Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet and Risk of Depression: A Cohort Study in Chinese Community Residents
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
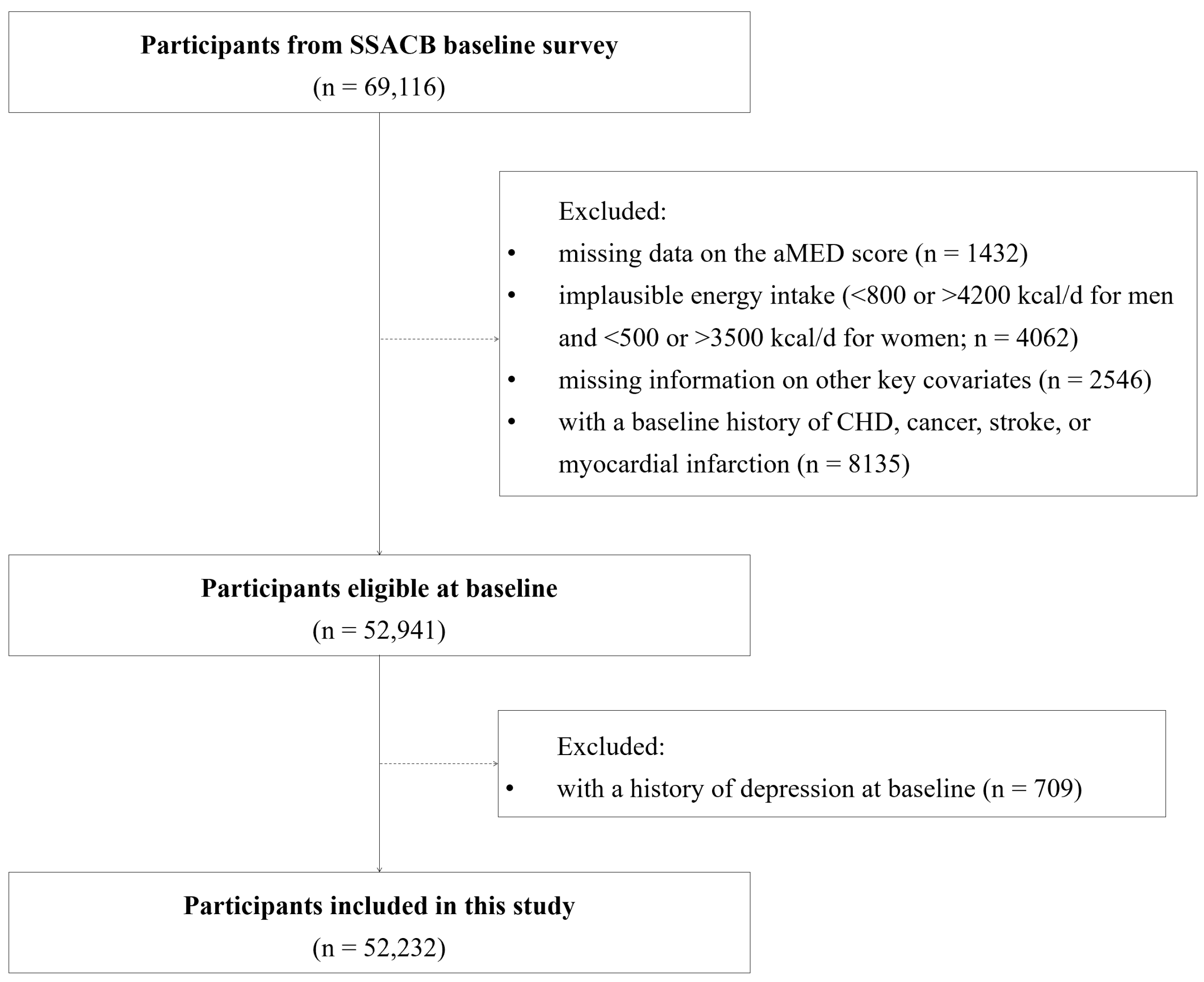
2.1. Subjects and Source
2.2. Dietary Assessment
2.3. Diagnosis of Depression
2.4. Assessment of Covariates
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics and the Incidence of Depression
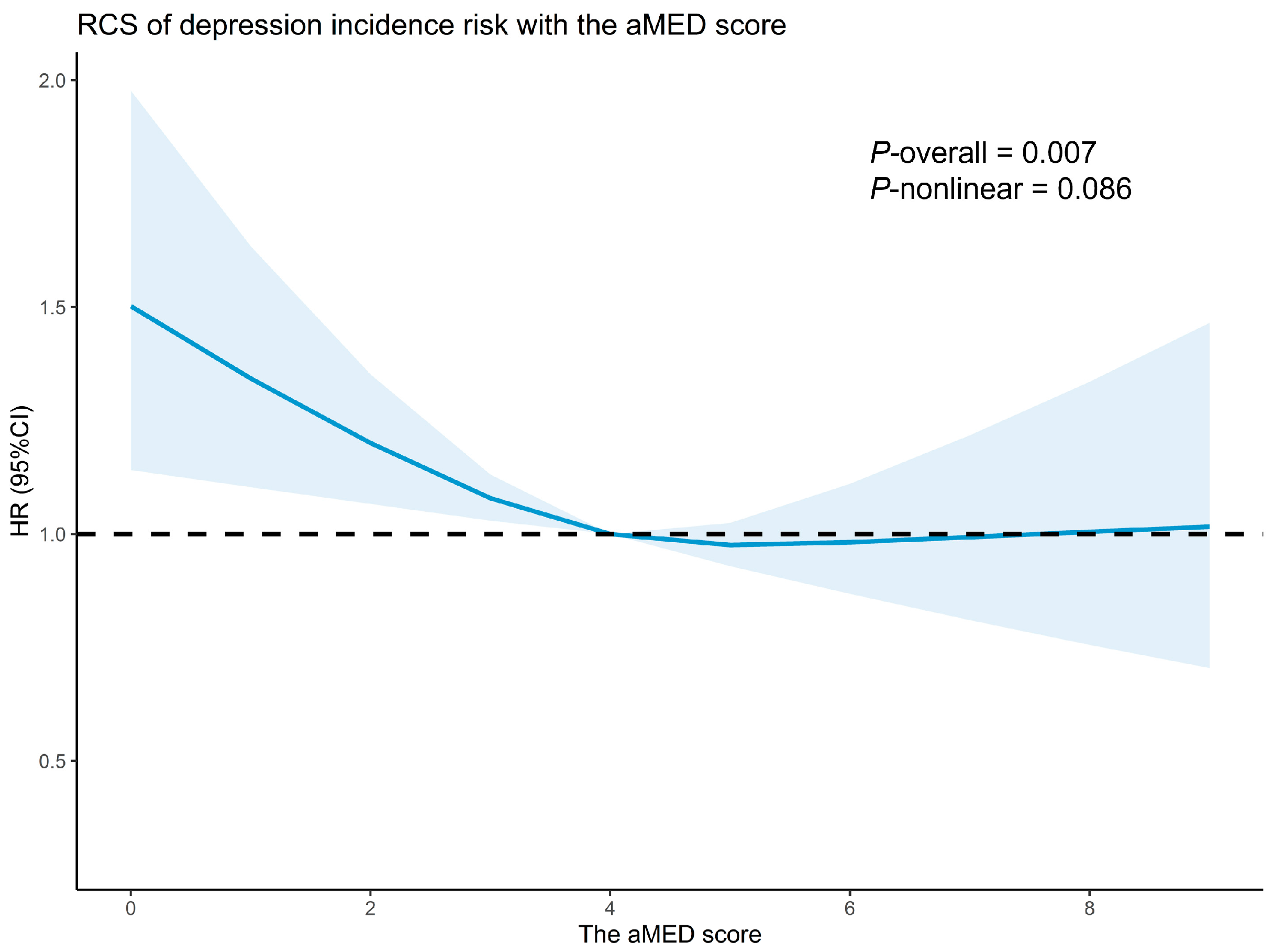
3.2. Association Between the aMED and Depression
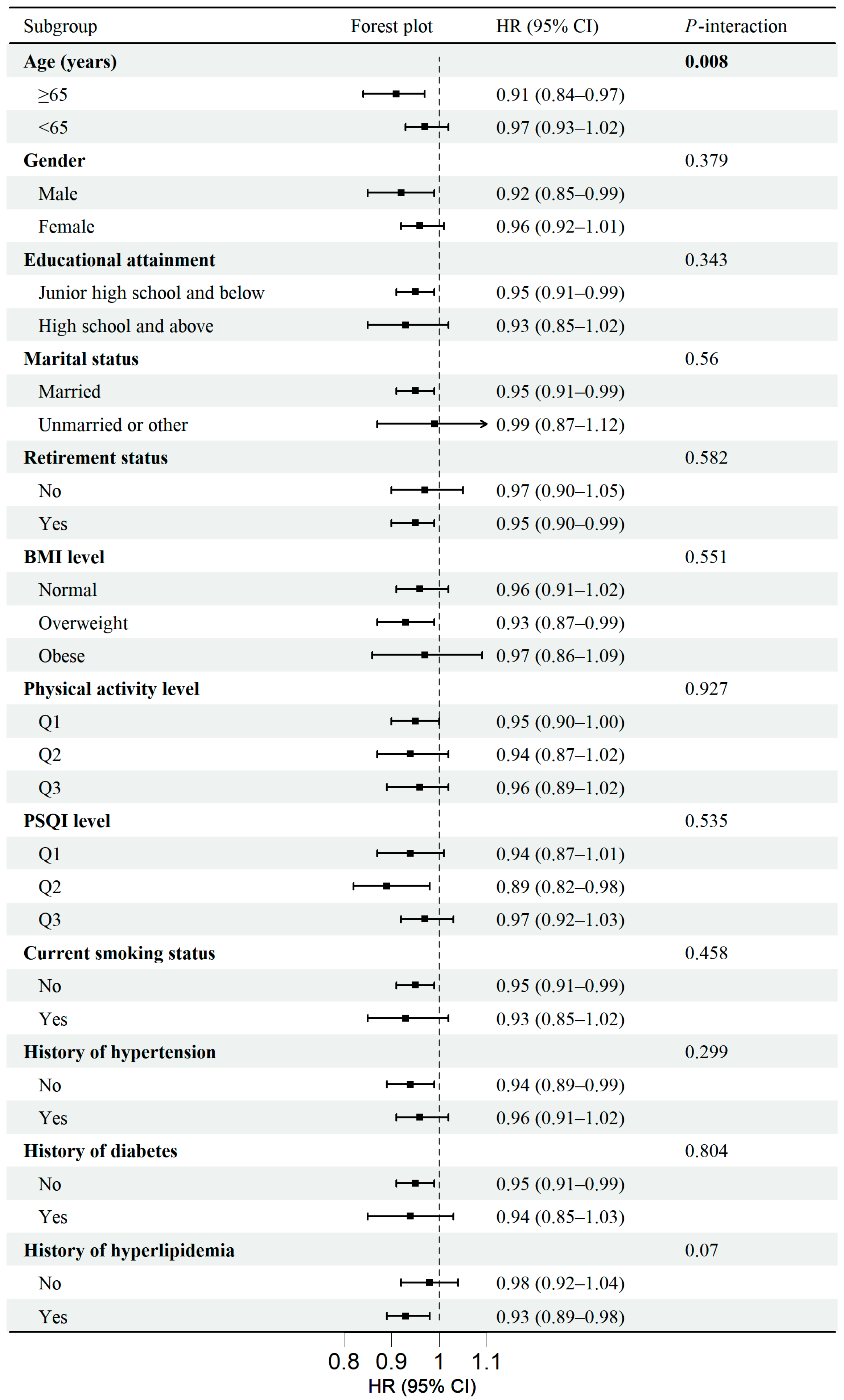
3.3. Subgroup Analyses
3.4. Sensitivity Analyses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| aMED | Alternate Mediterranean diet score |
| MD | Mediterranean diet |
| SSACB | Shanghai Suburban Adult Cohort and Biobank |
| FFQ | Food frequency questionnaire |
| ICD-10 | International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| CHD | Coronary heart disease |
| EMRS | Electronic medical record system |
| IPAQ | International physical activity questionnaire |
| MET | Metabolic equivalent of task |
| PSQI | Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index |
| RCS | Restricted cubic spline |
| BDNF | Brain-derived neurotrophic factor |
| HDL | High-density lipoprotein |
References
- GBD 2019 Mental Disorders Collaborators. Global, Regional, and National Burden of 12 Mental Disorders in 204 Countries and Territories, 1990–2019: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet Psychiatry 2022, 9, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nichols, E.; Steinmetz, J.D.; Vollset, S.E.; Fukutaki, K.; Chalek, J.; Abd-Allah, F.; Abdoli, A.; Abualhasan, A.; Abu-Gharbieh, E.; Akram, T.T.; et al. Estimation of the Global Prevalence of Dementia in 2019 and Forecasted Prevalence in 2050: An Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet Public Health 2022, 7, e105–e125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Xu, X.; Huang, Y.; Li, T.; Ma, C.; Xu, G.; Yin, H.; Xu, X.; Ma, Y.; Wang, L.; et al. Prevalence of Depressive Disorders and Treatment in China: A Cross-Sectional Epidemiological Study. Lancet Psychiatry 2021, 8, 981–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buckman, J.E.; Underwood, A.; Clarke, K.; Saunders, R.; Hollon, S.D.; Fearon, P.; Pilling, S. Risk Factors for Relapse and Recurrence of Depression in Adults and How They Operate: A Four-Phase Systematic Review and Meta-Synthesis. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 2018, 64, 13–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammen, C. Risk Factors for Depression: An Autobiographical Review. Annu. Rev. Clin. Psychol. 2018, 14, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.-M.; Ma, Y.; Du, L.-T.; Wang, K.; Li, Z.; Zhu, W.; Sun, Y.-H.; Lu, L.; Bao, Y.-P.; Li, S.-X. Sleep Disorders and Non-Sleep Circadian Disorders Predict Depression: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Longitudinal Studies. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2022, 134, 104532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, M.; Garcia, L.; Abbas, A.; Strain, T.; Schuch, F.B.; Golubic, R.; Kelly, P.; Khan, S.; Utukuri, M.; Laird, Y.; et al. Association Between Physical Activity and Risk of Depression: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. JAMA Psychiatry 2022, 79, 550–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marx, W.; Lane, M.; Hockey, M.; Aslam, H.; Berk, M.; Walder, K.; Borsini, A.; Firth, J.; Pariante, C.M.; Berding, K.; et al. Diet and Depression: Exploring the Biological Mechanisms of Action. Mol. Psychiatry 2021, 26, 134–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zajkowska, Z.; Walsh, A.; Zonca, V.; Gullett, N.; Pedersen, G.A.; Kieling, C.; Swartz, J.R.; Karmacharya, R.; Fisher, H.L.; Kohrt, B.A.; et al. A Systematic Review of the Association between Biological Markers and Environmental Stress Risk Factors for Adolescent Depression. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2021, 138, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandt, L.; Liu, S.; Heim, C.; Heinz, A. The Effects of Social Isolation Stress and Discrimination on Mental Health. Transl. Psychiatry 2022, 12, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarris, J.; Logan, A.C.; Akbaraly, T.N.; Amminger, G.P.; Balanzá-Martínez, V.; Freeman, M.P.; Hibbeln, J.; Matsuoka, Y.; Mischoulon, D.; Mizoue, T.; et al. Nutritional Medicine as Mainstream in Psychiatry. Lancet Psychiatry 2015, 2, 271–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, W.; Löf, M.; Chen, R.; Hultman, C.M.; Fang, F.; Sandin, S. Mediterranean Diet and Depression: A Population-Based Cohort Study. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2021, 18, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matison, A.P.; Mather, K.A.; Flood, V.M.; Reppermund, S. Associations between Nutrition and the Incidence of Depression in Middle-Aged and Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Prospective Observational Population-Based Studies. Ageing Res. Rev. 2021, 70, 101403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuoka, Y.J.; Sawada, N.; Mimura, M.; Shikimoto, R.; Nozaki, S.; Hamazaki, K.; Uchitomi, Y.; Tsugane, S. Dietary Fish, n-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Consumption, and Depression Risk in Japan: A Population-Based Prospective Cohort Study. Transl. Psychiatry 2017, 7, e1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Song, M.; Eliassen, A.H.; Wang, M.; Fung, T.T.; Clinton, S.K.; Rimm, E.B.; Hu, F.B.; Willett, W.C.; Tabung, F.K.; et al. Optimal Dietary Patterns for Prevention of Chronic Disease. Nat. Med. 2023, 29, 719–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metcalfe-Roach, A.; Yu, A.C.; Golz, E.; Cirstea, M.; Sundvick, K.; Kliger, D.; Foulger, L.H.; Mackenzie, M.; Finlay, B.B.; Appel-Cresswell, S. MIND and Mediterranean Diets Associated with Later Onset of Parkinson’s Disease. Mov. Disord. 2021, 36, 977–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballarini, T.; Melo van Lent, D.; Brunner, J.; Schröder, A.; Wolfsgruber, S.; Altenstein, S.; Brosseron, F.; Buerger, K.; Dechent, P.; Dobisch, L.; et al. Mediterranean Diet, Alzheimer Disease Biomarkers and Brain Atrophy in Old Age. Neurology 2021, 96, e2920–e2932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho-Júnior, H.J.; Trichopoulou, A.; Panza, F. Cross-Sectional and Longitudinal Associations between Adherence to Mediterranean Diet with Physical Performance and Cognitive Function in Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Ageing Res. Rev. 2021, 70, 101395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trichopoulou, A.; Costacou, T.; Bamia, C.; Trichopoulos, D. Adherence to a Mediterranean Diet and Survival in a Greek Population. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 2599–2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fung, T.T.; Rexrode, K.M.; Mantzoros, C.S.; Manson, J.E.; Willett, W.C.; Hu, F.B. Mediterranean Diet and Incidence of and Mortality from Coronary Heart Disease and Stroke in Women. Circulation 2009, 119, 1093–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crous-Bou, M.; Fung, T.T.; Prescott, J.; Julin, B.; Du, M.; Sun, Q.; Rexrode, K.M.; Hu, F.B.; De Vivo, I. Mediterranean Diet and Telomere Length in Nurses’ Health Study: Population Based Cohort Study. BMJ 2014, 349, g6674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarem, N.; Chau, K.; Miller, E.C.; Gyamfi-Bannerman, C.; Tous, I.; Booker, W.; Catov, J.M.; Haas, D.M.; Grobman, W.A.; Levine, L.D.; et al. Association of a Mediterranean Diet Pattern with Adverse Pregnancy Outcomes Among US Women. JAMA Netw. Open 2022, 5, e2248165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, E.Y.; Mahurkar-Joshi, S.; Liu, C.; Jaffe, N.; Labus, J.S.; Dong, T.S.; Gupta, A.; Patel, S.; Mayer, E.A.; Chang, L. The Association Between a Mediterranean Diet and Symptoms of Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 22, 164–172.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vries, E.; Van Schrojenstein Lantman, M.; Hoebregts, V.; Mackus, M.; Garssen, J.; Verster, J.C.; Scholey, A. Mediterranean Diet and Mood. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2017, 27, S879–S880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esgunoglu, L.; Jennings, A.; Connole, E.S.; Murphy, K.J.; Minihane, A.M. Short-Term Effects of a Mediterranean-Style Dietary Pattern on Cognition and Mental Well-Being: A Systematic Review of Clinical Trials. Br. J. Nutr. 2022, 128, 1247–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiei, F.; Salari-Moghaddam, A.; Larijani, B.; Esmaillzadeh, A. Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet and Risk of Depression: A Systematic Review and Updated Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. Nutr. Rev. 2019, 77, 230–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lassale, C.; Batty, G.D.; Baghdadli, A.; Jacka, F.; Sánchez-Villegas, A.; Kivimäki, M.; Akbaraly, T. Healthy Dietary Indices and Risk of Depressive Outcomes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. Mol. Psychiatry 2019, 24, 965–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gianfredi, V.; Koster, A.; Odone, A.; Amerio, A.; Signorelli, C.; Schaper, N.C.; Bosma, H.; Köhler, S.; Dagnelie, P.C.; Stehouwer, C.D.A.; et al. Associations of Dietary Patterns with Incident Depression: The Maastricht Study. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hershey, M.S.; Sanchez-Villegas, A.; Sotos-Prieto, M.; Fernandez-Montero, A.; Pano, O.; Lahortiga-Ramos, F.; Martínez-González, M.Á.; Ruiz-Canela, M. The Mediterranean Lifestyle and the Risk of Depression in Middle-Aged Adults. J. Nutr. 2022, 152, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marozoff, S.; Veugelers, P.J.; Dabravolskaj, J.; Eurich, D.T.; Ye, M.; Maximova, K. Diet Quality and Health Service Utilization for Depression: A Prospective Investigation of Adults in Alberta’s Tomorrow Project. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lugon, G.; Hernáez, Á.; Jacka, F.N.; Marrugat, J.; Ramos, R.; Garre-Olmo, J.; Elosua, R.; Lassale, C. Association between Different Diet Quality Scores and Depression Risk: The REGICOR Population-Based Cohort Study. Eur. J. Nutr. 2024, 63, 2885–2895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Li, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, D. Intakes of Specific Categories of Vegetables and Fruits Are Inversely Associated with Depressive Symptoms Among Adults. J. Epidemiol. 2021, 31, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, R.; Wang, L.; Jin, K.; Cao, S.; Wu, C.; Guo, J.; Chen, J.; Tang, H.; Tang, M. Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids Supplementation Alleviate Anxiety Rather Than Depressive Symptoms Among First-Diagnosed, Drug-Naïve Major Depressive Disorder Patients: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 876152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Q.; Yu, B.; He, H.; Zhang, Q.; Meng, G.; Wu, H.; Du, H.; Liu, L.; Shi, H.; Xia, Y.; et al. Nut Consumption Is Associated with Depressive Symptoms among Chinese Adults. Depress. Anxiety 2016, 33, 1065–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Chen, B.; Wang, R.; Zhu, M.; Shao, Y.; Wang, N.; Liu, X.; Zhang, T.; Jiang, F.; Wang, W.; et al. Cohort Profile: Protocol and Baseline Survey for the Shanghai Suburban Adult Cohort and Biobank (SSACB) Study. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e035430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, K.; Cui, S.; Tang, M.; Wu, Y.; Xiang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Tong, X.; Jiang, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Zhao, G. Adherence to DASH Dietary Pattern and Its Association with Incident Hyperuricemia Risk: A Prospective Study in Chinese Community Residents. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-González, M.A.; García-López, M.; Bes-Rastrollo, M.; Toledo, E.; Martínez-Lapiscina, E.H.; Delgado-Rodriguez, M.; Vazquez, Z.; Benito, S.; Beunza, J.J. Mediterranean Diet and the Incidence of Cardiovascular Disease: A Spanish Cohort. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2011, 21, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitrou, P.N.; Kipnis, V.; Thiébaut, A.C.M.; Reedy, J.; Subar, A.F.; Wirfält, E.; Flood, A.; Mouw, T.; Hollenbeck, A.R.; Leitzmann, M.F.; et al. Mediterranean Dietary Pattern and Prediction of All-Cause Mortality in a US Population: Results from the NIH-AARP Diet and Health Study. Arch. Intern. Med. 2007, 167, 2461–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Gu, Y.; Meng, G.; Wu, H.; Zhang, S.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Huang, T.; Niu, K. Quality of Plant-Based Diet and the Risk of Dementia and Depression among Middle-Aged and Older Population. Age Ageing 2023, 52, afad070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, C.L.; Marshall, A.L.; Sjöström, M.; Bauman, A.E.; Booth, M.L.; Ainsworth, B.E.; Pratt, M.; Ekelund, U.; Yngve, A.; Sallis, J.F.; et al. International Physical Activity Questionnaire: 12-Country Reliability and Validity. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2003, 35, 1381–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buysse, D.J.; Reynolds, C.F.; Monk, T.H.; Berman, S.R.; Kupfer, D.J. The Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index: A New Instrument for Psychiatric Practice and Research. Psychiatry Res. 1989, 28, 193–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, B.O.; Berdzuli, N.; Ilbawi, A.; Kestel, D.; Kluge, H.P.; Krech, R.; Mikkelsen, B.; Neufeld, M.; Poznyak, V.; Rekve, D.; et al. Health and Cancer Risks Associated with Low Levels of Alcohol Consumption. Lancet Public. Health 2023, 8, e6–e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Wang, H.; Li, M.; Shen, Q.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Peng, J.; Rong, X.; Peng, Y. Effect of Alcohol Use Disorders and Alcohol Intake on the Risk of Subsequent Depressive Symptoms: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Cohort Studies. Addiction 2020, 115, 1224–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masana, M.F.; Haro, J.M.; Mariolis, A.; Piscopo, S.; Valacchi, G.; Bountziouka, V.; Anastasiou, F.; Zeimbekis, A.; Tyrovola, D.; Gotsis, E.; et al. Mediterranean Diet and Depression among Older Individuals: The Multinational MEDIS Study. Exp. Gerontol. 2018, 110, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, Y.-G.; Pae, C.; Lee, S.-H.; Yook, K.-H.; Park, C.I. Relationship between Mediterranean Diet and Depression in South Korea: The Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1219743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bizzozero-Peroni, B.; Martínez-Vizcaíno, V.; Fernández-Rodríguez, R.; Jiménez-López, E.; Núñez de Arenas-Arroyo, S.; Saz-Lara, A.; Díaz-Goñi, V.; Mesas, A.E. The Impact of the Mediterranean Diet on Alleviating Depressive Symptoms in Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Nutr. Rev. 2025, 83, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saura-Calixto, F.; Goñi, I. Definition of the Mediterranean Diet Based on Bioactive Compounds. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2009, 49, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corella, D.; Coltell, O.; Macian, F.; Ordovás, J.M. Advances in Understanding the Molecular Basis of the Mediterranean Diet Effect. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 9, 227–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bizzozero-Peroni, B.; Ortolá, R.; Martínez-Vizcaíno, V.; Rodríguez-Artalejo, F.; Fernández-Rodríguez, R.; Banegas, J.R.; Lopez-Garcia, E.; Mesas, A.E. Proinflammatory Dietary Pattern and Depression Risk in Older Adults: Prospective Analyses from the Seniors-ENRICA Studies. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 41, 2614–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, I.J.; Idilman, R.; Fagan, A.; Turan, D.; Ajayi, L.; Le Guennec, A.D.; Taylor-Robinson, S.D.; Karakaya, F.; Gavis, E.; Andrew Atkinson, R.; et al. Metabolomics and Microbial Composition Increase Insight into the Impact of Dietary Differences in Cirrhosis. Liver Int. 2020, 40, 416–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maskarinec, G.; Hullar, M.A.J.; Monroe, K.R.; Shepherd, J.A.; Hunt, J.; Randolph, T.W.; Wilkens, L.R.; Boushey, C.J.; Le Marchand, L.; Lim, U.; et al. Fecal Microbial Diversity and Structure Are Associated with Diet Quality in the Multiethnic Cohort Adiposity Phenotype Study. J. Nutr. 2019, 149, 1575–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meslier, V.; Laiola, M.; Roager, H.M.; De Filippis, F.; Roume, H.; Quinquis, B.; Giacco, R.; Mennella, I.; Ferracane, R.; Pons, N.; et al. Mediterranean Diet Intervention in Overweight and Obese Subjects Lowers Plasma Cholesterol and Causes Changes in the Gut Microbiome and Metabolome Independently of Energy Intake. Gut 2020, 69, 1258–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, S.; Kim, W.J.; Lok, J.; Lee, S.-R.; Besancon, E.; Luo, B.-H.; Stins, M.F.; Wang, X.; Dedhar, S.; Lo, E.H. Neuroprotection via Matrix-Trophic Coupling between Cerebral Endothelial Cells and Neurons. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 7582–7587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Villegas, A.; Galbete, C.; Martinez-González, M.A.; Martinez, J.A.; Razquin, C.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; Estruch, R.; Buil-Cosiales, P.; Martí, A. The Effect of the Mediterranean Diet on Plasma Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) Levels: The PREDIMED-NAVARRA Randomized Trial. Nutr. Neurosci. 2011, 14, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanllorente, A.; Soria-Florido, M.T.; Castañer, O.; Lassale, C.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; Martínez-González, M.Á.; Subirana, I.; Ros, E.; Corella, D.; Estruch, R.; et al. A Lifestyle Intervention with an Energy-Restricted Mediterranean Diet and Physical Activity Enhances HDL Function: A Substudy of the PREDIMED-Plus Randomized Controlled Trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 114, 1666–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chourpiliadis, C.; Zeng, Y.; Lovik, A.; Wei, D.; Valdimarsdóttir, U.; Song, H.; Hammar, N.; Fang, F. Metabolic Profile and Long-Term Risk of Depression, Anxiety, and Stress-Related Disorders. JAMA Netw. Open 2024, 7, e244525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Wang, Y.U.; Wang, H.; Liu, Z.; Yu, X.; Yan, J.; Yu, Y.; Kou, C.; Xu, X.; Lu, J.; et al. Prevalence of Mental Disorders in China: A Cross-Sectional Epidemiological Study. Lancet Psychiatry 2019, 6, 211–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baierle, M.; Nascimento, S.N.; Moro, A.M.; Brucker, N.; Freitas, F.; Gauer, B.; Durgante, J.; Bordignon, S.; Zibetti, M.; Trentini, C.M.; et al. Relationship between Inflammation and Oxidative Stress and Cognitive Decline in the Institutionalized Elderly. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2015, 2015, 804198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawdin, B.J.; Mellon, S.H.; Dhabhar, F.S.; Epel, E.S.; Puterman, E.; Su, Y.; Burke, H.M.; Reus, V.I.; Rosser, R.; Hamilton, S.P.; et al. Dysregulated Relationship of Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in Major Depression. Brain Behav. Immun. 2013, 31, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, S.; Nagappa, A.N.; Patil, C.R. Role of Oxidative Stress in Depression. Drug Discov. Today 2020, 25, 1270–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitsavos, C.; Panagiotakos, D.B.; Tzima, N.; Chrysohoou, C.; Economou, M.; Zampelas, A.; Stefanadis, C. Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet Is Associated with Total Antioxidant Capacity in Healthy Adults: The ATTICA Study2. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 82, 694–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estruch, R. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of the Mediterranean Diet: The Experience of the PREDIMED Study. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2010, 69, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jimenez-Torres, J.; Alcalá-Diaz, J.F.; Torres-Peña, J.D.; Gutierrez-Mariscal, F.M.; Leon-Acuña, A.; Gómez-Luna, P.; Fernández-Gandara, C.; Quintana-Navarro, G.M.; Fernandez-Garcia, J.C.; Perez-Martinez, P.; et al. Mediterranean Diet Reduces Atherosclerosis Progression in Coronary Heart Disease: An Analysis of the CORDIOPREV Randomized Controlled Trial. Stroke 2021, 52, 3440–3449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, N.; Lin, Y.; Ye, Z.; Yang, C.; Huang, Y.; Duan, Q.; Xie, S. The Relationship between Dyslipidemia and Inflammation among Adults in East Coast China: A Cross-Sectional Study. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 937201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteve, E.; Ricart, W.; Fernández-Real, J.M. Dyslipidemia and Inflammation: An Evolutionary Conserved Mechanism. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 24, 16–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appel, L.J.; Brands, M.W.; Daniels, S.R.; Karanja, N.; Elmer, P.J.; Sacks, F.M.; American Heart Association. Dietary Approaches to Prevent and Treat Hypertension: A Scientific Statement from the American Heart Association. Hypertension 2006, 47, 296–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goode, A.D.; Reeves, M.M.; Eakin, E.G. Telephone-Delivered Interventions for Physical Activity and Dietary Behavior Change: An Updated Systematic Review. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2012, 42, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Q.; Xia, Y.; Wu, Q.; Chang, Q.; Niu, K.; Zhao, Y. Validity of the Food Frequency Questionnaire for Adults in Nutritional Epidemiological Studies: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 1670–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Ma, X.; Yu, Y.; Wang, G.; Zhuang, N.; Liu, H.; Wu, H.; Zhang, H.; Yu, F.; Hou, Y.; et al. “Healthy China 2030”: Promoting Health and Longevity of the Whole Nation. In Tutorial for Outline of the Healthy China 2030 Plan; Li, B., Ed.; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 1–9. ISBN 978-981-329-603-9. [Google Scholar]
| Characteristics | Adherence to the aMED, N (%) | p Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overall (n = 52,232) | Low (0–3) (n = 18,294) | Moderate (4–5) (n = 22,960) | High (6–9) (n = 10,978) | ||
| Age (years) | 58 (50–65) | 59 (51–65) | 57 (49–64) | 58 (50–65) | <0.001 |
| Males | 20,201 (38.7) | 6753 (36.9) | 9051 (39.4) | 4397 (40.1) | <0.001 |
| Educational attainment | <0.001 | ||||
| Junior high school or below | 37,232 (71.3) | 14,627 (80.0) | 15,969 (69.5) | 6636 (60.5) | |
| High school or above | 15,000 (28.7) | 3667 (20.0) | 6991 (30.5) | 4342 (39.5) | |
| Marital status | <0.001 | ||||
| Married | 47,688 (91.3) | 16,750 (91.6) | 20,968 (91.3) | 9970 (90.8) | |
| Unmarried | 1082 (2.1) | 315 (1.7) | 530 (2.3) | 237 (2.2) | |
| Divorced or other | 3462 (6.6) | 1229 (6.7) | 1462 (6.4) | 771 (7.0) | |
| Retired | 31,400 (60.1) | 11,272 (61.6) | 13,294 (57.9) | 6834 (62.3) | <0.001 |
| Total energy intake (kcal/d) | 1298.5 (1015.1–1671.0) | 1078.3 (872.1–1375.4) | 1345.3 (1073.7–1700.0) | 1583.2 (1285.7–1973.3) | <0.001 |
| BMI level | 0.041 | ||||
| Normal | 25,746 (49.3) | 9031 (49.4) | 11,440 (49.8) | 5275 (48.1) | |
| Overweight | 20,033 (38.4) | 7026 (38.4) | 8688 (37.8) | 4319 (39.3) | |
| Obese | 6453 (12.3) | 2237 (12.2) | 2832 (12.4) | 1384 (12.6) | |
| Smoking status | <0.001 | ||||
| Never | 40,695 (77.9) | 14,400 (78.7) | 17,880 (77.9) | 8415 (76.6) | |
| Stopped ≥ 10 years | 633 (1.2) | 243 (1.3) | 273 (1.2) | 117 (1.1) | |
| Stopped < 10 years | 502 (1.0) | 178 (1.0) | 215 (0.9) | 109 (1.0) | |
| Current | 10,402 (19.9) | 3473 (19.0) | 4592 (20.0) | 2337 (21.3) | |
| PSQI | 4 (2–6) | 4 (2–6) | 4 (2–6) | 4 (2–6) | <0.001 1 |
| Physical activity level | 0.214 | ||||
| Q1 | 23,353 (44.7) | 8101 (44.3) | 10,334 (45.0) | 4918 (44.8) | |
| Q2 | 11,832 (22.7) | 4134 (22.6) | 5251 (22.9) | 2447 (22.3) | |
| Q3 | 17,047 (32.6) | 6059 (33.1) | 7375 (32.1) | 3613 (32.9) | |
| Family history of depression | 291 (0.6) | 98 (0.5) | 132 (0.6) | 61 (0.6) | 0.868 |
| History of chronic diseases | |||||
| Hypertension | 24,988 (47.8) | 8773 (48.0) | 10,982 (47.8) | 5233 (47.7) | 0.892 |
| Diabetes | 7085 (13.6) | 2525 (13.8) | 3100 (13.5) | 1460 (13.3) | 0.445 |
| Hyperlipidemia | 29,415 (56.3) | 10,244 (56.0) | 12,833 (55.9) | 6338 (57.7) | 0.003 |
| Dementia | 111 (0.2) | 44 (0.2) | 41 (0.2) | 26 (0.2) | 0.328 |
| Parkinson’s disease | 188 (0.4) | 68 (0.4) | 83 (0.4) | 37 (0.3) | 0.890 |
| Adherence to the aMED | Cases/Person-Year | HR (95% CI) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model 1 1 | Model 2 2 | Model 3 3 | ||
| Low (0–3) | 517/119,729 | Reference | Reference | Reference |
| Moderate (4–5) | 495/144,031 | 0.82 (0.73, 0.93) | 0.87 (0.77, 0.99) | 0.87 (0.76, 0.99) |
| High (6–9) | 208/64,592 | 0.74 (0.63, 0.87) | 0.83 (0.70, 0.99) | 0.83 (0.70, 0.98) |
| Per unit increase | 0.92 (0.89, 0.96) | 0.95 (0.91, 0.99) | 0.95 (0.91, 0.99) | |
| p-trend | <0.001 | 0.010 | 0.009 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, K.; Wu, Y.; Yi, L.; Wu, Y.; Deng, Y.; Xu, X.; Wang, B.; Jiang, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Zhao, G. Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet and Risk of Depression: A Cohort Study in Chinese Community Residents. Nutrients 2025, 17, 942. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17060942
Zhang K, Wu Y, Yi L, Wu Y, Deng Y, Xu X, Wang B, Jiang Y, Zhao Q, Zhao G. Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet and Risk of Depression: A Cohort Study in Chinese Community Residents. Nutrients. 2025; 17(6):942. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17060942
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Kexin, Yanan Wu, Liping Yi, Yiling Wu, Yingqi Deng, Xinxin Xu, Biying Wang, Yonggen Jiang, Qi Zhao, and Genming Zhao. 2025. "Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet and Risk of Depression: A Cohort Study in Chinese Community Residents" Nutrients 17, no. 6: 942. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17060942
APA StyleZhang, K., Wu, Y., Yi, L., Wu, Y., Deng, Y., Xu, X., Wang, B., Jiang, Y., Zhao, Q., & Zhao, G. (2025). Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet and Risk of Depression: A Cohort Study in Chinese Community Residents. Nutrients, 17(6), 942. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17060942






