Metabolite-Induced Apoptosis by Gundelia tournefortii in A549 Lung Cancer Cells: A Cytotoxic and Gene Expression Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Source of Gundelia tournefortii and Preparation of Plant Extracts
2.2. Determination of Phenolic Components
2.3. Cell Line Culture Studies
2.4. Determination of Cell Viability
2.5. Array Experimental Method
2.6. Determination of Apoptosis with Flow Cytometry
2.7. Network Pharmacology
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. HPLC Analysis Findings
3.2. Anticancer Activity of Gundelia tournefortii Extract
3.3. Array Data Analysis by Gene Enrichment Method
3.4. Determination of Apoptosis
3.5. Network Pharmacology Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Upadhyay, A. Cancer: An unknown territory; rethinking before going ahead. Genes Dis. 2020, 8, 655–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- T.C. Ministry of Health, Department of Cancer. Causes of Cancer and Common Cancers. 2018. Available online: https://tektiklabilgielinde.saglik.gov.tr/kanserin-nedenleri-ve-sik-gorulen-kanserler.html (accessed on 14 February 2022).
- Pavlopoulou, A.; Spandidos, D.A.; Michalopoulos, I. Human cancer databases. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 33, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Global Cancer Observatory: Cancer Today. Available online: https://gco.iarc.fr (accessed on 14 February 2022).
- Turkish Immuno-Oncology Society, Turkish Lung Cancer Society, Turkish Society of Medical Oncology and Turkish Thoracic Society. Available online: https://toraks.org.tr/site/sf/nmf/pre_migration/81b06b2de39bb1a1673bc0eb3b8394de4eeeb0bf21cc67264b7485e224d08566.pdf (accessed on 14 February 2022).
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2020, 70, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbst, R.S.; Morgensztern, D.; Boshoff, C. The biology and management of non-small cell lung cancer. Nature 2018, 553, 446–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, D.J.; Cragg, G.M. Natural products as sources of new drugs over the nearly four decades from 1981 to 2019. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 770–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, A.G.; Sarker, S.D.; Saleem, I.Y.; Hutcheon, G.A. Delivery of natural phenolic compounds for the potential treatment of lung cancer. Daru 2019, 27, 433–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakrim, S.; Omari, N.E.; Hachlafi, E.N.; Bakri, Y.; Lee, L.H.; Bouyahya, B. Dietary Phenolic Compounds as Anticancer Natural Drugs: Recent Update on Molecular Mechanisms and Clinical Trials. Foods 2022, 11, 3323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceylan, S.; Cetin, S.; Camadan, Y.; Saral, O.; Ozsen, O.; Tutus, A. Antibacterial and antioxidant activities of traditional medicinal plants from the Erzurum region of Turkey. Ir. J. Med. Sci. 2019, 188, 1303–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anik, R. Akbaldir (Ornithogalum narbonense L.) Also Used as a Food Product in Şanliurfa and Kenger (Gundelia tournefortii L.) the Effect of the Most Widely Used Cooking Methods of Plants on Phenolic Compound, Vitamin C Amount and Antioxidant Activity Values. Master’s Thesis, Istanbul Aydın University, Istanbul, Turkey, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Farhang, H.R.; Vahabi, M.R.; Allafchian, A.R. Chemical compositions of the essential oil of Gundelia tournefortii L. (Asteraceae) from Central Zagros, Iran. J. Med. Herbs 2016, 6, 227–233. [Google Scholar]
- Konak, M.; Ateș, M.; Șahan, Y. Evaluation of antioxidant properties of Gundelia tournefortii: A wild edible plant. J. Agric. Fac. Uludag Univ. 2017, 31, 101–108. [Google Scholar]
- Sirri, M.; Sirri, G. Current Status of Wild Plant and Weed Species Consumed as Food in Hakkari Province. Eur. J. Sci. Technol. 2020, 19, 393–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cakmakci, S.; Dagdemir, E. A preliminary study on functionality of Gundelia tournefortii L. as a new stabiliser in ice cream production. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2013, 66, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lezzetler, Gundelia Meal. Available online: https://lezzetler.com/tarif-67136.html (accessed on 14 February 2022).
- Yemektarifi, Gundelia with Olive Oil. Available online: https://1001yemektarifi.com/zeytinyagli-kenger-yemegi/ (accessed on 14 February 2022).
- Nefisyemektarifleri, Roasted Gundelia with Egg. Available online: https://www.nefisyemektarifleri.com/yumurtali-kenger-kavurmasi/ (accessed on 14 February 2022).
- Asadi-Samani, M.; Rafieian-Kopaei, M.; Azimi, N. Gundelia: A systematic review of medicinal and molecular perspective. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 2013, 16, 1238–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hani, N.; Abulaila, K.; Howes, M.J.; Mattana, E.; Bacci, S.; Sleem, K.; Sarkis, L.; Eddine, N.S.; Baydoun, S.; Apostolides, N.A.; et al. Gundelia tournefortii L. (Akkoub): A review of a valuable wild vegetable from Eastern Mediterranean. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 2024, 71, 3987–3995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gezici, S.; Sekeroglu, N. Comparative biological analyses on kenger and kenger coffee as novel functional food products. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 59, 2328–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozgur., A.; Tutar, Y.; Ozgur., A.; Tutar, Y. Heat Shock Protein 90 Inhibition in Cancer Drug Discovery: From Chemistry to Futural Clinical Applications. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2016, 16, 260–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gümüş, M.; Koca, İ.; Sert, Y.; Dişli, A.; Tunoğlu, E.N.Y.; Tutar, L.; Tutar, Y. Triad pyrazole-thiazole-coumarin heterocyclic core effectively inhibit HSP and drive cancer cells to apoptosis. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2023, 41, 14382–14397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tunoğlu, S.; Tutar, L.; Gümüş, M.; Tunoğlu, E.N.Y.; Koca, İ.; Tutar, Y. Hsp Inhibitor is Affective Against Adenocarcinomic Human Alveolar Basal Epithelial Cells Through Modulating ERK/MAPK Signaling Pathway. Chem. Biodivers. 2024, 21, e202301422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Çapan, I.; Hawash, M.; Qaoud, M.T.; Gülüm, L.; Tunoglu, E.N.Y.; Çifci, K.U.; Çevrimli, B.S.; Sert, Y.; Servi, S.; Koca, I.; et al. Synthesis of novel carbazole hydrazine-carbothioamide scaffold as potent antioxidant, anticancer and antimicrobial agents. BMC Chem. 2024, 18, 102. [Google Scholar]
- Kadan, S.; Melamed, S.; Benvalid, S.; Tietel, Z.; Sasson, Y.; Zaid, H. Gundelia tournefortii: Fractionation, Chemical Composition and GLUT4 Translocation Enhancement in Muscle Cell Line. Molecules 2021, 26, 3785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tutar, Y. Metabologenomics and network pharmacology to understand the molecular mechanism of cancer research. World J. Clin. Cases 2024, 12, 474–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, E.Y.; Tan, C.M.; Kou, Y.; Duan, Q.; Wang, Z.; Meirelles, G.V.; Clark, N.R.; Ma’ayan, A. Enrichr: Interactive and collaborative HTML5 gene list enrichment analysis tool. BMC Bioinform. 2013, 14, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuleshov, M.V.; Jones, M.R.; Rouillard, A.D.; Fernandez, N.F.; Duan, Q.; Wang, Z.; Koplev, S.; Jenkins, S.L.; Jagodnik, K.M.; Lachmann, A.; et al. Enrichr: A comprehensive gene set enrichment analysis web server 2016 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, gkw377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Bailey, A.; Kuleshov, M.V.; Clarke, D.J.B.; Evangelista, J.E.; Jenkins, S.L.; Lachmann, A.; Wojciechowicz, M.L.; Kropiwnicki, E.; Jagodnik, K.M.; et al. Gene set knowledge discovery with Enrichr. Curr. Protoc. 2021, 1, e90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Lafi, S.; Rayan, B.; Kadan, S.; Abu-Lafi, M.; Rayan, A. Anticancer activity and phytochemical composition of wild Gundelia tournefortii. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 17, 713–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildiz, S. Determination of Phenolic Compounds and Metals in the Kenger (Gundelia tournefortii L.), Gulluk (Eremurus tpectabilis M. Bieb.) and Iskin (Rheum ribes L.) of the Plant Grown in Upper Euphrates Basin. Master’s Thesis, Firat University, Elazig, Turkey, 20 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Keskin, M.; Kaya, G.; Keskin, S. Gundelia Tournefortii L. (Kenger): Determination of in vitro Antidiabetic Activities. Prog. Nutr. 2021, 23, e2021163. [Google Scholar]
- Haghi, G.; Hatami, A.; Arshi, R. Distribution of caffeic acid derivatives in Gundelia tournefortii L. Food Chem. 2011, 124, 1029–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajizadeh-Sharafabad, F.; Alizadeh, M.; Mohammadzadeh, M.H.S.; Alizadeh-Salteh, S.; Kheirouri, S. Effect of Gundelia tournefortii L. extract on lipid profile and TAC in patients with coronary artery disease: A double-blind randomized placebo controlled clinical trial. J. Herb. Med. 2016, 6, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarac, H.; Demirbas, A.; Dastan, S.D.; Atas, M.; Cevik, Ö.; Eruygur, N. Evaluation of nutrients and biological activities of Kenger (Gundellia tournefortii L.) seeds cultivated in Sivas province. Turk. J. Agric.-Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 7, 52–58. [Google Scholar]
- Ozaltun, B.; Dastan, T. Evaluation of antimicrobial activities and in vitro cytotoxic activities of Gundelia tournefortii L. Plant extracts. SDÜ Tıp Fakültesi Derg. 2019, 26, 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amer, J.; Jaradat, N.; Aburas, H.; Hattab, S.; Abdallah, S. Gundelia Tournefortii extracts inhibit progressions of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in mice model through decrease in p53/Akt/PI3K signaling pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 156, 113885. [Google Scholar]


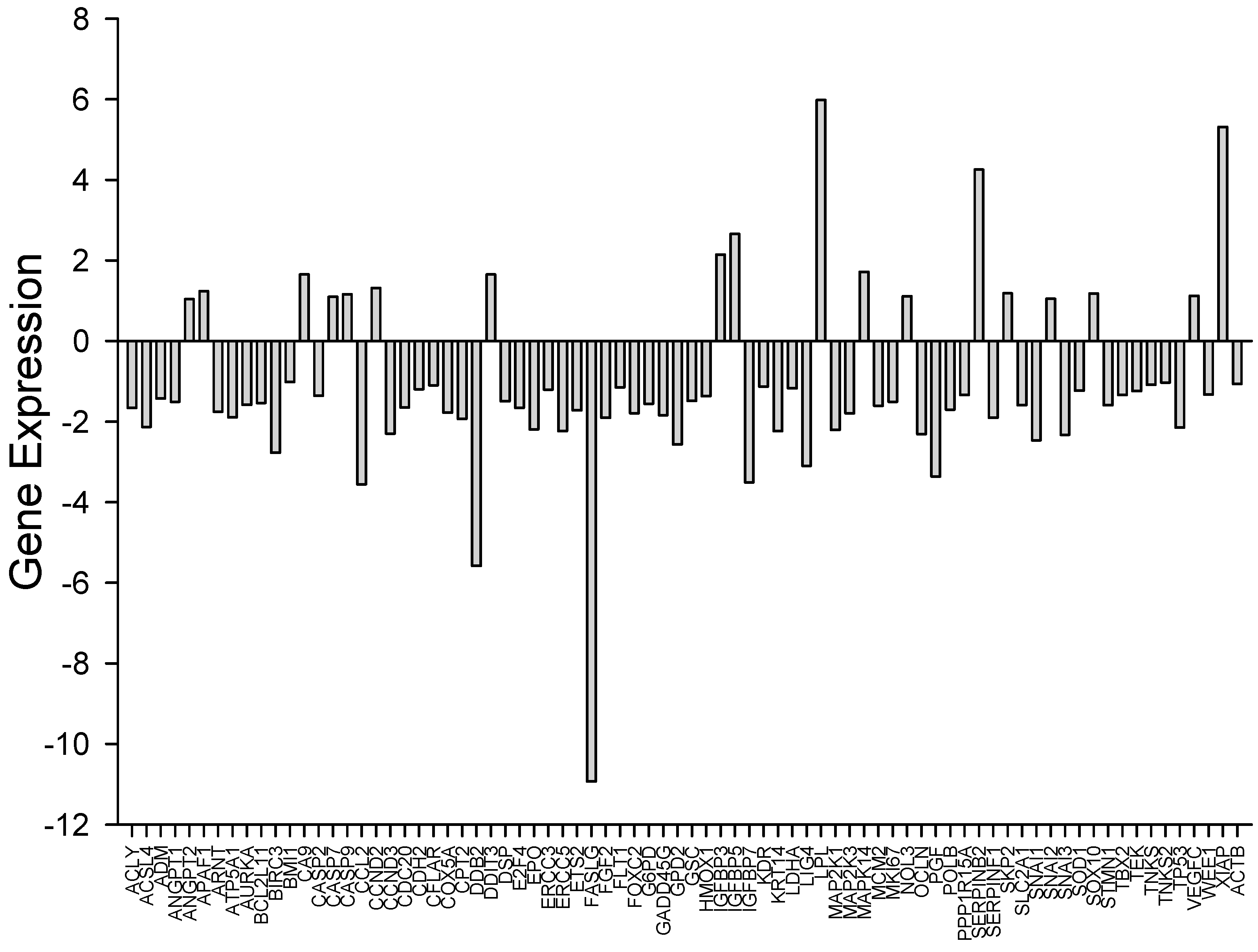
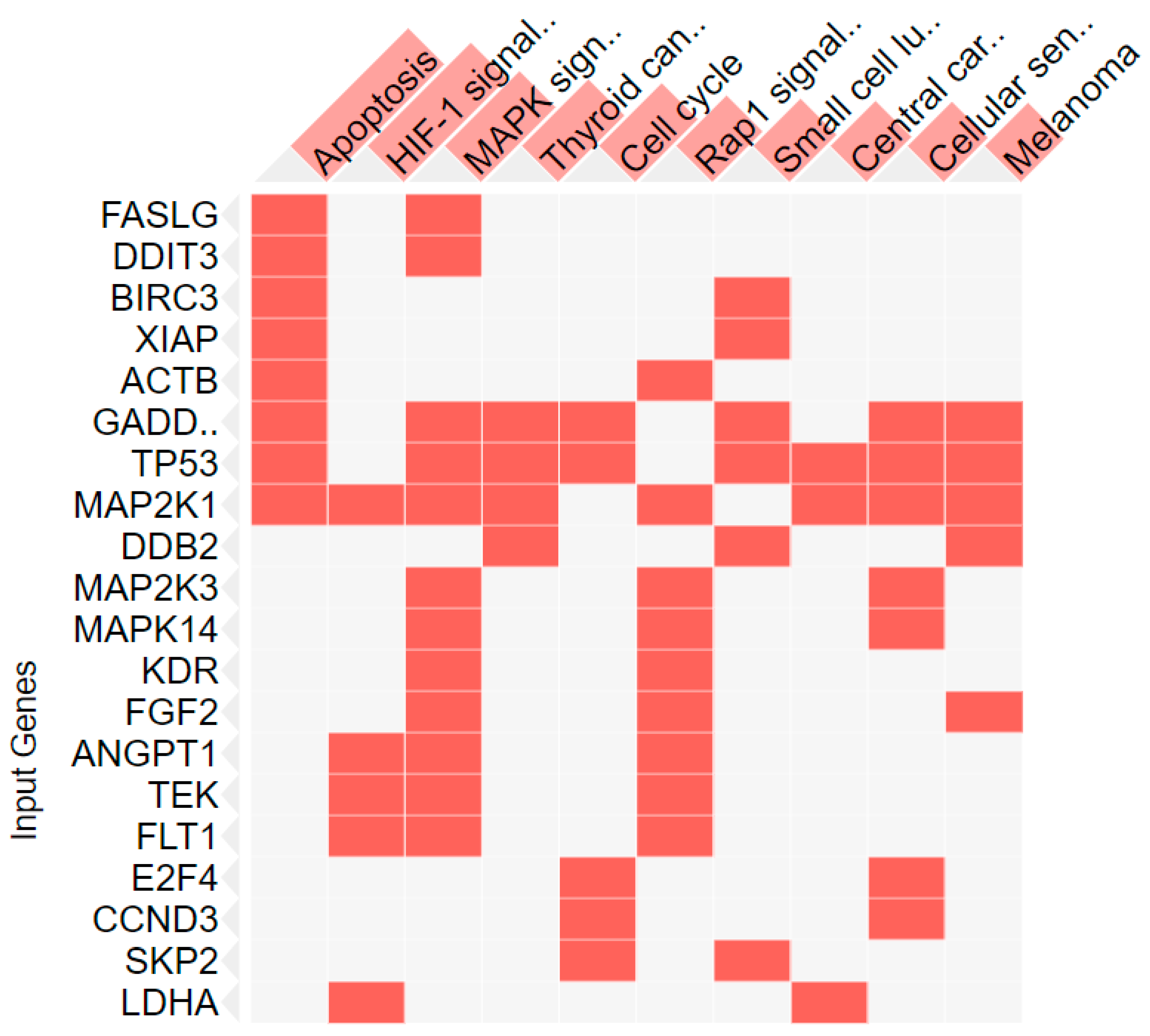
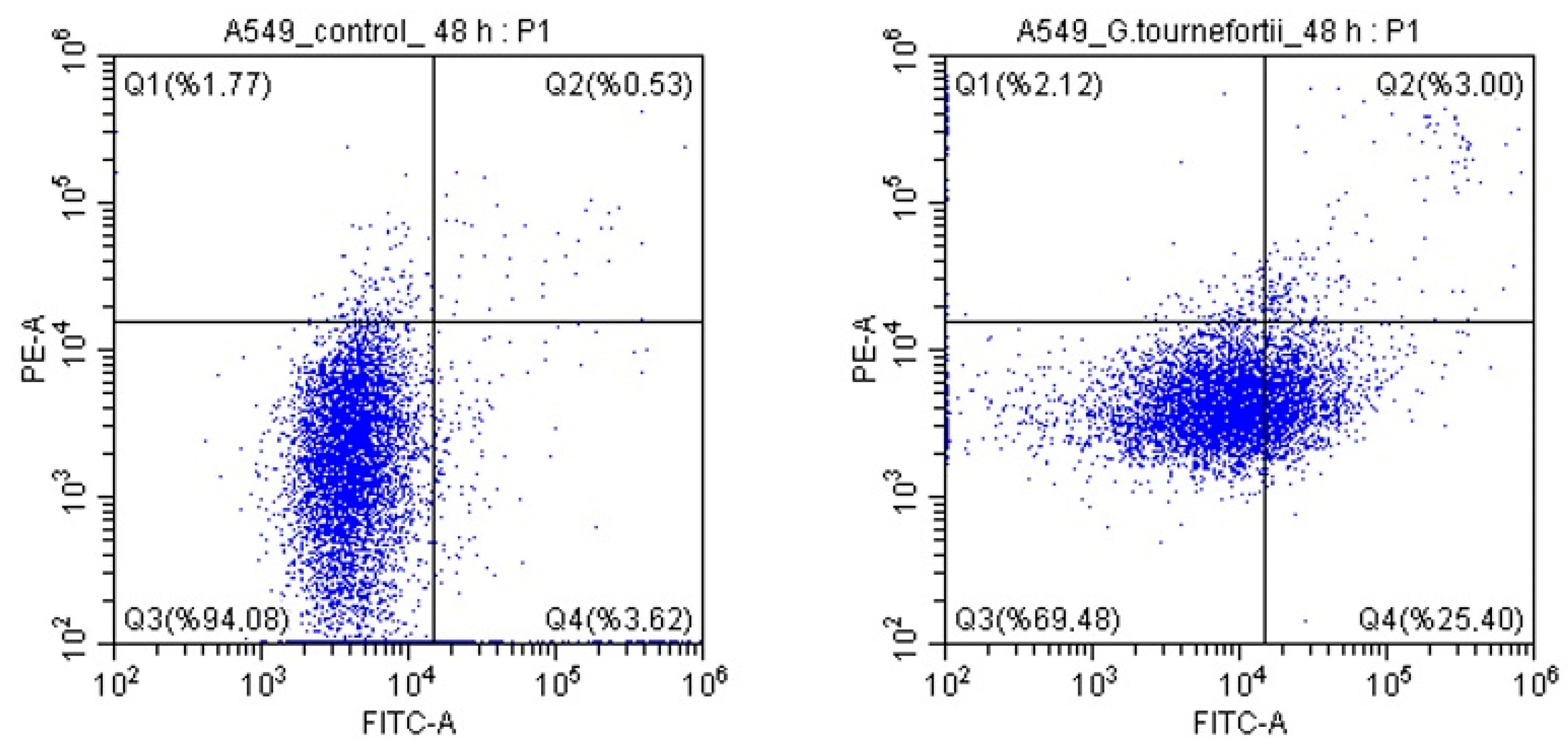
| Index | Name | p-Value | Adjusted p-Value | Odds Ratio | Combined Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Apoptosis | 1.01 × 10−9 | 1.89 × 10−7 | 30.80 | 850.69 |
| 2 | Pathways in cancer | 9.51 × 10−9 | 5.97 × 10−7 | 12.31 | 312.49 |
| 3 | MAPK signaling pathway | 9.52 × 10−9 | 5.97 × 10−7 | 17.49 | 443.75 |
| 4 | HIF-1 signaling pathway | 2.34 × 10−6 | 1.10 × 10−4 | 27.56 | 547.74 |
| 5 | Cell cycle | 6.53 × 10−6 | 2.45 × 10−4 | 23.98 | 451.95 |
| 6 | PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | 1.74 × 10−5 | 5.46 × 10−4 | 11.64 | 207.87 |
| 7 | Rap1 signaling pathway | 2.51 × 10−5 | 6.74 × 10−4 | 15.78 | 276.13 |
| 8 | Cellular senescence | 3.96 × 10−5 | 9.31 × 10−4 | 18.76 | 319.82 |
| 9 | Transcriptional misregulation in cancer | 1.97 × 10−4 | 0.000004117 | 15.07 | 232.61 |
| 10 | Focal adhesion | 2.80 × 10−4 | 0.000004965 | 14.36 | 216.63 |
| Control (%) | Gundelia(%) | p Value | Chi-Square | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q1 | 2 ± 1 | 2 ± 1 | 0.209 | 1.58 |
| Q2 | 1 ± 1 | 3 ± 1 | <0.0001 | 128.11 |
| Q3 | 94 ± 2 | 70 ± 2 | <0.0001 | 1412.79 |
| Q4 | 4 ± 2 | 25 ± 2 | <0.0001 | 1343.15 |
| Q2 + Q4 | 5 | 28 | <0.0001 | 1500.88 |
| Index | Name | p-Value | Adjusted p-Value | Odds Ratio | Combined Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Apoptotic signaling in response to DNA damage homo sapiens h chemical pathway | 1.353 × 10−8 | 9.740 × 10−7 | 221.67 | 4016.27 |
| 2 | Role of mitochondria in apoptotic signaling homo sapiens h mitochondrial pathway | 0.000002090 | 0.00006376 | 161.76 | 2115.50 |
| 3 | Stress induction of HSP regulation homo sapiens h hsp27 pathway | 0.000002657 | 0.00006376 | 147.04 | 1887.82 |
| 4 | Regulation of cell cycle progression by Plk3 homo sapiens h plk3 pathway | 0.000005922 | 0.0001066 | 107.81 | 1297.69 |
| 5 | Roles of beta-arrestin-dependent recruitment of Src kinases in GPCR signaling homo sapiens h b arrestin-src pathway | 0.00004248 | 0.0006117 | 52.12 | 524.71 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yuksel, A.; Celayir, D.N.; Yenilmez Tunoglu, E.N.; Tutar, L.; Tutar, Y. Metabolite-Induced Apoptosis by Gundelia tournefortii in A549 Lung Cancer Cells: A Cytotoxic and Gene Expression Study. Nutrients 2025, 17, 374. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17030374
Yuksel A, Celayir DN, Yenilmez Tunoglu EN, Tutar L, Tutar Y. Metabolite-Induced Apoptosis by Gundelia tournefortii in A549 Lung Cancer Cells: A Cytotoxic and Gene Expression Study. Nutrients. 2025; 17(3):374. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17030374
Chicago/Turabian StyleYuksel, Aysun, Damla Nur Celayir, Ezgi Nurdan Yenilmez Tunoglu, Lütfi Tutar, and Yusuf Tutar. 2025. "Metabolite-Induced Apoptosis by Gundelia tournefortii in A549 Lung Cancer Cells: A Cytotoxic and Gene Expression Study" Nutrients 17, no. 3: 374. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17030374
APA StyleYuksel, A., Celayir, D. N., Yenilmez Tunoglu, E. N., Tutar, L., & Tutar, Y. (2025). Metabolite-Induced Apoptosis by Gundelia tournefortii in A549 Lung Cancer Cells: A Cytotoxic and Gene Expression Study. Nutrients, 17(3), 374. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17030374






