S.J. Small Molecule Inhibitors of Bromodomain—Acetyl-lysine Interactions. ACS Chem. Biol. 2015, 10, 22–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conway, S.J. Bromodomains: Are Readers Right for Epigenetic Therapy? ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 3, 691–694. [Google Scholar]
- Andrieu, G.; Belkina, A.C.; Denis, G.V. Clinical trials for BET inhibitors run ahead of the science. Drug Discov. Today Technol. 2016, 19, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, D.; Jeong, H.; Lee, M.N.; Koh, A.; Kwon, O.; Yang, Y.R.; Noh, J.; Suh, P.-G.; Park, H.; Ryu, S.H. Resveratrol induces autophagy by directly inhibiting mTOR through ATP competition. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, H.S.; McBurney, M.; Robbins, P.D. SIRT1 negatively regulates the mammalian target of rapamycin. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakamaki, J.; Wilkinson, S.; Hahn, M.; Tasdemir, N.; O’Prey, J.; Clark, W.; Hedley, A.; Nixon, C.; Long, J.S.; New, M.; et al. Bromodomain Protein BRD4 Is a Transcriptional Repressor of Autophagy and Lysosomal Function. Mol. Cell 2017, 66, 517–532.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
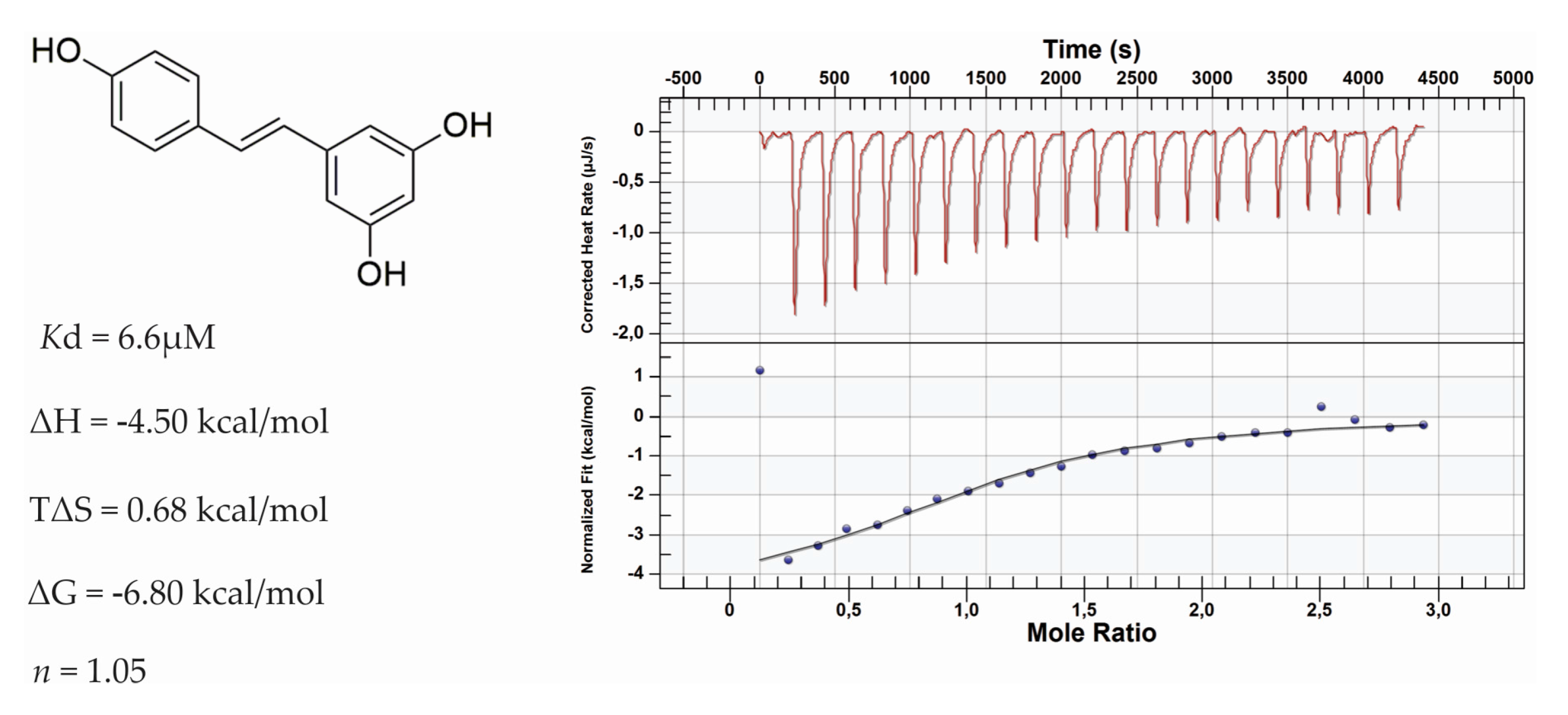
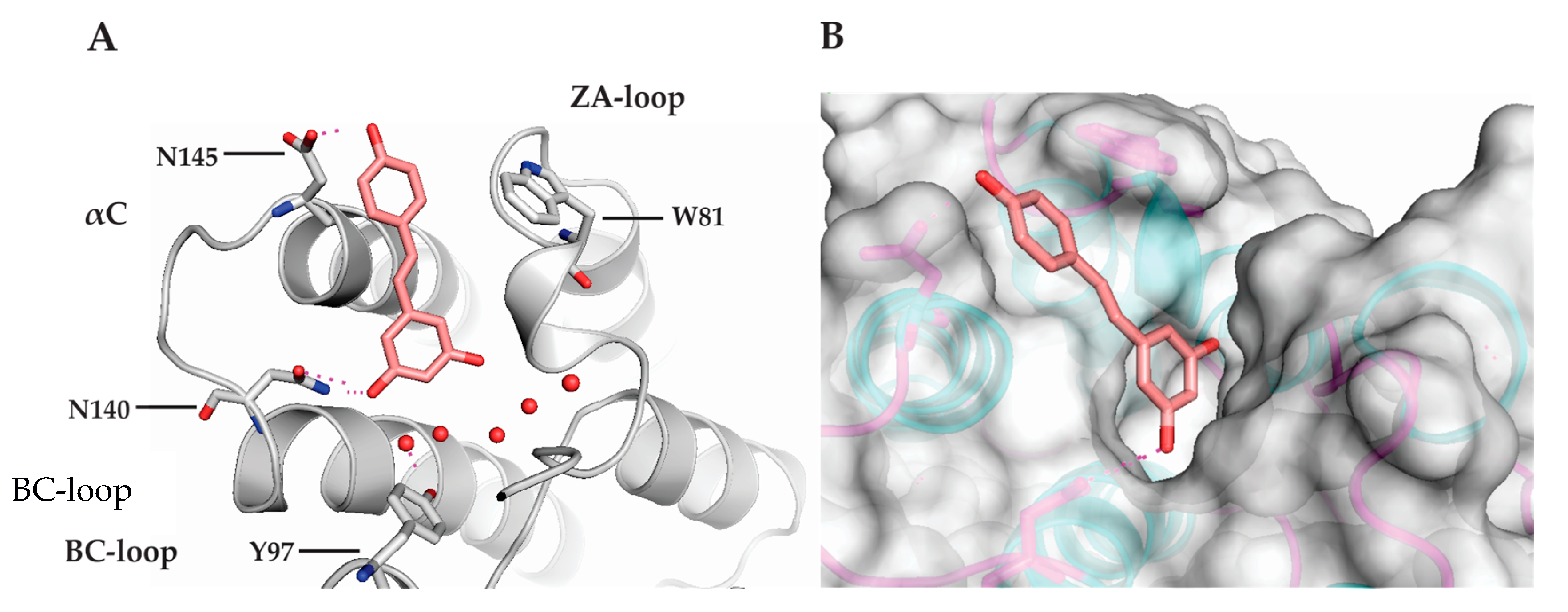
| Protein | Resveratrol 100 µM |
|---|---|
| ∆Tm (°C) | |
| BRD2(1) | 2.0 ± 0.5 |
| BRD3(1) | 1.8 ± 0.2 |
| BRD4(1) | 2.0 ± 0.6 |
| BRDT(1) | 1.5 ± 0.3 |
| BRD4(2) | 3.0 ± 0.5 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dutra, L.A.; Heidenreich, D.; Silva, G.D.B.d.; Man Chin, C.; Knapp, S.; Santos, J.L.d. Dietary Compound Resveratrol Is a Pan-BET Bromodomain Inhibitor. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1172. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9111172
Dutra LA, Heidenreich D, Silva GDBd, Man Chin C, Knapp S, Santos JLd. Dietary Compound Resveratrol Is a Pan-BET Bromodomain Inhibitor. Nutrients. 2017; 9(11):1172. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9111172
Chicago/Turabian StyleDutra, Luiz Antonio, David Heidenreich, Gabriel Dalio Bernardes da Silva, Chung Man Chin, Stefan Knapp, and Jean Leandro dos Santos. 2017. "Dietary Compound Resveratrol Is a Pan-BET Bromodomain Inhibitor" Nutrients 9, no. 11: 1172. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9111172
APA StyleDutra, L. A., Heidenreich, D., Silva, G. D. B. d., Man Chin, C., Knapp, S., & Santos, J. L. d. (2017). Dietary Compound Resveratrol Is a Pan-BET Bromodomain Inhibitor. Nutrients, 9(11), 1172. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9111172






