Validating a Revised Oral Frailty 5-Item Checklist (OF-5) to Detect Pre-Symptomatic Brain Changes in Cognitively Unimpaired Older Adults
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
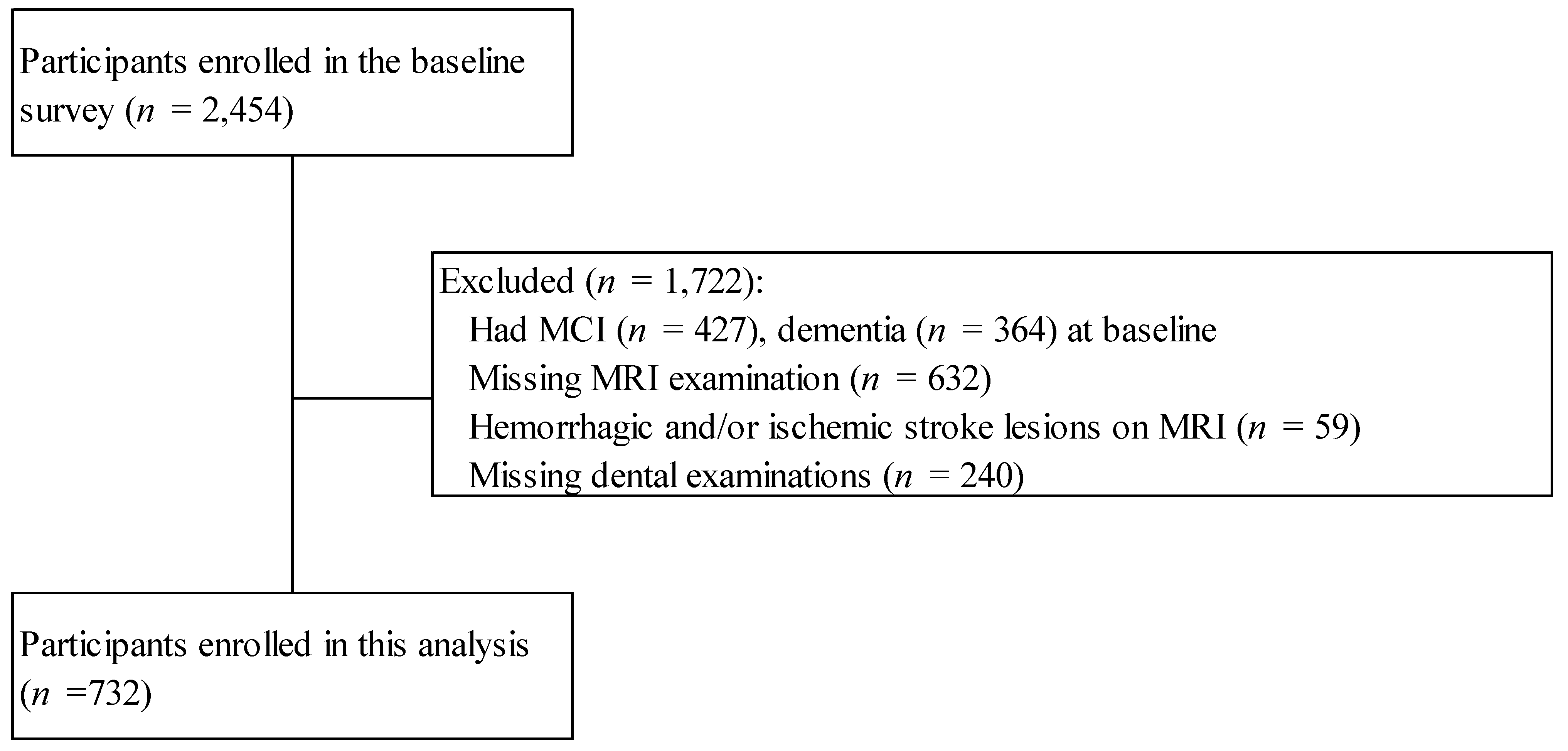
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Cognitive Status
2.3. Assessment of Oral Frailty
2.4. Magnetic Resonance Imaging Analysis
2.5. Nutritional Status
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Participant Characteristics According to the Oral Frailty Status
3.2. Association Between Oral Frailty and Regional Brain Volumes in Cognitively Unimpaired Older Adults
3.3. Nutrient Intake Patterns Associated with the Oral Frailty Status in Cognitively Unimpaired Older Adults
3.4. Food and Beverage Consumption Patterns Associated with the Oral Frailty Status in Cognitively Unimpaired Older Adults
3.5. Association Between Oral Frailty and Regional Brain Volumes After Adjustment for Nutrient Intake in Cognitively Unimpaired Older Adults
3.6. Association Between Oral Frailty and Regional Brain Volumes After Adjustment for Food and Beverage Intake in Cognitively Unimpaired Older Adults
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ninomiya, T. A Study on Future Estimates of the Elderly Population with Dementia in Japan; Research Report for 2024; Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research on Health, Labor and Welfare; Special Research Project on Health, Labor and Welfare Science; The Government of Japan: Tokyo, Japan, 2023. (In Japanese)
- Livingston, G.; Huntley, J.; Sommerlad, A.; Ames, D.; Ballard, C.; Banerjee, S.; Brayne, C.; Burns, A.; Cohen-Mansfield, J.; Cooper, C.; et al. Dementia Prevention, Intervention, and Care: 2020 Report of the Lancet Commission. Lancet 2020, 396, 413–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panza, F.; Lozupone, M.; Dibello, V. Multidimensional Complex Frailty Phenotypes: Epidemiological Impact of Oral Frailty in Older Age. Eur. Geriatr. Med. 2024, 15, 505–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tai, C.J.; Chen, J.H.; Tseng, T.G.; Lin, Y.T.; Hsiao, Y.H.; Lee, M.C.; Yang, Y.H. Prediction of Frailty and Dementia Using Oral Health Impact Profile from a Population-Based Survey. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, H.; Noguchi-Shinohara, M.; Ishimiya-Jokaji, M.; Kobayashi, Y.; Isa, M.; Ide, K.; Kawano, T.; Kawashiri, S.; Uchida, K.; Tatewaki, Y.; et al. Brain Atrophy in Normal Older Adult Links Tooth Loss and Diet Changes to Future Cognitive Decline. npj Aging 2024, 10, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, J.; Langerman, H. Alzheimer’s Disease-Why We Need Early Diagnosis. Degener. Neurol. Neuromuscul. Dis. 2019, 9, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crous-Bou, M.; Minguillón, C.; Gramunt, N.; Molinuevo, J.L. Alzheimer’s Disease Prevention: From Risk Factors to Early Intervention. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2017, 9, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasaki, M.; Shirobe, M.; Motokawa, K.; Tanaka, T.; Ikebe, K.; Ueda, T.; Minakuchi, S.; Akishita, M.; Arai, H.; Iijima, K.; et al. Prevalence of Oral Frailty and Its Association with Dietary Variety, Social Engagement, and Physical Frailty: Results from the Oral Frailty 5-Item Checklist. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2024, 24, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyahara, S.; Maeda, K.; Kawamura, K.; Matsui, Y.; Onaka, M.; Satake, S.; Arai, H. Concordance in Oral Frailty Five-Item Checklist and Oral Hypofunction: Examining Their Respective Characteristics. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2024, 118, 105305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishimiya, M.; Nakamura, H.; Kobayashi, Y.; Noguchi-Shinohara, M.; Abe, C.; Dohmoto, C.; Ikeda, Y.; Tokuno, K.; Ooi, K.; Yokokawa, M.; et al. Tooth Loss-Related Dietary Patterns and Cognitive Impairment in an Elderly Japanese Population: The Nakajima Study. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0194504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noguchi-Shinohara, M.; Yuki, S.; Dohmoto, C.; Ikeda, Y.; Samuraki, M.; Iwasa, K.; Yokogawa, M.; Asai, K.; Komai, K.; Nakamura, H.; et al. Differences in the Prevalence of Dementia and Mild Cognitive Impairment and Cognitive Functions between Early and Delayed Responders in a Community-Based Study of the Elderly. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2013, 37, 691–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 3rd ed.; American Psychiatric Association: Washington, DC, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Winblad, B.; Palmer, K.; Kivipelto, M.; Jelic, V.; Fratiglioni, L.; Wahlund, L.O.; Nordberg, A.; Bäckman, L.; Albert, M.; Almkvist, O.; et al. Mild Cognitive Impairment–beyond Controversies, towards a Consensus: Report of the International Working Group on Mild Cognitive Impairment. J. Intern. Med. 2004, 256, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Hirano, H.; Ikebe, K.; Ueda, T.; Iwasaki, M.; Shirobe, M.; Minakuchi, S.; Akishita, M.; Arai, H.; Iijima, K. Oral Frailty Five-Item Checklist to Predict Adverse Health Outcomes in Community-Dwelling Older Adults: A Kashiwa Cohort Study. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2023, 23, 651–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, L.J.; Brunelle, J.A.; Kingman, A. Periodontal Status in the United States, 1988-1991: Prevalence, Extent, and Demographic Variation. J. Dent. Res. 1996, 75, 672–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jack, C.R.; Petersen, R.C.; Xu, Y.; O’Brien, P.C.; Smith, G.E.; Ivnik, R.J.; Boeve, B.F.; Tangalos, E.G.; Kokmen, E. Rates of Hippocampal Atrophy Correlate with Change in Clinical Status in Aging and AD. Neurology 2000, 55, 484–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischl, B.; Salat, D.H.; Busa, E.; Albert, M.; Dieterich, M.; Haselgrove, C.; Van Der Kouwe, A.; Killiany, R.; Kennedy, D.; Klaveness, S.; et al. Whole Brain Segmentation: Automated Labeling of Neuroanatomical Structures in the Human Brain. Neuron 2002, 33, 341–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desikan, R.S.; Ségonne, F.; Fischl, B.; Quinn, B.T.; Dickerson, B.C.; Blacker, D.; Buckner, R.L.; Dale, A.M.; Maguire, R.P.; Hyman, B.T.; et al. An Automated Labeling System for Subdividing the Human Cerebral Cortex on MRI Scans into Gyral Based Regions of Interest. Neuroimage 2006, 31, 968–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shirota, T.; Yoshizumi, F. A Study on Convenient Dietary Assessment. Nihon Koshu Eisei Zasshi 1990, 37, 100–108. [Google Scholar]
- Science and Technology Agency, Standard Tables of Food Composition in Japan, 5th Revised and Enlarged ed.; Ministry of Finance: Tokyo, Japan, 2005.
- Willett, W.; Stampfer, M.J. Total Energy Intake: Implications for Epidemiologic Analyses. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1986, 124, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawagoe, T.; Matsushita, M.; Hashimoto, M.; Ikeda, M.; Sekiyama, K. Face-Specific Memory Deficits and Changes in Eye Scanning Patterns among Patients with Amnestic Mild Cognitive Impairment. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 14344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Susianti, N.A.; Prodjohardjono, A.; Vidyanti, A.N.; Setyaningsih, I.; Gofir, A.; Setyaningrum, C.T.S.; Effendy, C.; Setyawan, N.H.; Setyopranoto, I. The Impact of Medial Temporal and Parietal Atrophy on Cognitive Function in Dementia. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 5281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dibello, V.; Zupo, R.; Sardone, R.; Lozupone, M.; Castellana, F.; Dibello, A.; Daniele, A.; De Pergola, G.; Bortone, I.; Lampignano, L.; et al. Oral Frailty and Its Determinants in Older Age: A Systematic Review. Lancet Healthy Longev. 2021, 2, e507–e520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, D.; Fetahu, I.S.; Wang, M.; Fang, R.; Li, J.; Liu, H.; Gramyk, T.; Iwanicki, I.; Gu, S.; Xu, W.; et al. The Fusiform Gyrus Exhibits an Epigenetic Signature for Alzheimer’s Disease. Clin. Epigenet. 2020, 12, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro-dos-Santos, A.; de Brito, L.M.; de Araújo, G.S. The Fusiform Gyrus Exhibits Differential Gene-Gene Co-Expression in Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2023, 15, 1138336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Oral Frailty Component | Assessment Method | Definition of Oral Frailty | |
|---|---|---|---|
| OF-5 Score 2 Points or More | Revised OF-5 Score 2 Points or More | ||
| Fewer teeth | Count by dentist | ≤19 = 1 point | ≤9 = 1 point |
| Chewing difficulty | Do you have difficulty eating hard foods compared to six months ago? | Yes = 1 point | Yes = 1 point |
| Swallowing difficulty | Do you sometimes choke on tea, soup, etc.? | Yes = 1 point | Yes = 1 point |
| Dry mouth | Do you feel dry mouth? | Yes = 1 point | Yes = 1 point |
| Pronunciation difficulty | Do you have trouble pronouncing words clearly in everyday conversation? | Yes = 1 point | Yes = 1 point |
| Variables | Total | OF-5 | Revised OF-5 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Robust | Oral Frail | Robust | Oral Frail | ||
| N | 732 | 394 | 338 | 467 | 265 |
| Age, mean (SD), y | 70.32 (6.54) | 69.08 (5.80) | 71.75 (6.97) * | 69.22 (5.82) | 72.25 (7.18) * |
| Men, n (%) | 315 (43.0) | 173 (43.9) | 142 (42.0) | 195 (41.8) | 120 (45.3) |
| Women, n (%) | 417 (56.9) | 221 (56.1) | 196 (58) | 272 (58.2) | 145 (54.7) |
| Hypertension, n (%) | 384 (52.4) | 204 (51.8) | 180 (53.3) | 244 (52.2) | 140 (52.8) |
| Serum LDL-chol, mean (SD), mg/dL | 115.67 (32.49) | 116.71 (32.36) | 114.50 (32.70) | 116.94 (33.15) | 113.47 (31.25) |
| Serum HDL-chol, mean (SD), mg/dL | 61.05 (15.17) | 62.46 (16.08) | 59.50 (13.80) * | 62.08 (15.65) | 59.36 (14.05) * |
| Diabetes mellitus, n (%) | 113 (15.4) | 57 (14.5) | 56 (16.6) | 65 (13.9) | 48 (18.1) |
| Formal education, mean (SD), y | 11.34 (2.24) | 11.39 (2.17) | 11.31 (2.31) | 11.41 (2.16) | 11.25 (2.38) |
| BMI, mean (SD) | 23.85 (3.39) | 23.87 (3.23) | 23.81 (3.43) | 23.80 (3.22) | 23.86 (3.50) |
| Smoking, n (%) | 81 (11.1) | 36 (9.1) | 45 (13.3) | 47 (10.1) | 34 (12.8) |
| Exercise habits, n (%) | 322 (43.9) | 181 (46.1) | 141 (42.1) | 218 (46.9) | 104 (39.5) * |
| Oral frailty component | |||||
| Fewer teeth ≤ 19, n (%) | 397 (54.2) | 109 (27.7) | 288 (85.2) * | 182 (39) | 215 (81.1) * |
| Fewer teeth ≤ 9, n (%) | 240 (32.7) | 58 (14.7) | 182 (53.8) * | 58 (12.4) | 182 (68.7) * |
| Chewing difficulty, n (%) | 369 (50.3) | 74 (18.8) | 295 (87.3) * | 134 (28.7) | 235 (88.7) * |
| Swallowing difficulty, n (%) | 200 (27.3) | 44 (11.2) | 156 (46.2) * | 53 (11.3) | 147 (55.5) * |
| Dry mouth, n (%) | 82 (11.2) | 9 (2.3) | 73 (21.6) * | 12 (2.6) | 70 (26.4) * |
| Pronunciation difficulty, n (%) | 2 (0.3) | 0 (0) | 2 (0.6) | 1 (0.2) | 1 (0.4) |
| Variables | OF-5 | Revised OF-5 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Robust | Oral Frail | −Log10 (p-Value) | Robust | Oral Frail | −Log10 (p-Value) | |
| Brain volume to eTIV, % | ||||||
| TBV | 58.99 (58.69–59.29) | 58.81 (58.47–59.14) | 0.36 | 59.06 (58.78–59.34) | 58.63 (58.25–59.01) | 1.12 |
| WMH | 0.309 (0.278–0.339) | 0.344 (0.310–0.377) | 0.87 | 0.305 (0.277–0.333) | 0.360 (0.322–0.398) * | 1.63 |
| Frontal lobe | 9.127 (9.061–9.193) | 9.103 (9.030–9.176) | 0.2 | 9.133 (9.072–9.194) | 9.085 (9.002–9.168) | 0.44 |
| Pars triangularis gyrus | 0.411 (0.405–0.416) | 0.405 (0.399–0.411) | 0.78 | 0.412 (0.407–0.416) | 0.402 (0.395–0.409) * | 1.56 |
| Temporal lobe | 6.010 (5.964–6.055) | 5.981 (5.930–6.031) | 0.38 | 6.012 (5.970–6.054) | 5.968 (5.911–6.025) | 0.65 |
| Temporal lobe, medial | 1.855 (1.839–1.872) | 1.832 (1.814–1.851) | 1.13 | 1.856 (1.841–1.871) | 1.824 (1.803–1.845) * | 1.83 |
| Fusiform gyrus | 1.109 (1.097–1.121) | 1.088 (1.075–1.101) * | 1.69 | 1.111 (1.100–1.121) | 1.080 (1.065–1.095) * | 2.86 |
| Temporal lobe, lateral | 4.154 (4.120–4.189) | 4.148 (4.110–4.187) | 0.08 | 4.156 (4.124–4.188) | 4.144 (4.101–4.187) | 0.18 |
| Parietal lobe | 5.999 (5.954–6.044) | 6.013 (5.964–6.062) | 0.17 | 6.008 (5.967–6.049) | 6.000 (5.944–6.056) | 0.09 |
| Occipital lobe | 2.428 (2.407–2.450) | 2.428 (2.404–2.452) | 0.01 | 2.432 (2.412–2.452) | 2.422 (2.395–2.448) | 0.26 |
| Insula | 0.829 (0.821–0.836) | 0.832 (0.824–0.841) | 0.24 | 0.829 (0.822–0.836) | 0.833 (0.823–0.842) | 0.27 |
| Cingulate cortex | 1.135 (1.123–1.147) | 1.125 (1.111–1.138) | 0.57 | 1.134 (1.123–1.145) | 1.122 (1.107–1.137) | 0.68 |
| Hippocampus | 0.482 (0.476–0.487) | 0.483 (0.477–0.489) | 0.16 | 0.481 (0.476–0.486) | 0.485 (0.478–0.492) | 0.36 |
| Amygdala | 0.165 (0.163–0.167) | 0.165 (0.162–0.167) | 0.06 | 0.166 (0.164–0.167) | 0.164 (0.161–0.167) | 0.48 |
| Variables | OF-5 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Robust 7 | Oral Frail | −Log10 (p-Value) | |
| Total dietary fiber, g | 13.86 (13.36–14.35) | 12.46 (11.91–13.01) | 3.54 |
| Insoluble dietary fiber, g | 9.47 (9.13–9.82) | 8.57 (8.19–8.94) | 3.22 |
| Surplus ammonia, mg | 19.32 (18.33–20.30) | 16.72 (15.63–17.81) | 3.15 |
| Iodine, µg | 2250.91 (2098.87–2402.95) | 1858.06 (1690.46–2025.67) | 3.07 |
| Nitrate ion, g | 0.23 (0.21–0.24) | 0.20 (0.18–0.21) | 3.03 |
| Soluble dietary fiber, g | 3.14 (3.01–3.26) | 2.84 (2.71–2.98) | 2.65 |
| Potassium, mg | 2886.11 (2793.24–2978.98) | 2668.51 (2566.14–2770.89) | 2.61 |
| Vitamin K, µg | 286.75 (273.58–299.92) | 256.36 (241.84–270.88) | 2.54 |
| Water: fatty acids, g | 1109.14 (1069.12–1149.16) | 1021.63 (977.51–1065.75) | 2.33 |
| Folic acid, µg | 373.26 (358.12–388.39) | 341.05 (324.36–357.74) | 2.23 |
| Vitamin c, mg | 113.88 (108.70–119.06) | 103.03 (97.33–108.74) | 2.17 |
| Magnesium, mg | 382.90 (370.15–395.65) | 356.80 (342.74–370.85) | 2.09 |
| Beta-carotene equivalent, µg | 3849.57 (3639.63–4059.50) | 3419.49 (3188.06–3650.91) | 2.09 |
| Beta-carotene, µg | 3125.23 (2945.71–3304.74) | 2763.25 (2565.36–2961.14) | 2.04 |
| Water: carbon hydrate, g | 1007.86 (970.05–1045.66) | 933.38 (891.70–975.05) | 1.97 |
| Copper, mg | 1.19 (1.16–1.22) | 1.13 (1.09–1.16) | 1.91 |
| Unidentified fatty acid, mg | 40.74 (37.83–43.66) | 35.17 (31.96–38.38) | 1.88 |
| Alpha-carotene, µg | 623.38 (585.53–661.23) | 552.45 (510.73–594.17) | 1.82 |
| 18:4 n-3 octadecatetraenoic acid, mg | 95.72 (88.91–102.54) | 84.46 (76.94–91.97) | 1.49 |
| Niacin, mg | 18.57 (17.86–19.28) | 17.40 (16.61–18.19) | 1.47 |
| Variables | Revised OF-5 | ||
| Robust | Oral frail | −Log10 (p-value) | |
| Iodine, µg | 2221.82 (2082.24–2361.40) | 1802.26 (1612.03–1992.49) | 3.2 |
| Total dietary fiber, g | 13.70 (13.25–14.16) | 12.35 (11.73–12.97) | 3.13 |
| Insoluble dietary fiber, g | 9.36 (9.04–9.67) | 8.53 (8.10–8.96) | 2.57 |
| Vitamin K, µg | 283.95 (271.85–296.05) | 253.04 (236.55–269.53) | 2.44 |
| Folic acid, µg | 371.16 (357.26–385.06) | 335.95 (317.01–354.88) | 2.41 |
| Soluble dietary fiber, g | 3.10 (2.99–3.22) | 2.83 (2.67–2.98) | 2.27 |
| Surplus ammonia, mg | 18.93 (18.02–19.84) | 16.71 (15.47–17.95) | 2.27 |
| Potassium, mg | 2858.63 (2773.21–2944.05) | 2658.27 (2541.86–2774.68) | 2.12 |
| Nitrate ion, g | 0.22 (0.21–0.23) | 0.20 (0.18–0.21) | 2.12 |
| Copper, mg | 1.19 (1.16–1.22) | 1.12 (1.07–1.16) | 2.11 |
| Manganese, mg | 3.70 (3.58–3.83) | 3.42 (3.25–3.59) | 2.1 |
| Iron, mg | 8.45 (8.20–8.69) | 7.91 (7.58–8.25) | 1.87 |
| Vitamin c, mg | 112.60 (107.84–117.36) | 102.35 (95.86–108.84) | 1.85 |
| Magnesium, mg | 379.96 (368.25–391.68) | 354.91 (338.94–370.88) | 1.83 |
| Molybdenum, µg | 233.62 (227.32–239.92) | 220.59 (212.00–229.18) | 1.73 |
| Water, g | 1505.45 (1453.53–1557.38) | 1405.44 (1334.68–1476.21) | 1.55 |
| 18:1 count, mg | 15,856.74 (15,324.46–16,389.02) | 16,852.69 (16,127.28–17,578.09) | 1.48 |
| Beta-carotene, µg | 3067.39 (2902.22–3232.56) | 2768.26 (2543.16–2993.36) | 1.41 |
| Beta-carotene equivalent, µg | 3774.38 (3581.15–3967.62) | 3437.19 (3173.85–3700.54) | 1.33 |
| Variables | OF-5 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Robust | Oral Frail | −Log10 (p-Value) | |
| Other vegetables, g | 153.37 (144.89–161.85) | 130.45 (121.10–139.80) | 3.32 |
| Vegetables not high in beta-carotene, g | 153.08 (144.64–161.53) | 130.47 (121.16–139.78) | 3.26 |
| Seaweed, g | 14.82 (13.80–15.84) | 12.17 (11.04–13.29) | 3.1 |
| Nuts and bolts, g | 3.12 (2.60–3.65) | 1.76 (1.18–2.34) | 3.1 |
| Lard, g | 6.09 (5.56–6.61) | 7.40 (6.83–7.98) | 2.94 |
| Cider, g | 3.51 (−0.39–7.40) | 12.24 (7.95–16.54) | 2.43 |
| Fats and oils, g | 7.81 (7.20–8.42) | 9.11 (8.44–9.78) | 2.25 |
| Rolled oats, g | 0.57 (0.35–0.79) | 0.12 (−0.12–0.36) | 2.13 |
| Cheese, g | 3.86 (3.36–4.37) | 2.95 (2.39–3.51) | 1.72 |
| Udon noodles, g | 9.14 (6.12–12.17) | 14.54 (11.21–17.88) | 1.68 |
| Vegetables high in beta-carotene, g | 72.37 (67.78–76.95) | 64.29 (59.23–69.34) | 1.65 |
| Green fish, g | 33.33 (30.55–36.12) | 28.44 (25.37–31.51) | 1.64 |
| Japanese dressing type seasoning, g | 1.33 (0.99–1.67) | 0.75 (0.38–1.13) | 1.57 |
| White sugar, g | 7.80 (7.42–8.18) | 8.45 (8.02–8.87) | 1.53 |
| Noodles, g | 45.45 (39.88–51.03) | 54.85 (48.70–60.99) | 1.53 |
| Margarine, g | 0.70 (0.48–0.92) | 1.05 (0.81–1.29) | 1.4 |
| Yogurt nonfat-sweetened, g | 12.42 (9.37–15.47) | 17.16 (13.80–20.52) | 1.36 |
| Soybeans natto, g | 15.90 (14.50–17.31) | 13.72 (12.17–15.27) | 1.35 |
| Potato, g | 24.15 (22.63–25.67) | 21.81 (20.14–23.49) | 1.33 |
| All kinds of potatoes, g | 24.15 (22.63–25.67) | 21.81 (20.14–23.49) | 1.33 |
| Variables | Revised OF-5 | ||
| Robust | Oral frail | −Log10 (p-value) | |
| Seaweed, g | 14.61 (13.68–15.55) | 11.81 (10.53–13.09) | 3.17 |
| Fats and oils, g | 7.84 (7.28–8.39) | 9.42 (8.66–10.17) | 2.9 |
| Rolled oats, g | 0.56 (0.36–0.76) | 0.01 (−0.26–0.28) | 2.73 |
| Nuts and bolts, g | 2.96 (2.48–3.44) | 1.68 (1.03–2.34) | 2.58 |
| Other vegetables, g | 149.96 (142.15–157.77) | 130.30 (119.66–140.95) | 2.38 |
| Vegetables not high in beta-carotene, g | 149.70 (141.92–157.48) | 130.36 (119.76–140.96) | 2.34 |
| Blended oil, g | 6.80 (6.33–7.27) | 7.86 (7.22–8.50) | 2.02 |
| Soybeans natto, g | 15.93 (14.64–17.23) | 13.06 (11.30–14.82) | 1.95 |
| Lard, g | 6.30 (5.82–6.79) | 7.37 (6.72–8.03) | 1.94 |
| Canned coffee, g | 14.42 (6.68–22.15) | 30.90 (20.36–41.45) | 1.82 |
| Potato, g | 24.12 (22.72–25.51) | 21.23 (19.33–23.13) | 1.74 |
| All kinds of potatoes, g | 24.12 (22.72–25.51) | 21.23 (19.33–23.13) | 1.74 |
| Udon noodles, g | 9.71 (6.93–12.49) | 15.01 (11.22–18.80) | 1.52 |
| Green fish, g | 32.75 (30.19–35.31) | 28.14 (24.66–31.63) | 1.4 |
| Cider, g | 5.18 (1.59–8.77) | 11.61 (6.72–16.50) | 1.39 |
| French dressing, g | 1.76 (1.47–2.04) | 2.26 (1.87–2.65) | 1.34 |
| Instant noodles, g | 1.63 (0.75–2.50) | 3.14 (1.94–4.34) | 1.31 |
| Variables | OF-5 | Revised OF-5 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Robust | Oral Frail | −Log10 (p-Value) | Robust | Oral Frail | −Log10 (p-Value) | |
| Brain volume to eTIV, % | ||||||
| TBV | 58.95 (58.64–59.26) | 58.85 (58.51–59.19) | 0.17 | 59.03 (58.75–59.31) | 58.68 (58.30–59.07) | 0.79 |
| WMH | 0.304 (0.273–0.335) | 0.349 (0.315–0.384) | 1.22 | 0.302 (0.273–0.330) | 0.366 (0.327–0.405) * | 1.96 |
| Frontal lobe | 9.126 (9.059–9.193) | 9.103 (9.029–9.177) | 0.18 | 9.133 (9.072–9.195) | 9.084 (9.000–9.168) | 0.44 |
| Pars triangularis gyrus | 0.411 (0.405–0.416) | 0.405 (0.399–0.411) | 0.76 | 0.412 (0.407–0.417) | 0.401 (0.395–0.408) * | 1.78 |
| Temporal lobe, medial | 1.854 (1.837–1.871) | 1.833 (1.815–1.852) | 0.96 | 1.856 (1.841–1.872) | 1.824 (1.803–1.845) * | 1.78 |
| Fusiform gyrus | 1.109 (1.097–1.121) | 1.088 (1.075–1.102) * | 1.53 | 1.111 (1.100–1.122) | 1.080 (1.064–1.095) * | 2.8 |
| Temporal lobe, lateral | 4.152 (4.117–4.187) | 4.152 (4.113–4.190) | 0 | 4.155 (4.123–4.187) | 4.146 (4.103–4.190) | 0.11 |
| Parietal lobe | 5.998 (5.952–6.043) | 6.015 (5.964–6.065) | 0.2 | 6.007 (5.966–6.049) | 6.002 (5.944–6.059) | 0.06 |
| Occipital lobe | 2.427 (2.406–2.449) | 2.429 (2.405–2.453) | 0.03 | 2.431 (2.411–2.451) | 2.423 (2.395–2.450) | 0.2 |
| Insula | 0.829 (0.822–0.837) | 0.832 (0.823–0.840) | 0.19 | 0.830 (0.823–0.837) | 0.831 (0.822–0.841) | 0.09 |
| Cingulate cortex | 1.135 (1.123–1.147) | 1.124 (1.111–1.138) | 0.55 | 1.135 (1.124–1.146) | 1.122 (1.106–1.137) | 0.75 |
| Hippocampus | 0.481 (0.476–0.487) | 0.484 (0.478–0.490) | 0.36 | 0.481 (0.476–0.486) | 0.486 (0.479–0.493) | 0.59 |
| Amygdala | 0.165 (0.163–0.167) | 0.165 (0.163–0.167) | 0.03 | 0.165 (0.163–0.167) | 0.164 (0.161–0.167) | 0.39 |
| Variables | OF-5 | Revised OF-5 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Robust | Oral Frail | −Log10 (p-Value) | Robust | Oral Frail | −Log10 (p-Value) | |
| Brain volume to eTiv, % | ||||||
| TBV | 58.94 (58.63–59.26) | 58.86 (58.52–59.20) | 0.14 | 59.01 (58.73–59.29) | 58.72 (58.33–59.11) | 0.59 |
| WMH | 0.309 (0.277–0.340) | 0.344 (0.309–0.378) | 0.8 | 0.304 (0.276–0.333) | 0.361 (0.322–0.401) * | 1.57 |
| Frontal lobe | 9.124 (9.056–9.192) | 9.106 (9.031–9.181) | 0.13 | 9.131 (9.069–9.193) | 9.088 (9.002–9.174) | 0.36 |
| Pars triangularis gyrus | 0.411 (0.406–0.417) | 0.405 (0.399–0.411) | 0.87 | 0.412 (0.407–0.417) | 0.401 (0.394–0.408) * | 1.93 |
| Temporal lobe | 6.005 (5.958–6.052) | 5.986 (5.934–6.038) | 0.22 | 6.008 (5.965–6.050) | 5.976 (5.917–6.035) | 0.39 |
| Temporal lobe, medial | 1.855 (1.838–1.872) | 1.832 (1.813–1.851) | 1.07 | 1.855 (1.839–1.870) | 1.827 (1.806–1.848) * | 1.32 |
| Fusiform gyrus | 1.109 (1.097–1.122) | 1.088 (1.074–1.101) * | 1.6 | 1.110 (1.099–1.121) | 1.081 (1.066–1.097) * | 2.32 |
| Temporal lobe, lateral | 4.150 (4.115–4.185) | 4.154 (4.115–4.193) | 0.05 | 4.153 (4.121–4.185) | 4.149 (4.105–4.194) | 0.05 |
| Parietal lobe | 5.994 (5.948–6.040) | 6.019 (5.968–6.070) | 0.31 | 6.004 (5.963–6.046) | 6.007 (5.949–6.065) | 0.02 |
| Occipital lobe | 2.426 (2.404–2.448) | 2.430 (2.406–2.455) | 0.08 | 2.431 (2.411–2.451) | 2.423 (2.395–2.450) | 0.19 |
| Insula | 0.829 (0.821–0.837) | 0.832 (0.823–0.840) | 0.18 | 0.830 (0.823–0.837) | 0.832 (0.822–0.842) | 0.15 |
| Cingulate cortex | 1.135 (1.123–1.147) | 1.124 (1.111–1.138) | 0.56 | 1.134 (1.123–1.145) | 1.122 (1.107–1.138) | 0.63 |
| Hippocampus | 0.481 (0.476–0.487) | 0.484 (0.478–0.490) | 0.25 | 0.480 (0.475–0.486) | 0.487 (0.480–0.494) | 0.74 |
| Amygdala | 0.165 (0.163–0.167) | 0.165 (0.162–0.167) | 0.03 | 0.165 (0.163–0.167) | 0.164 (0.161–0.167) | 0.31 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Murahashi, M.; Ono, K.; Noguchi-Shinohara, M.; Ishimiya-Jokaji, M.; Ide, K.; Kawano, T.; Tokuchi, S.; Suzuki, R.; Isa, M.; Kawashiri, S.; et al. Validating a Revised Oral Frailty 5-Item Checklist (OF-5) to Detect Pre-Symptomatic Brain Changes in Cognitively Unimpaired Older Adults. Nutrients 2025, 17, 3058. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17193058
Murahashi M, Ono K, Noguchi-Shinohara M, Ishimiya-Jokaji M, Ide K, Kawano T, Tokuchi S, Suzuki R, Isa M, Kawashiri S, et al. Validating a Revised Oral Frailty 5-Item Checklist (OF-5) to Detect Pre-Symptomatic Brain Changes in Cognitively Unimpaired Older Adults. Nutrients. 2025; 17(19):3058. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17193058
Chicago/Turabian StyleMurahashi, Makoto, Kenjiro Ono, Moeko Noguchi-Shinohara, Mai Ishimiya-Jokaji, Kentaro Ide, Toshihiro Kawano, Shusuke Tokuchi, Risako Suzuki, Mikana Isa, Shuichi Kawashiri, and et al. 2025. "Validating a Revised Oral Frailty 5-Item Checklist (OF-5) to Detect Pre-Symptomatic Brain Changes in Cognitively Unimpaired Older Adults" Nutrients 17, no. 19: 3058. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17193058
APA StyleMurahashi, M., Ono, K., Noguchi-Shinohara, M., Ishimiya-Jokaji, M., Ide, K., Kawano, T., Tokuchi, S., Suzuki, R., Isa, M., Kawashiri, S., & Nakamura, H. (2025). Validating a Revised Oral Frailty 5-Item Checklist (OF-5) to Detect Pre-Symptomatic Brain Changes in Cognitively Unimpaired Older Adults. Nutrients, 17(19), 3058. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17193058







