The Identification of Biochanin A as a Potent and Selective β-Site App-Cleaving Enzyme 1 (Bace1) Inhibitor
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. General
2.2. Enzymatic Assay of BACE1, TACE and Other Serine Proteases
2.3. Kinetic Studies of Biochanin A against BACE1
2.4. Molecular Docking Studies of Biochanin A
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
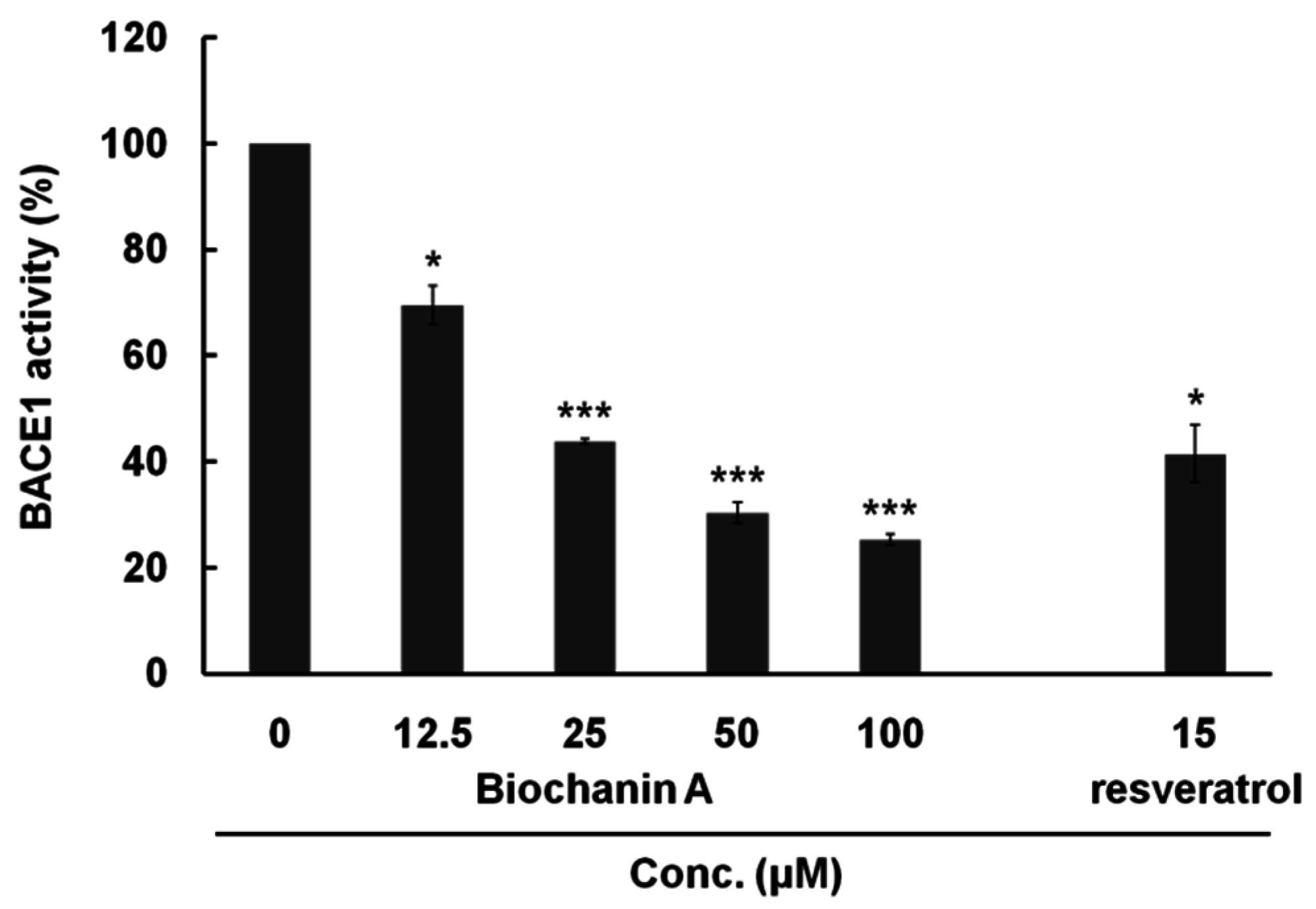
3.1. In Vitro BACE1 Inhibitory Activity of Biochanin A
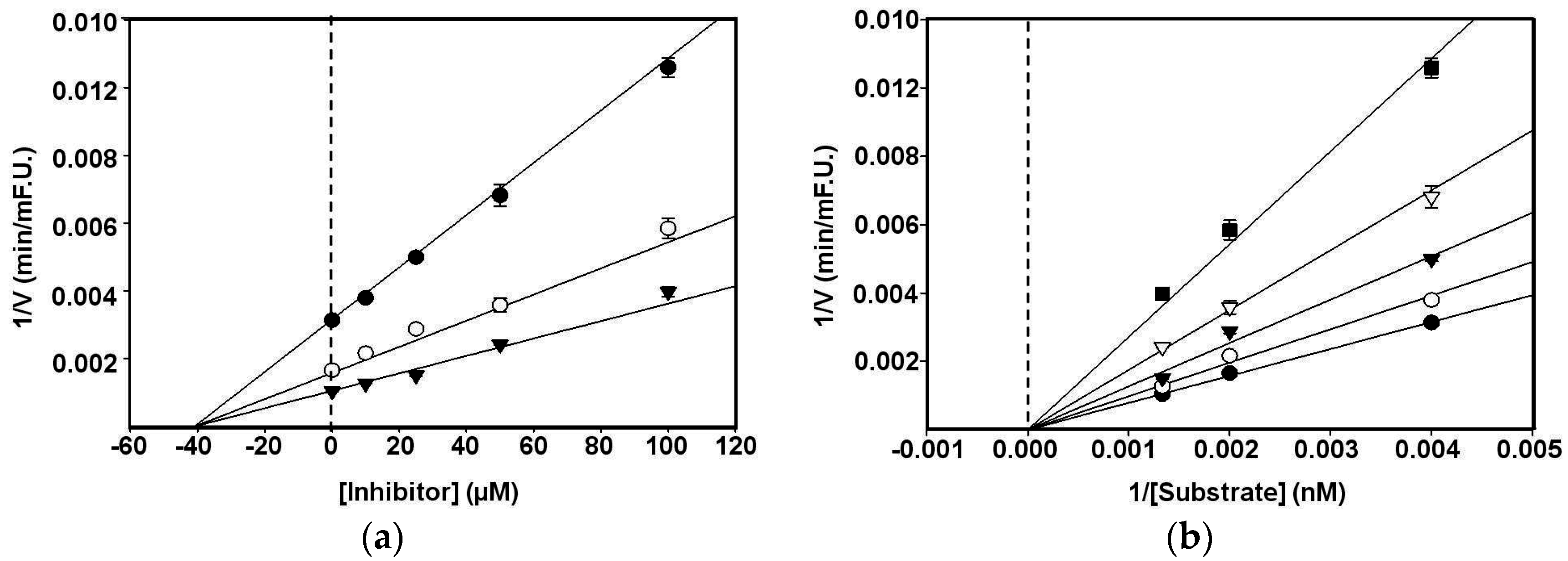
3.2. Kinetic Parameters of Biochanin A
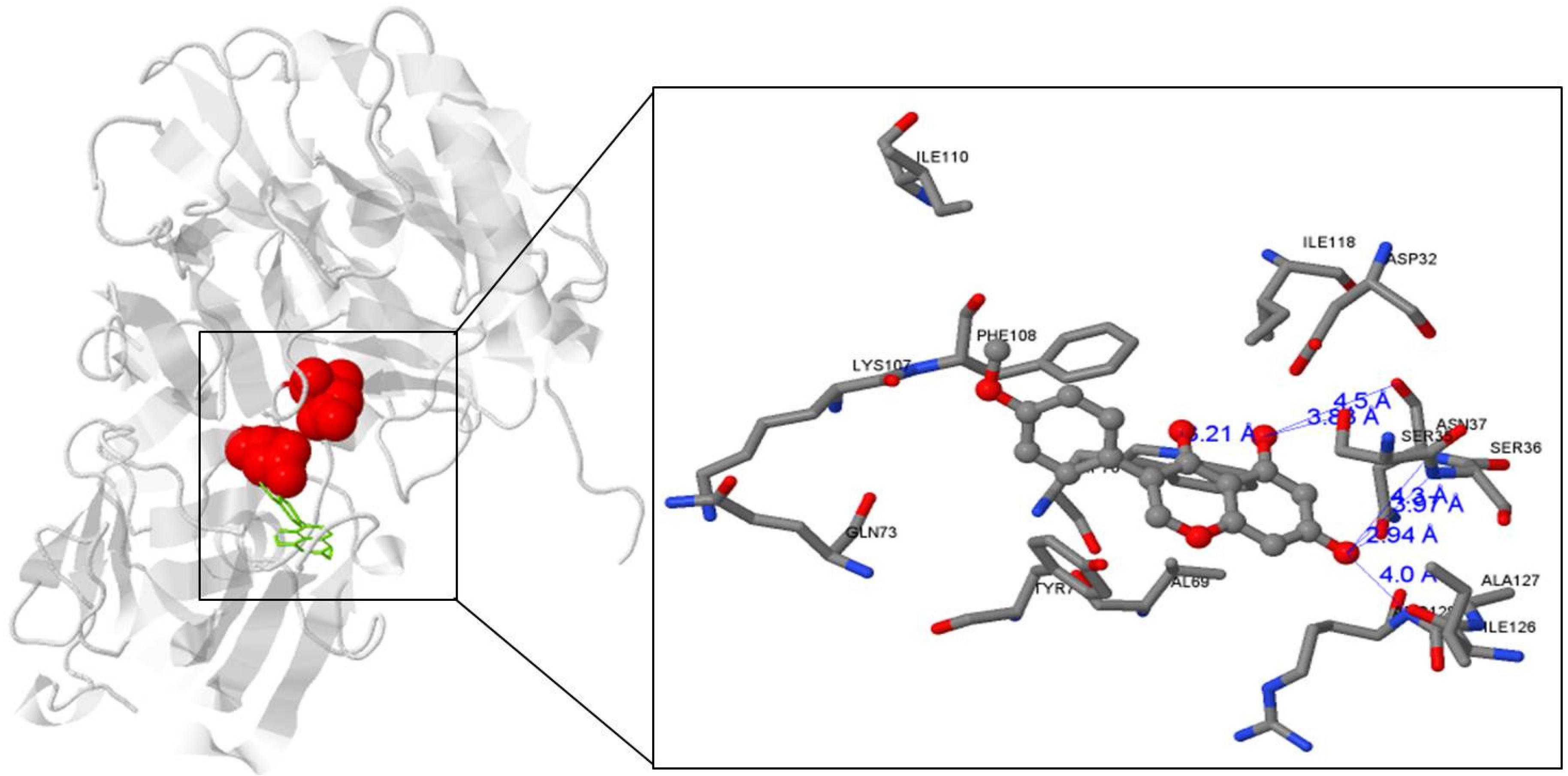
3.3. Biochanin A Interacts with BACE1 in Docking Analysis
3.4. Inhibition of TACE and Other Proteases Structurally Related to BACE1
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jakob-Roetne, R.; Jacobsen, H. Alzheimer’s Disease: From pathology to therapeutic approaches. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2009, 48, 3030–3059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardy, J.A.; Higgins, G.A. Alzheimer’s disease: The amyloid cascade hypothesis. Science 1992, 10, 184–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Citron, M. β-Secretase Inhibition for the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease Promise and challenge. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2004, 25, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoji, M.; Golde, T.E.; Ghiso, J.; Cheung, T.T.; Estus, S.; Shaffer, L.M.; Cai, X.D.; Mckay, D.M.; Tintner, R.; Frangione, B. Production of the Alzheimer amyloid beta protein by normal proteolytic processing. Science 1992, 258, 126–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urbanc, B.; Cruz, L.; Buldyrev, S.V.; Havlin, S.; Irizarry, M.C.; Stanley, H.E.; Hyman, H.T. Dynamics of plaque formation in Alzheimer’s disease. Biophys. J. 1999, 76, 1330–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holloway, M.K.; Hunt, P.; McGaughey, G.B. Structure and modeling in the design of β- and γ-secretase inhibitors. Drug Dev. Res. 2009, 70, 70–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.; Wang, Y.; McCarthy, D.; Wen, H.; Borchelt, D.R.; Price, D.L.; Wong, P.C. BACE1 is the major beta-secretase for generation of abeta peptides by neurons. Nat. Neurosci. 2001, 4, 233–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y. Ginkgo Biloba Neuroprotection: Therapeutic implications in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2001, 3, 401–407. [Google Scholar]
- McConlogue, L.; Buttini, M.; Anderson, J.P.; Brigham, E.F.; Chen, K.S.; Freedman, S.B.; Games, D.; Johnson-Wood, K.; Lee, M.; Zeller, M.; et al. Partial reduction of BACE has dramatic effects on Alzheimer plaque and synaptic pathology in APP transgenic mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 26326–26334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabe, S.; Reichwald, J.; Ammaturo, D.; de Strooper, B.; Saftig, P.; Neumann, U.; Staufenbiel, M. The Swedish APP mutation alters the effect of genetically reduced BACE1 expression on the APP processing. J. Neurochem. 2011, 119, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, X.Y.; Zhao, Y.; Yu, S.S.; Fang, W.S. BACE1 (beta-secretase) inhibitory phenolic acids and a novel sesquiterpenoid from Homalomena occulta. Chem. Biodivers. 2010, 7, 984–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saviranta, N.M.M.; Anttonen, M.J.; von Wright, A.; Karjalainen, R.O. Red clover (Trifoliumpratense L.) isoflavones: Determination of concentrations by plant stage, flower colour, plant part and cultivar. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2008, 88, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrepfer, S.; Deuse, T.; Münzel, T.; Schäfer, H.; Braendle, W.; Reichenspurner, H. The selective estrogen receptor-beta agonist biochanin A shows vasculoprotective effects without uterotrophic activity. Menopause 2006, 13, 489–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, J.W.; Kim, M.K. Neuroprotective effects of Biochanin A against β-amyloid-induced neurotoxicity in PC12 cells via a mitochondrial-dependent apoptosis pathway. Molecules 2016, 21, 548–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.Q.; Jin, Z.Y.; Li, G.H. Biochanin A protects dopaminergic neurons against lipopolysaccharide-induced damage through inhibition of microglia activation and proinflammatory factors generation. Neurosci. Lett. 2007, 417, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Occhiuto, F.; Palumbo, D.R.; Samperi, S.; Zangla, G.; Pino, A.; De Pasquale, R.; Circosta, C. The isoflavones mixture from Trifoliumpratense L. Protects HCN 1-A neurons from oxidative stress. Phytother. Res. 2009, 23, 192–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biradar, S.M.; Joshi, H.; Chheda, T.K. Biochanin-A ameliorates behavioural and neurochemical derangements in cognitive-deficit mice for the betterment of Alzheimer’s Disease. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2014, 33, 369–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youn, K.; Lee, J.; Yun, E.Y.; Ho, C.T.; Karwe, M.V.; Jeong, W.S.; Jun, M. Biological evaluation and in silico docking study of γ-linolenic acid as a potential BACE1 inhibitor. J. Funct. Foods 2014, 10, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marvin 5.11.4, 2012, ChemAxon. Available online: http://www.chemaxon.com.
- Trott, O.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock Vina: Improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornish-Bowden, A. A simple graphical method for determining the inhibition constants of mixed, uncompetitive and non-competitive inhibitors. Biochem. J. 1974, 137, 143–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahringer, A.; Karamustafa, S.; Klotz, D.; Kahl, S.; Konkimalla, V.B.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, H.Y.; Boechzelt, H.; Hao, X.; et al. Inhibition of P-glycoprotein at the blood-brain barrier by phytochemicals derived from traditional Chinese medicine. Cancer Genom. Proteom. 2010, 7, 191–205. [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh, A.K.; Brindisi, M.; Tang, J. Developing β-secretase inhibitors for treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurochem. 2012, 120, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Morris, M.E. Effect of the flavonoids biochanin A and silymarin on the P-glycoprotein-mediated transport of digoxin and vinblastine in human intestinal Caco-2 cells. Pharm. Res. 2003, 20, 1184–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Morris, M.E. Effects of the flavonoids biochanin A, morin, phloretin and silymarin on P-glycoprotein-mediated transport. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2003, 304, 1258–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sehm, T.; Fan, Z.; Weiss, R.; Schwarz, M.; Engelhorn, T.; Hore, N.; Doerfler, A.; Buchfelder, M.; Eyüpoglu, I.Y.; Savaskan, N.E. The impact of dietary isoflavonoids on malignant brain tumors. Cancer Med. 2014, 3, 865–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Setchell, K.D.; Brown, N.M.; Desai, P.; Zimmer-Nechemias, L.; Wolfe, B.E.; Brashear, W.T.; Kirschner, A.S.; Cassidy, A.; Heubi, J.E. Bioavailablity of Pure Isoflavones in Healthy Humans and Analysis of Commercial Soy Isoflavone Supplements. J. Nutr. 2001, 131, 1362S–1375S. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Moon, Y.J.; Sagawa, K.; Frederick, K.; Zhang, S.; Morris, M.E. Pharmacokinetics and bioavailability of the isoflavone biochanin A in rats. AAPS J. 2006, 8, E433–E442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, Y.J.; Morris, M.E. Pharmacokinetics and bioavailability of the bioflavonoid biochanin A: Effects of quercetin and EGCG on biochanin A disposition in rats. Mol. Pharm. 2007, 4, 865–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanagihara, K.; Ito, A.; Toge, T.; Numoto, M. Antiproliferative effects of isoflavones on human cancer cell lines established from the gasatrointestinal tract. Cancer Res. 1993, 53, 5815–5821. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
| Biochanin A (μM) | TACE | Trypsin | Chymotrypsin | Elastase |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 | 18.33 ± 2.14 | 11.69 ± 3.25 | 8.33 ± 1.89 | 15.01 ± 3.02 |
| 100 | 22.71 ± 2.54 | 14.14 ± 1.39 | 7.99 ± 1.78 | 17.78 ± 1.89 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Youn, K.; Park, J.-H.; Lee, J.; Jeong, W.-S.; Ho, C.-T.; Jun, M. The Identification of Biochanin A as a Potent and Selective β-Site App-Cleaving Enzyme 1 (Bace1) Inhibitor. Nutrients 2016, 8, 637. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu8100637
Youn K, Park J-H, Lee J, Jeong W-S, Ho C-T, Jun M. The Identification of Biochanin A as a Potent and Selective β-Site App-Cleaving Enzyme 1 (Bace1) Inhibitor. Nutrients. 2016; 8(10):637. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu8100637
Chicago/Turabian StyleYoun, Kumju, Ji-Hyun Park, Jinhyuk Lee, Woo-Sik Jeong, Chi-Tang Ho, and Mira Jun. 2016. "The Identification of Biochanin A as a Potent and Selective β-Site App-Cleaving Enzyme 1 (Bace1) Inhibitor" Nutrients 8, no. 10: 637. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu8100637
APA StyleYoun, K., Park, J.-H., Lee, J., Jeong, W.-S., Ho, C.-T., & Jun, M. (2016). The Identification of Biochanin A as a Potent and Selective β-Site App-Cleaving Enzyme 1 (Bace1) Inhibitor. Nutrients, 8(10), 637. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu8100637





