Effects of the Energy-Adjusted Dietary Inflammation Index During Pregnancy on Prenatal Depression: The Mediating Effect of Sleep Quality
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Dietary Assessment
2.3. Sleep Quality Assessment
2.4. Measurement of Depression
2.5. Covariate Assessment
2.6. Statistical Analysis
2.6.1. E-DII Calculation
global average per capita daily intake of nutrients)/the SD of the global average per capita daily intake of
this dietary ingredient or nutrient
2.6.2. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Basic Characteristics of the Participants
3.2. Relationship Between E-DII, Sleep Quality, and Prenatal Depression During Pregnancy
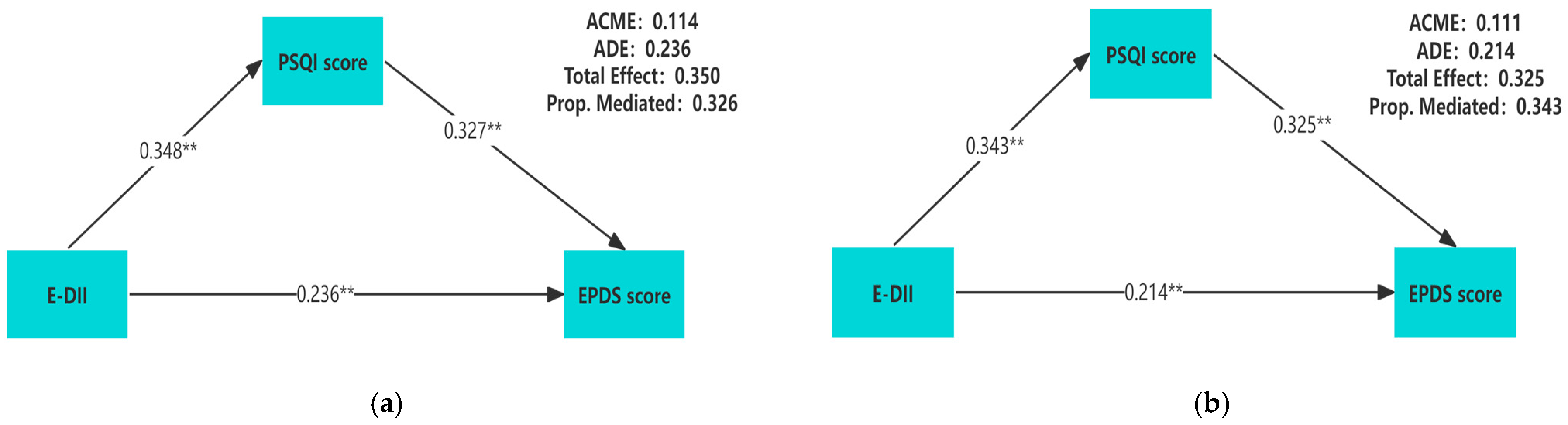
3.3. The Mediating Effect of Sleep Quality in the Association Between E-DII and Prenatal Depression
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACOG | American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists |
| DII | Dietary inflammatory index |
| NHANES | The United States National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey |
| FFQ | Food Frequency Questionnaire |
| PSQI | Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index |
| EPDS | Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| E-DII | Energy-adjusted dietary inflammatory index |
| ACEM | Average causal mediation effects |
| ADE | Average direct effects |
| OR | Odds ratio |
| CI | Confidence interval |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 |
| CRP | C-reactive protein |
References
- Lancaster, C.A.; Gold, K.J.; Flynn, H.A.; Yoo, H.; Marcus, S.M.; Davis, M.M. Risk Factors for Depressive Symptoms During Pregnancy: A Systematic Review. Am. J. Obs. Gynecol. 2010, 202, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buist, A. Perinatal Depression—Assessment and Management. Aust. Fam. Physician 2006, 35, 670–673. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Roy, U.; Swain, D. A Prospective Cohort Study to Assess the Prevalence and Risk Factors of Antepartum Depression and Its Effect on Maternal and Fetal Outcome. Asian J. Psychiatr. 2024, 91, 103873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witt, W.P.; Wisk, L.E.; Cheng, E.R.; Hampton, J.M.; Creswell, P.D.; Hagen, E.W.; Spear, H.A.; Maddox, T.; Deleire, T. Poor Prepregnancy and Antepartum Mental Health Predicts Postpartum Mental Health Problems among US Women: A Nationally Representative Population-Based Study. Womens Health Issues 2011, 21, 304–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, R.S.; Velazco, N.K.; Briggs, R.D.; Racine, A.D. Maternal Depressive Symptoms and Child Obesity in Low-Income Urban Families. Acad. Pediatr. 2013, 13, 356–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weobong, B.; ten Asbroek, A.H.A.; Soremekun, S.; Manu, A.A.; Owusu-Agyei, S.; Prince, M.; Kirkwood, B.R. Association of Antenatal Depression with Adverse Consequences for the Mother and Newborn in Rural Ghana: Findings from the DON Population-Based Cohort Study. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e116333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Wu, J.; Wang, L.; Hao, Y.; Zhang, C.; Liu, H.; Li, C.; Booij, L.; Herba, C.M.; Ouyang, F.; et al. Associations between Antenatal Depressive Symptoms in Different Trimesters and Perinatal Outcomes: A Prospective Multicenter Cohort Study in China. Asian J. Psychiatr. 2024, 100, 104165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvernaz, S.A.; Wenzel, E.S.; Nagelli, U.; Pezley, L.B.; LaBomascus, B.; Gilbert, J.A.; Maki, P.M.; Tussing-Humphreys, L.; Peñalver Bernabé, B. Inflammatory Dietary Potential Is Associated with Vitamin Depletion and Gut Microbial Dysbiosis in Early Pregnancy. Nutrients 2024, 16, 935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Zhou, Y.; Wen, Z.; Ye, W.; Gao, L.; Xu, Y. Association between Dietary Inflammatory Index and Bone Mineral Density Changes among Pregnant Women: A Prospective Study in China. Nutrients 2024, 16, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, S.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, W.; Jin, Y.; Long, Z.; Gu, W.; Ma, L.; Zhang, S.; Lin, J. Association between Dietary Inflammatory Index and Hyperemesis Gravidarum. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavicchia, P.P.; Steck, S.E.; Hurley, T.G.; Hussey, J.R.; Ma, Y.; Ockene, I.S.; Hébert, J.R. A New Dietary Inflammatory Index Predicts Interval Changes in Serum High-Sensitivity C-Reactive Protein. J. Nutr. 2009, 139, 2365–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shivappa, N.; Steck, S.E.; Hurley, T.G.; Hussey, J.R.; Hébert, J.R. Designing and Developing a Literature-Derived, Population-Based Dietary Inflammatory Index. Public Health Nutr. 2014, 17, 1689–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hébert, J.R.; Shivappa, N.; Wirth, M.D.; Hussey, J.R.; Hurley, T.G. Perspective: The Dietary Inflammatory Index (DII)-Lessons Learned, Improvements Made, and Future Directions. Adv. Nutr. 2019, 10, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shivappa, N.; Hebert, J.R.; Marcos, A.; Diaz, L.-E.; Gomez, S.; Nova, E.; Michels, N.; Arouca, A.; González-Gil, E.; Frederic, G.; et al. Association between Dietary Inflammatory Index and Inflammatory Markers in the HELENA Study. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2017, 61, 1600707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estruch, R.; Martínez-González, M.A.; Corella, D.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; Ruiz-Gutiérrez, V.; Covas, M.I.; Fiol, M.; Gómez-Gracia, E.; López-Sabater, M.C.; Vinyoles, E.; et al. Effects of a Mediterranean-Style Diet on Cardiovascular Risk Factors: A Randomized Trial. Ann. Intern Med. 2006, 145, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parletta, N.; Zarnowiecki, D.; Cho, J.; Wilson, A.; Bogomolova, S.; Villani, A.; Itsiopoulos, C.; Niyonsenga, T.; Blunden, S.; Meyer, B.; et al. A Mediterranean-Style Dietary Intervention Supplemented with Fish Oil Improves Diet Quality and Mental Health in People with Depression: A Randomized Controlled Trial (HELFIMED). Nutr. Neurosci. 2019, 22, 474–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmans, R.S.; Malecki, K.M. The Association of Dietary Inflammatory Potential with Depression and Mental Well-Being among U.S. Adults. Prev. Med. 2017, 99, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, M.; Yao, Z.; Zhang, T.; Li, Z. Dietary Inflammatory Potential and the Incidence of Depression and Anxiety: A Meta-Analysis. J. Health Popul. Nutr. 2022, 41, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, P.J.; von Känel, R.; Norman, D.; Natarajan, L.; Ziegler, M.G.; Dimsdale, J.E. Inflammation and Sleep in Healthy Individuals. Sleep 2007, 30, 729–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.P.; Buxton, M.; Rodríguez-Carmona, Y.; Peterson, K.E.; Liu, Y.; Burgess, H.J.; Cantoral, A.; Tellez-Rojo, M.M.; Torres-Olascoaga, L.A.; Arboleda-Merino, L.; et al. Duration, Timing, and Consistency of Sleep in Relation to Inflammatory Cytokines in Mexican Adolescents. Sleep Med. 2022, 100, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godos, J.; Ferri, R.; Caraci, F.; Cosentino, F.I.I.; Castellano, S.; Shivappa, N.; Hebert, J.R.; Galvano, F.; Grosso, G. Dietary Inflammatory Index and Sleep Quality in Southern Italian Adults. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casas, I.; Nakaki, A.; Pascal, R.; Castro-Barquero, S.; Youssef, L.; Genero, M.; Benitez, L.; Larroya, M.; Boutet, M.L.; Casu, G.; et al. Effects of a Mediterranean Diet Intervention on Maternal Stress, Well-Being, and Sleep Quality throughout Gestation-The IMPACT-BCN Trial. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, T.; Wang, C.; Yan, J.; Zeng, Q.; Ma, C. Relationship between Antenatal Sleep Quality and Depression in Perinatal Women: A Comprehensive Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. J. Affect Disord. 2023, 327, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Hu, J.; Yang, L.; Ding, N.; Wei, X.; Li, L.; Liu, L.; Ma, Y.; Wen, D. Association of Sleep Quality during Pregnancy with Stress and Depression: A Prospective Birth Cohort Study in China. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2019, 19, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buysse, D.J.; Reynolds, C.F.; Monk, T.H.; Berman, S.R.; Kupfer, D.J. The Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index: A New Instrument for Psychiatric Practice and Research. Psychiatry Res. 1989, 28, 193–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Zhao, X.; Mao, Z.; Abdulai, T.; Liu, X.; Tu, R.; Wang, Y.; Qian, X.; Jiang, J.; et al. The Association between PSQI Score and Hypertension in a Chinese Rural Population: The Henan Rural Cohort Study. Sleep Med. 2019, 58, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, P.-S.; Wang, S.-Y.; Wang, M.-Y.; Su, C.-T.; Yang, T.-T.; Huang, C.-J.; Fang, S.-C. Psychometric Evaluation of the Chinese Version of the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (CPSQI) in Primary Insomnia and Control Subjects. Qual. Life Res. 2005, 14, 1943–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergink, V.; Kooistra, L.; Lambregtse-van den Berg, M.P.; Wijnen, H.; Bunevicius, R.; van Baar, A.; Pop, V. Validation of the Edinburgh Depression Scale during Pregnancy. J. Psychosom. Res. 2011, 70, 385–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.T.; Yip, S.K.; Chiu, H.F.; Leung, T.Y.; Chan, K.P.; Chau, I.O.; Leung, H.C.; Chung, T.K. Detecting Postnatal Depression in Chinese Women. Validation of the Chinese Version of the Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale. Br. J. Psychiatry 1998, 172, 433–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yin, L.; Chan, K.S.; Guo, X. Validation of the Mainland Chinese Version of the Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale in Chengdu Mothers. Int. J. Nurs. Stud. 2010, 47, 1139–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bei-Fan, Z. Predictive Values of Body Mass Index and Waist Circumference for Risk Factors of Certain Related Diseases in Chinese Adults: Study on Optimal Cut-off Points of Body Mass Index and Waist Circumference in Chinese Adults. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2002, 11, S685–S693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Yin, P.; Ma, Z.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, H.; Kong, H.; Zhu, Y. Characteristics of Bile Acids Metabolism Profile in the Second and Third Trimesters of Normal Pregnancy. Metab. Clin. Exp. 2019, 95, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wu, Y.; Zhong, C.; Zhou, X.; Liu, C.; Li, Q.; Chen, R.; Gao, Q.; Li, X.; Zhang, H.; et al. Association between Dietary Inflammatory Index and Gestational Diabetes Mellitus Risk in a Prospective Birth Cohort Study. Nutrition 2021, 87–88, 111193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Sun, M.; Liu, Y.; Xi, Y.; Xiang, C.; Yong, C.; Liang, J.; Huo, J.; Lin, Q.; Deng, J. Relationship between Dietary Inflammatory Index and Postpartum Depression in Exclusively Breastfeeding Women. Nutrients 2022, 14, 5006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisar, A.; Yin, J.; Waqas, A.; Bai, X.; Wang, D.; Rahman, A.; Li, X. Prevalence of Perinatal Depression and Its Determinants in Mainland China: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Affect. Disord. 2020, 277, 1022–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, W.; Zhao, A.; Lan, H.; Ren, Z.; Mao, S.; Zhang, J.; Li, P.; Szeto, I.M.-Y.; Wang, P.; Zhang, Y. Sleep Quality, Antepartum Depression and Self-Harm Thoughts in Pregnant Chinese Women. J. Affect. Disord. 2023, 327, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Liu, B.; Cui, H.; Liu, Y.; Wan, N.; Li, L.; Zheng, L.; Wang, X.; Yang, Z.; Ma, Y.; et al. Dose-Response Associations of Maternal Prenatal Noise Exposure Duration with Antepartum Depression Status. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2024, 24, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; He, X.; Gu, X.; Yang, X. Risk Factors of Positive Depression Screening during the Third Trimester of Pregnancy in a Chinese Tertiary Hospital: A Cross-Sectional Study. BMC Psychiatry 2023, 23, 824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindqvist, D.; Janelidze, S.; Hagell, P.; Erhardt, S.; Samuelsson, M.; Minthon, L.; Hansson, O.; Björkqvist, M.; Träskman-Bendz, L.; Brundin, L. Interleukin-6 Is Elevated in the Cerebrospinal Fluid of Suicide Attempters and Related to Symptom Severity. Biol. Psychiatry 2009, 66, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindqvist, D.; Dhabhar, F.S.; James, S.J.; Hough, C.M.; Jain, F.A.; Bersani, F.S.; Reus, V.I.; Verhoeven, J.E.; Epel, E.S.; Mahan, L.; et al. Oxidative Stress, Inflammation and Treatment Response in Major Depression. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2017, 76, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Villegas, A.; Galbete, C.; Martinez-González, M.A.; Martinez, J.A.; Razquin, C.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; Estruch, R.; Buil-Cosiales, P.; Martí, A. The Effect of the Mediterranean Diet on Plasma Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) Levels: The PREDIMED-NAVARRA Randomized Trial. Nutr. Neurosci. 2011, 14, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrick, R.P.; Ames, B.N. Vitamin D and the Omega-3 Fatty Acids Control Serotonin Synthesis and Action, Part 2: Relevance for ADHD, Bipolar Disorder, Schizophrenia, and Impulsive Behavior. FASEB J. 2015, 29, 2207–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polokowski, A.R.; Shakil, H.; Carmichael, C.L.; Reigada, L.C. Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Anxiety: A Systematic Review of the Possible Mechanisms at Play. Nutr. Neurosci. 2020, 23, 494–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kase, B.E.; Liu, J.; Wirth, M.D.; Shivappa, N.; Hebert, J.R. Associations between Dietary Inflammatory Index and Sleep Problems among Adults in the United States, NHANES 2005-2016. Sleep Health 2021, 7, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melaku, Y.A.; Reynolds, A.C.; Appleton, S.; Sweetman, A.; Shi, Z.; Vakulin, A.; Catcheside, P.; Eckert, D.J.; Adams, R. High-Quality and Anti-Inflammatory Diets and a Healthy Lifestyle Are Associated with Lower Sleep Apnea Risk. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2022, 18, 1667–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Bao, J.; Tang, L.; Chen, C.; Guo, W.; Li, K.; Zhang, R.; Wu, J. Association between Weekend Catch-up Sleep and Depression of the United States Population from 2017 to 2018: A Cross-Sectional Study. Sleep Med. 2024, 119, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalmbach, D.A.; Cheng, P.; Arnedt, J.T.; Anderson, J.R.; Roth, T.; Fellman-Couture, C.; Williams, R.A.; Drake, C.L. Treating Insomnia Improves Depression, Maladaptive Thinking, and Hyperarousal in Postmenopausal Women: Comparing Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy for Insomnia (CBTI), Sleep Restriction Therapy, and Sleep Hygiene Education. Sleep Med. 2019, 55, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalmbach, D.A.; Cheng, P.; Ong, J.C.; Ciesla, J.A.; Kingsberg, S.A.; Sangha, R.; Swanson, L.M.; O’Brien, L.; Roth, T.; Drake, C.L. Depression and Suicidal Ideation in Pregnancy: Exploring Relationships with Insomnia, Short Sleep, and Nocturnal Rumination. Sleep Med. 2020, 65, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Wu, B.; Chen, B.; Lai, G.; Huang, S.; Li, S.; Liu, K.; Zhong, C.; Huang, W.; Yuan, S.; et al. Sleep Conditions Associate with Anxiety and Depression Symptoms among Pregnant Women during the Epidemic of COVID-19 in Shenzhen. J. Affect Disord. 2021, 281, 567–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irwin, M.R.; Olmstead, R.; Carroll, J.E. Sleep Disturbance, Sleep Duration, and Inflammation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Cohort Studies and Experimental Sleep Deprivation. Biol. Psychiatry 2016, 80, 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psaltopoulou, T.; Sergentanis, T.N.; Panagiotakos, D.B.; Sergentanis, I.N.; Kosti, R.; Scarmeas, N. Mediterranean Diet, Stroke, Cognitive Impairment, and Depression: A Meta-Analysis. Ann. Neurol. 2013, 74, 580–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, J.S.; Hiles, S.; Bisquera, A.; Hure, A.J.; McEvoy, M.; Attia, J. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Dietary Patterns and Depression in Community-Dwelling Adults. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 99, 181–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khaled, K.; Tsofliou, F.; Hundley, V.; Helmreich, R.; Almilaji, O. Perceived Stress and Diet Quality in Women of Reproductive Age: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutr. J. 2020, 19, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ljungberg, T.; Bondza, E.; Lethin, C. Evidence of the Importance of Dietary Habits Regarding Depressive Symptoms and Depression. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yelverton, C.A.; Rafferty, A.A.; Moore, R.L.; Byrne, D.F.; Mehegan, J.; Cotter, P.D.; Van Sinderen, D.; Murphy, E.F.; Killeen, S.L.; McAuliffe, F.M. Diet and Mental Health in Pregnancy: Nutrients of Importance Based on Large Observational Cohort Data. Nutrition 2022, 96, 111582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Characteristics | Population | EPDS Score < 10 | EPDS Score ≥ 10 | p Value 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | ||
| N | 749 (100) | 443 (59.15) | 306 (40.85) | |
| Age, years | 0.002 ** | |||
| ≤24 | 46 (6.14) | 15 (32.61) | 31 (67.39) | |
| 25~29 | 263 (35.11) | 163 (61.98) | 100 (38.02) | |
| 30~34 | 329 (43.93) | 201 (61.09) | 128 (38.91) | |
| ≥35 | 111 (14.82) | 64 (57.66) | 47 (42.34) | |
| Pregnancy stage | 0.978 | |||
| Middle Pregnancy | 423 (56.48) | 250 (59.10) | 173 (40.90) | |
| Late Pregnancy | 326 (43.52) | 193 (59.20) | 133 (40.80) | |
| Pre-pregnancy BMI, kg/m2 | 0.214 | |||
| <18.5 | 110 (14.69) | 71 (64.55) | 39 (35.45) | |
| 18.5~23.9 | 497 (66.36) | 298 (59.96) | 199 (40.04) | |
| 24.0~27.9 | 109 (14.55) | 56 (51.38) | 53 (48.62) | |
| ≥28 | 33 (4.41) | 18 (54.55) | 15 (45.45) | |
| Education level | <0.001 ** | |||
| Below bachelor’s degree | 370 (49.40) | 192 (51.89) | 178 (48.11) | |
| Bachelor’s degree | 304 (40.59) | 197 (64.80) | 107 (35.20) | |
| Postgraduate and above | 75 (10.01) | 54 (72.00) | 21 (28.00) | |
| Family income per capita, CNY/ month | <0.001 ** | |||
| <5000 | 201 (26.84) | 90 (44.78) | 111 (55.22) | |
| 5000~9999 | 284 (37.92) | 173 (60.92) | 111 (39.08) | |
| ≥10,000 | 264 (35.25) | 180 (68.18) | 84 (31.82) | |
| Mode of conception | 0.485 | |||
| Natural conception | 671 (89.59) | 394 (58.72) | 277 (41.28) | |
| Assisted reproduction | 78 (10.41) | 49 (62.82) | 29 (37.18) | |
| Number of fetuses | 0.634 | |||
| 1 | 719 (96.00) | 424 (58.97) | 295 (41.03) | |
| 2 | 30 (4.01) | 19 (63.33) | 11 (36.67) | |
| Gravidity | 0.273 | |||
| 1 | 336 (44.86) | 203 (60.42) | 133 (39.58) | |
| 2 | 211 (28.17) | 130 (61.61) | 81 (38.39) | |
| ≥3 | 202 (26.97) | 110 (54.46) | 92 (45.54) | |
| Parity | 0.082 | |||
| 0 | 446 (59.55) | 278 (62.33) | 168 (37.67) | |
| 1 | 264 (35.25) | 142 (53.79) | 122 (46.21) | |
| 2 | 39 (5.21) | 23 (58.97) | 16 (41.03) | |
| Passive smoking | 0.281 | |||
| Yes | 138 (18.42) | 76 (55.07) | 62 (44.93) | |
| No | 611 (81.58) | 367 (60.07) | 244 (39.93) | |
| Exercise habits | 0.161 | |||
| Yes | 378 (50.47) | 233 (61.64) | 145 (38.36) | |
| No | 371 (49.53) | 210 (56.60) | 161 (43.40) | |
| Employment status | <0.001 ** | |||
| Employed | 536 (71.56) | 338 (63.06) | 198 (36.94) | |
| Unemployed | 213 (28.44) | 105 (49.30) | 108 (50.70) | |
| Sleep quality | <0.001 ** | |||
| Good sleep quality | 299 (39.92) | 230 (76.92) | 69 (23.08) | |
| Poor sleep quality | 450 (60.08) | 213 (47.33) | 237 (52.67) | |
| E-DII | <0.001 ** | |||
| Q1 | 250 (33.38) | 177 (70.80) | 73 (29.20) | |
| Q2 | 250 (33.38) | 151 (60.40) | 99 (39.60) | |
| Q3 | 249 (33.24) | 115 (46.18) | 134 (53.82) |
| Outcome Variable | Model 1: Prenatal Depression | Model 1: Prenatal Depression | Model 3: Sleep Quality |
|---|---|---|---|
| OR, 95%CI | OR, 95%CI | OR, 95%CI | |
| E-DII (reference: Q1) | |||
| Q2 | 1.607 (1.087, 2.375) * | 1.454 (0.968, 2.185) | 0.701 (0.484, 1.017) |
| Q3 | 2.640 (1.789, 3.897) ** | 1.988 (1.323, 2.986) ** | 0.314 (0.211, 0.467) ** |
| Sleep quality (reference : poor) | |||
| Good | _ | 0.266 (0.186, 0.382) ** | _ |
| Age (reference: ≤24) | |||
| 25~29 | 0.392 (0.192, 0.799) * | 0.342 (0.161, 0.728) ** | 0.862 (0.431, 1.725) |
| 30~34 | 0.396 (0.193, 0.813) * | 0.313 (0.146, 0.672) ** | 0.616 (0.304, 1.245) |
| ≥35 | 0.474 (0.209, 1.077) | 0.411 (0.173, 0.976) * | 0.767 (0.342, 1.723) |
| Pre-pregnancy BMI (reference:<18.5) kg/m2 | |||
| 18.5~23.9 | 1.443 (0.908, 2.291) | 1.110 (0.680, 1.811) | 0.406 (0.259, 0.636) ** |
| 24.0~27.9 | 1.843 (1.034, 3.286) * | 1.562 (0.852, 2.866) | 0.532 (0.302, 0.937) * |
| ≥28 | 1.597 (0.695, 3.669) | 1.306 (0.560, 3.044) | 0.468 (0.205, 1.071) |
| Pregnancy stage (reference: middle Pregnancy) | |||
| Late Pregnancy | 1.104 (0.805, 1.515) | 1.007 (0.724, 1.401) | 0.731 (0.532, 1.005) |
| Education level (reference: Below bachelor’s degree) | |||
| Bachelor’s degree | 0.798 (0.548, 1.163) | 0.717 (0.483, 1.064) | 0.760 (0.520, 1.110) |
| Postgraduate and above | 0.691 (0.375, 1.276) | 0.565 (0.299, 1.066) | 0.560 (0.308, 1.017) |
| Family income per capita, CNY/ month (reference: <5000) | |||
| 5000~9999 | 0.651 (0.436, 0.970) * | 0.612 (0.402, 0.932) * | 0.912 (0.602, 1.382) |
| ≥10,000 | 0.554 (0.356, 0.862) ** | 0.564 (0.355, 0.896) * | 1.243 (0.790, 1.955) |
| Mode of conception (reference: Natural conception) Assisted reproduction | |||
| 0.972 (0.543, 1.740) | 1.122 (0.608, 2.071) | 1.608 (0.896, 2.885) | |
| Number of fetuses (reference: 1) | |||
| 2 | 0.839 (0.355, 1.982) | 0.757 (0.306, 1.870) | 0.805 (0.340, 1.904) |
| Gravidity (reference: 1) | |||
| 2 | 0.671 (0.416, 1.081) | 0.671 (0.408, 1.102) | 1.100 (0.691, 1.753) |
| ≥3 | 0.845 (0.488, 1.464) | 0.834 (0.469, 1.484) | 1.066 (0.615, 1.848) |
| Parity (reference: 0) | |||
| 1 | 1.416 (0.876, 2.289) | 1.510 (0.914, 2.495) | 1.078 (0.667, 1.744) |
| 2 | 0.893 ()0.382, 2.089 | 0.882 (0.366, 2.123) | 0.850 (0.353, 2.045) |
| Passive smoking (reference: No) | |||
| Yes | 1.071 (0.717, 1.600) | 1.029 (0.678, 1.562) | 0.850 (0.563, 1.283) |
| Exercise habits (reference: No) | |||
| Yes | 0.958 (0.698, 1.313) | 1.010 (0.727, 1.402) | 1.243 (0.905, 1.708) |
| Employment status (reference: Unemployed) | |||
| Employed | 0.811 (0.559, 1.177) | 0.909 (0.615, 1.343) | 1.523 (1.037, 2.253) * |
| Mediator Variable | β | p Value | 95% CI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PSQI | ACME | 0.111 | <0.001 ** | 0.088–0.137 |
| ADE | 0.214 | <0.001 ** | 0.163–0.266 | |
| Total Effect | 0.325 | <0.001 ** | 0.273–0.376 | |
| Prop. Mediated | 0.343 | |||
| Subjective Sleep Quality | ACME | 0.051 | <0.001 ** | 0.035–0.073 |
| ADE | 0.274 | <0.001 ** | 0.218–0.328 | |
| Total Effect | 0.325 | <0.001 ** | 0.273–0.376 | |
| Prop. Mediated | 0.158 | |||
| Sleep Latency | ACME | 0.036 | <0.001 ** | 0.022–0.053 |
| ADE | 0.290 | <0.001 ** | 0.238–0.338 | |
| Total Effect | 0.325 | <0.001 ** | 0.273–0.376 | |
| Prop. Mediated | 0.109 | |||
| Sleep Duration | ACME | 0.025 | 0.002 ** | 0.013–0.041 |
| ADE | 0.300 | <0.001 ** | 0.246–0.353 | |
| Total Effect | 0.325 | <0.001 ** | 0.273–0.376 | |
| Prop. Mediated | 0.078 | |||
| Sleep efficiency | ACME | 0.020 | 0.007 ** | 0.009–0.033 |
| ADE | 0.306 | <0.001 ** | 0.255–0.357 | |
| Total Effect | 0.325 | <0.001 ** | 0.273–0.376 | |
| Prop. Mediated | 0.060 | |||
| Sleep Disturbance | ACME | 0.063 | <0.001 ** | 0.044–0.088 |
| ADE | 0.262 | <0.001 ** | 0.209–0.317 | |
| Total Effect | 0.325 | <0.001 ** | 0.273–0.376 | |
| Prop. Mediated | 0.194 | |||
| Used Sleep Medication | ACME | 0.002 | 0.492 | −0.001–0.012 |
| ADE | 0.323 | <0.001 ** | 0.271–0.373 | |
| Total Effect | 0.325 | <0.001 ** | 0.273–0.376 | |
| Prop. Mediated | 0.007 | |||
| Daytime Dysfunction | ACME | 0.059 | <0.001 ** | 0.041–0.081 |
| ADE | 0.266 | <0.001 ** | 0.214–0.317 | |
| Total Effect | 0.325 | <0.001 ** | 0.273–0.376 | |
| Prop. Mediated | 0.181 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yuan, Y.; Xu, J.; Lin, Q.; Deng, J.; Pan, Y.; Chen, J. Effects of the Energy-Adjusted Dietary Inflammation Index During Pregnancy on Prenatal Depression: The Mediating Effect of Sleep Quality. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1197. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17071197
Yuan Y, Xu J, Lin Q, Deng J, Pan Y, Chen J. Effects of the Energy-Adjusted Dietary Inflammation Index During Pregnancy on Prenatal Depression: The Mediating Effect of Sleep Quality. Nutrients. 2025; 17(7):1197. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17071197
Chicago/Turabian StyleYuan, Yuehan, Jingjing Xu, Qian Lin, Jing Deng, Yunfeng Pan, and Jihua Chen. 2025. "Effects of the Energy-Adjusted Dietary Inflammation Index During Pregnancy on Prenatal Depression: The Mediating Effect of Sleep Quality" Nutrients 17, no. 7: 1197. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17071197
APA StyleYuan, Y., Xu, J., Lin, Q., Deng, J., Pan, Y., & Chen, J. (2025). Effects of the Energy-Adjusted Dietary Inflammation Index During Pregnancy on Prenatal Depression: The Mediating Effect of Sleep Quality. Nutrients, 17(7), 1197. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17071197







