Lactobacillus fermentum CRL1446 Ameliorates Oxidative and Metabolic Parameters by Increasing Intestinal Feruloyl Esterase Activity and Modulating Microbiota in Caloric-Restricted Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Bacterial Suspensions
2.2. Animals and Diets
2.3. Preparation of Intestinal Extracts
2.4. Determination of Intestinal FE Activity
2.5. DNA Extraction from Intestinal Contents
2.6. High-Throughput Sequencing (HTS) of 16S rRNA Gene Amplicons
2.7. Biochemical Assays
2.8. Lipoperoxidation and Glutathione Reductase (GR) Activity in Plasma
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effect of Caloric Restriction Diet and L. fermentum CRL1446 Administration on Body Weight
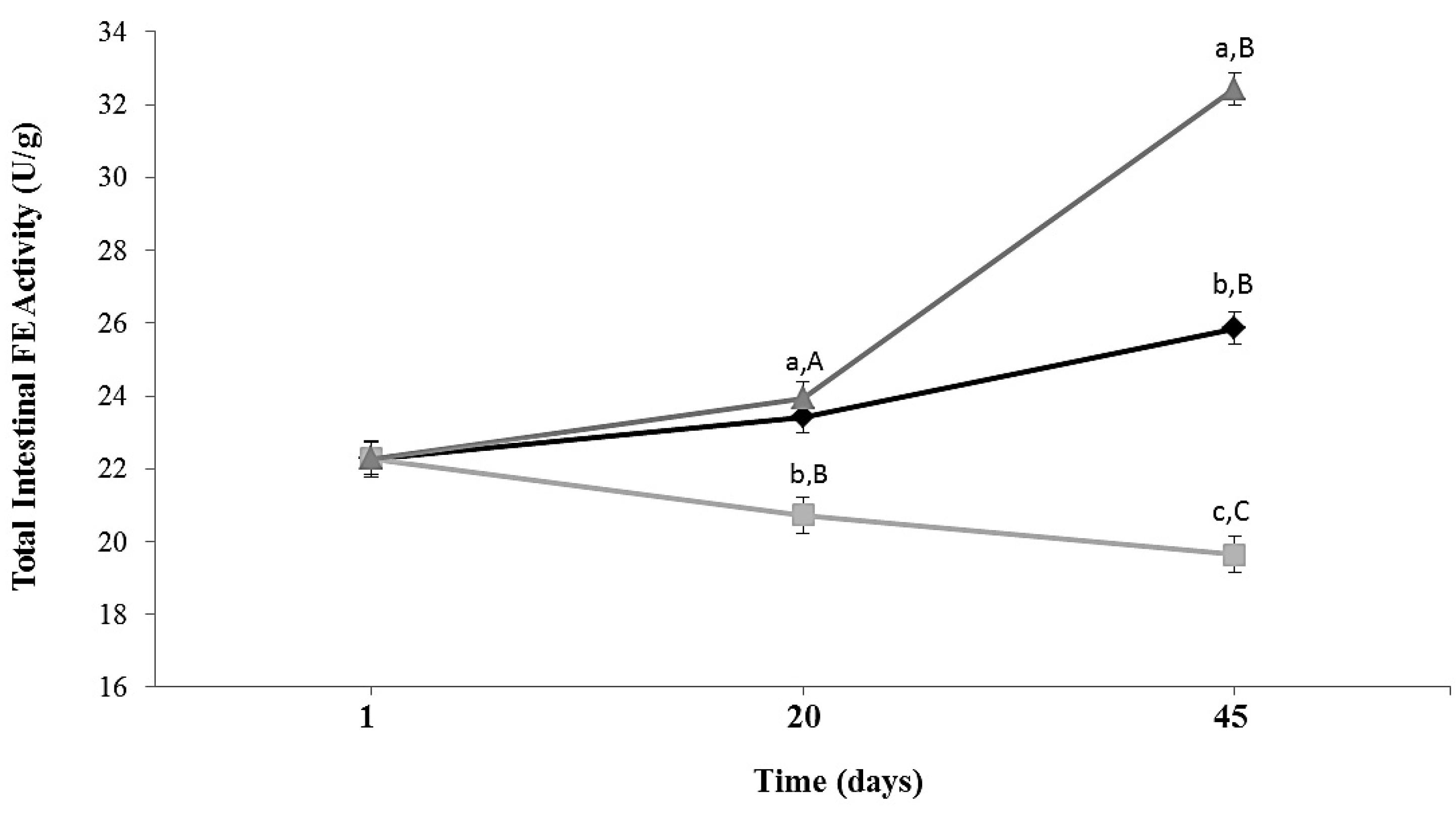
3.2. Total Intestinal Feruloyl Esterase Activity in Mice
3.3. Feruloyl Esterase Activity in Different Intestinal Fractions
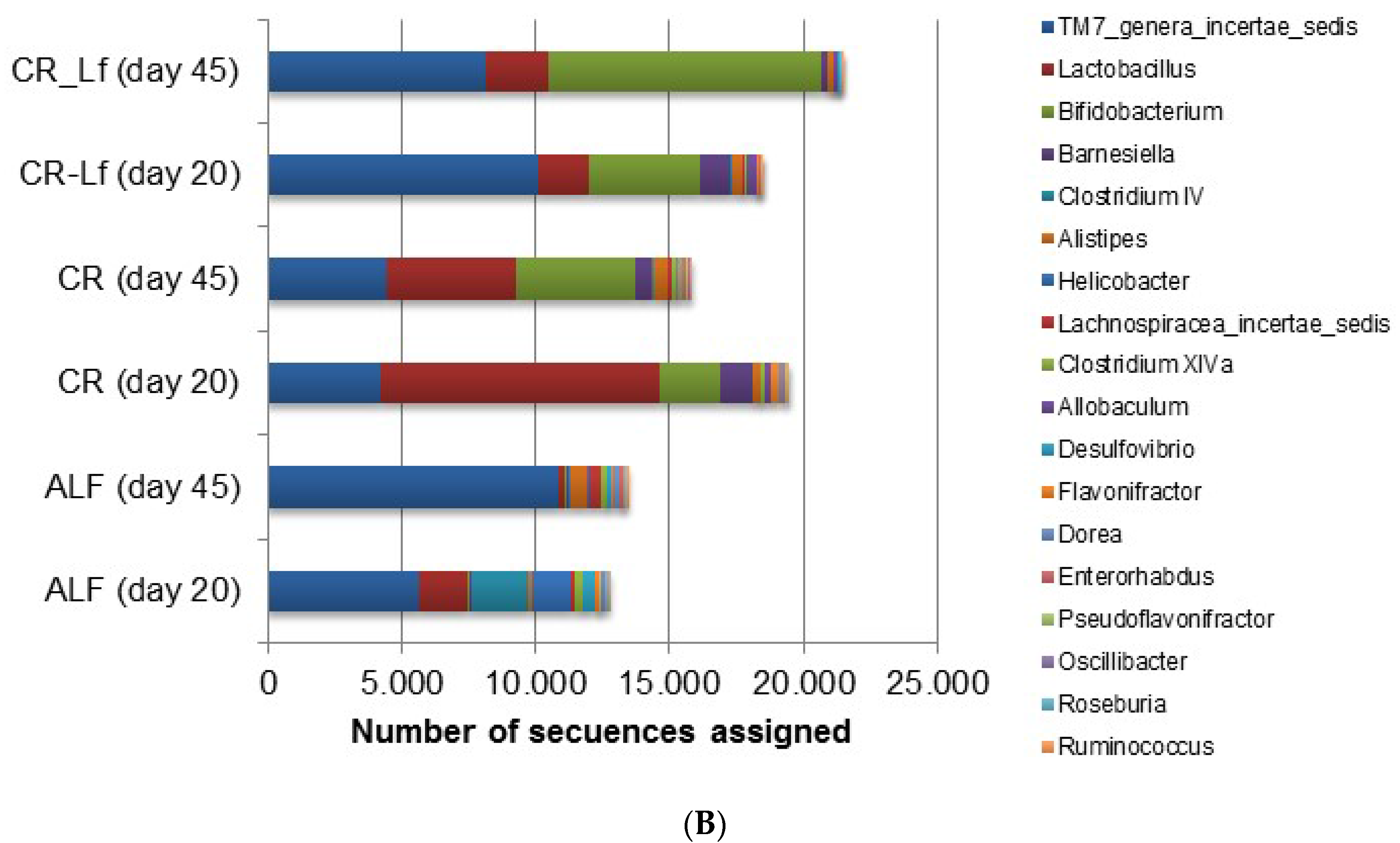
3.4. Effect of CR Diet and L. fermentum CRL1446 Administration on Intestinal Microbiota
3.5. Effect of CR Diet and L. fermentum CRL1446 Administration on Lipid Peroxidation and Glutathione Reductase Activity
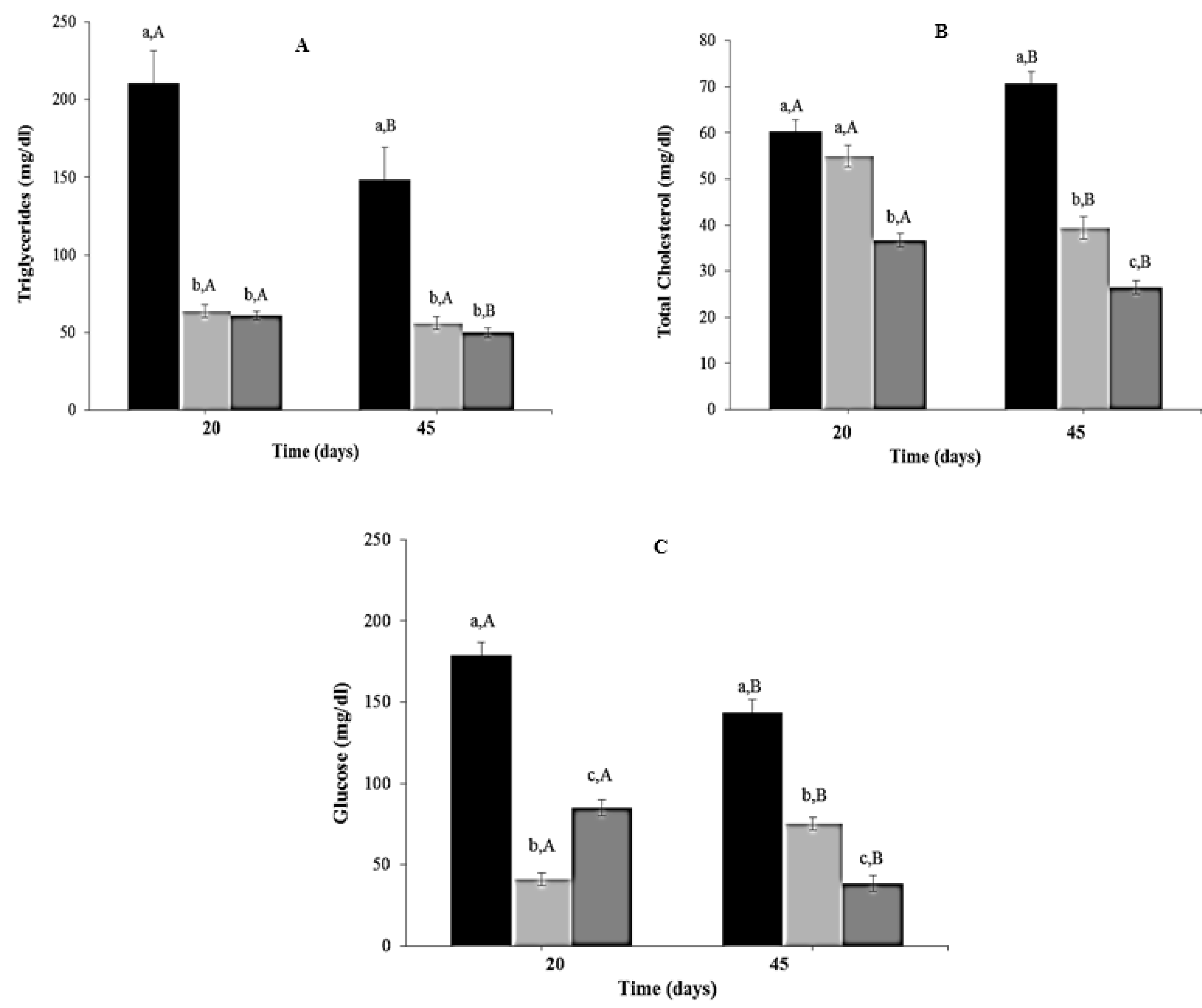
3.6. Effect of CR Diet and L. fermentum CRL1446 Administration on Biochemical Parameters
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bales, C.W.; Kraus, W.E. Caloric Restriction: Implications for human cardiometabolic health. J. Cardiopulm. Rehabil. Prev. 2013, 33, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holliday, R. Food, reproduction and longevity—Is the extended lifespan of calorie-restricted animals an evolutionary adaptation? Bioessays 1989, 10, 125–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masoro, E.J. Caloric restriction-induced life extension of rats and mice: A critique of proposed mechanisms. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBAGen. Subj. 2009, 1790, 1040–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Li, S.; Yang, L.; Huang, P.; Li, W.; Wang, S.; Zhao, G.; Zhang, M.; Pang, X.; Yan, Z.; et al. Structural modulation of gut microbiota in life-long calorie-restricted mice. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dao, M.; Everard, A.; Clément, K.; Cani, P. Losing weight for a better health: Role for the gut microbiota. Clin. Nutr. Exp. 2016, 6, 39–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz, Y.; Collado, M.C.; Haros, M.; Dalmau, J. Funciones metabólico-nutritivas de la microbiota intestinal y su modulación a través de la dieta: Probióticos y prebióticos. Acta Pediatr. Esp. 2004, 62, 520–526. [Google Scholar]
- Bhathena, J.; Martoni, C.; Kulamarva, A.; Urbanska, A.M.; Malhotra, M.; Prakash, S. Orally delivered microencapsulated live probiotic formulation lowers serum lipids in hypercholesterolemic hamsters. J. Med. Food 2009, 12, 310–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abeijón-Mukdsi, M.C.; Cano, M.P.G.; González, S.N.; Medina, R.B. Administration of Lactobacillus fermentum CRL1446 increases intestinal feruloyl esterase activity in mice. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2012, 54, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fazary, A.E.; Ju, Y.H. Feruloylesterases as biotechnological tools: Current and future perspectives. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2007, 39, 811–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srinivasan, M.; Sudheer, A.R.; Menon, V.P. Ferulic acid: Therapeutic potential through its antioxidant property. J. Clin. Biochem. Nut. 2007, 40, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreasen, M.F.; Kroon, P.A.; Williamson, G.; Garcia-Conesa, M.T. Esterase activity able to hydrolyze dietary antioxidant hydroxycinnamates is distributed along the intestine of mammals. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 5679–5684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Couteau, D.; McCartney, A.L.; Gibson, G.R.; Williamson, G.; Faulds, C.B. Isolation and characterization of human colonic bacteria able to hydrolysechlorogenic acid. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2001, 90, 873–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreasen, M.F.; Kroon, P.A.; Williamson, G.; Garcia-Conesa, M.T. Intestinal release and uptake of phenolic antioxidant diferulic acids. Free Radical Biol. Med. 2001, 31, 304–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AbeijónMukdsi, M.C.; Haro, C.; González, S.N.; Medina, R.B. Functional goat milk cheese with feruloyl esterase activity. J. Funct. Foods 2013, 5, 801–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhathena, J.; Tomaro-Duchesneau, C.; Martoni, C.; Malhotra, M.; Kulamarva, A.; Urbanska, M.A.; Paul, A.; Prakash, S. Effect of orally administered microencapsulated FA-producing L. fermentum on markers of metabolic syndrome: An in vivo analysis. J. Diabetes Metab. 2012, S2, 009. [Google Scholar]
- Tomaro-Duchesneau, C.; Saha, S.; Malhotra, M.; Jones, M.L.; Labbé, A.; Rodes, L.; Kahouli, I.; Prakash, S. Effect of orally administered L. fermentum NCIMB 5221 on markers of metabolic syndrome: An in vivo analysis using ZDF rats. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 115–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliszewski, R.; Medina, R.; Gonzalez, S.; Perez Chaia, A. Esterase activities of indigenous lactic acid bacteria from Argentinean goats’ milk and cheeses. Food Chem. 2007, 101, 1446–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abeijón-Mukdsi, M.C.; Argañaraz Martínez, E.; PerezChaia, A.; Medina, R.B. Feruloyl esterase activity is influenced by bile, probiotic intestinal adhesion and milk fat. Benef. Microbe 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polka, J.; Rebecchi, A.; Pisacane, V.; Morelli, L.; Puglis, E. Bacterial diversity in typical Italian salami at different ripening stages as revealed by high-throughput sequencing of 16S rRNAamplicons. Food Microbiol. 2015, 46, 342–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magoč, T.; Salzberg, S.L. FLASH: Fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2957–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C.; Haas, B.J.; Clemente, J.C.; Quince, C.; Knigh, R. UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2194–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 590–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schloss, P.D.; Westcott, S.L.; Ryabin, T.; Hall, J.R.; Hartmann, M.; Hollister, E.B.; Lesniewski, R.A.; Oakley, B.B.; Parks, D.H.; Robinson, C.J.; et al. Introducing mothur: Open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 7537–7541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Garrity, G.M.; Tiedje, J.M.; Cole, J.R. Naïve Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 5261–5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lozupone, C.; Lladser, M.E.; Knights, D.; Stombaugh, J.; Knight, R. UniFrac: An effective distance metric for microbial community comparison. ISME 2001, 5, 69–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okawa, H.; Ohsihi, N.; Yagi, K. Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal. Biochem. 1979, 95, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esterbauer, H.; Grill, D. Seasonal variation of glutathione and glutathione reductase in needles of Picea abies. Plant Physiol. 1978, 61, 119–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spindler, S.R. Caloric restriction: From soup to nuts. Ageing Res. Rev. 2010, 9, 324–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, R.M.; Weindruch, R. Metabolic reprogramming, caloric restriction and aging. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 21, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez, F.; Ramos Galván, R.; Frerenk, S.; Cravioto Muñoz, J.; Chavez, R.; Vasquez, J. Mortality in second and third degree malnutrition, 1956. Bull World Health Organ. 2000, 78, 1275–1280. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Geng, X.; Egashira, Y.; Sanada, H. Release of ferulic acid from wheat bran by an inducible feruloyl esterase from an intestinal bacterium Lactobacillus acidophilus. Food Sci. Technol. Res. 2005, 11, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ley, R.E.; Turnbaugh, P.J.; Klein, S.; Gordon, J.I. Microbial ecology: Human gut microbes associated with obesity. Brief Commun. Nat. 2006, 444, 1022–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, L.M.; Martínez, I.; Walter, J.; Goin, C.; Hutkins, R.W. Barcoded pyrosequencing reveals that consumption of galactooligosaccharides results in a highly specific bifidogenic response in humans. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e25200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, X.; Wang, J.; Yao, H. Feruloyl oligosaccharides stimulate the growth of Bifidobacterium bifidum. Anaerobe 2005, 11, 225–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernardeau, M.; Guguen, M.; Vernoux, J.P. Beneficial lactobacilli in food and feed: Long-term use, biodiversity and proposals for specific and realistic safety assessments. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2006, 30, 487–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zareie, M.; Johnson-Henry, K.; Jury, J.; Yang, P.C.; Ngan, B.; McKay, D.M.; Soderholm, J.D.; Perdue, M.H.; Sherman, P.M. Probiotics prevent bacterstinal barrier function in rats following chronic psychological stress. Gut 2006, 55, 1553–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graf, E. Antioxidant potential of ferulic acid. Free Radical Biol. Med. 1992, 13, 435–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruss, M.D.; Khambatta, C.F.; Ruby, M.A.; Aggarwal, I.; Hellerstein, M.K. Calorie restriction increases fatty acid synthesis and whole body fat oxidation rates. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 298, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skrha, J. Effect of caloric restriction on oxidative markers. Adv. Clin. Chem. 2009, 47, 223–247. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fontana, L. The scientific basis of caloric restriction leading to longer life. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2009, 25, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balasubashini, M.S.; Rukkumani, R.; Menon, V.P. Protective effects of ferulic acid on hyperlipidemic diabetic rats. Acta Diabetol. 2003, 40, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koubova, J.; Guarente, L. How does calorie restriction work? Genes Dev. 2003, 17, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adisakwattana, S.; Moonsan, P.; Yibchok-Anun, S. Insulin-releasing properties of a series of cinnamic acid derivatives in vitro and in vivo. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 7838–7844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Source of Enzyme | Day | Groups | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALF | CR | CR-Lf | ||
| SIM | 20 | 11.66 ± 0.06 a | 11.12 ± 0.08 a | 11.35 ± 0.09 a |
| 45 | 14.60± 0.07 b | 11.83 ± 0.53 c | 15.29 ± 0.04 a | |
| LIM | 20 | 10.20 ± 0.06 b | 8.29 ± 0.05 c | 11.05 ± 0.07 a |
| 45 | 14.21 ± 0.04 b | 12.99± 0.06 c | 14.40 ± 0.05 a | |
| SIC | 20 | 0.84 ± 0.05 a | 0.88 ± 0.08 a | 0.87 ± 0.04 a |
| 45 | 1.28 ± 0.06 a | 1.29 ± 0.07 a | 1.26 ± 0.06 a | |
| LIC | 20 | 0.91 ± 0.06 a | 0.47 ± 0.02 c | 0.62 ± 0.04 b |
| 45 | 1.14 ± 0.07 b | 0.85 ± 0.05 c | 1.49 ± 0.05 a | |
| Sample | Distance | Sobs | Chao’s Richness Index | Shannon Diversity Index | Simpson Index | Shannon Evenness Index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALF20 | 0.03 | 1374 | 10,684 | 3.677 | 0.083 | 0.508 |
| ALF45 | 0.03 | 1400 | 8550 | 3.477 | 0.196 | 0.479 |
| CR20 | 0.03 | 1275 | 10,536 | 3.022 | 0.160 | 0.422 |
| CR45 | 0.03 | 1399 | 11,768 | 3.628 | 0.084 | 0.500 |
| CR-Lf20 | 0.03 | 1269 | 9183 | 2.771 | 0.204 | 0.387 |
| CR-Lf45 | 0.03 | 1193 | 12,337 | 2.219 | 0.274 | 0.313 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Russo, M.; Fabersani, E.; Abeijón-Mukdsi, M.C.; Ross, R.; Fontana, C.; Benítez-Páez, A.; Gauffin-Cano, P.; Medina, R.B. Lactobacillus fermentum CRL1446 Ameliorates Oxidative and Metabolic Parameters by Increasing Intestinal Feruloyl Esterase Activity and Modulating Microbiota in Caloric-Restricted Mice. Nutrients 2016, 8, 415. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu8070415
Russo M, Fabersani E, Abeijón-Mukdsi MC, Ross R, Fontana C, Benítez-Páez A, Gauffin-Cano P, Medina RB. Lactobacillus fermentum CRL1446 Ameliorates Oxidative and Metabolic Parameters by Increasing Intestinal Feruloyl Esterase Activity and Modulating Microbiota in Caloric-Restricted Mice. Nutrients. 2016; 8(7):415. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu8070415
Chicago/Turabian StyleRusso, Matias, Emanuel Fabersani, María C. Abeijón-Mukdsi, Romina Ross, Cecilia Fontana, Alfonso Benítez-Páez, Paola Gauffin-Cano, and Roxana B. Medina. 2016. "Lactobacillus fermentum CRL1446 Ameliorates Oxidative and Metabolic Parameters by Increasing Intestinal Feruloyl Esterase Activity and Modulating Microbiota in Caloric-Restricted Mice" Nutrients 8, no. 7: 415. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu8070415
APA StyleRusso, M., Fabersani, E., Abeijón-Mukdsi, M. C., Ross, R., Fontana, C., Benítez-Páez, A., Gauffin-Cano, P., & Medina, R. B. (2016). Lactobacillus fermentum CRL1446 Ameliorates Oxidative and Metabolic Parameters by Increasing Intestinal Feruloyl Esterase Activity and Modulating Microbiota in Caloric-Restricted Mice. Nutrients, 8(7), 415. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu8070415









