Effect of Glutamine Dipeptide Supplementation on Primary Outcomes for Elective Major Surgery: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Literature Search
2.2. Study Selection
2.3. Data Extraction
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
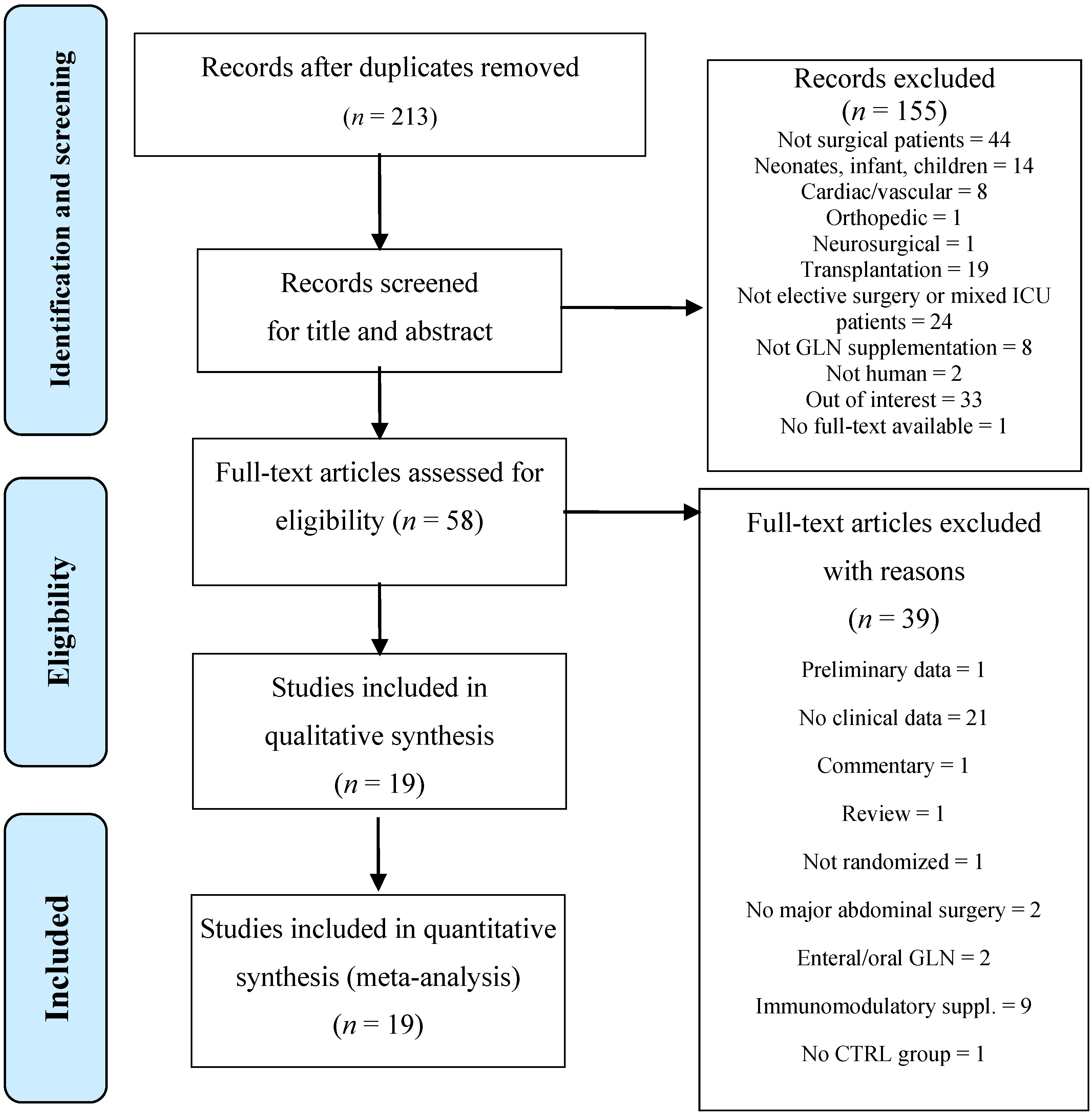
3.1. Study Characteristics
| Author | Year | Country | Population Analysed | Multi/Single Center | Blindness (Double/Single) | Type of Surgery | Cancer/Benign | Nutritional Status | GLN Dipeptide Dose (g/kg/day) | Artificial Nutrition (AN) | Type of AN | IC/IN Control | Onset | Study Power Calculation | ITT Morbidity | ITT LOS | Jadad Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| O’Riordain [38] | 1994 | UK | 22 | single | double | Lower GI | C/B | NA | 0.18 | Yes | TPN | YES | POD 1 | NO | Yes | NA | 3.5 |
| Morlion [39] | 1998 | Germany | 28 | single | double | Lower GI | C/B | NA | 0.30 | Yes | TPN | YES | POD 1 | NO | no | Yes | 3.5 |
| Jacobi [17] | 1999 | Germany | 34 | single | double | Upper GI | C/B | NA | 0.40 | Yes | TPN | YES | POD 1 | NO | Yes | Yes | 3.5 |
| Jiang [40] | 1999 | China | 60 | multi | double | Mixed GI | C/B | NA | 0.50 | Yes | TPN | YES | POD 1 | NO | Yes | Yes | 5 |
| Mertes [41] | 2000 | Germany | 37 | single | double | Mixed GI | NA | NA | 0.50 | Yes | TPN | YES | POD 1 | NO | no | No | 3 |
| Karwowska [42] | 2001 | Poland | 30 | single | NO | Vascular | B | Well nourished | 0.20 | Yes | TPN | YES | POD 1 | NO | Yes | Yes | 1.5 |
| Neri [43] | 2001 | Italy | 33 | single | double | Mixed GI | C | NA | 0.30 | Yes | TPN | YES | POD 1 | NO | Yes | Yes | 3 |
| Spittler [37] | 2001 | Austria | 30 | single | NO | Mixed GI | NA | NA | 0.50 | NO | - | NA | POD 0 | NO | Yes | Yes | 2 |
| Lin [20] | 2002 | China | 48 | single | double | Mixed GI | C | NA | 0.42 | Yes | TPN | YES | POD 1 | NO | Yes | NA | 4.5 |
| Exner [21] | 2003 | Austria | 45 | single | NO | Mixed GI | NA | NA | 0.50 | Yes | TPN | YES | POD −1 | NO | Yes | Yes | 2.5 |
| Klek [18] | 2005 | Poland | 60 | single | NO | Upper GI | C | Mixed | 0.40 | YES | TPN | YES | POD 1 | NO | No | No | 2 |
| Yao [44] | 2005 | China | 40 | single | double | Mixed GI | C/B | NA | 0.50 | Yes | TPN | YES | POD −1 | NO | Yes | Yes | 5 |
| Jo [22] | 2006 | Korea | 60 | single | double | Upper GI | C | Mixed | 0.30 | Yes | TPN | YES | POD −2 | NO | Yes | Yes | 4 |
| Oguz [19] | 2007 | Turkey | 109 | single | NO | Lower GI | C | Mixed | 1.00 | Yes | EN | NA | POD −5 | NO | No | No | 2 |
| Asprer [45] | 2009 | Philippines | 34 | multi | double | Mixed GI | C/B | Malnourished | 0.30 | Yes | mixed | YES | POD −5 | NO | Yes | NA | 5 |
| Fan [46] | 2009 | China | 40 | single | NO | Mixed GI | C/B | NA | 0.13 | Yes | TPN | YES | POD −1 | NO | Yes | Yes | 2 |
| Gianotti [47] | 2009 | Italy | 428 | multi | single | Mixed GI | C | Well nourished | 0.40 | NO | - | NA | POD −1 | YES | Yes | Yes | 5 |
| Marton [48] | 2010 | Hungary | 55 | single | NO | Upper GI | C | NA | 0.50 | Yes | EN | YES | POD −3 | YES | NA | NA | 4 |
| Lu [49] | 2011 | Taiwan | 50 | single | double | Mixed GI | C | NA | 0.30 | Yes | TPN | YES | POD 0 | NO | Yes | NA | 2.5 |
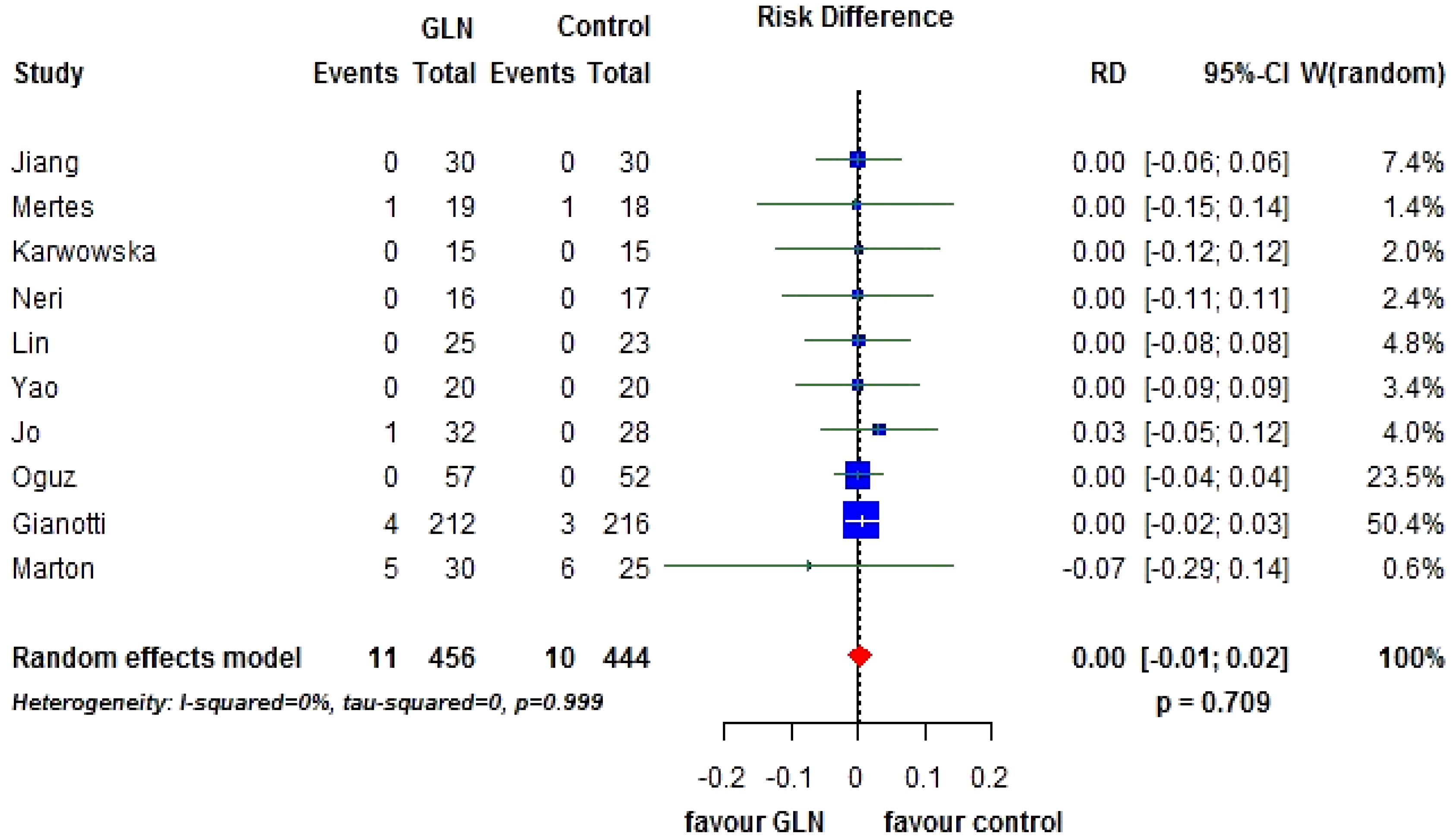
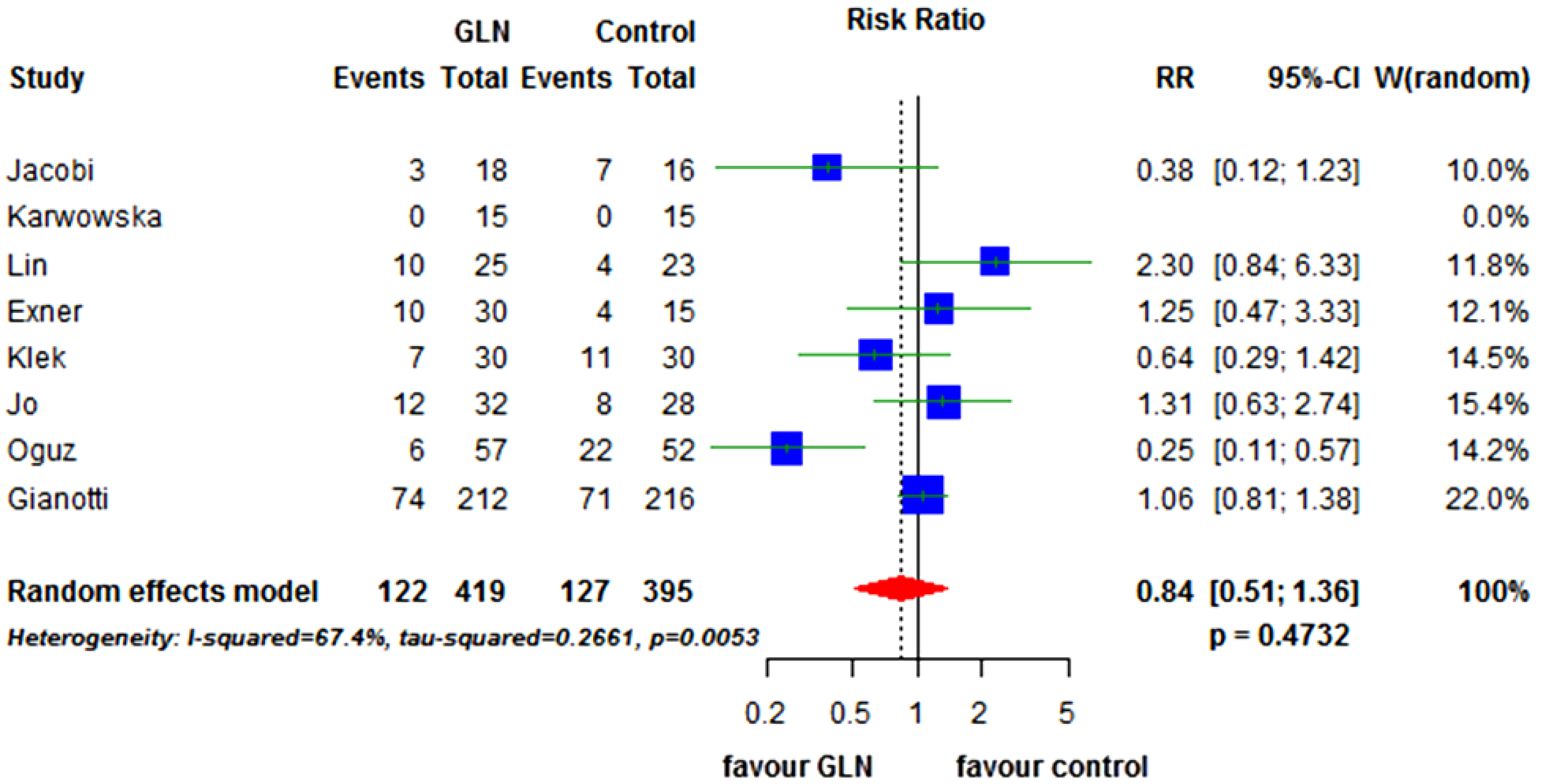
3.2. Primary End-Points
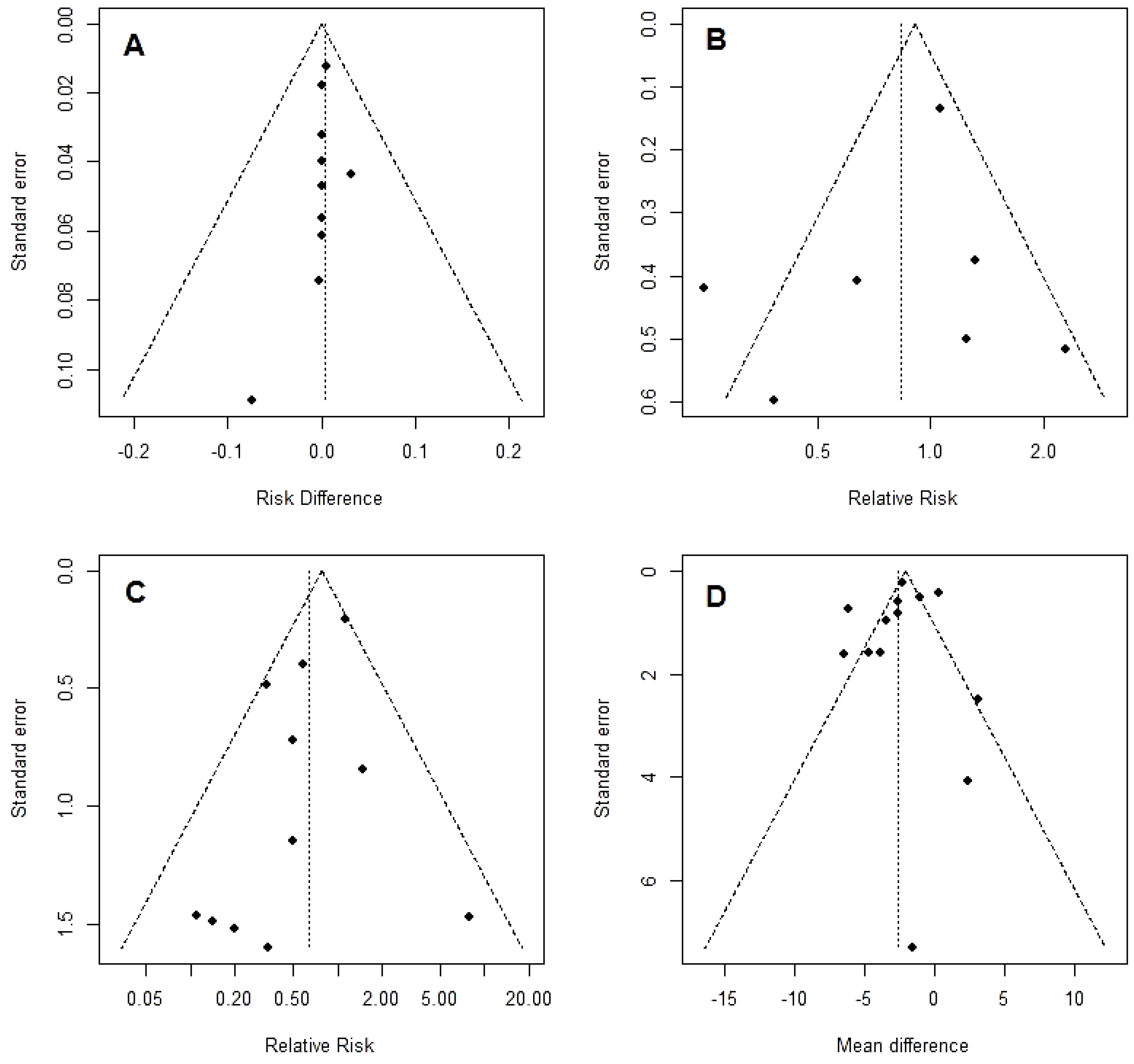
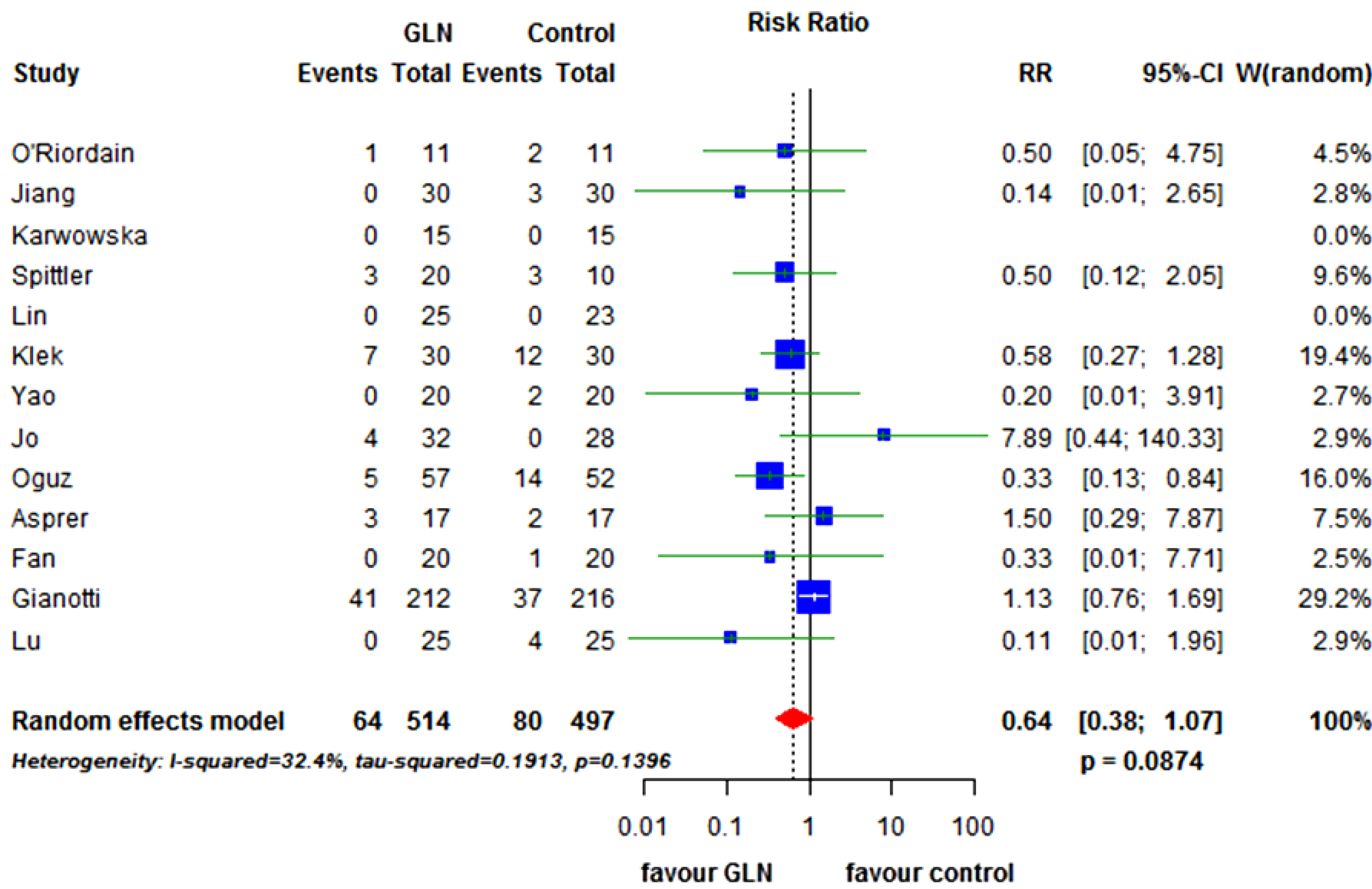
3.3. Secondary End-Points
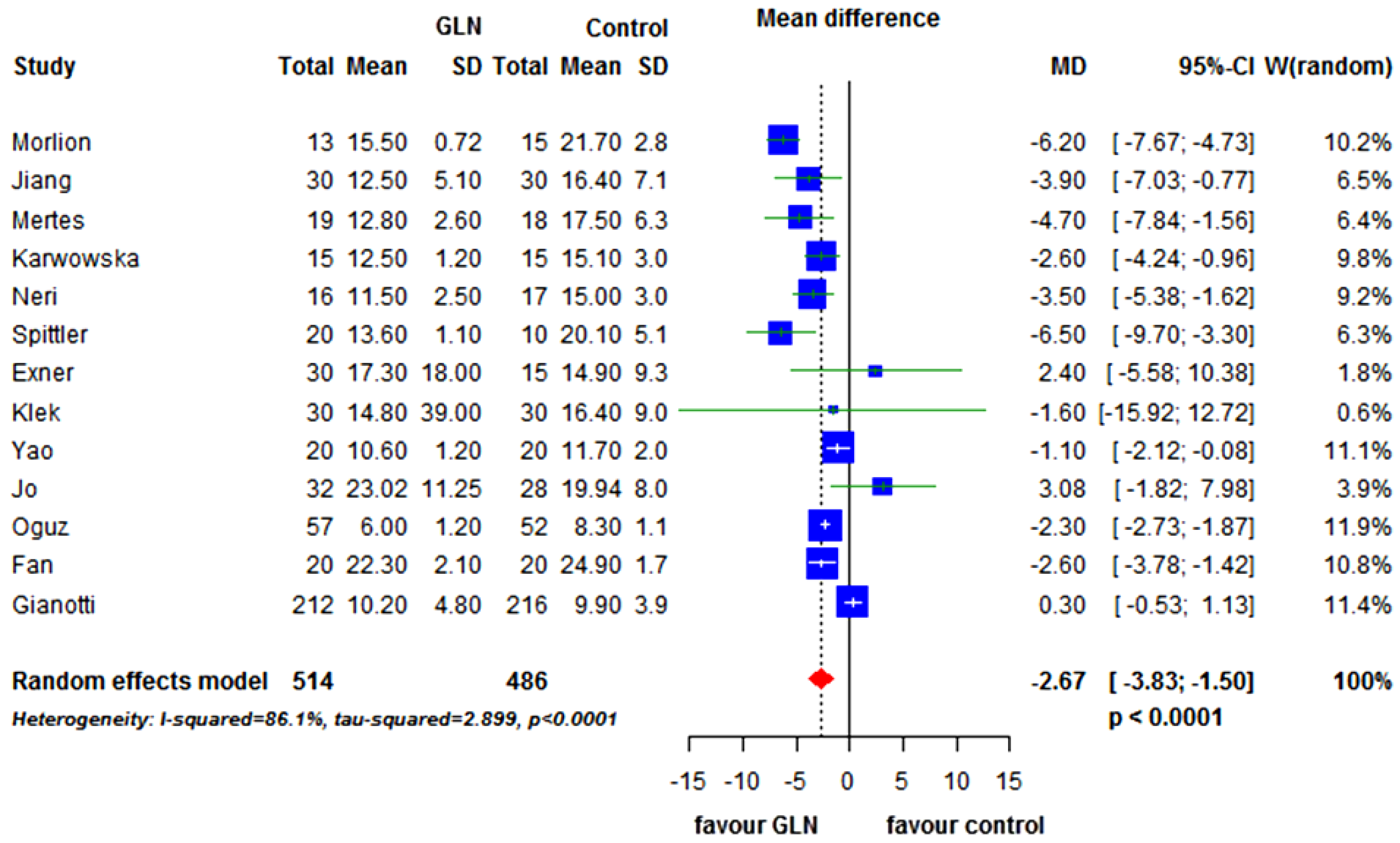
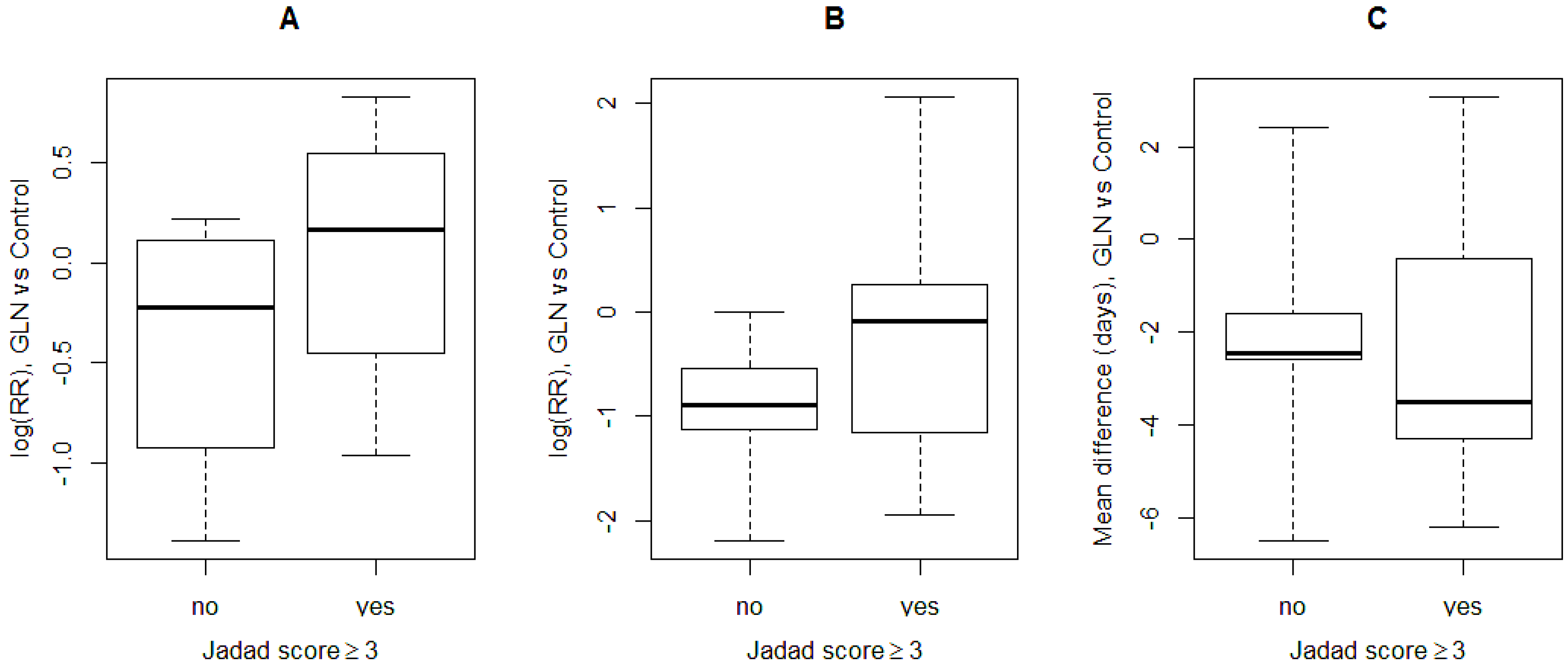
3.4. Subgroup Analysis
| Category | Study Characteristic (Number of Studies) | Overall RR (95% CI) | p-Value | I2% | p-Value for Heterogeneity between Strata |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dosage of GLN | >0.3 g per kg per day (6) | 0.77 (0.43; 1.37) | 0.3688 | 71.6 | 0.0035 |
| ≤0.3 g per kg per day (1) | 1.31 (0.63; 2.74) | 0.4695 | - | - | |
| Duration of GLN supplement | >5 days (5) | 0.87 (0.48; 1.57) | 0.6383 | 74.5 | 0.0035 |
| ≤5 days (2) | 0.72 (0.23; 2.31) | 0.5831 | 57 | 0.1271 | |
| Intention to treat | Yes (4) | 1.11 (0.69; 1.78) | 0.6713 | 45 | 0.1411 |
| No (1) | 0.25 (0.11; 0.57) | 0.0009 | - | - | |
| Blinding | Yes (3) | 1.11 (0.45; 2.74) | 0.8241 | 62.4 | 0.0699 |
| No (4) | 0.70 (0.35; 1.38) | 0.2974 | 75.7 | 0.0063 | |
| Jadad score | ≥3 (4) | 1.11 (0.69; 1.78) | 0.6713 | 45 | 0.1411 |
| <3 (3) | 0.57 (0.23; 1.39) | 0.2165 | 69.3 | 0.0384 | |
| Year of publication | >2002 (5) | 0.80 (0.46; 1.37) | 0.4064 | 69.6 | 0.0105 |
| ≤2002 (2) | 0.96 (0.17; 5.59) | 0.9640 | 80.7 | 0.0229 | |
| Type of surgery | Lower GI (1) | 0.25 (0.11; 0.57) | 0.0009 | - | - |
| Upper GI (3) | 0.75 (0.38; 1.49) | 0.4166 | 44.4 | 0.1655 | |
| Mixed GI or vascular (3) | 1.12 (0.85; 1.56) | 0.3596 | 7.3 | 0.3401 |
| Category | Study Characteristic (Number of Studies) | Overall RR (95% CI) | p-Value | I2% | p-Value for Heterogeneity between Strata |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dosage of GLN | >0.3 g per kg per day (6) | 0.58 (0.32; 1.06) | 0.0782 | 47.7 | 0.0887 |
| ≤0.3 g per kg per day (5) | 0.83 (0.24; 2.88) | 0.77 | 23.6 | 0.2639 | |
| Duration of GLN supplement | >5 days (7) | 0.61 (0.30; 1.23) | 0.1677 | 53 | 0.0470 |
| ≤5 days (4) | 0.64 (0.26; 1.62) | 0.3472 | 0 | 0.6211 | |
| Intention to treat | Yes (9) | 0.81 (0.45; 1.46) | 0.486 | 15.5 | 0.3043 |
| No (2) | 0.46 (0.25; 0.84) | 0.0119 | 0 | 0.3484 | |
| Blinding | Yes (6) | 0.61 (0.18; 2.02) | 0.4135 | 28.7 | 0.2196 |
| No (5) | 0.64 (0.36; 1.14) | 0.1329 | 47.3 | 0.1078 | |
| Jadad score | ≥3 (6) | 1.03 (0.57; 1.87) | 0.9155 | 10.1 | 0.3509 |
| <3 (5) | 0.44 (0.26; 0.75) | 0.0027 | 0 | 0.7490 | |
| Year of publication | >2002 (8) | 0.69 (0.37; 1.28) | 0.2391 | 44.8 | 0.0802 |
| ≤2002 (3) | 0.42 (0.14; 1.26) | 0.1218 | 0 | 0.7205 | |
| Type of surgery | Lower GI (2) | 0.35 (0.14; 0.83) | 0.0179 | 0 | 0.7310 |
| Upper GI (2) | 1.53 (0.11; 21.38) | 0.7504 | 70.1 | 0.0674 | |
| Mixed GI or vascular (7) | 0.75 (0.40; 1.41) | 0.3772 | 17.4 | 0.2969 |
| Category | Study Characteristic (Number of Studies) | Overall MD (95% CI) | p-Value | I2% | p-Value for Heterogeneity between Strata |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dosage of GLN | >0.3 g per kg per day (8) | −2.26 (−3.71; −0.81) | 0.0023 | 84.8 | <0.0001 |
| ≤0.3 g per kg per day (5) | −3.06 (−4.99; −1.13) | 0.0019 | 82.8 | 0.0001 | |
| Duration of GLN supplement | >5 days (8) | −1.95 (−3.19; −0.71) | 0.002 | 82.8 | <0.0001 |
| ≤5 days (5) | −3.85 (−6.96; −0.73) | 0.0155 | 89.7 | <0.0001 | |
| Intention to treat | Yes (10) | −2.53 (−4.16; 0.89) | 0.0024 | 89 | <0.0001 |
| No (3) | −2.54 (−3.59; −1.49) | <0.0001 | 9.8 | 0.3299 | |
| Blinding | Yes (6) | −3.06 (−5.40; −0.72) | 0.0103 | 87.2 | <0.0001 |
| No (7) | −2.16 (−3.60; −0.71) | 0.0034 | 85.5 | <0.0001 | |
| Jadad score | ≥3 (7) | −2.48 (−4.66; −0.31) | 0.0252 | 91.7 | <0.0001 |
| <3 (6) | −2.66 (−3.53; −1.78) | <0.0001 | 38.2 | 0.1512 | |
| Year of publication | >2002 (7) | −1.08 (−2.38; 0.23) | 0.1067 | 84.2 | <0.0001 |
| ≤2002 (6) | −4.47 (−5.93; −3.01) | <0.0001 | 61.7 | 0.0228 | |
| Type of surgery | Lower GI (2) | −4.18 (−8.00; −0.36) | 0.0318 | 96 | <0.0001 |
| Upper GI (2) | 2.59 (−2.04; 7.22) | 0.2732 | 0 | 0.5445 | |
| Mixed GI or vascular (9) | −2.55 (−3.93; −1.18) | 0.0003 | 82.1 | <0.0001 |
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vonlanthen, R.; Slankamenac, K.; Breitenstein, S.; Puhan, M.A.; Muller, M.K.; Hahnloser, D.; Hauri, D.; Graf, R.; Clavien, P.-A. The impact of complications on costs of major surgical procedures: A cost analysis of 1200 patients. Ann. Surg. 2011, 254, 907–913. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Braga, M.; Gianotti, L.; Vignali, A.; Schmid, A.; Nespoli, L.; Di Carlo, V. Hospital resources consumed for surgical morbidity: Effects of preoperative arginine and omega-3 fatty acid supplementation on costs. Nutrition 2005, 21, 1078–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marik, P.E.; Flemmer, M. The immune response to surgery and trauma: Implications for treatment. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2012, 73, 801–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, G.L.; Douglas, R.G.; Schroeder, D. Metabolic basis for the management of patients undergoing major surgery. World J. Surg. 1993, 17, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senkal, M.; Kemen, M.; Homann, H.H.; Eickhoff, U.; Baier, J.; Zumtobel, V. Modulation of postoperative immune response by enteral nutrition with a diet enriched with arginine, RNA, and omega-3 fatty acids in patients with upper gastrointestinal cancer. Eur. J. Surg. 1995, 161, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gianotti, L.; Braga, M.; Fortis, C. A prospective randomized clinical trial on perioperative feeding with arginine, omega 3 fatty acids, and RNA enriched enteral diets: Effect on host response and nutritional status. JPEN J. Parenter. Enteral Nutr. 1999, 23, 314–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braga, M.; Gianotti, L.; Radaelli, G.; Vignali, A.; Mari, G.; Gentilini, O.; Di Carlo, V. Perioperative immunonutrition in patients undergoing cancer surgery: Results of a randomized double-blind phase III trial. Arch. Surg. 1999, 134, 428–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marimuthu, K.; Varadhan, K.K.; Ljungqvist, O.; Lobo, D.N. A meta-analysis of the effect of combinations of immune modulating nutrients on outcome in patients undergoing major open gastrointestinal surgery. Ann. Surg. 2012, 255, 1060–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soeters, P.B.; Grecu, I. Have we enough glutamine and how does it work? A clinician’s view. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2012, 60, 7–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersson, B.; Vinnars, E.; Waller, S.O.; Wernerman, J. Long-term changes in muscle free amino acid levels after elective abdominal surgery. Br. J. Surg. 1992, 79, 212–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Acker, B.A.; Hulsewé, K.W.; Wagenmakers, A.J.; Soeters, P.B.; von Meyenfeldt, M.F. Glutamine appearance rate in plasma is not increased after gastrointestinal surgery in humans. J. Nutr. 2000, 130, 1566–1571. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, H. Glutamine as an immunonutrient. Yonsei Med. J. 2011, 52, 892–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souba, W.W.; Klimberg, V.S.; Hautamaki, R.D.; Mendenhall, W.H.; Bova, F.C.; Howard, R.J.; Bland, K.I.; Copeland, E.M. Oral glutamine reduces bacterial translocation following abdominal radiation. J. Surg. Res. 1990, 48, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souba, W.W.; Klimberg, V.S.; Plumley, D.A.; Salloum, R.M.; Flynn, T.C.; Bland, K.I.; Copeland, E.M., III. The role of glutamine in maintaining a healthy gut and supporting the metabolic response to injury and infection. J. Surg. Res. 1990, 48, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braga, M.; Wischmeyer, P.E.; Dover, J.; Heyland, D.K. Clinical evidence for pharmaconutrition in major elective surgery. JPEN J. Parenter. Enteral Nutr. 2013, 37, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stehle, P.; Zander, J.; Mertes, N.; Albers, S.; Puchstein, C.; Lawin, P.; Fürst, P. Effect of parenteral glutamine peptide supplements on muscle glutamine loss and nitrogen balance after major surgery. Lancet 1989, 1, 231–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobi, C.A.; Ordemann, J.; Zuckermann, H.; Döcke, W.; Volk, H.D.; Müller, J.M. The influence of alanyl-glutamine on immunologic functions and morbidity in postoperative total parenteral nutrition. Preliminary results of a prospective randomized trial. Zentralbl. Chir. 1999, 124, 199–205. [Google Scholar]
- Kłek, S.; Kulig, J.; Szczepanik, A.M.; Jedrys, J.; Kołodziejczyk, P. The clinical value of parenteral immunonutrition in surgical patients. Acta Chir. Belg. 2005, 105, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Oguz, M.; Kerem, M.; Bedirli, A.; Mentes, B.B.; Sakrak, O.; Salman, B.; Bostanci, H. l-alanin-l-glutamine supplementation improves the outcome after colorectal surgery for cancer. Colorectal Dis. 2007, 9, 515–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, M.T.; Kung, S.P.; Yeh, S.L.; Lin, C.; Lin, T.H.; Chen, K.H.; Liaw, K.Y.; Lee, P.H.; Chang, K.J.; Chen, W.J. The effect of glutamine-supplemented total parenteral nutrition on nitrogen economy depends on severity of diseases in surgical patients. Clin. Nutr. 2002, 21, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Exner, R.; Tamandl, D.; Goetzinger, P.; Mittlboeck, M.; Fuegger, R.; Sautner, T.; Spittler, A.; Roth, E. Perioperative GLY-GLN infusion diminishes the surgery-induced period of immunosuppression: Accelerated restoration of the lipopolysaccharide-stimulated tumor necrosis factor-alpha response. Ann. Surg. 2003, 237, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jo, S.; Choi, S.H.; Heo, J.S.; Kim, E.M.; Min, M.S.; Choi, D.W.; Seo, J.M.; Chung, J.C.; Kim, Y.I. Missing effect of glutamine supplementation on the surgical outcome after pancreaticoduodenectomy for periampullary tumors: A prospective, randomized, double-blind, controlled clinical trial. World J. Surg. 2006, 30, 1974–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bollhalder, L.; Pfeil, A.M.; Tomonaga, Y.; Schwenkglenks, M. A systematic literature review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials of parenteral glutamine supplementation. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 32, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novak, F.; Heyland, D.K.; Avenell, A.; Drover, J.W.; Su, X. Glutamine supplementation in serious illness: A systematic review of the evidence. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 30, 2022–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Li, F.; Qi, B.; Luo, B.; Sun, H.; Liu, S.; Wu, X. Application of perioperative immunonutrition for gastrointestinal surgery: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 16, 253–257. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Jiang, Z.M.; Nolan, M.T.; Jiang, H.; Han, H.R.; Yu, K.; Li, H.L.; Jie, B.; Liang, X.K. The impact of glutamine dipeptide-supplemented parenteral nutrition on outcomes of surgical patients: A meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. JPEN J. Parenter. Enteral Nutr. 2010, 34, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G.; PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DerSimonian, R.; Laird, N. Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control Clin. Trials 1986, 7, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sweeting, M.J.; Sutton, A.J.; Lambert, P.C. What to add to nothing? Use and avoidance of continuity corrections in meta-analysis of sparse data. Stat. Med. 2004, 23, 1351–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hozo, S.; Djulbegovic, B.; Hozo, I. Estimating the mean and variance from the median, range, and the size of a sample. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2005, 5, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sterne, J.A.C.; Egger, M. Funnel plots for detecting bias in meta-analysis: Guidelines on choice of axis. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2001, 54, 1046–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, T.; Li, X.L.; Cai, D.L.; Zhong, Y.; Geng, S.S. Effects of glutamine-supplemented enteral or parenteral nutrition on apoptosis of intestinal mucosal cells in rats with severe acute pancreatitis. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2013, 17, 1529–1535. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mc Anena, O.; Moore, F.M.; Moore, E.; Jones, T.; Parsons, P. Selective uptake of glutamine in the gastrointestinal tract: Confirmation in a human study. Br. J. Surg. 1991, 78, 480–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, X.; Yan, H.; You, Z.; Wang, P.; Wang, S. Effects of enteral supplementation with glutamine granules on intestinal mucosal barrier function in severe burned patients. Burns 2004, 30, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Ling, W.; Shen, Z.Y.; Jin, X.; Cao, H. Clinical application of immune-enhanced enteral nutrition in patients with advanced gastric cancer after total gastrectomy. J. Dig. Dis. 2012, 13, 401–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quan, Z.F.; Yang, C.; Li, N.; Li, J.S. Effect of glutamine on change in early postoperative intestinal permeability and its relation to systemic inflammatory response. World J. Gastroenterol. 2004, 10, 1992–1994. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Spittler, A.; Sautner, T.; Gornikiewicz, A.; Manhart, N.; Oehler, R.; Bergmann, M.; Függer, R.; Roth, E. Postoperative glycyl-glutamine infusion reduces immunosuppression: Partial prevention of the surgery induced decrease in HLA-DR expression on monocytes. Clin. Nutr. 2001, 20, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Riordain, M.G.; Fearon, K.C.; Ross, J.A.; Rogers, P.; Falconer, J.S.; Bartolo, D.C.; Garden, O.J.; Carter, D.C. Glutamine-supplemented total parenteral nutrition enhances T-lymphocyte response in surgical patients undergoing colorectal resection. Ann. Surg. 1994, 220, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morlion, B.J.; Stehle, P.; Wachtler, P.; Siedhoff, H.P.; Köller, M.; König, W.; Fürst, P.; Puchstein, C. Total parenteral nutrition with glutamine dipeptide after major abdominal surgery: A randomized, double-blind, controlled study. Ann. Surg. 1998, 227, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Z.M.; Cao, J.D.; Zhu, X.G.; Zhao, W.X.; Yu, J.C.; Ma, E.L.; Wang, X.R.; Zhu, M.W.; Shu, H.; Liu, Y.W. The impact of alanyl-glutamine on clinical safety, nitrogen balance, intestinal permeability, and clinical outcome in postoperative patients: A randomized, double-blind, controlled study of 120 patients. JPEN J. Parenter. Enteral. Nutr. 1999, 23, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mertes, N.; Schulzki, C.; Goeters, C.; Winde, G.; Benzing, S.; Kuhn, K.S.; Van Aken, H.; Stehle, P.; Fürst, P. Cost containment through l-alanyl-l-glutamine supplemented total parenteral nutrition after major abdominal surgery: A prospective randomized double-blind controlled study. Clin. Nutr. 2000, 19, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karwowska, K.A.; Dworacki, G.; Trybus, M.; Zeromski, J.; Szulc, R. Influence of glutamine-enriched parenteral nutrition on nitrogen balance and immunologic status in patients undergoing elective aortic aneurysm repair. Nutrition 2001, 17, 475–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neri, A.; Mariani, F.; Piccolomini, A.; Testa, M.; Vuolo, G.; Di Cosmo, L. Glutamine-supplemented total parenteral nutrition in major abdominal surgery. Nutrition 2001, 17, 968–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, G.X.; Xue, X.B.; Jiang, Z.M.; Yang, N.F.; Wilmore, D.W. Effects of perioperative parenteral glutamine-dipeptide supplementation on plasma endotoxin level, plasma endotoxin inactivation capacity and clinical outcome. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 24, 510–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asprer, J.M.; Llido, L.O.; Sinamban, R.; Schlotzer, E.; Kulkarni, H. Effect on immune indices of preoperative intravenous glutamine dipeptide supplementation in malnourished abdominal surgery patients in the preoperative and postoperative periods. Nutrition 2009, 25, 920–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.P.; Yu, J.C.; Kang, W.M.; Zhang, Q. Effects of glutamine supplementation on patients undergoing abdominal surgery. Chin. Med. Sci. J. 2009, 24, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gianotti, L.; Braga, M.; Biffi, R.; Bozzetti, F.; Mariani, L. Perioperative intravenous glutamine supplemetation in major abdominal surgery for cancer: A randomized multicenter trial. Ann. Surg. 2009, 250, 684–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marton, S.; Ghosh, S.; Papp, A.; Bogar, L.; Koszegi, T.; Juhasz, V.; Cseke, L.; Horvath, P.O. Effect of glutamine in patients with esophagus resection. Dis. Esophagus 2010, 23, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, C.Y.; Shih, Y.L.; Sun, L.C.; Chuang, J.F.; Ma, C.J.; Chen, F.M.; Wu, D.C.; Hsieh, J.S.; Wang, J.Y. The inflammatory modulation effect of glutamine-enriched total parenteral nutrition in postoperative gastrointestinal cancer patients. Am. Surg. 2011, 77, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Goeters, C.; Wenn, A.; Mertes, N.; Wempe, C.; van Aken, H.; Stehle, P.; Bone, H.G. Parenteral l-alanyl-l-glutamine improves 6-month outcome in critically ill patients. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 30, 2032–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuentes-Orozco, C.; Anaya-Prado, R.; Gonzalez-Ojeda, A.; Arenas-Marquez, H.; Cabrera-Pivaral, C.; Cervantes-Guevara, G.; Barrera-Zepeda, L.M. l-alanyl-l-glutamine-supplemented parenteral nutrition improves infectious morbidity in secondary peritonitis. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 23, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estivariz, C.F.; Griffith, D.P.; Luo, M.; Szeszycki, E.E.; Bazargan, N.; Dave, N.; Daignault, N.M.; Bergman, G.F.; McNally, T.; Battey, C.H.; et al. Efficacy of parenteral nutrition supplemented with glutamine dipeptide to decrease hospital infections in critically ill surgical patients. JPEN J. Parenter. Enteral Nutr. 2008, 32, 389–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, C.N.; Lee, H.L.; Liu, Y.Y.; Chiang, K.C.; Hwang, T.L.; Jan, Y.Y.; Chen, M.F. The role of parenteral glutamine supplement for surgical patient perioperatively: Result of a single center, prospective and controlled study. Langenbecks Arch. Surg. 2008, 393, 849–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engel, J.M.; Pitz, S.; Muhling, J.; Menges, T.; Martens, F.; Kwapisz, M.; Hempelmann, G. Role of glutamine administration on T-cell derived inflammatory response after cardiopulmonary bypass. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 28, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilmore, D.W.; Smith, R.J.; O’Dwyer, S.T.; Jacobs, D.O.; Ziegler, T.R.; Wang, X.D. The gut: A central organ after surgical stress. Surgery 1988, 104, 917–923. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Baue, A.E. Nutrition and metabolism in sepsis and multisystem organ failure. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 1991, 71, 549–565. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Alexander, J.W. Immunonutrition: An emerging strategy in the ICU. J. Crit. Care Nutr. 1993, 1, 21. [Google Scholar]
- Gianotti, L.; Alexander, J.W.; Gennari, R.; Pyles, T.; Babcock, G.F. Oral glutamine decreases bacterial translocation and improves survival in experimental gut-origin sepsis. JPEN J. Parenter. Enteral Nutr. 1995, 19, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gianotti, L.; Braga, M.; Nespoli, L.; Radaelli, G.; Beneduce, A.; Di Carlo, V. A randomized controlled trial of preoperative oral supplementation with a specialized diet in patients with gastrointestinal cancer. Gastroenterology 2002, 122, 1763–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braga, M.; Gianotti, L.; Nespoli, L.; Radaelli, G.; Di Carlo, V. Nutritional approach in malnourished surgical patients: A prospective randomized study. Arch. Surg. 2002, 137, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerantola, Y.; Hübner, M.; Grass, F.; Demartines, N.; Schäfer, M. Immunonutrition in gastrointestinal surgery. Br. J. Surg. 2011, 98, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bozzetti, F.; Gianotti, L.; Braga, M.; Di Carlo, V.; Mariani, L. Postoperative complications in gastrointestinal cancer patients: The joint role of the nutritional status and the nutritional support. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 26, 698–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braga, M.; Ljungqvist, O.; Soeters, P.; Fearon, K.; Weimann, A.; Bozzetti, F. ESPEN Guidelines on Parenteral Nutrition: Surgery. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 28, 378–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krell, R.W.; Girotti, M.E.; Dimick, J.B. Extended length of stay after surgery complications: Inefficient practice, or sick patients? JAMA Surg. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taheri, P.A.; Butz, D.A.; Greenfield, L.J. Length of stay has minimal impact on the cost of hospital admission. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2000, 191, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maessen, J.M.; Dejong, C.H.; Kessels, A.G.; von Meyenfeldt, M.F.; Enhanced recovery after surgery (ERAS) group. Length of stay: An inappropriate readout of the success of enhanced recovery programs. World J. Surg. 2008, 32, 971–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Royall, R.M. The effect of sample size on the meaning of significance tests. Am. Stat. 1986, 40, 313–315. [Google Scholar]
- Kjaergard, L.L.; Villumsen, J.; Gluud, C. Reported methodologic quality and discrepancies between large and small randomized trials in meta-analyses. Ann. Intern. Med. 2001, 135, 982–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reichenbach, S.; Sterchi, R.; Scherer, M.; Trelle, S.; Bürgi, E.; Bürgi, U.; Dieppe, P.A.; Jüni, P. Meta-analysis: Chondroitin for osteoarthritis of the knee or hip. Ann. Intern. Med. 2007, 146, 580–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rerkasem, K.; Rothwell, P.M. Meta-analysis of small randomized controlled trials in surgery may be unreliable. Br. J. Surg. 2010, 97, 466–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nüesch, E.; Trelle, S.; Reichenbach, S.; Rutjes, A.W.; Tschannen, B.; Altman, D.G.; Egger, M.; Jüni, P. Small study effects in meta-analyses of osteoarthritis trials: Meta-epidemiological study. BMJ 2010, 341, c3515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedges, L.V.; Pigott, T.D. The power of statistical tests in meta-analysis. Psychol. Methods 2001, 6, 203–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sandini, M.; Nespoli, L.; Oldani, M.; Bernasconi, D.P.; Gianotti, L. Effect of Glutamine Dipeptide Supplementation on Primary Outcomes for Elective Major Surgery: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2015, 7, 481-499. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu7010481
Sandini M, Nespoli L, Oldani M, Bernasconi DP, Gianotti L. Effect of Glutamine Dipeptide Supplementation on Primary Outcomes for Elective Major Surgery: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients. 2015; 7(1):481-499. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu7010481
Chicago/Turabian StyleSandini, Marta, Luca Nespoli, Massimo Oldani, Davide Paolo Bernasconi, and Luca Gianotti. 2015. "Effect of Glutamine Dipeptide Supplementation on Primary Outcomes for Elective Major Surgery: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Nutrients 7, no. 1: 481-499. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu7010481
APA StyleSandini, M., Nespoli, L., Oldani, M., Bernasconi, D. P., & Gianotti, L. (2015). Effect of Glutamine Dipeptide Supplementation on Primary Outcomes for Elective Major Surgery: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients, 7(1), 481-499. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu7010481






