Potassium and Obesity/Metabolic Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Epidemiological Evidence
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Study Selection
2.3. Data Extraction
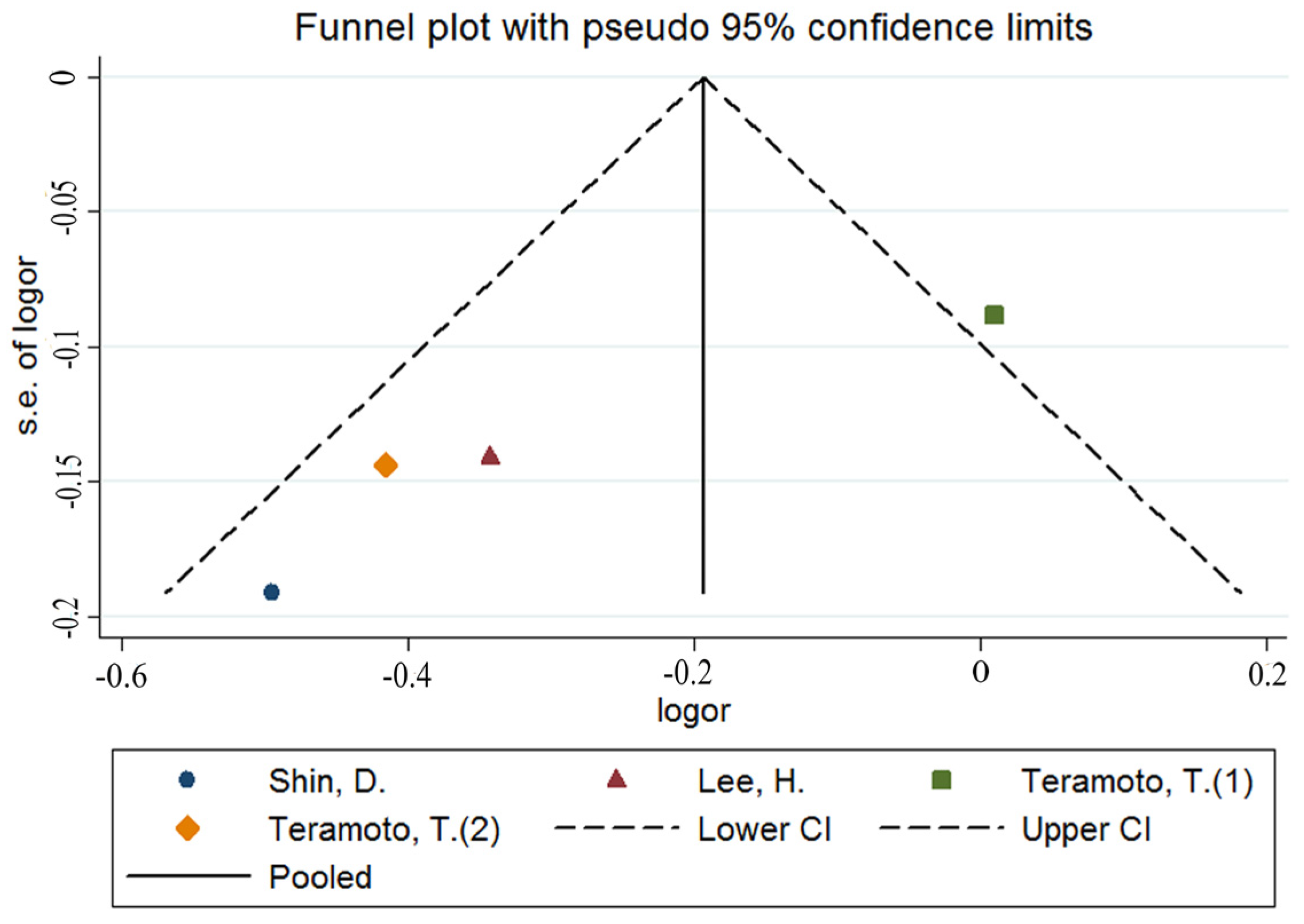
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
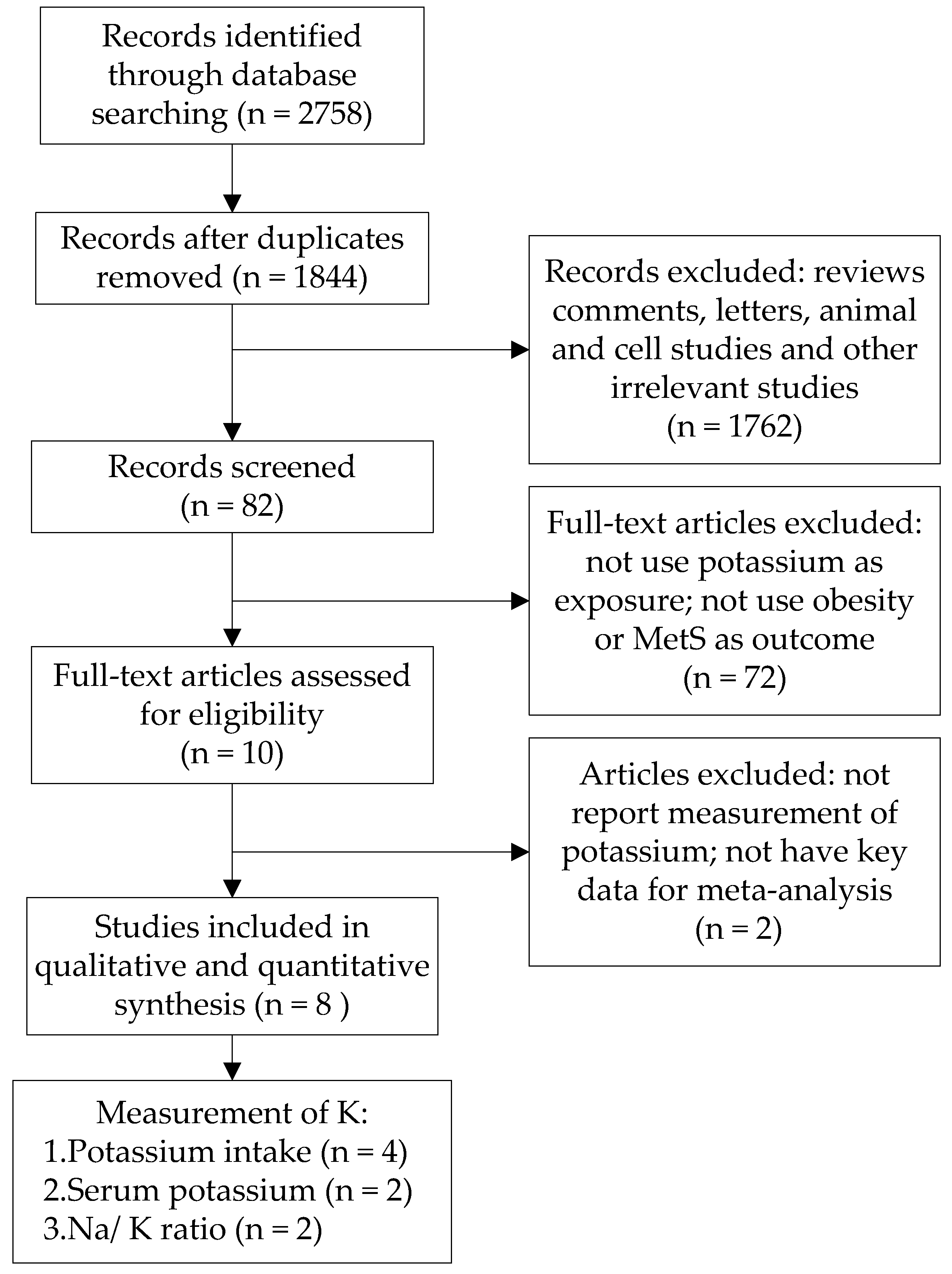
3.1. Characteristics of the Identified Studies
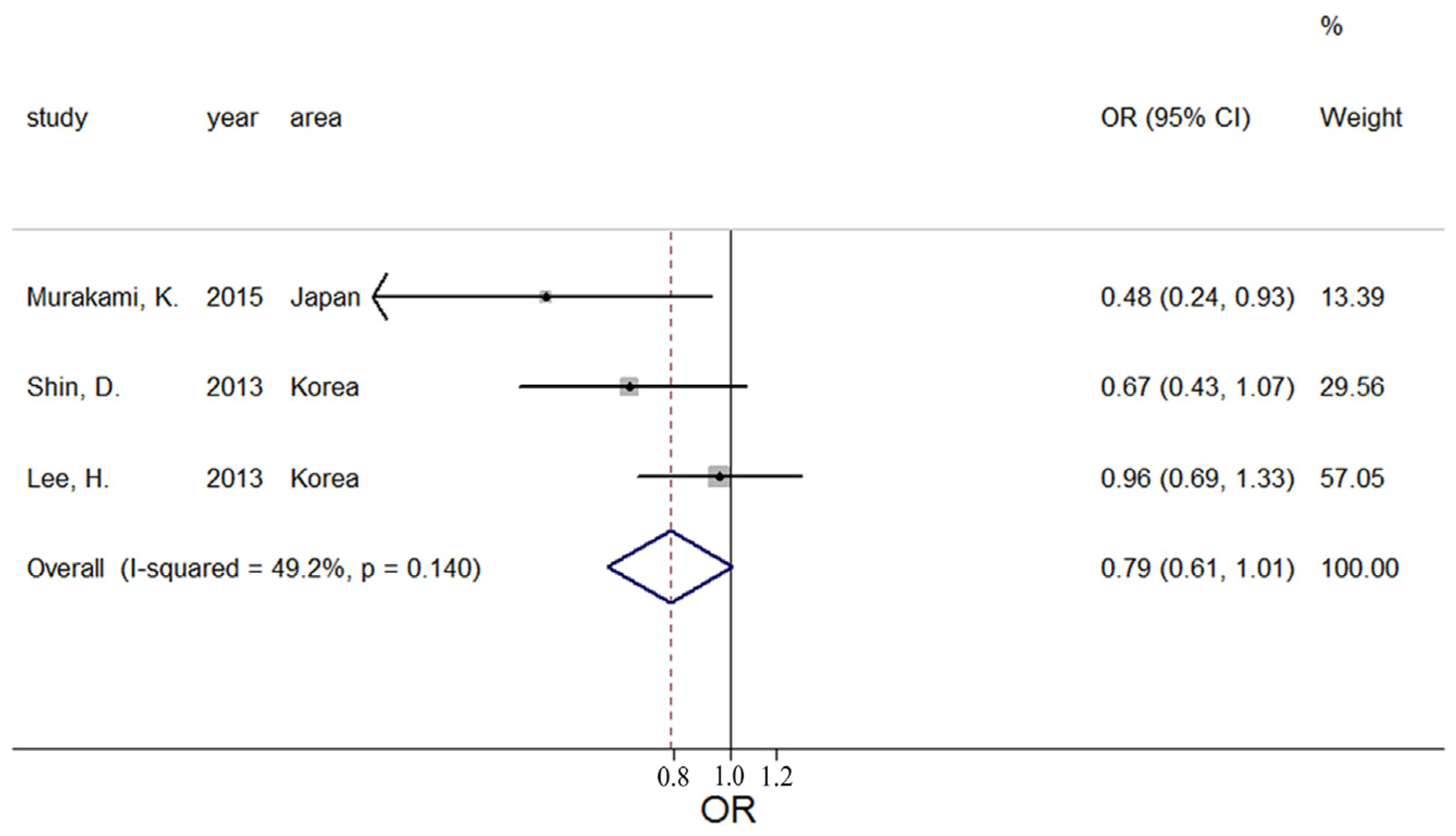
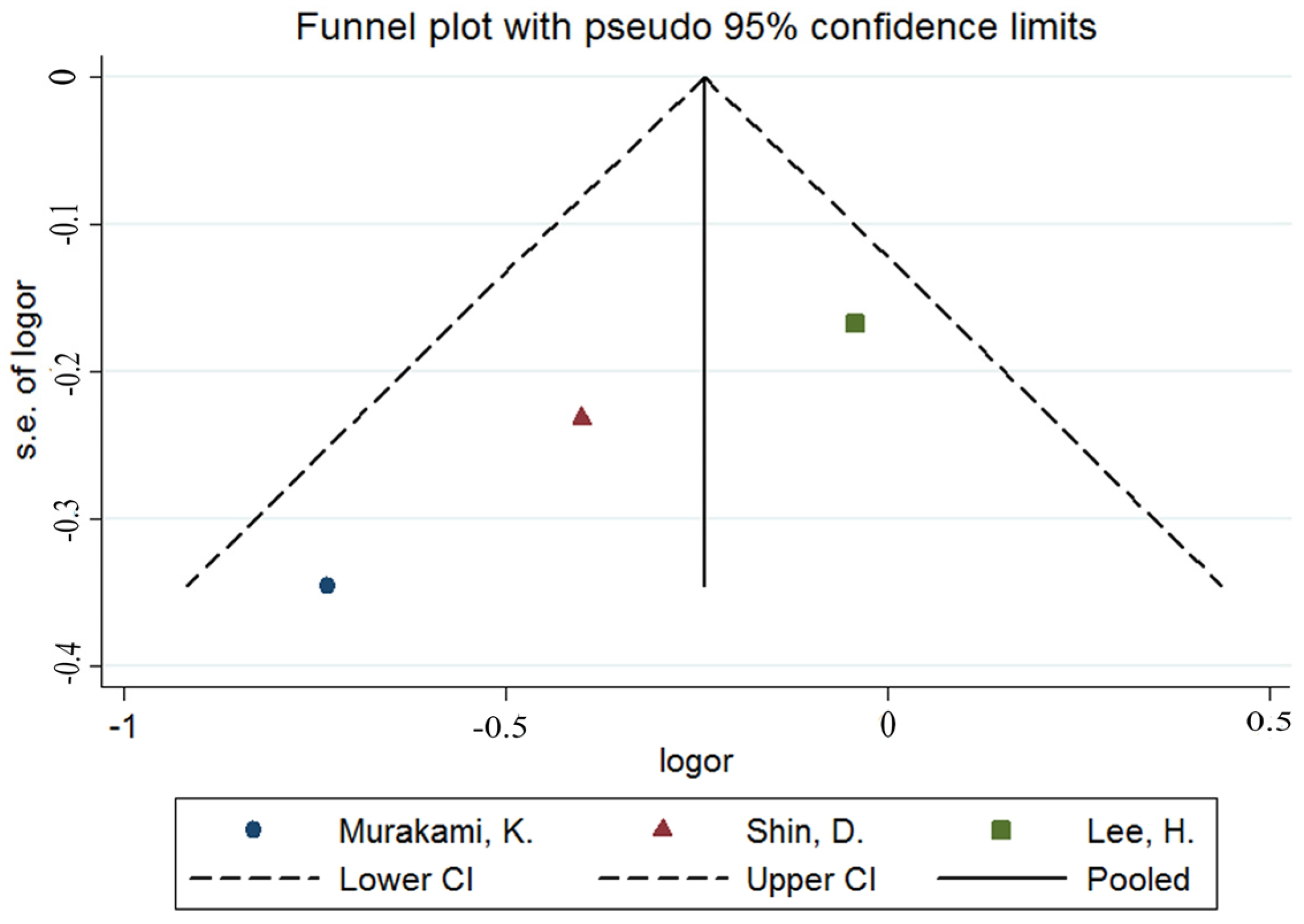
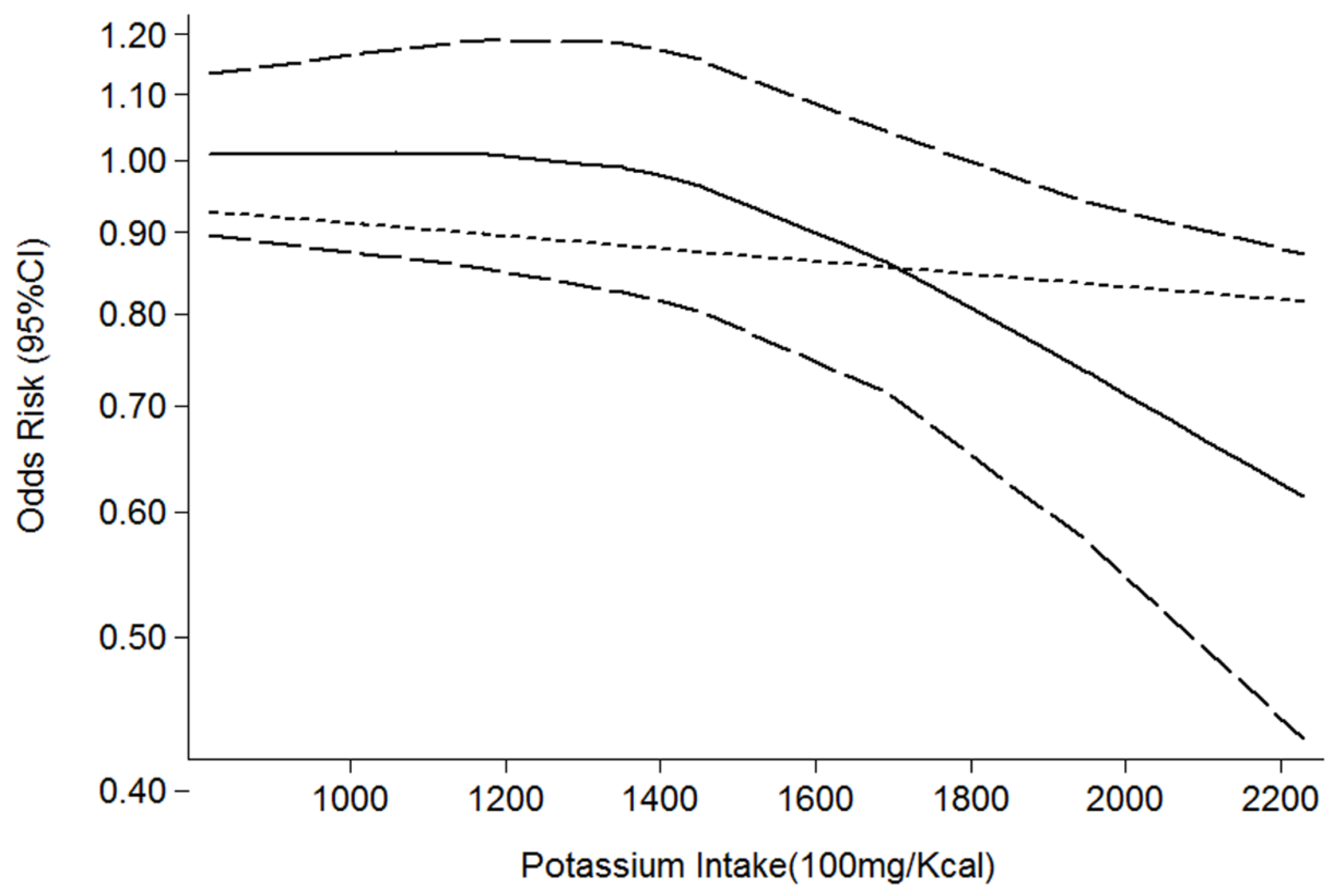
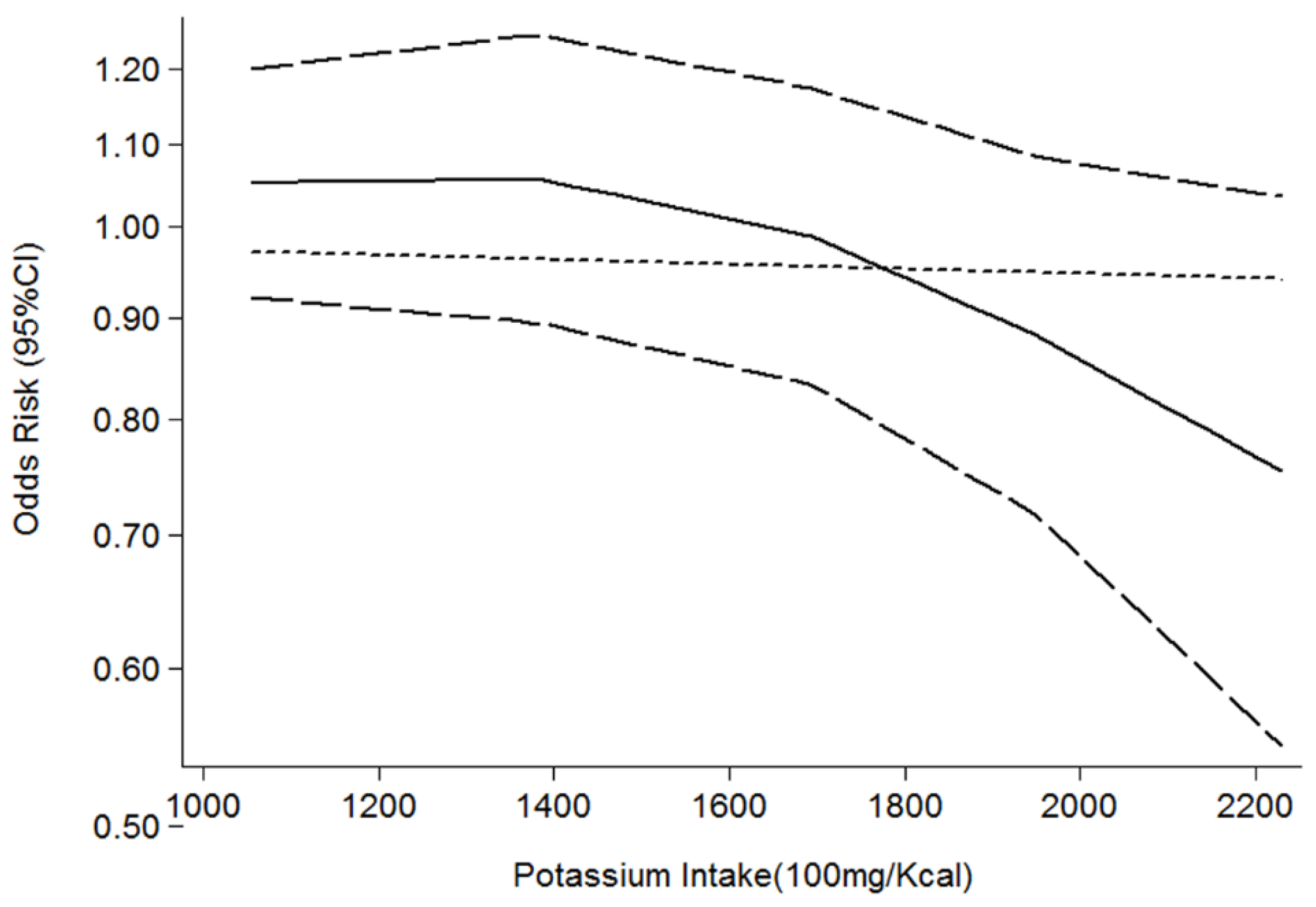
3.2. Potassium and Obesity
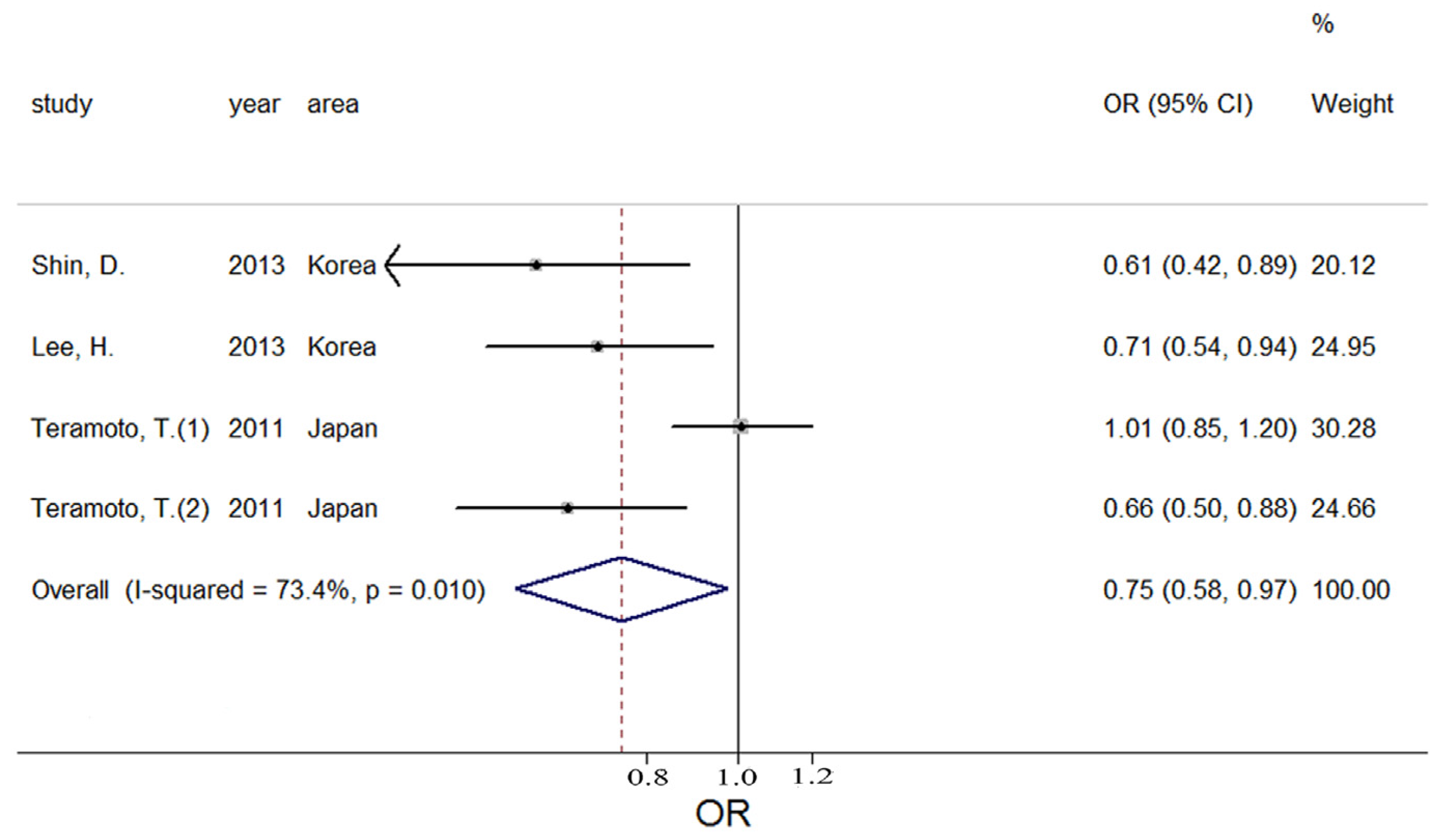
3.3. Potassium and Metabolic Syndrome
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ogden, C.L.; Carroll, M.D.; Kit, B.K.; Flegal, K.M. Prevalence of childhood and adult obesity in the United States, 2011–2012. JAMA 2014, 311, 806–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Vliet-Ostaptchouk, J.V.; Nuotio, M.L.; Slagter, S.N.; Doiron, D.; Fischer, K.; Foco, L.; Gaye, A.; Gogele, M.; Heier, M.; Hiekkalinna, T.; et al. The prevalence of metabolic syndrome and metabolically healthy obesity in Europe: A collaborative analysis of ten large cohort studies. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2014, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzarella, L. Why does obesity promote cancer? Epidemiology, biology, and open questions. Ecancermedicalscience 2015, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grundy, S.M.; Cleeman, J.I.; Daniels, S.R.; Donato, K.A.; Eckel, R.H.; Franklin, B.A.; Gordon, D.J.; Krauss, R.M.; Savage, P.J.; Smith, S.C., Jr.; et al. Diagnosis and management of the metabolic syndrome: An American heart association/national heart, lung, and blood institute scientific statement: Executive summary. Crit. Pathw. Cardiol. 2005, 4, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mozumdar, A.; Liguori, G. Persistent increase of prevalence of metabolic syndrome among U.S. Adults: Nhanes III to NHANES 1999–2006. Diabetes Care 2011, 34, 216–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokdad, A.H.; Ford, E.S.; Bowman, B.A.; Dietz, W.H.; Vinicor, F.; Bales, V.S.; Marks, J.S. Prevalence of obesity, diabetes, and obesity-related health risk factors, 2001. JAMA 2003, 289, 76–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grundy, S.M. Metabolic syndrome: Connecting and reconciling cardiovascular and diabetes worlds. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2006, 47, 1093–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canoy, D.; Boekholdt, S.M.; Wareham, N.; Luben, R.; Welch, A.; Bingham, S.; Buchan, I.; Day, N.; Khaw, K.T. Body fat distribution and risk of coronary heart disease in men and women in the European prospective investigation into cancer and nutrition in norfolk cohort: A population-based prospective study. Circulation 2007, 116, 2933–2943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, J.Y.; Choi, Y.H.; Song, Y.M. Metabolic syndrome in Korean cancer survivors and family members: A study in a health promotion center. Nutr. Cancer 2015, 67, 1075–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, D.; Joh, H.K.; Kim, K.H.; Park, S.M. Benefits of potassium intake on metabolic syndrome: The fourth Korean national health and nutrition examination survey (KNHANES IV). Atherosclerosis 2013, 230, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stang, A. Critical evaluation of the Newcastle-Ottawa scale for the assessment of the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2010, 25, 603–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DerSimonian, R.; Laird, N. Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control. Clin. Trials 1986, 7, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantel, N.; Haenszel, W. Statistical aspects of the analysis of data from retrospective studies of disease. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1959, 22, 719–748. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Orsini, N.; Li, R.; Wolk, A.; Khudyakov, P.; Spiegelman, D. Meta-analysis for linear and nonlinear dose-response relations: Examples, an evaluation of approximations, and software. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2012, 175, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egger, M.; Smith, G.D. Bias in location and selection of studies. BMJ 1998, 316, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, K.; Livingstone, M.B.; Sasaki, S.; Uenishi, K. Ability of self-reported estimates of dietary sodium, potassium and protein to detect an association with general and abdominal obesity: Comparison with the estimates derived from 24 h urinary excretion. Br. J. Nutr. 2015, 113, 1308–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, K.; Su, T.; Li, M.; Xu, B.; Xu, M.; Lu, J.; Liu, J.; Bi, Y.; Ning, G. Serum potassium level is associated with metabolic syndrome: A population-based study. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 33, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, K.; Lu, J.; Jiang, Y.; Xu, M.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xu, B.; Sun, J.; Sun, W.; Ren, C.; et al. Low serum potassium level is associated with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and its related metabolic disorders. Clin. Endocrinol. 2014, 80, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Lee, J.; Hwang, S.S.; Kim, S.; Chin, H.J.; Han, J.S.; Heo, N.J. Potassium intake and the prevalence of metabolic syndrome: The Korean national health and nutrition examination survey 2008–2010. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e55106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teramoto, T.; Kawamori, R.; Miyazaki, S.; Teramukai, S. Sodium intake in men and potassium intake in women determine the prevalence of metabolic syndrome in Japanese hypertensive patients: Omega study. Hypertens. Res. 2011, 34, 957–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, N.; Minhajuddin, A.T.; Neeland, I.J.; Elsayed, E.F.; Vega, G.L.; Hedayati, S.S. Association of urinary sodium-to-potassium ratio with obesity in a multiethnic cohort. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 99, 992–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, Z.; Zhang, J.; Chen, X.; Yan, L.; Guo, X.; Lu, Z.; Xu, A.; Ma, J. Are 24 h urinary sodium excretion and sodium: Potassium independently associated with obesity in Chinese adults? Public Health Nutr. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabara, Y.; Takahashi, Y.; Kumagai, K.; Setoh, K.; Kawaguchi, T.; Takahashi, M.; Muraoka, Y.; Tsujikawa, A.; Gotoh, N.; Terao, C.; et al. Descriptive epidemiology of spot urine sodium-to-potassium ratio clarified close relationship with blood pressure level: The Nagahama study. J. Hypertens. 2015, 33, 2407–2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binia, A.; Jaeger, J.; Hu, Y.; Singh, A.; Zimmermann, D. Daily potassium intake and sodium-to-potassium ratio in the reduction of blood pressure: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J. Hypertens. 2015, 33, 1509–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, Z.; Guo, X.; Chen, X.; Tang, J.; Yan, L.; Ren, J.; Zhang, J.; Lu, Z.; Dong, J.; Xu, J.; et al. Association between 24 h urinary sodium and potassium excretion and the metabolic syndrome in Chinese adults: The Shandong and ministry of health action on salt and hypertension (smash) study. Br. J. Nutr. 2015, 113, 996–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Climent, B.; Simonsen, U.; Rivera, L. Effects of obesity on vascular potassium channels. Curr. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2014, 12, 438–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crunkhorn, S. Metabolic disease: Potassium channel blocker prevents obesity. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2013, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Jiang, H.; Wang, M.; Korpelainen, H.; Li, C. Male poplars have a stronger ability to balance growth and carbohydrate accumulation than do females in response to a short-term potassium deficiency. Physiol. Plant. 2015, 155, 400–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mariosa, L.S.; Ribeiro-Filho, F.F.; Batista, M.C.; Hirota, A.H.; Borges, R.L.; Ribeiro, A.B.; Zanella, M.T. Abdominal obesity is associated with potassium depletion and changes in glucose homeostasis during diuretic therapy. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2008, 10, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashcroft, F.M. Atp-sensitive potassium channelopathies: Focus on insulin secretion. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 2047–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatterjee, R.; Yeh, H.C.; Shafi, T.; Selvin, E.; Anderson, C.; Pankow, J.S.; Miller, E.; Brancati, F. Serum and dietary potassium and risk of incident type 2 diabetes mellitus: The atherosclerosis risk in communities (ARIC) study. Arch. Intern. Med. 2010, 170, 1745–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, T.N.; Gu, D.; Rao, D.C.; Chen, J.; Chen, J.; Cao, J.; Li, J.; Lu, F.; Ma, J.; Mu, J.; et al. Maternal history of hypertension and blood pressure response to potassium intake: The gensalt study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2012, 176, S55–S63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Cogswell, M.E.; Gillespie, C.; Fang, J.; Loustalot, F.; Dai, S.; Carriquiry, A.L.; Kuklina, E.V.; Hong, Y.; Merritt, R.; et al. Association between usual sodium and potassium intake and blood pressure and hypertension among U.S. Adults: NHANES 2005–2010. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e75289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, K.; Sasaki, S.; Uenishi, K. The degree of misreporting of the energy-adjusted intake of protein, potassium, and sodium does not differ among under-, acceptable, and over-reporters of energy intake. Nutr. Res. 2012, 32, 741–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esmaillzadeh, A.; Kimiagar, M.; Mehrabi, Y.; Azadbakht, L.; Hu, F.B.; Willett, W.C. Fruit and vegetable intakes, c-reactive protein, and the metabolic syndrome. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 84, 1489–1497. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
| Study | Country | Age | Participants | Cases | Measurement of K | Gender | Outcome | OR (95% CI) | Controlled Factor |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Murakami, K. (2015) | Japan | 18–22 y | 1043 | 136 | Intake | Women | Obesity | 0.48 (0.24, 0.93) | year, region, municipality level, residential status, living alone or living with others, alcohol drinking, smoking, physical activity, other nutrients |
| Shin, D. (2013) | Korea | ≥20 y | 7542 | 1568 | Intake | M and F | Obesity | 0.67 (0.43, 1.07) | total energy, carbohydrate, total fat, fibre, vitamin C, and sodium intakes |
| 1269 | Intake | M and F | MetS | 0.61 (0.42, 0.89) | |||||
| Lee, H. (2013) | Korea | Mean 45.3 y | 9911 | 3885 | Intake | Women | Obesity | 0.96 (0.69, 1.33) | age, BMI, alcohol intake, exercise, education, income, residential area, frequency of fruit intake, energy, and carbohydrate energy ratio |
| 2012 | Intake | Women | MetS | 0.71 (0.54, 0.94) | |||||
| Teramoto, T. (2011) | Japan | Mean 64.9 y | 4656 | 2277 | Intake | Men | MetS | 1.01 (0.85, 1.20) | Unadjusted |
| 4929 | 943 | Intake | Women | MetS | 0.66 (0.50, 0.88) | ||||
| Ge, Z. (2015) | China | 18–69 y | 1906 | 992 | Na/K ratio | M and F | Obesity | 0.74 (0.56, 0.98) | age, sex, education, urbanization, leisure-time physical activity, alcohol consumption, smoking, hypertension, antihypertensive treatment, fasting plasma glucose and TAG |
| Jain, N. (2014) | USA | Mean 44 y | 2782 | 890 | Na/K ratio | M and F | Obesity | 0.43 (0.15, 0.72) | age, sex, race, DM, SBP, DBP, and serum glucose and triglyceride concentrations |
| Sun, K. (a) (2014) | China | ≥40 y | 10,341 | 4361 | Serum | M and F | Obesity | 0.76 (0.70, 0.82) | age, sex, BMI, current smoking and drinking status; other components of metabolic syndrome as dichotomised variables |
| 3981 | Serum | M and F | MetS | 0.68 (0.53, 0.86) | |||||
| Sun, K. (b) (2014) | China | Mean 58.6 y | 8592 | 3695 | Serum | M and F | Obesity | 0.63 (0.52, 0.77) | age, sex, BMI, current smoking status, use of drug, FPG, HbA1C, TG, TC, LDL-C, HDL-C, SBP, DBP, ALT, AST, serum sodium, serum magnesium, eGFR and HOMA-IR |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cai, X.; Li, X.; Fan, W.; Yu, W.; Wang, S.; Li, Z.; Scott, E.M.; Li, X. Potassium and Obesity/Metabolic Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Epidemiological Evidence. Nutrients 2016, 8, 183. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu8040183
Cai X, Li X, Fan W, Yu W, Wang S, Li Z, Scott EM, Li X. Potassium and Obesity/Metabolic Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Epidemiological Evidence. Nutrients. 2016; 8(4):183. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu8040183
Chicago/Turabian StyleCai, Xianlei, Xueying Li, Wenjie Fan, Wanqi Yu, Shan Wang, Zhenhong Li, Ethel Marian Scott, and Xiuyang Li. 2016. "Potassium and Obesity/Metabolic Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Epidemiological Evidence" Nutrients 8, no. 4: 183. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu8040183
APA StyleCai, X., Li, X., Fan, W., Yu, W., Wang, S., Li, Z., Scott, E. M., & Li, X. (2016). Potassium and Obesity/Metabolic Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Epidemiological Evidence. Nutrients, 8(4), 183. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu8040183






