Validity and Reliability of the Danish Version of the Adult Eating Behavior Questionnaire—Results from the South Danish Obesity Initiative
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Instrument: Adult Eating Behavior Questionnaire
2.3. Translation Procedure
2.4. Content Validity Assessment: Three-Step Test Interview
2.5. Test–Retest Reliability
2.6. Baseline Characteristics
2.7. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Participant Charectaristics
3.2. Content Validity
3.3. Test–Retest Reliability
3.4. Confirmatory Factor Analysis
3.5. Internal Consistency and Factor Loadings
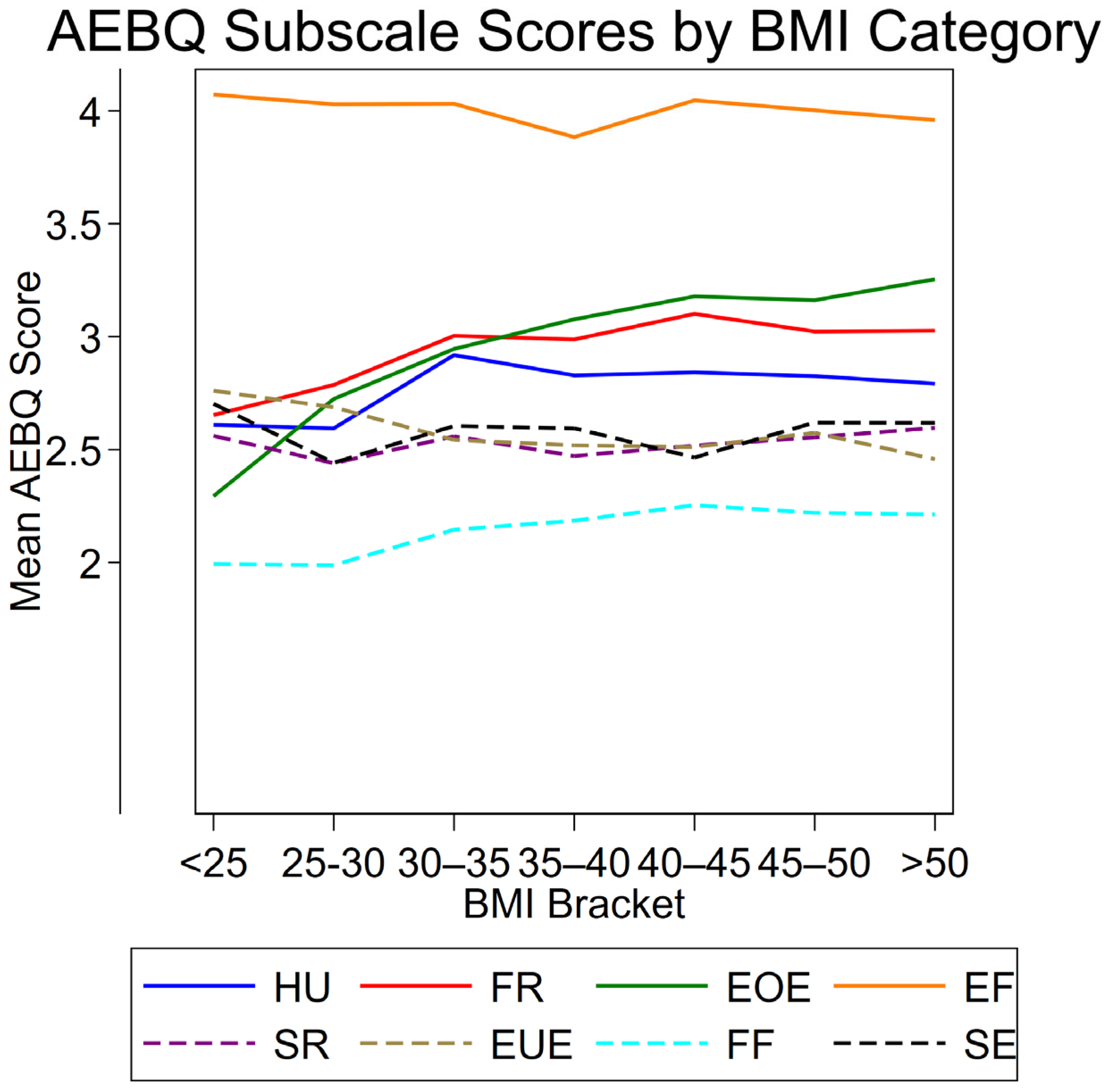
3.6. Associations Between Subscales and Adiposity Measures
4. Discussion
Strengths and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Abbrev. | Meaning |
| AEBQ | Adult Eating Behavior Questionnaire |
| AIC | Akaike information criterion |
| BIC | Bayesian information criterion |
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
| CEBQ | Child Eating Behavior Questionnaire |
| CFA | Confirmatory factor analysis |
| CFI | Comparative fit index |
| CI | Confidence interval |
| EOE | Emotional Overeating (AEBQ subscale) |
| EF | Enjoyment of Food (AEBQ subscale) |
| EUE | Emotional Undereating (AEBQ subscale) |
| FF | Food Fussiness (AEBQ subscale) |
| FR | Food Responsiveness (AEBQ subscale) |
| HU | Hunger (AEBQ subscale) |
| ICC | Intraclass correlation coefficient |
| LIX | Læse IndeX (readability index) |
| MASLD | Metabolic dysfunction–associated steatotic liver disease |
| MDC | Minimal detectable change |
| OPEN | Open Patient data Explorative Network |
| RMSEA | Root mean square error of approximation (90% CI) |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| SE | Slowness in Eating (AEBQ subscale) |
| SDOI | South Danish Obesity Initiative |
| SR | Satiety Responsiveness (AEBQ subscale) |
| SRMR | Standardized root mean square residual |
| TLI | Tucker–Lewis index |
| TSTI | Three-Step Test Interview |
| WHR | Waist-to-hip ratio |
Appendix A
| Danish title | Spørgeskema om spiseadfærd hos voksne | ||||
| Original English title | Adult Eating Behavior Questionnaire | ||||
| Danish instruction | Læs venligst hvert udsagn og sæt kryds ved det udsagn der passer bedst for dig | ||||
| Original English instruction | Please read each statement and tick the response that best reflects how much you agree or disagree | ||||
| Response option and scale values: | |||||
| Code | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Danish label | Meget uenig | Uenig | Hverken enig eller uenig | Enig | Meget enig |
| English label | Strongly disagree | Disagree | Neither agree nor disagree | Agree | Strongly agree |
| Item | Subscale | Danish Wording | Original English Wording |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Enjoyment of Food | Jeg elsker mad | I love food |
| 2 | Food Fussiness | Jeg beslutter ofte at jeg ikke kan lide maden inden jeg smager på den | I often decide that I don’t like a food before tasting it |
| 3 | Enjoyment of Food | Jeg nyder at spise | I enjoy eating |
| 4 | Enjoyment of Food | Jeg ser frem til spisetiderne | I look forward to mealtimes |
| 5 | Emotional Overeating | Jeg spiser mere, når jeg er irriteret | I eat more when I’m annoyed |
| 6 | Hunger | Jeg lægger ofte mærke til, at min mave rumler | I often notice my stomach rumbling |
| 7 | Food Fussiness | Jeg afviser nye typer mad i starten | I refuse new foods at first |
| 8 | Emotional Overeating | Jeg spiser mere, når jeg er bekymret | I eat more when I’m worried |
| 9 | Hunger | Hvis jeg springer et måltid over, bliver jeg irritabel | If I miss a meal I get irritable |
| 10 | Emotional Overeating | jeg spiser mere, når jeg er oprevet | I eat more when I’m upset |
| 11 | Satiety Responsiveness | Jeg levner ofte mad på min tallerken | I often leave food on my plate at the end of a meal |
| 12 R | Food Fussiness | Jeg nyder at smage nye madvarer | I enjoy tasting new foods |
| 13 | Food Responsiveness | Jeg føler mig ofte sulten, når jeg er sammen med nogen der spiser | I often feel hungry when I am with someone who is eating |
| 14 R | Slowness in Eating | Jeg bliver ofte hurtig færdig med at spise min mad | I often finish my meals quickly |
| 15 | Emotional Undereating | Jeg spiser mindre, når jeg er bekymret | I eat less when I’m worried |
| 16 | Emotional Overeating | Jeg spiser mere, når jeg er ængstelig | I eat more when I’m anxious |
| 17 | Food Responsiveness | Hvis jeg havde valget, ville jeg spise det meste af tiden | Given the choice, I would eat most of the time |
| 18 | Emotional Undereating | Jeg spiser mindre, når jeg er vred | I eat less when I’m angry |
| 19 R | Food Fussiness | Jeg er interesseret i at smage ny mad, som jeg ikke har smagt før | I am interested in tasting new food I haven’t tasted before |
| 20 | Emotional Undereating | Jeg spiser mindre, når jeg er oprevet | I eat less when I’m upset |
| 21 | Emotional Overeating | Jeg spiser mere, når jeg er vred | I eat more when I’m angry |
| 22 | Food Responsiveness | Jeg tænker altid på mad | I am always thinking about food |
| 23 | Satiety Responsiveness | Jeg bliver ofte mæt før mit måltid er færdigt | I often get full before my meal is finished |
| 24 R | Food Fussiness | Jeg kan godt lide mange forskellige slags mad | I enjoy a wide variety of foods |
| 25 | Slowness in Eating | Jeg er ofte sidst til at blive færdig med et måltid | I am often last at finishing a meal |
| 26 | Slowness in Eating | Jeg spiser mere og mere langsomt i løbet af et måltid | I eat more and more slowly during the course of a meal |
| 27 | Emotional Undereating | Jeg spiser mindre, når jeg er irriteret | I eat less when I’m annoyed |
| 28 | Hunger | Jeg føler mig ofte så sulten, at jeg må spise noget med det samme | I often feel so hungry that I have to eat something right away |
| 29 | Slowness in Eating | Jeg spiser langsomt | I eat slowly |
| 30 | Satiety Responsiveness | Jeg kan ikke spise et måltid, hvis jeg lige har spist en snack | I cannot eat a meal if I have had a snack just before |
| 31 | Satiety Responsiveness | Jeg bliver nemt mæt | I get full up easily |
| 32 | Hunger | Jeg føler mig ofte sulten | I often feel hungry |
| 33 | Food Responsiveness | Når jeg ser eller dufter mad, som jeg kan lide, får jeg lyst til at spise | When I see or smell food that I like, it makes me want to eat |
| 34 | Hunger | Jeg bliver svimmel, hvis mine måltider bliver forsinket | If my meals are delayed I get light-headed |
| 35 | Emotional Undereating | Jeg spiser mindre, når jeg er ængstelig | I eat less when I’m anxious |
Appendix B
| Test 1 | Test 2 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Subscale | Mean (SD) | Mean (SD) | SEM | MDC | ICC (95% CI) |
| Food Approach Subscales | |||||
| HU | 2.78 (0.75) | 2.76 (0.74) | 0.319 | 0.885 | 0.815 (0.752; 0.866) |
| FR | 2.85 (0.82) | 2.82 (0.82) | 0.318 | 0.882 | 0.849 (0.796; 0.891) |
| EOE | 3.03 (1.03) | 2.98 (1.07) | 0.449 | 1.243 | 0.817 (0.754; 0.867) |
| EF | 3.81 (0.85) | 3.80 (0.82) | 0.311 | 0.861 | 0.860 (0.810; 0.899) |
| Food Avoidance Subscales | |||||
| SR | 2.81 (0.83) | 2.82 (0.78) | 0.344 | 0.955 | 0.816 (0.752; 0.866) |
| EUE | 2.45 (0.89) | 2.55 (0.89) | 0.474 | 1.315 | 0.716 (0.626; 0.791) |
| FF | 2.30 (0.91) | 2.28 (0.86) | 0.277 | 0.769 | 0.902 (0.865; 0.929) |
| SE | 2.56 (0.92) | 2.58 (0.89) | 0.359 | 0.994 | 0.843 (0.787; 0.886) |
References
- OECD. Obesity Update 2017; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Sundhedsstyrelsen [Danish Health Authority]. Danskernes Sundhed—Den Nationale Sundhedsprofil 2021 [The Health of the Danes—The National Health Profile 2021]; Sundhedsstyrelsen: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2022.
- Mainous, A.G., III; Tanner, R.J.; Jo, A.; Anton, S.D. Prevalence of prediabetes and abdominal obesity among healthy-weight adults: 18-year trend. Ann. Fam. Med. 2016, 14, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, E.S.; Roberts, S.K.; Nicoll, A.J.; Reddy, A.; Paris, T.; Itsiopoulos, C.; Tierney, A.C. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease patients attending two metropolitan hospitals in Melbourne, Australia: High risk status and low prevalence. Intern. Med. J. 2018, 48, 1369–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luque-Ramirez, M.; Marti, D.; Fernandez-Duran, E.; Alpañés, M.; Álvarez-Blasco, F.; Escobar-Morreale, H.F. Office blood pressure, ambulatory blood pressure monitoring, and echocardiographic abnormalities in women with polycystic ovary syndrome: Role of obesity and androgen excess. Hypertension 2014, 63, 624–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkelstein, E.A.; Brown, D.S.; Wrage, L.A.; Allaire, B.T.; Hoerger, T.J. Individual and aggregate years-of-life-lost associated with overweight and obesity. Obesity 2010, 18, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernaes, U.J.; Andersen, J.R.; Norheim, O.F.; Vage, V. Work participation among the morbidly obese seeking bariatric surgery: An exploratory study from Norway. Obes. Surg. 2015, 25, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolotkin, R.L.; Andersen, J.R. A systematic review of reviews: Exploring the relationship between obesity, weight loss and health-related quality of life. Clin. Obes. 2017, 7, 273–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bleich, S.N.; Cutler, D.M.; Murray, C.; Adams, A.S. Why Is the Developed World Obese? Annu. Rev. Public Health 2008, 29, 273–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FAO; IFAD; UNICEF; WFP; WHO. The State of Food Security and Nutrition in the World 2021; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Llewellyn, C.; Wardle, J. Behavioral susceptibility to obesity: Gene–environment interplay in the development of weight. Physiol. Behav. 2015, 152, 494–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llewellyn, C.H.; Fildes, A. Behavioural susceptibility theory: Professor Jane Wardle and the role of appetite in genetic risk of obesity. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2017, 6, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunot, C.; Fildes, A.; Croker, H.; Llewellyn, C.H.; Wardle, J.; Beeken, R.J. Appetitive traits and relationships with BMI in adults: Development of the Adult Eating Behaviour Questionnaire. Appetite 2016, 105, 356–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gritti, E.S.; Cionti, L.; Cortesi, F.; Torelli, A.; Gambarini, A.; Hunot-Alexander, C.; Ogliari, A.L. Validation of the Adult Eating Behavior Questionnaire in an Italian Community Sample. Nutrients 2024, 16, 829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallan, K.M.; Fildes, A.; de la Piedad Garcia, X.; Drzezdzon, J.; Sampson, M.; Llewellyn, C. Appetitive traits associated with higher and lower body mass index: Evaluating the validity of the adult eating behaviour questionnaire in an Australian sample. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2017, 14, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, R.; Tremblay, A.; Fildes, A.; Jacob, R.; Tremblay, A.; Fildes, A.; Llewellyn, C.; Beeken, R.J.; Panahi, S.; Provencher, V.; et al. Validation of the Adult Eating Behaviour Questionnaire adapted for the French-speaking Canadian population. Eat. Weight Disord. 2022, 27, 1163–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuno, C.B.; Frankel, L.; Ofosuhene, P.; Keen, L., II. Validation of the Adult Eating Behavior Questionnaire (AEBQ) in a young adult Black sample in the US: Evaluating the psychometric properties and associations with BMI. Curr. Psychol. 2024, 43, 28590–28603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Sun, S.; Zickgraf, H.F.; Ellis, J.M.; Fan, X. Assessing appetitive traits among Chinese young adults using the AEBQ: Factor structure, gender invariance and latent mean differences, and associations with BMI. Assessment 2021, 28, 877–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zickgraf, H.F.; Rigby, A. The AEBQ in a bariatric surgery-seeking sample: Factor structure, convergent validity, and associations with BMI. Eur. Eat. Disord. Rev. 2019, 27, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjørklund, O.; Wichstrøm, L.; Llewellyn, C.; Steinsbekk, S. Validation of the AEBQ in a Norwegian sample of adolescents. Appetite 2024, 192, 107116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, T.R.; Kakinami, L.; Plourde, H.; Hunot-Alexander, C.; Beeken, R.J. Concurrent Validity of the Adult Eating Behavior Questionnaire in a Canadian Sample. Front. Psychol. 2021, 12, 779041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunot-Alexander, C.; Arellano-Gómez, L.P.; Smith, A.D.; Kaufer-Horwitz, M.; Vásquez-Garibay, E.M.; Romero-Velarde, E.; Fildes, A.; Croker, H.; Llewellyn, C.H.; Beeken, R.J. Examining the validity and consistency of the Adult Eating Behaviour Questionnaire-Español (AEBQ-Esp) and its relationship to BMI in a Mexican population. Eat. Weight Disord. 2022, 27, 651–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warkentin, S.; Costa, A.; Oliveira, A. Validity of the AEBQ and Its Relationship with Parent-Reported Eating Behaviors among Adolescents in Portugal. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yardımcı, H.; Ersoy, N.; Aslan Çin, N.N. Validity and reliability of Turkish version of the AEBQ for adult participants. Public Health Nutr. 2023, 26, 2218–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzek, D.; Skolmowska, D.; Głąbska, D. Appetitive traits in a population-based study of Polish adolescents within PLACE-19: Validation of the AEBQ. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juhl, C.B.; Bladbjerg, E.M.; Gram, B.; Knudsen, T.; Lauridsen, M.M.; Nygaard, N.-P.B.; Drøjdahl Ryg, N.; Skadhauge, L.; Münster, A.-M.B. Prevalence of Obesity-Related Disease in a Danish Population—The Results of an Algorithm-Based Screening Program. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2024, 17, 2505–2517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Björnsson, C.-H. Läsbarhet (Readability); Liber: Stockholm, Sweden, 1968. [Google Scholar]
- Hak, T.; van der Veer, K.; Jansen, H. The Three-Step Test-Interview (TSTI): An Observational Instrument for Pretesting Self-Completion Questionnaires. ERIM Report Series Research in Management; No. ERS-2004-029-ORG; Erasmus Research Institute of Management: Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Gagnier, J.J.; Lai, J.; Mokkink, L.B.; Terwee, C.B. COSMIN reporting guideline for studies on measurement properties of PROMs. Qual. Life Res. 2021, 30, 2197–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGraw, K.O.; Wong, S.P. Forming inferences about some intraclass correlation coefficients. Psychol. Methods. 1996, 1, 30–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, T.K.; Li, M.Y. A guideline of selecting and reporting intraclass correlation coefficients for reliability research. J. Chiropr. Med. 2016, 15, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayes, A.F.; Coutts, J.J. Use omega rather than Cronbach’s alpha for estimating reliability. But…. Commun. Methods Meas. 2020, 14, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunot-Alexander, C.; Beeken, R.J.; Goodman, W.; Fildes, A.; Croker, H.; Llewellyn, C.; Steinsbekk, S. Confirmation of the Factor Structure and Reliability of the AEBQ in an Adolescent Sample. Front. Psychol. 2019, 10, 1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molitor, S.J.; Fox, C.K.; Bensignor, M.O.; Gross, A.C. Validity of the Adult Eating Behavior Questionnaire for adolescents treated in a weight management clinic. Int. J. Obes. 2021, 45, 1086–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spence, J.C.; Carson, V.; Casey, L.; Boule, N. Examining behavioural susceptibility to obesity among Canadian pre-school children: The role of eating behaviours. Int. J. Pediatr. Obes. 2011, 6 (Suppl. S3), e501–e507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kauer, J.; Pelchat, M.L.; Rozin, P.; Zickgraf, H.F. Adult picky eating: Phenomenology, taste sensitivity, and psychological correlates. Appetite 2015, 90, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hebert, J.R.; Clemow, L.; Pbert, L.; Ockene, I.S.; Ockene, J.K. Social desirability bias in dietary self-report may compromise the validity of dietary intake measures. Int. J. Epidemiol. 1995, 24, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolind, M.E.I.; Beier, C.P.; Nygaard, N.-P.B.; Stenager, E.; Juhl, C.B. Obesity Associated Disease in People with Mental Disorders: The Role of Psychotropic Medication and BMI. Community Ment. Health J. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Characteristic | SDOI Cohort (n = 1257) | Test–Retest Group (n = 256) |
|---|---|---|
| Sex (female), n (%) | 895 (71.2) | 184 (71.9) |
| Ethnicity (Danish), n (%) | 1166 (92.8) | 244 (95.3) |
| Living arrangement: | ||
| Living with others, n (%) | 955 (76.0) | 197 (77.0) |
| Living alone, n (%) | 301 (24.0) | 59 (23.0) |
| Highest achieved education: | ||
| Primary school, n (%) | 209 (16.6) | 40 (15.6) |
| Secondary education, n (%) | 210 (16.7) | 31 (12.1) |
| Medium-length, n (%) | 661 (52.6) | 133 (52.0) |
| University, n (%) | 109 (8.7) | 22 (8.6) |
| No answer provided, n (%) | 68 (5.4) | 30 (11.7) |
| BMI categories | ||
| <25 kg/m2 | 111 (8.8) | 26 (10.2) |
| 25–30 kg/m2 | 103 (8.2) | 30 (11.7) |
| 30–35 kg/m2 | 182 (14.5) | 34 (13.3) |
| 35–40 kg/m2 | 311 (24.7) | 57 (22.3) |
| 40–45 kg/m2 | 265 (21.1) | 47 (18.4) |
| 45–50 kg/m2 | 163 (13.0) | 39 (15.2) |
| >50 kg/m2 | 122 (9.7) | 23 (9.0) |
| Age, mean (SD), years | 42.2 (11.1) | 45.1 (10.8) * |
| Height, mean (SD), cm | 171.5 (9.2) | 170.9 (8.9) |
| Weight, mean (SD), kg | 113.8 (28.7) | 111.2 (28.0) |
| BMI, mean (SD), kg/m2 | 38.7 (9.0) | 38.1 (9.3) |
| Waist circumference, mean (SD), cm | 117.6 (20.7) | 115.8 (21.4) |
| Body fat percentage, mean (SD), % | 126.5 (17.7) | 125.8 (18.5) |
| Test 1 | Test 2 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (SD) | Mean (SD) | SEM | MDC | ICC (95% CI) | |
| Food Approach (excl. Hunger) | 3.04 (0.64) | 3.03 (0.67) | 0.26 | 0.71 | 0.877 (0.846; 0.903) |
| Food Approach (incl. Hunger) | 3.17 (0.71) | 3.16 (0.74) | 0.22 | 0.62 | 0.885 (0.856; 0.910) |
| Food Approach Subscales | |||||
| HU | 2.73 (0.72) | 2.73 (0.72) | 0.324 | 0.898 | 0.798 (0.750; 0.839) |
| FR | 2.82 (0.82) | 2.86 (0.78) | 0.327 | 0.907 | 0.832 (0.791; 0.867) |
| EOE | 3.01 (1.00) | 2.96 (1.03) | 0.431 | 1.195 | 0.820 (0.776; 0.857) |
| EF | 3.90 (0.80) | 3.89 (0.79) | 0.326 | 0.905 | 0.831 (0.790; 0.866) |
| Food Avoidance | 2.50 (0.54) | 2.53 (0.53) | 0.23 | 0.64 | 0.815 (0.770; 0.853) |
| Food Avoidance Subscales | |||||
| SR | 2.79 (0.86) | 2.81 (0.81) | 0.350 | 0.971 | 0.823 (0.780; 0.859) |
| EUE | 2.49 (0.84) | 2.57 (0.86) | 0.512 | 1.419 | 0.640 (0.565; 0.709) |
| FF | 2.22 (0.90) | 2.21 (0.84) | 0.304 | 0.842 | 0.878 (0.847; 0.904) |
| SE | 2.59 (0.97) | 2.62 (0.94) | 0.360 | 0.997 | 0.857 (0.822; 0.887) |
| Model | Items | Factors | CFI | TLI | RMSEA | SRMR | χ2 (df) | AIC | BIC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 35 | 8 | 0.917 | 0.907 | 0.052 (0.050; 0.054) | 0.053 | 2318.3 (532) | 110,476 | 111,158 |
| 2 | 30 | 7 | 0.923 | 0.913 | 0.056 (0.053; 0.058) | 0.051 | 1875.2 (384) | 93,129 | 93,698 |
| Eight-Factor Model | Seven-Factor Model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Factor | Item | α | ω | λ (95% CI) | λ (95% CI) |
| HU | Q6 | 0.6995 | 0.7065 | 0.375 (0.321; 0.429) | - |
| Q9 | 0.492 (0.444; 0.541) | - | |||
| Q28 | 0.728 (0.693; 0.762) | - | |||
| Q32 | 0.789 (0.758; 0.820) | - | |||
| Q34 | 0.391 (0.338; 0.445) | - | |||
| FR | Q13 | 0.7823 | 0.7841 | 0.633 (0.595; 0.670) | 0.618 (0.578; 0.658) |
| Q17 | 0.775 (0.746; 0.804) | 0.795 (0.766; 0.823) | |||
| Q22 | 0.762 (0.733; 0.791) | 0.761 (0.731; 0.792) | |||
| Q33 | 0.604 (0.564; 0.644) | 0.596 (0.555; 0.638) | |||
| EOE | Q5 | 0.9062 | 0.9066 | 0.815 (0.794; 0.837) | 0.816 (0.794; 0.837) |
| Q8 | 0.877 (0.861; 0.893) | 0.878 (0.862; 0.894) | |||
| Q10 | 0.906 (0.892; 0.920) | 0.906 (0.892; 0.919) | |||
| Q16 | 0.753 (0.727; 0.780) | 0.753 (0.727; 0.780) | |||
| Q21 | 0.706 (0.675; 0.736) | 0.705 (0.675; 0.736) | |||
| EF | Q1 | 0.8287 | 0.8357 | 0.786 (0.758; 0.815) | 0.785 (0.757; 0.814) |
| Q3 | 0.823 (0.797; 0.850) | 0.823 (0.797; 0.849) | |||
| Q4 | 0.773 (0.743; 0.803) | 0.774 (0.744; 0.803) | |||
| SR | Q11 | 0.6874 | 0.6922 | 0.488 (0.435; 0.541) | 0.495 (0.443; 0.548) |
| Q23 | 0.519 (0.468; 0.569) | 0.522 (0.471; 0.572) | |||
| Q30 | 0.616 (0.571; 0.662) | 0.621 (0.575; 0.666) | |||
| Q31 | 0.755 (0.714; 0.796) | 0.746 (0.705; 0.787) | |||
| EUE | Q15 | 0.8935 | 0.8962 | 0.783 (0.758; 0.808) | 0.783 (0.757; 0.808) |
| Q18 | 0.716 (0.686; 0.747) | 0.715 (0.685; 0.746) | |||
| Q20 | 0.866 (0.848; 0.885) | 0.866 (0.848; 0.885) | |||
| Q27 | 0.854 (0.834; 0.873) | 0.854 (0.835; 0.874) | |||
| Q35 | 0.763 (0.736; 0.790) | 0.763 (0.736; 0.790) | |||
| FF | Q2 | 0.8701 | 0.8717 | 0.620 (0.582; 0.659) | 0.620 (0.582; 0.659) |
| Q7 | 0.692 (0.658; 0.725) | 0.692 (0.659; 0.725) | |||
| Q12R * | 0.873 (0.854; 0.892) | 0.873 (0.854; 0.892) | |||
| Q19R * | 0.841 (0.820; 0.863) | 0.841 (0.820; 0.863) | |||
| Q24R * | 0.752 (0.724; 0.780) | 0.752 (0.724; 0.780) | |||
| SE | Q14R * | 0.8362 | 0.8441 | 0.757 (0.729; 0.786) | 0.753 (0.723; 0.782) |
| Q25 | 0.787 (0.760; 0.815) | 0.788 (0.760; 0.815) | |||
| Q26 | 0.553 (0.511; 0.595) | 0.554 (0.511; 0.596) | |||
| Q29 | 0.913 (0.893; 0.934) | 0.913 (0.893; 0.934) |
| FR | EOE | EF | SR | EUE | FF | SE | BMI | WHR | Fat% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HU | 0.60 *** | 0.42 *** | 0.31 *** | −0.18 *** | −0.02 | 0.02 | −0.08 ** | 0.04 | −0.03 | 0.10 *** |
| FR | 0.56 *** | 0.53 *** | −0.33 *** | −0.16 *** | −0.03 | −0.16 *** | 0.11 *** | 0.03 | 0.12 *** | |
| EOE | 0.23 *** | −0.19 *** | −0.31 *** | 0.07 * | −0.07 ** | 0.22 *** | −0.03 | 0.27 *** | ||
| EF | −0.34 *** | −0.11 *** | −0.32 *** | −0.13 *** | −0.03 | 0.05 | −0.09 ** | |||
| SR | 0.32 *** | 0.18 *** | 0.29 *** | 0.03 | −0.08 ** | 0.12 *** | ||||
| EUE | 0.04 | 0.15 *** | −0.08 ** | −0.04 | −0.06 * | |||||
| FF | 0.03 | 0.08 ** | −0.01 | 0.14 *** | ||||||
| SE | −0.01 | −0.12 *** | 0.08 ** |
| Dimension | BMI β (p) | WHR β (p) | Fat% β (p) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Food approach scales | |||
| HU | 0.251 | 0.004 | 0.606 |
| FR | 1.100 *** | 0.013 *** | 1.086 *** |
| EOE | 2.014 *** | 0.009 *** | 2.119 *** |
| EF | −0.236 | 0.004 | −0.666 |
| Food avoidance scales | |||
| SR | −0.005 | 0.000 | 0.425 |
| EUE | −1.143 *** | −0.002 | −1.118 *** |
| FF | 0.422 | 0.003 | 1.003 ** |
| SE | −0.212 | −0.004 | −0.044 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kolind, M.E.I.; Windedal, T.M.; Andersen, B.V.; Drøjdahl Ryg, N.; Berg-Beckhoff, G.; Juhl, C.B. Validity and Reliability of the Danish Version of the Adult Eating Behavior Questionnaire—Results from the South Danish Obesity Initiative. Nutrients 2025, 17, 3824. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17243824
Kolind MEI, Windedal TM, Andersen BV, Drøjdahl Ryg N, Berg-Beckhoff G, Juhl CB. Validity and Reliability of the Danish Version of the Adult Eating Behavior Questionnaire—Results from the South Danish Obesity Initiative. Nutrients. 2025; 17(24):3824. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17243824
Chicago/Turabian StyleKolind, Mikkel Emil Iwanoff, Tobias Midtvedt Windedal, Barbara Vad Andersen, Nina Drøjdahl Ryg, Gabriele Berg-Beckhoff, and Claus Bogh Juhl. 2025. "Validity and Reliability of the Danish Version of the Adult Eating Behavior Questionnaire—Results from the South Danish Obesity Initiative" Nutrients 17, no. 24: 3824. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17243824
APA StyleKolind, M. E. I., Windedal, T. M., Andersen, B. V., Drøjdahl Ryg, N., Berg-Beckhoff, G., & Juhl, C. B. (2025). Validity and Reliability of the Danish Version of the Adult Eating Behavior Questionnaire—Results from the South Danish Obesity Initiative. Nutrients, 17(24), 3824. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17243824







