The Influence of Intensive Nutritional Education on the Iron Status in Infants—Randomised Controlled Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
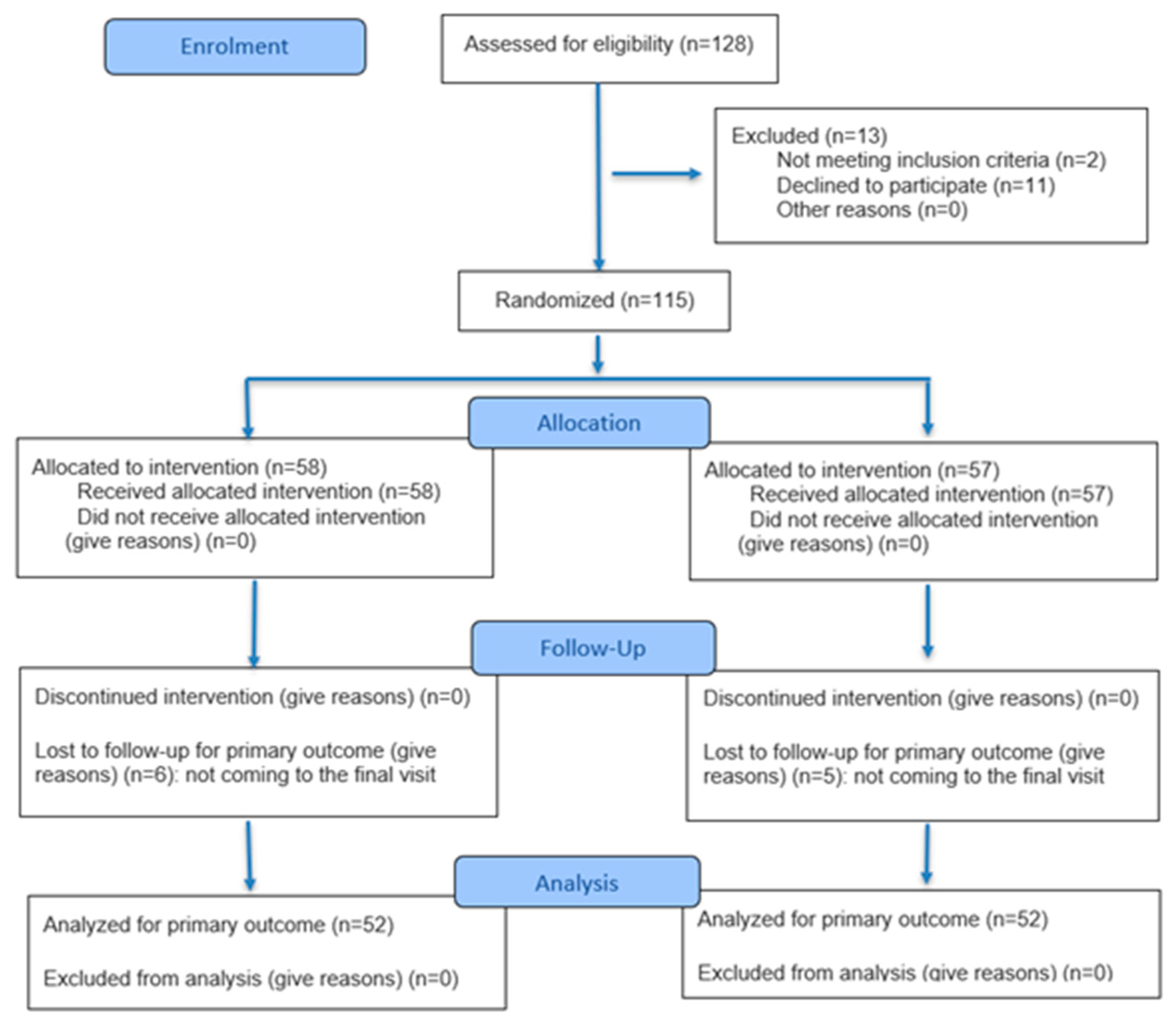
2. Materials and Methods
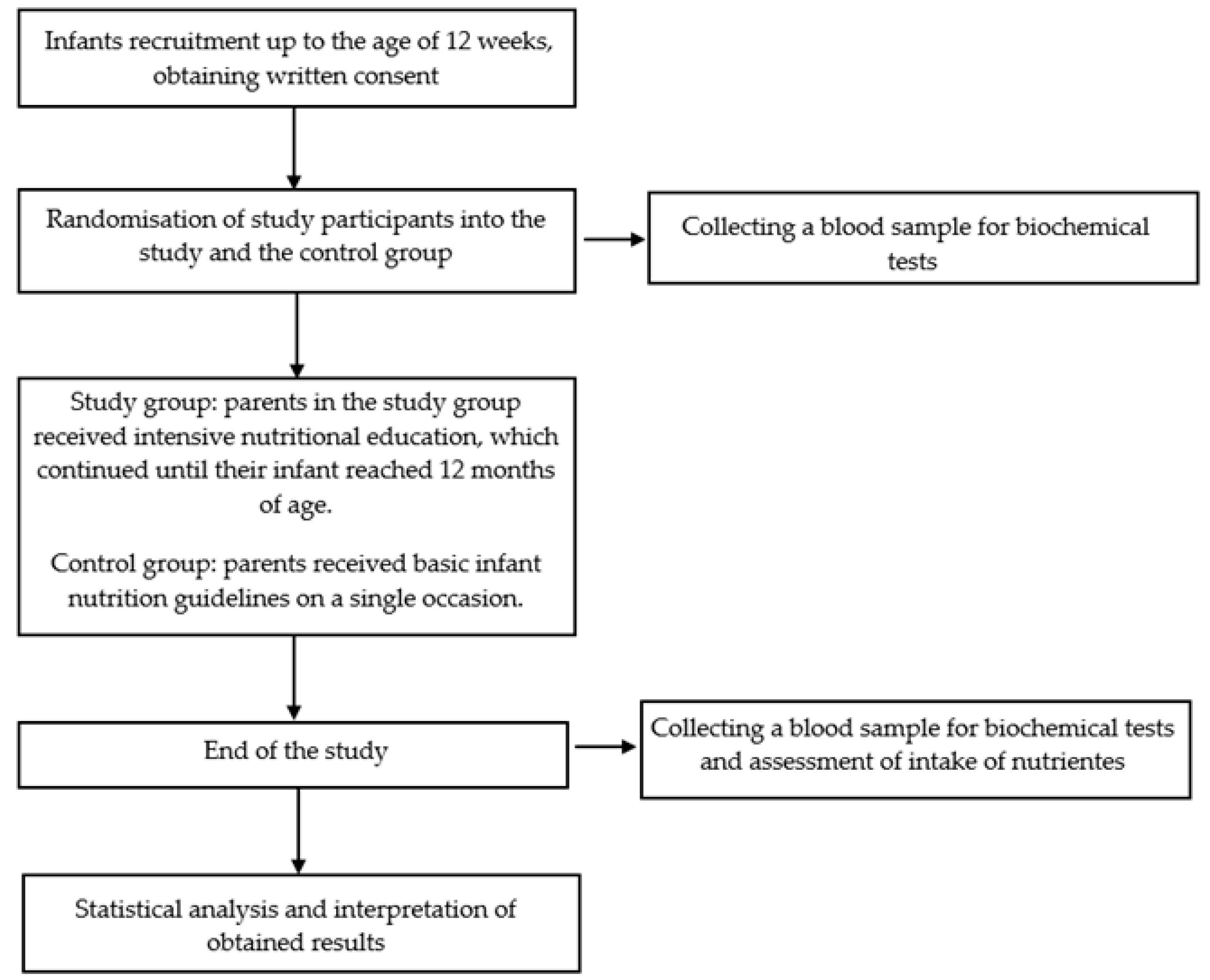
2.1. Study Overview
2.2. Participants
2.3. Intervention
2.4. Outcomes
2.5. Blood Collection
2.6. Biochemical Measurements
2.7. Body Weight Assessment
2.8. Dietary Intake
2.9. Minimum Sample Size
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Warner, M.J.; Kamran, M.T. Iron Deficiency Anemia. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Cerami, C. Iron Nutriture of the Fetus, Neonate, Infant, and Child. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2017, 71, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koleini, N.; Shapiro, J.S.; Geier, J.; Ardehali, H. Ironing out Mechanisms of Iron Homeostasis and Disorders of Iron Deficiency. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 131, e148671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Means, R.T. Iron Deficiency and Iron Deficiency Anemia: Implications and Impact in Pregnancy, Fetal Development, and Early Childhood Parameters. Nutrients 2020, 12, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kassebaum, N.J.; Jasrasaria, R.; Naghavi, M.; Wulf, S.K.; Johns, N.; Lozano, R.; Regan, M.; Weatherall, D.; Chou, D.P.; Eisele, T.P.; et al. A Systematic Analysis of Global Anemia Burden from 1990 to 2010. Blood 2014, 123, 615–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burden, M.J.; Westerlund, A.J.; Armony-Sivan, R.; Nelson, C.A.; Jacobson, S.W.; Lozoff, B.; Angelilli, M.L.; Jacobson, J.L. An Event-Related Potential Study of Attention and Recognition Memory in Infants With Iron-Deficiency Anemia. Pediatrics 2007, 120, e336–e345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecilia, A.; Patricio, P.; Donna, C.; Rakibul, H.; Sussanne, R.; Betsy, L.; Bharat, B. Cognitive Control Inhibition Networks in Adulthood Are Impaired by Early Iron Deficiency in Infancy. NeuroImage Clin. 2022, 35, 103089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, P.-T.; Cheng, Y.-S.; Yen, C.-F.; Chen, Y.-W.; Stubbs, B.; Whiteley, P.; Carvalho, A.F.; Li, D.-J.; Chen, T.-Y.; Yang, W.-C.; et al. Peripheral Iron Levels in Children with Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farkhondeh, T.; Mansouri, B.; Binkowski, L.J.; Błaszczyk, M.; Pirsaheb, M.; Azadi, N.A.; Słoboda, M.; Amirabadizadeh, A.; Javadmoosavi, S.Y. Blood Lead Concentrations in Children with Iron Deficiency Anemia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 3199–3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puri, S.; Shaheen, M.; Grover, B. Nutrition and Cognitive Health: A Life Course Approach. Front. Public Health 2023, 11, 1023907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ren, W.; Wang, S.; Xiang, M.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, F. Global Burden of Anemia and Cause among Children under Five Years 1990–2019: Findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1474664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCann, S.; Amadó, M.P.; Moore, S.E. The Role of Iron in Brain Development: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.M.; Hamner, H.C.; Suchdev, P.S.; Flores-Ayala, R.; Mei, Z. Iron Status of Toddlers, Nonpregnant Females, and Pregnant Females in the United States. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 106, 1640S–1646S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soh, P.; Ferguson, E.L.; McKenzie, J.E.; Homs, M.Y.V.; Gibson, R.S. Iron Deficiency and Risk Factors for Lower Iron Stores in 6–24-Month-Old New Zealanders. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 58, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmlund-Suila, E.M.; Hauta-Alus, H.H.; Enlund-Cerullo, M.; Rosendahl, J.; Valkama, S.M.; Andersson, S.; Mäkitie, O. Iron Status in Early Childhood is Modified by Diet, Sex and Growth: Secondary Analysis of a Randomized Controlled Vitamin D Trial. Clin. Nutr. Edinb. Scotl. 2022, 41, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gompakis, N.; Economou, M.; Tsantali, C.; Kouloulias, V.; Keramida, M.; Athanasiou-Metaxa, M. The Effect of Dietary Habits and Socioeconomic Status on the Prevalence of Iron Deficiency in Children of Northern Greece. Acta Haematol. 2007, 117, 200–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundararajan, S.; Rabe, H. Prevention of Iron Deficiency Anemia in Infants and Toddlers. Pediatr. Res. 2021, 89, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. The Global Prevalence of Anaemia in 2011; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Leung, A.K.C.; Lam, J.M.; Wong, A.H.C.; Hon, K.L.; Li, X. Iron Deficiency Anemia: An Updated Review. Curr. Pediatr. Rev. 2024, 20, 339–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, M.; Tadi, P. Iron Supplementation. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- East, P.; Doom, J.R.; Blanco, E.; Burrows, R.; Lozoff, B.; Gahagan, S. Iron Deficiency in Infancy and Neurocognitive and Educational Outcomes in Young Adulthood. Dev. Psychol. 2021, 57, 962–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koletzko, B.; Godfrey, K.M.; Poston, L.; Szajewska, H.; van Goudoever, J.B.; de Waard, M.; Brands, B.; Grivell, R.M.; Deussen, A.R.; Dodd, J.M.; et al. Nutrition During Pregnancy, Lactation and Early Childhood and Its Implications for Maternal and Long-Term Child Health: The Early Nutrition Project Recommendations. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2019, 74, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, T.P.; Guest, P.C. Nutritional Programming Effects on Development of Metabolic Disorders in Later Life. In Investigations of Early Nutrition Effects on Long-Term Health; Guest, P.C., Ed.; Methods in Molecular Biology; Springer New York: New York, NY, USA, 2018; Volume 1735, pp. 3–17. ISBN 978-1-4939-7613-3. [Google Scholar]
- Koletzko, B.; Brands, B.; Grote, V.; Kirchberg, F.F.; Prell, C.; Rzehak, P.; Uhl, O.; Weber, M.; Early Nutrition Programming Project. Long-Term Health Impact of Early Nutrition: The Power of Programming. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2017, 70, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woźniak, D.; Podgórski, T.; Dobrzyńska, M.; Przysławski, J.; Cichy, W.; Drzymała-Czyż, S. Mothers’ Knowledge of Nutritional Programming Influences DHA Intake in Children—Analysis of Nutrition of Children Aged 13–36 Months in Poland. J. Health Inequalities 2022, 8, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woźniak, D.; Podgórski, T.; Dobrzyńska, M.; Przysławski, J.; Drzymała, S.; Drzymała-Czyż, S. The Influence of Parents’ Nutritional Education Program on Their Infants’ Metabolic Health. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, D.J. Study Designs in Medical Research and Their Key Characteristics. J. Med. Sci. 2024, 92, e928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The WHO Child Growth Standards. Available online: https://www.who.int/tools/child-growth-standards/standards (accessed on 7 August 2025).
- Charzewska, J. Instruction of the Dietary Recall Gathering from the Last 24 Hours; National Food and Nutrition In Stitute: Warsaw, Poland, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Wojtasik, A.; Woźniak, A.; Stoś, K.; Jarosz, M. Normy Żywienia Dla Populacji Polski i Ich Zastosowani; Narodowy Instytut Zdrowia Publicznego—Państwowy Zakład Higieny: Warszawa, Poland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Hopewell, S.; Chan, A.-W.; Collins, G.S.; Hróbjartsson, A.; Moher, D.; Schulz, K.F.; Tunn, R.; Aggarwal, R.; Berkwits, M.; Berlin, J.A.; et al. CONSORT 2025 Statement: Updated Guideline for Reporting Randomised Trials. BMJ 2025, 389, e081123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, M.B. Global Look at Nutritional and Functional Iron Deficiency in Infancy. Hematology 2020, 2020, 471–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gedfie, S.; Getawa, S.; Melku, M. Prevalence and Associated Factors of Iron Deficiency and Iron Deficiency Anemia Among Under-5 Children: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Glob. Pediatr. Health 2022, 9, 2333794X221110860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasetyo, Y.B.; Permatasari, P.; Susanti, H.D. The Effect of Mothers’ Nutritional Education and Knowledge on Children’s Nutritional Status: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Child Care Educ. Policy 2023, 17, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lassi, Z.S.; Rind, F.; Irfan, O.; Hadi, R.; Das, J.K.; Bhutta, Z.A. Impact of Infant and Young Child Feeding (IYCF) Nutrition Interventions on Breastfeeding Practices, Growth and Mortality in Low- and Middle-Income Countries: Systematic Review. Nutrients 2020, 12, 722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu Alhaija, R.; Hasab, A.A.H.; El-Nimr, N.A.; Tayel, D.I. Impact of Educational Intervention on Mothers of Infants with Iron-Deficiency Anemia. Health Educ. Res. 2024, 39, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nahdi, R.; Mosha, T. Effect of Nutrition Education Intervention on the Use of Micronutrients Powders for Children Aged 6–59 Months in Zanzibar City. J. Food Nutr. Sci. 2024, 12, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapur, D.; Sharma, S.; Agarwal, K.N. Effectiveness of Nutrition Education, Iron Supplementation or Both on Iron Status in Children. Indian Pediatr. 2003, 40, 1131–1144. [Google Scholar]
- Osei, A.K.; Pandey, P.; Spiro, D.; Adhikari, D.; Haselow, N.; De Morais, C.; Davis, D. Adding Multiple Micronutrient Powders to a Homestead Food Production Programme Yields Marginally Significant Benefit on Anaemia Reduction Among Young Children in N Epal. Matern. Child. Nutr. 2015, 11, 188–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA Panel on Dietetic Products Nutrition Allergies (NDA). Scientific Opinion on the Substantiation of a Health Claim Related to Vitamin, C.; Increasing Non Haem Iron Absorption Pursuant to Article 14 of Regulation (EC) No 1924/2006. EFSA J. 2014, 12, 3514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gallahan, S.; Brower, S.; Wapshott-Stehli, H.; Santos, J.; Ho, T.T.B. A Systematic Review of Isotopically Measured Iron Absorption in Infants and Children Under 2 Years. Nutrients 2024, 16, 3834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dierkes, J.; Nwaru, B.I.; Ramel, A.; Arnesen, E.K.; Thorisdottir, B.; Lamberg-Allardt, C.; Spielau, U.; Söderlund, F.; Bärebring, L.; Åkesson, A. Dietary Fiber and Growth, Iron Status and Bowel Function in Children 0–5 Years Old: A Systematic Review. Food Nutr. Res. 2023, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verediano, T.A.; Agarwal, N.; Gomes, M.J.C.; Martino, H.S.D.; Tako, E. Effects of Dietary Fiber on Intestinal Iron Absorption, and Physiological Status: A Systematic Review of in Vivo and Clinical Studies. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 9017–9032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallberg, L. Wheat Fiber, Phytates and Iron Absorption. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. Suppl. 1987, 129, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vonderheid, S.C.; Tussing-Humphreys, L.; Park, C.; Pauls, H.; OjiNjideka Hemphill, N.; LaBomascus, B.; McLeod, A.; Koenig, M.D. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis on the Effects of Probiotic Species on Iron Absorption and Iron Status. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pustjens, A.M.; Castenmiller, J.J.M.; Biesebeek, J.D.T.; Boon, P.E. Dietary Intake of Protein and Fat of 12- to 36-Month-Old Children in a Dutch Total Diet Study. Eur. J. Nutr. 2022, 61, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chouraqui, J.-P.; Darmaun, D.; Salmon-Legagneur, A.; Shamir, R. Protein Intake Pattern in Non-Breastfed Infants and Toddlers: A Survey in a Nationally Representative Sample of French Children. Clin. Nutr. Edinb. Scotl. 2022, 41, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foterek, K.; Hilbig, A.; Kersting, M.; Alexy, U. Age and Time Trends in the Diet of Young Children: Results of the DONALD Study. Eur. J. Nutr. 2016, 55, 611–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldbohm, R.A.; Rubingh, C.M.; Lanting, C.I.; Joosten, K.F.M. Food Consumption and Nutrient Intake by Children Aged 10 to 48 Months Attending Day Care in The Netherlands. Nutrients 2016, 8, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M. Protein Intake during the First Two Years of Life and Its Association with Growth and Risk of Overweight. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2018, 15, 1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soldin, O.P.; Bierbower, L.H.; Choi, J.J.; Choi, J.J.; Thompson-Hoffman, S.; Soldin, S.J. Serum Iron, Ferritin, Transferrin, Total Iron Binding Capacity, hs-CRP, LDL Cholesterol and Magnesium in Children; New Reference Intervals Using the Dade Dimension Clinical Chemistry System. Clin. Chim. Acta 2004, 342, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaber, R.; Helwich, E.; Lauterbach, R.; Mastalerz-Migas, A.; Matysiak, M.; Peregud-Pogorzelski, J.; Styczyński, J.; Szczepański, T.; Jackowska, T. Diagnostyka i Leczenie Niedoboru Żelaza Oraz Niedokrwistości z Niedoboru Żelaza u Dzieci i Młodzieży. Rekomendacje Polskiego Towarzystwa Pediatrycznego, Polskiego Towarzystwa Onkologii i Hematologii Dziecięcej, Polskiego Towarzystwa Neonatologicznego, Polskiego Towarzystwa Medycyny Rodzinnej. Prz. Pediatr. 2023, 52, 29–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Guideline on Use of Ferritin Concentrations to Assess Iron Status in Individuals and Populations; WHO Guidelines Approved by the Guidelines Review Committee; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020; ISBN 978-92-4-000012-4. [Google Scholar]
- Mattiello, V.; Schmugge, M.; Hengartner, H.; Von Der Weid, N.; Renella, R. Diagnosis and Management of Iron Deficiency in Children with or without Anemia: Consensus Recommendations of the SPOG Pediatric Hematology Working Group. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2020, 179, 527–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasvosve, I.; Delanghe, J. Total Iron Binding Capacity and Transferrin Concentration in the Assessment of Iron Status. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2002, 40, 1014–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wan, J.; Xia, H.; Li, Y.; Xu, Y.; Lin, H.; Iftikhar, H. Total Iron Binding Capacity (TIBC) Is a Potential Biomarker of Left Ventricular Remodelling for Patients with Iron Deficiency Anaemia. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2020, 20, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, D.M.; Kaplan, J. Ferroportin-Mediated Iron Transport: Expression and Regulation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA—Mol. Cell Res. 2012, 1823, 1426–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemeth, E.; Ganz, T. Hepcidin-Ferroportin Interaction Controls Systemic Iron Homeostasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Parameter | Study Group | Control Group | p | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (n = 58) | (n = 57) | ||||
| Median | Mean ± SD | Median | Mean ± SD | ||
| (Q1–Q3) | (95% CI) | (Q1–Q3) | (95% CI) | ||
| Infants | |||||
| Body weight [g] | 5280 | 5646 ± 1660 | 6175 | 5841 ± 1326 | 0.3105 |
| (4305–7230) | (4992–6300) | (4810–6795) | (5471–6428) | ||
| Z-score for body weight at baseline | −0.12 | 0.59 ± 2.53 | 0.26 | 0.23 ± 1.39 | 0.6851 |
| (−1.19–2.88) | (−0.45–1.47) | (−0.43–1.08) | (−0.27–0.78) | ||
| Sex: female | 50.00% | 45.60% | 0.6415 | ||
| Parents | |||||
| Place of residence | |||||
| Village (from the city agglomeration) | 61% | 57% | |||
| a city with fewer than 500,000 residents | 24% | 28% | 0.7248 | ||
| a city with more than 500,000 residents | 15% | 15% | |||
| Education | |||||
| Primary | 2% | 2% | |||
| Secondary | 25% | 22% | 0.6983 | ||
| Higher | 73% | 76% | |||
| Parameters | Baseline | Follow-Up | p I | p II | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study Group (n = 52) | Control Group (n = 52) | p | Study Group (n = 52) | Control Group (n = 52) | p | |||||||
| Median (Q1–Q3) | Mean ± SD (95% CI) | Median (Q1–Q3) | Mean ± SD (95% CI) | Median (Q1–Q3) | Mean ± SD (95% CI) | Median (Q1–Q3) | Mean ± SD (95% CI) | |||||
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 12.0 (11.2–12.7) | 12.0 ± 1.6 (11.4–12.6) | 11.9 (11.1–12.8) | 11.9 ± 1.3 (11.4–12.4) | 0.7834 1 | 12.0 (11.0–12.8) | 11.9 ± 0.9 (11.6–12.8) | 11.2 (10.6–12.1) | 11.5 ± 1.2 (11.0–11.9) | 0.0499 2 | 0.6811 3 | 0.0165 3 |
| Iron (µg/dL) | 76.3 (51.9–108.4) | 77.9 ± 40.0 (63.5–92.3) | 58.5 (44.5–75.5) | 65.8 ± 31.4 (54.5–77.2) | 0.1951 1 | 65.0 (52.6–87.0) | 67.7 ± 25.7 (58.1–77.3) | 55.6 (37.1–70.9) | 58.8 ± 35.1 (46.1–71.5) | 0.1038 1 | 0.0840 3 | 0.0788 3 |
| Ferritin (ng/mL) | 175.5 (71.9–274.8) | 207.0 ± 169.0 (146.1–267.9) | 151.3 (77.5–219.1) | 170.3 ± 99.1 (134.6–206.1) | 0.7119 1 | 35.1 (27.9–42.4) | 46.3 ± 53.3 (26.4–66.3) | 18.9 (14.9–37.6) | 29.1 ± 21.1 (21.5–36.7) | 0.0067 1 | <0.0001 3 | <0.0001 3 |
| Transferrin (g/L) | 2.07 (1.77–2.51) | 2.18 ± 0.59 (1.97–2.39) | 2.33 (2.09–2.65) | 2.38 ± 0.48 (2.20–2.55) | 0.1131 2 | 3.09 (2.82–3.31) | 3.06 ± 0.51 (2.87–3.25) | 3.02 (2.69–3.25) | 3.01 ± 0.46 (2.84–3.17) | 0.4681 2 | <0.0001 2 | <0.0001 2 |
| UIBC (µg/dL) | 169.0 (136.5–265.7) | 196.3± 80.1 (167.5–225.2) | 222.0 (176.5–261.0) | 225.4 ± 70.1 (199.9–250.9) | 0.1470 2 | 286.0 (259.7–309.7) | 280.4± 37.9 (266.2–294.5) | 300.0 (264.5–331.0) | 287.6 ± 55.4 (267.6–307.6) | 0.2480 1 | <0.0001 3 | 0.0003 3 |
| TIBC (µg/dL) | 259.0 (226.0–324.2) | 272.4 ± 61.9 (250.1–294.8) | 285.0 (257.5–304.5) | 285.8 ± 55.8 (265.7–305.9) | 0.2797 2 | 356.5 (330.5–379.5) | 347.1 ± 45.4 (330.8–364.7) | 382.0 (293.5–406.5) | 361.5 ± 68.7 (336.7–386.2) | 0.0478 1 | <0.0001 3 | <0.0001 3 |
| Hepcidin (ng/mL) | 244.0 (132.6–444.2) | 395.9 ± 386.1 (256.7–535.1) | 339.3 (239.9–521.0) | 416.8 ± 259.9 (323.1–510.5) | 0.1086 1 | 729.7 (379.4–902.8) | 649.3 ± 338.5 (520.6–778.1) | 699.5 (422.7–1076.1) | 727.7 ± 431.5 (572.1–883.2) | 0.6388 2 | 0.0031 3 | 0.0004 3 |
| Ferroportin (ng/mL) | 9.2 (6.4–15.6) | 15.6 ± 15.4 (10.0–21.1) | 12.7 (9.7–220.9) | 16.0 ± 9.5 (12.6–19.4) | 0.0820 1 | 22.8 (15.3–28.5) | 22.9 ± 11.8 (18.4–27.4) | 32.8 (17.5–50.3) | 34.4 ± 20.9 (26.9–41.9) | 0.0410 1 | 0.0107 3 | 0.0002 3 |
| hsCRP (ng/mL) | 9.7 (2.8–30.1) | 32.0 ± 54.9 (12.3–51.9) | 15.6 (3.6–35.0) | 26.3 ± 28.9 (15.9–36.7) | 0.5101 1 | 7.2 (2.2–16.1) | 35.8 ± 76.4 (6.8–64.9) | 17.5 (7.4–40.3) | 24.0 ± 24.6 (15.1–32.9) | 0.2599 1 | 0.2893 3 | 0.6469 3 |
| Parameters | Study Group (n = 52) | Control Group (n = 52) | p | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Δ Follow-Up—Baseline | Δ Follow-Up—Baseline | ||||
| Median (Q1–Q3) | Mean ± SD (95% CI) | Median (Q1–Q3) | Mean ± SD (95% CI) | ||
| Δ Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 0.0 (−0.7–0.9) | −0.1 ± 1.4 (−0.6–0.4) | −0.4 (−1.2–0.1) | −0.4 ± 1.1 (−0.8–−0.1) | 0.1000 1 |
| Δ Iron (µg/dL) | −13.5 (−34.4–0.0) | −14.5 ± 48.2 (−31.8–2.9) | −1.4 (−18.1–1.5) | −7.0 ± 23.9 (−15.6–1.6) | 0.1397 1 |
| Δ Ferritin (ng/mL) | −138.0 (−223.7–−30.3) | −163.5 ± 174.6 (−226.5–−100.5) | −137.1 (−201.3–−52.8) | −141.3 ± 89.8 (−173.7–−108.9) | 0.8351 1 |
| Δ Transferrin (g/L) | 0.75 (0.27–1.33) | 0.69 ± 0.82 (0.39–0.99) | 0.44 (0.34–1.14) | 0.63 ± 0.61 (0.41–0.85) | 0.4766 2 |
| Δ UIBC (µg/dL) | 62.0 (3.0–144.5) | 66.5 ± 86.9 (35.2–97.8) | 54.0 (7.5–108.0) | 62.2 ± 80.1 (33.1–91.2) | 0.8932 1 |
| Δ TIBC (µg/dL) | 67.0 (0.25–118.0) | 53.5 ± 91.0 (21.7–87.5) | 96.0 (15.5–128.0) | 75.7 ± 76.8 (48.0–103.4) | 0.4089 1 |
| Δ Hepcidin (ng/mL) | 218.2 (−124.7–505.9) | 192.6 ± 410.1 (44.7–340.4) | 210.8 (61.7–626.9) | 310.8 ± 464.1 (143.6–478.2) | 0.3507 2 |
| Δ Ferroportin (ng/mL) | 6.7 (−2.5–17.0) | 5.2 ± 16.1 (−0.6–11.0) | 17.4 (0.8–1.1) | 18.4 ± 22.2 (10.4–26.4) | 0.0237 2 |
| Δ hsCRP (ng/mL) | −1.3 (−23.9–1.9) | 0.4 ± 95.7 (−34.1–34.9) | 4.5 (−7.6–12.9) | −2.3 ± 36.7 (−15.4–10.8) | 0.1527 1 |
| Dietary Intake (% RDA) | Study Group (n = 52) | Control Group (n = 52) | p | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Follow-Up | Follow-Up | ||||
| Median (Q1–Q3) | Mean ± SD (95% CI) | Median (Q1–Q3) | Mean ± SD (95% CI) | ||
| Iron | 96.1 (78.3–124.3) | 102.6 ± 48.2 (77.7–127.4) | 58.6 (44.3–88.6) | 77.6 ± 65.0 (44.2–111.1) | 0.0252 1 |
| Proteins | 305.6 (271.1–343.4) | 314.6 ± 73.3 (276.9–352.3) | 271.9 (233.8–291.5) | 279.6 ± 58.0 (249.8–309.5) | 0.1386 1 |
| Fiber | 106.3 (87.1–145.0) | 122.6 ± 62.5 (90.4–154.7) | 102.0 (29.5–170.0) | 118.5 ± 86.7 (73.9–163.1) | 0.5816 2 |
| Vitamin C | 195.4 (149.9–312.4) | 260.0 ± 171.8 (171.7–348.4) | 144.8 (110.0–232.5) | 161.8 ± 77.0 (122.3–201.4) | 0.0458 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ilnicka-Borowczyk, K.; Woźniak, D.; Dobrzyńska, M.; Podgórski, T.; Szymanowski, K.; Blask-Osipa, A.; Mieloszyk, K.; Drzymała-Czyż, S. The Influence of Intensive Nutritional Education on the Iron Status in Infants—Randomised Controlled Study. Nutrients 2025, 17, 3103. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17193103
Ilnicka-Borowczyk K, Woźniak D, Dobrzyńska M, Podgórski T, Szymanowski K, Blask-Osipa A, Mieloszyk K, Drzymała-Czyż S. The Influence of Intensive Nutritional Education on the Iron Status in Infants—Randomised Controlled Study. Nutrients. 2025; 17(19):3103. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17193103
Chicago/Turabian StyleIlnicka-Borowczyk, Kinga, Dagmara Woźniak, Małgorzata Dobrzyńska, Tomasz Podgórski, Karol Szymanowski, Anna Blask-Osipa, Klaudia Mieloszyk, and Sławomira Drzymała-Czyż. 2025. "The Influence of Intensive Nutritional Education on the Iron Status in Infants—Randomised Controlled Study" Nutrients 17, no. 19: 3103. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17193103
APA StyleIlnicka-Borowczyk, K., Woźniak, D., Dobrzyńska, M., Podgórski, T., Szymanowski, K., Blask-Osipa, A., Mieloszyk, K., & Drzymała-Czyż, S. (2025). The Influence of Intensive Nutritional Education on the Iron Status in Infants—Randomised Controlled Study. Nutrients, 17(19), 3103. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17193103









