Measures of Adiposity and Risk of Rheumatoid Arthritis in Middle-Aged UK Women: A Prospective Cohort Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Anthropometric Assessments
2.3. Assessment of Lifestyle Factors and Other Covariates
2.4. Ascertainment of RA Cases and Mortality from CVD and Cancer
2.5. Statistical Methods
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of Included Participants
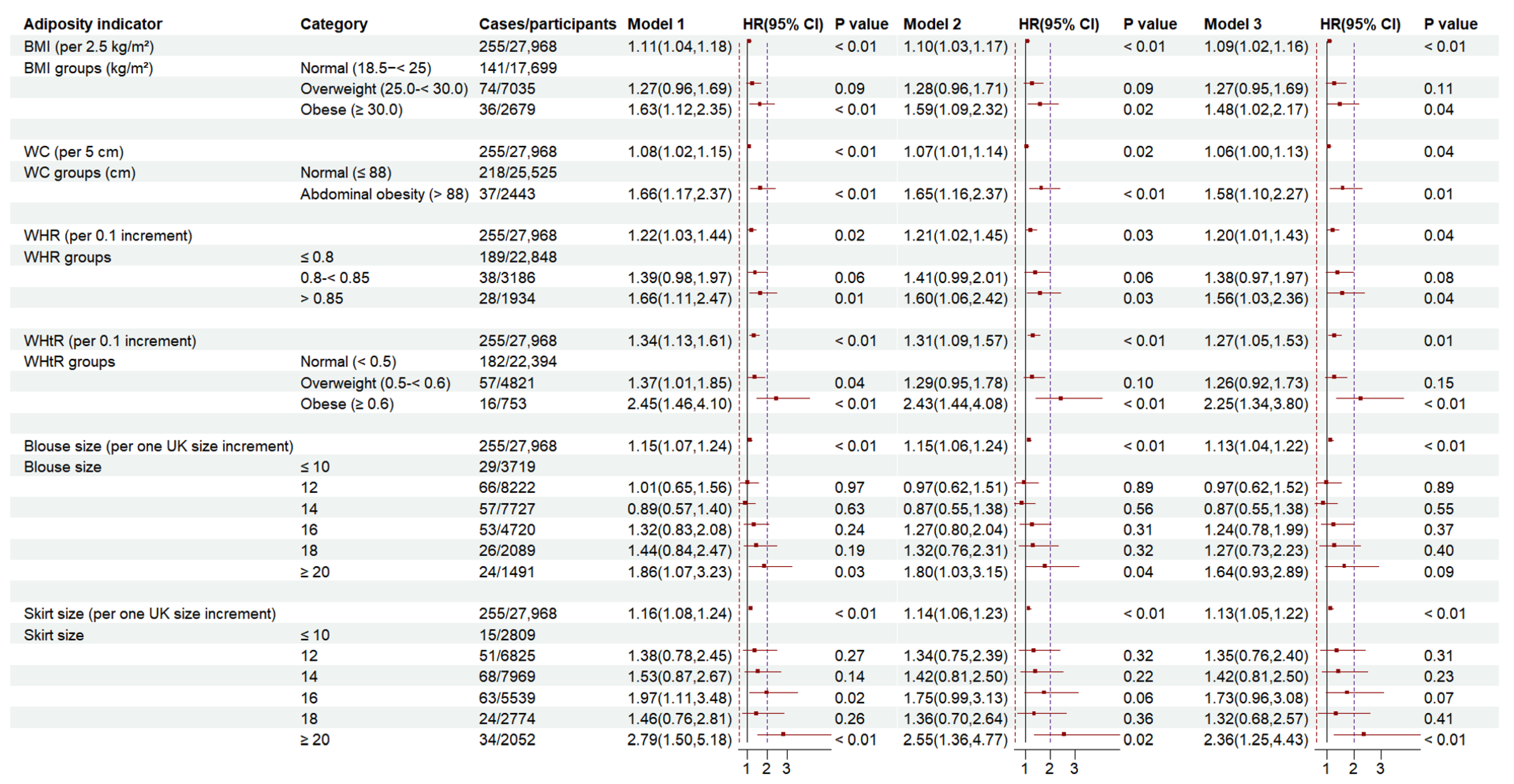
3.2. Associations of BMI, WC, WHR, WHtR, Blouse Size, Skirt Size with RA Risk
3.3. Subgroup Analysis
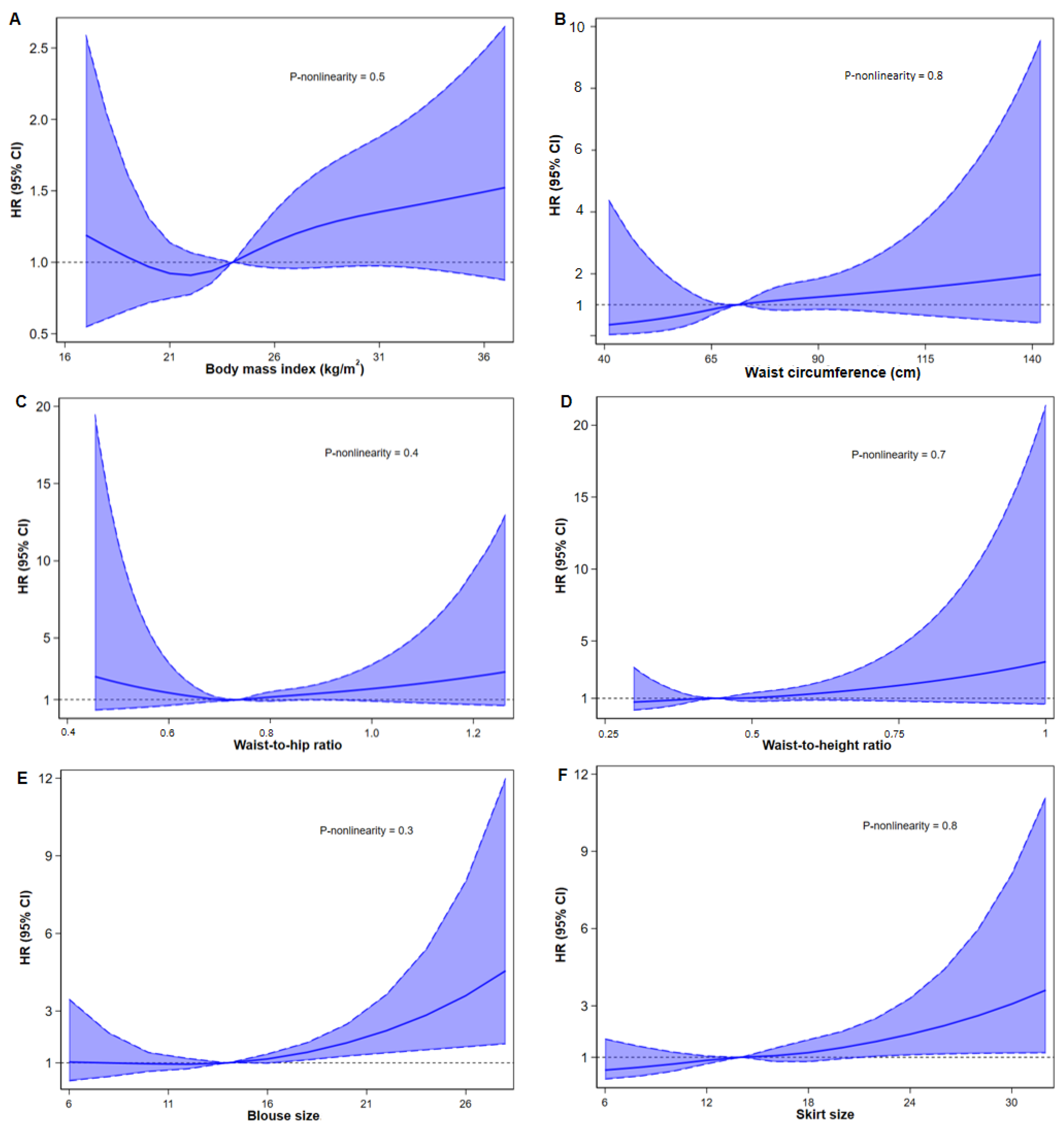
3.4. Sensitivity Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Main Findings
4.2. Comparison with Previous Studies
4.3. Possible Mechanistic Explanations
5. Strengths and Limitations
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Global, regional, and national burden of rheumatoid arthritis, 1990–2020, and projections to 2050: A systematic analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet Rheumatol. 2023, 5, e594–e610. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casale, R.; Atzeni, F.; Bazzichi, L.; Beretta, G.; Costantini, E.; Sacerdote, P.; Tassorelli, C. Pain in Women: A Perspective Review on a Relevant Clinical Issue that Deserves Prioritization. Pain Ther. 2021, 10, 287–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Digital N: Health Survey for England 2021: Overweight and Obesity (Part 2). 2022. Available online: https://digital.nhs.uk/data-and-information/publications/statistical/health-survey-for-england/2021/part-2-overweight-and-obesity (accessed on 15 January 2025).
- Rubino, F.; Cummings, D.E.; Eckel, R.H.; Cohen, R.V.; Wilding, J.P.H.; Brown, W.A.; Stanford, F.C.; Batterham, R.L.; Farooqi, I.S.; Farpour-Lambert, N.J.; et al. Definition and diagnostic criteria of clinical obesity. Lancet. Diabetes Endocrinol. 2025, 13, 221–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell-Wiley, T.M.; Poirier, P.; Burke, L.E.; Després, J.P.; Gordon-Larsen, P.; Lavie, C.J.; Lear, S.A.; Ndumele, C.E.; Neeland, I.J.; Sanders, P.; et al. Obesity and Cardiovascular Disease: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2021, 143, e984–e1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NICE. Keep the Size of Your Waist to Less Than Half of Your Height, NICE Recommends. 2022. Available online: https://www.nice.org.uk/news/articles/keep-the-size-of-your-waist-to-less-than-half-of-your-height-nice--recommends (accessed on 15 January 2025).
- Zhou, Y.; Sun, M. A meta-analysis of the relationship between body mass index and risk of rheumatoid arthritis. EXCLI J. 2018, 17, 1079–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, B.; Yang, M.; Fu, H.; Ma, N.; Wei, T.; Tang, Q.; Hu, Z.; Liang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Zhong, R. Body mass index and the risk of rheumatoid arthritis: A systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2015, 17, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, L.A.; Tolosa, L.B.; Ruigómez, A.; Johansson, S.; Wallander, M.A. Rheumatoid arthritis in UK primary care: Incidence and prior morbidity. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 2009, 38, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Oh, J.S.; Kim, S.; Kim, Y.J.; Hong, S.; Kim, Y.G.; Lee, C.K.; Yoo, B. The association of obesity and the risk of rheumatoid arthritis according to abdominal obesity status: A nationwide population-based study in Korea. Rheumatol. Int. 2024, 44, 2863–2871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohno, T.; Aune, D.; Heath, A.K. Adiposity and the risk of rheumatoid arthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchand, N.E.; Sparks, J.A.; Tedeschi, S.K.; Malspeis, S.; Costenbader, K.H.; Karlson, E.W.; Lu, B. Abdominal Obesity in Comparison with General Obesity and Risk of Developing Rheumatoid Arthritis in Women. J. Rheumatol. 2021, 48, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachat, C.; Hawwash, D.; Ocké, M.C.; Berg, C.; Forsum, E.; Hörnell, A.; Larsson, C.; Sonestedt, E.; Wirfält, E.; Åkesson, A.; et al. Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology-Nutritional Epidemiology (STROBE-nut): An Extension of the STROBE Statement. PLoS Med. 2016, 13, e1002036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cade, J.E.; Burley, V.J.; Alwan, N.; Hutchinson, J. Cohort profile: The UK Women’s cohort study (UKWCS). Int. J. Epidemiol. 2017, 46, e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moy, F.M.; Greenwood, D.C.; Cade, J.E. Associations of clothing size, adiposity and weight change with risk of postmenopausal breast cancer in the UK Women’s Cohort Study (UKWCS). BMJ Open 2018, 8, e022599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Threapleton, D.E.; Greenwood, D.C.; Burley, V.J.; Aldwairji, M.; Cade, J.E. Dietary fibre and cardiovascular disease mortality in the UK Women’s Cohort Study. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2013, 28, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Heianza, Y.; Sun, D.; Huang, T.; Ma, W.; Rimm, E.B.; Manson, J.E.; Hu, F.B.; Willett, W.C.; Qi, L. Improving adherence to healthy dietary patterns, genetic risk, and long term weight gain: Gene-diet interaction analysis in two prospective cohort studies. BMJ 2018, 360, j5644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.; Hiraki, L.T.; Sparks, J.A.; Malspeis, S.; Chen, C.Y.; Awosogba, J.A.; Arkema, E.V.; Costenbader, K.H.; Karlson, E.W. Being overweight or obese and risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis among women: A prospective cohort study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2014, 73, 1914–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salliot, C.; Nguyen, Y.; Mariette, X.; Boutron-Ruault, M.C.; Seror, R. Anthropometric Measures and Risk of Rheumatoid Arthritis in the French E3N Cohort Study. Nutrients 2022, 14, 934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linauskas, A.; Overvad, K.; Symmons, D.; Johansen, M.B.; Stengaard-Pedersen, K.; de Thurah, A. Body Fat Percentage, Waist Circumference, and Obesity As Risk Factors for Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Danish Cohort Study. Arthritis Care Res. 2019, 71, 777–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ljung, L.; Rantapää-Dahlqvist, S. Abdominal obesity, gender and the risk of rheumatoid arthritis—A nested case-control study. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2016, 18, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, T.; Chen, Z.Y.; Li, T.; Lin, X.; Hu, H.G.; Tang, J.D.; Wu, C. Association between body roundness index and osteoarthritis/rheumatoid arthritis: A cross-sectional study. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 9682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaiss, M.M.; Joyce Wu, H.-J.; Mauro, D.; Schett, G.; Ciccia, F.J.N.R.R. The gut–joint axis in rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2021, 17, 224–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohm, T.V.; Meier, D.T.; Olefsky, J.M.; Donath, M.Y. Inflammation in obesity, diabetes, and related disorders. Immunity 2022, 55, 31–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiernan, K.; MacIver, N.J. The Role of the Adipokine Leptin in Immune Cell Function in Health and Disease. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 622468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolau, J.; Lequerré, T.; Bacquet, H.; Vittecoq, O. Rheumatoid arthritis, insulin resistance, and diabetes. Jt. Bone Spine 2017, 84, 411–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payet, M.; Dargai, F.; Gasque, P.; Guillot, X. Epigenetic regulation (including micro-RNAs, DNA methylation and histone modifications) of rheumatoid arthritis: A systematic review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costenbader, K.H.; Prescott, J.; Zee, R.Y.; De Vivo, I. Immunosenescence and rheumatoid arthritis: Does telomere shortening predict impending disease? Autoimmun. Rev. 2011, 10, 569–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, E.; Haynes, A.; Sutin, A.; Daly, M. Practice: Self-perception of overweight and obesity: A review of mental and physical health outcomes. Obes. Sci. Pract. 2020, 6, 552–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, F.L.; Green, J.; Reeves, G.; Beral, V.; Cairns, B.J. Validity over time of self-reported anthropometric variables during follow-up of a large cohort of UK women. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2015, 15, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristics | Total | Cases | Non-Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| Participants (%) | 27,968 | 255 (1.0) | 27,713 (99.0) |
| Age, years (SD) | 51.9 (9.2) | 53.9 (9.0) | 51.9 (9.2) |
| Degree-level education (%) | 7057 (25.2) | 48 (18.8) | 7009 (25.3) |
| Socio-economic status (%) | |||
| Professional or managerial | 17,753 (63.5) | 146 (57.3) | 17,607 (63.5) |
| Intermediate | 7735 (27.7) | 80 (31.4) | 7655 (27.6) |
| Routine or manual | 2480 (8.9) | 29 (11.4) | 2451 (8.8) |
| Married (%) | 21,207 (75.8) | 189 (74.1) | 21,018 (75.8) |
| Anthropometric indices | |||
| Height, cm (SD) | 163.7 (6.6) | 162.8 (6.8) | 163.7 (6.6) |
| Weight, kg (SD) | 65.4 (11.6) | 67.2 (14.3) | 65.4 (11.5) |
| Waist circumference, cm (SD) | 74.2 (9.6) | 76.2 (11.4) | 74.2 (9.6) |
| BMI at year 20, kg/m2 (SD) | 21.4(2.9) | 21.7(3.0) | 21.4(2.9) |
| BMI at recruitment, kg/m2 (SD) | 24.4 (4.2) | 25.4 (5.3) | 24.4 (4.2) |
| Waist-to-hip ratio (SD) | 0.8 (0.1) | 0.8 (0.1) | 0.8 (0.1) |
| Waist-to-height ratio (SD) | 0.5 (0.1) | 0.5 (0.1) | 0.5 (0.1) |
| Blouse size (SD) | 13.9 (2.9) | 14.7 (3.6) | 13.9 (2.9) |
| Skirt size (SD) | 14.5 (3.2) | 15.4 (3.7) | 14.5 (3.2) |
| Physical activity (METs), hours/week (SD) | 16.6 (11.5) | 15.4 (9.8) | 16.6 (11.5) |
| Smoking status (%) | |||
| Current | 3081 (11.0) | 41 (16.1) | 3040 (11.0) |
| Former | 8722 (31.2) | 89 (34.9) | 8633 (31.2) |
| Never | 16,165 (57.8) | 125 (49.0) | 16,040 (57.9) |
| Alcohol consumption, grams/week (SD) | 9.0 (10.5) | 7.1 (8.4) | 9.0 (10.5) |
| Total energy intake, kcal/day (SD) | 2334.2 (701.5) | 2352.8 (847.3) | 2334.1 (700.0) |
| AHEI-2010 score (SD) | 65.6 (11.0) | 65.8 (10.1) | 65.6 (11.0) |
| Menopausal status (%) | |||
| Premenopausal | 13,571 (48.5) | 93 (36.5) | 13,571 (49.0) |
| Postmenopausal | 14,397 (51.5) | 162 (63.5) | 14,397 (52.0) |
| Hormone replacement therapy (%) | 7698 (27.5) | 82 (32.2) | 7616 (27.5) |
| Prevalence of CVD, cancer, or diabetes (%) | 1908 (6.8) | 30 (11.8) | 1878 (6.8) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dong, Y.; Greenwood, D.C.; Hardie, L.J.; Cade, J.E. Measures of Adiposity and Risk of Rheumatoid Arthritis in Middle-Aged UK Women: A Prospective Cohort Study. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1557. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17091557
Dong Y, Greenwood DC, Hardie LJ, Cade JE. Measures of Adiposity and Risk of Rheumatoid Arthritis in Middle-Aged UK Women: A Prospective Cohort Study. Nutrients. 2025; 17(9):1557. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17091557
Chicago/Turabian StyleDong, Yuanyuan, Darren C. Greenwood, Laura J. Hardie, and Janet E. Cade. 2025. "Measures of Adiposity and Risk of Rheumatoid Arthritis in Middle-Aged UK Women: A Prospective Cohort Study" Nutrients 17, no. 9: 1557. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17091557
APA StyleDong, Y., Greenwood, D. C., Hardie, L. J., & Cade, J. E. (2025). Measures of Adiposity and Risk of Rheumatoid Arthritis in Middle-Aged UK Women: A Prospective Cohort Study. Nutrients, 17(9), 1557. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17091557








