Association of Obesity and Malnutrition with In-Hospital Mortality and Clinical Outcomes in Patients Receiving Maintenance Dialysis: A National Database Study
Abstract
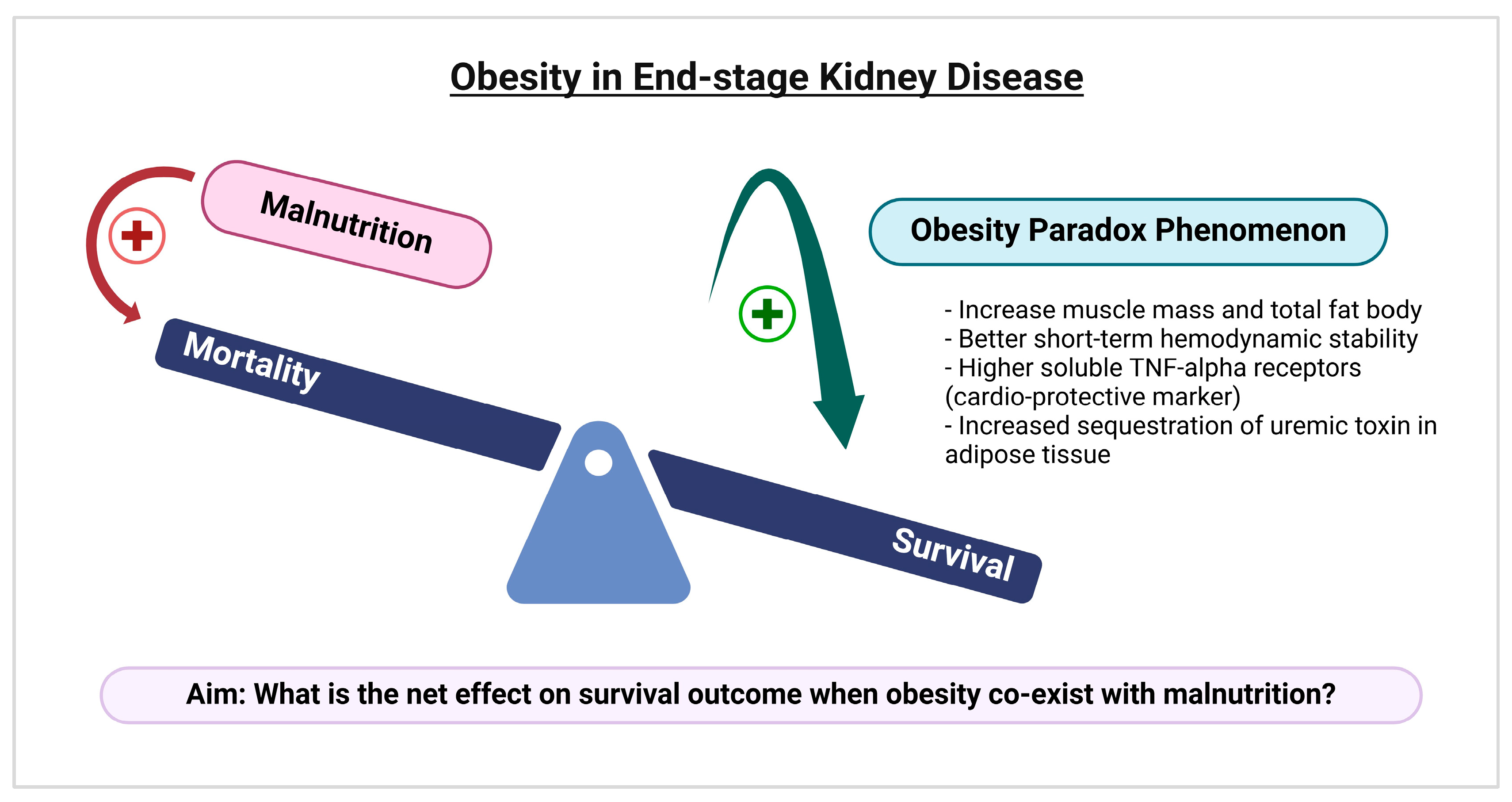
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Dataset
2.2. Study Population
2.3. Study Variables and Outcomes
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
3.2. Association Between Obesity with/Without Malnutrition and In-Hospital Outcomes
3.2.1. In-Hospital Mortality
3.2.2. Adverse Clinical Outcomes
3.2.3. Inpatient Treatments
3.2.4. Resource Utilization
3.2.5. Subgroup Analysis Stratified by Dialysis Modality
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
| CKD | Chronic Kidney Disease |
| CRBSI | Catheter-Related Bloodstream Infections |
| ESKD | End-Stage Kidney Disease |
| HCUP | Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project |
| HD | Hemodialysis |
| ICD-10-CM | International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, Clinical Modification |
| ICU | Intensive Care Unit |
| IQR | Interquartile Ranges |
| KRT | Kidney Replacement Therapy |
| LOS | Length of Stay |
| NIS | National Inpatient Sample |
| NND | Non-Dialysis Dependent |
| ORs | Odds Ratios |
| PN | Parenteral Nutrition |
| PD | Peritoneal Dialysis |
| RKF | Residual Kidney Function |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
| TNF | Tumor Necrosis Factor |
| TPN | Total Parenteral Nutrition |
| URR | Urea Reduction Ratio |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
References
- Liyanage, T.; Ninomiya, T.; Jha, V.; Neal, B.; Patrice, H.M.; Okpechi, I.; Zhao, M.-h.; Lv, J.; Garg, A.X.; Knight, J. Worldwide access to treatment for end-stage kidney disease: A systematic review. Lancet 2015, 385, 1975–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lovasik, B.P.; Zhang, R.; Hockenberry, J.M.; Schrager, J.D.; Pastan, S.O.; Mohan, S.; Patzer, R.E. Emergency department use and hospital admissions among patients with end-stage renal disease in the United States. JAMA Intern. Med. 2016, 176, 1563–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foreman, K.J.; Marquez, N.; Dolgert, A.; Fukutaki, K.; Fullman, N.; McGaughey, M.; Pletcher, M.A.; Smith, A.E.; Tang, K.; Yuan, C.-W. Forecasting life expectancy, years of life lost, and all-cause and cause-specific mortality for 250 causes of death: Reference and alternative scenarios for 2016–40 for 195 countries and territories. Lancet 2018, 392, 2052–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhandari, S.K.; Zhou, H.; Shaw, S.F.; Shi, J.; Tilluckdharry, N.S.; Rhee, C.M.; Jacobsen, S.J.; Sim, J.J. Causes of death in end-stage kidney disease: Comparison between the United States renal data system and a large integrated health care system. Am. J. Nephrol. 2022, 53, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrero, J.J.; Thomas, F.; Nagy, K.; Arogundade, F.; Avesani, C.M.; Chan, M.; Chmielewski, M.; Cordeiro, A.C.; Espinosa-Cuevas, A.; Fiaccadori, E. Global prevalence of protein-energy wasting in kidney disease: A meta-analysis of contemporary observational studies from the international society of renal nutrition and metabolism. J. Ren. Nutr. 2018, 28, 380–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, I.; Sahu, G.; Tiwari, P.; Willis, C.; Asche, C.V.; Bagga, T.K.; Ghule, P.; Bland, A. Malnutrition as a potential predictor of mortality in chronic kidney disease patients on dialysis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Nutr. 2024, 43, 1760–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wathanavasin, W.; Thongprayoon, C.; Kaewput, W.; Tangpanithandee, S.; Suppadungsuk, S.; Cheungpasitporn, W. Temporal Trends and Clinical Impact of Malnutrition on In-Hospital Outcomes Among Patients with Advanced Chronic Kidney Disease: A Nationwide Inpatient Analysis. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, Y.; Qian, Q. Protein nutrition and malnutrition in CKD and ESRD. Nutrients 2017, 9, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendriks, F.K.; Smeets, J.S.J.; Broers, N.J.H.; van Kranenburg, J.M.X.; van der Sande, F.M.; Kooman, J.P.; van Loon, L.J.C. End-Stage Renal Disease Patients Lose a Substantial Amount of Amino Acids during Hemodialysis. J. Nutr. 2020, 150, 1160–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikizler, T.A.; Wingard, R.L.; Sun, M.; Harvell, J.; Parker, R.A.; Hakim, R.M. Increased energy expenditure in hemodialysis patients. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 1996, 7, 2646–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Dai, L.; Ma, J.; Gu, L.; Xie, H.; Fu, J. Malnutrition accelerates the occurrence of infectious complications in patients with chronic kidney disease: A cross-sectional survey of 682 patients with chronic kidney disease. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2023, 38, 1167–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Malnutrition. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/malnutrition (accessed on 22 March 2025).
- Patel, S.A.; Ali, M.K.; Alam, D.; Yan, L.L.; Levitt, N.S.; Bernabe-Ortiz, A.; Checkley, W.; Wu, Y.; Irazola, V.; Gutierrez, L.; et al. Obesity and its Relation With Diabetes and Hypertension: A Cross-Sectional Study Across 4 Geographical Regions. Glob. Heart 2016, 11, 71–79.e74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flegal, K.M.; Kit, B.K.; Orpana, H.; Graubard, B.I. Association of all-cause mortality with overweight and obesity using standard body mass index categories: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA 2013, 309, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Rhee, C.M.; Chou, J.; Ahmadi, S.F.; Park, J.; Chen, J.L.; Amin, A.N. The Obesity Paradox in Kidney Disease: How to Reconcile it with Obesity Management. Kidney Int. Rep. 2017, 2, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaewput, W.; Thongprayoon, C.; Suppadungsuk, S.; Tangpanithandee, S.; Wathanavasin, W.; Qureshi, F.; Cheungpasitporn, W. Impact of obesity on in-hospital outcomes in peritoneal dialysis patients: Insights from a nationwide analysis. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2025, 57, 2595–2601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.; Ahmadi, S.F.; Streja, E.; Molnar, M.Z.; Flegal, K.M.; Gillen, D.; Kovesdy, C.P.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K. Obesity paradox in end-stage kidney disease patients. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2014, 56, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, M.K.; Mogensen, K.M.; Casey, J.D.; McKane, C.K.; Moromizato, T.; Rawn, J.D.; Christopher, K.B. The relationship among obesity, nutritional status, and mortality in the critically ill. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 43, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Androga, L.; Sharma, D.; Amodu, A.; Abramowitz, M.K. Sarcopenia, obesity, and mortality in US adults with and without chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. Rep. 2017, 2, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wathanavasin, W.; Banjongjit, A.; Avihingsanon, Y.; Praditpornsilpa, K.; Tungsanga, K.; Eiam-Ong, S.; Susantitaphong, P. Prevalence of sarcopenia and its impact on cardiovascular events and mortality among dialysis patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goossens, G.H. The Metabolic Phenotype in Obesity: Fat Mass, Body Fat Distribution, and Adipose Tissue Function. Obes. Facts 2017, 10, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iida, T.; Morimoto, S.; Okuda, H.; Amari, Y.; Yurugi, T.; Nakajima, F.; Ichihara, A. Impact of abdominal fat distribution on mortality and its changes over time in patients undergoing hemodialysis: A prospective cohort study. J. Ren. Nutr. 2023, 33, 575–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwala, N.N.; Borkent, J.W.; van der Meij, B.S.; de van der Schueren, M.A. Challenges in identifying malnutrition in obesity; An overview of the state of the art and directions for future research. Nutr. Res. Rev. 2024, 38, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okazaki, M.; Obi, Y.; Shafi, T.; Rhee, C.M.; Kovesdy, C.P.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K. Residual Kidney Function and Cause-Specific Mortality Among Incident Hemodialysis Patients. Kidney Int. Rep. 2023, 8, 1989–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Sequera, P.; Corchete, E.; Bohorquez, L.; Albalate, M.; Perez-Garcia, R.; Alique, M.; Marques, M.; García-Menéndez, E.; Portolés, J.; Ramirez, R. Residual Renal Function in Hemodialysis and Inflammation. Ther. Apher. Dial. 2017, 21, 592–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blankestijn, P.J.; Vernooij, R.W.M.; Hockham, C.; Strippoli, G.F.M.; Canaud, B.; Hegbrant, J.; Barth, C.; Covic, A.; Cromm, K.; Cucui, A.; et al. Effect of Hemodiafiltration or Hemodialysis on Mortality in Kidney Failure. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 700–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecoits-Filho, R.; Lindholm, B.; Stenvinkel, P. The malnutrition, inflammation, and atherosclerosis (MIA) syndrome—The heart of the matter. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2002, 17, 28–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benner, D.; Brunelli, S.M.; Brosch, B.; Wheeler, J.; Nissenson, A.R. Effects of Oral Nutritional Supplements on Mortality, Missed Dialysis Treatments, and Nutritional Markers in Hemodialysis Patients. J. Ren. Nutr. 2018, 28, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, M.; Melchor, J.; Carr, R.; Karjoo, S. Obesity and malnutrition in children and adults: A clinical review. Obes. Pillars 2023, 8, 100087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elizabeth, L.; Machado, P.; Zinöcker, M.; Baker, P.; Lawrence, M. Ultra-Processed Foods and Health Outcomes: A Narrative Review. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avesani, C.M.; Cuppari, L.; Nerbass, F.B.; Lindholm, B.; Stenvinkel, P. Ultraprocessed foods and chronic kidney disease-double trouble. Clin. Kidney J. 2023, 16, 1723–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gai, W.; Lin, L.; Wang, Y.; Bian, J.; Tao, Y. Relationship between dietary fiber and all-cause mortality, cardiovascular mortality, and cardiovascular disease in patients with chronic kidney disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Nephrol. 2024, 37, 77–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wathanavasin, W.; Cheungpasitporn, W.; Thongprayoon, C.; Fülöp, T. Effects of Dietary Fiber Supplementation on Modulating Uremic Toxins and Inflammation in Chronic Kidney Disease Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Toxins 2025, 17, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wathanavasin, W.; Kittiskulnam, P.; Johansen, K.L. Plant-based diets in patients with chronic kidney disease. Asian Biomed. Res. Rev. News 2024, 18, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macallan, D. Infection and malnutrition. Medicine 2009, 37, 525–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekker, M.J.E.; Konings, C.; Canaud, B.; van der Sande, F.M.; Stuard, S.; Raimann, J.G.; Öztürk, E.; Usvyat, L.; Kotanko, P.; Kooman, J.P. Interactions Between Malnutrition, Inflammation, and Fluid Overload and Their Associations With Survival in Prevalent Hemodialysis Patients. J. Ren. Nutr. 2018, 28, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiaccadori, E.; Sabatino, A.; Barazzoni, R.; Carrero, J.J.; Cupisti, A.; De Waele, E.; Jonckheer, J.; Singer, P.; Cuerda, C. ESPEN guideline on clinical nutrition in hospitalized patients with acute or chronic kidney disease. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 1644–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emiroglu, C.; Görpelioglu, S.; Aypak, C. The relationship between nutritional status, anemia and other vitamin deficiencies in the elderly receiving home care. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2019, 23, 677–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Ikizler, T.A.; Block, G.; Avram, M.M.; Kopple, J.D. Malnutrition-inflammation complex syndrome in dialysis patients: Causes and consequences. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2003, 42, 864–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsayed, M.E.; Morris, A.D.; Li, X.; Browne, L.D.; Stack, A.G. Propensity score matched mortality comparisons of peritoneal and in-centre haemodialysis: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2020, 35, 2172–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisch, N.; Wessell, N.M.; Charters, M.; Peterson, E.; Cann, B.; Greenstein, A.; Silverton, C.D. Effect of body mass index on blood transfusion in total hip and knee arthroplasty. Orthopedics 2016, 39, e844–e849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variables | Non-Obese (n = 548,389) | Obesity | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Without Malnutrition (n = 119,155) | With Malnutrition (n = 6823) | |||
| Age (years) | 62.1 ± 15.5 | 59.9 ± 13.1 | 62.5 ± 12.8 | <0.001 |
| Male sex, n (%) | 309,052 (56.4) | 56,490 (47.4) | 2920 (42.8) | <0.001 |
| Race, n (%) - White - Black - Hispanic - Asian or Pacific Islander | 209,489 (40.7) 184,923 (35.9) 94,710 (18.4) 25,404 (4.9) | 51,537 (45.8) 40,123 (35.6) 18,085 (16.1) 2877 (2.6) | 3130 (48.9) 2120 (33.1) 993 (15.5) 162 (2.5) | <0.001 |
| Mode of KRT, n (%) - Hemodialysis - Peritoneal dialysis | 508,983 (92.8) 39,406 (7.2) | 111,288 (93.4) 7867 (6.6) | 6267 (91.8) 556 (8.2) | <0.001 |
| Elixhauser score, median (IQR) | 6 (4–7) | 7 (6–8) | 8(7–10) | <0.001 |
| Charlson comorbidity score, median (IQR) | 5 (4–7) | 6 (4–7) | 6 (5–7) | <0.001 |
| Comorbidity, n (%) - Diabetes mellitus - Hypertension - Dyslipidemia - Congestive heart failure - Coronary artery disease - Cerebrovascular disease - Peripheral vascular disease - Cancer - Cirrhosis - Dementia/cognitive impairment | 338,002 (61.6) 521,290 (95.1) 218,487 (39.8) 276,133 (50.3) 91,643 (16.7) 51,505 (9.4) 71,184 (13.0) 29,515 (5.4) 54,236 (9.9) 35,401 (6.5) | 93,201 (78.2) 114,574 (96.2) 58,674 (49.2) 65,840 (55.3) 19,795 (16.6) 8895 (7.5) 13,247 (11.1) 4280 (3.6) 8748 (7.3) 3680 (3.1) | 5225 (76.6) 6388 (93.6) 2970 (43.5) 3802 (55.7) 997 (14.6) 648 (9.5) 848 (12.4) 446 (6.5) 993 (14.6) 399 (5.9) | <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 |
| Smoking, n (%) | 122,164 (22.3) | 26,622 (22.3) | 1083 (15.9) | <0.001 |
| Alcohol use, n (%) | 15,125 (2.8) | 1944 (1.6) | 217 (3.2) | <0.001 |
| Elective admission type, n (%) | 37,819 (6.9) | 9956 (8.4) | 485 (7.1) | <0.001 |
| Length of stay, days median (IQR) | 5 (3–9) | 5 (3–9) | 10 (5–19) | <0.001 |
| Hospitalization cost ($) median (IQR) | 54,157 (29,140–107,001) | 58,611 (31,598–113,183) | 109,981 (54,656–229,221) | <0.001 |
| Hospital location/ teaching status, n (%) - Rural - Urban-nonteaching - Urban-teaching | 25,195 (4.6) 99,559 (18.2) 423,635 (77.2) | 6028 (5.1) 21,557 (18.1) 91,570 (76.8) | 277 (4.1) 1341 (19.6) 5205 (76.3) | <0.001 |
| In-Hospital Outcomes | Non-Obese (n = 548,389) | Obesity Without Malnutrition (n = 119,155) | Obesity with Malnutrition (n = 6823) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Univariable Analysis | Multivariable Analysis | Univariable Analysis | Multivariable Analysis | ||||||
| OR (95% CI) | p-Value | Adjusted OR * (95% CI) | p-Value | OR (95% CI) | p-Value | Adjusted OR * (95% CI) | p-Value | ||
| Adverse clinical outcomes | |||||||||
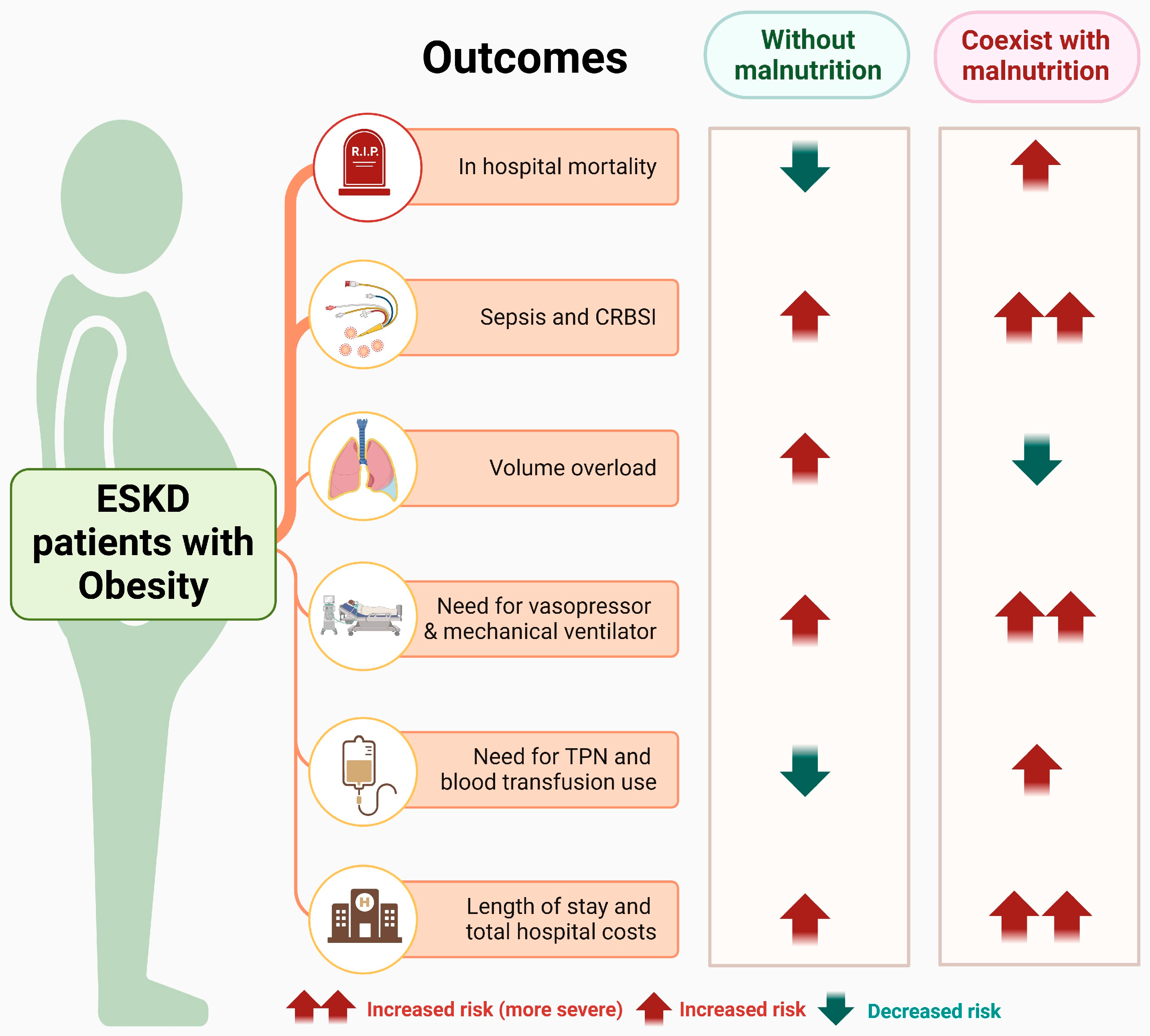
| In hospital mortality | Ref. | 0.75 (0.73–0.78) | <0.001 | 0.87 (0.84–0.91) | <0.001 | 2.20 (2.02–2.39) | <0.001 | 2.08 (1.90–2.27) | <0.001 |
| Sepsis | Ref. | 1.01 (0.99–1.03) | 0.12 | 1.07 (1.05–1.08) | <0.001 | 2.77 (2.63–2.91) | <0.001 | 2.63 (2.50–2.77) | <0.001 |
| CRBSI | Ref. | 1.09 (1.03–1.15) | 0.003 | 1.09 (1.03–1.15) | 0.003 | 1.68 (1.43–1.98) | <0.001 | 1.70 (1.44–2.00) | <0.001 |
| Volume overload | Ref. | 1.08 (1.05–1.10) | <0.001 | 1.08 (1.06–1.11) | <0.001 | 0.84 (0.77–0.92) | <0.001 | 0.91 (0.83–0.99) | 0.03 |
| Inpatient treatments | |||||||||
| Need for vasopressors | Ref. | 0.96 (0.91–1.01) | 0.10 | 1.06 (1.01–1.12) | 0.02 | 2.80 (2.49–3.15) | <0.001 | 2.56 (2.26–2.89) | <0.001 |
| TPN use | Ref. | 0.49 (0.43–0.57) | <0.001 | 0.57 (0.50–0.66) | <0.001 | 4.83 (4.04–5.77) | <0.001 | 4.36 (3.63–5.24) | <0.001 |
| Mechanical ventilation | Ref. | 1.84 (1.79–1.89) | <0.001 | 1.85 (1.80–1.90) | <0.001 | 1.98 (1.82–2.16) | <0.001 | 1.95 (1.79–2.13) | <0.001 |
| Blood transfusion | Ref. | 0.82 (0.80–0.84) | <0.001 | 0.89 (0.87–0.91) | <0.001 | 1.61 (1.50–1.72) | <0.001 | 1.60 (1.49–1.72) | <0.001 |
| Coefficient (95% CI) | p-value | Adjusted coefficient * (95% CI) | p-value | Coefficient (95% CI) | p-value | Adjusted coefficient * (95% CI) | p-value | ||
| Resource utilization | |||||||||
| LOS (days) | Ref. | 0.00 (−0.07, 0.06) | 0.93 | 0.14 (0.08, 0.20) | <0.001 | 7.57 (7.12, 8.02) | <0.001 | 7.14 (6.69, 7.58) | <0.001 |
| Hospitalization cost ($) | Ref. | −948 (−2385, 489) | 0.20 | 2811 (1561, 4061) | <0.001 | 104,245 (95,581, 112,908) | <0.001 | 99,514 (90,932, 108,096) | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2026 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Wathanavasin, W.; Kaewput, W.; Thongprayoon, C.; Tangpanithandee, S.; Suppadungsuk, S.; Cheungpasitporn, W. Association of Obesity and Malnutrition with In-Hospital Mortality and Clinical Outcomes in Patients Receiving Maintenance Dialysis: A National Database Study. Nutrients 2026, 18, 157. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu18010157
Wathanavasin W, Kaewput W, Thongprayoon C, Tangpanithandee S, Suppadungsuk S, Cheungpasitporn W. Association of Obesity and Malnutrition with In-Hospital Mortality and Clinical Outcomes in Patients Receiving Maintenance Dialysis: A National Database Study. Nutrients. 2026; 18(1):157. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu18010157
Chicago/Turabian StyleWathanavasin, Wannasit, Wisit Kaewput, Charat Thongprayoon, Supawit Tangpanithandee, Supawadee Suppadungsuk, and Wisit Cheungpasitporn. 2026. "Association of Obesity and Malnutrition with In-Hospital Mortality and Clinical Outcomes in Patients Receiving Maintenance Dialysis: A National Database Study" Nutrients 18, no. 1: 157. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu18010157
APA StyleWathanavasin, W., Kaewput, W., Thongprayoon, C., Tangpanithandee, S., Suppadungsuk, S., & Cheungpasitporn, W. (2026). Association of Obesity and Malnutrition with In-Hospital Mortality and Clinical Outcomes in Patients Receiving Maintenance Dialysis: A National Database Study. Nutrients, 18(1), 157. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu18010157









