Alpha-Lipoic Acid Reduces Neuroinflammation and Oxidative Stress Induced by Dapsone in an Animal Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
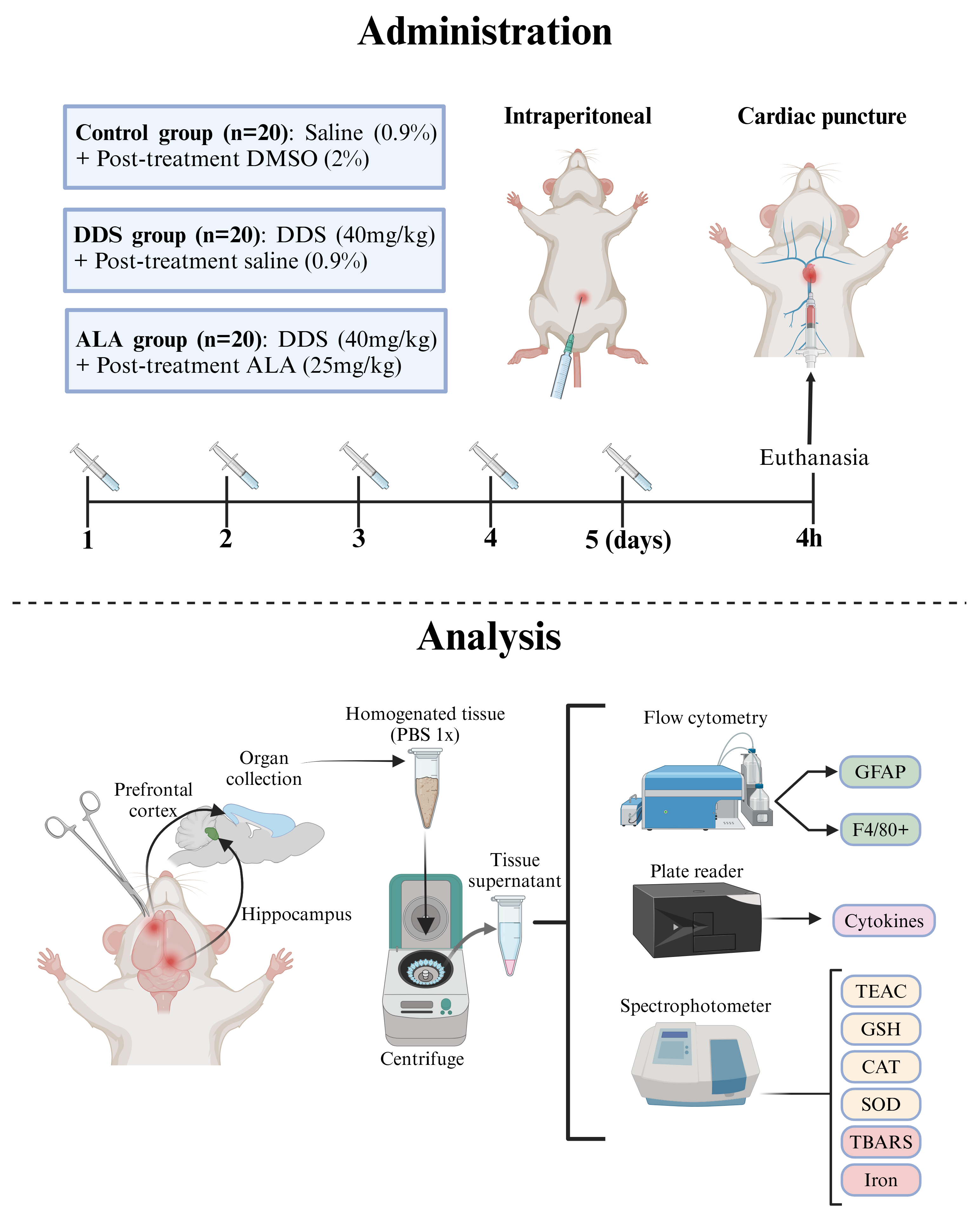
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Ethics Statement
2.3. Mice
2.4. Administration of Dapsone and ALA
2.5. Determination of Trolox Equivalent Antioxidant Capacity (TEAC)
2.6. Determination of Superoxide Dismutase Activity
2.7. Determination of Catalase Activity
2.8. Determination of Reduced Glutathione Activity
2.9. Determination of Lipid Peroxidation
2.10. Determination of Iron Concentration
2.11. Flow Cytometry
2.12. Determination of IL-1β, IL-17, IL-4 and BDNF Expression
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
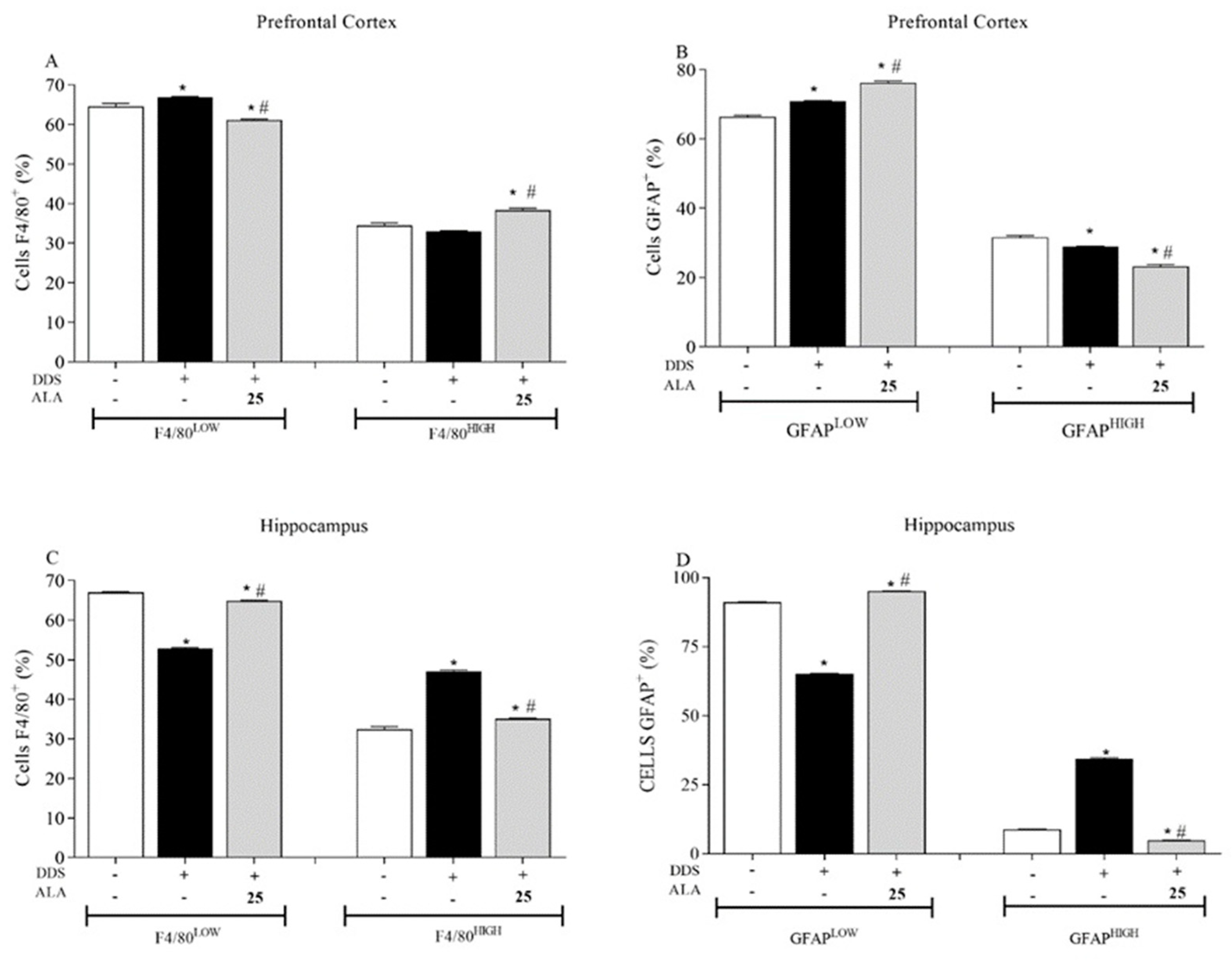
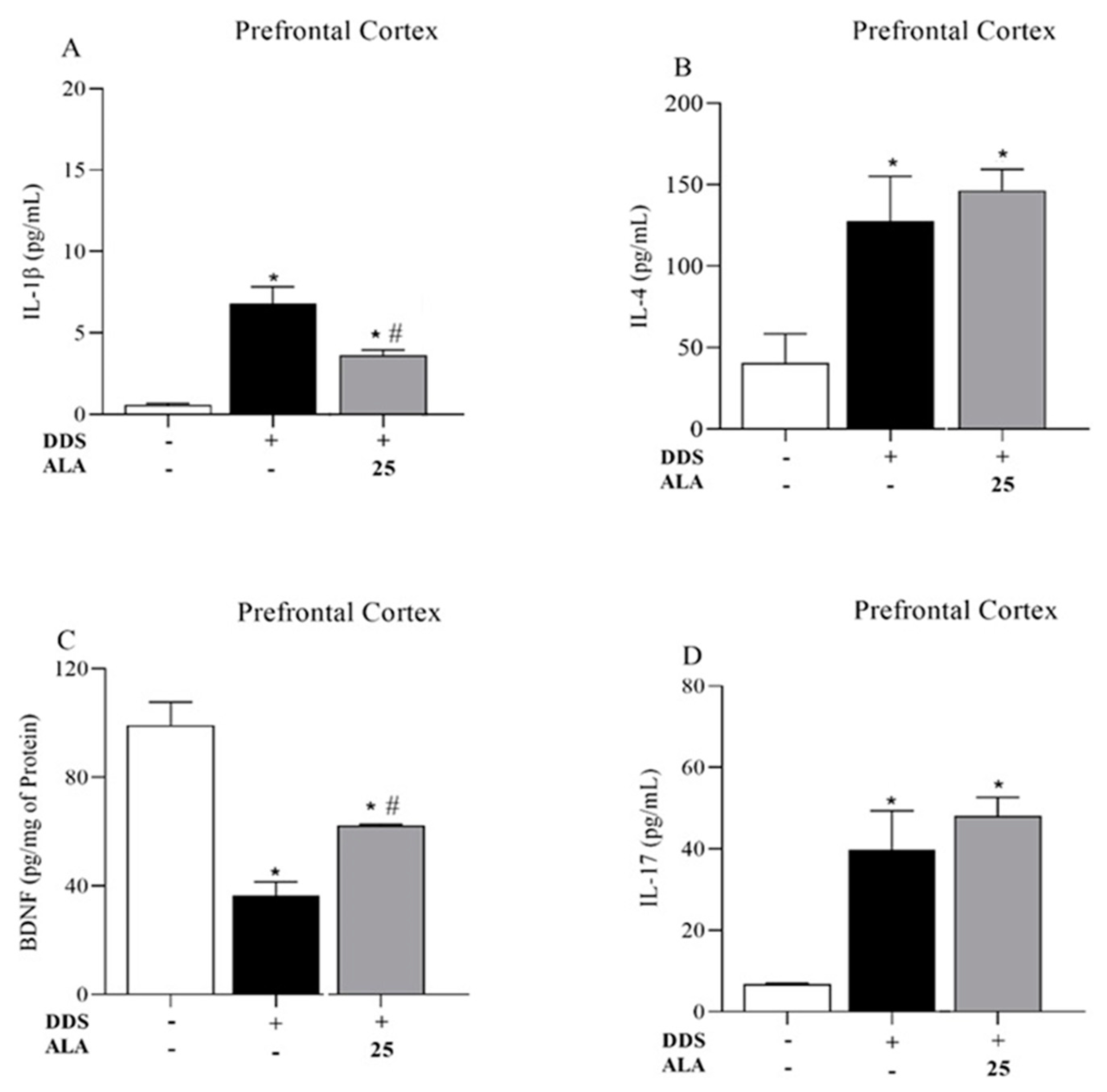
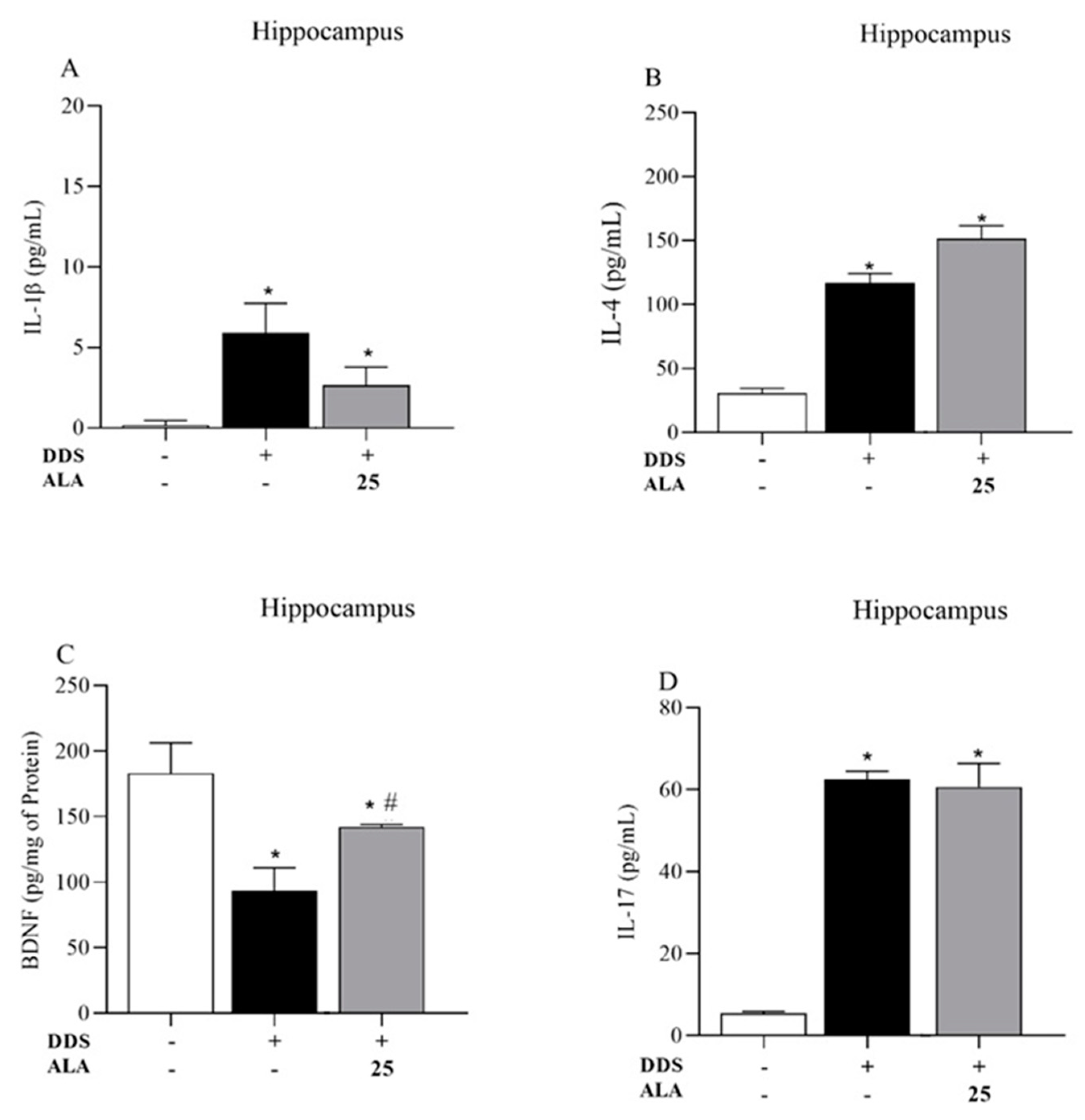
3.1. Effects of DDS and ALA on the Cellular Profile and Cytokines in the Prefrontal Cortex and Hippocampus
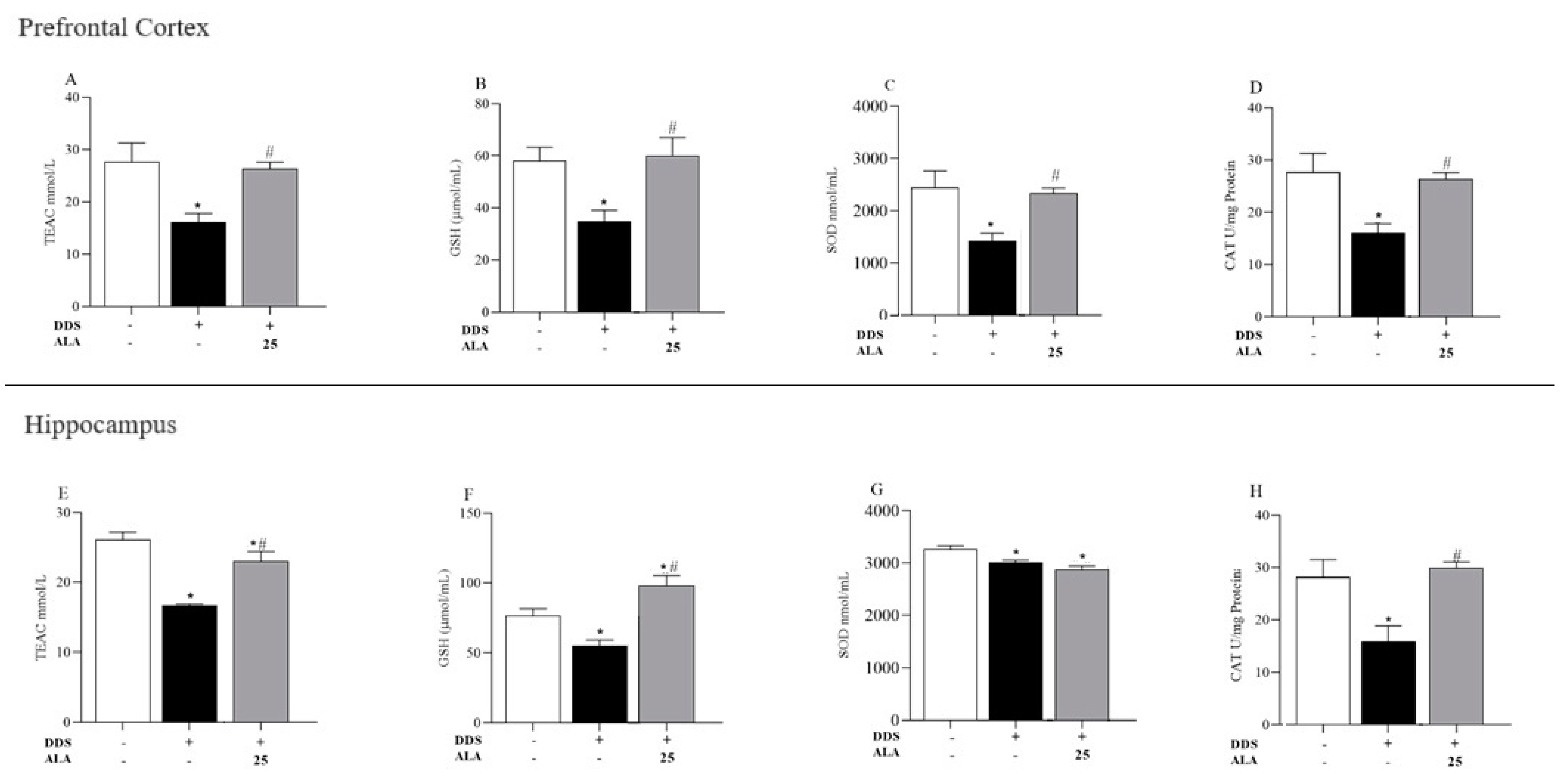
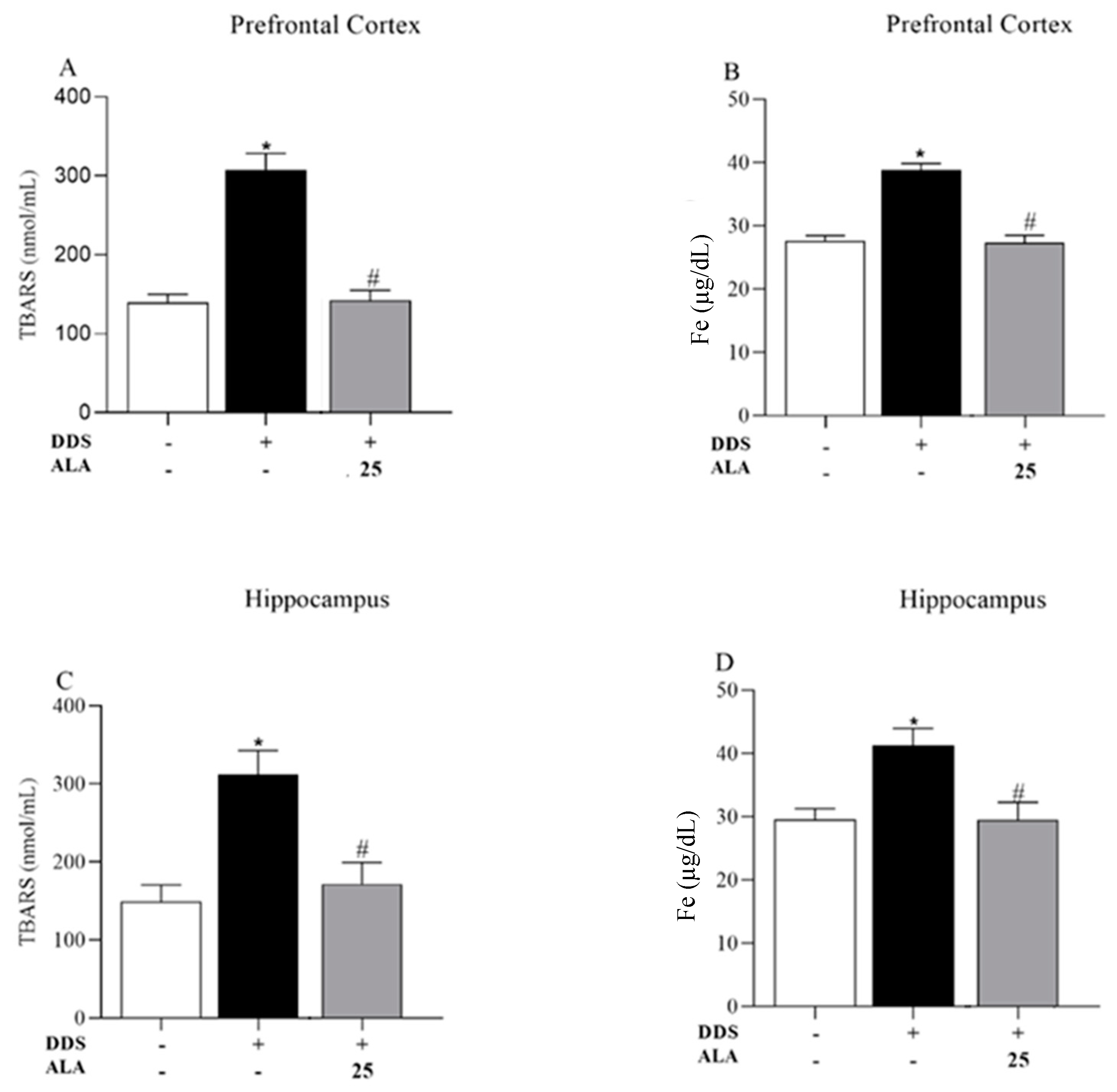
3.2. Effects of DDS and ALA on Antioxidant Capacity and Oxidative Stress in the Prefrontal Cortex and Hippocampus
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Galrão, L.; Reale, J.; Lima, I.; Santiago, M. Eficácia da dapsona em dois casos de dermatomiosite amiopática. An. Bras. Dermatol. 2006, 81, 181–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guragain, S.; Upadhayay, N.; Bhattarai, B.M. Adverse reactions in leprosy patients who underwent dapsone multidrug therapy: A retrospective study. Clin. Pharmacol. 2017, 9, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, R.J.; Zucca, F.A.; Duyn, J.H.; Crichton, R.R.; Zecca, L. The role of iron in brain ageing and neurodegenerative disorders. Lancet Neurol. 2014, 13, 1045–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carocci, A.; Catalano, A.; Sinicropi, M.S.; Genchi, G. Oxidative stress and neurodegeneration: The involvement of iron. BioMetals 2018, 31, 715–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, E.S.; de A Roland, I.; Maroja, M.d.F.; Marcon, J.L. Vitamin A and lipid peroxidation in patients with different forms of leprosy. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. Sao Paulo 2007, 49, 211–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Chu, J.M.T.; Yan, T.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Chang, R.C.C.; Wong, G.T.C. Short-term resistance exercise inhibits neuroinflammation and attenuates neuropathological changes in 3xTg Alzheimer’s disease mice. J. Neuroinflamm. 2020, 17, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Yuan, M.; Yang, S.; Chen, X.; Wu, J.; Wen, M.; Yan, K.; Bi, X. Enriched environment improves post-stroke cognitive impairment and inhibits neuroinflammation and oxidative stress by activating Nrf2-ARE pathway. Int. J. Neurosci. 2021, 131, 641–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Cao, J.B.; Zhang, L.M.; Li, Y.F.; Mi, W.D. Deferoxamine attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced neuroinflammation and memory impairment in mice. J. Neuroinflamm. 2015, 12, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urrutia, P.J.; Mena, N.P.; Núñez, M.T. The interplay between iron accumulation, mitochondrial dysfunction, and inflammation during the execution step of neurodegenerative disorders. Front. Pharmacol. 2014, 5, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, A.-K.; Thompson, J.; Chen, L.; Dagda, M.; Dertien, J.; Dossou, K.S.S.; Moaddel, R.; Bergeson, S.E.; Kruman, I.I. Differential sensitivity of prefrontal cortex and hippocampus to alcohol-induced toxicity. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e106945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zlatković, J.; Todorović, N.; Bošković, M.; Pajović, S.B.; Demajo, M.; Filipović, D. Different susceptibility of prefrontal cortex and hippocampus to oxidative stress following chronic social isolation stress. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2014, 393, 43–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fell, J.; Klaver, P.; Lehnertz, K.; Grunwald, T.; Schaller, C.; Elger, C.E.; Fernández, G. Human memory formation is accompanied by rhinal-hippocampal coupling and decoupling. Nat. Neurosci. 2001, 4, 1259–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, A.; Hami, J.; Razavi, S.; Esfandiary, E.; Hejazi, Z. The effect of diabetes mellitus on apoptosis in hippocampus: Cellular and molecular aspects. Int. J. Prev. Med. 2016, 7, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, L.; Jiang, Z.; Cai, Z.; Cai, M.; Zhang, Q.; Ma, Y.; Li, G.; Zhao, F.; Ma, Q. Brain iron deposition analysis using susceptibility weighted imaging and its association with body iron level in patients with mild cognitive impairment. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 8209–8215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Liu, L.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yang, L.; Pu, J.; Zhu, D.; Zhou, C.; Xie, P. The identification of metabolic disturbances in the prefrontal cortex of the chronic restraint stress rat model of depression. Behav. Brain Res. 2016, 305, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, F.; Zheng, J.; Sun, X.; Tang, H. Inward rectifier K+ channel and T-type Ca2+ channel contribute to enhancement of GABAergic transmission induced by β1-adrenoceptor in the prefrontal cortex. Exp. Neurol. 2017, 288, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smaers, J.B.; Gómez-Robles, A.; Parks, A.N.; Sherwood, C.C. Exceptional Evolutionary Expansion of Prefrontal Cortex in Great Apes and Humans. Curr. Biol. 2017, 27, 1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawdin, B.; Mellon, S.; Dhabhar, F.; Epel, E.; Puterman, E.; Su, Y.; Burke, H.; Reus, V.; Rosser, R.; Hamilton, S.; et al. Dysregulated relationship of inflammation and oxidative stress in major depression. Brain Behav. Immun. 2013, 31, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, D.; Li, G.; Liao, X.; Yu, D.; Wu, J.; Zhang, M. Developmental loss of parvalbumin-positive cells in the prefrontal cortex and psychiatric anxiety after intermittent hypoxia exposures in neonatal rats might be mediated by NADPH oxidase-2. Behav. Brain Res. 2016, 296, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadeem, M.S.; Kazmi, I.; Ullah, I.; Muhammad, K.; Anwar, F. Allicin, an antioxidant and neuroprotective agent, ameliorates cognitive impairment. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franzoni, F.; Scarfò, G.; Guidotti, S.; Fusi, J.; Asomov, M.; Pruneti, C. Oxidative Stress and Cognitive Decline: The Neuroprotective Role of Natural Antioxidants. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 729757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.M.; He, W.; Liou, Y.C. The redox language in neurodegenerative diseases: Oxidative post-translational modifications by hydrogen peroxide. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, Y.H.; Kwon, S.H.; Lee, S.Y.; Jang, C.G. Isoorientin improves scopolamine-induced cognitive impairments by restoring the cholinergic system, antioxidant defense, and p-CREB/BDNF signaling in the hippocampus and frontal cortex. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2019, 42, 722–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camiolo, G.; Tibullo, D.; Giallongo, C.; Romano, A.; Parrinello, N.L.; Musumeci, G.; Di Rosa, M.; Vicario, N.; Brundo, M.V.; Amenta, F.; et al. α-lipoic acid reduces iron-induced toxicity and oxidative stress in a model of iron overload. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, S.M.D.; Romeiro, C.F.R.; Rodrigues, C.A.; Cerqueira, A.R.L.; Monteiro, M.C. Mitochondrial dysfunction and alpha-lipoic acid: Beneficial or harmful in Alzheimer’s disease? Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 8409329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, B.; Berkay Yılmaz, Y.; Antika, G.; Boyunegmez Tumer, T.; Fawzi Mahomoodally, M.; Lobine, D.; Akram, M.; Riaz, M.; Capanoglu, E.; Sharopov, F.; et al. Insights on the use of α-lipoic acid for therapeutic purposes. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seifar, F.; Khalili, M.; Khaledyan, H.; Moghadam, S.A.; Izadi, A.; Azimi, A.; Shakouri, S.K. α-Lipoic acid, functional fatty acid, as a novel therapeutic alternative for central nervous system diseases: A review. Nutr. Neurosci. 2019, 22, 306–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghafour-boroujerdi, E.; Rahmani, S.; Sanadgol, N.; Baeeri, M.; Hassani, S. Investigation of alpha-lipoic acid effect on memory impairment considering strain-dependent differences in mice. Life Sci. 2021, 281, 119766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.R.; Shenvi, S.V.; Widlansky, M.; Suh, J.H.; Hagen, T.M. Lipoic Acid as a Potential Therapy for Chronic Diseases Associated with Oxidative Stress. Curr. Med. Chem. 2004, 11, 1135–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shindyapina, A.V.; Komarova, T.V.; Sheshukova, E.V.; Ershova, N.M.; Tashlitsky, V.N.; Kurkin, A.V.; Yusupov, I.R.; Mkrtchyan, G.V.; Shagidulin, M.Y.; Dorokhov, Y.L. The antioxidant cofactor alpha-lipoic acid may control endogenous formaldehyde metabolism in mammals. Front. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arivazhagan, P.; Panneerselvam, C. Neurochemical changes related to ageing in the rat brain and the effect of DL-a-lipoic acid. Exp. Gerontol. 2002, 37, 1487–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fava, A.; Pirritano, D.; Plastino, M.; Cristiano, D.; Puccio, G.; Colica, C.; Ermio, C.; De Bartolo, M.; Mauro, G.; Bosco, D. The Effect of Lipoic Acid Therapy on Cognitive Functioning in Patients with Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Neurodegener. Dis. 2013, 2013, 454253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hager, K.; Kenklies, M.; Mcafoose, J.; Engel, J.; Münch, G. a-Lipoic Acid as a New Treatment Option for Alzheimer’s Disease-a 48 Months Follow-up Analysis; Springer-Verlag: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- de Sousa, C.N.S.; Meneses, L.N.; Vasconcelos, G.S.; Silva, M.C.C.; da Silva, J.C.; Macêdo, D.; de Lucena, D.F.; Vasconcelos, S.M.M. Reversal of corticosterone-induced BDNF alterations by the natural antioxidant alpha-lipoic acid alone and combined with desvenlafaxine: Emphasis on the neurotrophic hypothesis of depression. Psychiatry Res. 2015, 230, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasconcelos, G.S.; Ximenes, N.C.; de Sousa, C.N.S.; Oliveira, T.d.Q.; Lima, L.L.L.; de Lucena, D.F.; Gama, C.S.; Macêdo, D.; Vasconcelos, S.M.M. Alpha-lipoic acid alone and combined with clozapine reverses schizophrenia-like symptoms induced by ketamine in mice: Participation of antioxidant, nitrergic and neurotrophic mechanisms. Schizophr. Res. 2015, 165, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, S.; Zheng, Q.; Zhai, S.; Cai, T.; Xu, L.; Yang, L.; Jiao, L.; Zhang, C. Alpha-Lipoic Acid Mediates Clearance of Iron Accumulation by Regulating Iron Metabolism in a Parkinson’s Disease Model Induced by 6-OHDA. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Liu, H.; Liu, Y.; Wei, W.; Sun, Q.; Wen, D.; Jia, L. Protective effect of alpha-lipoic acid on bisphenol A-induced learning and memory impairment in developing mice: nNOS and keap1/Nrf2 pathway. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 154, 112307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Triggiani, L. Potential therapeutic effects of alpha lipoic acid in memory disorders. Prog. Nutr. 2020, 22, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilska, A.; Dubiel, M.; Sokołowska-Jezewicz, M.; Lorenc-Koci, E.; Włodek, L. Alpha-lipoic acid differently affects the reserpine-induced oxidative stress in the striatum and prefrontal cortex of rat brain. Neuroscience 2007, 146, 1758–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-H.; Wang, D.-W.; Xu, S.-F.; Zhang, S.; Fan, Y.-G.; Yang, Y.-Y.; Guo, S.-Q.; Wang, S.; Guo, T.; Wang, Z.-Y.; et al. α-Lipoic acid improves abnormal behavior by mitigation of oxidative stress, inflammation, ferroptosis, and tauopathy in P301S Tau transgenic mice. Redox Biol. 2018, 14, 535–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergamaschi, M.M.; Alcantara, G.K.S.; Valério, D.A.R.; Queiroz, R.H.C. Curcumin could prevent methemoglobinemia induced by dapsone in rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2011, 49, 1638–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, M.; Gupta, Y.K. Effect of alpha lipoic acid on intracerebroventricular streptozotocin model of cognitive impairment in rats. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2003, 13, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cremer, D.R.; Rabeler, R.; Roberts, A.; Lynch, B. Safety evaluation of α-lipoic acid (ALA). Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2006, 46, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molinelli, E.; Paolinelli, M.; Campanati, A.; Brisigotti, V.; Offidani, A. Metabolic, pharmacokinetic, and toxicological issues surrounding dapsone. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2019, 15, 367–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pellegrini, R.; Proteggente, N.; Pannala, A.; Yang, A.; Rice-Evans, M.E. Antioxidant Activity Applying an Improved ABTS Radical Cation Decolorization Assay. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1999, 26, 1231–1237. [Google Scholar]
- Fridovich, I.; Mccords, J.M. Superoxide Dismutase an Enzymic Function for Erythrocuprein (Hemocuprein)*. J. Biol. Chem. 1969, 244, 6049–6065. [Google Scholar]
- Aebi, H. Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol. 1984, 105, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasconcelos, S.M.L.; Goulart, M.O.F.; Moura, J.B.d.F.; Benfato, M.d.S.; Kubota, L.T. Reactive Oxygen and Nitrogen Species, Antioxidants and Markers of Oxidative Damage in Human Blood: Main Analytical Methods for Their Determination. Quim. Nova 2007, 30, 1323–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liversedge, M.; Kohr, H.I. On A New Aerobic Metabolite Whose Production by Brain is Inhibited by Apomorphine, Emetine, Ergotamine, Epinephrine and menadione. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1944, 82, 292–300. [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarti, S.; Gorai, S.; Pahan, K. A simple protocol for isolating microglia from adult mouse brain. NeuroImmune Pharm. Ther. 2023, 2, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Srakočić, S.; Josić, P.; Trifunović, S.; Gajović, S.; Grčević, D.; Glasnović, A. Proposed practical protocol for flow cytometry analysis of microglia from the healthy adult mouse brain: Systematic review and isolation methods’ evaluation. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2022, 16, 1017976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kim, S.M.; Ha, J.S.; Han, A.R.; Cho, S.W.; Yang, S.J. Effects of α-lipoic acid on LPS-induced neuroinflammation and NLRP3 inflammasome activation through the regulation of BV-2 microglial cells activation. BMB Rep. 2019, 52, 613–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Lv, C.; Sun, Y.; Han, X.; Wang, S.; Mao, Z.; Xin, Y.; Zhang, B. The Role of Alpha-Lipoic Acid in the Pathomechanism of Acute Ischemic Stroke. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 48, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.; Ren, J.; Jiang, L.; Liu, J.; Jiang, B.; Zhang, X. α-lipoic acid attenuates obesity-associated hippocampal neuroinflammation and increases the levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in ovariectomized rats fed a high-fat diet. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2013, 32, 1179–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kotlega, D.; Zembron-Lacny, A.; Morawin, B.; Golab-Janowska, M.; Nowacki, P.; Szczuko, M. Free fatty acids and their inflammatory derivatives affect BDNF in Stroke Patients. Mediators Inflamm. 2020, 2020, 6676247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Li, S.; Chang, C.; Gao, X.; Zhao, J.; Yang, G. Alpha lipoic acid treatment in late middle age improves cognitive function: Proteomic analysis of the protective mechanisms in the hippocampus. Neurosci. Lett. 2023, 798, 137098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Ma, L.; Kulesskaya, N.; Võikar, V.; Tian, L. Microglia are polarized to M1 type in high-anxiety inbred mice in response to lipopolysaccharide challenge. Brain Behav. Immun. 2014, 38, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinicola, S.; Proietti, S.; Cucina, A.; Bizzarri, M.; Fuso, A. Alpha-lipoic acid downregulates IL-1β and IL-6 by DNA hypermethylation in SK-N-BE neuroblastoma cells. Antioxidants 2017, 6, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, L.D.; Le, T.; Fan, G. DNA methylation and its basic function. Neuropsychopharmacology 2013, 38, 23–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della Giustina, A.; Goldim, M.P.; Danielski, L.G.; Florentino, D.; Mathias, K.; Garbossa, L.; Junior, A.N.O.; Fileti, M.E.; Zarbato, G.F.; da Rosa, N.; et al. Alpha-lipoic acid attenuates acute neuroinflammation and long-term cognitive impairment after polymicrobial sepsis. Neurochem. Int. 2017, 108, 436–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.D.; Roychowdhury, S.; Nemes, R.; Vyas, P.M.; Woster, P.M.; Svensson, C.K. Effect of pro-inflammatory cytokines on the toxicity of the arylhydroxylamine metabolites of sulphamethoxazole and dapsone in normal human keratinocytes. Toxicology 2006, 218, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Shahrani, M.; Heales, S.; Hargreaves, I.; Orford, M. Oxidative stress: Mechanistic insights into inherited mitochondrial disorders and Parkinson’s disease. J. Clin. Med. 2017, 6, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanbek, K.; Ozerol, E.; Yilmaz, U.; Yilmaz, N.; Gul, M.; Colak, C. Alpha lipoic acid decreases neuronal damage on brain tissue of STZ-induced diabetic rats. Physiol. Behav. 2022, 248, 113727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzvetanova, E.R. Georgieva, A.P.; Alexandrova, A.V.; Tancheva, L.P.; Lazarova, M.I.; Dragomanova, S.T.; Alova, L.G.; Stefanova, M.O.; Kalfin, R.E. Antioxidant mechanisms in neuroprotective action of lipoic acid on learning and memory of rats with experimental dementia. Bulg. Chem. Commun. 2018, 50, 52–57. [Google Scholar]
- De Freitas, R.M. Lipoic acid alters δ-aminolevulinic dehydratase, glutathione peroxidase and Na+,K+-ATPase activities and glutathione-reduced levels in rat hippocampus after pilocarpine-induced seizures. Cell Mol. Neurobiol. 2010, 30, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, L.; Li, S.; Bai, J.; Zhang, Q.; Han, Z. α-Lipoic acid protects against microcystin-LR induced hepatotoxicity through regeneration of glutathione via activation of Nrf2. Env. Toxicol. 2020, 35, 738–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, A.K.; Ray, A.K.; Mishra, S.K.; Bishen, S.M.; Mishra, H.; Khurana, A. Molecular and Therapeutic Insights of Alpha-Lipoic Acid as a Potential Molecule for Disease Prevention. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 2023, 33, 272–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaasch, J.A.; Lockman, P.R.; Geldenhuys, W.J.; Allen, D.D.; Van Der Schyf, C.J. Brain iron toxicity: Differential responses of astrocytes, neurons, and endothelial cells. Neurochem. Res. 2007, 32, 1196–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wessling-Resnick, M. Iron homeostasis and the inflammatory response. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2010, 30, 105–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piloni, N.E.; Fermandez, V.; Videla, L.A.; Puntarulo, S. Acute iron overload and oxidative stress in brain. Toxicology 2013, 314, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, M.K.; Labhasetwar, V. Nanoparticle-mediated delivery of superoxide dismutase to the brain: An effective strategy to reduce ischemia-reperfusion injury. FASEB J. 2009, 23, 1384–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Lv, H.; Zhao, B.; Zhou, L.; Wang, S.; Luo, J.; Liu, J.; Shang, P. Iron and leukemia: New insights for future treatments. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raven, E.P.; Lu, P.H.; Tishler, T.A.; Heydari, P.; Bartzokis, G. Increased Iron Levels and Decreased Tissue Integrity in Hippocampus of Alzheimer’s Disease Detected in vivo with Magnetic Resonance Imaging. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2013, 37, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahanshahi, M.; Khalili, M.; Margedari, A. Naringin Chelates Excessive Iron and Prevents the Formation of Amyloid-Beta Plaques in the Hippocampus of Iron-Overloaded Mice. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 651156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, E.; Gim, J.; Do; Kim, K.; Kim, C.-S.; Chun, H.S. Protective Effects of Alpha-Lipoic Acid on Glutamate-Induced Cytotoxicity in C6 Glioma Cells. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2019, 42, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanadgol, N.; Golab, F.; Askari, H.; Moradi, F.; Ajdary, M.; Mehdizadeh, M. Alpha-lipoic acid mitigates toxic-induced demyelination in the corpus callosum by lessening of oxidative stress and stimulation of polydendrocytes proliferation. Metab. Brain Dis. 2018, 33, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixit, S.; Mehra, R.D.; Dhar, P. Effect of α-lipoic acid on spatial memory and structural integrity of developing hippocampal neurons in rats subjected to sodium arsenite exposure. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2020, 75, 103323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Sousa, C.N.S.; Meneses, L.N.; Vasconcelos, G.S.; Medeiros, I.d.S.; Silva, M.C.C.; Mouaffak, F.; Kebir, O.; Leite, C.M.G.d.S.; Patrocinio, M.C.A.; Macedo, D.; et al. Neuroprotective evidence of alpha-lipoic acid and desvenlafaxine on memory deficit in a neuroendocrine model of depression. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 2018, 391, 803–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, O.A.; Abdel-Hafez, A.M.M.; Abd el Kareim, A. Rat hippocampal CA3 neuronal injury induced by limb ischemia/reperfusion: A possible restorative effect of alpha lipoic acid. Ultrastruct. Pathol. 2018, 42, 133–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Rosso, J.Q.; McCarty, M. How Clinically Relevant is Dapsone-related Peripheral Neuropathy? An Overview of Available Data with Emphasis on Clinical Recognition. J. Clinial Aesthetic Dermatol. 2010, 3, 19–21. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, P.; Li, F.-M.; Zhou, Y.-F.; Qian, C.; Li, J.; Jiang, L.-R.; Qian, Z.-M. Effects of alpha-lipoic acid on expression of iron transport and storage proteins in BV-2 microglia cells. Pharmacol. Rep. 2017, 69, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Hou, W.; Song, X.; Yu, Y.; Huang, J.; Sun, X.; Kang, R.; Tang, D. Ferroptosis: Process and function. Cell Death Differ. 2016, 23, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gomes, B.A.Q.; Santos, S.M.d.; Gato, L.d.S.; Espíndola, K.M.M.; Silva, R.K.M.d.; Davis, K.; Navegantes-Lima, K.C.; Burbano, R.M.R.; Romao, P.R.T.; Coleman, M.D.; et al. Alpha-Lipoic Acid Reduces Neuroinflammation and Oxidative Stress Induced by Dapsone in an Animal Model. Nutrients 2025, 17, 791. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17050791
Gomes BAQ, Santos SMd, Gato LdS, Espíndola KMM, Silva RKMd, Davis K, Navegantes-Lima KC, Burbano RMR, Romao PRT, Coleman MD, et al. Alpha-Lipoic Acid Reduces Neuroinflammation and Oxidative Stress Induced by Dapsone in an Animal Model. Nutrients. 2025; 17(5):791. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17050791
Chicago/Turabian StyleGomes, Bruno Alexandre Quadros, Savio Monteiro dos Santos, Lucas da Silva Gato, Kaio Murilo Monteiro Espíndola, Rana Karen Mesquita da Silva, Kelly Davis, Kely Campos Navegantes-Lima, Rommel Mario Rodriguez Burbano, Pedro Roosevelt Torres Romao, Michael D. Coleman, and et al. 2025. "Alpha-Lipoic Acid Reduces Neuroinflammation and Oxidative Stress Induced by Dapsone in an Animal Model" Nutrients 17, no. 5: 791. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17050791
APA StyleGomes, B. A. Q., Santos, S. M. d., Gato, L. d. S., Espíndola, K. M. M., Silva, R. K. M. d., Davis, K., Navegantes-Lima, K. C., Burbano, R. M. R., Romao, P. R. T., Coleman, M. D., & Monteiro, M. C. (2025). Alpha-Lipoic Acid Reduces Neuroinflammation and Oxidative Stress Induced by Dapsone in an Animal Model. Nutrients, 17(5), 791. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17050791






