Reasoning-Driven Food Energy Estimation via Multimodal Large Language Models †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- We introduce an approach that leverages fine-tuning and volume injection to enhance the reasoning and recognition capabilities of MLLMs for image-based food energy estimation.
- We propose a fine-grained estimation prompting method to address the challenges of food volume recognition in MLLMs.
- We evaluated the proposed approach on the Nutrition5k dataset, showing significant improvements over baseline methods and discussing its strengths and limitations.
2. Related Work
2.1. Image-Based Food Energy Estimation
2.2. Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs)
3. Methods
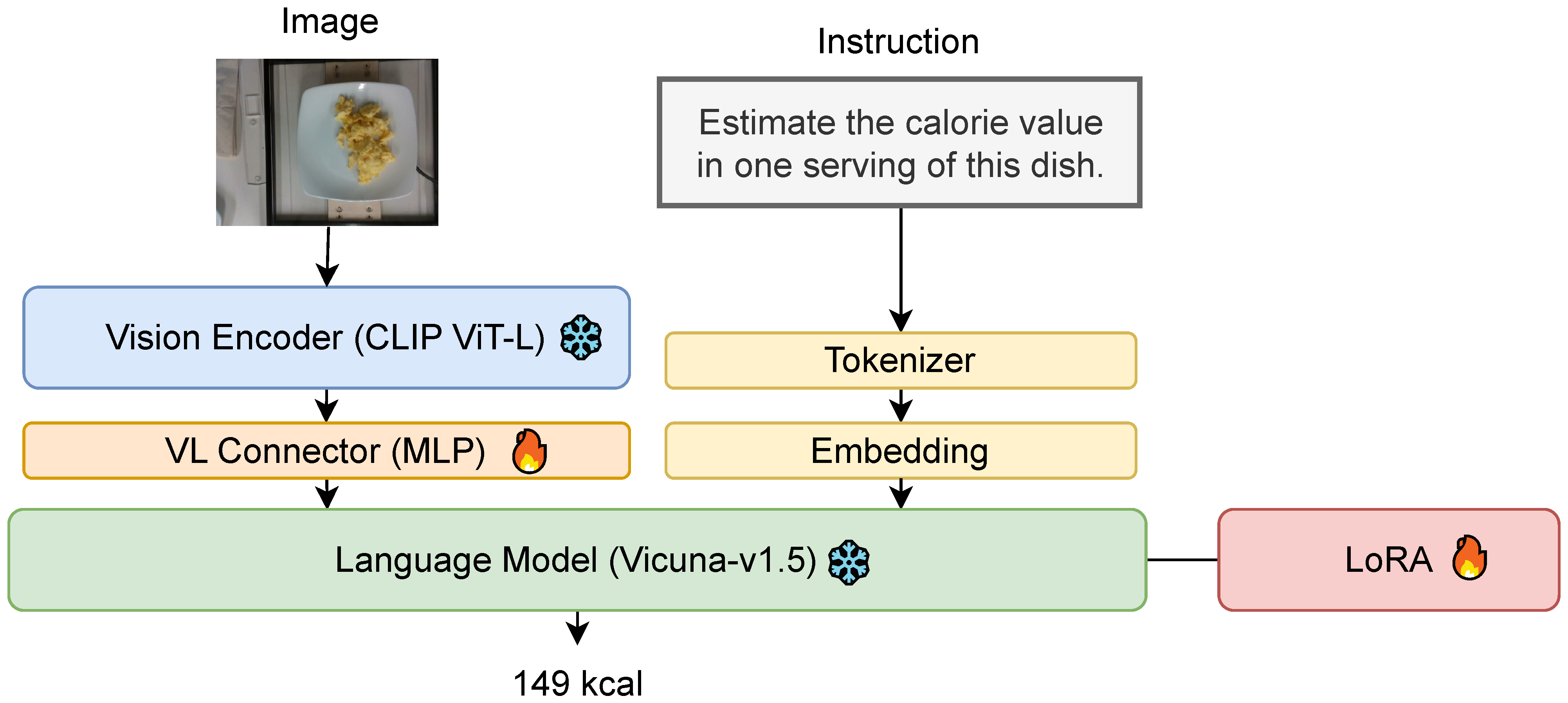
3.1. Fine-Tuning MLLMs
3.2. Volume Injection
3.2.1. Overall Architecture
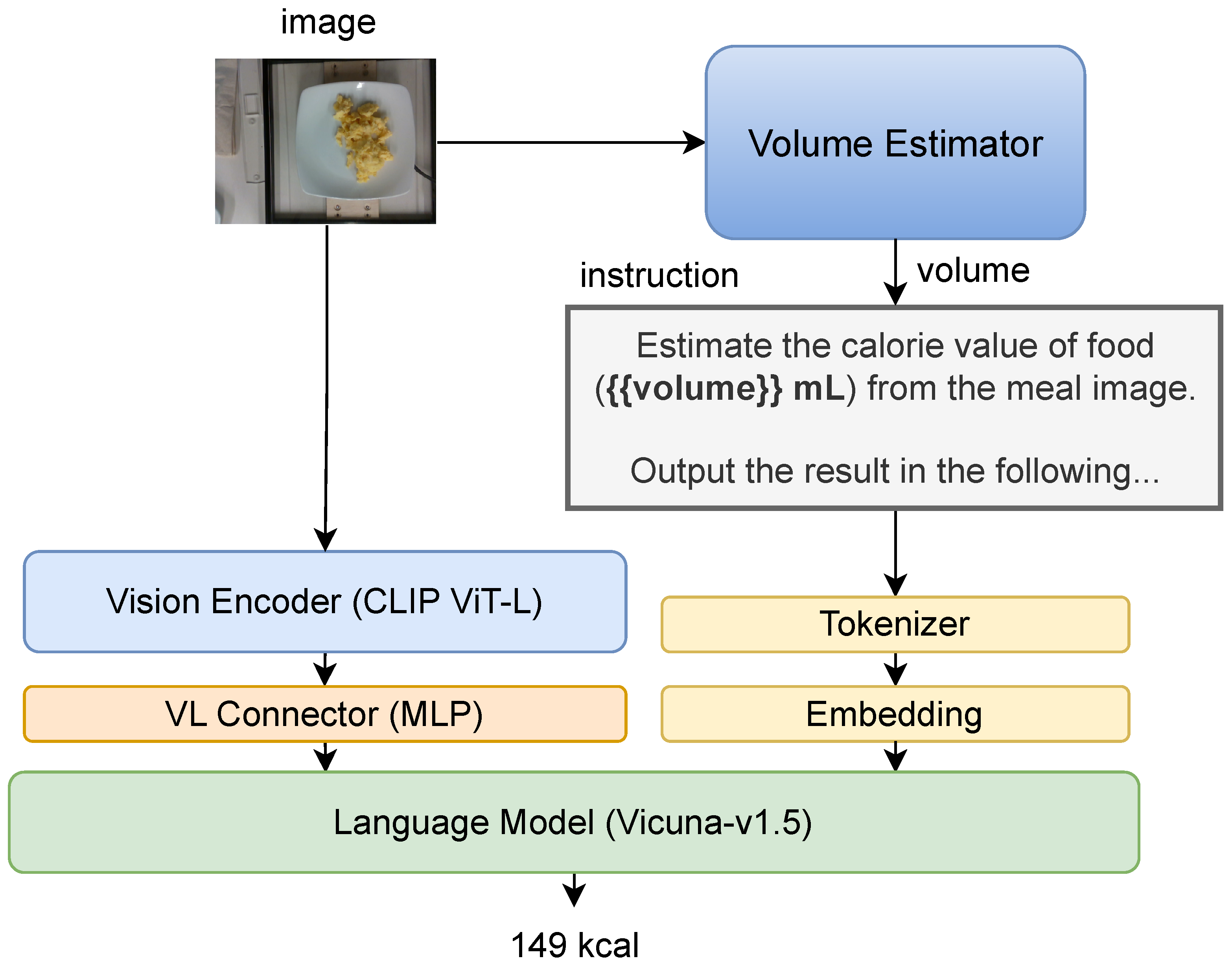

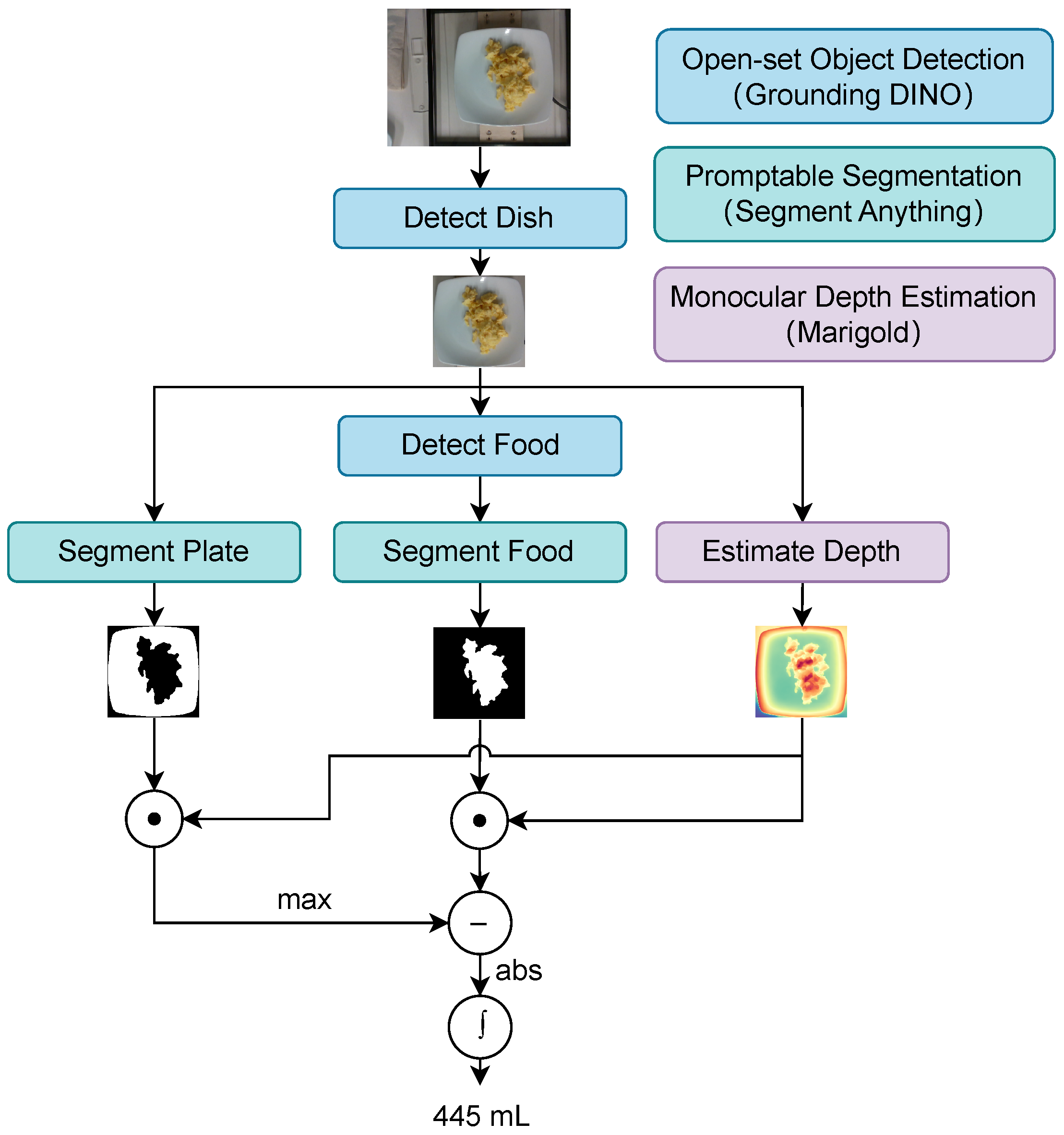
3.2.2. Volume Estimation Module
4. Experimental Results
4.1. Experiment Settings
4.2. Fine-Tuning Results
4.3. Zero-Shot Results with Volume Injection
5. Discussion
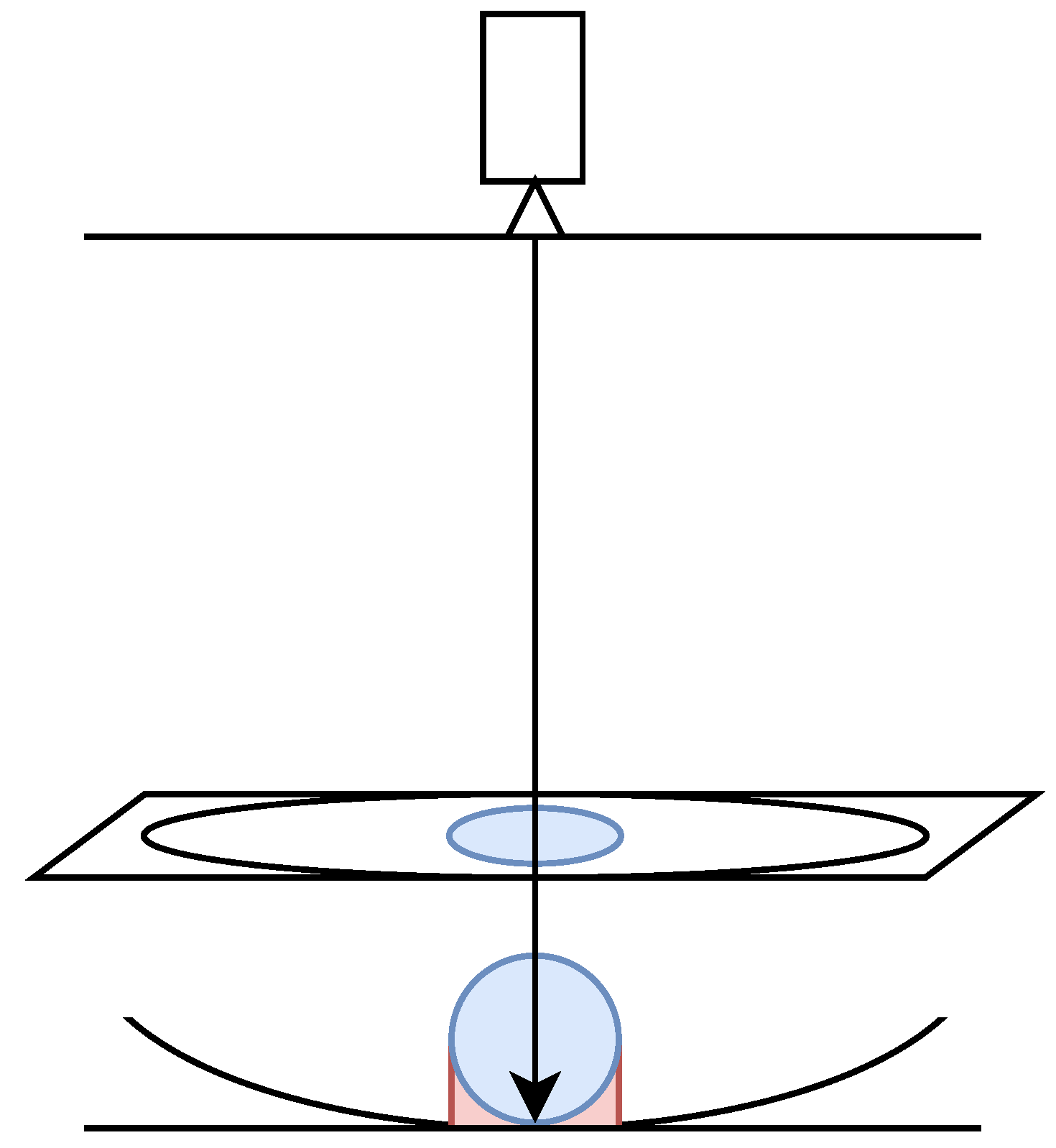
5.1. Challenges in Volume Estimation
- The estimated volume between the bottom of the food and the reference plane of the dish could be over-calculated.
- If the lowest part of the dish is obscured by food, an incorrect reference plane for the dish may be selected.
5.2. Improving Commonsense Reasoning in MLLMs
5.3. Future Directions
5.4. Discussion Summary
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Naska, A.; Lagiou, A.; Lagiou, P. Dietary assessment methods in epidemiological research: Current state of the art and future prospects. F1000Research 2017, 6, 926. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bailey, R.L. Overview of dietary assessment methods for measuring intakes of foods, beverages, and dietary supplements in research studies. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2021, 70, 91–96. [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto, K.; Yanai, K. An automatic calorie estimation system of food images on a smartphone. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Workshop on Multimedia Assisted Dietary Management, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 16 October 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Tanno, R.; Ege, T.; Yanai, K. AR DeepCalorieCam V2: Food Calorie Estimation with CNN and AR-Based Actual Size Estimation. In Proceedings of the 24th ACM Symposium on Virtual Reality Software and Technology, Tokyo, Japan, 28 November–1 December 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ando, Y.; Ege, T.; Cho, J.; Yanai, K. DepthCalorieCam: A Mobile Application for Volume-Based FoodCalorie Estimation Using Depth Cameras. In Proceedings of the 5th International Workshop on Multimedia Assisted Dietary Management, Nice, France, 21 October 2019; pp. 76–81. [Google Scholar]
- Thames, Q.; Karpur, A.; Norris, W.; Xia, F.; Panait, L.; Weyand, T.; Sim, J. Nutrition5k: Towards Automatic Nutritional Understanding of Generic Food. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 8903–8911. [Google Scholar]
- Sultana, J.; Ahmed, B.M.; Masud, M.M.; Huq, A.K.O.; Ali, M.E.; Naznin, M. A Study on Food Value Estimation From Images: Taxonomies, Datasets, and Techniques. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 45910–45935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Li, C.; Wu, Q.; Lee, Y.J. Visual Instruction Tuning. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, San Diego, CA, USA, 2–7 December 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, Y.; Qi, H.; Zhu, B.; Chen, J.; Jiang, Y.G.; Ngo, C.W. FoodLMM: A Versatile Food Assistant using Large Multi-modal Model. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2312.14991. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Li, L.; Lin, K.; Wang, J.; Lin, C.C.; Liu, Z.; Wang, L. The Dawn of LMMs: Preliminary Explorations with GPT-4V (ision). arXiv 2023, arXiv:2309.17421. [Google Scholar]
- Tanabe, H.; Yanai, K. CalorieLLaVA: Image-based Calorie Estimation with Multimodal Large Language Models. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of ICPR Workshop on Multimedia Assisted Dietary Management, Kolkata, India, 1 December 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Tanabe, H.; Yanai, K. CalorieVoL: Integrating Volumetric Context Into Multimodal Large Language Models for Image-Based Calorie Estimation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on MultiMedia Modeling, Nara, Japan, 8–10 January 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Akpa, E.A.H.; Suwa, H.; Arakawa, Y.; Yasumoto, K. Smartphone-Based Food Weight and Calorie Estimation Method for Effective Food Journaling. SICE J. Control. Meas. Syst. Integr. 2017, 10, 360–369. [Google Scholar]
- Ege, T.; Shimoda, W.; Yanai, K. A New Large-scale Food Image Segmentation Dataset and Its Application to Food Calorie Estimation Based on Grains of Rice. In Proceedings of the ICPR Workshop on Multimedia Assisted Dietary Management, Nice, France, 21–25 October 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Naritomi, S.; Yanai, K. Hungry Networks: 3D mesh reconstruction of a dish and a plate from a single dish image for estimating food volume. In Proceedings of the 2nd ACM International Conference on Multimedia in Asia, Singapore, 7 March 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Ege, T.; Yanai, K. Image-based food calorie estimation using knowledge on food categories, ingredients and cooking directions. In Proceedings of the on Thematic Workshops of ACM Multimedia 2017, Mountain View, CA, USA, 23–27 October 2017; pp. 367–375. [Google Scholar]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan, J.; McCandlish, S.; Henighan, T.; Brown, T.B.; Chess, B.; Child, R.; Gray, S.; Radford, A.; Wu, J.; Amodei, D. Scaling laws for neural language models. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2001.08361. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, J.; Tay, Y.; Bommasani, R.; Raffel, C.; Zoph, B.; Borgeaud, S.; Yogatama, D.; Bosma, M.; Zhou, D.; Metzler, D.; et al. Emergent abilities of large language models. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2206.07682. [Google Scholar]
- Alayrac, J.B.; Donahue, J.; Luc, P.; Miech, A.; Barr, I.; Hasson, Y.; Lenc, K.; Mensch, A.; Millican, K.; Reynolds, M.; et al. Flamingo: A visual language model for few-shot learning. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, New Orleans, LA, USA, 28 November–9 December 2022; Volume 35, pp. 23716–23736. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Li, D.; Savarese, S.; Hoi, S. BLIP-2: Bootstrapping Language-Image Pre-training with Frozen Image Encoders and Large Language Models. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Honolulu, HI, USA, 23–29 July 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, D.; Chen, J.; Shen, X.; Li, X.; Elhoseiny, M. MiniGPT-4: Enhancing vision-language understanding with advanced large language models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2304.10592. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, W.; Li, J.; Li, D.; Tiong, A.M.H.; Zhao, J.; Wang, W.; Li, B.; Fung, P.; Hoi, S. InstructBLIP: Towards General-purpose Vision-Language Models with Instruction Tuning. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2305.06500. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Li, C.; Li, Y.; Lee, Y.J. Improved baselines with visual instruction tuning. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2310.03744. [Google Scholar]
- Radford, A.; Kim, J.W.; Hallacy, C.; Ramesh, A.; Goh, G.; Agarwal, S.; Sastry, G.; Askell, A.; Mishkin, P.; Clark, J.; et al. Learning transferable visual models from natural language supervision. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Shenzhen, China, 26 February–1 March 2021; pp. 8748–8763. [Google Scholar]
- Chiang, W.L.; Li, Z.; Lin, Z.; Sheng, Y.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Zheng, L.; Zhuang, S.; Zhuang, Y.; Gonzalez, J.E.; et al. Vicuna: An Open-Source Chatbot Impressing GPT-4 with 90%* ChatGPT Quality. 2023. Available online: https://lmsys.org/blog/2023-03-30-vicuna/ (accessed on 17 March 2025).
- Hu, E.J.; Shen, Y.; Wallis, P.; Allen-Zhu, Z.; Li, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, L.; Chen, W. LoRA: Low-Rank Adaptation of Large Language Models. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations, Virtual, 25–29 April 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Zeng, Z.; Ren, T.; Li, F.; Zhang, H.; Yang, J.; Li, C.; Yang, J.; Su, H.; Zhu, J.; et al. Grounding DINO: Marrying dino with grounded pre-training for open-set object detection. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.05499. [Google Scholar]
- Kirillov, A.; Mintun, E.; Ravi, N.; Mao, H.; Rolland, C.; Gustafson, L.; Xiao, T.; Whitehead, S.; Berg, A.C.; Lo, W.Y.; et al. Segment anything. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2304.02643. [Google Scholar]
- Ke, B.; Obukhov, A.; Huang, S.; Metzger, N.; Daudt, R.C.; Schindler, K. Repurposing Diffusion-Based Image Generators for Monocular Depth Estimation. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2312.02145. [Google Scholar]
- Mildenhall, B.; Srinivasan, P.P.; Tancik, M.; Barron, J.T.; Ramamoorthi, R.; Ng, R. NeRF: Representing Scenes as Neural Radiance Fields for View Synthesis. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Kerbl, B.; Kopanas, G.; Leimkühler, T.; Drettakis, G. 3D Gaussian Splatting for Real-Time Radiance Field Rendering. ACM Trans. Graph. 2023, 42, 139:1–139:14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heighington-Wansbrough, A.J.; Gemming, L. Dietary intake in hospitals: A systematic literature review of the validity of the visual estimation method to assess food consumption and energy and protein intake. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2022, 52, 296–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, S.; Hopper, Z.; Chaboyer, W.; Gonzalez, R.; Banks, M.; Desbrow, B.; Marshall, A.P. Engaging hospitalised patients in their nutrition care using technology: Development of the NUTRI-TEC intervention. BMC Health Serv. Res. 2020, 20, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhry, B.M.; Siek, K.A.; Connelly, K. The Usability and Feasibility of a Dietary Intake Self-Monitoring Application in a Population with Varying Literacy Levels. J. Pers. Med. 2024, 14, 1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfisterer, K.J.; Boger, J.; Wong, A. Prototyping the automated food imaging and nutrient intake tracking system: Modified participatory iterative design sprint. JMIR Hum. Factors 2019, 6, e13017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yinusa, G.; Scammell, J.; Murphy, J.; Ford, G.; Baron, S. Multidisciplinary provision of food and nutritional care to hospitalized adult in-patients: A scoping review. J. Multidiscip. Healthc. 2021, 14, 459–491. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lo, F.P.W.; Qiu, J.; Jobarteh, M.L.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, S.; Baranowski, T.; Anderson, A.K.; McCrory, M.A.; Sazonov, E.; et al. AI-enabled wearable cameras for assisting dietary assessment in African populations. NPJ Digit. Med. 2024, 7, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phalle, A.; Gokhale, D. Navigating next-gen nutrition care using artificial intelligence-assisted dietary assessment tools—A scoping review of potential applications. Front. Nutr. 2025, 12, 1518466. [Google Scholar]
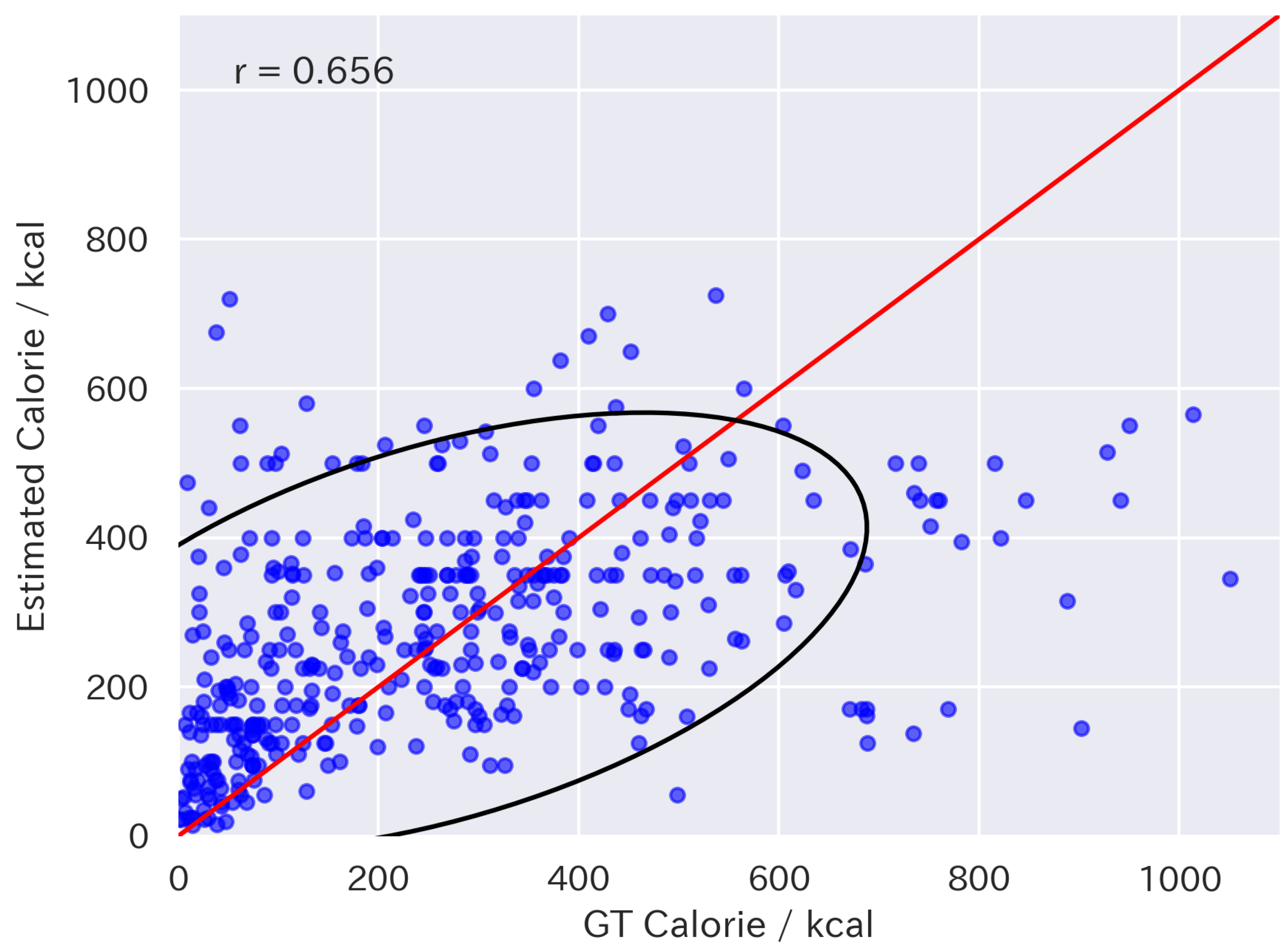

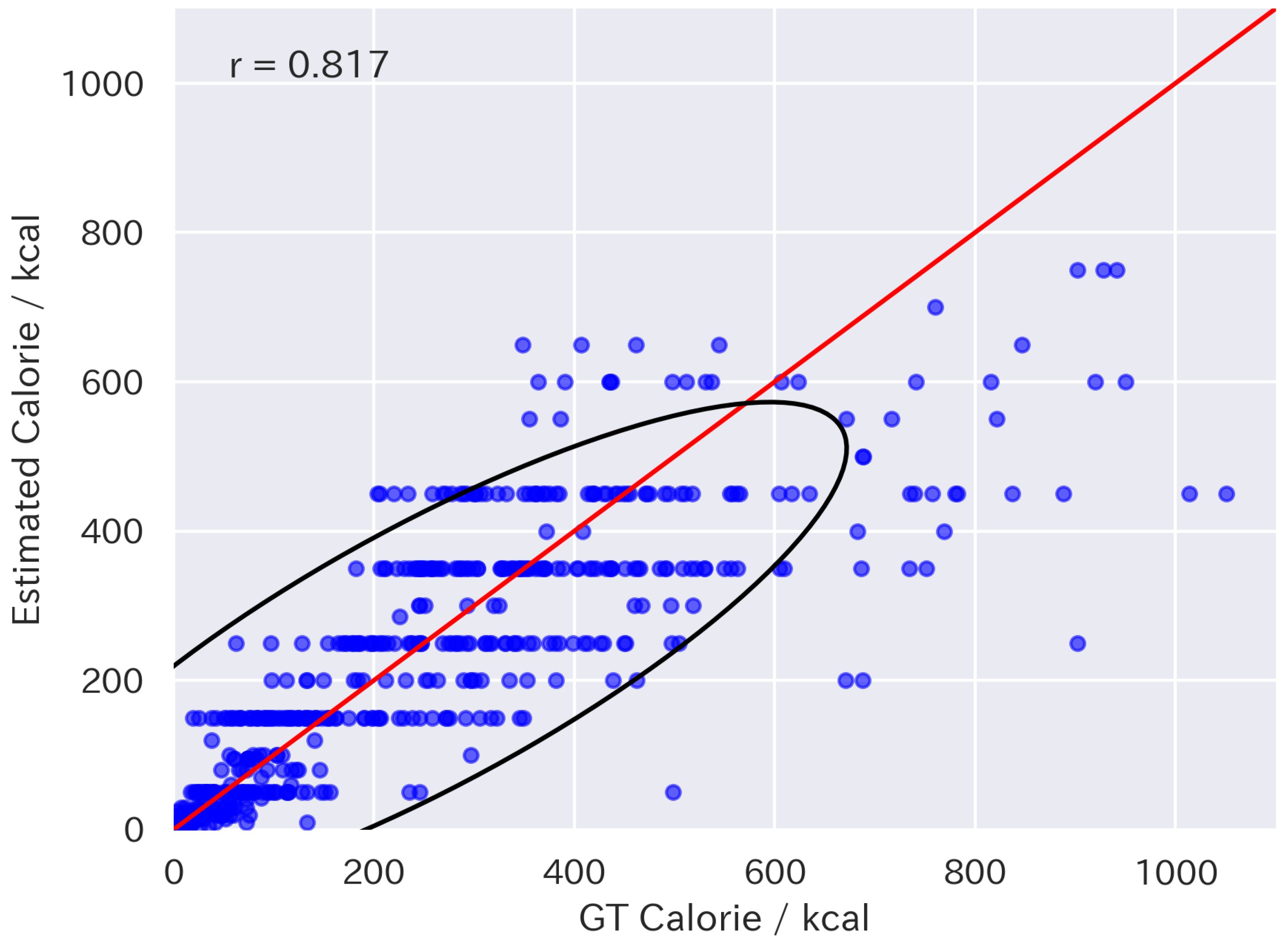
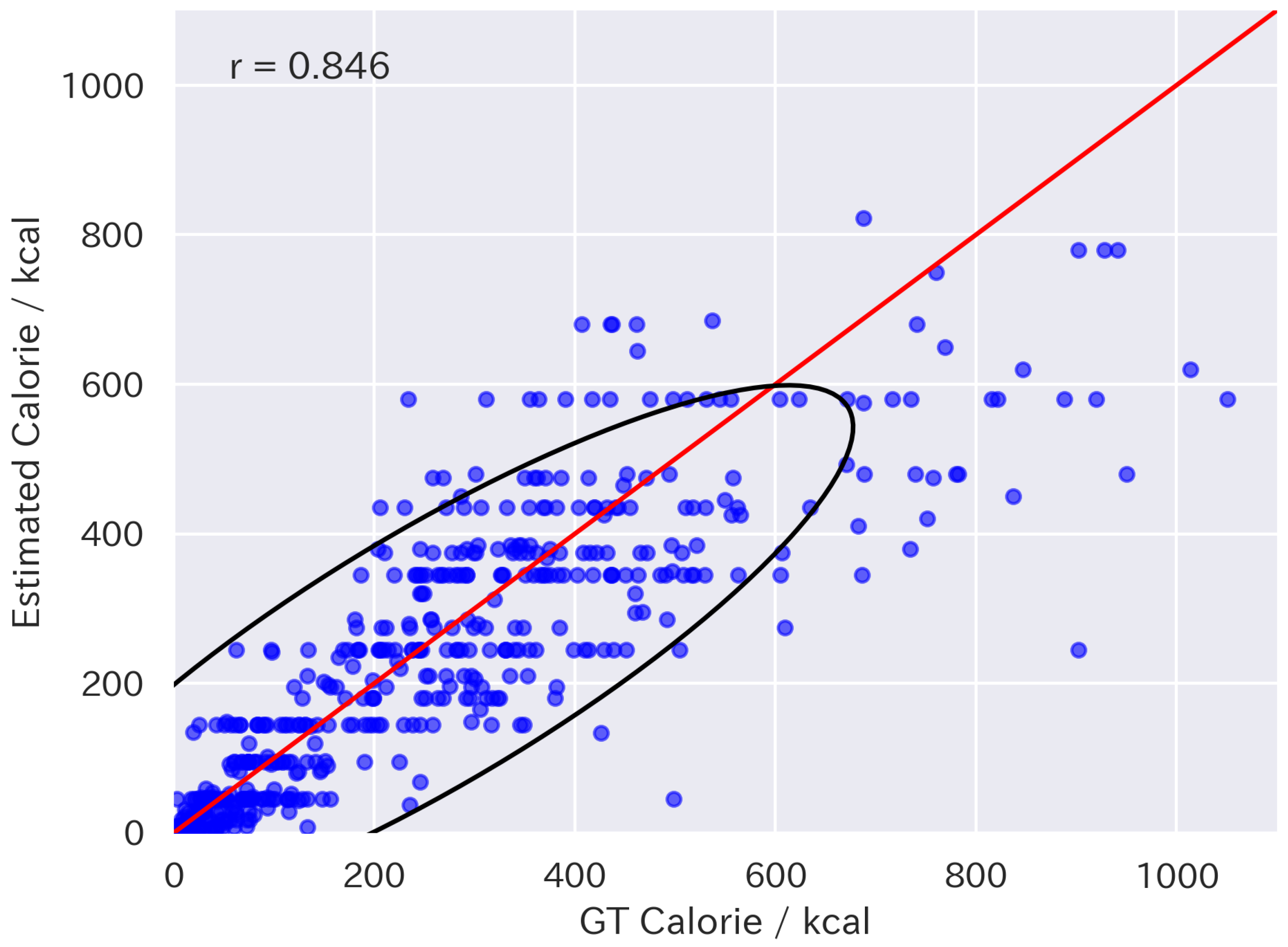

| Method | MAE ↓ | MAPE ↓ | r ↑ |
|---|---|---|---|
| Google-nutrition-monocular [6] | 70.6 | 26.1 | - |
| LLaVA-1.5-7B | 178.8 | 129.5 | 0.637 |
| LLaVA-1.5-13B | 177.1 | 92.8 | 0.656 |
| GPT-4V | 80.7 | 55.7 | 0.833 |
| GPT-4o | 82.7 | 46.7 | 0.817 |
| FoodLMM FT [9] | 67.3 | 26.6 | - |
| LLaVA-1.5-7B FT | 74.2 | 41.5 | 0.927 |
| LLaVA-1.5-13B FT | 64.3 | 39.8 | 0.934 |
| Method | MAE ↓ | MAPE ↓ | r ↑ |
|---|---|---|---|
| LLaVA-1.5-13B FT (Full) | 77.7 | 48.8 | 0.869 |
| LLaVA-1.5-13B FT (LoRA) | 64.3 | 39.8 | 0.934 |
| Model | MAE ↓ | MAPE ↓ | r ↑ |
|---|---|---|---|
| LLaVA-1.5-13B | 109.6 | 92.8 | 0.656 |
| GPT-4V | 80.7 | 55.7 | 0.833 |
| GPT-4o | 82.7 | 46.7 | 0.817 |
| LLaVA-1.5-13B w/vol | 6122.7 | 6591.4 | −0.041 |
| GPT-4V w/vol | 83.8 | 54.1 | 0.816 |
| GPT-4o w/vol | 78.8 | 43.4 | 0.846 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tanabe, H.; Yanai, K. Reasoning-Driven Food Energy Estimation via Multimodal Large Language Models. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1128. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17071128
Tanabe H, Yanai K. Reasoning-Driven Food Energy Estimation via Multimodal Large Language Models. Nutrients. 2025; 17(7):1128. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17071128
Chicago/Turabian StyleTanabe, Hikaru, and Keiji Yanai. 2025. "Reasoning-Driven Food Energy Estimation via Multimodal Large Language Models" Nutrients 17, no. 7: 1128. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17071128
APA StyleTanabe, H., & Yanai, K. (2025). Reasoning-Driven Food Energy Estimation via Multimodal Large Language Models. Nutrients, 17(7), 1128. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17071128






