Cholesin mRNA Expression in Human Intestinal, Liver, and Adipose Tissues
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Ethical Approval
2.2. Study Participants
2.3. Biopsy Sampling
2.4. Tissue Handling and mRNA Analyses
2.5. Data Analysis and Statistical Analyses
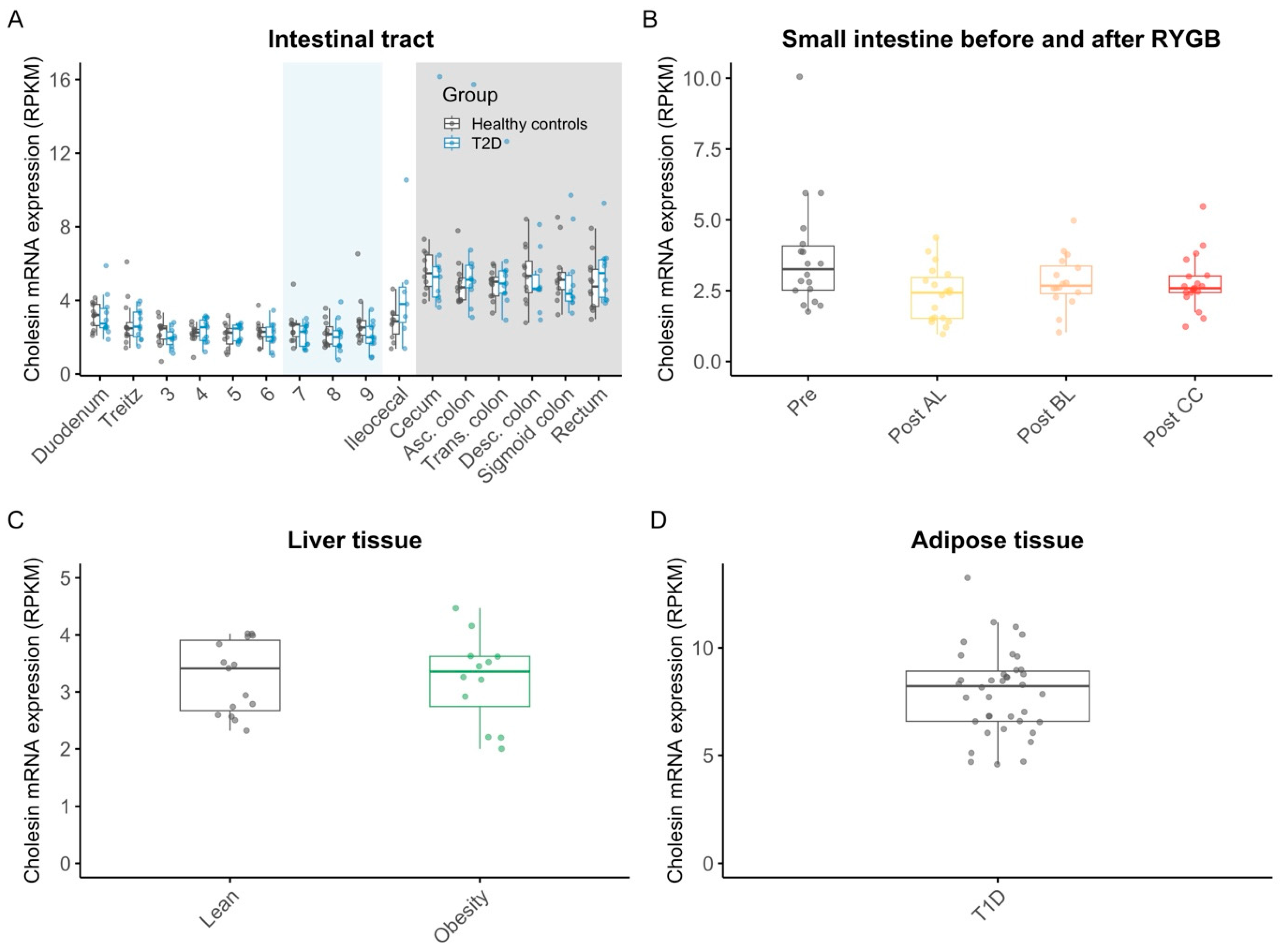
3. Results
3.1. Nieman–Pick Disease C1-like Intracellular Cholesterol Transporter 1 (NPC1L1)
3.2. Cholesin (c7orf50)
3.3. G Protein-Coupled Receptor 146 (GPR146)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Luo, J.; Yang, H.; Song, B.-L. Mechanisms and regulation of cholesterol homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 225–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gidding, S.S.; Allen, N.B. Cholesterol and Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease: A Lifelong Problem. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2019, 8, e012924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Chen, F.; Jia, L.; Long, A.; Peng, Y.; Li, X.; Huang, J.; Wei, X.; Fang, X.; Gao, Z.; et al. A gut-derived hormone regulates cholesterol metabolism. Cell 2024, 187, 1685–1700.e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryk, A.; Marcinkiewicz, A.; Chrzanowski, J.; Michalak, A.M.; Dróżdz, I.; Burzyński, J.; Krejca, M.; Fendler, W. Cholesin receptor signalling is active in cardiovascular system-associated adipose tissue and correlates with SGLT2i treatment in patients with diabetes. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2024, 23, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhee, N.A.; Vilmann, P.; Hassan, H.; Hendel, J.W.; Holst, J.J.; Vilsbøll, T.; Knop, F.K. The use of double-balloon enteroscopy in retrieving mucosal biopsies from the entire human gastrointestinal tract. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 49, 1143–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jorsal, T.; Christensen, M.M.; Mortensen, B.; Nygaard, E.B.; Zhang, C.; Rigbolt, K.; Wandall, E.; Langholz, E.; Friis, S.; Worm, D.; et al. Gut Mucosal Gene Expression and Metabolic Changes After Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass Surgery. Obesity 2020, 28, 2163–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suppli, M.P.; Bagger, J.I.; Lund, A.; Demant, M.; van Hall, G.; Strandberg, C.; Kønig, M.J.; Rigbolt, K.; Langhoff, J.L.; Albrechtsen, N.J.W.; et al. Glucagon Resistance at the Level of Amino Acid Turnover in Obese Subjects with Hepatic Steatosis. Diabetes 2020, 69, 1090–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heimbürger, S.M.N.; Hoe, B.; Nielsen, C.N.; Bergman, N.C.; Skov-Jeppesen, K.; Hartmann, B.; Holst, J.J.; Dela, F.; Overgaard, J.; Størling, J.; et al. GIP Affects Hepatic Fat and Brown Adipose Tissue Thermogenesis but Not White Adipose Tissue Transcriptome in Type 1 Diabetes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 107, 3261–3274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RStudio Team. RStudio: Integrated Development for R. RStudio. 2020. Available online: http://www.rstudio.com/ (accessed on 12 May 2024).
- American Diabetes Association. Dyslipidemia Management in Adults with Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2004, 27 (Suppl. S1), s68–s71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pihlajamäki, J.; Grönlund, S.; Simonen, M.; Käkelä, P.; Moilanen, L.; Pääkkönen, M.; Pirinen, E.; Kolehmainen, M.; Kärjä, V.; Kainulainen, S.; et al. Cholesterol absorption decreases after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass but not after gastric banding. Metabolism 2010, 59, 866–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Study 1 [5] | Study 2 [6] | Study 3 [7] | Study 4 [8] | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type 2 Diabetes | Healthy | p Value * | RYGB Patients | With Obesity | Without Obesity | p Value † | Type 1 Diabetes | |
| Participants | 12 | 12 | 20 | 12 | 15 | 20 | ||
| Sex ratio (M/F) | 9/3 | 8/4 | 1.00 | 6/14 | 12/0 | 15/0 | 1.00 | 20/0 |
| Age (years) | 51 (34–63) | 50 (41–67) | 0.66 | 44 (29–56) | 36 (25–58) | 41 (25–68) | 0.315 | 26 (18–49) |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 27 (23–32) | 27 (20–31) | 0.92 | 43.3 (36–52) | 33.6 (31–40) | 23.2 (21–25) | <0.0001 | 23.8 (20–27) |
| HbA1c (mmol/mol) | 48 (36–85) | 34 (29–43) | 0.008 | 37.9 (25–70) | 31 (26–37) | 30 (23–34) | 0.34 | 51 (32–71) |
| Disease duration (years) | 5 (1–9) | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9.1 (2–15) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gilliam-Vigh, H.; Suppli, M.P.; Heimbürger, S.M.N.; Lund, A.B.; Knop, F.K.; Ellegaard, A.-M. Cholesin mRNA Expression in Human Intestinal, Liver, and Adipose Tissues. Nutrients 2025, 17, 619. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17040619
Gilliam-Vigh H, Suppli MP, Heimbürger SMN, Lund AB, Knop FK, Ellegaard A-M. Cholesin mRNA Expression in Human Intestinal, Liver, and Adipose Tissues. Nutrients. 2025; 17(4):619. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17040619
Chicago/Turabian StyleGilliam-Vigh, Hannah, Malte P. Suppli, Sebastian M. N. Heimbürger, Asger B. Lund, Filip K. Knop, and Anne-Marie Ellegaard. 2025. "Cholesin mRNA Expression in Human Intestinal, Liver, and Adipose Tissues" Nutrients 17, no. 4: 619. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17040619
APA StyleGilliam-Vigh, H., Suppli, M. P., Heimbürger, S. M. N., Lund, A. B., Knop, F. K., & Ellegaard, A.-M. (2025). Cholesin mRNA Expression in Human Intestinal, Liver, and Adipose Tissues. Nutrients, 17(4), 619. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17040619







