The Impact of Weizmannia coagulans BC99 on Anxiety and Depression: An 8-Week Clinical Pilot Study Through the Gut Microbiota–Brain Axis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
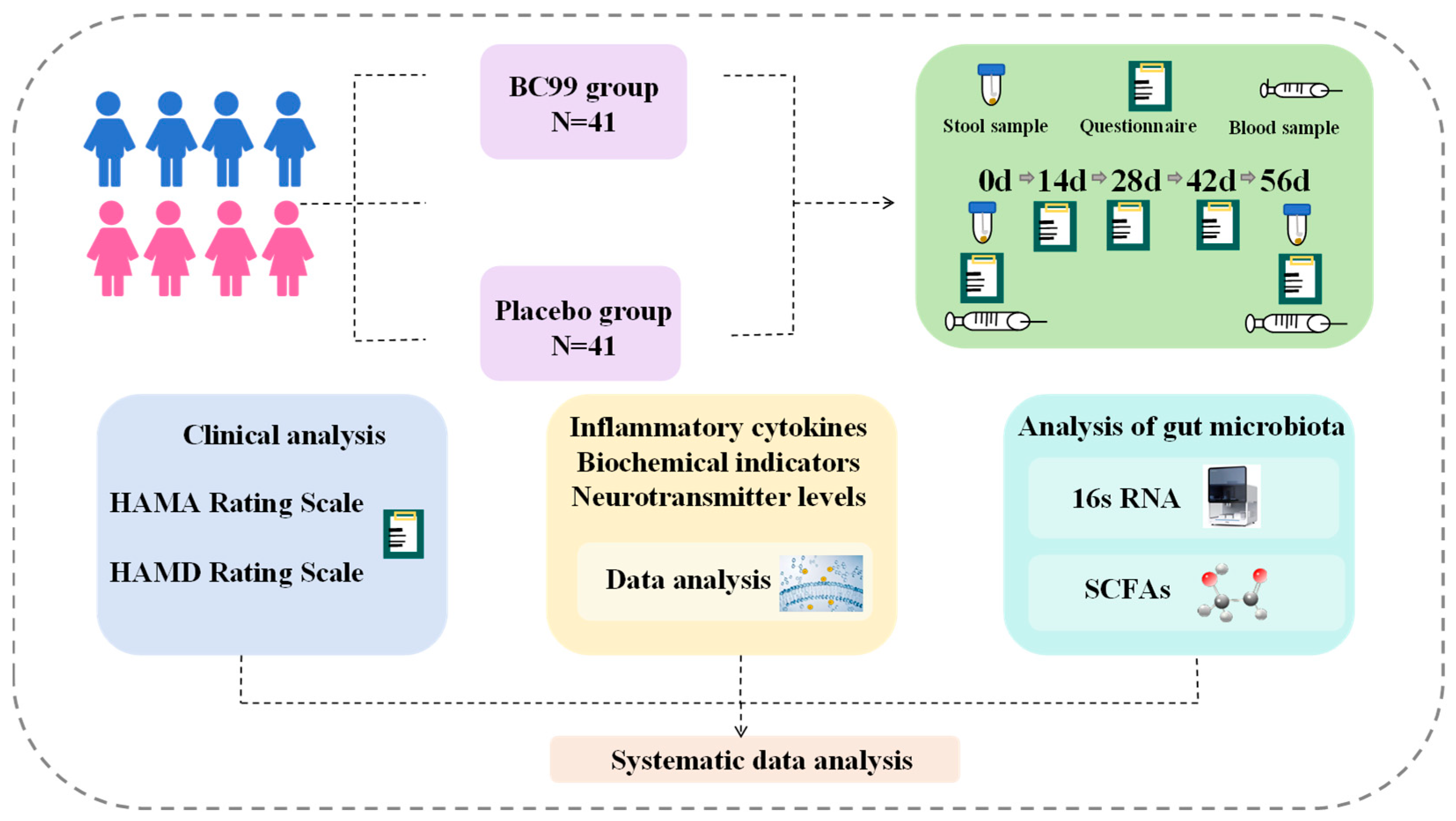
2.2. Experimental Design and Intervention
2.3. Study Products
2.4. Questionnaires
2.5. Clinical Measure
2.6. Collection of Fecal Samples
2.7. Gut Microbiota
2.8. Determination of the Level of SCFAs
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
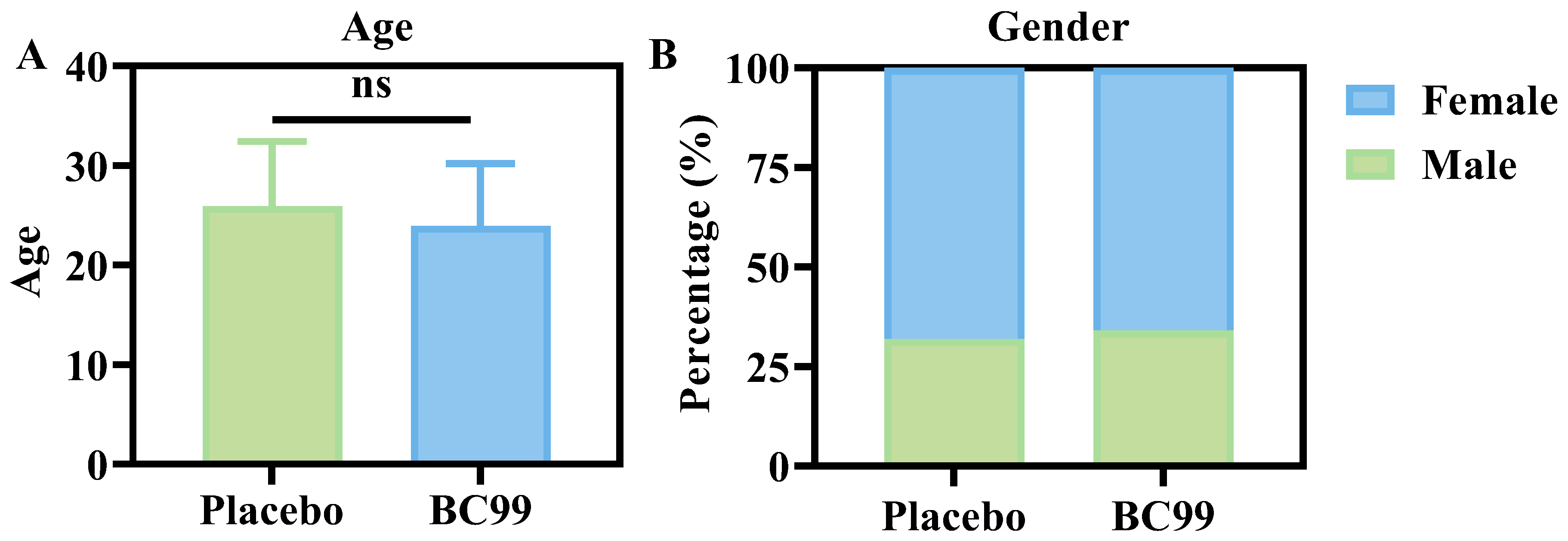
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
3.2. Comparison of HAMD and HAMA
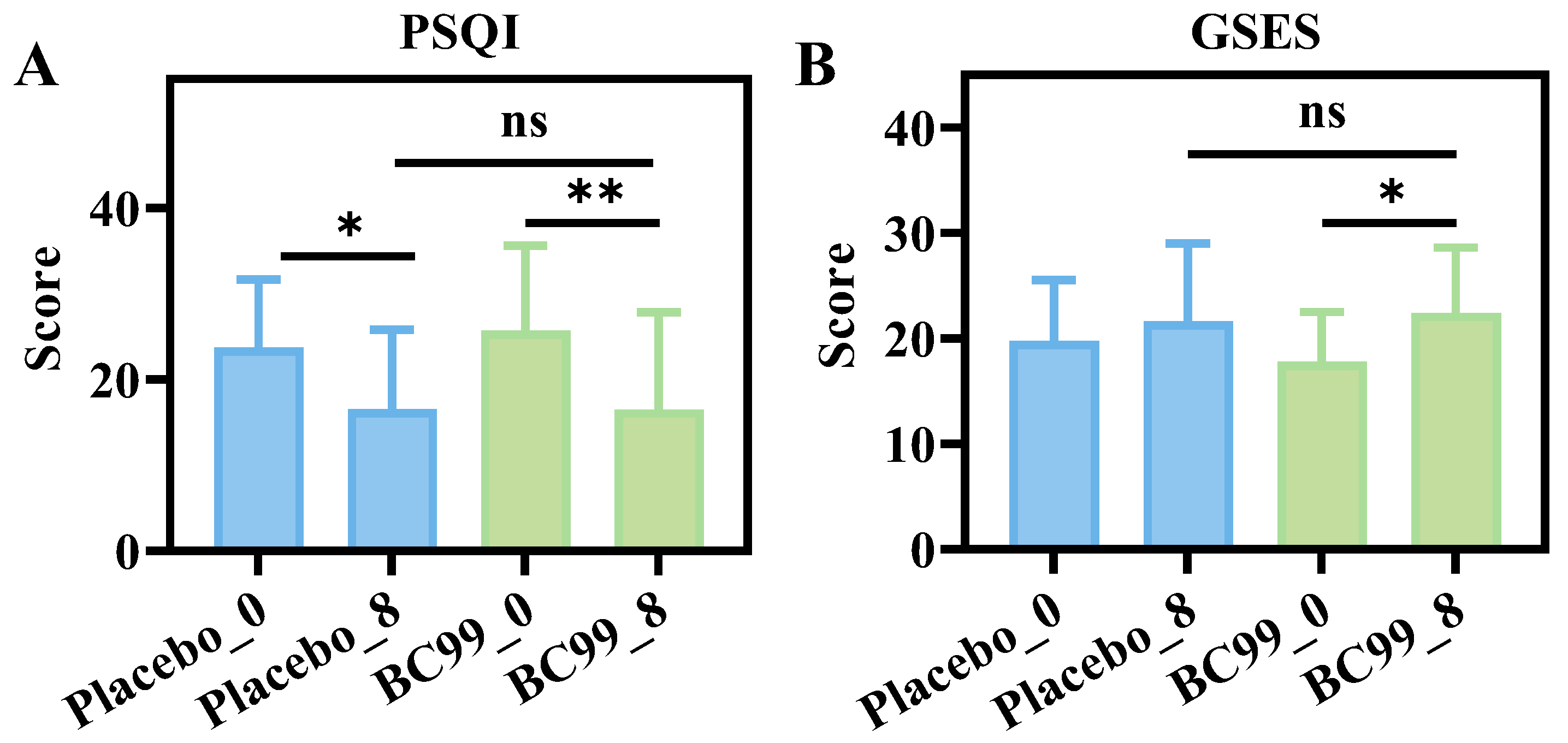
3.3. Comparison of PSQI and GSES Questionnaires
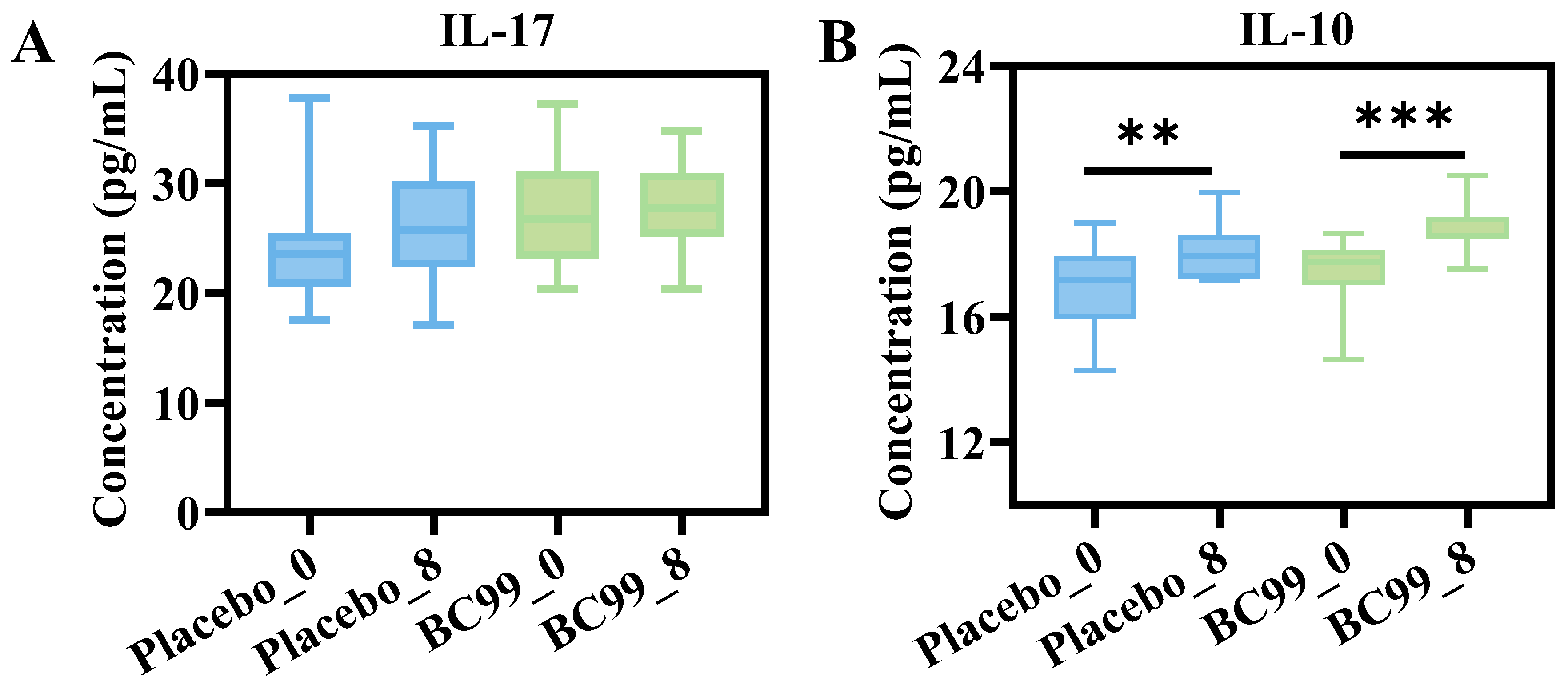
3.4. Inflammatory Cytokines Analysis
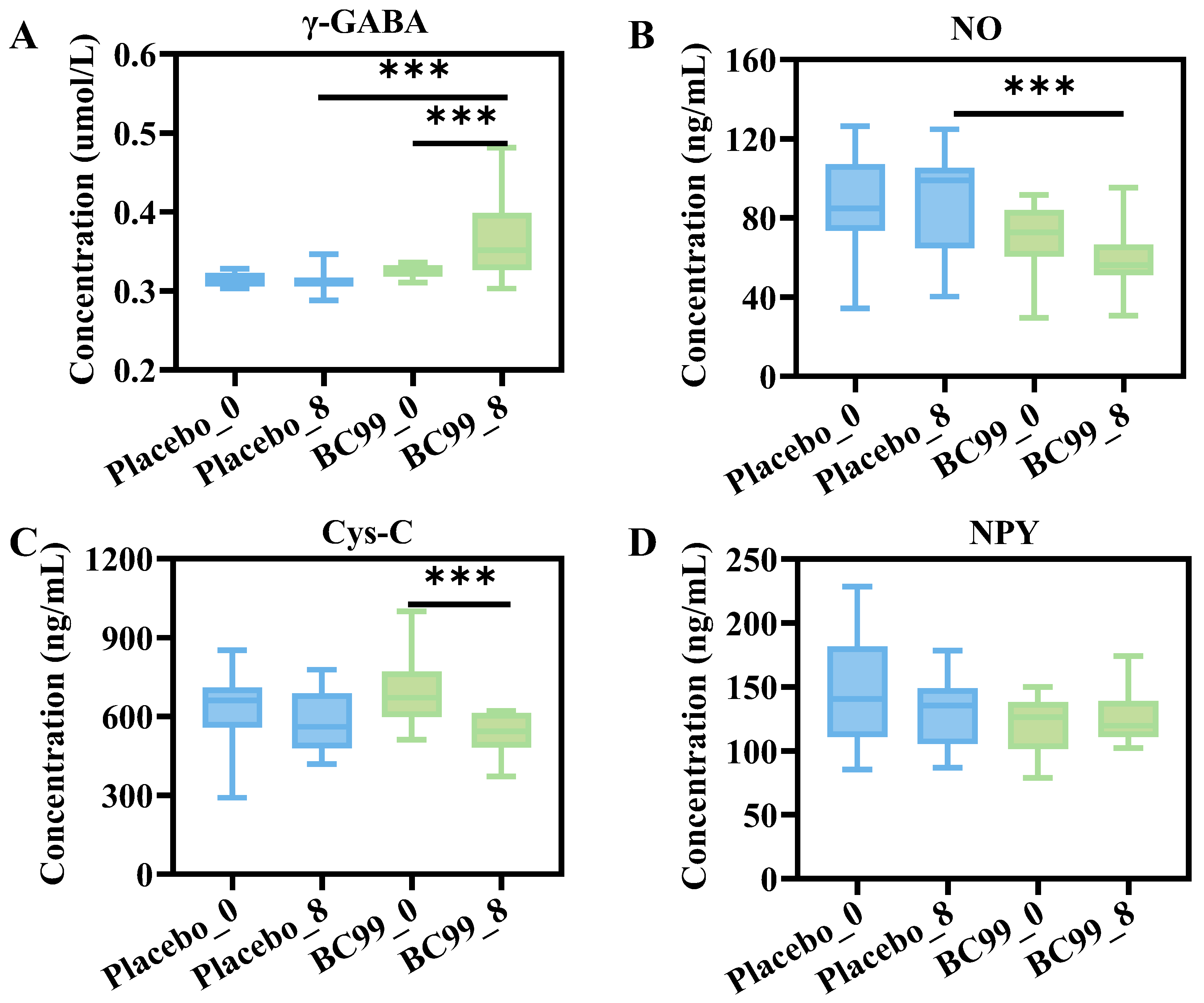
3.5. Blood Hormone Levels and Neurotransmitter Indexes Analysis
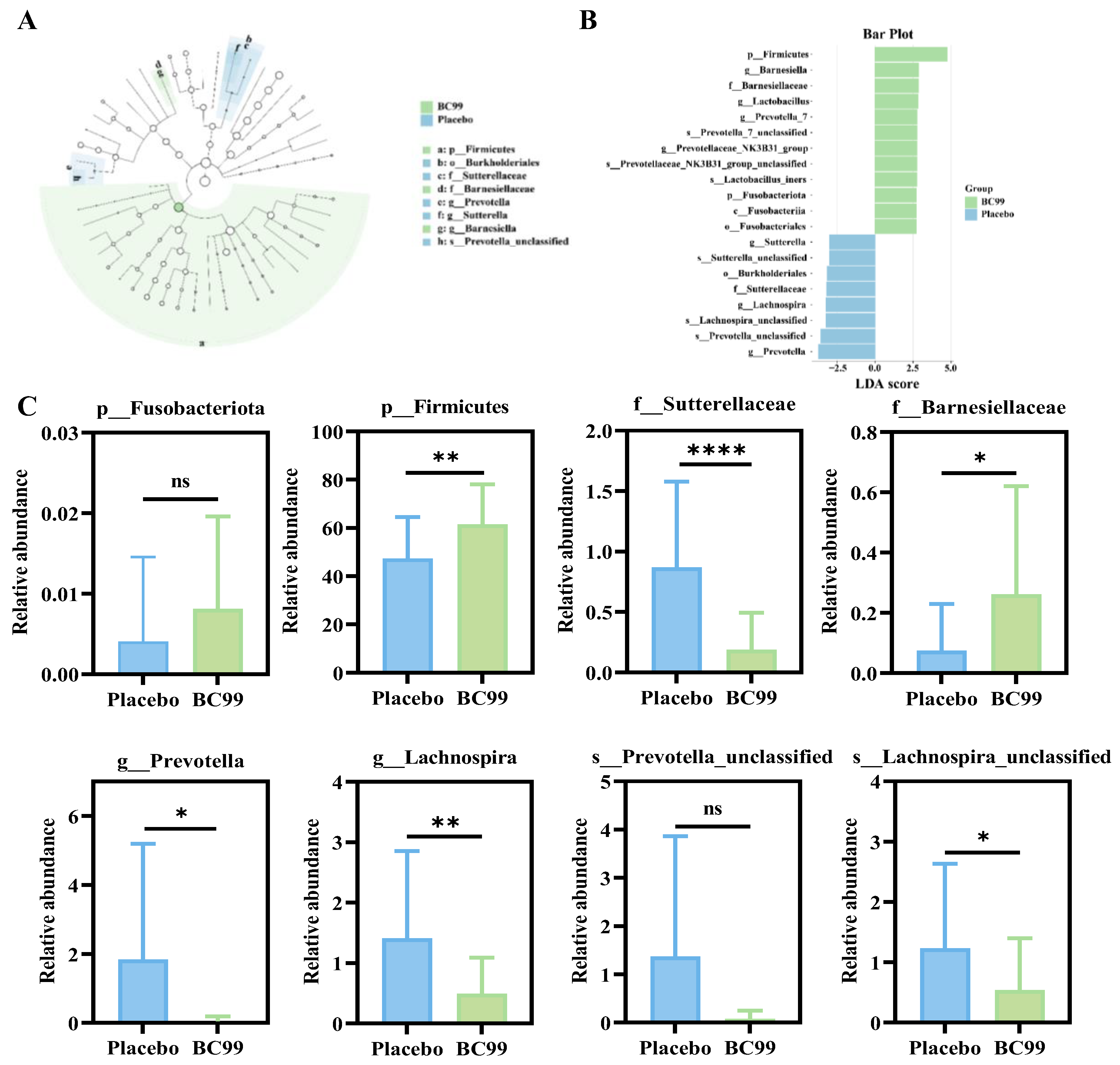
3.6. Effect of BC99 Intervention on Gut Microbiota
3.7. SCFAs Level Analysis
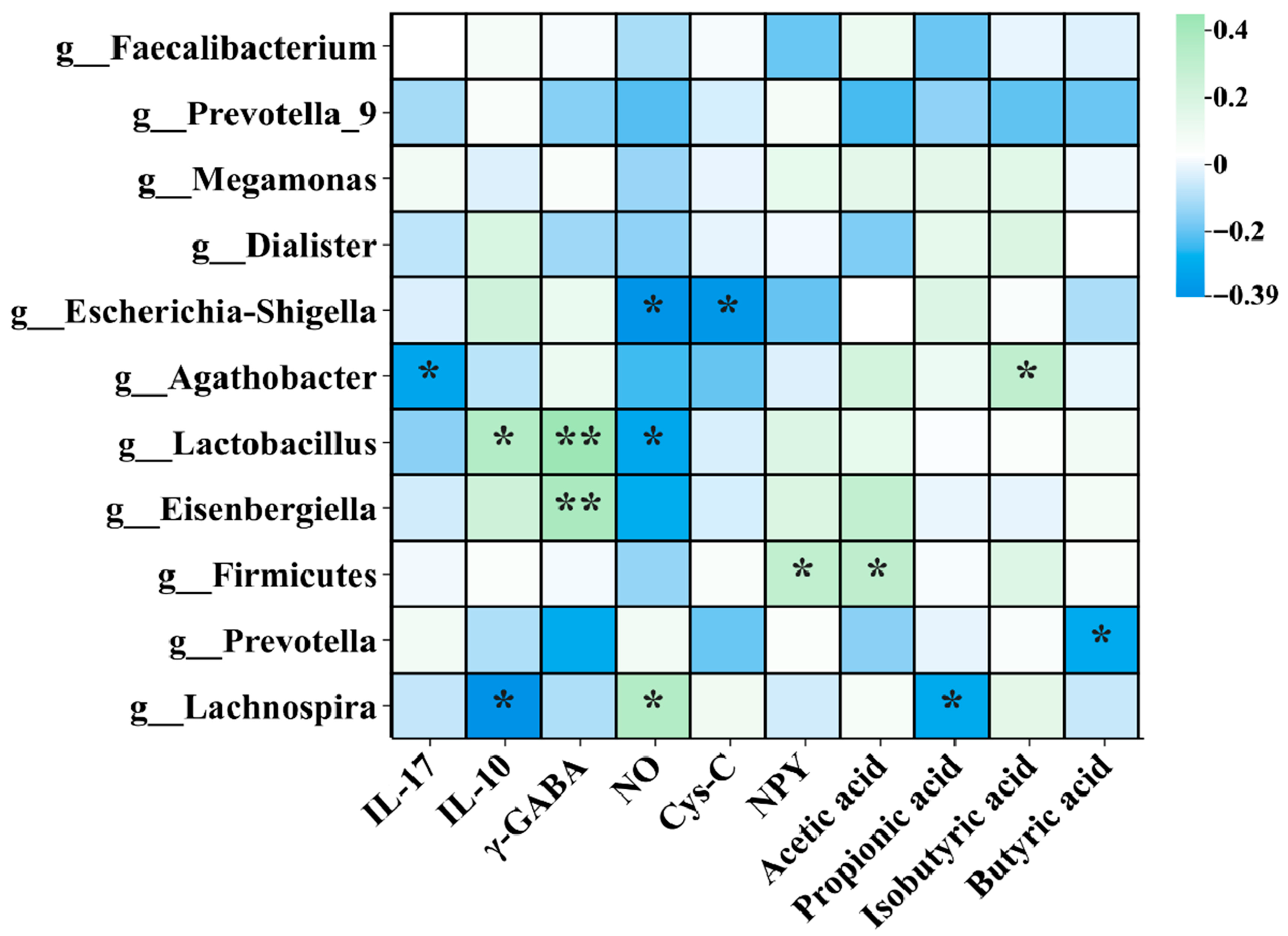
3.8. Correlation Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- El Dib, R.; Periyasamy, A.G.; de Barros, J.L.; França, C.G.; Senefonte, F.L.; Vesentini, G.; Alves, M.G.O.; da Silva Rodrigues, J.V.; Gomaa, H.; Júnior, J.R.G. Probiotics for the treatment of depression and anxiety: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2021, 45, 75–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Si, C.; Sun, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, X. The intervention of prebiotics on depression via the Gut–Brain axis. Molecules 2022, 27, 3671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, J.; Yang, L.; Jia, T.; Zhang, W.; Wang, L.-B.; Zhao, Y.-J.; You, J.; Deng, Y.-T.; Ge, Y.-J.; Liu, W.-S. Plasma proteomics identifies proteins and pathways associated with incident depression in 46,165 adults. Sci. Bull. 2025, 70, 573–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bear, T.; Dalziel, J.; Coad, J.; Roy, N.; Butts, C.; Gopal, P. The microbiome-gut-brain axis and resilience to developing anxiety or depression under stress. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, D.; Liu, P.; Wang, Y.; Tai, X.; Ma, S. Unveiling the gut microbiota blueprint of schizophrenia: A multilevel omics approach. Front. Psychiatry 2024, 15, 1452604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, L.; Li, S.; Wang, S.; Wu, X.; Liu, Y.; Yu, W.; Wang, Y.; Tang, Y.; Xia, M.; Li, B. Major depressive disorder: Hypothesis, mechanism, prevention and treatment. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Cao, L.; Li, S.; Zhang, M.; Li, Y.; Duan, J.; Li, Y.; Hu, Z.; Wu, J.; Ni, J. Gut microbiota dysbiosis-mediated ceramides elevation contributes to corticosterone-induced depression by impairing mitochondrial function. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes 2024, 10, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, W.; Ma, Q.; Wang, L.; Yuan, N.; Gan, H.; He, L.; Li, X.; Huang, J.; Chen, J. Gut dysbiosis induces the development of depression-like behavior through abnormal synapse pruning in microglia-mediated by complement C3. Microbiome 2024, 12, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Pereira, J.S.; Rea, K.; Nolan, Y.M.; O’Leary, O.F.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. Depression’s unholy trinity: Dysregulated stress, immunity, and the microbiome. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2020, 71, 49–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morais, L.H.; Schreiber IV, H.L.; Mazmanian, S.K. The gut microbiota–brain axis in behaviour and brain disorders. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 241–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carabotti, M.; Scirocco, A.; Maselli, M.A.; Severi, C. The gut-brain axis: Interactions between enteric microbiota, central and enteric nervous systems. Ann. Gastroenterol. 2015, 28, 203. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Yang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Ban, S.; Gu, S.; Li, F.; Xue, M.; Sun, J.; Li, X.; Tie, S. Optimization of pH-responsive microgel for the co-delivery of Weizmannia coagulans and procyanidins to enhance survival rate and tolerance. Food Chem. 2025, 464, 141691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merkouris, E.; Mavroudi, T.; Miliotas, D.; Tsiptsios, D.; Serdari, A.; Christidi, F.; Doskas, T.K.; Mueller, C.; Tsamakis, K. Probiotics’ effects in the treatment of anxiety and depression: A comprehensive review of 2014–2023 clinical trials. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, J.A.; Neufeld, K.-A.M. Gut–brain axis: How the microbiome influences anxiety and depression. Trends Neurosci. 2013, 36, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, S.; Wang, C.; Song, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Chen, X.; Suo, H. Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus KY16 improves depression by promoting intestinal secretion of 5-HTP and altering the gut microbiota. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 21560–21573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolova, V.L.; Cleare, A.J.; Young, A.H.; Stone, J.M. Acceptability, tolerability, and estimates of putative treatment effects of probiotics as adjunctive treatment in patients with depression: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA Psychiatry 2023, 80, 842–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R.; Fang, Y.; Li, H.; Liu, Y.; Wei, J.; Zhang, S.; Wang, L.; Fan, R.; Wang, L.; Li, S. Psychobiotic Lactobacillus plantarum JYLP-326 relieves anxiety, depression, and insomnia symptoms in test anxious college via modulating the gut microbiota and its metabolism. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1158137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, M.; Zheng, L.; Cen, Q.; Wang, F.; Zhu, L.; Pang, R.; Zhang, A. Bifidobacterium: A probiotic for the prevention and treatment of depression. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1174800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, X.; Li, Q.; Zhu, H.; Chen, Y.; Lin, G.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W.; Wang, G.; Tian, P. Bifidobacteria with indole-3-lactic acid-producing capacity exhibit psychobiotic potential via reducing neuroinflammation. Cell Rep. Med. 2024, 5, 101798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Li, P.; Lee, S.; Wang, Y.; Tan, C.; Shang, N. Weizmannia coagulans: An ideal probiotic for gut health. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2024, 13, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Li, C.; Li, J.; Duan, M.; Li, X.; Zhao, L.; Wu, Y.; Gu, S. Weizmannia coagulans BC99 alleviates hyperuricemia and oxidative stress via DAF-16/SKN-1 activation in Caenorhabditis elegan. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1498540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Fan, J.; Zhao, L.; Qu, Z.; Dong, Y.; Wu, Y.; Gu, S. Weizmannia coagulans BC99 improve cognitive impairment induced by chronic sleep deprivation via inhibiting the brain and intestine’s NLRP3 inflammasome. Foods 2025, 14, 989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Du, M.; Lu, S.; Zhao, Q.; Yang, S. The correlation between probiotics and anxiety and depression levels in cancer patients: A retrospective cohort study. Front. Psychiatry 2022, 13, 830081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, C.; Gelaye, B.; Zhong, Q.-Y.; Enquobahrie, D.A.; Frederick, I.O.; Williams, M.A. Construct validity and factor structure of the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index among pregnant women in a Pacific-Northwest cohort. Sleep Breath. 2016, 20, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonsaksen, T.; Grimholt, T.K.; Skogstad, L.; Lerdal, A.; Ekeberg, Ø.; Heir, T.; Schou-Bredal, I. Self-diagnosed depression in the Norwegian general population–associations with neuroticism, extraversion, optimism, and general self-efficacy. BMC Public Health 2018, 18, 1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, S.; Gao, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Li, Y.; Fan, Q.; Tie, S.; Wu, Y.; Gu, S. Weizmannia coagulans BC99 affects valeric acid production via regulating gut microbiota to ameliorate inflammation and oxidative stress responses in Helicobacter pylori mice. J. Food Sci. 2024, 89, 9985–10002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, Z.F.; Yao, W.; Xie, Y.C.; Chen, W.; Zhu, Y.Y.; Chen, J.Q.; Zhou, X.Y.; Huang, J.Q.; Wu, M.S.; Chen, J.X. Oral troxerutin alleviates depression symptoms in mice by modulating gut microbiota and microbial metabolism. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2024, 68, 2300603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magne, F.; Gotteland, M.; Gauthier, L.; Zazueta, A.; Pesoa, S.; Navarrete, P.; Balamurugan, R. Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes Ratio: A Relev. Marker Gut Dysbiosis Obese Patients? Nutrition 2020, 12, 1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.; Yang, Z.; Yan, H.; Chen, G.; Zhong, S.; Chen, P.; Zhong, H.; Yang, H.; Jia, Y.; Yin, Z. Gut proinflammatory bacteria is associated with abnormal functional connectivity of hippocampus in unmedicated patients with major depressive disorder. Transl. Psychiatry 2024, 14, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, B.; Biswas, P.; Gulati, M.; Rani, P.; Gupta, R. Gut microbiome and Alzheimer’s disease: What we know and what remains to be explored. Ageing Res. Rev. 2024, 102, 102570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Chai, J.; Xu, W.; Zhao, Y. Exploring the potential of probiotics and prebiotics in major depression: From molecular function to clinical therapy. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2024, 16, 2187–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, S.; Mulè, S.; Parini, F.; Galla, R.; Ruga, S.; Rosso, G.; Brovero, A.; Molinari, C.; Uberti, F. The influence of the gut-brain axis on anxiety and depression: A review of the literature on the use of probiotics. J. Tradit. Complement. Med. 2024, 14, 237–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Jin, H.; Kwok, L.-Y.; Sun, Z.; Liong, M.-T.; Zhang, H. Probiotic consumption relieved human stress and anxiety symptoms possibly via modulating the neuroactive potential of the gut microbiota. Neurobiol. Stress 2021, 14, 100294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murack, M.; Kadamani, A.K.; Guindon-Riopel, A.; Traynor, O.H.; Iqbal, U.H.; Bronner, S.; Messier, C.; Ismail, N. The effect of probiotic supplementation on sleep, depression-like behaviour, and central glucose and lactate metabolism in male and female pubertal mice exposed to chronic sleep disruption. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2024, 168, 107146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loh, J.S.; Mak, W.Q.; Tan, L.K.S.; Ng, C.X.; Chan, H.H.; Yeow, S.H.; Foo, J.B.; Ong, Y.S.; How, C.W.; Khaw, K.Y. Microbiota–gut–brain axis and its therapeutic applications in neurodegenerative diseases. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullah, H.; Arbab, S.; Tian, Y.; Liu, C.-q.; Chen, Y.; Qijie, L.; Khan, M.I.U.; Hassan, I.U.; Li, K. The gut microbiota–brain axis in neurological disorder. Front. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1225875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirsch, I. Placebo effect in the treatment of depression and anxiety. Front. Psychiatry 2019, 10, 464277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romijn, A.R.; Rucklidge, J.J.; Kuijer, R.G.; Frampton, C. A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial of Lactobacillus helveticus and Bifidobacterium longum for the symptoms of depression. Aust. N. Z. J. Psychiatry 2017, 51, 810–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, K.K.; Liu, Y.-W.; Kuo, P.-H.; Chung, Y.-C.E.; Lu, M.-L.; Chen, C.-H. Effect of probiotics on depressive symptoms: A meta-analysis of human studies. Psychiatry Res. 2019, 282, 112568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slykerman, R.F.; Hood, F.; Wickens, K.; Thompson, J.M.D.; Barthow, C.; Murphy, R.; Kang, J.; Rowden, J.; Stone, P.; Crane, J.; et al. Effect of Lactobacillus rhamnosus HN001 in pregnancy on postpartum symptoms of depression and anxiety: A randomised double-blind placebo-controlled trial. EBioMedicine 2017, 24, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Wang, Z.; Tan, Y.; Ma, J.; Huang, W.; Zhang, X.; Jin, C.; Zhang, T.; Liu, W.; Yang, Y.-G. IL-17A/CEBPβ/OPN/LYVE-1 axis inhibits anti-tumor immunity by promoting tumor-associated tissue-resident macrophages. Cell Rep. 2024, 43, 115039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Mon, M.A.; Gómez-Lahoz, A.M.; Orozco, A.; Lahera, G.; Diaz, D.; Ortega, M.A.; Albillos, A.; Quintero, J.; Aubá, E.; Monserrat, J. Expansion of CD4 T lymphocytes expressing interleukin 17 and tumor necrosis factor in patients with major depressive disorder. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizk, M.M.; Bolton, L.; Cathomas, F.; He, H.; Russo, S.J.; Guttman-Yassky, E.; Mann, J.J.; Murrough, J. Immune-targeted therapies for depression: Current evidence for antidepressant effects of monoclonal antibodies. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2024, 85, 55778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, T.-T.; Wang, B.; Wu, M.; Li, Z.-L.; Feng, Y.; Cao, J.-Y.; Yin, D.; Liu, H.; Tang, R.-N.; Crowley, S.D. Extracellular vesicle–encapsulated IL-10 as novel nanotherapeutics against ischemic AKI. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaaz0748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuchs, T.; Jefferson, S.J.; Hooper, A.; Yee, P.-H.; Maguire, J.; Luscher, B. Disinhibition of somatostatin-positive GABAergic interneurons results in an anxiolytic and antidepressant-like brain state. Mol. Psychiatry 2017, 22, 920–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Landa, J.F.; German-Ponciano, L.J.; Puga-Olguín, A.; Olmos-Vázquez, O.J. Pharmacological, neurochemical, and behavioral mechanisms underlying the anxiolytic-and antidepressant-like effects of flavonoid chrysin. Molecules 2022, 27, 3551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, P.; Zhou, M.; Wang, Y.; Li, L.; Guo, J.; Zhu, X.; Qing, X.; Qian, J.; Huang, X. Gasotransmitter-nanodonor for spatial regulation of anxiety-like behavior and bone metastasis. Adv. Mater. 2025, 37, e2416481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Liu, C.; Zhang, K.; Xue, W. The role of gut microbiota and its metabolites short-chain fatty acids in food allergy. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2023, 12, 702–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Pan, W.; Diao, J.; Sun, L.; Meng, M. Gut microbiota variations in depression and anxiety: A systematic review. BMC Psychiatry 2025, 25, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barroso, A.; Mahler, J.V.; Fonseca-Castro, P.H.; Quintana, F.J. The aryl hydrocarbon receptor and the gut–brain axis. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2021, 18, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Li, D.; Sun, H. Herba Origani alleviated DSS-induced ulcerative colitis in mice through remolding gut microbiota to regulate bile acid and short-chain fatty acid metabolisms. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 161, 114409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, C.A.; Diaz-Arteche, C.; Eliby, D.; Schwartz, O.S.; Simmons, J.G.; Cowan, C.S.M. The gut microbiota in anxiety and depression—A systematic review. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 2021, 83, 101943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Z.; Wang, W.; Guo, R.; Liu, H. Faecalibacterium prausnitzii (ATCC 27766) has preventive and therapeutic effects on chronic unpredictable mild stress-induced depression-like and anxiety-like behavior in rats. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2019, 104, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.; Ling, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Mao, H.; Ma, Z.; Yin, Y.; Wang, W.; Tang, W.; Tan, Z.; Shi, J.; et al. Altered fecal microbiota composition in patients with major depressive disorder. Brain Behav. Immun. 2015, 48, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valles-Colomer, M.; Falony, G.; Darzi, Y.; Tigchelaar, E.F.; Wang, J.; Tito, R.Y.; Schiweck, C.; Kurilshikov, A.; Joossens, M.; Wijmenga, C.; et al. The neuroactive potential of the human gut microbiota in quality of life and depression. Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 623–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clapp, M.; Aurora, N.; Herrera, L.; Bhatia, M.; Wilen, E.; Wakefield, S. Gut microbiota’s effect on mental health: The gut-brain axis. Clin. Pr. 2017, 7, 987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hays, K.E.; Pfaffinger, J.M.; Ryznar, R. The interplay between gut microbiota, short-chain fatty acids, and implications for host health and disease. Gut Microbes 2024, 16, 2393270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, Y.; Wang, X.; Yan, F.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, S.; Song, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X. Quinoa saponin ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced behavioral disorders in mice by inhibiting neuroinflammation, modulating gut microbiota, and counterbalancing intestinal inflammation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2025, 73, 4700–4715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Sun, J.; Liu, X.; Fan, B.; Lu, C.; Wang, F. Polygonum sibiricum polysaccharides exert the antidepressant-like effects in chronic unpredictable mild stress-induced depressive mice by modulating microbiota-gut-brain axis. Phytother. Res. 2023, 37, 3408–3423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Projects | Placebo (n = 40) | BC99 (n = 39) | p-Value | Cohen’s d | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | |||
| Age (years) | 25.94 | 6.48 | 23.93 | 6.25 | 0.1840 a | 0.3157 |
| Sex (M/F) | 13/27 | 13/26 | >0.9999 b | |||
| Weight (kg) | 64.22 | 14.07 | 66.92 | 16.87 | 0.4420 a | −0.1738 |
| White blood cell (109/L) | 5.62 | 1.39 | 5.59 | 0.72 | 0.9110 a | 0.0271 |
| Red blood cells (1012/L) | 4.42 | 0.57 | 4.38 | 0.31 | 0.7503 a | 0.0872 |
| Hemoglobin (g/L) | 128.18 | 16.63 | 126.82 | 9.10 | 0.7062 a | 0.1015 |
| Hematocrit (%) | 40.35 | 4.13 | 40.04 | 2.68 | 0.7397 a | 0.0891 |
| Mean corpuscular volume (fL) | 91.82 | 4.50 | 92.53 | 2.48 | 0.4696 a | −0.1954 |
| Mean corpuscular hemoglobin (pg) | 29.04 | 0.90 | 29.26 | 0.97 | 0.3956 a | −0.2351 |
| Mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration (g/L) | 318.50 | 12.09 | 316.04 | 7.43 | 0.3622 a | 0.2452 |
| Platelet (109/L) | 201.36 | 50.27 | 208.14 | 31.88 | 0.5489 a | −0.1611 |
| Lymphocyte count (109/L) | 1.88 | 0.37 | 1.98 | 0.25 | 0.2022 a | −0.3167 |
| Neutrophil count (109/L) | 3.28 | 1.06 | 3.23 | 0.57 | 0.8104 a | 0.0588 |
| Lymphocyte ratio (%) | 39.91 | 6.78 | 36.14 | 3.52 | 0.8768 a | 0.6979 |
| Group | Week 0 | Week 8 | Change from Baseline | p-Value | Cohen’s d |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HAMD | |||||
| Placebo (n = 40) | 19.77 ± 7.18 | 12.47 ± 7.84 | 7.30 | 0.0082 | 0.9711 |
| BC99 (n = 39) | 20.80 ± 9.26 | 11.10 ± 10.24 | 9.70 | 0.0002 | 0.9936 |
| p-Value | 0.9677 | 0.9295 | |||
| Cohen’s d | −0.1243 | 0.1502 | |||
| HAMA | |||||
| Placebo (n = 40) | 19.80 ± 8.97 | 12.83 ± 9.61 | 6.97 | 0.0505 | 0.7498 |
| BC99 (n = 39) | 23.27 ± 11.94 | 10.77 ± 10.71 | 12.50 | <0.0001 | 1.1021 |
| p-Value | 0.5679 | 0.8669 | |||
| Cohen’s d | −0.3286 | 0.2025 | |||
| Outcome | Placebo | BC99 | OR a (95% CI) | ARD b (95% CI) | p-Value c |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HAMD Response (≥50% reduction) | 37.5% (15/40) | 56.4% (22/39) | 2.41 (0.97–6.25) | 18.9% (−11.99–46.47) | 0.063 |
| HAMD Remission (Score < 8) | 42.5% (17/40) | 56.4% (22/39) | 2.57 (0.94–7.48) | 13.9% (−16.83–42.19) | 0.073 |
| HAMA Response (≥50% reduction) | 50.0% (20/40) | 64.1% (25/39) | 1.92 (0.76–4.96) | 14.1% (−16.38–42.06) | 0.17 |
| HAMA Remission (Score < 7) | 42.5% (17/40) | 46.2% (18/39) | 1.77 (0.66–4.98) | 3.7% (−26.24–32.92) | 0.268 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tie, S.; Pan, Y.; Pang, C.; Saman, A.; Dong, Y.; Fang, S.; Zhu, J.; Wu, Y.; Gu, S. The Impact of Weizmannia coagulans BC99 on Anxiety and Depression: An 8-Week Clinical Pilot Study Through the Gut Microbiota–Brain Axis. Nutrients 2025, 17, 3087. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17193087
Tie S, Pan Y, Pang C, Saman A, Dong Y, Fang S, Zhu J, Wu Y, Gu S. The Impact of Weizmannia coagulans BC99 on Anxiety and Depression: An 8-Week Clinical Pilot Study Through the Gut Microbiota–Brain Axis. Nutrients. 2025; 17(19):3087. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17193087
Chicago/Turabian StyleTie, Shanshan, Yujia Pan, Chenguang Pang, Azeem Saman, Yao Dong, Shuguang Fang, Jianguo Zhu, Ying Wu, and Shaobin Gu. 2025. "The Impact of Weizmannia coagulans BC99 on Anxiety and Depression: An 8-Week Clinical Pilot Study Through the Gut Microbiota–Brain Axis" Nutrients 17, no. 19: 3087. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17193087
APA StyleTie, S., Pan, Y., Pang, C., Saman, A., Dong, Y., Fang, S., Zhu, J., Wu, Y., & Gu, S. (2025). The Impact of Weizmannia coagulans BC99 on Anxiety and Depression: An 8-Week Clinical Pilot Study Through the Gut Microbiota–Brain Axis. Nutrients, 17(19), 3087. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17193087





