Comparing Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis, Air Displacement Plethysmography, and Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry for Body Composition in Pediatric Obesity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Participants
2.2. Measurements
2.2.1. Anthropometry
2.2.2. Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis
2.2.3. Air Displacement Plethysmography
2.2.4. Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Participants Characteristics
3.2. Comparison of the Different Body Composition Methods
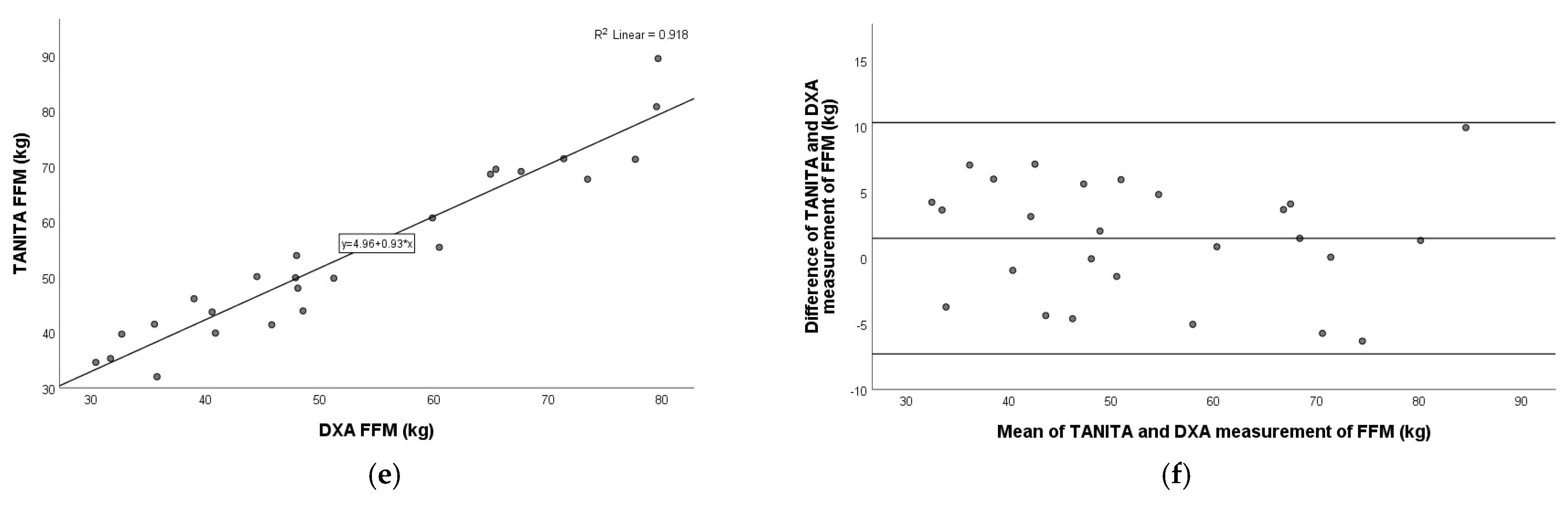
3.3. Comparison of TANITA Versus DXA
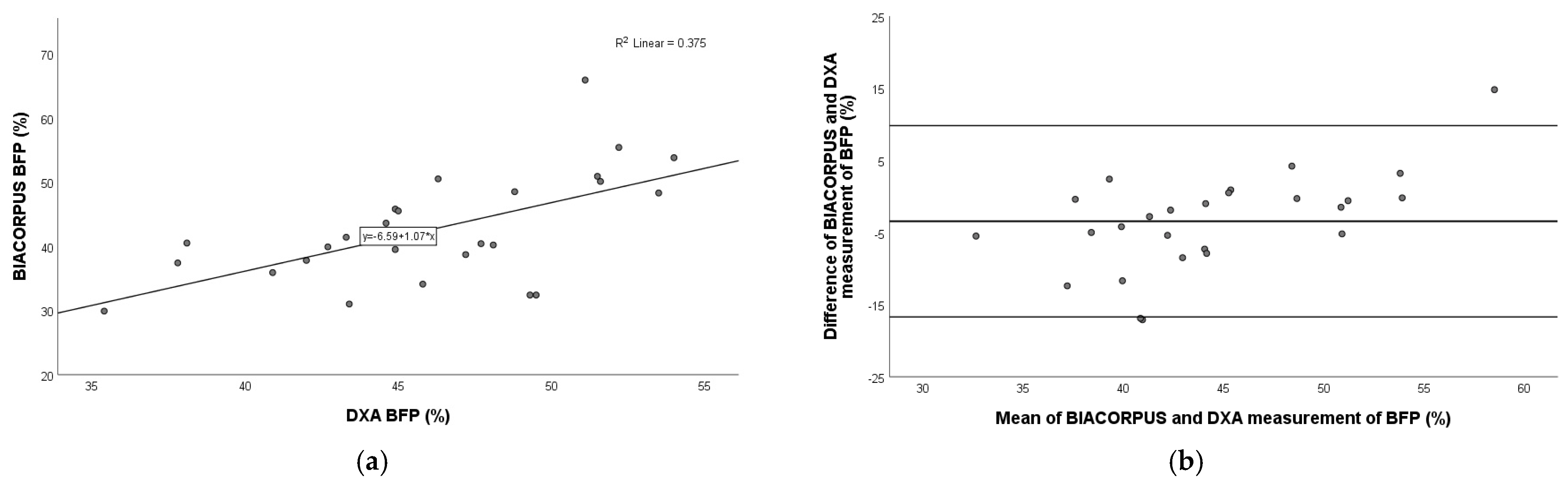
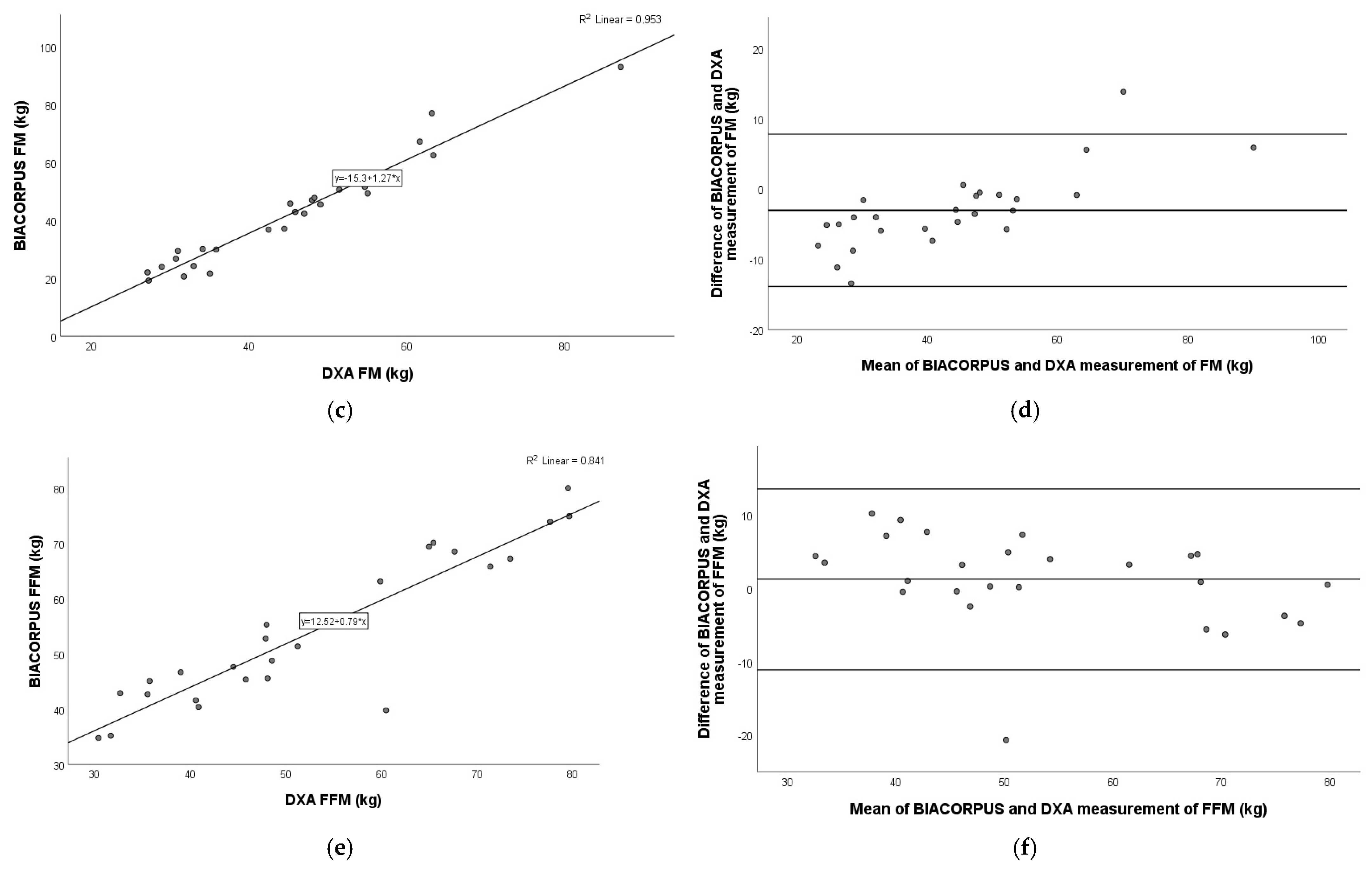
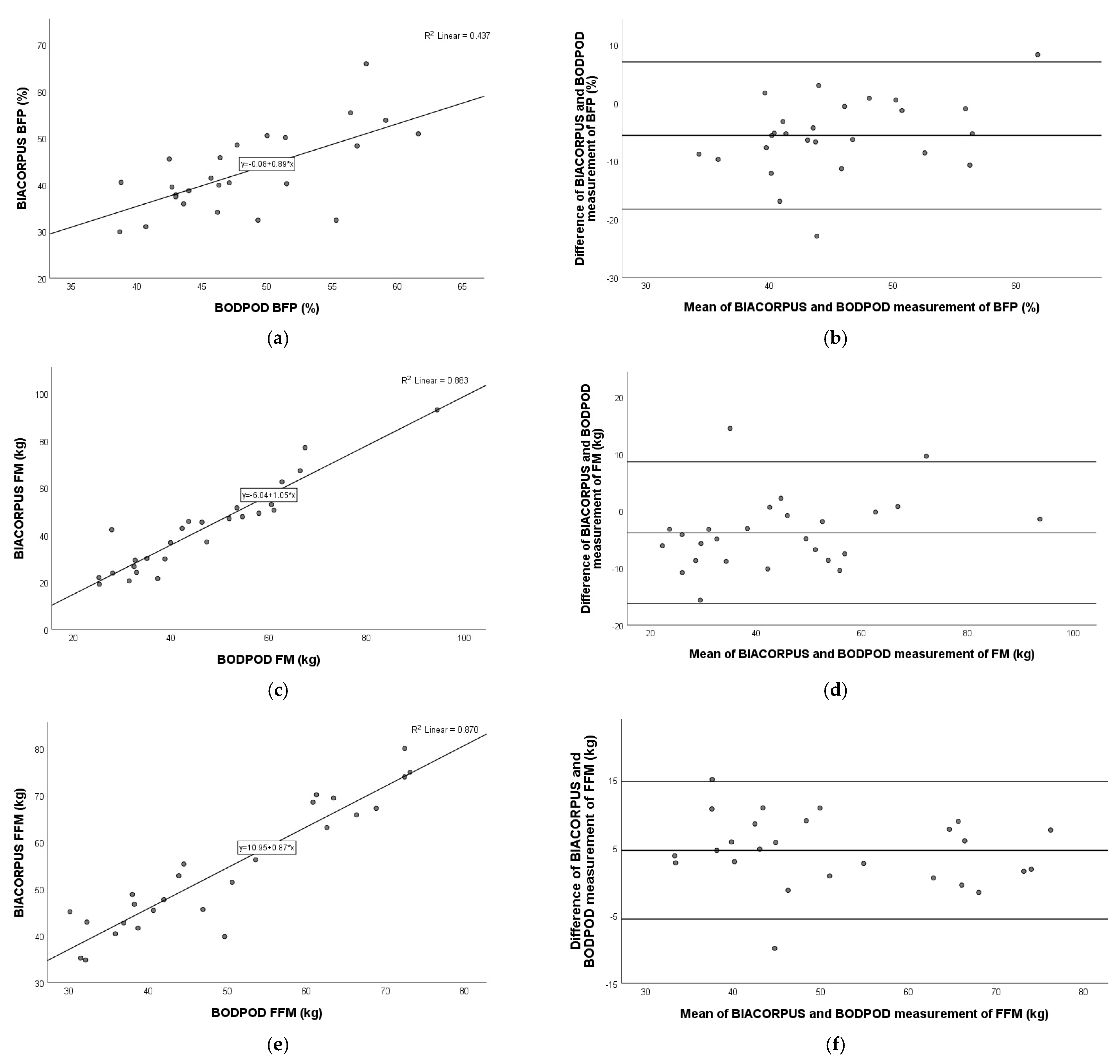
3.4. Comparison of BIACORPUS Versus DXA
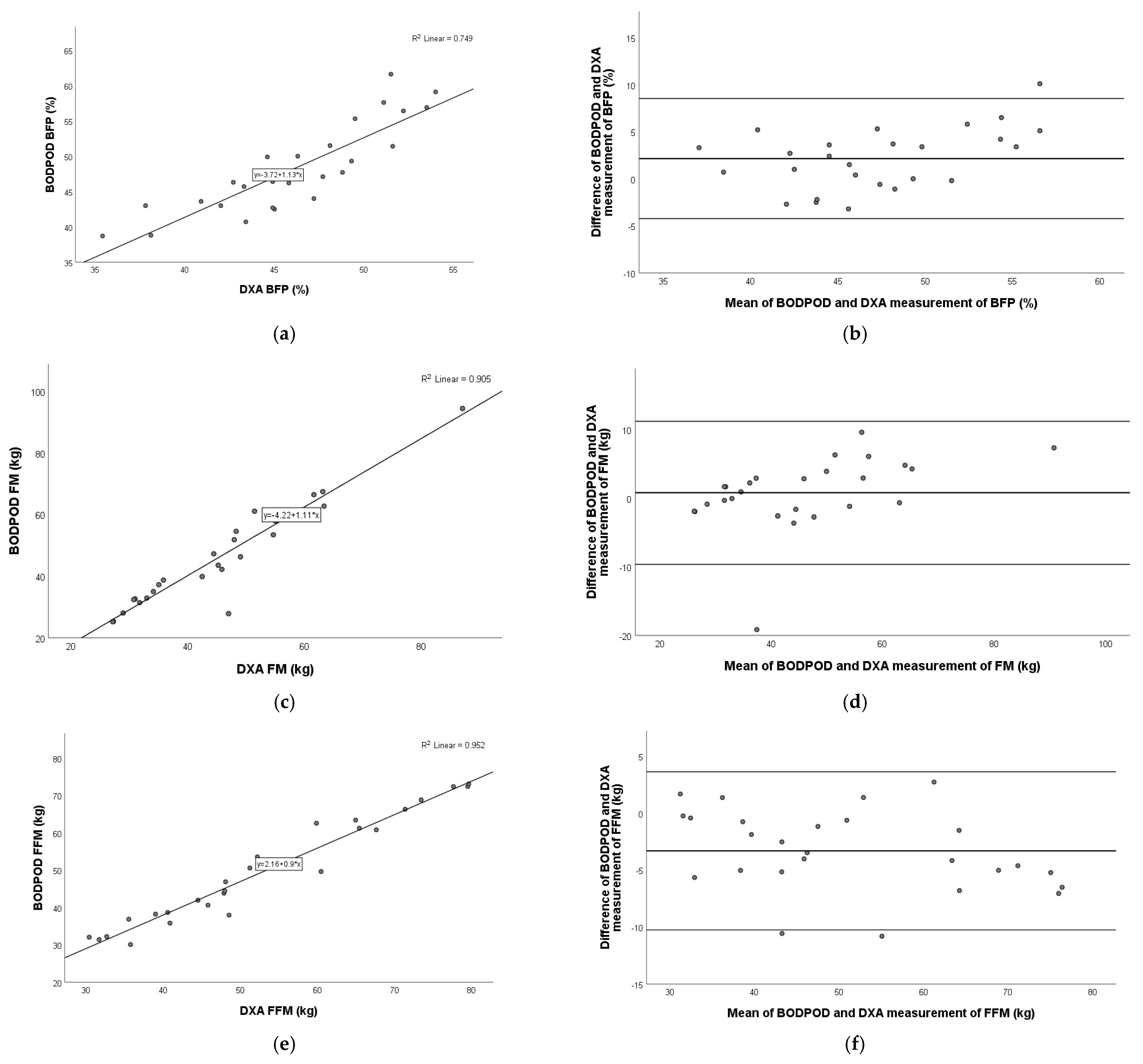
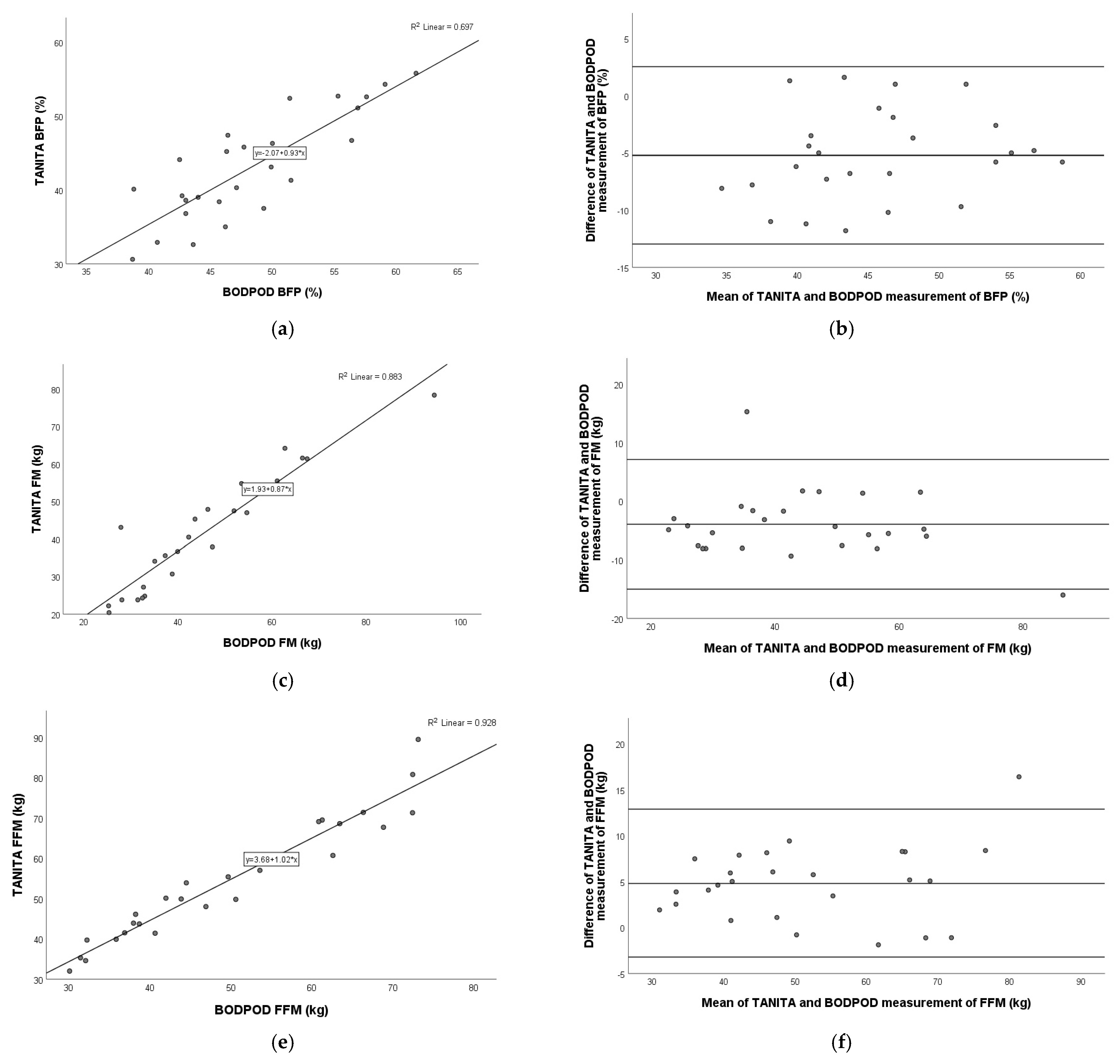
3.5. Comparison of BODPOD Versus DXA
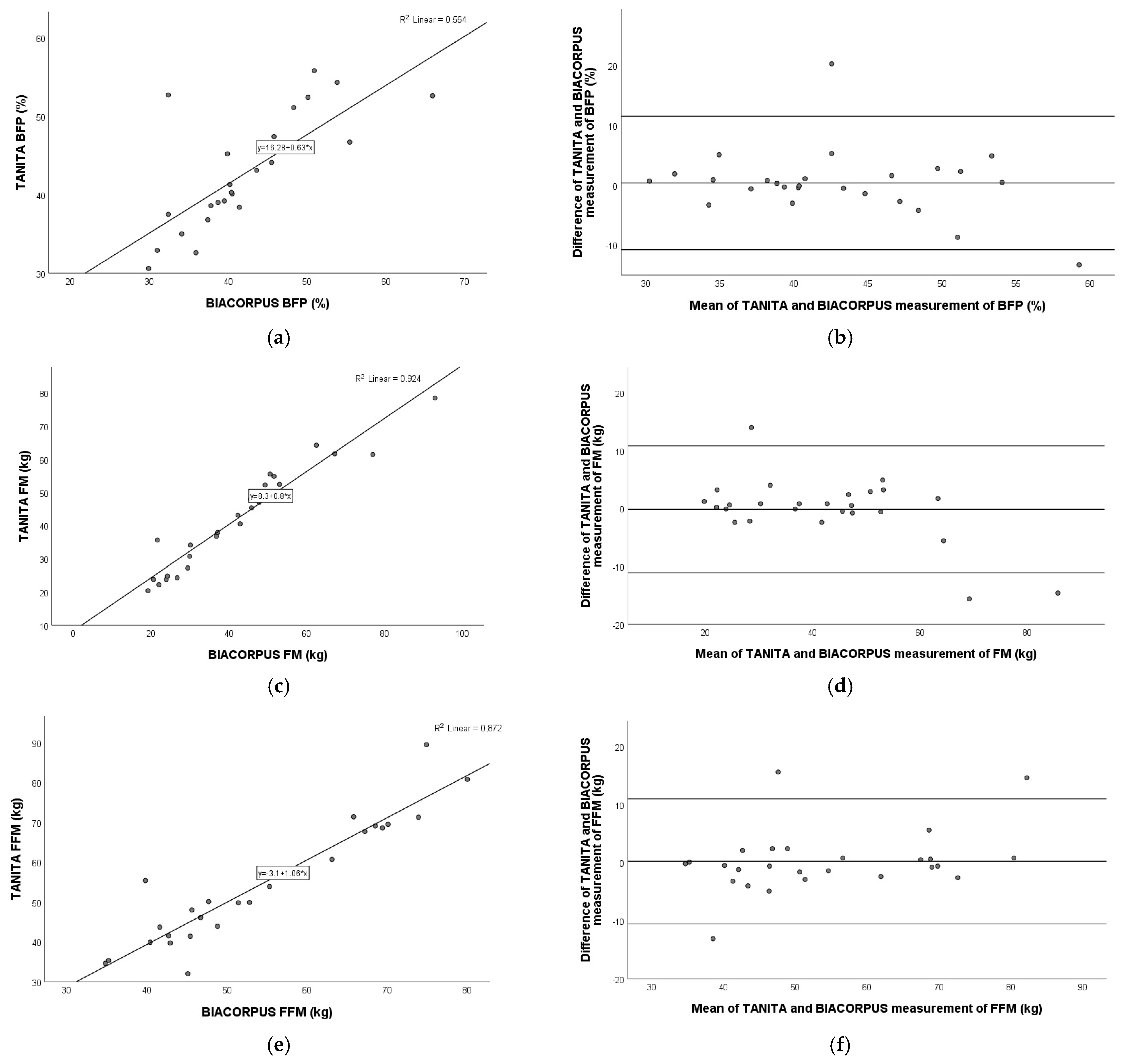
3.6. Comparison of TANITA Versus BIACORPUS
3.7. Comparison of TANITA Versus BODPOD
3.8. Comparison of BIACORPUS Versus BODPOD
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thibault, R.; Genton, L.; Pichard, C. Body composition: Why, when and for who? Clin. Nutr. 2012, 31, 435–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmes, C.J.; Racette, S.B. The Utility of Body Composition Assessment in Nutrition and Clinical Practice: An Overview of Current Methodology. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duren, D.L.; Sherwood, R.J.; Czerwinski, S.A.; Lee, M.; Choh, A.C.; Siervogel, R.M.; Cameron Chumlea, W. Body composition methods: Comparisons and interpretation. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2008, 2, 1139–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madden, A.M.; Smith, S. Body composition and morphological assessment of nutritional status in adults: A review of anthropometric variables. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2016, 29, 7–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sweatt, K.; Garvey, W.T.; Martins, C. Strengths and Limitations of BMI in the Diagnosis of Obesity: What is the Path Forward? Curr. Obes. Rep. 2024, 13, 584–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubino, F.; Cummings, D.E.; Eckel, R.H.; Cohen, R.V.; Wilding, J.P.H.; Brown, W.A.; Stanford, F.C.; Batterham, R.L.; Farooqi, I.S.; Farpour-Lambert, N.J.; et al. Definition and diagnostic criteria of clinical obesity. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2025, 13, 221–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemos, T.; Gallagher, D. Current body composition measurement techniques. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes. 2017, 24, 310–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamel, E.G.; McNeill, G.; Han, T.S.; Smith, F.W.; Avenell, A.; Davidson, L.; Tothill, P. Measurement of abdominal fat by magnetic resonance imaging, dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry and anthropometry in non-obese men and women. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 1999, 23, 686–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imboden, M.T.; Welch, W.A.; Swartz, A.M.; Montoye, A.H.; Finch, H.W.; Harber, M.P.; Kaminsky, L.A. Reference standards for body fat measures using GE dual energy x-ray absorptiometry in Caucasian adults. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0175110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.K. Body composition measurement in severe obesity. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2005, 8, 602–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fosbol, M.O.; Zerahn, B. Contemporary methods of body composition measurement. Clin. Physiol. Funct. Imaging 2015, 35, 81–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nassis, G.P.; Sidossis, L.S. Methods for assessing body composition, cardiovascular and metabolic function in children and adolescents: Implications for exercise studies. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2006, 9, 560–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simoni, P.; Guglielmi, R.; Aparisi Gomez, M.P. Imaging of body composition in children. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2020, 10, 1661–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodpaster, B.H.; Kelley, D.E.; Thaete, F.L.; He, J.; Ross, R. Skeletal muscle attenuation determined by computed tomography is associated with skeletal muscle lipid content. J. Appl. Physiol. 2000, 89, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreissl, A.; Jorda, A.; Truschner, K.; Skacel, G.; Greber-Platzer, S. Clinically relevant body composition methods for obese pediatric patients. BMC Pediatr. 2019, 19, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thajer, A.; Skacel, G.; Truschner, K.; Jorda, A.; Vasek, M.; Horsak, B.; Strempfl, J.; Kautzky-Willer, A.; Kainberger, F.; Greber-Platzer, S. Comparison of Bioelectrical Impedance-Based Methods on Body Composition in Young Patients with Obesity. Children 2021, 8, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butcher, A.; Kabiri, L.S.; Brewer, W.; Ortiz, A. Criterion Validity and Sensitivity to Change of a Pediatric Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis Scale in Adolescents. Child. Obes. 2019, 15, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabiri, L.S.; Hernandez, D.C.; Mitchell, K. Reliability, Validity, and Diagnostic Value of a Pediatric Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis Scale. Child. Obes. 2015, 11, 650–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Silva, M.; Hewawasam, R.P.; Lekamwasam, S. Concordance between Body Composition Indices Measured with Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry and Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis in Obese Children in Sri Lanka. Int. J. Pediatr. 2021, 2021, 6638057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verney, J.; Metz, L.; Chaplais, E.; Cardenoux, C.; Pereira, B.; Thivel, D. Bioelectrical impedance is an accurate method to assess body composition in obese but not severely obese adolescents. Nutr. Res. 2016, 36, 663–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thivel, D.; Verney, J.; Miguet, M.; Masurier, J.; Cardenoux, C.; Lambert, C.; Courteix, D.; Metz, L.; Pereira, B. The accuracy of bioelectrical impedance to track body composition changes depends on the degree of obesity in adolescents with obesity. Nutr. Res. 2018, 54, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Wang, X.; Cheng, H.; Dong, H.; Shan, X.; Zhao, X.; Wang, X.; Xie, X.; Mi, J. Differences in air displacement plethysmography, bioelectrical impedance analysis and dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry for estimating body composition in Chinese children and adolescents. J. Paediatr. Child Health 2023, 59, 470–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samouda, H.; Langlet, J. Body fat assessment in youth with overweight or obesity by an automated bioelectrical impedance analysis device, in comparison with the dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry: A cross sectional study. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2022, 22, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bijlsma, A.; van Beijsterveldt, I.; Vermeulen, M.J.; Beunders, V.A.A.; Dorrepaal, D.J.; Boeters, S.C.M.; van den Akker, E.L.T.; Vlug, L.E.; de Koning, B.A.E.; Bracke, K.F.M.; et al. Challenges in body composition assessment using air-displacement plethysmography by BOD POD in pediatric and young adult patients. Clin. Nutr. 2023, 42, 1588–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Wang, J.; Liu, J.; Huang, G.; Hou, D.; Liao, Z.; Zhang, T.; Liu, G.; Xie, X.; Tai, J. Characteristics of Body Composition Estimated by Air-Displacement Plethysmography in Chinese Preschool Children. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 926819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Dong, H.; Cheng, H.; Shan, X.; Yu, X.; Xie, X.; Mi, J. Differences in body composition measurements assessed by air displacement plethysmography and dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry in young and middle-aged adults. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2022, 50, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucke, L.A.; Rochow, N.; Knab, K.; Schafer, S.; Zimmermann, J.L.; Meis, A.; Lohmuller-Weiss, S.; Szakacs-Fusch, A.; Felderhoff-Muser, U.; Fusch, C. Body Composition Analysis of the Clinical Routine Using Air Displacement Plethysmography: Age-Group-Specific Feasibility Analysis among Preterm Infants. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucke, L.; Fusch, C.; Knab, K.; Schafer, S.; Zimmermann, J.L.; Felderhoff-Muser, U.; Meis, A.; Lohmuller-Weiss, S.; Szakacs-Fusch, A.; Rochow, N. Reproducibility of Air Displacement Plethysmography in Term and Preterm Infants-A Study to Enhance Body Composition Analysis in Clinical Routine. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petroni, M.L.; Bertoli, S.; Maggioni, M.; Morini, P.; Battezzati, A.; Tagliaferri, M.A.; Liuzzi, A.; Testolin, G. Feasibility of air plethysmography (BOD POD) in morbid obesity: A pilot study. Acta Diabetol. 2003, 40 (Suppl. S1), S59–S62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginde, S.R.; Geliebter, A.; Rubiano, F.; Silva, A.M.; Wang, J.; Heshka, S.; Heymsfield, S.B. Air displacement plethysmography: Validation in overweight and obese subjects. Obes. Res. 2005, 13, 1232–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horsak, B.; Durstberger, S.; Krondorfer, P.; Thajer, A.; Greber-Platzer, S.; Kranzl, A. Which method should we use to determine the hip joint center location in individuals with a high amount of soft tissue? Clin. Biomech. 2024, 115, 106254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kromeyer-Hauschild, K.; Wabitsch, M.; Kunze, D.; Geller, F.; Geiß, H.C.; Hesse, V.; Von Hippel, A.; Jaeger, U.; Johnsen, D.; Korte, W.; et al. Percentiles of Body Mass Index in Children and Adolescents Evaluated from Different Regional German Studies. Monatsschr. Kinderheilkd. 2001, 149, 807–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyle, U.G.; Bosaeus, I.; De Lorenzo, A.D.; Deurenberg, P.; Elia, M.; Gomez, J.M.; Heitmann, B.L.; Kent-Smith, L.; Melchior, J.C.; Pirlich, M.; et al. Bioelectrical impedance analysis--part I: Review of principles and methods. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 23, 1226–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanita, C. Instruction Manual Body Composition Analyzer MC-980MA-N plus. 2018, pp. 1–58. Available online: https://tanita.eu/media/pdf/products-tanita/professional/MC-980/MC-980MA-N%20PLus%20Instruction%20Manual%20%28EN%29%202018.pdf (accessed on 13 December 2024).
- Medical Healthcare GmbH. Instruction Manual of the BiIACORPUS RX 4000; Medical Health Care GmbH: Karlsruhe, Germany, 2013; pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Potter, A.W.; Nindl, L.J.; Soto, L.D.; Pazmino, A.; Looney, D.P.; Tharion, W.J.; Robinson-Espinosa, J.A.; Friedl, K.E. High precision but systematic offset in a standing bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA) compared with dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA). BMJ Nutr. Prev. Health 2022, 5, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosy-Westphal, A.; Danielzik, S.; Becker, C.; Geisler, C.; Onur, S.; Korth, O.; Bührens, F.; Müller, M.J. Need for Optimal Body Composition Data Analysis Using Air-Displacement Plethysmography in Children and Adolescents. J. Nutr. 2005, 135, 2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heden, T.; Shepard, S.; Smith, J.; Covington, K.; Lecheminant, J. Resulting Shifts in Percentile and Standard Placements after Comparison of the BOD POD and DXA. Int. J. Exerc. Sci. 2008, 1, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dempster, P.; Aitkens, S. A new air displacement method for the determination of human body composition. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 1995, 27, 1692–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, M.; Ma, W.K.; Chan, E.; Mui, C.; Ma, V.; Ho, W.Y.; Yip, L.; Lam, W. Cumulative Effective Dose and Cancer Risk of Pediatric Population in Repetitive Whole-Body Scan Using Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry. J. Clin. Densitom. 2019, 22, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuriyan, R. Body composition techniques. Indian J. Med. Res. 2018, 148, 648–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, M.K.; Kharb, S. Dual energy X-ray absorptiometry: Pitfalls in measurement and interpretation of bone mineral density. Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 17, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, Y.H. Biostatistics 104: Correlational analysis. Singap. Med. J. 2003, 44, 614–619. [Google Scholar]
- Akoglu, H. User’s guide to correlation coefficients. Turk. J. Emerg. Med. 2018, 18, 91–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bland, J.M.; Altman, D.G. Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. Lancet 1986, 1, 307–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogan, N.O. Bland-Altman analysis: A paradigm to understand correlation and agreement. Turk. J. Emerg. Med. 2018, 18, 139–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giavarina, D. Understanding Bland Altman analysis. Biochem. Med. 2015, 25, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppini, L.Z.; Waitzberg, D.L.; Campos, A.C. Limitations and validation of bioelectrical impedance analysis in morbidly obese patients. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2005, 8, 329–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.J.; Jeon, H.J.; Kim, Y.H.; Jeon, J.; Ham, Y.R.; Chung, S.; Choi, D.E.; Na, K.R.; Lee, K.W. Overhydration measured by bioimpedance analysis and the survival of patients on maintenance hemodialysis: A single-center study. Kidney Res. Clin. Pract. 2015, 34, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deurenberg, P. Limitations of the bioelectrical impedance method for the assessment of body fat in severe obesity. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1996, 64, 449S–452S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Xanthakos, S.A.; Hornung, L.; Arce-Clachar, C.; Siegel, R.; Kalkwarf, H.J. Relative Accuracy of Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis for Assessing Body Composition in Children With Severe Obesity. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2020, 70, e129–e135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Androutsos, O.; Gerasimidis, K.; Karanikolou, A.; Reilly, J.J.; Edwards, C.A. Impact of eating and drinking on body composition measurements by bioelectrical impedance. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2015, 28, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fields, D.A.; Higgins, P.B.; Hunter, G.R. Assessment of body composition by air-displacement plethysmography: Influence of body temperature and moisture. Dyn. Med. 2004, 3, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nana, A.; Slater, G.J.; Stewart, A.D.; Burke, L.M. Methodology review: Using dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) for the assessment of body composition in athletes and active people. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2015, 25, 198–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepherd, J.A.; Ng, B.K.; Sommer, M.J.; Heymsfield, S.B. Body composition by DXA. Bone 2017, 104, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toombs, R.J.; Ducher, G.; Shepherd, J.A.; De Souza, M.J. The impact of recent technological advances on the trueness and precision of DXA to assess body composition. Obesity 2012, 20, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballard, T.P.; Fafara, L.; Vukovich, M.D. Comparison of Bod Pod and DXA in female collegiate athletes. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2004, 36, 731–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutierrez-Marin, D.; Luque, V.; Ferre, N.; Fewtrell, M.S.; Williams, J.E.; Wells, J.C.K. Associations of age and body mass index with hydration and density of fat-free mass from 4 to 22 years. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 73, 1422–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, J.C.; Fewtrell, M.S. Measuring body composition. Arch. Dis. Child. 2006, 91, 612–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez-Marin, D.; Escribano, J.; Closa-Monasterolo, R.; Ferre, N.; Venables, M.; Singh, P.; Wells, J.C.K.; Munoz-Hernando, J.; Zaragoza-Jordana, M.; Gispert-Llaurado, M.; et al. A novel approach to assess body composition in children with obesity from density of the fat-free mass. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 1102–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rush, E.C.; Bristow, S.; Plank, L.D.; Rowan, J. Bioimpedance prediction of fat-free mass from dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry in a multi-ethnic group of 2-year-old children. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 67, 214–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiech, P.; Woloszyn, F.; Trojnar, P.; Skorka, M.; Bazalinski, D. Does Body Position Influence Bioelectrical Impedance? An Observational Pilot Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 9908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamilton-James, K.; Collet, T.H.; Pichard, C.; Genton, L.; Dupertuis, Y.M. Precision and accuracy of bioelectrical impedance analysis devices in supine versus standing position with or without retractable handle in Caucasian subjects. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2021, 45, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, H.; Hunt, E.T.; Brazendale, K.; Klinggraeff, L.V.; Jones, A.; Burkart, S.; Dugger, R.; Armstrong, B.; Beets, M.W.; Weaver, R.G. Accuracy and Precision of Opportunistic Measures of Body Composition from the Tanita DC-430U. Child. Obes. 2023, 19, 470–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, V.; Short, M.; Smith, S.; Senechal, M.; Bouchard, D.R. Testing Bioimpedance to Estimate Body Fat Percentage across Different Hip and Waist Circumferences. J. Sports Med. 2019, 2019, 7624253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazzer, S.; Boirie, Y.; Meyer, M.; Vermorel, M. Evaluation of two foot-to-foot bioelectrical impedance analysers to assess body composition in overweight and obese adolescents. Br. J. Nutr. 2003, 90, 987–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rush, E.C.; Crowley, J.; Freitas, I.F.; Luke, A. Validity of hand-to-foot measurement of bioimpedance: Standing compared with lying position. Obesity 2006, 14, 252–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, B.; Braun, W.; Both, M.; Gallagher, D.; Clark, P.; Gonzalez, D.L.; Kluckmann, K.; Bosy-Westphal, A. Configuration of bioelectrical impedance measurements affects results for phase angle. Med. Eng. Phys. 2020, 84, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, C.S.; Ward, L.C.; Halim, J.; Gow, M.L.; Ho, M.; Briody, J.N.; Leung, K.; Cowell, C.T.; Garnett, S.P. Bioelectrical impedance analysis to estimate body composition, and change in adiposity, in overweight and obese adolescents: Comparison with dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry. BMC Pediatr. 2014, 14, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, M.G.; Crabtree, N.J.; Shaw, N.J.; Kirk, J.M. Body fat estimation using bioelectrical impedance. Horm. Res. 2007, 68, 8–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Characteristics | Patients (n = 26) | Male (n = 17) | Female (n = 9) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 13.1 ± 2.5 | 13.2 ± 2.2 | 12.9 ± 3.0 |
| Height (cm) | 162.7 ± 10.5 | 165.4 ± 10.7 | 158.8 ± 9.8 |
| Weight (kg) | 95.8 ± 27.6 | 101.5 ± 30.1 | 87.6 ± 21.4 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 35.6 ± 6.9 | 36.4 ± 7.2 | 34.4 ± 6.7 |
| Mid-upper arm circumference (cm) | 35.0 ± 4.4 | 35.0 ± 4.3 | 35.2 ± 4.9 |
| Abdominal circumference (cm) | 103.7 ± 12.4 | 109.0 ± 12.1 | 97.2 ± 9.8 |
| Hip circumference (cm) | 112.3 ± 15.8 | 116.8 ± 15.3 | 106.6 ± 15.6 |
| Waist circumference (cm) | 114.8 ± 20.1 | 115.4 ± 22.7 | 114.6 ± 15.9 |
| Waist-to-hip ratio | 0.93 ± 0.20 | 0.98 ± 0.24 | 0.85 ± 0.06 |
| Waist-to-height ratio | 0.64 ± 0.06 | 0.66 ± 0.06 | 0.61 ± 0.06 |
| ANOVA | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | Df | p | ηp2 | |
| BFP (%) | ||||
| BFP | 9.921 | 2.042 | 0.000 | 0.292 |
| Gender | 1.905 | 1 | 0.180 | 0.074 |
| BFP × gender | 2.929 | 2.042 | 0.062 | 0.109 |
| FM (kg) | ||||
| FM | 5.649 | 2.983 | 0.002 | 0.191 |
| Gender | 0.168 | 1 | 0.686 | 0.007 |
| FM × gender | 1.091 | 2.983 | 0.358 | 0.043 |
| FFM (kg) | ||||
| FFM | 7.491 | 2.169 | 0.001 | 0.238 |
| Gender | 3.424 | 1 | 0.077 | 0.125 |
| FFM × gender | 3.032 | 2.169 | 0.053 | 0.112 |
| Parameter | TANITA | BIACORPUS | BODPOD | DXA |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BFP (%) | 43.0 ± 7.1 | 39.9 ± 8.4 | 48.5 ± 6.1 | 46.4 ± 4.6 |
| FM (kg) | 41.7 ± 15.3 | 39.0 ± 17.0 | 45.9 ± 16.5 | 45.1 ± 14.2 |
| FFM (kg) | 53.7 ± 15.0 | 56.3 ± 14.6 | 48.7 ± 13.8 | 51.8 ± 15.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Thajer, A.; Vasek, M.; Schneider, S.; Kautzky-Willer, A.; Kainberger, F.; Durstberger, S.; Kranzl, A.; Horsak, B.; Greber-Platzer, S. Comparing Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis, Air Displacement Plethysmography, and Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry for Body Composition in Pediatric Obesity. Nutrients 2025, 17, 971. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17060971
Thajer A, Vasek M, Schneider S, Kautzky-Willer A, Kainberger F, Durstberger S, Kranzl A, Horsak B, Greber-Platzer S. Comparing Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis, Air Displacement Plethysmography, and Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry for Body Composition in Pediatric Obesity. Nutrients. 2025; 17(6):971. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17060971
Chicago/Turabian StyleThajer, Alexandra, Martin Vasek, Sophie Schneider, Alexandra Kautzky-Willer, Franz Kainberger, Sebastian Durstberger, Andreas Kranzl, Brian Horsak, and Susanne Greber-Platzer. 2025. "Comparing Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis, Air Displacement Plethysmography, and Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry for Body Composition in Pediatric Obesity" Nutrients 17, no. 6: 971. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17060971
APA StyleThajer, A., Vasek, M., Schneider, S., Kautzky-Willer, A., Kainberger, F., Durstberger, S., Kranzl, A., Horsak, B., & Greber-Platzer, S. (2025). Comparing Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis, Air Displacement Plethysmography, and Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry for Body Composition in Pediatric Obesity. Nutrients, 17(6), 971. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17060971






