Prediction of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: A Nomogram Model Incorporating Lifestyle, Nutrition and Health Literacy Factors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
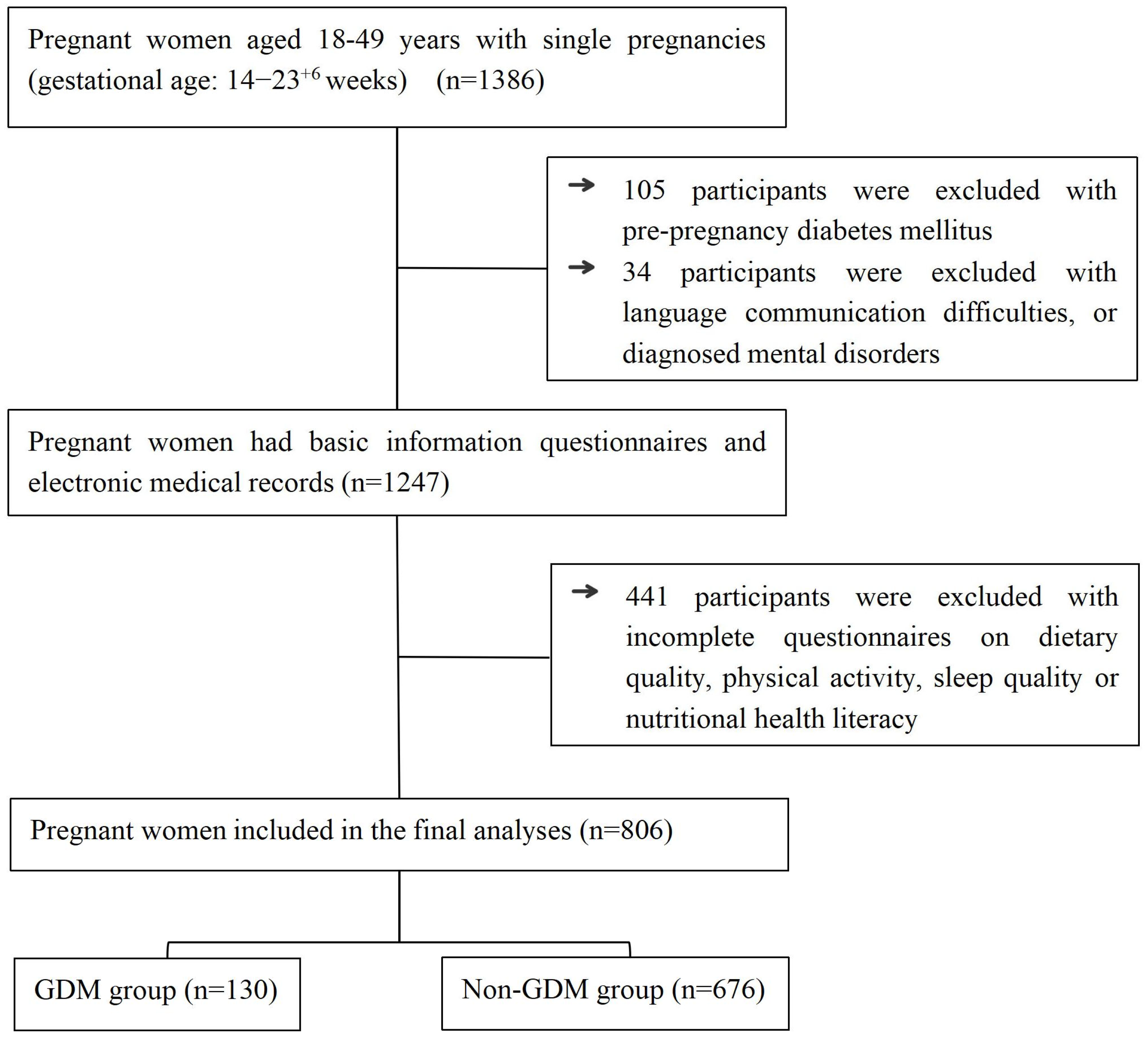
2.1. Participants
2.2. Data Collection Process
2.2.1. The Evaluation Criteria for Pre-Pregnancy BMI
2.2.2. Dietary Quality Assessment
2.2.3. Physical Activity Assessment
2.2.4. Sleep Quality Assessment
2.2.5. Nutrition and Health Literacy Assessment
2.3. The Diagnostic Criteria for GDM
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Comparison of Non-Modifiable Factors
3.2. Comparison of Modifiable Factors
3.3. Multivariate Analysis of GDM
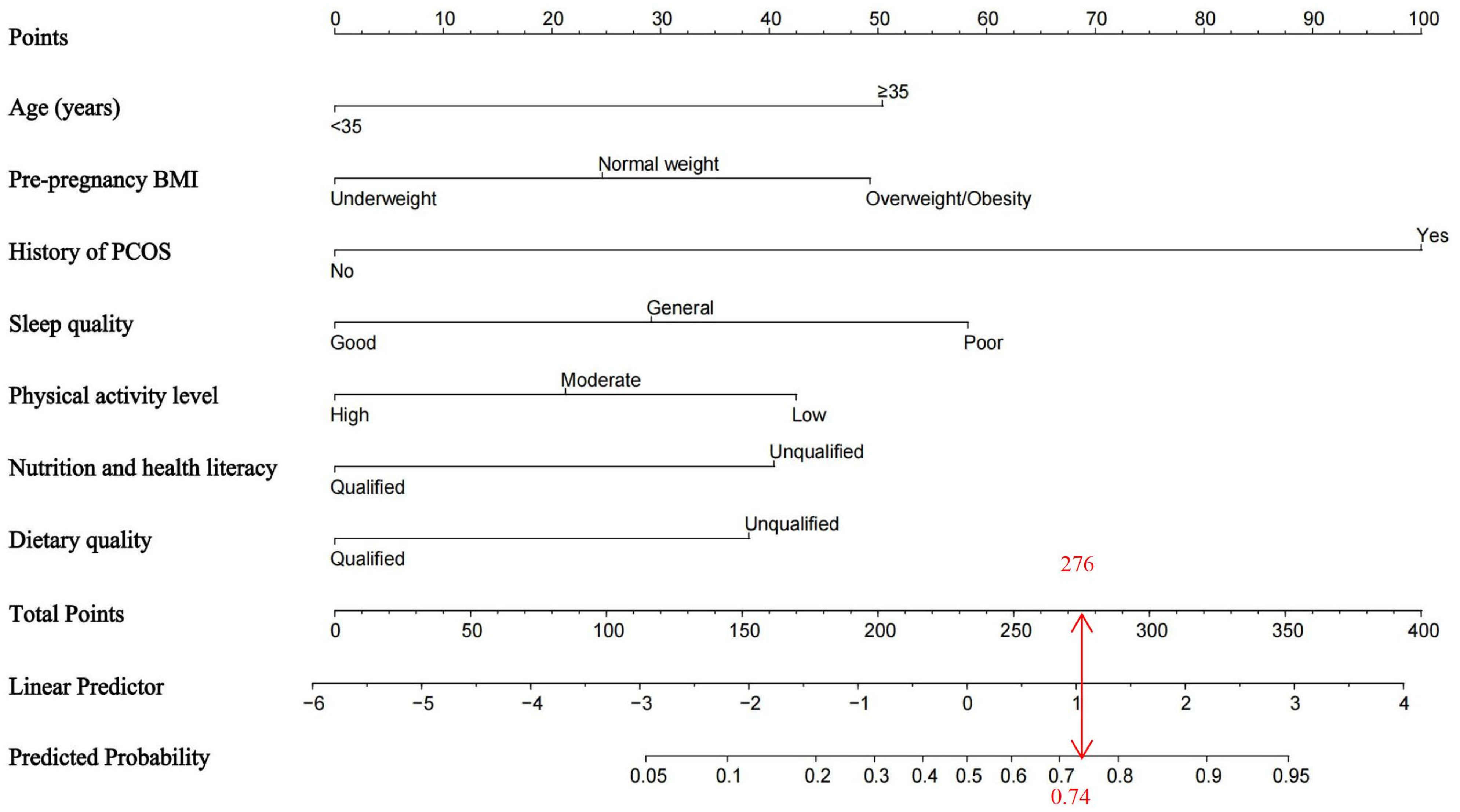
3.4. Establishment of the Nomogram Model for GDM Risk
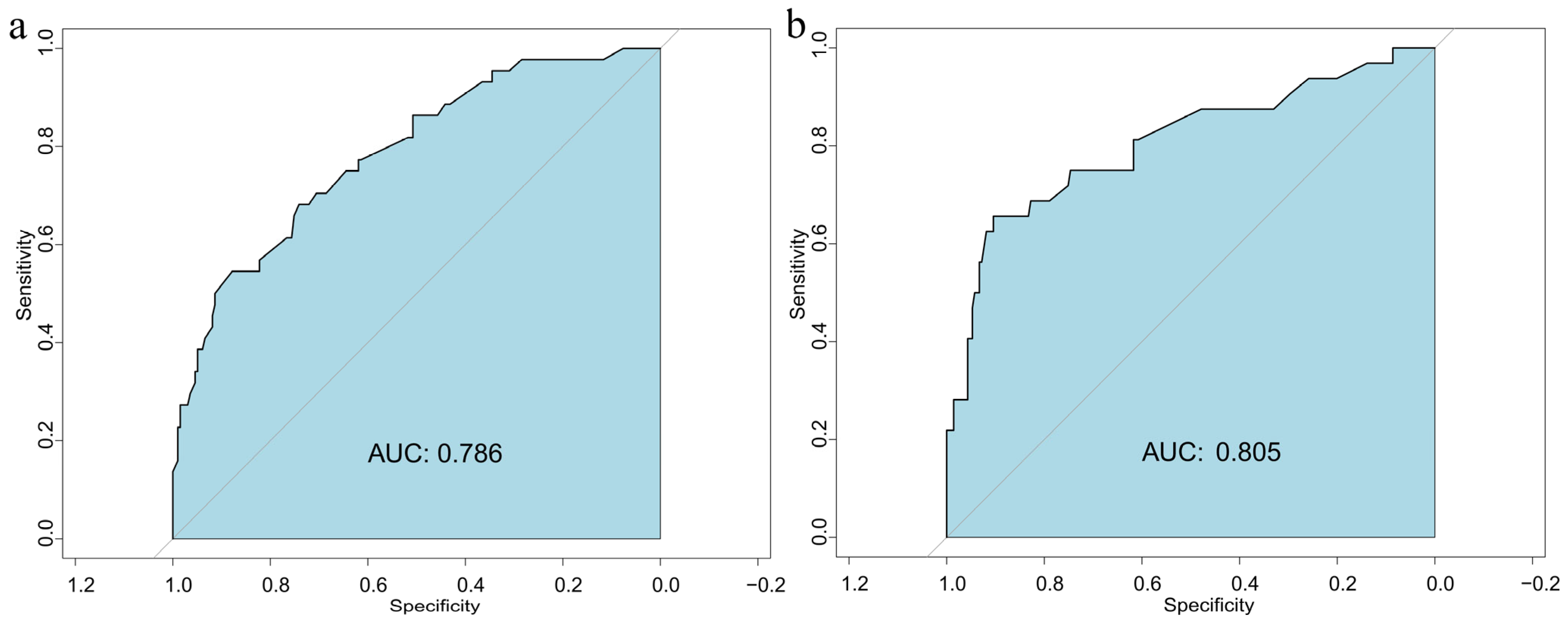
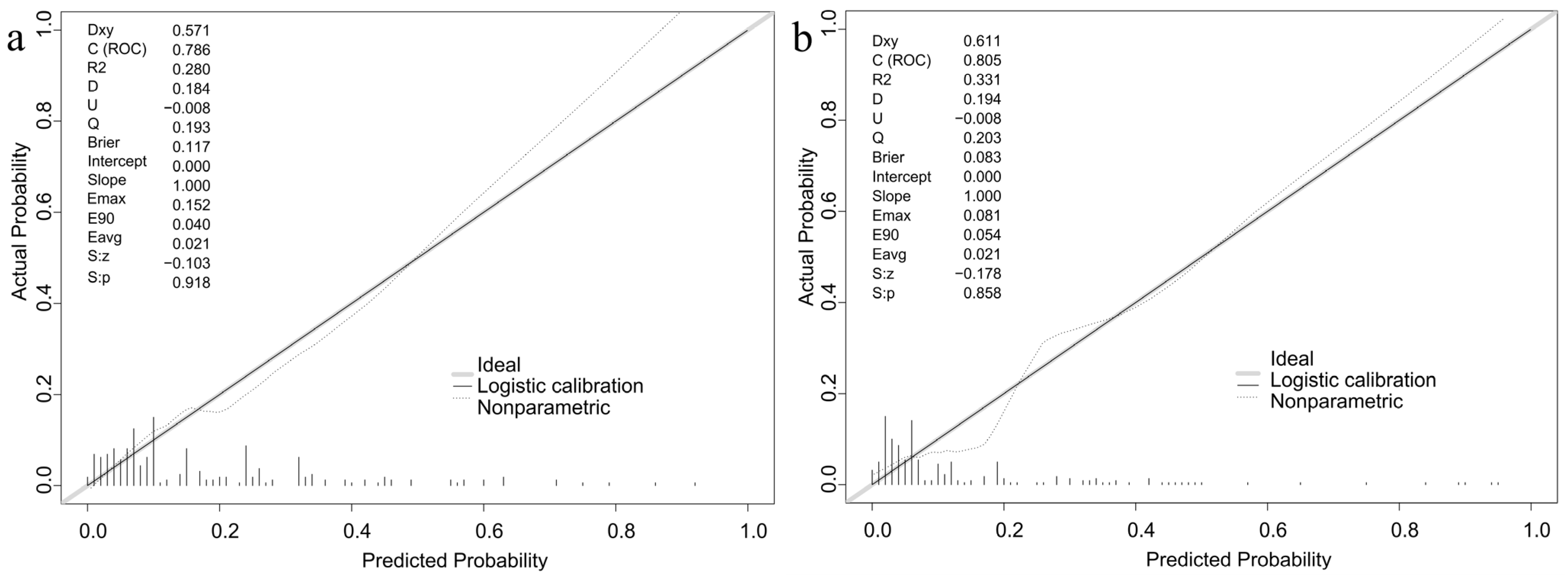
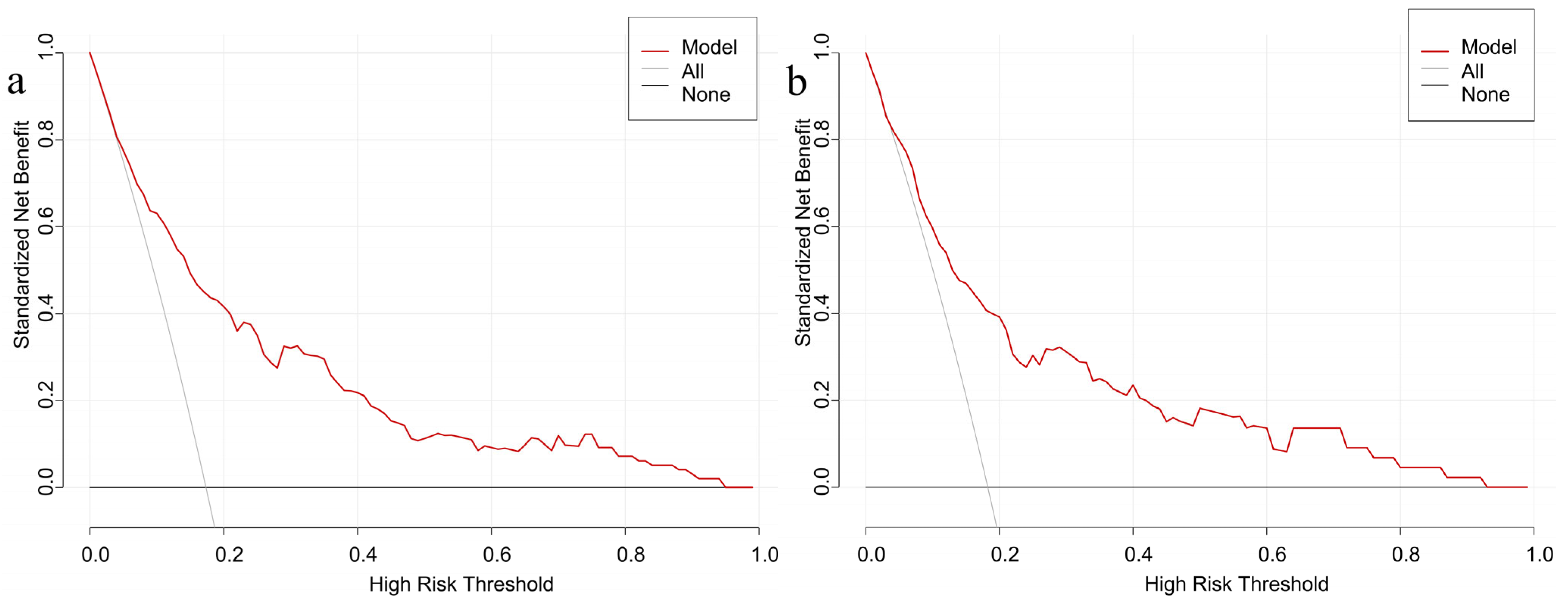
3.5. Validation of the Nomogram Model for GDM Risk
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, L.; Wang, F.; Tashiro, S.; Liu, P.J. Effects of Dietary Approaches and Exercise Interventions on Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Bayesian Network Meta-analysis. Adv. Nutr. 2024, 15, 100330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Li, N.; Chivese, T.; Werfalli, M.; Sun, H.; Yuen, L.; Hoegfeldt, C.A.; Elise Powe, C.; Immanuel, J.; Karuranga, S.; et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Estimation of Global and Regional Gestational Diabetes Mellitus Prevalence for 2021 by International Association of Diabetes in Pregnancy Study Group’s Criteria. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2022, 183, 109050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Sun, X.; Lu, L.; Liu, F.; Yuan, J. Prevalence of gestational diabetes mellitus in mainland China: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Diabetes Investig. 2019, 10, 154–162. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, W.; Luo, C.; Huang, J.; Li, C.; Liu, Z.; Liu, F. Gestational diabetes mellitus and adverse pregnancy outcomes: Systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ 2022, 377, e067946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugwudike, B.; Kwok, M. Update on gestational diabetes and adverse pregnancy outcomes. Curr. Opin. Obstet. Gynecol. 2023, 35, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, S.T.; Lee, M.C.; Tsai, Y.T.; Lu, M.C.; Yu, S.C.; Tsai, I.J.; Lee, I.T.; Yan, Y.H. Risks after Gestational Diabetes Mellitus in Taiwanese Women: A Nationwide Retrospective Cohort Study. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nijs, H.; Benhalima, K. Gestational Diabetes Mellitus and the Long-Term Risk for Glucose Intolerance and Overweight in the Offspring: A Narrative Review. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thapa, S.; Ahmed, K.Y.; Bizuayehu, H.M.; Huda, M.M.; Chalise, B.; Bore, M.G.; Belachew, S.A.; Hassen, T.A.; Amsalu, E.; Shifti, D.M.; et al. Trends and social determinants of the obesity epidemic among reproductive-age women in ten Asian countries. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 22545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Q.; Fang, Z.J. Establishment and evaluation of a risk prediction model for gestational diabetes mellitus. World J. Diabetes 2023, 14, 1541–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Li, L.; Liu, H.; Li, X.; Gu, W. Development and validation of a risk prediction model for gestational diabetes mellitus in women of advanced maternal age during the first trimester. FASEB J. 2025, 39, e70334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Xu, F.; Zhong, C.; Tong, L.; Li, F.; Li, Q.; Chen, R.; Zhou, X.; Li, X.; Cui, W.; et al. Association between Chinese Dietary Guidelines Compliance Index for Pregnant Women and Risks of Pregnancy Complications in the Tongji Maternal and Child Health Cohort. Nutrients 2021, 13, 829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.H.; Kim, M.H.; Han, H.J.; Yang, S.J.; Kim, M.G.; Lee, H.J.; Han, Y.J.; Chung, J.H.; Kwak, D.W.; Yang, S.; et al. The Preventive Effect of Physical Activity on Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: A Korean Longitudinal Prospective Cohort Study. Diabetes Metab. J. 2025, 49, 1116–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, Y.; Wang, C.; Ouyang, J.; Wu, L.; Wang, Y.; Wu, P.; Ye, Y.X.; Yang, X.; Gao, Y.; Wang, Y.X.; et al. Association between nighttime sleep duration, midday napping, and sleep quality during early pregnancy and risk of gestational diabetes mellitus: A prospective cohort study in China. Sleep Med. 2024, 119, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakai, H.; Kawata, R.; Adhikari, R.; Thapa, Y.O.; Bhandari, T.R. Effectiveness of art-based health education on anemia and health literacy among pregnant women in Western Nepal: A randomized controlled trial. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0281789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, F.; Zhong, X.; Liu, S.; Guo, X.; Li, D. Pathway analysis of the impact of health literacy, social support and self-efficacy on self-management behaviors in pregnant women with gestational diabetes mellitus. Front. Public Health 2023, 11, 1188072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Tan, W.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Zou, J.; Zhang, J.; Huang, W. Development and validation of a nomogram prediction model for hypertension-diabetes comorbidity based on chronic disease management in the community. Lipids Health Dis. 2023, 22, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Kang, S.; Kang, H. Development and validation of nomograms for predicting cardiovascular disease risk in patients with prediabetes and diabetes. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 20909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhu, H.; Yuan, J.; Wu, G. A nomogram for predicting breast cancer based on hematologic and ultrasound parameters. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2023, 15, 5602–5612. [Google Scholar]
- Balachandran, V.P.; Gonen, M.; Smith, J.J.; DeMatteo, R.P. Nomograms in oncology: More than meets the eye. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, e173–e180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhu, Q.; Wang, Z.; Tao, Y.; Liu, H.; Tang, F.; Liu, S.M.; Zhang, Y. Establishment and validation of a predictive nomogram for gestational diabetes mellitus during early pregnancy term: A retrospective study. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1087994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Yang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhang, C.; Fan, J. Nomogram for prediction of gestational diabetes mellitus in urban, Chinese, pregnant women. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2020, 20, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Qiu, M.; Guo, L.; Li, Y.; Xie, Z.; Yang, W.; Ouyang, L.; Yin, J.; Zhou, Y.; Fu, M.; et al. Association between maternal weight perception before and during pregnancy and postpartum depression status in Southern China. Nutrients 2024, 16, 3696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WS/T 428-2013; Criteria of Weight for Adults. National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2013.
- Zhang, H.; Qiu, X.; Zhong, C.; Zhang, K.; Xiao, M.; Yi, N.; Xiong, G.; Wang, J.; Yao, J.; Hao, L.; et al. Reproducibility and relative validity of a semi-quantitative food frequency questionnaire for Chinese pregnant women. Nutr. J. 2015, 14, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Y.; Yang, Y.; Li, F.; Shao, Y.; Sun, Z.; Zhong, C.; Fan, P.; Li, Z.; Zhang, M.; Li, X.; et al. Development and validation of a photographic atlas of food portions for accurate quantification of dietary intakes in China. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2021, 34, 604–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y. China Food Composition Tables, 6th ed.; Peking University Medical Press: Beijing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, B.; Lin, L.F.; Zhuang, M.Q.; Yuan, Z.Y.; Li, S.Y.; Yang, Y.J.; Lu, M.; Yu, S.Z.; Jin, L.; Ye, W.M.; et al. Reliability and relative validity of three physical activity questionnaires in Taizhou population of China: The Taizhou Longitudinal Study. Public Health 2015, 129, 1211–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.; Li, Y.; Xia, P.; Zhang, G.; Wu, D. Analysis on reliability and validity of the Pittsburgh sleep quality index. Chongqing Med. 2014, 43, 260–263. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, Y.; Li, G.; Shi, X.; Wang, M.; Peng, Y.; Deng, H.; Yang, Z.; Liang, Q.; Wang, Z. Correlation of lifestyle behaviors during pregnancy with postpartum depression status of puerpera in the rural areas of South China. Front. Public Health 2023, 11, 1304226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obstetrics Subgroup, Chinese Society of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Chinese Medicine Association; Chinese Society of Perinatal Medicine, Chinese Medicine Association; Commitee of Pregnancy with Diabetes Mellitus, China Maternal and Child Health Association. Guideline of diagnosis and treatment of hyperglycemia in pregnancy (2022). Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi 2022, 57, 3–12. [Google Scholar]
- Iwasaki, K.; Lalani, B.; Kahng, J.; Carapeto, P.; Sanjines, S.; Hela, F.; Abarca, C.; Tsuji, T.; Darcy, J.; Bartke, A.; et al. Decreased IGF1R attenuates senescence and improves function in pancreatic β-cells. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1203534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Cao, Q.; Mao, C.; Xu, J.; Li, Y.; Mu, Y.; Huang, G.; Chen, D.; Deng, X.; Xu, T.; et al. Development and validation of a prediction model for gestational diabetes mellitus risk among women from 8 to 14 weeks of gestation in Western China. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2025, 25, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Zhang, S.; Li, G.; Lai, Y.; Hao, Y.T.; Chen, W.Q.; Wu, Y.; Chen, C.; Pan, W.; Liu, Z.M. A clinical model and nomogram for early prediction of gestational diabetes based on common maternal demographics and routine clinical parameters. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Res. 2022, 48, 2738–2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, A.C.; Powell, T.L.; Jansson, T. Placental function in maternal obesity. Clin. Sci. 2020, 134, 961–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernhardt, G.V.; Shivappa, P.; Bernhardt, K.; Bhat, S.; Pinto, J.R.T.; Jhancy, M.; Kumar, S. Markers of inflammation in obese pregnant women: Adenosine deaminase and high sensitive C-reactive protein. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. X 2022, 16, 100167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, A.A.; Rajeswari, V.D. Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) increases the risk of subsequent gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM): A novel therapeutic perspective. Life Sci. 2022, 310, 121069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selen, D.J.; Powe, C.E. Gestational diabetes and other adverse pregnancy outcomes in polycystic ovary syndrome. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes. 2022, 29, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mustaniemi, S.; Vääräsmäki, M.; Eriksson, J.G.; Gissler, M.; Laivuori, H.; Ijäs, H.; Bloigu, A.; Kajantie, E.; Morin-Papunen, L. Polycystic ovary syndrome and risk factors for gestational diabetes. Endocr. Connect. 2018, 7, 859–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zakaria, H.; Abusanana, S.; Mussa, B.M.; Al Dhaheri, A.S.; Stojanovska, L.; Mohamad, M.N.; Saleh, S.T.; Ali, H.I.; Cheikh Ismail, L. The Role of Lifestyle Interventions in the Prevention and Treatment of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Medicina 2023, 59, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zheng, H.; Jiang, W.; Chi, Y.; Meng, Y.; Mo, Y.; Chen, C.; Qu, B.; He, J.; Chen, F. Which dietary pattern should be adopt by age-appropriate pregnant women to avoid gestational weight gain and gestational diabetes mellitus. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2025, 25, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsay, K.L.; Milone, G.F.; Grobman, W.A.; Haas, D.M.; Mercer, B.M.; Simhan, H.N.; Saade, G.R.; Silver, R.M.; Chung, J.H. Periconceptional diet quality is associated with gestational diabetes risk and glucose concentrations among nulliparous gravidas. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 940870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laredo-Aguilera, J.A.; Gallardo-Bravo, M.; Rabanales-Sotos, J.A.; Cobo-Cuenca, A.I.; Carmona-Torres, J.M. Physical Activity Programs during Pregnancy Are Effective for the Control of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 6151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Fang, X.; Wong, T.H.; Chan, S.N.; Akinwunmi, B.; Ming, W.K.; Zhang, C.J.P.; Wang, Z. Physical Activity during Pregnancy: Comparisons between Objective Measures and Self-Reports in Relation to Blood Glucose Levels. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 8064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Zhao, H.; Zhao, M.; Huang, H.; Liu, C.; Huang, F.; Wu, J. Effects of resistance exercise on blood glucose level and pregnancy outcome in patients with gestational diabetes mellitus: A randomized controlled trial. BMJ Open Diabetes Res. Care 2022, 10, e002622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Xu, Y.; Song, X.; Su, S.; Zhu, X.; Vitiello, M.V.; Shi, J.; et al. Sleep disturbances during pregnancy and adverse maternal and fetal outcomes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sleep Med. Rev. 2021, 58, 101436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, B.; Shi, C.; Park, C.G.; Reutrakul, S. Sleep quality and gestational diabetes in pregnant women: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sleep Med. 2020, 67, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myoga, M.; Tsuji, M.; Tanaka, R.; Shibata, E.; Askew, D.J.; Aiko, Y.; Senju, A.; Kawamoto, T.; Hachisuga, T.; Araki, S.; et al. Impact of sleep duration during pregnancy on the risk of gestational diabetes in the Japan environmental and Children’s study (JECS). BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2019, 19, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Leng, J.; Li, W.; Wang, L.; Zhang, C.; Li, W.; Liu, H.; Zhang, S.; Chan, J.; Hu, G.; et al. Sleep duration and quality, and risk of gestational diabetes mellitus in pregnant Chinese women. Diabet. Med. 2017, 34, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Yue, W.; Liu, N.; Han, X.; Yang, M. The progression on the measurement instruments of maternal health literacy: A scoping review. Midwifery 2022, 109, 103308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, X.; Lu, Y.; Ma, W.; Kang, G.; Li, J. Study on maternal and infant health literacy and influencing factors among maternal in Lanzhou, 2017. Chin. Prim. Health Care 2021, 35, 64–66. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, L.; Wan, J.; Bing, J.; Ma, Y.; Lu, N.; Shi, L. Investigation and analysis on influencing factors of maternal and child health literacy of pregnant and parturient women in Jilin Province. Matern. Child Health Care China 2020, 35, 529–532. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Cui, Y.; Du, J.; Liu, Z.; Duan, Y.; Qi, Q.; Liu, H.; Zhang, M. Association between nutritional literacy and nutrition label use in Chinese community residents. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1380310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, M.K.; Sullivan, D.K.; Ellerbeck, E.F.; Gajewski, B.J.; Gibbs, H.D. Nutrition literacy predicts adherence to healthy/unhealthy diet patterns in adults with a nutrition-related chronic condition. Public Health Nutr. 2019, 22, 2157–2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawabi, F.; Krebs, F.; Lorenz, L.; Shukri, A.; Alayli, A.; Stock, S. Health Literacy among Pregnant Women in a Lifestyle Intervention Trial. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 5808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkin, N. The relationship between health literacy and healthy lifestyle behaviors: A meta-analysis. Medicine 2024, 103, e40260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristics | Non-GDM (n = 676) | GDM (n = 130) | p | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | % | n | % | ||
| Age (years) | <0.001 | ||||
| <35 | 575 | 85.1 | 78 | 60.0 | |
| ≥35 | 101 | 14.9 | 52 | 40.0 | |
| Pre-pregnancy BMI (kg/m2) | <0.001 | ||||
| Underweight | 109 | 16.1 | 23 | 17.7 | |
| Normal weight | 496 | 73.4 | 47 | 36.2 | |
| Overweight/Obesity | 71 | 10.5 | 60 | 46.2 | |
| Ethnicity | 0.270 | ||||
| Han | 160 | 23.7 | 25 | 19.2 | |
| Minority | 516 | 76.3 | 105 | 80.8 | |
| Education level | 0.728 | ||||
| Junior high school and below | 203 | 30.0 | 44 | 33.8 | |
| Senior high school | 120 | 17.8 | 22 | 16.9 | |
| Junior college/vocational university | 156 | 23.1 | 25 | 19.2 | |
| Bachelor’s degree or above | 197 | 29.1 | 39 | 30.0 | |
| Per capitamonthly income (RMB) | 0.358 | ||||
| <2999 | 242 | 30.0 | 34 | 26.2 | |
| 3000~4999 | 190 | 23.6 | 27 | 20.8 | |
| 5000~9999 | 240 | 29.8 | 42 | 32.3 | |
| ≥10,000 | 134 | 16.6 | 27 | 20.8 | |
| Lifestyle and behavior in the first trimester | |||||
| Exercise | 245 | 36.2 | 48 | 36.9 | 0.883 |
| Insomnia | 105 | 15.5 | 19 | 14.6 | 0.119 |
| Smoking | 3 | 0.4 | 1 | 0.8 | 0.629 |
| Drinking | 43 | 6.4 | 12 | 9.2 | 0.235 |
| Mode of conception | 0.767 | ||||
| Spontaneous | 755 | 93.7 | 121 | 93.1 | |
| Assisted reproductive technology | 51 | 6.3 | 9 | 6.9 | |
| Parity | 0.723 | ||||
| Primiparous | 427 | 53.0 | 72 | 55.4 | |
| Secundiparous | 279 | 34.6 | 41 | 31.5 | |
| Multiparous (parity ≥ 3) | 100 | 12.4 | 17 | 13.1 | |
| Variables | Non-GDM (n = 676) | GDM (n = 130) | p | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | % | n | % | ||
| Maternal medical history | |||||
| Hypertension | 3 | 0.4 | 3 | 2.3 | 0.024 |
| Thyroid disease | 61 | 9.1 | 10 | 7.7 | 0.491 |
| Polycystic ovary syndrome | 23 | 3.4 | 25 | 19.2 | <0.001 |
| Familial medical history | |||||
| Obesity | 48 | 7.1 | 11 | 8.5 | 0.585 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 67 | 9.9 | 15 | 11.5 | 0.574 |
| Hypertension | 124 | 18.3 | 23 | 17.7 | 0.860 |
| Hyperlipidemia | 43 | 6.4 | 9 | 6.9 | 0.811 |
| Polycystic ovary syndrome | 44 | 6.5 | 8 | 6.2 | 0.880 |
| Variables | Non-GDM (n = 676) | GDM (n = 130) | p | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | % | n | % | ||
| Dietary quality | 0.016 | ||||
| Qualified | 188 | 27.8 | 23 | 17.7 | |
| Unqualified | 488 | 72.2 | 107 | 82.3 | |
| Physical activity level | 0.001 | ||||
| High | 200 | 29.6 | 22 | 16.9 | |
| Moderate | 329 | 48.7 | 47 | 36.2 | |
| Low | 147 | 21.7 | 61 | 46.9 | |
| Sleep quality | <0.001 | ||||
| Good | 433 | 64.1 | 65 | 50.0 | |
| General | 219 | 32.4 | 46 | 35.4 | |
| Poor | 24 | 3.5 | 19 | 14.6 | |
| Nutrition and health literacy | <0.001 | ||||
| Qualified | 187 | 27.7 | 13 | 10.0 | |
| Unqualified | 489 | 72.3 | 117 | 90.0 | |
| Variables | β | p | OR (95% CI) | VIF | Tolerance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 1.138 | <0.001 | 3.119 (1.912–5.075) | 1.090 | 0.917 |
| Pre-pregnancy body mass index | 0.760 | <0.001 | 2.138 (1.462–3.149) | 1.097 | 0.912 |
| Maternal hypertension | 1.741 | 0.099 | 5.702 (0.629–45.693) | 1.016 | 0.984 |
| Maternal Polycystic ovary syndrome | 2.205 | <0.001 | 9.074 (4.416–18.831) | 1.011 | 0.989 |
| Dietary quality | −0.639 | 0.019 | 0.527 (0.302–0.889) | 1.013 | 0.987 |
| Physical activity level | −0.386 | 0.012 | 0.679 (0.499–0.918) | 1.013 | 0.987 |
| Sleep quality | −0.961 | <0.001 | 0.382 (0.266–0.545) | 1.019 | 0.981 |
| Nutrition and health literacy | −1.595 | <0.001 | 0.202 (0.096–0.390) | 1.009 | 0.991 |
| Predictive Factors | Classifications | Values |
|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | <35 | 0 |
| ≥35 | 1 | |
| Pre-pregnancy body mass index (kg/m2) | Underweight | 1 |
| Normal weight | 2 | |
| Overweight/Obesity | 3 | |
| Maternal Polycystic ovary syndrome | No | 0 |
| Yes | 1 | |
| Dietary quality | Qualified | 1 |
| Unqualified | 0 | |
| Physical activity level | High | 3 |
| Moderate | 2 | |
| Low | 1 | |
| Sleep quality | Good | 3 |
| General | 2 | |
| Poor | 1 | |
| Nutrition and health literacy | Qualified | 1 |
| Unqualified | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fu, M.; Qiu, M.; Xie, Z.; Guo, L.; Zhou, Y.; Yin, J.; Yang, W.; Ouyang, L.; Ding, Y.; Wang, Z. Prediction of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: A Nomogram Model Incorporating Lifestyle, Nutrition and Health Literacy Factors. Nutrients 2025, 17, 3400. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17213400
Fu M, Qiu M, Xie Z, Guo L, Zhou Y, Yin J, Yang W, Ouyang L, Ding Y, Wang Z. Prediction of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: A Nomogram Model Incorporating Lifestyle, Nutrition and Health Literacy Factors. Nutrients. 2025; 17(21):3400. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17213400
Chicago/Turabian StyleFu, Minghan, Menglu Qiu, Zhencheng Xie, Laidi Guo, Yun Zhou, Jia Yin, Wanyi Yang, Lishan Ouyang, Ye Ding, and Zhixu Wang. 2025. "Prediction of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: A Nomogram Model Incorporating Lifestyle, Nutrition and Health Literacy Factors" Nutrients 17, no. 21: 3400. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17213400
APA StyleFu, M., Qiu, M., Xie, Z., Guo, L., Zhou, Y., Yin, J., Yang, W., Ouyang, L., Ding, Y., & Wang, Z. (2025). Prediction of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: A Nomogram Model Incorporating Lifestyle, Nutrition and Health Literacy Factors. Nutrients, 17(21), 3400. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17213400






