Effect of 1-Kestose on Lipid Metabolism in a High-Fat-Diet Rat Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Experiments
2.2. Measurement of Blood Components
2.3. Analysis of mRNA Gene Expression in Liver Tissues by Quantitative Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction
2.4. Measurement of Metabolite Levels in the Cecum
2.5. 16S rRNA Sequencing
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
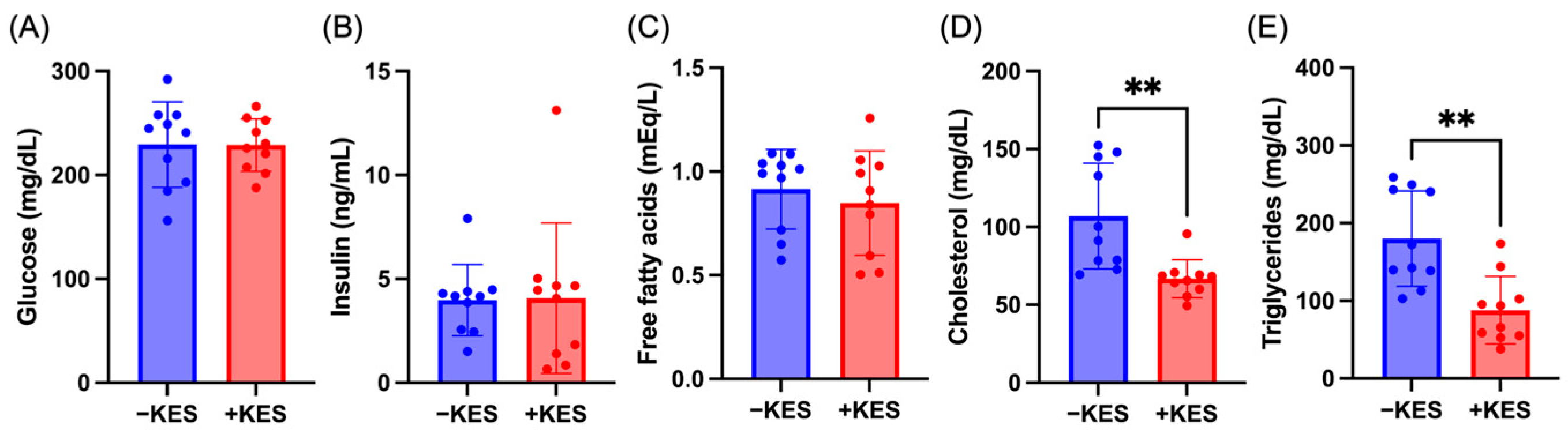
3.1. 1-Kestose Suppressed Weight Gain and Reduced Blood Lipid Levels
3.2. 1-Kestose Altered mRNA Gene Expression in Liver Tissues
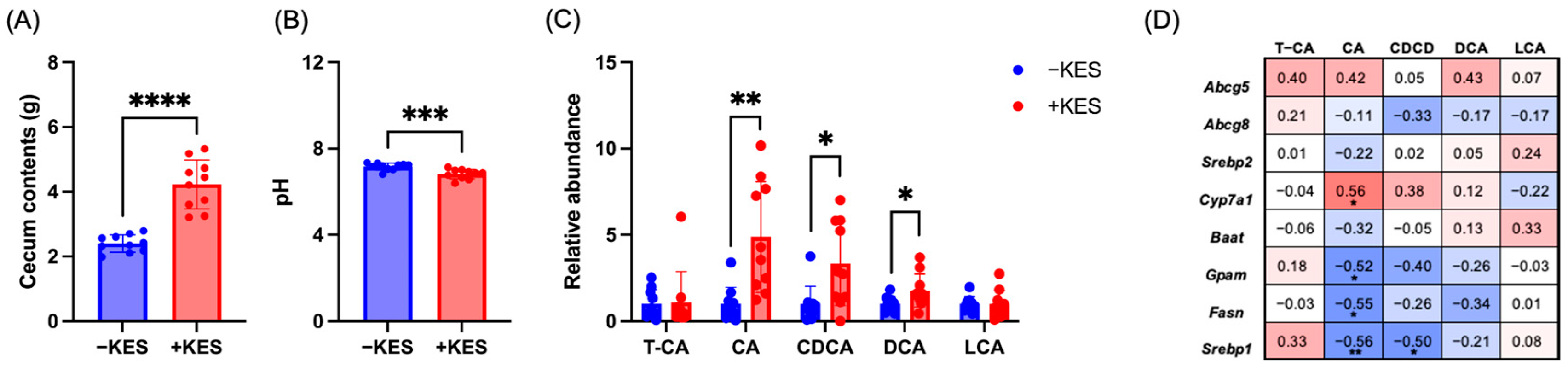
3.3. 1-Kestose Intake Altered the Bile Acid Composition in Cecal Contents
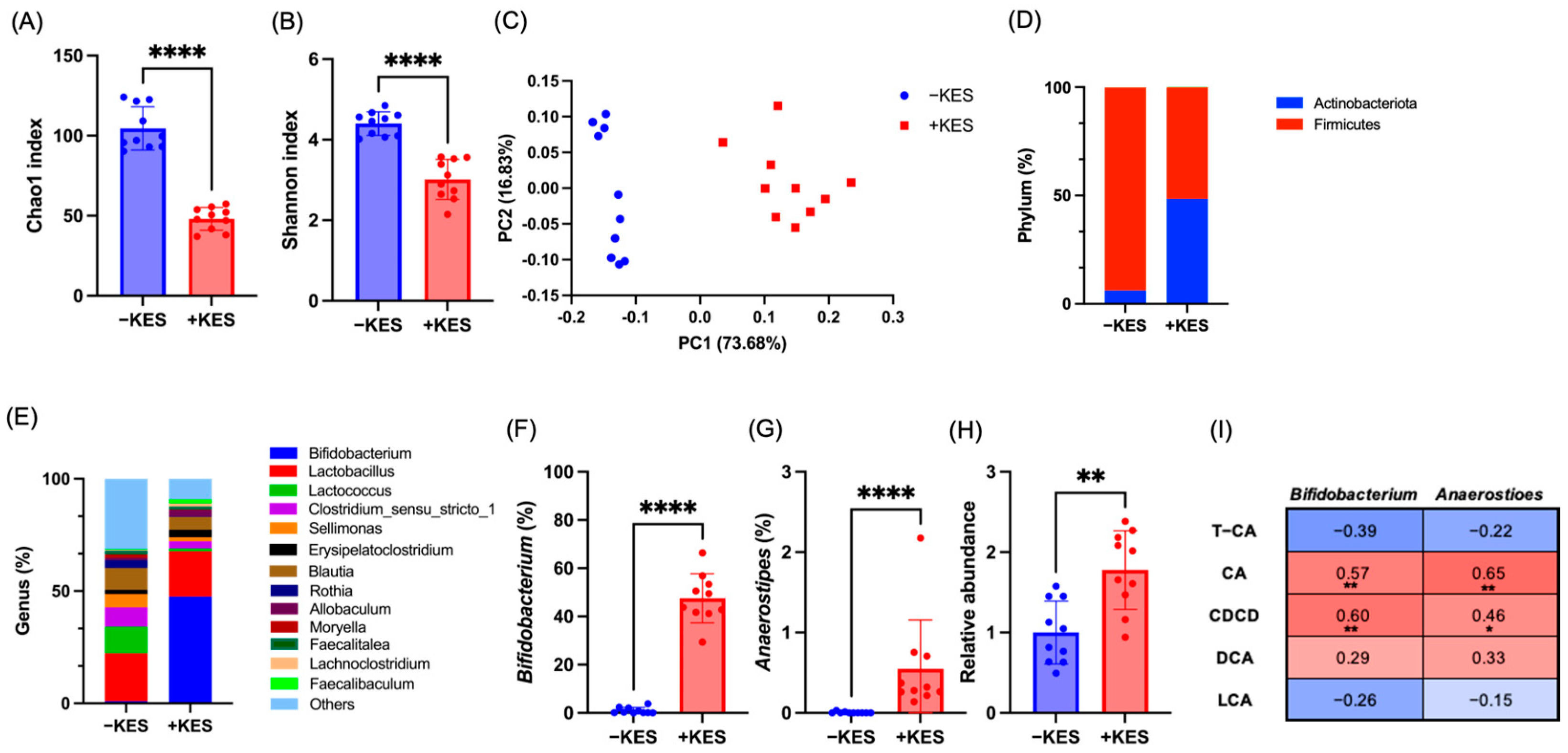
3.4. 1-Kestose Intake Altered the Microbiota in Cecal Contents
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Virani, S.S.; Alonso, A.; Aparicio, H.J.; Benjamin, E.J.; Bittencourt, M.S.; Callaway, C.W.; Carson, A.P.; Chamberlain, A.M.; Cheng, S.; Delling, F.N.; et al. Heart disease and stroke Statistics-2021 update: A report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2021, 143, e254–e743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timmis, A.; Vardas, P.; Townsend, N.; Torbica, A.; Katus, H.; De, S.; Gale, C.P.; Maggioni, A.P.; Petersen, S.E.; Huculeci, R.; et al. European Society of Cardiology: Cardiovascular disease statistics 2021. Eur. Heart J. 2022, 43, 716–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varbo, A.; Benn, M.; Smith, G.D.; Timpson, N.J.; Tybjaerg-Hansen, A.; Nordestgaard, B.G. Remnant cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, and blood pressure as mediators from obesity to ischemic heart disease. Circ. Res. 2015, 116, 665–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldstein, J.L.; Brown, M.S. A century of cholesterol and coronaries: From plaques to genes to statins. Cell 2015, 161, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordestgaard, B.G.; Varbo, A. Triglycerides and cardiovascular disease. Lancet 2014, 384, 626–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramkumar, S.; Raghunath, A.; Raghunath, S. Statin therapy: Review of safety and potential side effects. Acta Cardiol. Sin. 2016, 32, 631–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulipati, V.P.; Davidson, M.H. How I treat statin-associated side effects in an outpatient setting. Future Cardiol. 2021, 17, 1249–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolk, M.F.J.; Becx, M.C.J.M.; Kuypers, K.C.; Seldenrijk, C.A. Severe hepatic side effects of ezetimibe. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2006, 4, 908–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimano, H. Sterol regulatory element-binding proteins (SREBPs): Transcriptional regulators of lipid synthetic genes. Prog. Lipid Res. 2001, 40, 439–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, K.; Wu, Z.X.; Chen, X.Y.; Wang, J.Q.; Zhang, D.; Xiao, C.; Zhu, D.; Koya, J.B.; Wei, L.; Li, J.; et al. Microbiota in health and diseases. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Roy, T.; Lécuyer, E.; Chassaing, B.; Rhimi, M.; Lhomme, M.; Boudebbouze, S.; Ichou, F.; Haro Barceló, J.; Huby, T.; Guerin, M.; et al. The intestinal microbiota regulates host cholesterol homeostasis. BMC Biol. 2019, 17, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaden-Volynets, V.; Basic, M.; Neumann, U.; Pretz, D.; Rings, A.; Bleich, A.; Bischoff, S.C. Lack of liver steatosis in germ-free mice following hypercaloric diets. Eur. J. Nutr. 2019, 58, 1933–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pols, T.W.H.; Puchner, T.; Korkmaz, H.I.; Vos, M.; Soeters, M.R.; de Vries, C.J.M. Lithocholic acid controls adaptive immune responses by inhibition of Th1 activation through the Vitamin D receptor. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, J.B.J.; Lajczak, N.K.; Kelly, O.B.; O’Dwyer, A.M.; Giddam, A.K.; Ní Gabhann, J.; Franco, P.; Tambuwala, M.M.; Jefferies, C.A.; Keely, S.; et al. Ursodeoxycholic acid and lithocholic acid exert anti-inflammatory actions in the colon. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2017, 312, G550–G558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernstein, H.; Bernstein, C.; Payne, C.M.; Dvorakova, K.; Garewal, H. Bile acids as carcinogens in human gastrointestinal cancers. Mutat. Res. 2005, 589, 47–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahlström, A.; Kovatcheva-Datchary, P.; Ståhlman, M.; Khan, M.T.; Bäckhed, F.; Marschall, H.U. Induction of farnesoid X receptor signaling in germ-free mice colonized with a human microbiota. J. Lipid Res. 2017, 58, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makishima, M.; Okamoto, A.Y.; Repa, J.J.; Tu, H.; Learned, R.M.; Luk, A.; Hull, M.V.; Lustig, K.D.; Mangelsdorf, D.J.; Shan, B. Identification of a nuclear receptor for bile acids. Science 1999, 284, 1362–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, M.; Houten, S.M.; Wang, L.; Moschetta, A.; Mangelsdorf, D.J.; Heyman, R.A.; Moore, D.D.; Auwerx, J. Bile acids lower triglyceride levels via a pathway involving FXR, SHP, and SREBP-1c. J. Clin. Investig. 2004, 113, 1408–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, B.; Zou, Y.; Han, X.; Bae, J.W.; Jeon, C.O. Gut microbiome-mediated mechanisms for reducing cholesterol levels: Implications for ameliorating cardiovascular disease. Trends Microbiol. 2023, 31, 76–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, G.R.; Hutkins, R.; Sanders, M.E.; Prescott, S.L.; Reimer, R.A.; Salminen, S.J.; Scott, K.; Stanton, C.; Swanson, K.S.; Cani, P.D.; et al. Expert consensus document: The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP) consensus statement on the definition and scope of prebiotics. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 14, 491–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, J.M.; Bauer, L.L.; Fahey, G.C.; Hogarth, A.J.C.L.; Wolf, B.W.; Hunter, D.E. Selected Fructooligosaccharide (1-Kestose, Nystose, and 1 F-β-Fructofuranosylnystose) Composition of Foods and Feeds. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1997, 45, 3076–3082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, A.; Tochio, T.; Kadota, Y.; Takahashi, M.; Kitaura, Y.; Ishikawa, H.; Yasutake, T.; Nakano, M.; Shinohara, H.; Kudo, T.; et al. Supplementation of 1-kestose modulates the gut microbiota composition to ameliorate glucose metabolism in obesity-prone Hosts. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuramitsu, K.; Kadota, Y.; Watanabe, A.; Endo, A.; Shimomura, Y.; Kitaura, Y. The effects of 1-kestose on the abundance of inflammation-related gene mRNA in adipose tissue and the gut microbiota composition in rats fed a high-fat diet. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 2024, 70, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, A.; Kadota, Y.; Kamio, R.; Tochio, T.; Endo, A.; Shimomura, Y.; Kitaura, Y. 1-Kestose supplementation mitigates the progressive deterioration of glucose metabolism in type 2 diabetes OLETF rats. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 15674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, H.; Fujii, T.; Yamakawa, S.; Yamada, C.; Fujiki, K.; Kondo, N.; Funasaka, K.; Hirooka, Y.; Tochio, T. Combined oral intake of short and long fructans alters the gut microbiota in food allergy model mice and contributes to food allergy prevention. BMC Microbiol. 2023, 23, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikegami, S.; Nakamura, M.; Honda, T.; Yamamura, T.; Maeda, K.; Sawada, T.; Ishikawa, E.; Yamamoto, K.; Furune, S.; Ishikawa, T.; et al. Efficacy of 1-kestose supplementation in patients with mild to moderate ulcerative colitis: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled pilot study. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2023, 57, 1249–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibata, R.; Koga, Y.; Takahashi, M.; Murakami, Y.; Tochio, T.; Kadota, Y. In children with cow’s milk allergy, 1-kestose affects the gut microbiota and reaction threshold. Pediatr. Res. 2023, 94, 1067–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tochio, T.; Kitaura, Y.; Nakamura, S.; Sugawa, C.; Takahashi, M.; Endo, A.; Shimomura, Y. An alteration in the cecal microbiota composition by feeding of 1-kestose results in a marked increase in the cecal butyrate content in rats. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0166850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coy, D.J.; Wooton-Kee, C.R.; Yan, B.; Sabeva, N.; Su, K.; Graf, G.; Vore, M. ABCG5/ABCG8-independent biliary cholesterol excretion in lactating rats. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2010, 299, G228–G235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zhou, Z.; Ren, X.; Wang, Y.; Yang, R.; Luo, J.; Strappe, P. Effect of Ganoderma lucidum spores intervention on glucose and lipid metabolism gene expression profiles in type 2 diabetic rats. Lipids Health Dis. 2015, 14, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, X.; Chen, L.; Wu, J.; Dang, H.; Wei, M.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, N.; et al. Expression profiling of hepatic genes associated with lipid metabolism in nephrotic rats. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2008, 295, F662–F671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hisada, T.; Endoh, K.; Kuriki, K. Inter- and intra-individual variations in seasonal and daily stabilities of the human gut microbiota in Japanese. Arch. Microbiol. 2015, 197, 919–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douglas, G.M.; Maffei, V.J.; Zaneveld, J.R.; Yurgel, S.N.; Brown, J.R.; Taylor, C.M.; Huttenhower, C.; Langille, M.G.I. PICRUSt2 for prediction of metagenome functions. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 685–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, S.; Van Treuren, W.; White, R.A.; Eggesbø, M.; Knight, R.; Peddada, S.D. Analysis of composition of microbiomes: A novel method for studying microbial composition. Microb. Ecol. Health Dis. 2015, 26, 27663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, H.M.; Park, S.Y.; Lee, D.K.; Kim, J.R.; Cha, M.K.; Lee, S.W.; Lim, H.T.; Kim, K.J.; Ha, N.J. Antiobesity and lipid-lowering effects of Bifidobacterium spp. in high fat diet-induced obese rats. Lipids Health Dis. 2011, 10, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, K.; Lan, Y.; Zhu, X.; Li, J.; Chen, T.; Huang, Q.; Ho, C.T.; Chen, Y.; Cao, Y. Hepatic lipidomics analysis reveals the antiobesity and cholesterol-lowering effects of tangeretin in high-fat diet-fed rats. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 6142–6153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Pastén, A.; Fernández-Martínez, E.; Pérez-Hernández, N.; Soria-Jasso, L.E.; Cariño-Cortés, R. Prebiotics and probiotics: Effects on dyslipidemia and NAFLD/NASH and the associated mechanisms of action. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2023, 24, 633–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hira, T.; Suto, R.; Kishimoto, Y.; Kanahori, S.; Hara, H. Resistant maltodextrin or fructooligosaccharides promotes GLP-1 production in male rats fed a high-fat and high-sucrose diet, and partially reduces energy intake and adiposity. Eur. J. Nutr. 2018, 57, 965–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodwin, B.; Jones, S.A.; Price, R.R.; Watson, M.A.; McKee, D.D.; Moore, L.B.; Galardi, C.; Wilson, J.G.; Lewis, M.C.; Roth, M.E.; et al. A regulatory cascade of the nuclear receptors FXR, SHP-1, and LRH-1 represses bile acid biosynthesis. Mol. Cell 2000, 6, 517–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moschetta, A.; Bookout, A.L.; Mangelsdorf, D.J. Prevention of cholesterol gallstone disease by FXR agonists in a mouse model. Nat. Med. 2004, 10, 1352–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Dury, S.; Marschall, H.U. Ileal bile acid transporter inhibition for the treatment of chronic constipation, cholestatic pruritus, and NASH. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, A.F.; Mysels, K.J. Bile acid solubility and precipitation in vitro and in vivo: The role of conjugation, pH, and Ca2+ ions. J. Lipid Res. 1992, 33, 617–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ley, R.E.; Turnbaugh, P.J.; Klein, S.; Gordon, J.I. Microbial ecology: Human gut microbes associated with obesity. Nature 2006, 444, 1022–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crawford, M.; Whisner, C.; Al-Nakkash, L.; Sweazea, K.L. Six-week high-fat diet alters the gut microbiome and promotes cecal inflammation, endotoxin production, and simple steatosis without obesity in male rats. Lipids 2019, 54, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanno, H.; Fujii, T.; Ose, R.; Hirano, K.; Tochio, T.; Endo, A. Characterization of fructooligosaccharide-degrading enzymes in human commensal Bifidobacterium longum and Anaerostipes caccae. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 518, 294–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarocki, P.; Podleśny, M.; Glibowski, P.; Targoński, Z. A new insight into the physiological role of bile salt hydrolase among intestinal bacteria from the genus Bifidobacterium. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e114379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xu, H.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, W.; Li, S.; Gao, J. Bifidobacterium breve Protects the Intestinal Epithelium and Mitigates Inflammation in Colitis via Regulating the Gut Microbiota-Cholic Acid Pathway. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 3572–3583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Zhang, J.; Liu, C.; Le, T.N.; Lu, Y.; Feng, F.; Zhao, M. High-Fat Diet-Induced Decreased Circulating Bile Acids Contribute to Obesity Associated with Gut Microbiota in Mice. Foods 2024, 13, 699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Gene | Sequence (5′–3′) | |
|---|---|---|
| Abcg5 | F | CGCAGGAACCGCATTGAAA |
| R | TGTCGAAGTGGTGGAAGAGCT | |
| Abcg8 | F | GATGCTGGCTATCATAGGGAGC |
| R | TCTCTGCCTGTGATAACGTCGA | |
| Srebp2 | F | GGTACGCTGGTTACTCAAAAAGG |
| R | CCCTCGCACTGCTCTTAGCT | |
| Cyp7a1 | F | CCAAGTCAAGTGTCCCCCTCTA |
| R | GACTCTCAGCCGCCAAGTG | |
| Baat | F | CTGTCGAACTACGGTTTTGGCCAA |
| R | TCAGGCCTGTGACCCGGATA | |
| Gpam | F | CCTGTGGGCATCTCGTATGAT |
| R | TTCCGCAGCATTCTGATAAC | |
| Fasn | F | CTGCTGCGGGCCAAGACAG |
| R | GCTGTGGATGATGTTGATGATAG | |
| Srebp1 | F | GCAAGGCCATCGACTACATC |
| R | TTTCATGCCCTCCATAGACAC | |
| Gapdh | F | CTTCACCACCATGGAGAAGGC |
| R | GGCATGGACTGTGGTCATGAG |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kuramitsu, K.; Kubo, M.; Cindy, F.; Shibata, T.; Kadota, Y.; Kitaura, Y. Effect of 1-Kestose on Lipid Metabolism in a High-Fat-Diet Rat Model. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1362. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17081362
Kuramitsu K, Kubo M, Cindy F, Shibata T, Kadota Y, Kitaura Y. Effect of 1-Kestose on Lipid Metabolism in a High-Fat-Diet Rat Model. Nutrients. 2025; 17(8):1362. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17081362
Chicago/Turabian StyleKuramitsu, Kento, Mikoto Kubo, Felicia Cindy, Takahiro Shibata, Yoshihiro Kadota, and Yasuyuki Kitaura. 2025. "Effect of 1-Kestose on Lipid Metabolism in a High-Fat-Diet Rat Model" Nutrients 17, no. 8: 1362. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17081362
APA StyleKuramitsu, K., Kubo, M., Cindy, F., Shibata, T., Kadota, Y., & Kitaura, Y. (2025). Effect of 1-Kestose on Lipid Metabolism in a High-Fat-Diet Rat Model. Nutrients, 17(8), 1362. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17081362






