Anti-Diabetic and Hepato-Renal Protective Effects of Ziyuglycoside II Methyl Ester in Type 2 Diabetic Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Plant Material and Preparation of ZG02-ME
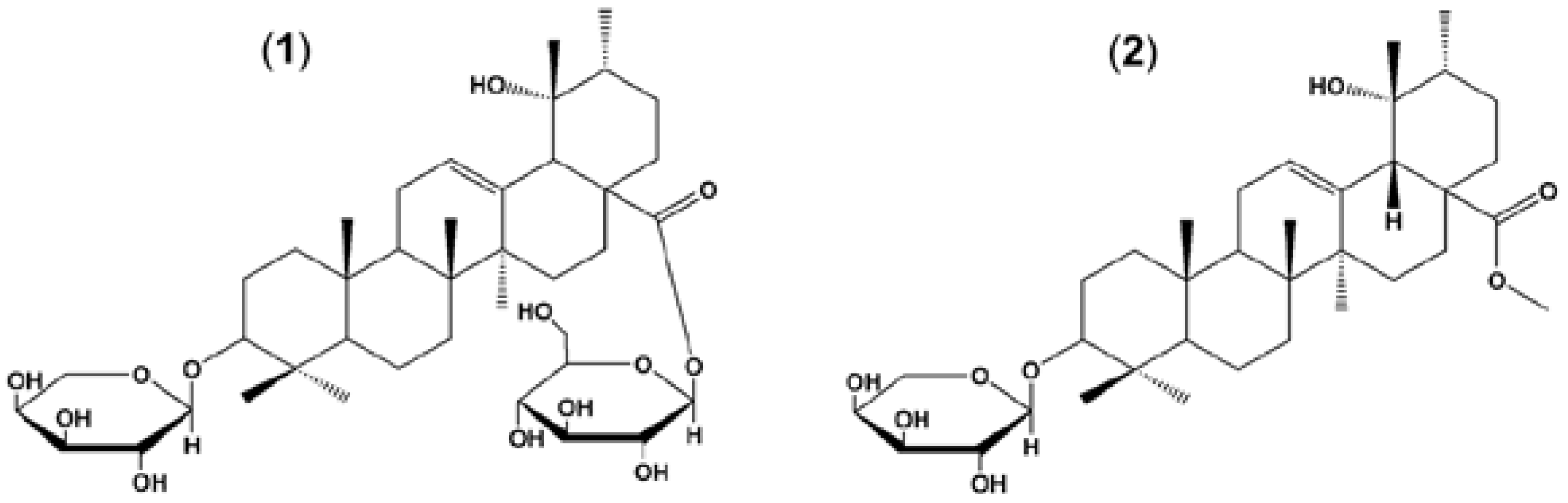
2.2. Animals and Administration
2.3. Body Weight and Food Consumption Measurements
2.4. Blood Biochemistry and Lipid Peroxidation
2.5. Measurement of Serum Insulin, C-Peptide, and Leptin
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effects of Ziyuglycosides on Blood Glucose and Insulin Levels in db/db Mice
| Treatment | Dose (mg/kg Body Weight) | Glucose (mg/dL) | HbA1c (%) | Insulin (ng/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal control | – | 112.3 ± 6.9 | 5.96 ± 0.04 | 2.42 ± 0.19 |
| Vehicle control | – | 693.5 ± 52.3 # | 8.16 ± 1.25 # | 3.67 ± 0.54 # |
| ZG01 | 5 | 675.2 ± 86.7 | 6.58 ± 1.13 * | 2.96 ± 0.49 * |
| ZG02-ME | 5 | 614.4 ± 55.6 * | 5.12 ± 1.32 * | 2.74 ± 0.67 * |
| Treatment | Dose (mg/kg Body Weight) | Glucose (mg/dL) | HbA1c (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Normal control | – | 152.3 ± 7.6 | 6.72 ± 0.94 |
| Vehicle control | – | 621.6 ± 10.26 # | 9.23 ± 1.66 # |
| ZG02-ME | 1 | 552.5 ± 18.2 * | 8.26 ± 1.27 |
| 3 | 512.4 ± 13.5 * | 7.32 ± 1.43 * | |
| 5 | 482.3 ± 19.6 * | 7.13 ± 0.86 * |
3.2. Effect of ZG02-ME on Serum Insulin, C-Peptide and Leptin Levels in db/db Mice
| Treatment | Dose (mg/kg Body Weight) | Hormone Parameters (ng/mL) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Insulin | Leptin | C-peptide | ||
| Normal control | – | 2.7 ± 0.2 | 28.6 ± 2.1 | 1.66 ± 0.23 |
| Vehicle control | – | 3.4 ± 0.4 # | 45.5 ± 2.6 # | 1.88 ± 0.25 # |
| ZG02-ME | 1 | 3.1 ± 0.5 | 42.6 ± 5.2 | 1.75 ± 0.18 |
| 3 | 2.9 ± 0.5 * | 38.4 ± 3.9 * | 1.72 ± 0.26 * | |
| 5 | 2.7 ± 0.6 * | 35.4 ± 2.4 * | 1.69 ± 0.16 * | |
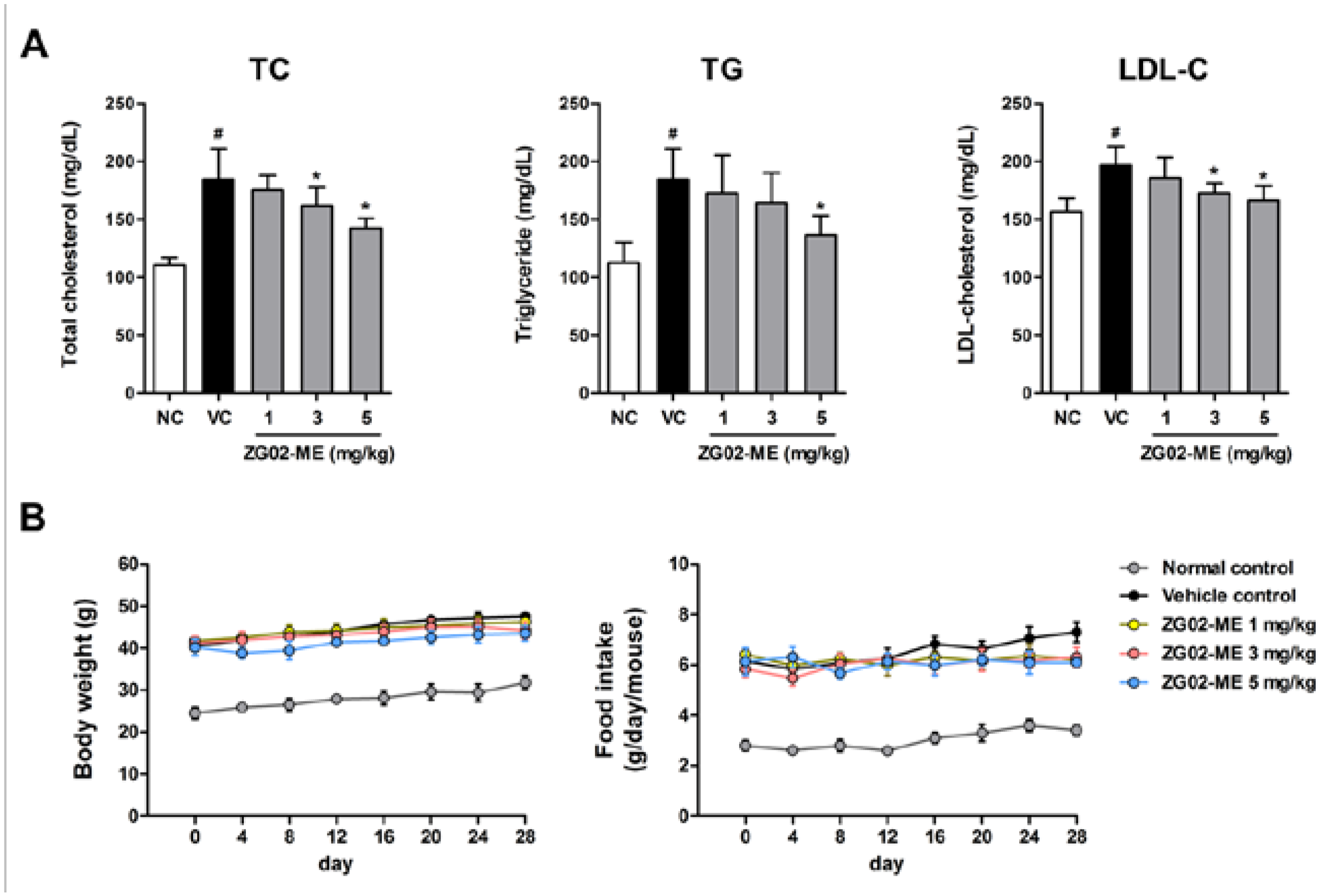
3.3. Effect on the Basal Blood Lipid Levels in db/db Mice
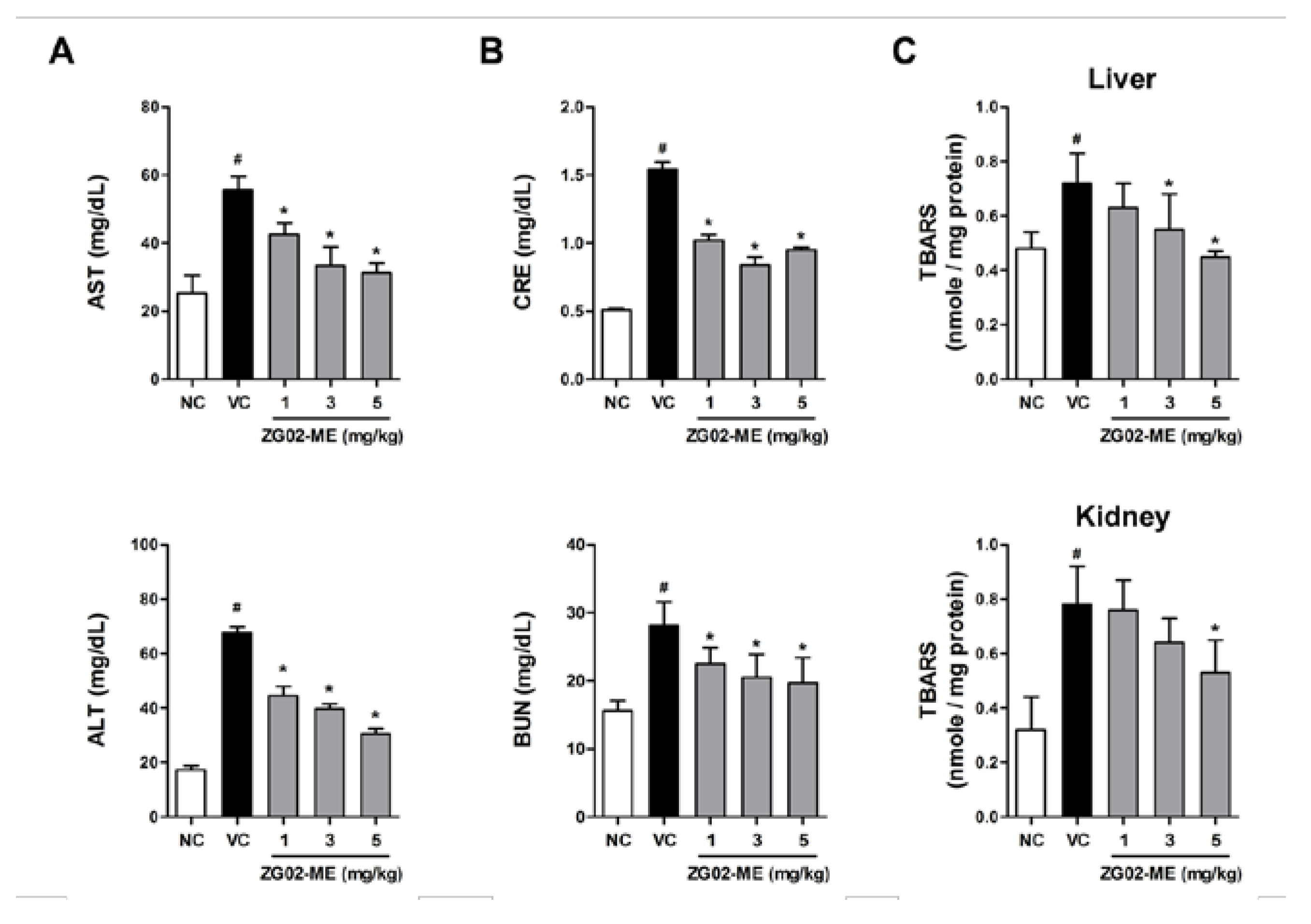
3.4. Effect on Liver and Renal Function in db/db Mice
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- American Diabetes Association. Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 2009, 32, S62–S67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Triggle, C.R.; Ding, H. Cardiovascular impact of drugs used in the treatment of diabetes. Ther. Adv. Chronic Dis. 2014, 5, 245–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warren, R.E. The stepwise approach to the management of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2004, 65, S3–S8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, J.; Leung, A.K.; Rabi, D. Hypoglycemic agents in the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Recent Pat. Endocr. Metab. Immune Drug Discov. 2011, 5, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, M.T.; Lyon, M.R. How to Prevent and Treat Diabetes with Natural Medicine; Riverhead Books: New York, NY, USA, 2003; p. 369. [Google Scholar]
- Fuhrman, J. The End of Diabetes : The Eat to Live Plan to Prevent and Reverse Diabetes, 1st ed.; HarperOne, an Imprint of HarperCollins Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2013; p. 301. [Google Scholar]
- Pasupuleti, V.K.; Anderson, J.W. Nutraceuticals, Glycemic Health and Type 2 Diabetes, 1st ed.; Wiley-Blackwell/IFT Press: Ames, IA, USA, 2008; Volume 17, p. 489. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, J.B.; Hogger, P. Dietary polyphenols and type 2 diabetes: Current insights and future perspectives. Curr. Med. Chem. 2015, 22, 23–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habicht, S.D.; Ludwig, C.; Yang, R.Y.; Krawinkel, M.B. Momordica charantia and type 2 diabetes: From in vitro to human studies. Curr. Diabetes Rev. 2014, 10, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dembinska-Kiec, A.; Mykkanen, O.; Kiec-Wilk, B.; Mykkanen, H. Antioxidant phytochemicals against type 2 diabetes. Br. J. Nutr. 2008, 99, ES109–ES117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Z.L.; He, L.; Wang, Z.; Wang, G.S. Isolation and identification of the phenolic compounds from the roots of sanguisorba officinalis l and their antioxidant activities. Molecules 2012, 17, 13917–13922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravipati, A.S.; Zhang, L.; Koyyalamudi, S.R.; Jeong, S.C.; Reddy, N.; Bartlett, J.; Smith, P.T.; Shanmugam, K.; Munch, G.; Wu, M.J.; et al. Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of selected chinese medicinal plants and their relation with antioxidant content. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 12, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Wu, J.; Zou, W.; Dai, Y. Two ellagic acids isolated from roots of sanguisorba officinalis l promote hematopoietic progenitor cell proliferation and megakaryocyte differentiation. Molecules 2014, 19, 5448–5458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, J.A.; Kim, J.S.; Kwon, K.H.; Nam, J.S.; Jung, J.Y.; Cho, N.P.; Cho, S.D. Apoptotic effect of hot water extract of sanguisorba officinalis L. in human oral cancer cells. Oncol. Lett. 2012, 4, 489–494. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Choi, E.S.; Kim, J.S.; Kwon, K.H.; Kim, H.S.; Cho, N.P.; Cho, S.D. Methanol extract of sanguisorba officinalis l with cytotoxic activity against pc3 human prostate cancer cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2012, 6, 670–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, J.G.; Chen, J.P.; Tan, Z.W.; Peng, J.; Zheng, X.; Nishiura, K.; Ng, J.; Wang, Z.Y.; Wang, D.M.; Chen, Z.W.; et al. Extracts of the medicinal herb sanguisorba officinalis inhibit the entry of human immunodeficiency virus-1. J. Food Drug Anal. 2013, 21, S52–S58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Nielsen, M.; Staerk, D.; Jager, A.K. High-resolution bacterial growth inhibition profiling combined with hplc-hrms-spe-nmr for identification of antibacterial constituents in chinese plants used to treat snakebites. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 155, 1276–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Koyyalamudi, S.R.; Jeong, S.C.; Reddy, N.; Smith, P.T.; Ananthan, R.; Longvah, T. Antioxidant and immunomodulatory activities of polysaccharides from the roots of sanguisorba officinalis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2012, 51, 1057–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Z.; Li, W.; Wang, H.; Yan, W.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, G.; Cui, J.; Wang, F. Anti-tumor and immunomodulating activities of a polysaccharide from the root of sanguisorba officinalis l. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2012, 51, 484–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Song, Y.; Li, H.; Yang, B.; Mao, X.; Zhao, Y.; Shi, X. Cytotoxic triterpene glycosides from the roots of sanguisorba officinalis. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, H.; Song, J.; Zhang, Z.; Mao, D.; Sun, G.; Jiang, G. Inhibitory function of p-selectin-mediated leukocyte adhesion by the polysaccharides from sanguisorba officinalis. Pharm. Biol. 2015, 53, 354–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Zhang, Z.L.; Liu, X.; Zhang, S.; He, L.; Wang, Z.; Wang, G.S. Terpene glycosides from the roots of sanguisorba officinalis l. And their hemostatic activities. Molecules 2012, 17, 7629–7636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Wang, K.; Zhang, K.; Zhu, L.; Zhou, F. Ziyuglycoside ii induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis through activation of ros/jnk pathway in human breast cancer cells. Toxicol. Lett. 2014, 227, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Wang, K.; Zhang, K.; Huang, B.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, L.; Zhou, B.; Zhou, F. Ziyuglycoside ii inhibits the growth of human breast carcinoma mda-mb-435 cells via cell cycle arrest and induction of apoptosis through the mitochondria dependent pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 18041–18055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, A.K.; Zhou, H.; Xia, J.Z.; Jin, H.C.; Wang, K.; Yan, J.; Zuo, J.B.; Zhu, X.; Shan, T. Ziyuglycoside ii-induced apoptosis in human gastric carcinoma bgc-823 cells by regulating bax/bcl-2 expression and activating caspase-3 pathway. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2013, 46, 670–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, P.K.; Maity, N.; Nema, N.K.; Sarkar, B.K. Bioactive compounds from natural resources against skin aging. Phytomedicine 2011, 19, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.H.; Chung, C.B.; Kim, J.G.; Ko, K.I.; Park, S.H.; Kim, J.H.; Eom, S.Y.; Kim, Y.S.; Hwang, Y.I.; Kim, K.H. Anti-wrinkle activity of ziyuglycoside i isolated from a sanguisorba officinalis root extract and its application as a cosmeceutical ingredient. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2008, 72, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Cui, Y.; Yu, Q.; Yu, B. Triterpenoids from sanguisorba officinalis. Phytochemistry 2005, 66, 1671–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.; Kim, M.Y.; Cha, B.C.; Yoo, E.S.; Yoon, K.; Lee, J.; Rho, H.S.; Kim, S.Y.; Cho, J.Y. Zym-201 sodium succinate ameliorates streptozotocin-induced hyperlipidemic conditions. Planta Med. 2012, 78, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.; Yu, T.; Cha, B.C.; Rhee, M.H.; Yoo, E.S.; Kim, M.Y.; Lee, J.; Cho, J.Y. Modulatory effects of zym-201 sodium succinate on dietary-induced hyperlipidemic conditions. Die Pharm. 2011, 66, 791–797. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, J.Y.; Choi, J.; Park, J.G.; Yi, Y.S.; Hossen, M.J.; Kim, H.; Ro, J.; Cha, B.C.; Yoo, E.S.; Kim, J.H.; et al. Alcohol-induced hyperlipidemia is ameliorated by orally administered dwp208, a sodium succinate form of zym201. Korean J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2014, 18, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.E.; Kim, S.; Jung, W.J.; Lee, H.S.; Kim, M.Y. Immunomodulatory effects of zym-201 on lps-stimulated b cells. Immune Netw. 2014, 14, 260–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, J.Y.; Yoo, E.S.; Cha, B.C.; Park, H.J.; Rhee, M.H.; Han, Y.N. The inhibitory effect of triterpenoid glycosides originating from sanguisorba officinalis on tissue factor activity and the production of tnf-alpha. Planta Med. 2006, 72, 1279–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasmakov, S.A.; Putieva, Z.M.; Kachala, V.V.; Saatov, Z.; Shashkov, A.S. Triterpene glycosides of zygophyllum eichwaldii. Ii. Structure of zygoeichwaloside i. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2001, 37, 347–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tze, W.J.; Thompson, K.H.; Leichter, J. Hbalc—An indicator of diabetic control. J. Pediatr. 1978, 93, 13–16. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jamall, I.S.; Smith, J.C. Effects of cadmium on glutathione peroxidase, superoxide dismutase, and lipid peroxidation in the rat heart: A possible mechanism of cadmium cardiotoxicity. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1985, 80, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orland, M.J.; Permutt, M.A. Quantitative analysis of pancreatic proinsulin mrna in genetically diabetic (db/db) mice. Diabetes 1987, 36, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, M.M. Subcutaneous and visceral adipose tissue: Structural and functional differences. Obes. Rev. 2010, 11, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sader, S.; Nian, M.; Liu, P. Leptin: A novel link between obesity, diabetes, cardiovascular risk, and ventricular hypertrophy. Circulation 2003, 108, 644–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, A.G.; Hattersley, A.T. The clinical utility of c-peptide measurement in the care of patients with diabetes. Diabet. Med. 2013, 30, 803–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez-Quesada, J.L.; Perez, A. Modified lipoproteins as biomarkers of cardiovascular risk in diabetes mellitus. Endocrinol. Y Nutr. 2013, 60, 518–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.M.; Yi, S.J.; Cho, I.J.; Ku, S.K. Red-koji fermented red ginseng ameliorates high fat diet-induced metabolic disorders in mice. Nutrients 2013, 5, 4316–4332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hijmans, B.S.; Grefhorst, A.; Oosterveer, M.H.; Groen, A.K. Zonation of glucose and fatty acid metabolism in the liver: Mechanism and metabolic consequences. Biochimie 2014, 96, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolman, K.G.; Fonseca, V.; Dalpiaz, A.; Tan, M.H. Spectrum of liver disease in type 2 diabetes and management of patients with diabetes and liver disease. Diabetes Care 2007, 30, 734–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torbenson, M.; Chen, Y.Y.; Brunt, E.; Cummings, O.W.; Gottfried, M.; Jakate, S.; Liu, Y.C.; Yeh, M.M.; Ferrell, L. Glycogenic hepatopathy: An underrecognized hepatic complication of diabetes mellitus. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2006, 30, 508–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, G.C.; Tang, S.C. Diabetic nephropathy: Landmark clinical trials and tribulations. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garg, M.C.; Chaudhary, D.P.; Bansal, D.D. Effect of vitamin e supplementation on diabetes induced oxidative stress in experimental diabetes in rats. Indian J. Exp. Biol. 2005, 43, 177–180. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ceriello, A.; Quatraro, A.; Giugliano, D. New insights on non-enzymatic glycosylation may lead to therapeutic approaches for the prevention of diabetic complications. Diabet. Med. 1992, 9, 297–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, B.; Mukherjee, J.R.; Chatterjee, M. Lipid peroxidation, glutathione levels and changes in glutathione-related enzyme activities in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Immunol. Cell Biol. 1994, 72, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, U.J.; Park, Y.B.; Kim, S.R.; Choi, M.S. Supplementation of persimmon leaf ameliorates hyperglycemia, dyslipidemia and hepatic fat accumulation in type 2 diabetic mice. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e49030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Son, D.J.; Hwang, S.Y.; Kim, M.-H.; Park, U.K.; Kim, B.S. Anti-Diabetic and Hepato-Renal Protective Effects of Ziyuglycoside II Methyl Ester in Type 2 Diabetic Mice. Nutrients 2015, 7, 5469-5483. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu7075232
Son DJ, Hwang SY, Kim M-H, Park UK, Kim BS. Anti-Diabetic and Hepato-Renal Protective Effects of Ziyuglycoside II Methyl Ester in Type 2 Diabetic Mice. Nutrients. 2015; 7(7):5469-5483. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu7075232
Chicago/Turabian StyleSon, Dong Ju, Seock Yeon Hwang, Myung-Hyun Kim, Un Kyu Park, and Byoung Soo Kim. 2015. "Anti-Diabetic and Hepato-Renal Protective Effects of Ziyuglycoside II Methyl Ester in Type 2 Diabetic Mice" Nutrients 7, no. 7: 5469-5483. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu7075232
APA StyleSon, D. J., Hwang, S. Y., Kim, M.-H., Park, U. K., & Kim, B. S. (2015). Anti-Diabetic and Hepato-Renal Protective Effects of Ziyuglycoside II Methyl Ester in Type 2 Diabetic Mice. Nutrients, 7(7), 5469-5483. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu7075232




