Minimum Dietary Fat Threshold for Effective Ketogenesis and Obesity Control in Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The Animals
2.2. Hematoxylin & Eosin (H&E) Staining and Alcian Blue Staining
2.3. Glucose and Ketone Body Measurement
2.4. Metabolite Measurement
2.5. Gene Expression Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Diets with Different Fat Levels Exert Distinct Effects on Body Weight and Circulating Metabolites
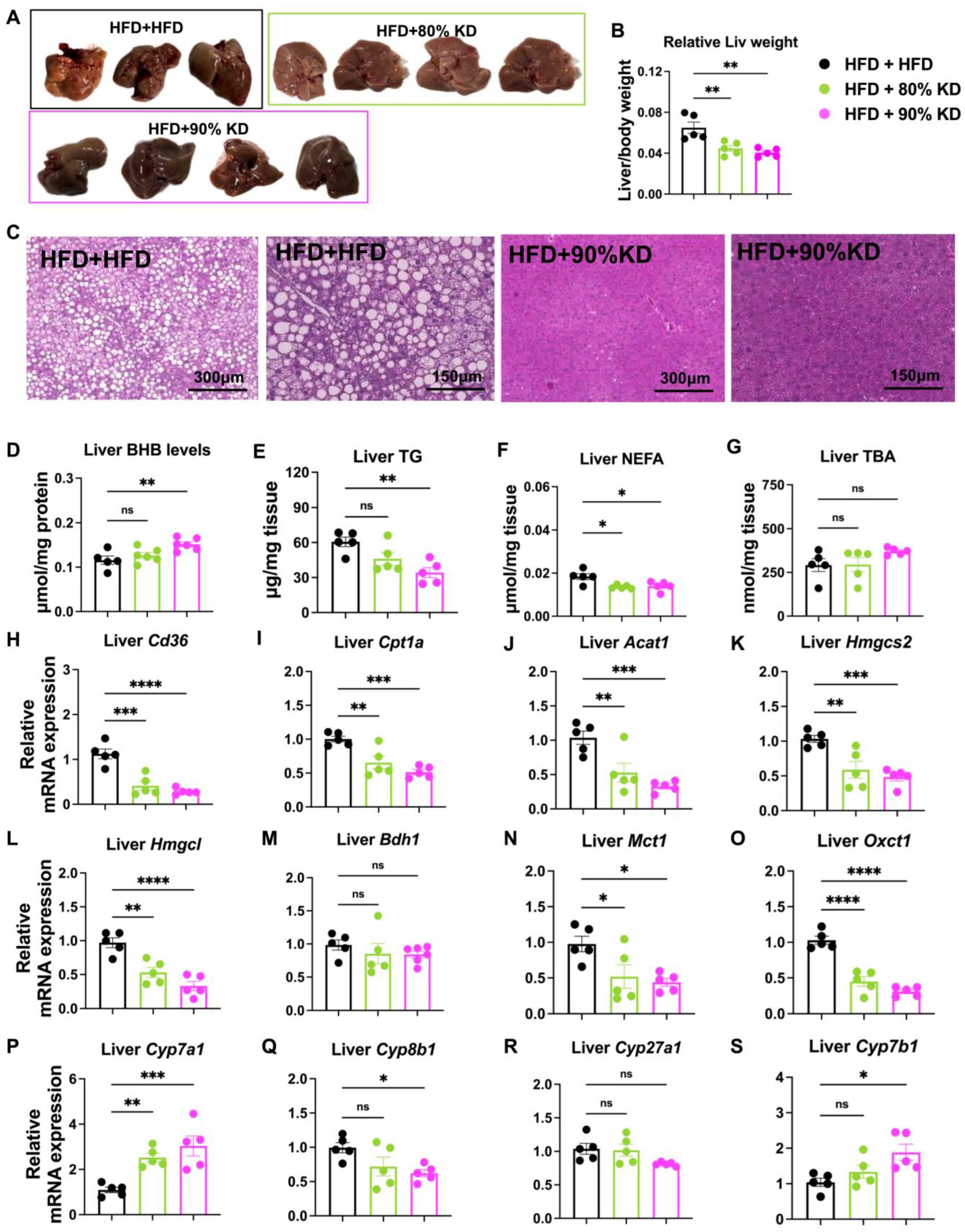
3.2. Hepatic Adaptations to Ketogenic Diets Reflected in Morphology, Metabolite Levels, and Gene Expression
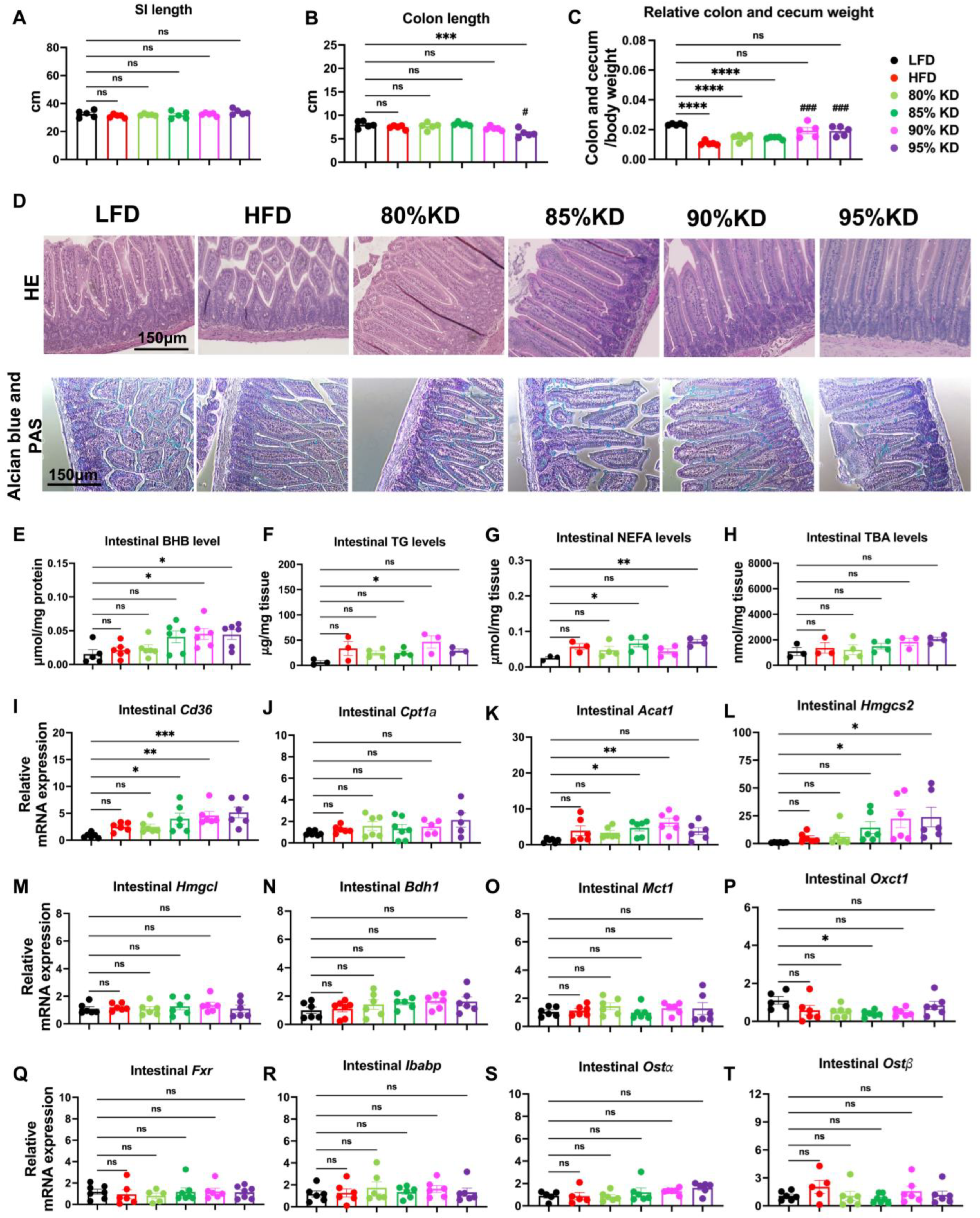
3.3. Intestinal Responses to Ketogenic Diets Reflected in Morphology, Metabolite Levels, and Gene Expression
3.4. Effects of Ketogenic Diet Interventions on Diet-Induced Obesity on Systemic Metabolic Parameters in Mice
3.5. Effects of Ketogenic Diet Interventions on Hepatic Morphology, Lipid Accumulation, and Gene Expression
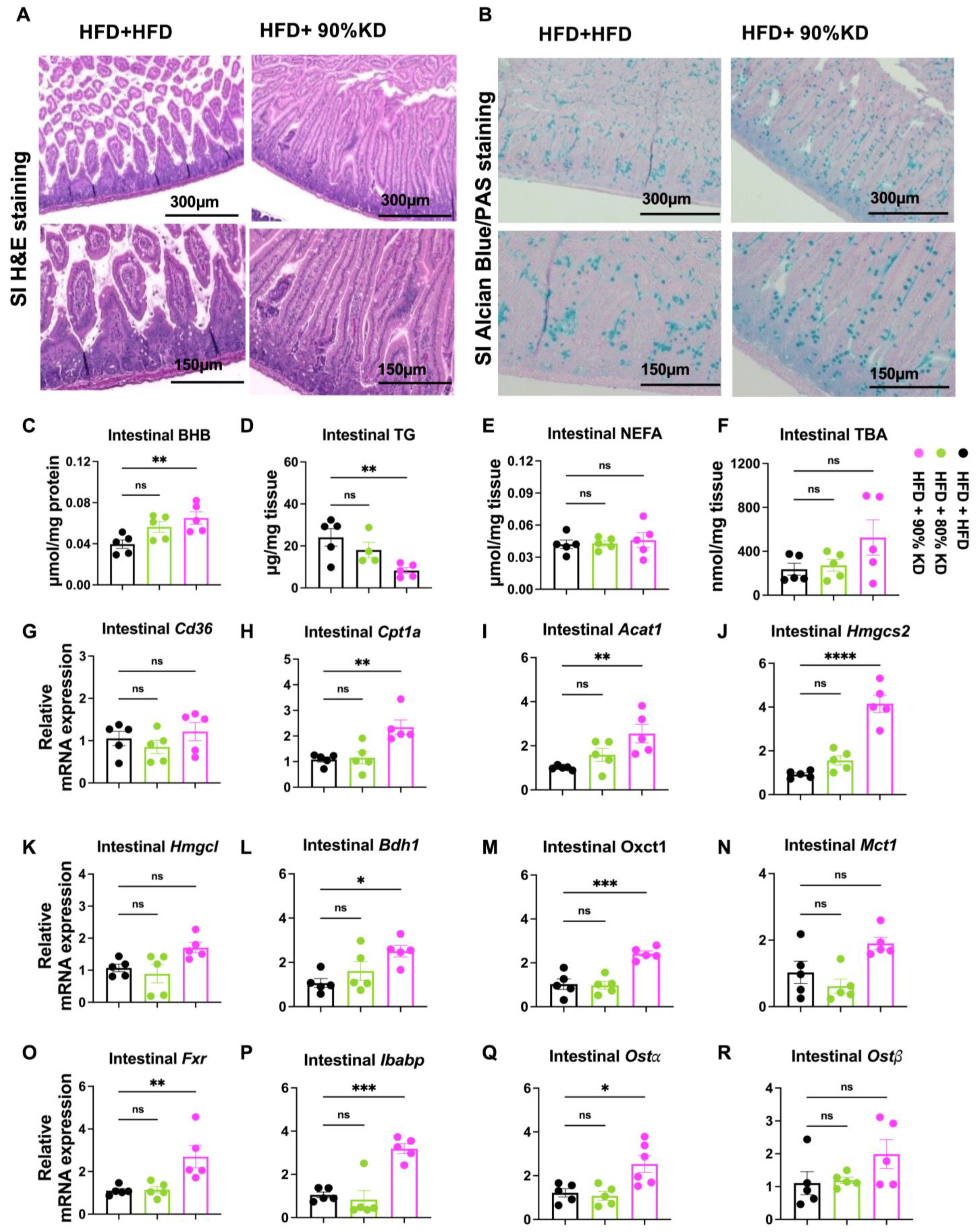
3.6. Effects of Ketogenic Diet Interventions on Intestinal Morphology, Lipid Accumulation, and Gene Expression
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AAALAC | Association for Assessment and Accreditation of Laboratory Animal Care |
| Acat1 | Acetyl-CoA Acetyltransferase 1 |
| BA | Bile acid |
| Bdh1 | 3-Hydroxybutyrate Dehydrogenase 1 |
| BHB | Beta-hydroxybutyrate |
| DIO | Diet-induced obese |
| Cd36 | Cluster of Differentiation 36 |
| Cpt1a | Carnitine Palmitoyltransferase 1A |
| Cyp7a1 | Cytochrome P450 family 7 subfamily A member 1 |
| Cyp7b1 | Cytochrome P450 family 7 subfamily B member 1 |
| Cyp8b1 | Cytochrome P450 family 8 subfamily B member 1 |
| Cyp27a1 | Cytochrome P450 family 27 subfamily A member 1 |
| FFA | Free fatty acid |
| FITC | Fluorescein Isothiocyanate |
| Fxr | Farnesoid X Receptor |
| HDACs | Histone deacetylases |
| H&E | Hematoxylin & Eosin |
| HFD | High-fat diet |
| Hmgcs2 | 3-Hydroxy-3-Methylglutaryl-CoA Synthase 2 |
| Hmgcl | 3-Hydroxy-3-Methylglutaryl-CoA Lyase |
| ISC | Intestinal Stem Cells |
| IACUC | Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee |
| Ibabp | Ileal Bile Acid-Binding Protein |
| KD | Ketogenic diet |
| Mct1 | Monocarboxylate transporter 1 |
| ND | Normal diet |
| NEFA | Non-esterified fatty acids |
| Ostα | Organic solute transporter alpha |
| Ostβ | Organic solute transporter beta |
| Oxct1 | 3-oxoacid CoA-transferase 1 |
| SI | small intestine |
| TBA | Total bile acid |
| TDCA | Taurodeoxycholic acid |
| TG | Triglyceride |
| TUDCA | Tauroursodeoxycholic acid |
| Th17 | T helper 17 cells |
| WT | Wild type |
References
- Bluher, M. Obesity: Global epidemiology and pathogenesis. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2019, 15, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heymsfield, S.B.; Wadden, T.A. Mechanisms, Pathophysiology, and Management of Obesity. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 254–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adolph, T.E.; Tilg, H. Western diets and chronic diseases. Nat. Med. 2024, 30, 2133–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakhra, V.; Galappaththy, S.L.; Bulchandani, S.; Cabandugama, P.K. Obesity and the Western Diet: How We Got Here. Mo. Med. 2020, 117, 536–538. [Google Scholar]
- de Moura, E.D.M.; Dos Reis, S.A.; da Conceicao, L.L.; Sediyama, C.; Pereira, S.S.; de Oliveira, L.L.; Gouveia Peluzio, M.D.C.; Martinez, J.A.; Milagro, F.I. Diet-induced obesity in animal models: Points to consider and influence on metabolic markers. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2021, 13, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodpaster, B.H.; Sparks, L.M. Metabolic Flexibility in Health and Disease. Cell Metab. 2017, 25, 1027–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.L.; Soeters, M.R.; Wust, R.C.I.; Houtkooper, R.H. Metabolic Flexibility as an Adaptation to Energy Resources and Requirements in Health and Disease. Endocr. Rev. 2018, 39, 489–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fulghum, K.; Salathe, S.F.; Davis, X.; Thyfault, J.P.; Puchalska, P.; Crawford, P.A. Ketone body metabolism and cardiometabolic implications for cognitive health. npj Metab. Health Dis. 2024, 2, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sears, B.; Perry, M. The role of fatty acids in insulin resistance. Lipids Health Dis. 2015, 14, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hengist, A.; Davies, R.G.; Walhin, J.P.; Buniam, J.; Merrell, L.H.; Rogers, L.; Bradshaw, L.; Moreno-Cabanas, A.; Rogers, P.J.; Brunstrom, J.M.; et al. Ketogenic diet but not free-sugar restriction alters glucose tolerance, lipid metabolism, peripheral tissue phenotype, and gut microbiome: RCT. Cell Rep. Med. 2024, 5, 101667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emanuele, F.; Biondo, M.; Tomasello, L.; Arnaldi, G.; Guarnotta, V. Ketogenic Diet in Steatotic Liver Disease: A Metabolic Approach to Hepatic Health. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puchalska, P.; Crawford, P.A. Metabolic and Signaling Roles of Ketone Bodies in Health and Disease. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2021, 41, 49–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, J.C.; Verdin, E. Ketone bodies as signaling metabolites. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 25, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Rodriguez, D.; Gimenez-Cassina, A. Ketone Bodies in the Brain Beyond Fuel Metabolism: From Excitability to Gene Expression and Cell Signaling. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2021, 14, 732120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cahill, G.F., Jr. Fuel metabolism in starvation. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2006, 26, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGarry, J.; Wright, P.H.; Foster, D.W. Hormonal control of ketogenesis. Rapid activation of hepatic ketogenic capacity in fed rats by anti-insulin serum and glucagon. J. Clin. Investig. 1975, 55, 1202–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukao, T.; Song, X.Q.; Mitchell, G.A.; Yamaguchi, S.; Sukegawa, K.; Orii, T.; Kondo, N. Enzymes of ketone body utilization in human tissues: Protein and messenger RNA levels of succinyl-coenzyme A (CoA):3-ketoacid CoA transferase and mitochondrial and cytosolic acetoacetyl-CoA thiolases. Pediatr. Res. 1997, 42, 498–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.W.; Biton, M.; Haber, A.L.; Gunduz, N.; Eng, G.; Gaynor, L.T.; Tripathi, S.; Calibasi-Kocal, G.; Rickelt, S.; Butty, V.L.; et al. Ketone Body Signaling Mediates Intestinal Stem Cell Homeostasis and Adaptation to Diet. Cell 2019, 178, 1115–1131.E15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasse, E.O.; Fery, F. Ketone body production and disposal: Effects of fasting, diabetes, and exercise. Diabetes Metab. Rev. 1989, 5, 247–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, J.C.; Verdin, E. beta-Hydroxybutyrate: A Signaling Metabolite. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2017, 37, 51–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemingway, C.; Freeman, J.M.; Pillas, D.J.; Pyzik, P.L. The ketogenic diet: A 3- to 6-year follow-up of 150 children enrolled prospectively. Pediatrics 2001, 108, 898–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckett, T.L.; Studzinski, C.M.; Keller, J.N.; Paul Murphy, M.; Niedowicz, D.M. A ketogenic diet improves motor performance but does not affect beta-amyloid levels in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Res. 2013, 1505, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prins, M.L.; Lee, S.M.; Fujima, L.S.; Hovda, D.A. Increased cerebral uptake and oxidation of exogenous betaHB improves ATP following traumatic brain injury in adult rats. J. Neurochem. 2004, 90, 666–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yurista, S.R.; Nguyen, C.T.; Rosenzweig, A.; de Boer, R.A.; Westenbrink, B.D. Ketone bodies for the failing heart: Fuels that can fix the engine? Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 32, 814–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dmitrieva-Posocco, O.; Wong, A.C.; Lundgren, P.; Golos, A.M.; Descamps, H.C.; Dohnalova, L.; Cramer, Z.; Tian, Y.; Yueh, B.; Eskiocak, O.; et al. beta-Hydroxybutyrate suppresses colorectal cancer. Nature 2022, 605, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, Q.Y.; Alexander, M.; Newman, J.C.; Tian, Y.; Cai, J.; Upadhyay, V.; Turnbaugh, J.A.; Verdin, E.; Hall, K.D.; Leibel, R.L.; et al. Ketogenic Diets Alter the Gut Microbiome Resulting in Decreased Intestinal Th17 Cells. Cell 2020, 181, 1263–1275.E16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yang, J.; Zhou, X.; Dai, C.; Kong, M.; Xie, L.; Liu, C.; Liu, Y.; Li, D.; Ma, X.; et al. Ketogenic diet-induced bile acids protect against obesity through reduced calorie absorption. Nat. Metab. 2024, 6, 1397–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Bi, D.; Zhang, Y.; Kong, C.; Du, J.; Wu, X.; Wei, Q.; Qin, H. Ketogenic diet for human diseases: The underlying mechanisms and potential for clinical implementations. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rynders, C.A.; Thomas, E.A.; Zaman, A.; Pan, Z.; Catenacci, V.A.; Melanson, E.L. Effectiveness of Intermittent Fasting and Time-Restricted Feeding Compared to Continuous Energy Restriction for Weight Loss. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasim, I.; Majeed, C.N.; DeBoer, M.D. Intermittent Fasting and Metabolic Health. Nutrients 2022, 14, 631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muscella, A.; Stefano, E.; Lunetti, P.; Capobianco, L.; Marsigliante, S. The Regulation of Fat Metabolism During Aerobic Exercise. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storoschuk, K.L.; Wood, T.R.; Stubbs, B.J. A systematic review and meta-regression of exogenous ketone infusion rates and resulting ketosis-A tool for clinicians and researchers. Front. Physiol. 2023, 14, 1202186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Rychahou, P.; Fan, T.W.; Lane, A.N.; Weiss, H.L.; Evers, B.M. Ketogenesis contributes to intestinal cell differentiation. Cell Death Differ. 2017, 24, 458–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, F.; Wang, K.; Dong, X.; Secaira-Morocho, H.; Hui, A.; Cai, C.; Sze, J.J.; Low, B.; Udgata, S.; Pasch, C.A.; et al. The Microbial Bile Acid Metabolite 3-oxo-LCA Inhibits Colorectal Cancer Progression. Cancer Res. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Sun, F.; Secaira-Morocho, H.; Hui, A.; Wang, K.; Cai, C.; Udgata, S.; Low, B.; Wei, S.; Chen, X.; et al. The dichotomous roles of microbial-modified bile acids 7-oxo-DCA and isoDCA in intestinal tumorigenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2024, 121, e2317596121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moro, C.; Magnan, C. Revisited guidelines for metabolic tolerance tests in mice. Lab Anim. 2025, 54, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Li, B.; Li, L.; Mitchell, S.E.; Green, C.L.; D’Agostino, G.; Wang, G.; Wang, L.; Li, M.; Li, J.; et al. Very-low-protein diets lead to reduced food intake and weight loss, linked to inhibition of hypothalamic mTOR signaling, in mice. Cell Metab. 2021, 33, 888–904.E6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augustin, K.; Khabbush, A.; Williams, S.; Eaton, S.; Orford, M.; Cross, J.H.; Heales, S.J.R.; Walker, M.C.; Williams, R.S.B. Mechanisms of action for the medium-chain triglyceride ketogenic diet in neurological and metabolic disorders. Lancet Neurol. 2018, 17, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosinski, C.; Jornayvaz, F.R. Effects of Ketogenic Diets on Cardiovascular Risk Factors: Evidence from Animal and Human Studies. Nutrients 2017, 9, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Y.W.; Morrison, D.; Lu, J.C.; Lee, M.H.; Jenkins, A.J.; O’Neal, D.N. Continuous ketone monitoring: Exciting implications for clinical practice. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2024, 26 (Suppl. 7), 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosier, R.; McPherson, R. Profound Elevation in LDL Cholesterol Level Following a Ketogenic Diet: A Case Series. CJC Open 2022, 4, 732–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bueno, N.B.; de Melo, I.S.; de Oliveira, S.L.; da Rocha Ataide, T. Very-low-carbohydrate ketogenic diet v. low-fat diet for long-term weight loss: A meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Br. J. Nutr. 2013, 110, 1178–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuenoud, B.; Hartweg, M.; Godin, J.P.; Croteau, E.; Maltais, M.; Castellano, C.A.; Carpentier, A.C.; Cunnane, S.C. Metabolism of Exogenous D-Beta-Hydroxybutyrate, an Energy Substrate Avidly Consumed by the Heart and Kidney. Front. Nutr. 2020, 7, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Diet | LFD | HFD | 80% KD | 80% Fat, 5% Carb KD | 85% KD | 90% KD | 95% KD | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| g% | kcal% | g% | kcal% | g% | kcal% | g% | kcal% | g% | kcal% | g% | kcal% | g% | kcal% | |
| Protein | 19 | 20 | 26 | 20 | 31 | 20 | 23 | 15 | 24 | 15 | 17 | 10 | 9 | 5 |
| Carbohydrate | 67 | 70 | 26 | 20 | 0 | 0 | 8 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Fat | 4 | 10 | 35 | 60 | 54 | 80 | 55 | 80 | 60 | 85 | 67 | 90 | 74 | 95 |
| Total | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | |||||||
| kcal/g | 3.9 | 5.2 | 6.1 | 6.1 | 6.4 | 6.7 | 7.0 | |||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shou, J.; Dong, X.; Sun, F.; Li, J.; Wang, H.; Ai, Q.; Pellizzon, M.; Fu, T. Minimum Dietary Fat Threshold for Effective Ketogenesis and Obesity Control in Mice. Nutrients 2025, 17, 3203. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17203203
Shou J, Dong X, Sun F, Li J, Wang H, Ai Q, Pellizzon M, Fu T. Minimum Dietary Fat Threshold for Effective Ketogenesis and Obesity Control in Mice. Nutrients. 2025; 17(20):3203. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17203203
Chicago/Turabian StyleShou, Jiawen, Xingchen Dong, Fei Sun, Jia Li, Huiren Wang, Qing Ai, Michael Pellizzon, and Ting Fu. 2025. "Minimum Dietary Fat Threshold for Effective Ketogenesis and Obesity Control in Mice" Nutrients 17, no. 20: 3203. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17203203
APA StyleShou, J., Dong, X., Sun, F., Li, J., Wang, H., Ai, Q., Pellizzon, M., & Fu, T. (2025). Minimum Dietary Fat Threshold for Effective Ketogenesis and Obesity Control in Mice. Nutrients, 17(20), 3203. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17203203







