Effects of Caffeine Intake Combined with Self-Selected Music During Warm-Up on Anaerobic Performance: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Crossover Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Participants
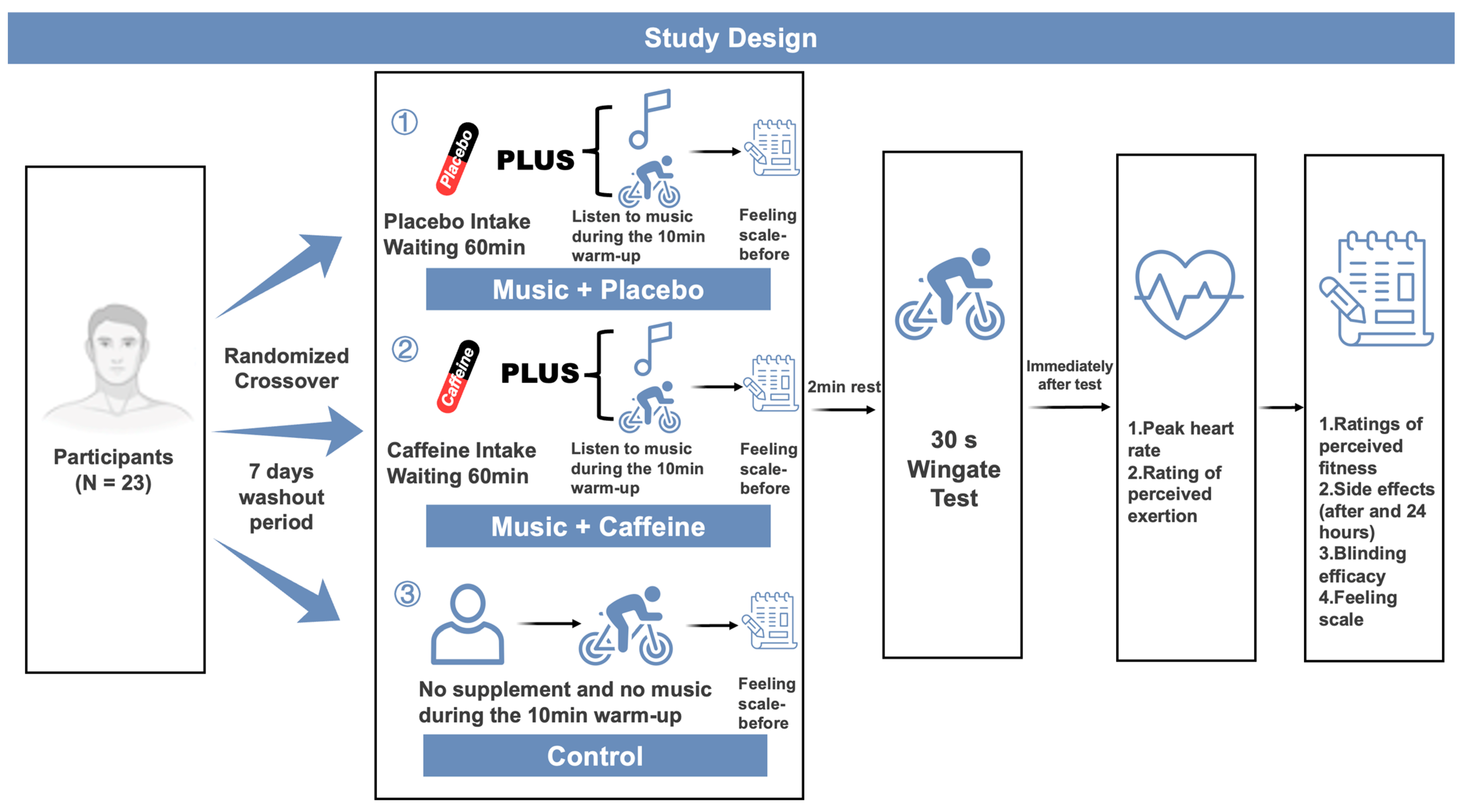
2.2. Study Design
2.3. Experimental Protocol
2.4. Analysis of Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Wingate Anaerobic Test Performance, Heart Rate, and Ratings of Perceived Exertion
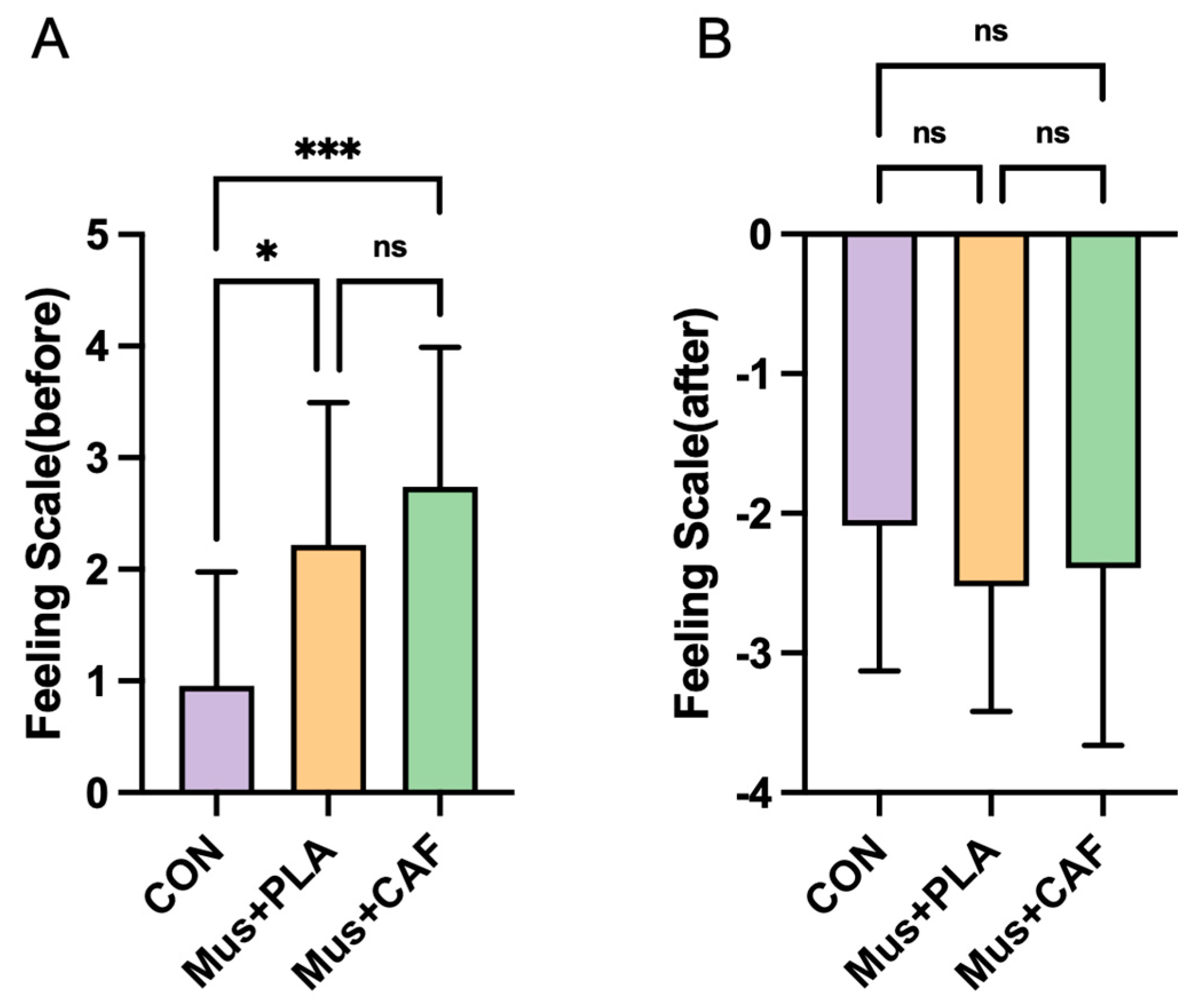
3.2. Feeling Scale
3.3. Perceived Fitness, Side Effects, and Blinding Efficacy
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Losnegard, T.; Myklebust, H.; Hallén, J. Anaerobic capacity as a determinant of performance in sprint skiing. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2012, 44, 673–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noordhof, D.A.; Skiba, P.F.; de Koning, J.J. Determining anaerobic capacity in sporting activities. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2013, 8, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loizou, G.; Karageorghis, C.I. Effects of psychological priming, video, and music on anaerobic exercise performance. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2015, 25, 909–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atan, T. Effect of music on anaerobic exercise performance. Biol. Sport. 2013, 30, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lara, B.; Salinero, J.J.; Giráldez-Costas, V.; Del Coso, J. Similar ergogenic effect of caffeine on anaerobic performance in men and women athletes. Eur. J. Nutr. 2021, 60, 4107–4114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jodra, P.; Lago-Rodríguez, A.; Sánchez-Oliver, A.J.; López-Samanes, A.; Pérez-López, A.; Veiga-Herreros, P.; San Juan, A.F.; Domínguez, R. Effects of caffeine supplementation on physical performance and mood dimensions in elite and trained-recreational athletes. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2020, 17, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doma, K.; Leicht, A.S.; Schumann, M.; Nagata, A.; Senzaki, K.; Woods, C.E. Postactivation potentiation effect of overloaded cycling on subsequent cycling Wingate performance. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fit. 2019, 59, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ktenidis, C.K.; Margaritelis, N.V.; Cherouveim, E.D.; Stergiopoulos, D.C.; Malliou, V.J.; Geladas, N.D.; Nikolaidis, M.G.; Paschalis, V. Priming exercise increases Wingate cycling peak power output. Eur. J. Sport. Sci. 2021, 21, 705–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, D.J.; Fletcher, D. Effects of Psychological and Psychosocial Interventions on Sport Performance: A Meta-Analysis. Sports Med. 2017, 47, 77–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terry, P.C.; Karageorghis, C.I.; Curran, M.L.; Martin, O.V.; Parsons-Smith, R.L. Effects of music in exercise and sport: A meta-analytic review. Psychol. Bull. 2020, 146, 91–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Yang, J.; Tao, X.; Du, L.; Li, X.; Lv, Y.; Hou, X.; Yu, L. Listening to Self-Selected Music during Warm-Up Improves Anaerobic Performance through Enhancement of the Excitability of the Cerebral Cortex. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 7180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stork, M.J.; Kwan, M.Y.; Gibala, M.J.; Martin Ginis, K.A. Music enhances performance and perceived enjoyment of sprint interval exercise. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2015, 47, 1052–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terry, P.C.; Karageorghis, C.I. Psychophysical effects of music in sport and exercise: An update on theory, research and application. In Proceedings of the 2006 Joint Conference of the Australian Psychological Society and New Zealand Psychological Society, Auckland, New Zealand, 26–30 September 2006; pp. 415–419. [Google Scholar]
- Castañeda-Babarro, A.; Marqués-Jiménez, D.; Calleja-González, J.; Viribay, A.; León-Guereño, P.; Mielgo-Ayuso, J. Effect of Listening to Music on Wingate Anaerobic Test Performance. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 4564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smirmaul, B.P. Effect of pre-task music on sports or exercise performance. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fit. 2017, 57, 976–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhang, L.; Yang, H.; Lu, C.; Jiang, L.; Chen, Y. The Effect of Music Tempo on Fatigue Perception at Different Exercise Intensities. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 3869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, P.M.; Pereira, G.; Papini, C.B.; Nakamura, F.Y.; Kokubun, E. Effects of preferred and nonpreferred music on continuous cycling exercise performance. Percept. Mot. Ski. 2010, 110, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Copeland, B.L.; Franks, B.D. Effects of types and intensities of background music on treadmill endurance. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fit. 1991, 31, 100–103. [Google Scholar]
- Feiss, R.; Kostrna, J.; Scruggs, J.W.; Pangelinan, M.; Tenenbaum, G. Effects of music tempo on perceived exertion, attention, affect, heart rate, and performance during isometric strength exercise. J. Sports Sci. 2021, 39, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballmann, C.G.; McCullum, M.J.; Rogers, R.R.; Marshall, M.R.; Williams, T.D. Effects of Preferred vs. Nonpreferred Music on Resistance Exercise Performance. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2021, 35, 1650–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballmann, C.G.; Maynard, D.J.; Lafoon, Z.N.; Marshall, M.R.; Williams, T.D.; Rogers, R.R. Effects of Listening to Preferred versus Non-Preferred Music on Repeated Wingate Anaerobic Test Performance. Sports 2019, 7, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chtourou, H.; Jarraya, M.; Aloui, A.; Hammouda, O.; Souissi, N. The effects of music during warm-up on anaerobic performances of young sprinters. Sci. Sports 2012, 27, e85–e88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Close, G.L.; Hamilton, D.L.; Philp, A.; Burke, L.M.; Morton, J.P. New strategies in sport nutrition to increase exercise performance. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2016, 98, 144–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguilar-Navarro, M.; Muñoz, G.; Salinero, J.J.; Muñoz-Guerra, J.; Fernández-Álvarez, M.; Plata, M.D.M.; Del Coso, J. Urine Caffeine Concentration in Doping Control Samples from 2004 to 2015. Nutrients 2019, 11, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Coso, J.; Muñoz, G.; Muñoz-Guerra, J. Prevalence of caffeine use in elite athletes following its removal from the World Anti-Doping Agency list of banned substances. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2011, 36, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cappelletti, S.; Piacentino, D.; Sani, G.; Aromatario, M. Caffeine: Cognitive and physical performance enhancer or psychoactive drug? Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2015, 13, 71–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Qiu, B.; Gao, J.; Del Coso, J. Effects of Caffeine Intake on Endurance Running Performance and Time to Exhaustion: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2022, 15, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grgic, J.; Grgic, I.; Pickering, C.; Schoenfeld, B.J.; Bishop, D.J.; Pedisic, Z. Wake up and smell the coffee: Caffeine supplementation and exercise performance-an umbrella review of 21 published meta-analyses. Br. J. Sports Med. 2020, 54, 681–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giráldez-Costas, V.; Del Coso, J.; Mañas, A.; Salinero, J.J. The Long Way to Establish the Ergogenic Effect of Caffeine on Strength Performance: An Overview Review. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, T.E. Caffeine and exercise: Metabolism, endurance and performance. Sports Med. 2001, 31, 785–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.M.; Zhao, Z.; Stock, H.S.; Mehl, K.A.; Buggy, J.; Hand, G.A. Central nervous system effects of caffeine and adenosine on fatigue. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2003, 284, R399–R404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, G. Caffeine and other sympathomimetic stimulants: Modes of action and effects on sports performance. Essays Biochem. 2008, 44, 109–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daly, J.W.; Shi, D.; Nikodijevic, O.; Jacobson, K.A. The role of adenosine receptors in the central action of caffeine. Pharmacopsychoecologia 1994, 7, 201–213. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, J.; Green, J.M. Caffeine and anaerobic performance: Ergogenic value and mechanisms of action. Sports Med. 2009, 39, 813–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guest, N.S.; VanDusseldorp, T.A.; Nelson, M.T.; Grgic, J.; Schoenfeld, B.J.; Jenkins, N.D.M.; Arent, S.M.; Antonio, J.; Stout, J.R.; Trexler, E.T.; et al. International society of sports nutrition position stand: Caffeine and exercise performance. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2021, 18, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grgic, J. Caffeine ingestion enhances Wingate performance: A meta-analysis. Eur. J. Sport. Sci. 2018, 18, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delleli, S.; Ouergui, I.; Messaoudi, H.; Ballmann, C.G.; Ardigò, L.P.; Chtourou, H. Effects of caffeine consumption combined with listening to music during warm-up on taekwondo physical performance, perceived exertion and psychological aspects. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0292498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delleli, S.; Ouergui, I.; Messaoudi, H.; Bridge, C.; Ardigò, L.P.; Chtourou, H. Warm-up music and low-dose caffeine enhance the activity profile and psychophysiological responses during simulated combat in female taekwondo athletes. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 14302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mielgo-Ayuso, J.; Marques-Jiménez, D.; Refoyo, I.; Del Coso, J.; León-Guereño, P.; Calleja-González, J. Effect of Caffeine Supplementation on Sports Performance Based on Differences Between Sexes: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filip, A.; Wilk, M.; Krzysztofik, M.; Del Coso, J. Inconsistency in the Ergogenic Effect of Caffeine in Athletes Who Regularly Consume Caffeine: Is It Due to the Disparity in the Criteria That Defines Habitual Caffeine Intake? Nutrients 2020, 12, 1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardy, C.J.; Rejeski, W.J. Not what, but how one feels: The measurement of affect during exercise. J. Sport Exerc. Psychol. 1989, 11, 304–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magkos, F.; Kavouras, S.A. Caffeine use in sports, pharmacokinetics in man, and cellular mechanisms of action. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2005, 45, 535–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Diao, P.; Wang, J.; Li, S.; Fan, Q.; Han, Y.; Liang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Del Coso, J. The Effect of Post-Activation Potentiation Enhancement Alone or in Combination with Caffeine on Anaerobic Performance in Boxers: A Double-Blind, Randomized Crossover Study. Nutrients 2024, 16, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borg, G. Subjective effort and physical activities. Scand. J. Rehabil. Med. 1978, 6, 108–113. [Google Scholar]
- Lara, B.; Ruiz-Vicente, D.; Areces, F.; Abián-Vicén, J.; Salinero, J.J.; Gonzalez-Millán, C.; Gallo-Salazar, C.; Del Coso, J. Acute consumption of a caffeinated energy drink enhances aspects of performance in sprint swimmers. Br. J. Nutr. 2015, 114, 908–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khcharem, A.; Souissi, M.; Atheymen, R.; Souissi, W.; Sahnoun, Z. Acute caffeine ingestion improves 3-km run performance, cognitive function, and psychological state of young recreational runners. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2021, 207, 173219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varillas-Delgado, D.; Aguilar-Navarro, M.; Muñoz, A.; López-Samanés, Á.; Ruiz-Moreno, C.; Posada-Ayala, M.; Amaro-Gahete, F.J.; Del Coso, J.; Gutiérrez-Hellín, J. Effect of 3 and 6 mg/kg of caffeine on fat oxidation during exercise in healthy active females. Biol. Sport. 2023, 40, 827–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giráldez-Costas, V.; Aguilar-Navarro, M.; González-García, J.; Del Coso, J.; Salinero, J.J. Acute caffeine supplementation enhances several aspects of shot put performance in trained athletes. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2022, 19, 366–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballmann, C.G. The Influence of Music Preference on Exercise Responses and Performance: A Review. J. Funct. Morphol. Kinesiol. 2021, 6, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karow, M.C.; Rogers, R.R.; Pederson, J.A.; Williams, T.D.; Marshall, M.R.; Ballmann, C.G. Effects of Preferred and Nonpreferred Warm-Up Music on Exercise Performance. Percept. Mot. Ski. 2020, 127, 912–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, Z.; Maeda, H. Effects of Listening to Preferential Music on Sex Differences in Endurance Running Performance. Percept. Mot. Ski. 2015, 121, 390–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bishop, D.T.; Wright, M.J.; Karageorghis, C.I. Tempo and intensity of pre-task music modulate neural activity during reactive task performance. Psychol. Music. 2014, 42, 714–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biagini, M.S.; Brown, L.E.; Coburn, J.W.; Judelson, D.A.; Statler, T.A.; Bottaro, M.; Tran, T.T.; Longo, N.A. Effects of self-selected music on strength, explosiveness, and mood. J. Strength. Cond. Res. 2012, 26, 1934–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, S.; Iwai, K.; Akimoto, T.; Sugawara, J.; Kono, I. Effects of music during exercise on RPE, heart rate and the autonomic nervous system. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fit. 2006, 46, 425–430. [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto, T.; Ohkuwa, T.; Itoh, H.; Kitoh, M.; Terasawa, J.; Tsuda, T.; Kitagawa, S.; Sato, Y. Effects of pre-exercise listening to slow and fast rhythm music on supramaximal cycle performance and selected metabolic variables. Arch. Physiol. Biochem. 2003, 111, 211–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, L.A.; MacDonald, R.A.; Brodie, E.E. A comparison of the effects of preferred music, arithmetic and humour on cold pressor pain. Eur. J. Pain 2006, 10, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dyrlund, A.K.; Wininger, S.R. The effects of music preference and exercise intensity on psychological variables. J. Music. Ther. 2008, 45, 114–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLellan, T.M.; Caldwell, J.A.; Lieberman, H.R. A review of caffeine’s effects on cognitive, physical and occupational performance. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2016, 71, 294–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San Juan, A.F.; López-Samanes, Á.; Jodra, P.; Valenzuela, P.L.; Rueda, J.; Veiga-Herreros, P.; Pérez-López, A.; Domínguez, R. Caffeine Supplementation Improves Anaerobic Performance and Neuromuscular Efficiency and Fatigue in Olympic-Level Boxers. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scapec, B.; Grgic, J.; Varovic, D.; Mikulic, P. Caffeine, but not paracetamol (acetaminophen), enhances muscular endurance, strength, and power. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2024, 21, 2400513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salimpoor, V.N.; Benovoy, M.; Larcher, K.; Dagher, A.; Zatorre, R.J. Anatomically distinct dopamine release during anticipation and experience of peak emotion to music. Nat. Neurosci. 2011, 14, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duncan, M.J.; Oxford, S.W. The effect of caffeine ingestion on mood state and bench press performance to failure. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2011, 25, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, H.; Lu, B.; Su, W.; Wang, J.; Zheng, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Sun, Y.; Liu, C. Combined effects of Rhodiola rosea and caffeine supplementation on aerobic endurance and muscle explosiveness: A synergistic approach. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1335950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bar-Or, O. The Wingate anaerobic test. An update on methodology, reliability and validity. Sports Med. 1987, 4, 381–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Moreno, C.; Gutiérrez-Hellín, J.; Lara, B.; Del Coso, J. Effect of caffeine on muscle oxygen saturation during short-term all-out exercise: A double-blind randomized crossover study. Eur. J. Nutr. 2022, 61, 3109–3117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jebabli, N.; Ben Aabderrahman, A.; Boullosa, D.; Chtourou, H.; Ouerghi, N.; Rhibi, F.; Govindasamy, K.; Saeidi, A.; Clark, C.C.T.; Granacher, U.; et al. Listening to music during a repeated sprint test improves performance and psychophysiological responses in healthy and physically active male adults. BMC Sports Sci. Med. Rehabil. 2023, 15, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Souza, J.G.; Del Coso, J.; Fonseca, F.S.; Silva, B.V.C.; de Souza, D.B.; da Silva Gianoni, R.L.; Filip-Stachnik, A.; Serrão, J.C.; Claudino, J.G. Risk or benefit? Side effects of caffeine supplementation in sport: A systematic review. Eur. J. Nutr. 2022, 61, 3823–3834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variables | Mean ± SD |
|---|---|
| Age (year) | 21.00 ± 1.62 |
| Body height (cm) | 181.43 ± 4.64 |
| Body weight (kg) | 76.09 ± 7.17 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 23.08 ± 1.47 |
| Variable (Units) | CON | Mus + PLA | Mus + CAF | p | F |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PP (W) | 888.08 ± 133.20 | 943.95 ± 139.25 * | 1017.39 ± 155.23 *** # | <0.001 | 14.38 |
| MP (W) | 621.11 ± 75.55 | 657.65 ± 64.55 *** | 665.41 ± 66.54 *** | <0.001 | 15.44 |
| TW (J) | 17,822.43 ± 2232.28 | 18,871.13 ± 1828.08 *** | 19,160.08 ± 1960.68 *** | <0.001 | 13.36 |
| FI (%) | 61.39 ± 10.57 | 63.12 ± 8.69 | 64.70 ± 8.10 | 0.44 | -- |
| RPE (arbitrary units) | 17.30 ± 1.29 | 17.52 ± 0.85 | 17.74 ± 0.81 | 0.37 | -- |
| HR (bpm) | 184.35 ± 8.09 | 185.04 ± 8.46 | 185.86 ± 8.69 | 0.278 | 1.27 |
| Variable (Units) | CON | Mus + PLA | Mus + CAF | p | F |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FS–before (arbitrary units) | 0.96 ± 1.02 | 2.21 ± 1.28 * | 2.74 ± 1.25 *** | <0.001 | -- |
| FS–after (arbitrary units) | −2.09 ± 1.04 | −2.52 ± 0.90 | −2.39 ± 1.27 | 0.67 | -- |
| Items (Units) | CON | Mus + PLA | Mus + CAF | p for After | p for 24 h After | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Just After | 24 h After | Just After | 24 h After | Just After | 24 h After | |||
| Power (arbitrary units) | 5.09 ± 2.30 | — | 5.83 ± 1.30 | — | 6.43 ± 1.73 * | — | 0.036 | — |
| Endurance (arbitrary units) | 4.70 ± 2.31 | — | 5.17 ± 1.70 | — | 5.52 ± 1.90 | — | 0.661 | — |
| Fatigue (arbitrary units) | 6.30 ± 1.99 | — | 6.70 ± 2.01 | — | 6.57 ± 1.93 | — | 0.615 | — |
| Abdominal/gut discomfort (%) | 4% | 4% | 13% | 9% | 17% | 13% | 0.882 | 0.607 |
| Muscle soreness (%) | 57% | 65% | 52% | 70% | 70% | 78% | 0.338 | 0.584 |
| Increased urine output (%) | 0% | 0% | 0% | 9% | 9% | 17% | 0.135 | 0.091 |
| Headache (%) | 0% | 17% | 4% | 22% | 0% | 22% | 0.368 | 0.882 |
| Anxiety or nervousness (%) | 0% | 4% | 0% | 13% | 9% | 17% | 0.135 | 0.311 |
| Insomnia (%) | — | 8% | — | 13% | — | 22% | — | 0.459 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qiu, B.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, Y.; Diao, P.; Liu, K.; Del Coso, J.; Liu, C. Effects of Caffeine Intake Combined with Self-Selected Music During Warm-Up on Anaerobic Performance: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Crossover Study. Nutrients 2025, 17, 351. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17020351
Qiu B, Wang Z, Zhang Y, Cui Y, Diao P, Liu K, Del Coso J, Liu C. Effects of Caffeine Intake Combined with Self-Selected Music During Warm-Up on Anaerobic Performance: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Crossover Study. Nutrients. 2025; 17(2):351. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17020351
Chicago/Turabian StyleQiu, Bopeng, Ziyu Wang, Yinkai Zhang, Yusong Cui, Penglin Diao, Kaiji Liu, Juan Del Coso, and Chang Liu. 2025. "Effects of Caffeine Intake Combined with Self-Selected Music During Warm-Up on Anaerobic Performance: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Crossover Study" Nutrients 17, no. 2: 351. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17020351
APA StyleQiu, B., Wang, Z., Zhang, Y., Cui, Y., Diao, P., Liu, K., Del Coso, J., & Liu, C. (2025). Effects of Caffeine Intake Combined with Self-Selected Music During Warm-Up on Anaerobic Performance: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Crossover Study. Nutrients, 17(2), 351. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17020351











