The Positive Effect of Akkermansia muciniphila postbiotics on the Glycolipid Metabolism of Caenorhabditis elegans Induced by High-Glucose Diet
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Culture Conditions and Strains
2.2. Lifespan Assay
2.3. Healthy Lifespan: Body Bends/Movements on mNGM Plates
2.4. Biochemical Assay
2.5. Oil Red O (ORO) Staining of Adipose Tissue
2.6. Measurement of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS)
2.7. Antioxidant Enzyme Assay
2.8. Free Fatty Acid Composition Analysis
2.9. Transcriptome Sequencing
2.10. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
2.11. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Healthy Lifespan of Nematodes Affected by P-AKK Under High Glucose Conditions
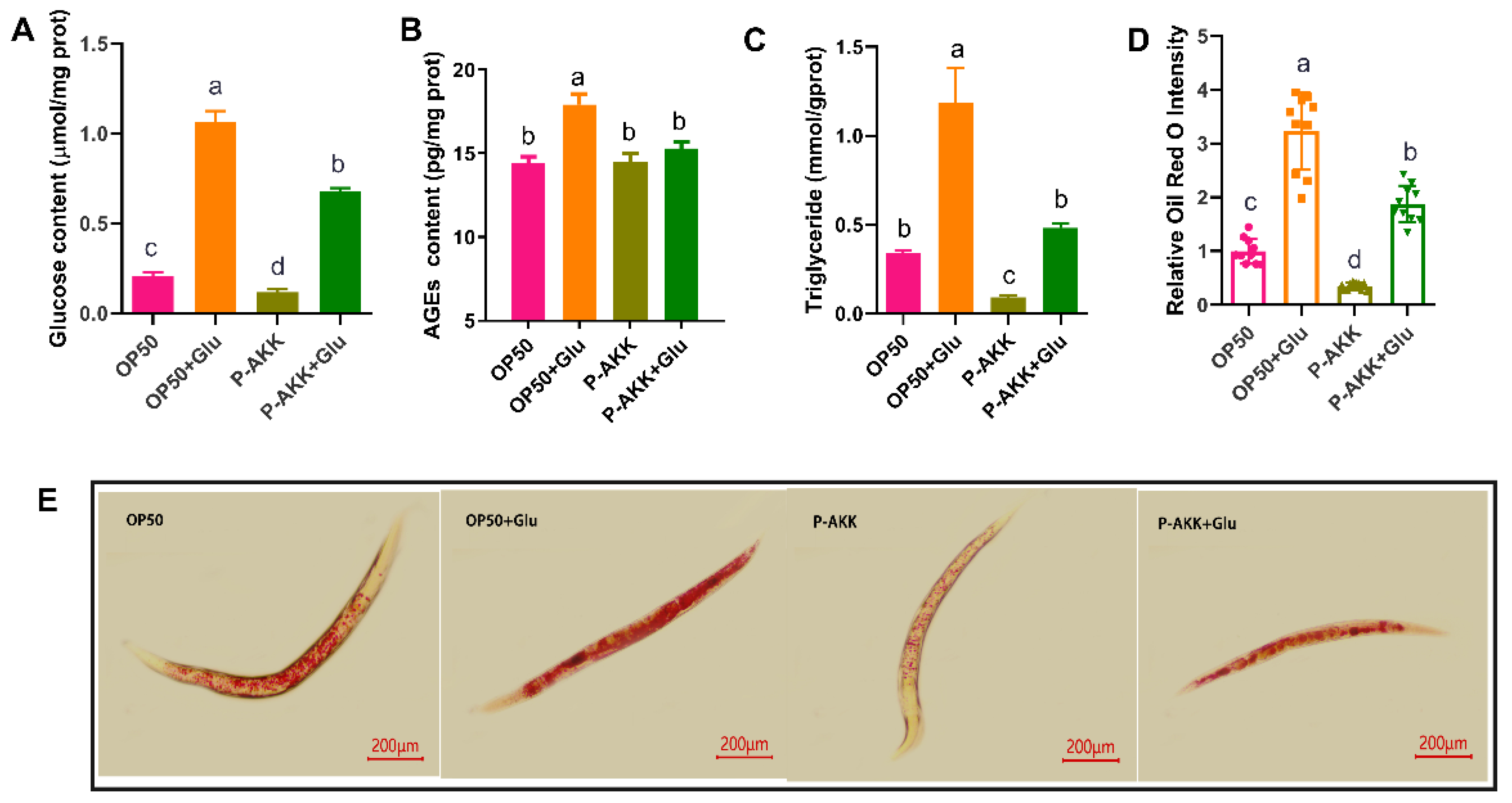
3.2. Effects of P-AKK on Biomarkers of Glucose and Lipid Metabolism in Nematodes Under High Glucose Conditions
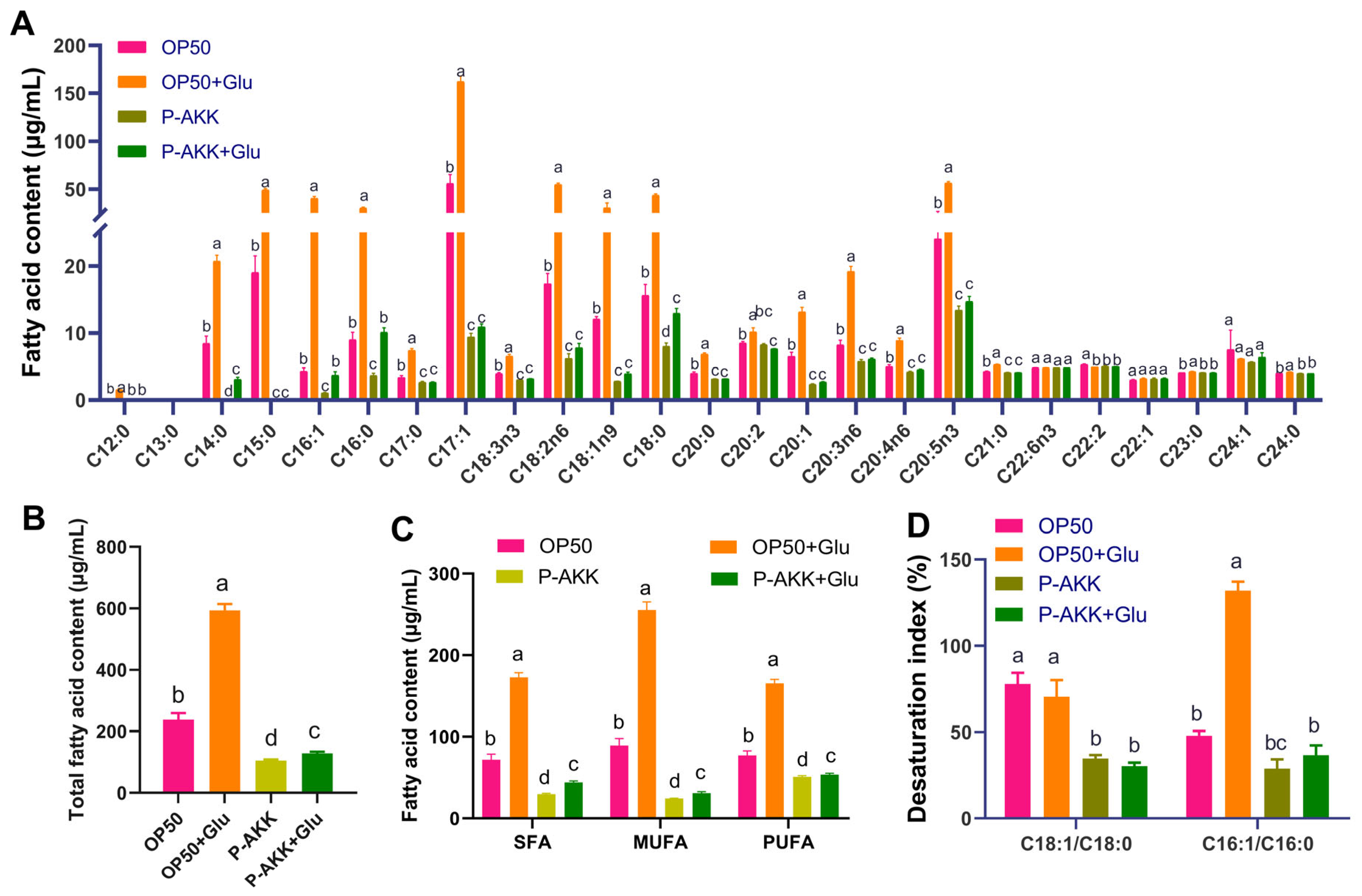
3.3. P-AKK Changed the Level of Free Fatty Acids in Nematodes
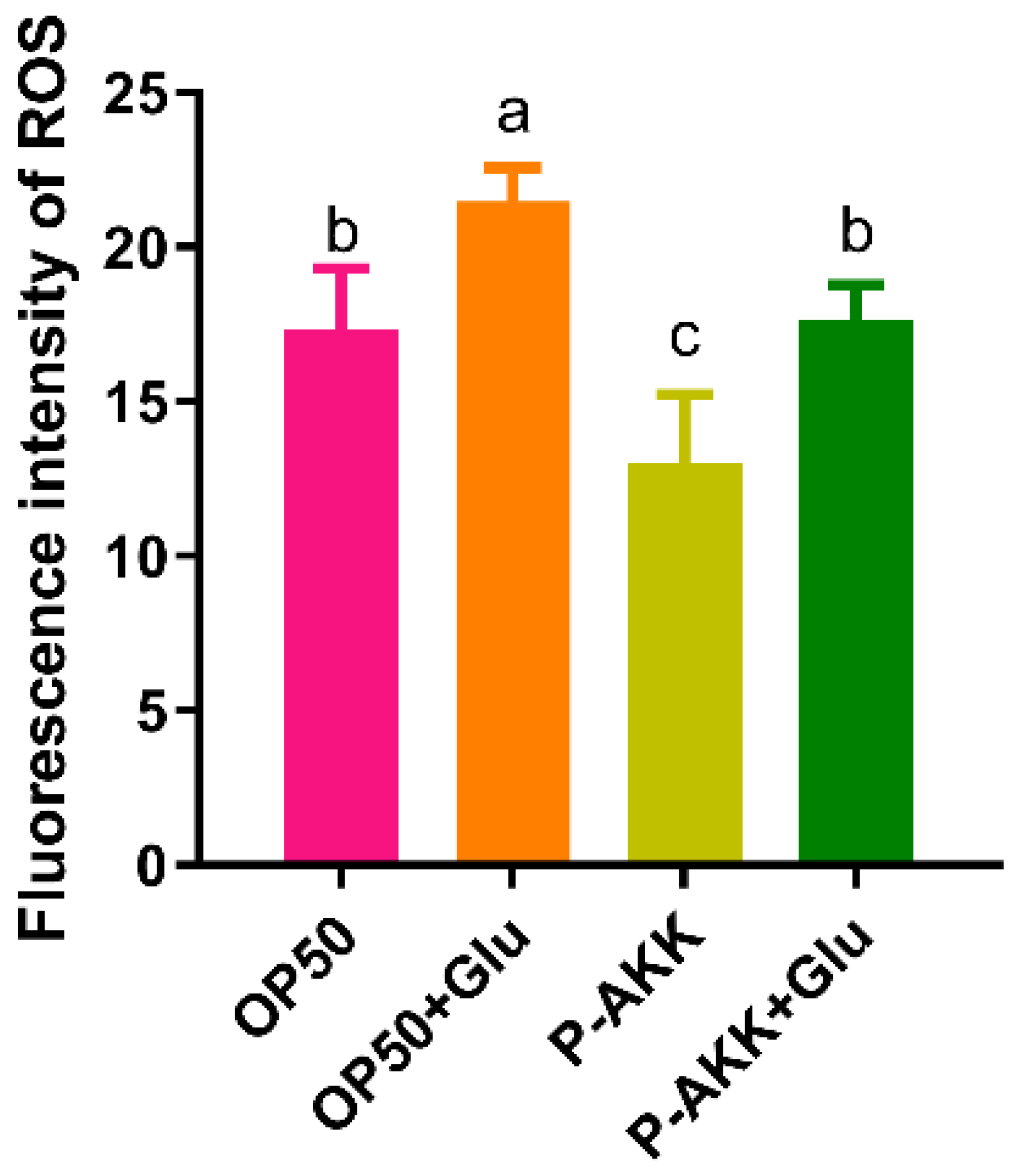
3.4. Effects of P-AKK on the Intracellular ROS Level of Nematodes Under High Glucose Conditions
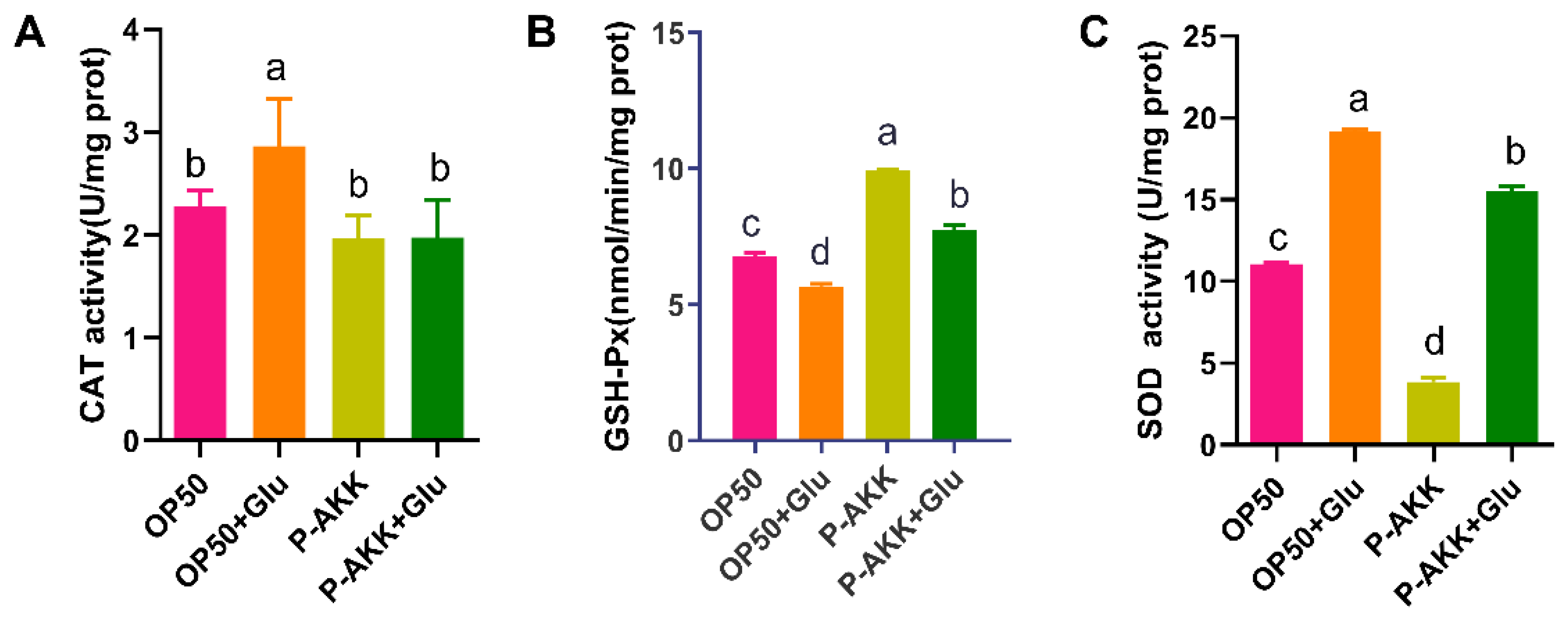
3.5. Effects of P-AKK on the Antioxidant Activity of Nematodes Under High Glucose
3.6. Effects of P-AKK on Lipid Metabolism in Nematodes According to Gene Expression Profiles Under High Glucose Conditions
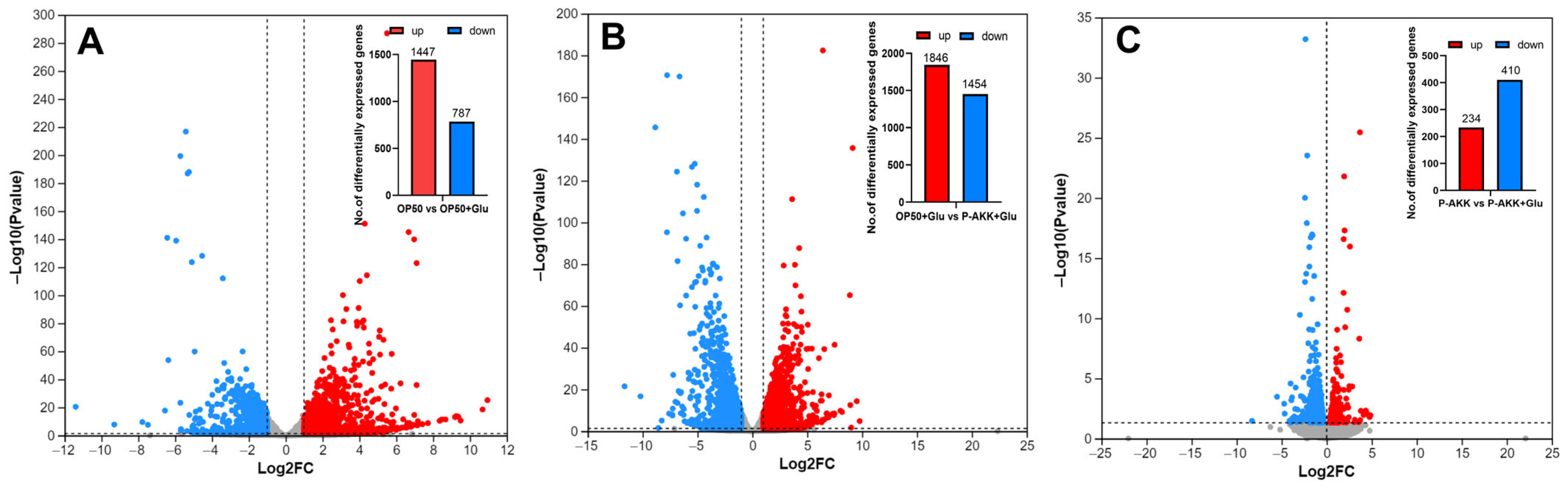
3.6.1. Identification of DEGs
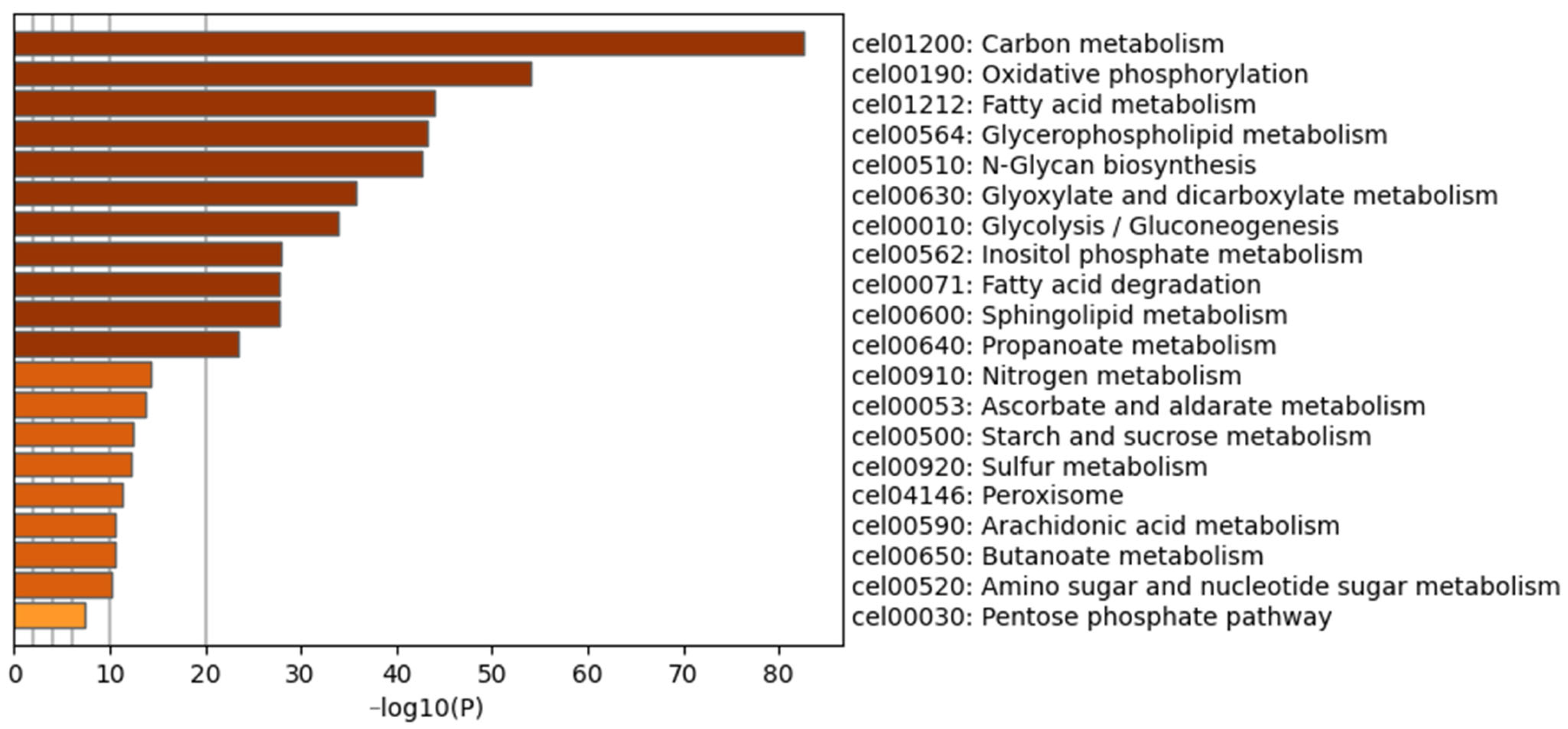
3.6.2. Functional Prediction of DEGs Induced by P-AKK in the High-Glucose Diet
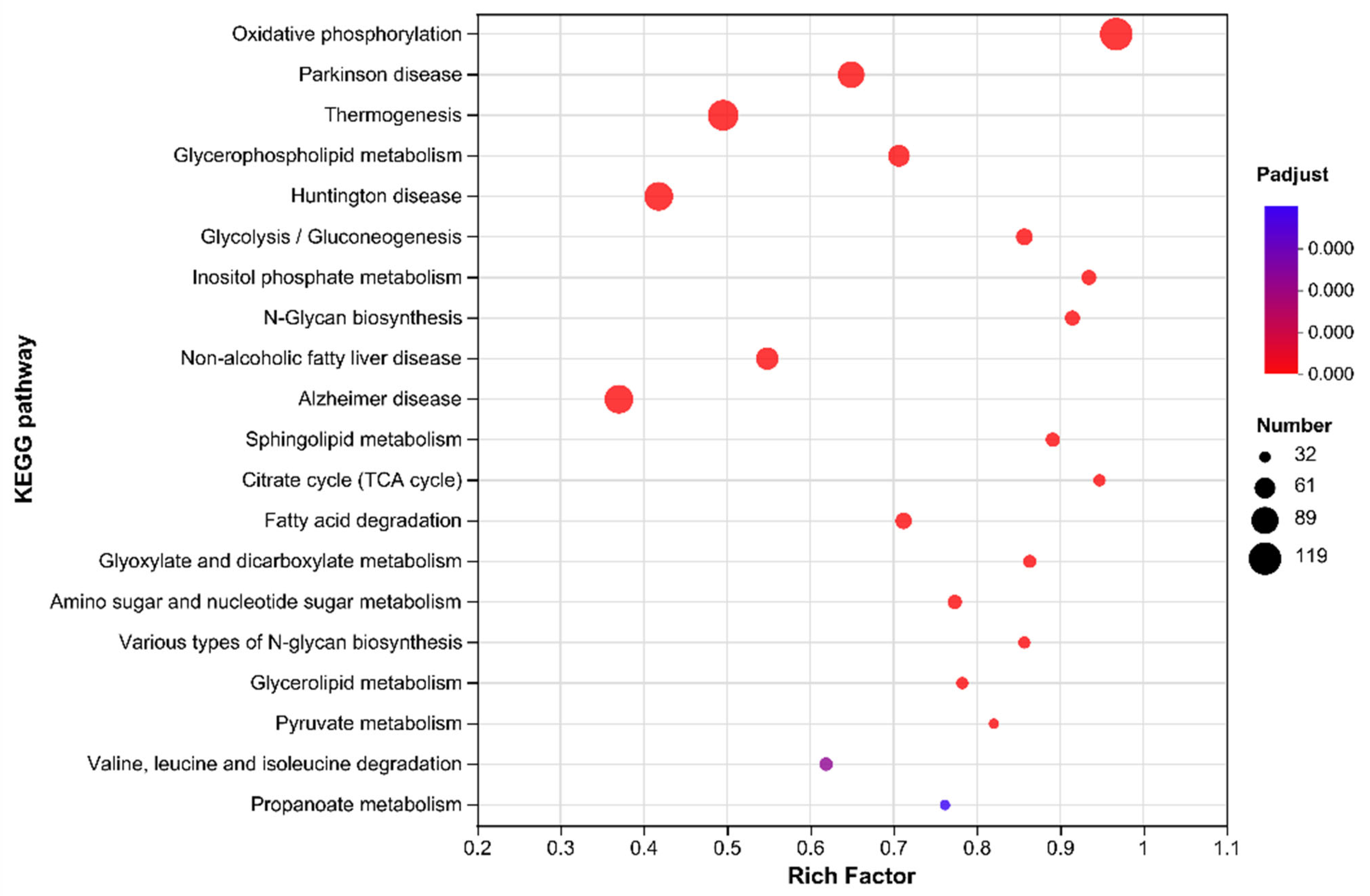
3.6.3. KEGG Pathway Analysis
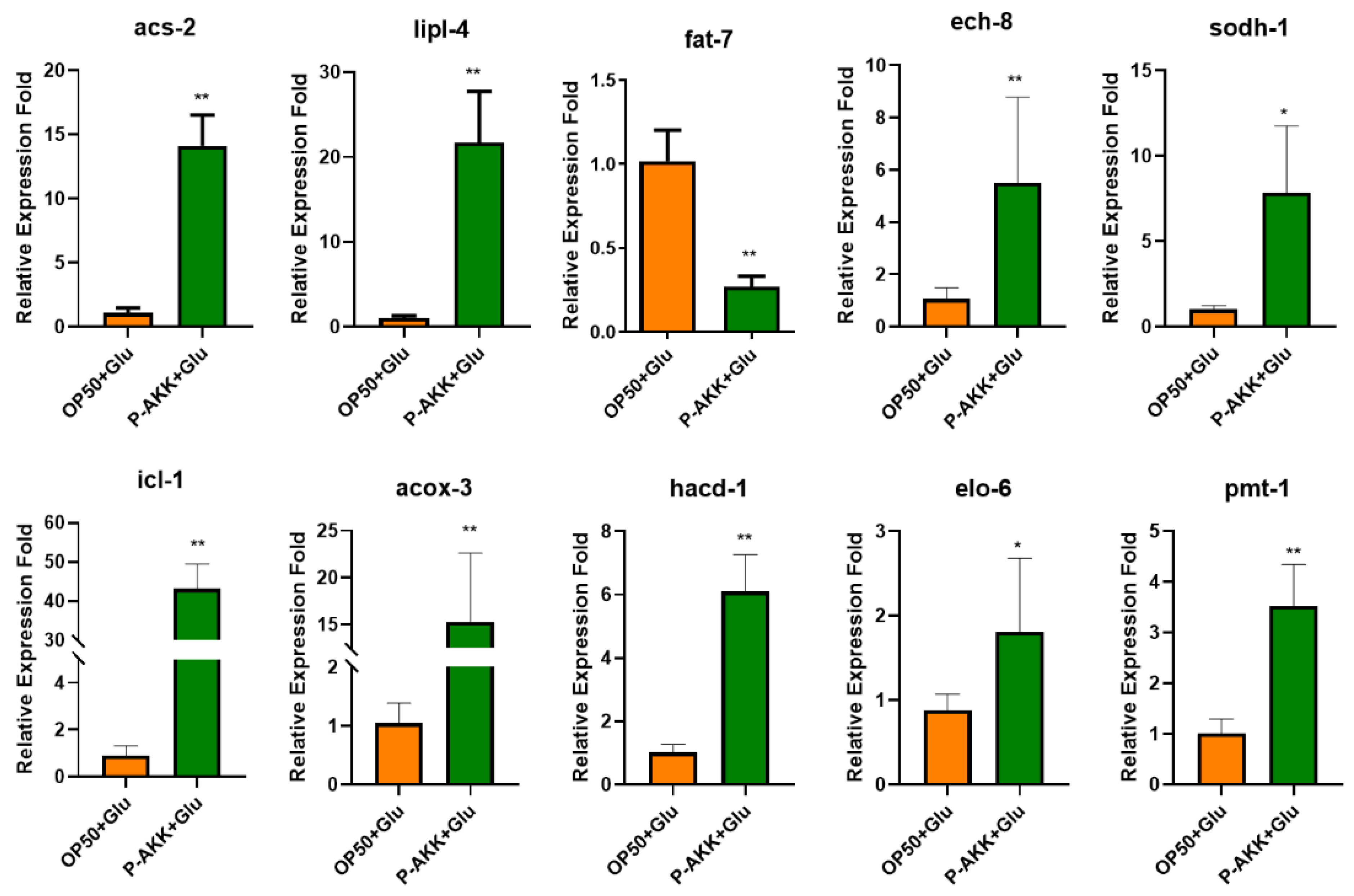
3.7. qPCR Validation of Differentially Expressed Genes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ladher, N.; Hinton, R.; Veitch, E. Challenges of obesity and type 2 diabetes require more attention to food environment. BMJ 2023, 383, p2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnbaugh, P.J.; Ridaura, V.K.; Faith, J.J.; Rey, F.E.; Knight, R.; Gordon, J.I. The Effect of Diet on the Human Gut Microbiome: A Metagenomic Analysis in Humanized Gnotobiotic Mice. Sci. Transl. Med. 2009, 1, 6ra14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Lu, H.; Zhao, S.; Yan, B.; Wang, H.; Zhou, X.; Xiao, Y. The beneficial effects of Tartary buckwheat (Fagopyrum tataricum Gaertn.) on diet-induced obesity in mice are related to the modulation of gut microbiota composition. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2023, 12, 1323–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, K.; Yang, Y.; Wang, J.; Bian, H.; Lei, X.; Chen, J.; Li, Q.; Wang, L.; Zhong, Q.; Fang, X. Comparative study on the weight loss and lipid metabolism by tea polyphenols in diet induced obese C57BL/6J pseudo germ free and conventionalized mice. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2022, 11, 697–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Shen, D.; Fang, Z.; Jie, Z.; Qiu, X.; Zhang, C.; Chen, Y.; Ji, L. Human Gut Microbiota Changes Reveal the Progression of Glucose Intolerance. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e71108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reunanen, J.; Kainulainen, V.; Huuskonen, L.; Ottman, N.; Belzer, C.; Huhtinen, H.; de Vos, W.M.; Satokari, R. Akkermansia muciniphila Adheres to Enterocytes and Strengthens the Integrity of the Epithelial Cell Layer. Appl. Env. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 3655–3662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rg, A.; Envelope, E.; Envelope, M.; Wmhl, D.; Mao, B.; Ma, E.; Myf, G.; Hk, B.; Rh, A.; Sb, H. The metabolic, protective, and immune functions of Akkermansia muciniphila. Microbiol. Res. 2023, 266, 127245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Zhou, W.; Shan, M.; Lu, Z.; Lu, Y. Yogurt-derived Lactobacillus plantarum Q16 alleviated high-fat diet-induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in mice. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2022, 11, 1428–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plovier, H.; Everard, A.; Druart, C.; Depommier, C.; Van Hul, M.; Geurts, L.; Chilloux, J.; Ottman, N.; Duparc, T.; Lichtenstein, L.; et al. A purified membrane protein from Akkermansia muciniphila or the pasteurized bacterium improves metabolism in obese and diabetic mice. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.J.; Tang, L.; Feng, Y.M.; Zhao, S.Y.; Han, M.; Zhang, C.; Yuan, G.H.; Zhu, J.; Cao, S.Y.; Wu, Q.; et al. A purified membrane protein from Akkermansia muciniphila or the pasteurised bacterium blunts colitis associated tumourigenesis by modulation of CD8+T cells in mice. Gut 2020, 69, 1988–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Zhou, F.; Chen, J.; Chen, X.; Hou, A.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z. Pasteurized Akkermansia muciniphila Reduces Fat Accumulation via nhr-49-Mediated Nuclear Hormone Signaling Pathway in Caenorhabditis elegans. Molecules 2022, 27, 6159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Liu, H.; Liu, H.; Teng, Y.; Qin, N.; Ren, X.; Xia, X. Live and pasteurized Akkermansia muciniphila decrease susceptibility to Salmonella Typhimurium infection in mice. J. Adv. Res. 2023, 52, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.; Jeong, D.E.; Son, H.G.; Yamaoka, Y.; Lee, S.J.V. SREBP and MDT-15 protect C. elegans from glucose-induced accelerated aging by preventing accumulation of saturated fat. Genes. Dev. 2015, 29, 2490–2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, G.; Lee, J.; Lim, Y.H. Dairy Propionibacterium extends the mean lifespan of Caenorhabditis elegans via activation of the innate immune system. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 31713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Zhu, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, Y.; Xiao, X. Effects of Bitter Melon Saponin on the Glucose and Lipid Metabolism in HepG2 Cell and C. elegans. J. Food Qual. 2020, 2020, 8860356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Wu, B.; Liang, S.; Min, D.; Jiang, H. Insight of Silkworm Pupa Oil Regulating Oxidative Stress and Lipid Metabolism in Caenorhabditis elegans. Foods 2022, 11, 4084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carranza, A.D.V.; Saragusti, A.; Chiabrando, G.A.; Carrari, F.; Asis, R. Effects of chlorogenic acid on thermal stress tolerance in C. elegans via HIF-1, HSF-1 and autophagy. Phytomedicine 2020, 66, 153132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, M.; Werlinger, P.; Cho, J.-H.; Jang, N.; Choi, S.S.; Suh, J.-W.; Cheng, J. Lactobacillus pentosus MJM60383 Inhibits Lipid Accumulation in Caenorhabditis elegans Induced by Enterobacter cloacae and Glucose. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Y.; Shen, P.; Chang, A.L.; Qi, W.; Kim, K.H.; Kim, D.; Park, Y. trans-Trismethoxy resveratrol decreased fat accumulation dependent on fat-6 and fat-7 in Caenorhabditis elegans. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 4966–4974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Tan, C.; Sun, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhou, X. Fermented Barley β-lucan Regulates Fat Deposition in Caenorhabditis elegans. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 100, 3408–3417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcela, S.-G.; Martha, R.C.; Escalona-Cardoso, G.N.; Norma, P.C. Evaluation of Hypoglycemic and Genotoxic Effect of Polyphenolic Bark Extract from Quercus sideroxyla. Evid. -Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 2016, 4032618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mota, M.; Banini, B.A.; Cazanave, S.C.; Sanyal, A.J. Molecular mechanisms of lipotoxicity and glucotoxicity in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Metabolism 2016, 65, 1049–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richard, J.P. Mechanism for the formation of methylglyoxal from triosephosphates. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 1993, 21, 549–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srinivasan, S. Regulation of body fat in Caenorhabditis elegans. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2015, 77, 161–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Sánchez, A.; Madrigal-Santillán, E.; Bautista, M.; Esquivel-Soto, J.; Morales-González, Á.; Esquivel-Chirino, C.; Durante-Montiel, I.; Sánchez-Rivera, G.; Valadez-Vega, C.; Morales-González, J. Inflammation, Oxidative Stress, and Obesity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 3117–3132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S. Oxidative stress from environmental pollutants. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 1995, 29, 135–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurent, D.; Yerby, B.; Deacon, R.; Gao, J. Diet-induced modulation of mitochondrial activity in rat muscle. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 293, E1169–E1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mondoux, M.A.; Love, D.C.; Ghosh, S.K.; Fukushige, T.; Bond, M.; Weerasinghe, G.R.; Hanover, J.A.; Krause, M.W. O-Linked-N-Acetylglucosamine Cycling and Insulin Signaling Are Required for the Glucose Stress Response in Caenorhabditis Elegans. Genet 2011, 188, 369–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Yin, F.; Wang, L.; Wei, W.; Jiang, L.; Qin, J. Modeling type 2 diabetes-like hyperglycemia in C. elegans on a microdevice. Integr. Biol. 2016, 8, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, L.-G.; Pan, L.-Y.; Gong, Y.-S.; Huang, J.-A.; Liu, Z.-H. Fuzhuan Tea protects Caenorhabditis elegans from glucose and advanced glycation end products via distinct pathways. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 59, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.; Zhang, Y.; Qian, W.; Leng, Y.; Long, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, J.; Wan, X.; Wei, X. Pediococcus acidilactici Promotes the Longevity of C. elegans by Regulating the Insulin/IGF-1 and JNK/MAPK Signaling, Fat Accumulation and Chloride Ion. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 821685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svensk, E.; Devkota, R.; Stahlman, M.; Ranji, P.; Rauthan, M.; Magnusson, F.; Hammarsten, S.; Johansson, M.; Boren, J.; Pilon, M. Caenorhabditis elegans PAQR-2 and IGLR-2 Protect against Glucose Toxicity by Modulating Membrane Lipid Composition. PLoS Genet. 2016, 12, e1005982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Depommier, C.; Van Hul, M.; Everard, A.; Delzenne, N.M.; De Vos, W.M.; Cani, P.D. Pasteurized Akkermansia muciniphila increases whole-body energy expenditure and fecal energy excretion in diet-induced obese mice. Gut Microbes 2020, 11, 1231–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, A.M.; Ladage, M.L.; Dumesnil, D.R.; Zaman, K.; Shulaev, V.; Azad, R.K.; Padilla, P.A. Glucose induces sensitivity to oxygen deprivation and modulates insulin/IGF-1 signaling and lipid biosynthesis in Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics 2015, 200, 167–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachandran, P.V.; Savini, M.; Folick, A.K.; Hu, K.; Wang, M.C. Lysosomal Signaling Promotes Longevity by Adjusting Mitochondrial Activity. Dev. Cell 2019, 48, 685–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Li, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, C.; Bai, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xiao, X. Bisphenol S promotes fat storage in multiple generations of Caenorhabditis elegans in a daf-16/nhr-49 dependent manner. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2021, 250, 109175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zou, X.; Liang, B. Identification of cytochrome b5 CYTB-5.1 and CYTB-5.2 in C. elegans; evidence for differential regulation of SCD. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2017, 1863, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landry, F.; Chan, C.C.; Huang, Z.; Leclair, G.; Bateman, K. Plasma-based approach to measure target engagement for liver-targeting stearoyl-CoA desaturase 1 inhibitors. J. Lipid Res. 2011, 52, 1494–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Group | Number of Worms | Mean Lifespan (Days) | Maximum Lifespan (Days) | Median (Days) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OP50 | 63 | 14.94 ± 0.58 a | 23 | 15.5 |
| OP50 + Glu | 68 | 11.92 ± 0.69 b | 19 | 14.0 |
| P-AKK | 68 | 13.78 ± 0.81 ab | 27 | 14.0 |
| P-AKK + Glu | 63 | 13.60 ± 0.78 ab | 24 | 16.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, Z.; Li, K.; Hou, A.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z. The Positive Effect of Akkermansia muciniphila postbiotics on the Glycolipid Metabolism of Caenorhabditis elegans Induced by High-Glucose Diet. Nutrients 2025, 17, 976. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17060976
Wu Z, Li K, Hou A, Wang Y, Li Z. The Positive Effect of Akkermansia muciniphila postbiotics on the Glycolipid Metabolism of Caenorhabditis elegans Induced by High-Glucose Diet. Nutrients. 2025; 17(6):976. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17060976
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Zhongqin, Ke Li, Aixing Hou, Yuanliang Wang, and Zongjun Li. 2025. "The Positive Effect of Akkermansia muciniphila postbiotics on the Glycolipid Metabolism of Caenorhabditis elegans Induced by High-Glucose Diet" Nutrients 17, no. 6: 976. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17060976
APA StyleWu, Z., Li, K., Hou, A., Wang, Y., & Li, Z. (2025). The Positive Effect of Akkermansia muciniphila postbiotics on the Glycolipid Metabolism of Caenorhabditis elegans Induced by High-Glucose Diet. Nutrients, 17(6), 976. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17060976






