A High-Dose Shiitake Mushroom Increases Hepatic Accumulation of Triacylglycerol in Rats Fed a High-Fat Diet: Underlying Mechanism
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Animals and Diet
2.2. Tissue Collection and Fractionation
2.3. Liver Crude Fat Weight and Liver TAG Analysis
2.4. Liver Histology
2.5. Liver Phospholipids Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Liver Weight
| Parameter 1 | HFD | LD-M | MD-M | HD-M | ANOVA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Body Weight | 479 ± 7 | 512 ± 23 | 516 ± 26 | 480 ± 20 | NS |
| Liver | |||||
| Liver weight (g) | 19 ± 1 | 18 ± 1 | 17 ± 1 | 20 ± 1 | NS |
| Liver/100 g body weight | 3.9 ± 0.2 a,b | 3.6 ± 0.2 b | 3.5 ± 0.1 b | 4.1 ± 0.1 a | 0.008 |
| Liver TAG (μmol/g tissue) | 45 ± 11 a,b | 21 ± 2 a | 19 ± 4 a | 69 ± 14 b | 0.001 |
| Liver Phospholipid | |||||
| PC (nmol/mg) | 34 ± 1 | 38 ± 2 | 39 ± 2 | 34 ± 0.2 | NS |
| PE (nmol/mg) | 9.7 ± 0.4 a | 10.6 ± 0.6 a,b | 11.9 ± 0.4 b | 11.8 ± 0.6 a,b | 0.037 |
| Ratio PC/PE (mol/mol) | 3.5 ± 0.1 b | 3.5 ± 0.1 b | 3.3 ± 0.1 a,b | 2.9 ± 0.1 a | 0.001 |
3.2. Liver Total Fat Content
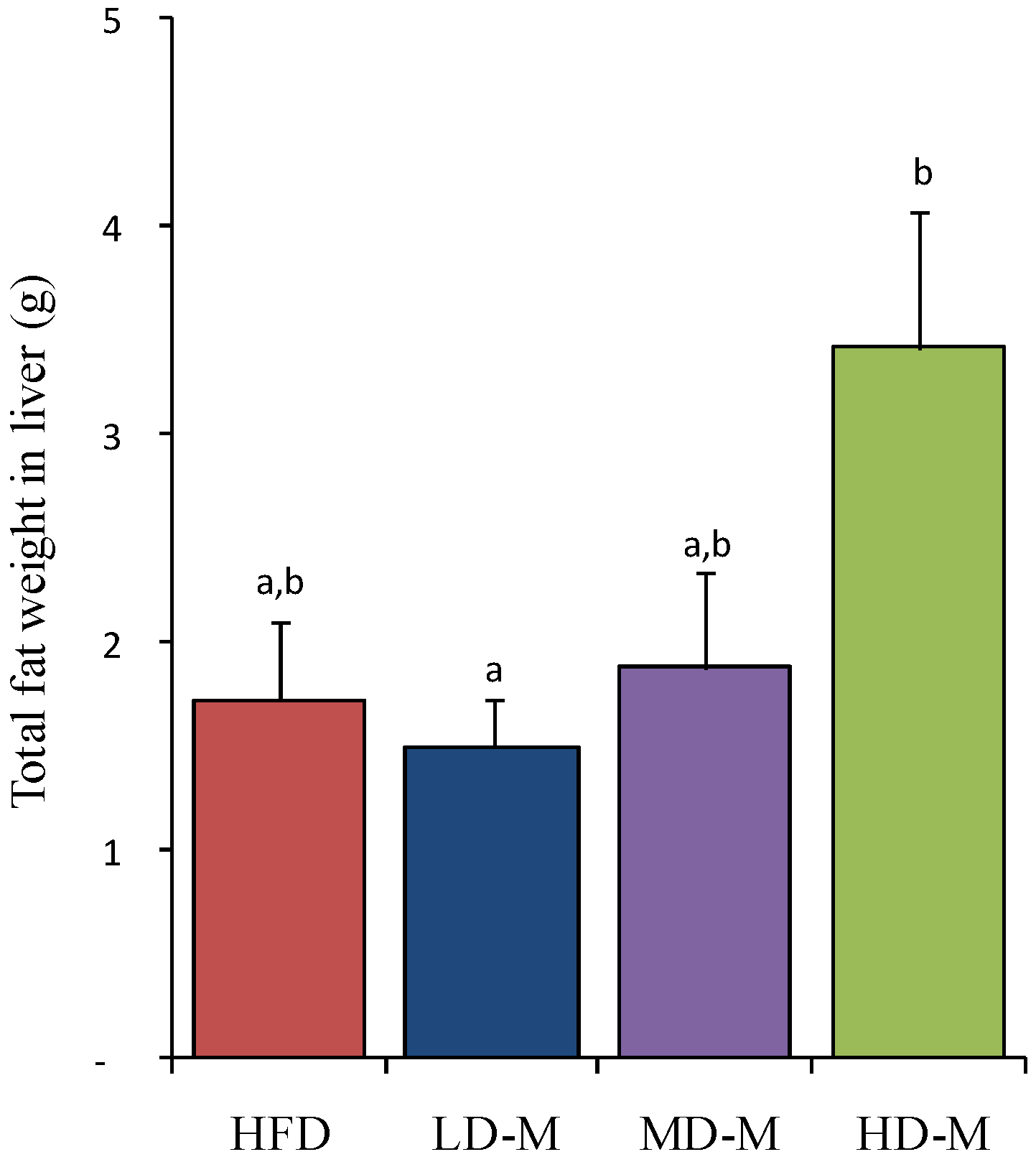
3.3. Liver Histology
| Parameter 1 | HFD | LD-M | MD-M | HD-M | ANOVA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liver steatosis | 2.70 ± 0.20 | 2.83 ± 0.17 | 2.67 ± 0.21 | 3.00 ± 0.09 | NS |
| Hepatic ballooning | 0.0 ± 0.0 a | 0.5 ± 0.2 a | 0.3 ± 0.2 a | 2.0 ± 0.0 b | 0.000 |
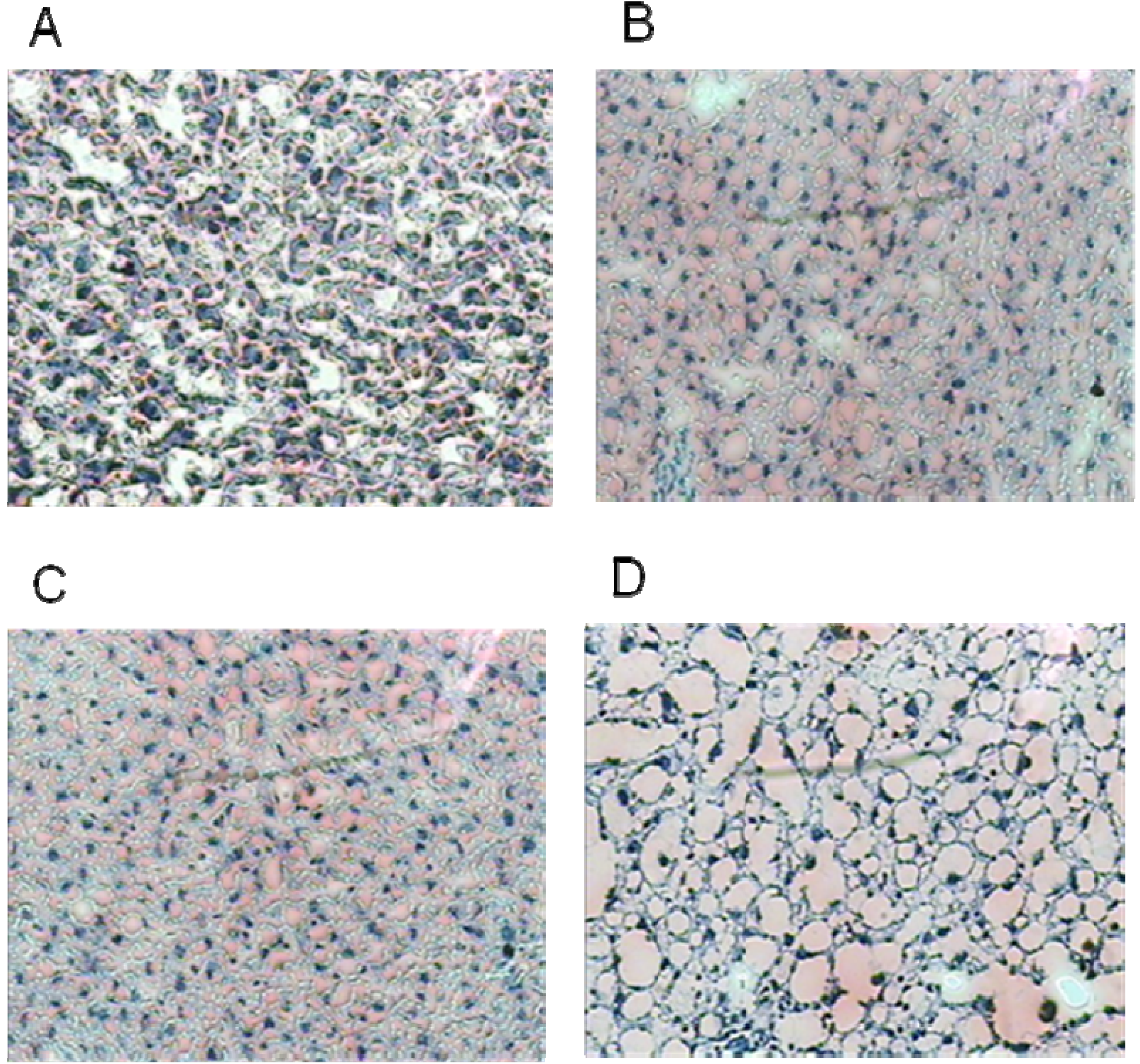
3.4. Liver Triacylglycerol (TAG)
3.5. Liver Phosphatidylcholine (PC) and Phosphatidylethanolamine (PE)
3.6. Correlation between the Dosages of Shiitake Mushrooms on Liver Weight, Liver Histology, Liver TAG, and Liver PC:PE Ratio
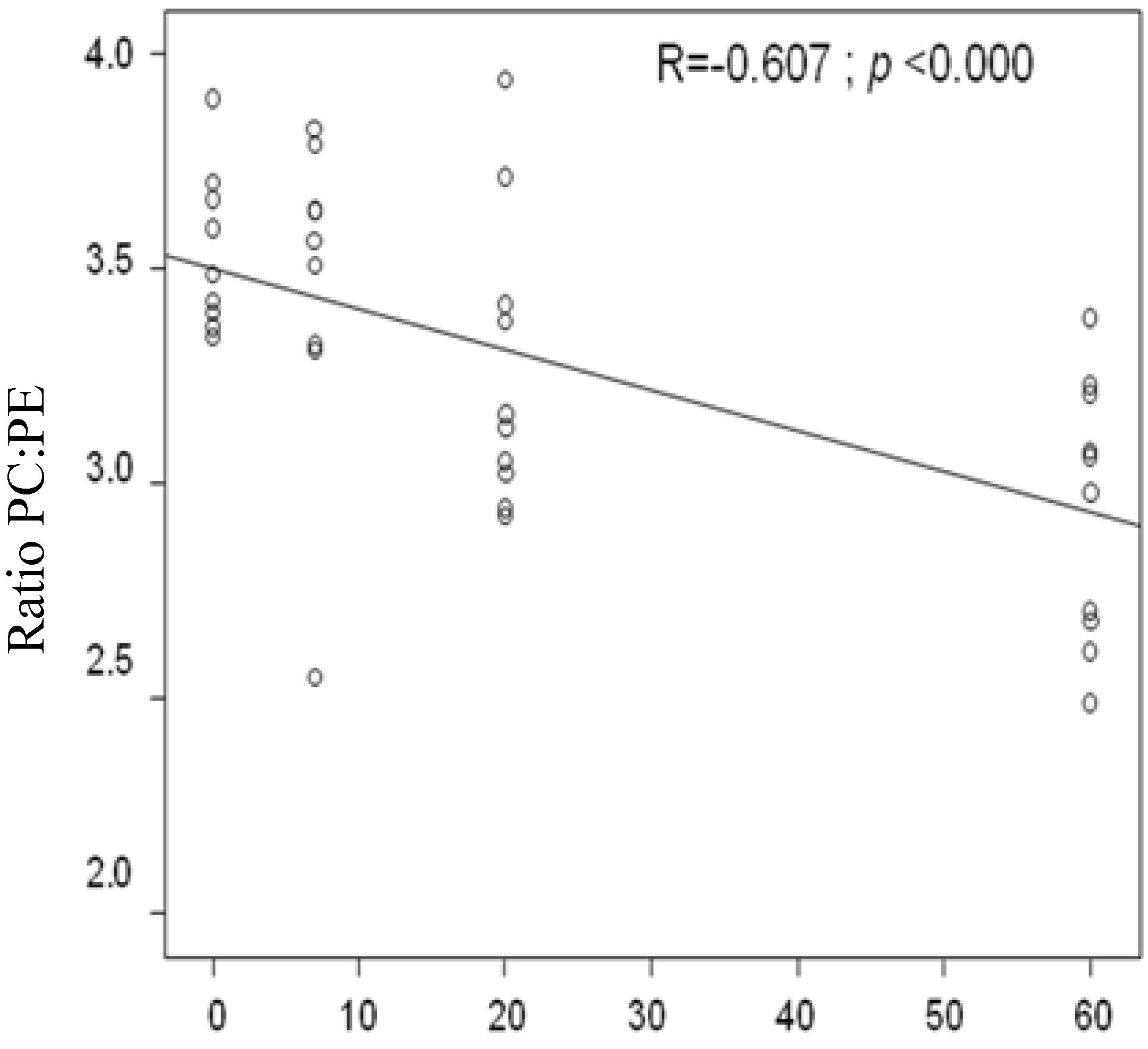
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kabir, Y.; Kimura, S. Dietary mushrooms reduce blood pressure in spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR). J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 1989, 35, 91–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takashima, K.; Izumi, H.; Iwai, H.; Takeyama, S. The hypocholesterolemic action of eritadenine in the rat. Atherosclerosis 1973, 17, 491–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhong, H.Y.; Zeng, J.H.; Ge, J. The pharmacological effect of polysaccharides from Lentinus edodes on the oxidative status and expression of VCAM-1mRNA of thoracic aorta endothelial cell in high-fat-diet rats. Carbohydr. Polym. 2008, 74, 445–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukushima, M.; Ohashi, T.; Fujiwara, Y.; Sonoyama, K.; Nakano, M. Cholesterol-lowering effects of maitake (Grifola frondosa) fiber, shiitake (Lentinus edodes) fiber, and enokitake (Flammulina velutipes) fiber in rats. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 2001, 226, 758–765. [Google Scholar]
- Handayani, D.; Chen, J.; Meyer, B.J.; Huang, X.F. Dietary Shiitake mushroom (Lentinus edodes) prevents fat deposition and lowers triglyceride in rats fed a high-fat diet. J. Obes. 2011, 2011, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handayani, D.; Meyer, B.J.; Chen, J.; Tang, P.; Kwok, P.C.L.; Chan, H.-K.; Huang, X.-F. The comparison of the effect of oat and shiitake mushroom powder to prevent body weight gain in rats fed high fat diet. Food Nutr. Sci. 2012, 3, 1009–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Williams, B.A.; Kwakkel, R.P.; Li, H.S.; Li, X.P.; Luo, J.Y.; Li, W.K.; Verstegen, M.W. Effects of mushroom and herb polysaccharides, as alternatives for an antibiotic, on the cecal microbial ecosystem in broiler chickens. Poult. Sci. 2004, 83, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudo, T.; Tamagawa, T.; Kawashima, M.; Mito, N.; Shibata, S. Attenuating effect of clock mutation on tryglyceride contents in the ICR mouse liver under a high high-fat diet. J. Biol. Rhythm. 2007, 22, 312–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takashima, K.; Sato, C.; Sasaki, Y.; Takashi, M.; Shigeyuki, T. Effect of eritadenine on cholesterol metabolism in the rat. Biochem. Pharmachol. 1974, 23, 433–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, Y.; Morita, T.; Sugiyama, K. Eritadenine-induced alterations of plasma lipoprotein lipid concentrations and phosphatidylcholine molecular species profile in rats fed cholesterol-free and cholesterol-enriched diets. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2003, 67, 996–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiyama, K.; Akachi, T.; Yamakawa, A. Hypocholesterolemic action of eritadenine is mediated by a modification of hepatic phospholipid metabolism in rats. J. Nutr. 1995, 125, 2134–2144. [Google Scholar]
- Walkey, C.J.; Yu, L.; Agellon, L.B.; Vance, D.E. Biochemical and evolutionary significance of phospholipid methylation. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 27043–27046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, L.; Vance, J.; Vance, D. Phosphatidylcholine biosynthesis and lipoprotein metabolism. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1821, 754–761. [Google Scholar]
- Kleiner, D.E.; Brunt, E.M.; van Natta, M.; Behling, C.; Contos, M.J.; Cummings, O.W.; Ferrell, L.D.; Liu, Y.C.; Torbenson, M.S.; Unalp-Arida, A.; et al. Design and validation of a histological scoring system for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2005, 41, 1313–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, L.; Smith, B.J.; Clarke, S.L.; Marlow, D.; D’Offay, J.M.; Kuvibidila, S.R. Differential effects of Shiitake and white button mushroom-supplemented diets on hepatic steatosis in C57BL/6 mice. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2011, 49, 3074–3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enman, J.; Rova, U.; Berglund, K. Quantification of the bioactive compound eritadenine in selected strains of shiitake mushroom (Lentinus edodes). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 1177–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folch, J.; Lees, M.; Sloane Stanley, G.H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipids from animal tissues. J. Biol. Chem. 1957, 226, 497–509. [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell, T.; Turner, N.; Hulbert, A.J.; Else, P.L.; Hawley, J.A.; Lee, J.S.; Bruce, C.R.; Blanksby, S.J. Exercise alters the profile of phospholipid molecular species in rat skeletal muscle. J. Appl. Physiol. 2004, 97, 1823–1829. [Google Scholar]
- Villanueva, M.J.; Yokoyama, W.H.; Hong, Y.J.; Barttley, G.E.; Rupérez, P. Effect of high-fat diets supplemented with okara soybean by-product on lipid profiles of plasma, liver and faeces in Syrian hamsters. Food Chem. 2011, 124, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deeley, J.M.; Mitchell, T.W.; Wei, X.; Korth, J.; Nealon, J.R.; Blanksby, S.J.; Truscott, R.J. Human lens lipids differ markedly from those of commonly used experimental animals. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2008, 1781, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ejsing, C.S.; Duchoslav, E.; Sampaio, J.; Simons, K.; Bonner, R.; Thiele, C.; Ekroos, K.; Shevchenko, A. Automated identification and quantification of glycerophospholipid molecular species by multiple precursor ion scanning. Anal. Chem 2006, 78, 6202–6214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Excel, version 2010; Microsoft Corporation: Redmond, WA, USA.
- Cheung, P.C. Plasma and hepatic cholesterol levels and fecal neutral sterol excretion are altered in hamsters fed straw mushroom diets. J. Nutr. 1998, 128, 1512–1516. [Google Scholar]
- Sugiyama, K.; Yamakawa, A.; Kawagishi, H.; Saeki, S. Dietary eritadenine modifies plasma phosphatidylcholine molecular species profile in rats fed different types of fat. J. Nutr. 1997, 127, 593–599. [Google Scholar]
- Fukushima, M.; Nakano, M.; Morii, Y.; Ohashi, T.; Fujiwara, Y.; Sonoyama, K. Hepatic LDL receptor m RNA in rats is increased by dietary mushroom (Agaricus bisporus) fiber and sugar bit. J. Nutr. 2000, 130, 2151–2156. [Google Scholar]
- Jeong, S.C.; Jeong, Y.T.; Yang, B.K.; Islam, R.; Koyyalamudi, S.R.; Pang, G.; Cho, K.Y.; Song, C.H. White button mushroom (Agaricus bisporus) lowers blood glucose and cholesterol levels in diabetic and hypercholesterolemic rats. Nutr. Res. 2010, 30, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubo, K.; Nanba, H. Anti-hyperliposis effect of Maitake fruit body (Grifola frondosa). Biol. Pharm. Bull. 1997, 20, 781–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kubo, K.; Nanba, H. The effect of Maitake mushroom on liver and serum lipids. Altern. Ther. Health Med. 1996, 2, 62–66. [Google Scholar]
- Sugiyama, K.; Akachi, T.; Yamakawa, A. Eritadenine-induced alteration of hepatic phospholipid metabolism in relation to its hypocholesterolemic action in rats. J. Nutr. Biochem. 1995, 6, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handayani, D.; Chen, J.; Meyer, B.J.; Huang, X.F. Shiitake mushroom β-glucan but not oat β-glucan prevents body weight gain in rat fed a high fat diet. Aust. Med. J. 2010, 3, 939. [Google Scholar]
- Tamura, S.; Shimomura, I. Contribution of adipose tissue and de novo lipogenesis to nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 1139–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.; Vance, D. The active synthesis of phosphatidylcholine is required for very low density lipoprotein secretion from rat hepatocy. J. Biol. Chem. 1988, 263, 2998–3004. [Google Scholar]
- Pynn, C.J.; Henderson, N.G.; Clark, H.; Koster, G.; Bernhard, W.; Postle, A.D. Specificity and rate of human and mouse liver and plasma phosphatidylcholine synthesis analyzed in vivo. J. Lipid Res. 2011, 52, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkins, S.; Zhu, X.; Zeisel, S. Phosphatidylethanolamine-N-methyltransferase activity and dietary choline regulate liver-plasma lipid flux and essential fatty acid metabolism in mice1. J. Nutr. 2003, 133, 3386–3391. [Google Scholar]
- Sugiyama, K.; Yamakawa, A.; Saeki, S. Correlation of suppressed linoleic acid metabolism with the hypocholesterolemic action of eritadenine in rats. Lipids 1997, 32, 859–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Votruba, I.; Holý, A. Eritadenines—Novel type of potent inhibitors of S-adenosyl-l-homocysteine hydrolase. Collect. Czechoslov. Chem. Commun. 1982, 47, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Agellon, L.B.; Allen, T.M.; Umeda, M.; Jewell, L.; Mason, A.; Vance, D.E. The ratio of phosphatidylcholine to phosphatidylethanolamine influences membrane integrity and steatohepatitis. Cell Metab. 2006, 3, 321–331. [Google Scholar]
- Vance, D.; Li, Z.; Jacobs, R. Hepatic phosphatidylethanolamine N-methyltransferase, unexpected roles in animal biochemistry and physiology. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 33237–33241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Handayani, D.; Meyer, B.J.; Chen, J.; Brown, S.H.J.; Mitchell, T.W.; Huang, X.-F. A High-Dose Shiitake Mushroom Increases Hepatic Accumulation of Triacylglycerol in Rats Fed a High-Fat Diet: Underlying Mechanism. Nutrients 2014, 6, 650-662. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu6020650
Handayani D, Meyer BJ, Chen J, Brown SHJ, Mitchell TW, Huang X-F. A High-Dose Shiitake Mushroom Increases Hepatic Accumulation of Triacylglycerol in Rats Fed a High-Fat Diet: Underlying Mechanism. Nutrients. 2014; 6(2):650-662. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu6020650
Chicago/Turabian StyleHandayani, Dian, Barbara J. Meyer, Jiezhong Chen, Simon H. J. Brown, Todd W. Mitchell, and Xu-Feng Huang. 2014. "A High-Dose Shiitake Mushroom Increases Hepatic Accumulation of Triacylglycerol in Rats Fed a High-Fat Diet: Underlying Mechanism" Nutrients 6, no. 2: 650-662. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu6020650
APA StyleHandayani, D., Meyer, B. J., Chen, J., Brown, S. H. J., Mitchell, T. W., & Huang, X.-F. (2014). A High-Dose Shiitake Mushroom Increases Hepatic Accumulation of Triacylglycerol in Rats Fed a High-Fat Diet: Underlying Mechanism. Nutrients, 6(2), 650-662. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu6020650






