Association Between the Dietary Inflammatory Index and Life’s Essential 8 in Older Adults Based on Gut Microbiota Profiles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Assessment of Dietary Intake
2.3. Inflammatory Potential of the Diet
2.4. Measurement of CVH
2.5. Measurement of Skin Advanced Glycation End-Products (AGEs)
2.6. 16S rRNA Gene Amplicon Sequencing
2.7. Bioinformatic Analysis
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographic Characteristics by DII Groups
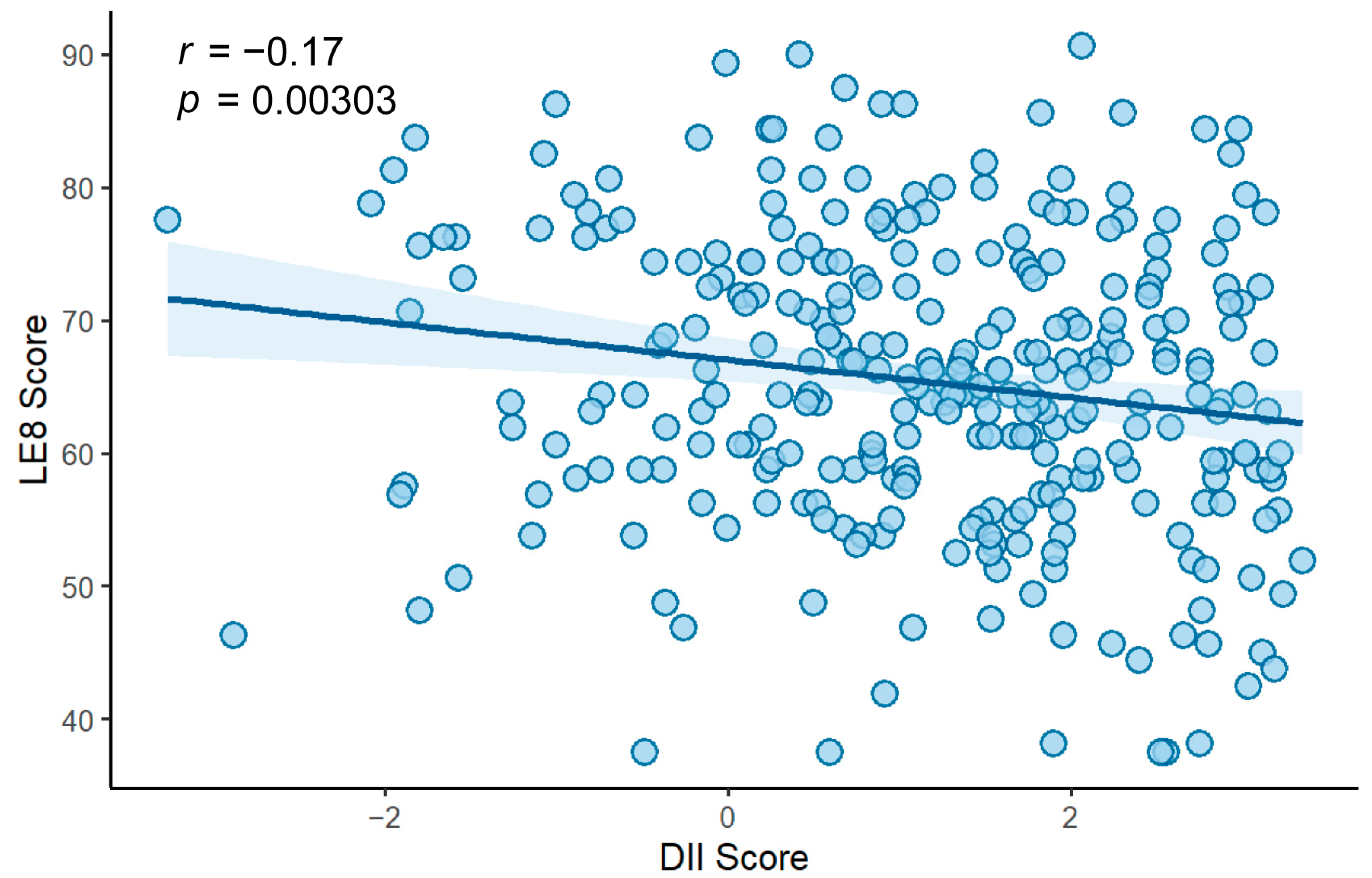
3.2. Association Between DII and LE8
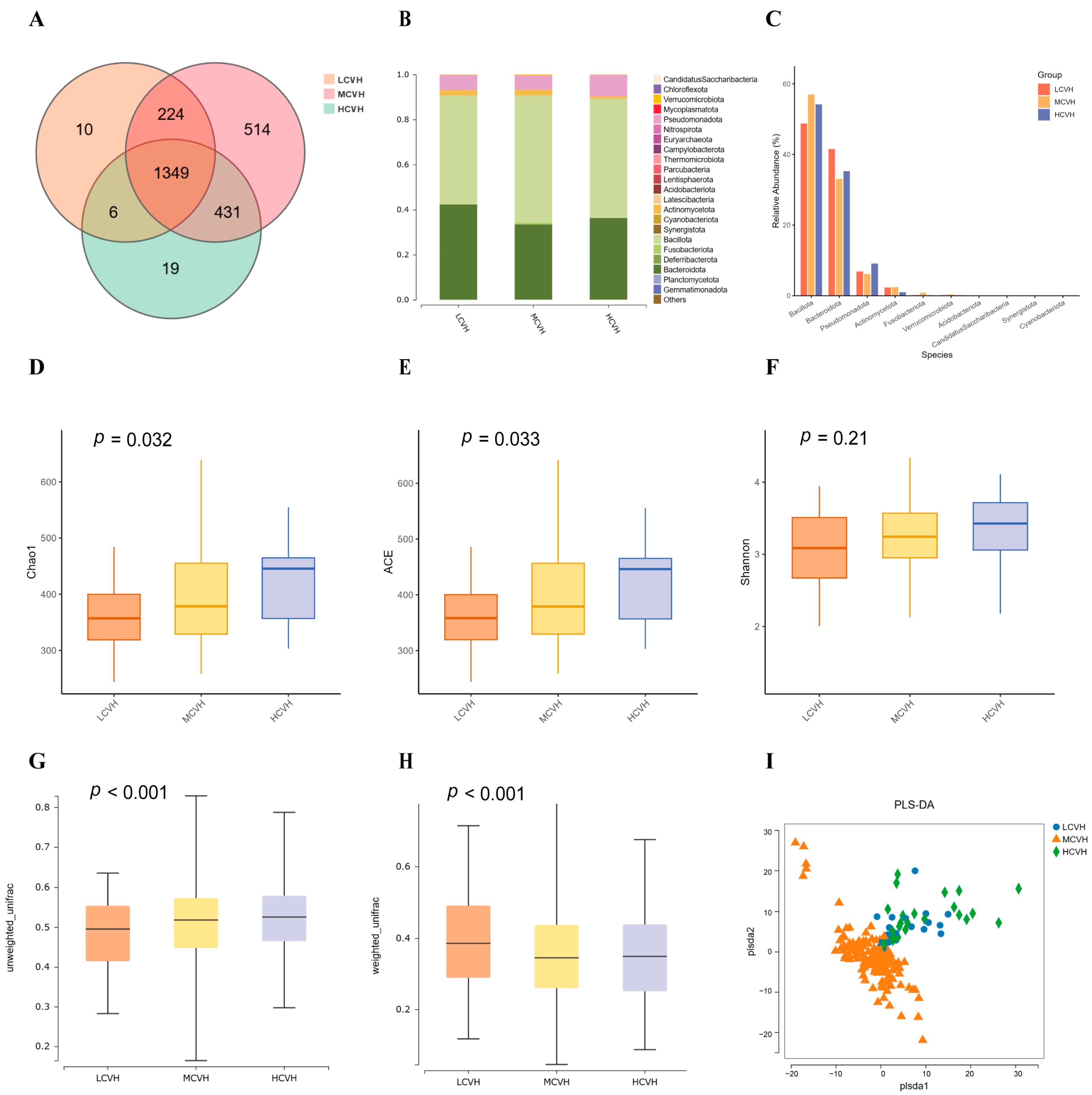
3.3. Gut Microbiota Composition Across CVH Groups
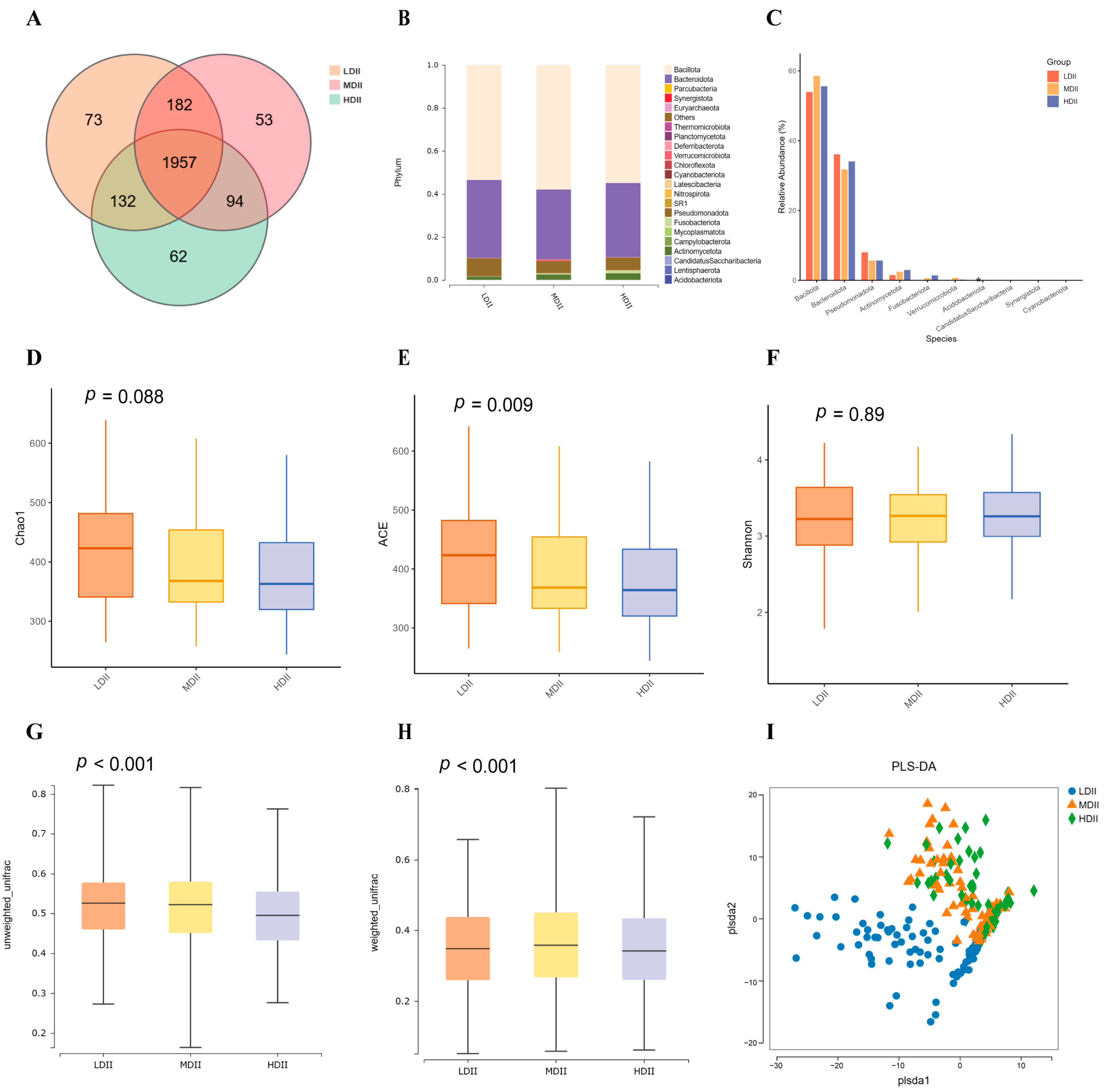
3.4. Gut Microbiota Composition Across DII Groups
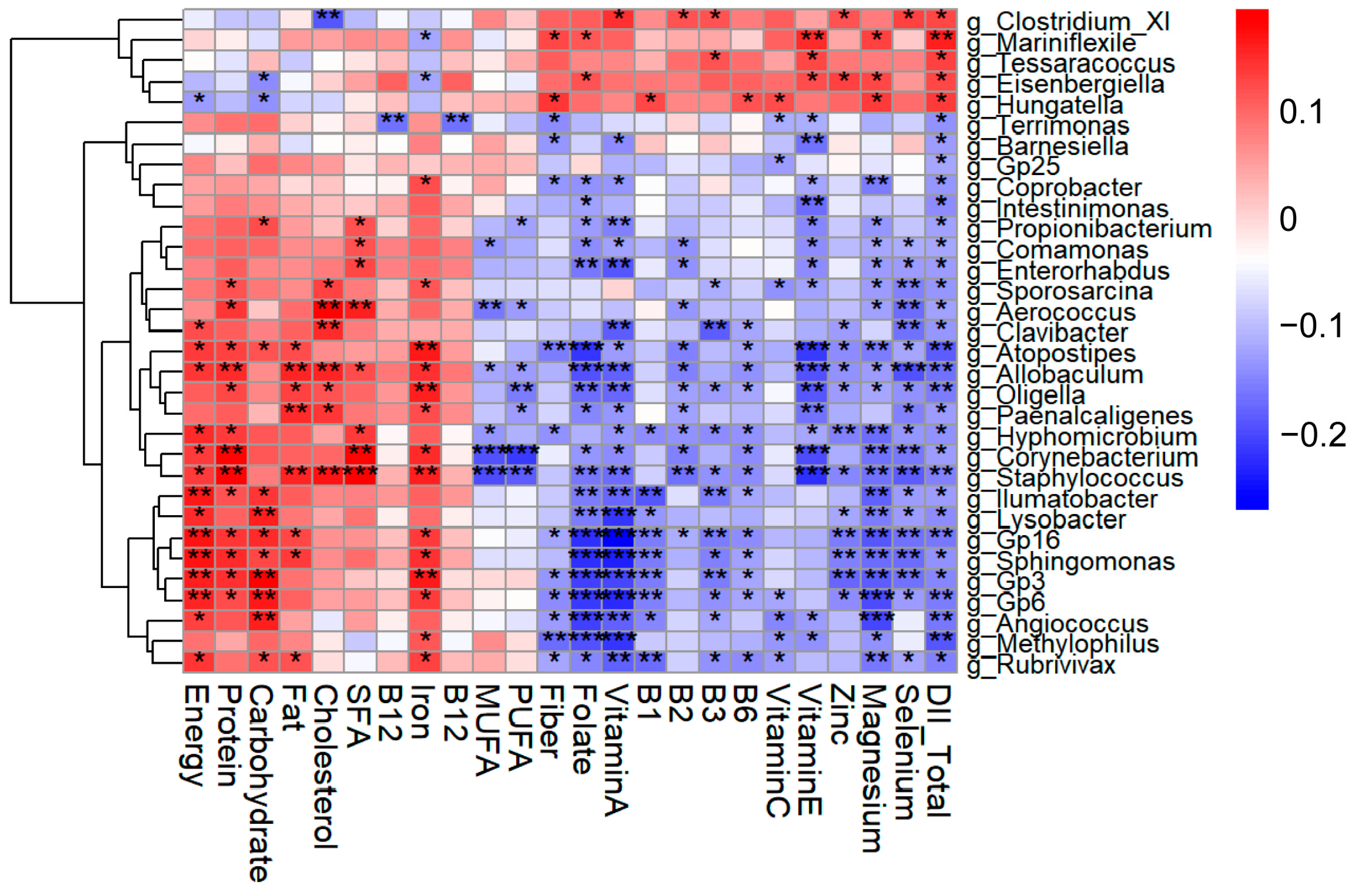
3.5. Identification of Key Gut Microbial Genera Associated with Both DII and LE8
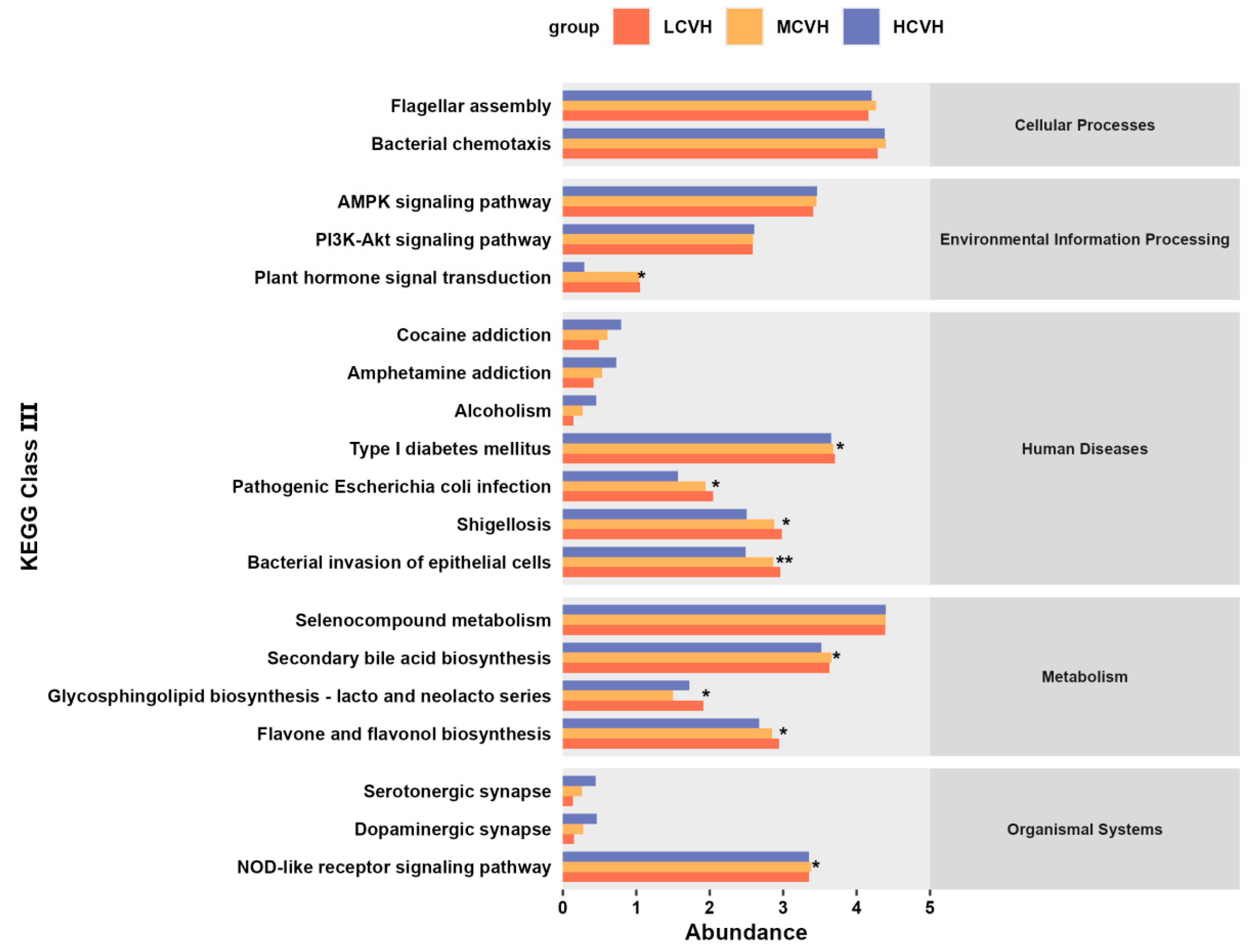
3.6. Functional Prediction of Key Gut Microbiota
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CVD | cardiovascular disease |
| CVH | cardiovascular health |
| AHA | American Heart Association |
| LE8 | Life’s Essential 8 |
| PA | physical activity |
| BMI | body mass index |
| BP | blood pressure |
| DII | Dietary Inflammatory Index |
| CRP | C-reactive protein |
| IL-6 | interleukin-6 |
| TNF-α | tumor necrosis factor-alpha |
| PAD | photo-assisted dietary intake assessment |
| MEPA | Mediterranean Eating Pattern Assessment |
| HbA1c | glycated hemoglobin A1c |
| OTUs | operational taxonomic units |
| ANOSIM | Analysis of Similarities |
| PLS-DA | Partial Least Squares Discriminant Analysis |
| CI | confidence intervals |
| AGEs | Advanced Glycation End-products |
| KEGG | Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes |
| SCFAs | short-chain fatty acids |
| TMAO | trimethylamine N-oxide |
| TMA | trimethylamine |
| LPS | lipopolysaccharide |
| TLR | Toll-like receptor |
| MACE | major adverse cardiovascular events |
| NO | nitric oxide |
References
- Roth, G.A.; Mensah, G.A.; Johnson, C.O.; Addolorato, G.; Ammirati, E.; Baddour, L.M.; Barengo, N.C.; Beaton, A.Z.; Benjamin, E.J.; Benziger, C.P.; et al. Global Burden of Cardiovascular Diseases and Risk Factors, 1990–2019: Update from the GBD 2019 Study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 76, 2982–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lloyd-Jones, D.M.; Allen, N.B.; Anderson, C.A.M.; Black, T.; Brewer, L.C.; Foraker, R.E.; Grandner, M.A.; Lavretsky, H.; Perak, A.M.; Sharma, G.; et al. Life’s Essential 8: Updating and Enhancing the American Heart Association’s Construct of Cardiovascular Health: A Presidential Advisory from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2022, 146, e18–e43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shetty, N.S.; Parcha, V.; Patel, N.; Yadav, I.; Basetty, C.; Li, C.; Pandey, A.; Kalra, R.; Li, P.; Arora, G.; et al. AHA Life’s essential 8 and ideal cardiovascular health among young adults. Am. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2023, 13, 100452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petermann-Rocha, F.; Deo, S.; Celis-Morales, C.; Ho, F.K.; Bahuguna, P.; McAllister, D.; Sattar, N.; Pell, J.P. An Opportunity for Prevention: Associations Between the Life’s Essential 8 Score and Cardiovascular Incidence Using Prospective Data from UK Biobank. Curr. Probl. Cardiol. 2023, 48, 101540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Li, Y.; Zhao, M.; Yu, X.; Zhang, C.; Magnussen, C.G.; Xi, B. Association of the American Heart Association’s new “Life’s Essential 8” with all-cause and cardiovascular disease-specific mortality: Prospective cohort study. BMC Med. 2023, 21, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isiozor, N.M.; Kunutsor, S.K.; Voutilainen, A.; Laukkanen, J.A. Life’s Essential 8 and the risk of cardiovascular disease death and all-cause mortality in Finnish men. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2023, 30, 658–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivappa, N.; Steck, S.E.; Hurley, T.G.; Hussey, J.R.; Hébert, J.R. Designing and developing a literature-derived, population-based dietary inflammatory index. Public Health Nutr. 2014, 17, 1689–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marx, W.; Veronese, N.; Kelly, J.T.; Smith, L.; Hockey, M.; Collins, S.; Trakman, G.L.; Hoare, E.; Teasdale, S.B.; Wade, A.; et al. The Dietary Inflammatory Index and Human Health: An Umbrella Review of Meta-Analyses of Observational Studies. Adv. Nutr. 2021, 12, 1681–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, C.M.; Shivappa, N.; Hébert, J.R.; Perry, I.J. Dietary Inflammatory Index and Biomarkers of Lipoprotein Metabolism, Inflammation and Glucose Homeostasis in Adults. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyrovolas, S.; Koyanagi, A.; Kotsakis, G.A.; Panagiotakos, D.; Shivappa, N.; Wirth, M.D.; Hébert, J.R.; Haro, J.M. Dietary inflammatory potential is linked to cardiovascular disease risk burden in the US adult population. Int. J. Cardiol. 2017, 240, 409–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pocovi-Gerardino, G.; Correa-Rodríguez, M.; Callejas-Rubio, J.L.; Ríos-Fernández, R.; Martín-Amada, M.; Cruz-Caparros, M.G.; Rueda-Medina, B.; Ortego-Centeno, N. Dietary Inflammatory Index Score and Cardiovascular Disease Risk Markers in Women with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2020, 120, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhett, L.G.; Ribeiro, S.A.V.; Hermsdorff, H.H.M.; Silva, M.A.; Shivappa, N.; Hébert, J.R.; Novaes, J.F. Dietary inflammatory index scores are associated with atherogenic risk in Brazilian schoolchildren. Public Health Nutr. 2021, 24, 6191–6200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sethna, C.B.; Alanko, D.; Wirth, M.D.; Shivappa, N.; Hebert, J.R.; Khan, S.; Sen, S. Dietary inflammation and cardiometabolic health in adolescents. Pediatr. Obes. 2021, 16, e12706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Xu, Q.; Liu, W.; Xiong, J.; Li, H.; Xiong, N.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z. Dietary inflammatory index and its associations with cardiovascular diseases and cancer: Evidence form NHANES 2017-2018 and Mendelian randomization analysis. Exp. Gerontol. 2025, 199, 112665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrasco-Marín, F.; Zhao, L.; Hébert, J.R.; Wirth, M.D.; Petermann-Rocha, F.; Phillips, N.; Malcomson, F.C.; Mathers, J.C.; Ferguson, L.D.; Ho, F.; et al. Association of a dietary inflammatory index with cardiometabolic, endocrine, liver, renal and bones biomarkers: Cross-sectional analysis of the UK Biobank study. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. NMCD 2024, 34, 1731–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebert, J.R.; Clemow, L.; Pbert, L.; Ockene, I.S.; Ockene, J.K. Social desirability bias in dietary self-report may compromise the validity of dietary intake measures. Int. J. Epidemiol. 1995, 24, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witkowski, M.; Weeks, T.L.; Hazen, S.L. Gut Microbiota and Cardiovascular Disease. Circ. Res. 2020, 127, 553–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jie, Z.; Xia, H.; Zhong, S.L.; Feng, Q.; Li, S.; Liang, S.; Zhong, H.; Liu, Z.; Gao, Y.; Zhao, H.; et al. The gut microbiome in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emoto, T.; Yamashita, T.; Kobayashi, T.; Sasaki, N.; Hirota, Y.; Hayashi, T.; So, A.; Kasahara, K.; Yodoi, K.; Matsumoto, T.; et al. Characterization of gut microbiota profiles in coronary artery disease patients using data mining analysis of terminal restriction fragment length polymorphism: Gut microbiota could be a diagnostic marker of coronary artery disease. Heart Vessel. 2017, 32, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, T.N.; Bazzano, L.A.; Ajami, N.J.; He, H.; Zhao, J.; Petrosino, J.F.; Correa, A.; He, J. Gut Microbiome Associates with Lifetime Cardiovascular Disease Risk Profile Among Bogalusa Heart Study Participants. Circ. Res. 2016, 119, 956–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhao, F.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Tao, J.; Tian, G.; Wu, S.; Liu, W.; Cui, Q.; Geng, B.; et al. Gut microbiota dysbiosis contributes to the development of hypertension. Microbiome 2017, 5, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natarajan, N.; Hori, D.; Flavahan, S.; Steppan, J.; Flavahan, N.A.; Berkowitz, D.E.; Pluznick, J.L. Microbial short chain fatty acid metabolites lower blood pressure via endothelial G protein-coupled receptor 41. Physiol. Genom. 2016, 48, 826–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battson, M.L.; Lee, D.M.; Li Puma, L.C.; Ecton, K.E.; Thomas, K.N.; Febvre, H.P.; Chicco, A.J.; Weir, T.L.; Gentile, C.L. Gut microbiota regulates cardiac ischemic tolerance and aortic stiffness in obesity. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2019, 317, H1210–H1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Q.; Zhang, C.; Chen, R.; Jiang, L.; Li, H.; Wu, P.; Li, L. Quinic acid regulated TMA/TMAO-related lipid metabolism and vascular endothelial function through gut microbiota to inhibit atherosclerotic. J. Transl. Med. 2024, 22, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, S.R.; Tong, Q.; Lin, Y.; Pan, L.B.; Fu, J.; Peng, R.; Zhang, X.F.; Zhao, Z.X.; Li, Y.; Yu, J.B.; et al. Berberine treats atherosclerosis via a vitamine-like effect down-regulating Choline-TMA-TMAO production pathway in gut microbiota. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, P.; Xie, C.; Nichols, R.G.; Ferrell, J.M.; Boehme, S.; Krausz, K.W.; Patterson, A.D.; Gonzalez, F.J.; Chiang, J.Y.L. Intestine farnesoid X receptor agonist and the gut microbiota activate G-protein bile acid receptor-1 signaling to improve metabolism. Hepatology 2018, 68, 1574–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemet, I.; Saha, P.P.; Gupta, N.; Zhu, W.; Romano, K.A.; Skye, S.M.; Cajka, T.; Mohan, M.L.; Li, L.; Wu, Y.; et al. A Cardiovascular Disease-Linked Gut Microbial Metabolite Acts via Adrenergic Receptors. Cell 2020, 180, 862–877.e822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graf, D.; Di Cagno, R.; Fåk, F.; Flint, H.J.; Nyman, M.; Saarela, M.; Watzl, B. Contribution of diet to the composition of the human gut microbiota. Microb. Ecol. Health Dis. 2015, 26, 26164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirhosseini, S.M.; Mahdavi, A.; Yarmohammadi, H.; Razavi, A.; Rezaei, M.; Soltanipur, M.; Karimi Nemch, M.; Jafari Naeini, S.; Siadat, S.D. What is the link between the dietary inflammatory index and the gut microbiome? A systematic review. Eur. J. Nutr. 2024, 63, 2407–2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perler, B.K.; Friedman, E.S.; Wu, G.D. The Role of the Gut Microbiota in the Relationship Between Diet and Human Health. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2023, 85, 449–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Nepovimova, E.; Adam, V.; Heger, Z.; Valko, M.; Wu, Q.; Kuca, K. Age-associated changes in innate and adaptive immunity: Role of the gut microbiota. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1421062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Qu, Z.; Chu, J.; Han, S. Aging Gut Microbiome in Healthy and Unhealthy Aging. Aging Dis. 2024, 16, 980–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Song, L.; Fan, R.; Chen, Q.; You, M.; Cai, M.; Wu, Y.; Li, Y.; Xu, M. Targeting Aging and Longevity with Exogenous Nucleotides (TALENTs): Rationale, Design, and Baseline Characteristics from a Randomized Controlled Trial in Older Adults. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, R.; Chen, Q.; Song, L.; Wang, S.; You, M.; Cai, M.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Xu, M. The Validity and Feasibility of Utilizing the Photo-Assisted Dietary Intake Assessment among College Students and Elderly Individuals in China. Nutrients 2024, 16, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazidi, M.; Shivappa, N.; Wirth, M.D.; Hebert, J.R.; Mikhailidis, D.P.; Kengne, A.P.; Banach, M. Dietary inflammatory index and cardiometabolic risk in US adults. Atherosclerosis 2018, 276, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerwinske, L.A.; Rasmussen, H.E.; Lipson, S.; Volgman, A.S.; Tangney, C.C. Evaluation of a dietary screener: The Mediterranean Eating Pattern for Americans tool. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. Off. J. Br. Diet. Assoc. 2017, 30, 596–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koetsier, M.; Lutgers, H.L.; de Jonge, C.; Links, T.P.; Smit, A.J.; Graaff, R. Reference values of skin autofluorescence. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2010, 12, 399–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, J.R.; Wang, Q.; Fish, J.A.; Chai, B.; McGarrell, D.M.; Sun, Y.; Brown, C.T.; Porras-Alfaro, A.; Kuske, C.R.; Tiedje, J.M. Ribosomal Database Project: Data and tools for high throughput rRNA analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D633–D642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrucci, L.; Fabbri, E. Inflammageing: Chronic inflammation in ageing, cardiovascular disease, and frailty. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2018, 15, 505–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandhorst, S.; Longo, V.D. Dietary Restrictions and Nutrition in the Prevention and Treatment of Cardiovascular Disease. Circ. Res. 2019, 124, 952–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rippe, J.M. Lifestyle Strategies for Risk Factor Reduction, Prevention, and Treatment of Cardiovascular Disease. Am. J. Lifestyle Med. 2019, 13, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlawat, S.; Asha; Sharma, K.K. Gut-organ axis: A microbial outreach and networking. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2021, 72, 636–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Vincenzo, F.; Del Gaudio, A.; Petito, V.; Lopetuso, L.R.; Scaldaferri, F. Gut microbiota, intestinal permeability, and systemic inflammation: A narrative review. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2024, 19, 275–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sittipo, P.; Shim, J.W.; Lee, Y.K. Microbial Metabolites Determine Host Health and the Status of Some Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivera, K.; Gonzalez, L.; Bravo, L.; Manjarres, L.; Andia, M.E. The Gut-Heart Axis: Molecular Perspectives and Implications for Myocardial Infarction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 12465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bui, T.V.A.; Hwangbo, H.; Lai, Y.; Hong, S.B.; Choi, Y.J.; Park, H.J.; Ban, K. The Gut-Heart Axis: Updated Review for The Roles of Microbiome in Cardiovascular Health. Korean Circ. J. 2023, 53, 499–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trøseid, M.; Andersen, G.; Broch, K.; Hov, J.R. The gut microbiome in coronary artery disease and heart failure: Current knowledge and future directions. EBioMedicine 2020, 52, 102649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zmora, N.; Suez, J.; Elinav, E. You are what you eat: Diet, health and the gut microbiota. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 35–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, I.; Torrinhas, R.; Fonseca, D.; Lyra, C.O.; de Sousa Alves Neri, J.L.; Balmant, B.D.; Callado, L.; Charlton, K.; Queiroz, N.; Waitzberg, D.L. Pro-Inflammatory Diet Is Correlated with High Veillonella rogosae, Gut Inflammation and Clinical Relapse of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivappa, N.; Wirth, M.D.; Murphy, E.A.; Hurley, T.G.; Hébert, J.R. Association between the Dietary Inflammatory Index (DII) and urinary enterolignans and C-reactive protein from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey—2003–2008. Eur. J. Nutr. 2019, 58, 797–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhaar, B.J.H.; Prodan, A.; Nieuwdorp, M.; Muller, M. Gut Microbiota in Hypertension and Atherosclerosis: A Review. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Du, D.; Fu, T.; Han, Y.; Li, P.; Ju, H. Alterations of the Gut Microbiota in Patients with Severe Chronic Heart Failure. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 813289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Q.; He, C.; Fu, C.; Wei, Q. The role of the gut microbiota in health and cardiovascular diseases. Mol. Biomed. 2022, 3, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, F.; Jin, Q.; Jin, Q.; Qian, Y.; Ren, X.; Liu, T.; Zhan, Y. Genetic evidence supporting the causal role of gut microbiota in chronic kidney disease and chronic systemic inflammation in CKD: A bilateral two-sample Mendelian randomization study. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1287698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kameyama, K.; Itoh, K. Intestinal colonization by a Lachnospiraceae bacterium contributes to the development of diabetes in obese mice. Microbes Environ. 2014, 29, 427–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, X.; Cai, R.; Shaoyong, W.; Wang, G.; Yan, W.; He, Z.; Li, R.; Chao, M.; Zhao, T.; Deng, L.; et al. Melatonin promotes gut anti-oxidative status in perinatal rat by remodeling the gut microbiome. Redox Biol. 2023, 65, 102829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pujo, J.; Petitfils, C.; Le Faouder, P.; Eeckhaut, V.; Payros, G.; Maurel, S.; Perez-Berezo, T.; Van Hul, M.; Barreau, F.; Blanpied, C.; et al. Bacteria-derived long chain fatty acid exhibits anti-inflammatory properties in colitis. Gut 2021, 70, 1088–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallianou, N.; Dalamaga, M.; Stratigou, T.; Karampela, I.; Tsigalou, C. Do Antibiotics Cause Obesity Through Long-term Alterations in the Gut Microbiome? A Review of Current Evidence. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2021, 10, 244–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, Y.Y.; Ha, C.W.; Hoffmann, J.M.; Oscarsson, J.; Dinudom, A.; Mather, T.J.; Cook, D.I.; Hunt, N.H.; Caterson, I.D.; Holmes, A.J.; et al. Effects of dietary fat profile on gut permeability and microbiota and their relationships with metabolic changes in mice. Obesity 2015, 23, 1429–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Fan, X.; Ye, R.; Hu, Y.; Zheng, T.; Shi, R.; Cheng, W.; Lv, X.; Chen, L.; Liang, P. The Effect of Simvastatin on Gut Microbiota and Lipid Metabolism in Hyperlipidemic Rats Induced by a High-Fat Diet. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Dong, J.; Lu, J.; Cai, Z.; Zhou, B.; Zhang, Q.; Zhu, C.; Laghi, L. Dietary Interventions with Bletilla striata Polysaccharides and/or Composite Polysaccharides Remodel Liver Lipid Profiles and Ameliorate Gut Metabolic Disturbances in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Mice. Foods 2025, 14, 2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.P.; Zheng, T.T.; Zeng, B.F.; Wu, M.L.; Shi, R.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, L.J.; Cheng, W.J.; Liang, P. Effects of Lactobacillus plantarum FZU3013-Fermented Laminaria japonica on Lipid Metabolism and Gut Microbiota in Hyperlipidaemic Rats. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 786571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, P.; Li, H.; Jia, W.; Shou, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Mao, L.; Wang, W.; Wu, F.; Chen, X.; Wan, X.; et al. Eicosapentaenoic and docosahexaenoic acids attenuate hyperglycemia through the microbiome-gut-organs axis in db/db mice. Microbiome 2021, 9, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, G.A.; Chassard, C.; Hennet, T. Selective proliferation of intestinal Barnesiella under fucosyllactose supplementation in mice. Br. J. Nutr. 2014, 111, 1602–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Yang, C.; Chen, M.; Lv, X.; Liu, B.; Yi, L.; Cornara, L.; Wei, M.C.; Yang, Y.C.; Tundis, R.; et al. Regulatory Efficacy of Brown Seaweed Lessonia nigrescens Extract on the Gene Expression Profile and Intestinal Microflora in Type 2 Diabetic Mice. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2018, 62, 1700730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fongang, B.; Satizabal, C.; Kautz, T.F.; Wadop, Y.N.; Muhammad, J.A.S.; Vasquez, E.; Mathews, J.; Gireud-Goss, M.; Saklad, A.R.; Himali, J.; et al. Cerebral small vessel disease burden is associated with decreased abundance of gut Barnesiella intestinihominis bacterium in the Framingham Heart Study. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 13622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gryaznova, M.V.; Solodskikh, S.A.; Panevina, A.V.; Syromyatnikov, M.Y.; Dvoretskaya, Y.D.; Sviridova, T.N.; Popov, E.S.; Popov, V.N. Study of microbiome changes in patients with ulcerative colitis in the Central European part of Russia. Heliyon 2021, 7, e06432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Yue, S.; Hao, Z.; Ren, G.; Lu, D.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, M. Pubertal exposure to the endocrine disruptor mono-2-ethylhexyl ester at body burden level caused cholesterol imbalance in mice. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 244, 657–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Wang, Z.; Xiao, C.; Zhu, Q.; Song, Z. Glycerol Monolaurate Ameliorated Intestinal Barrier and Immunity in Broilers by Regulating Intestinal Inflammation, Antioxidant Balance, and Intestinal Microbiota. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 713485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afouda, P.; Durand, G.A.; Lagier, J.C.; Labas, N.; Cadoret, F.; Armstrong, N.; Raoult, D.; Dubourg, G. Noncontiguous finished genome sequence and description of Intestinimonas massiliensis sp. nov strain GD2(T), the second Intestinimonas species cultured from the human gut. MicrobiologyOpen 2019, 8, e00621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Yan, L.; Chen, H.; Wu, N.; Wang, W.; Wang, D. Cyclocarya paliurus polysaccharides alleviate type 2 diabetic symptoms by modulating gut microbiota and short-chain fatty acids. Phytomedicine Int. J. Phytother. Phytopharm. 2020, 77, 153268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Gimenez, R.; Ahmed-Khodja, W.; Molina, Y.; Peiró, O.M.; Bonet, G.; Carrasquer, A.; Fragkiadakis, G.A.; Bulló, M.; Bardaji, A.; Papandreou, C. Gut Microbiota-Derived Metabolites and Cardiovascular Disease Risk: A Systematic Review of Prospective Cohort Studies. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, B.J.; de Aguiar Vallim, T.Q.; Wang, Z.; Shih, D.M.; Meng, Y.; Gregory, J.; Allayee, H.; Lee, R.; Graham, M.; Crooke, R.; et al. Trimethylamine-N-oxide, a metabolite associated with atherosclerosis, exhibits complex genetic and dietary regulation. Cell Metab. 2013, 17, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayerhofer, C.C.K.; Kummen, M.; Holm, K.; Broch, K.; Awoyemi, A.; Vestad, B.; Storm-Larsen, C.; Seljeflot, I.; Ueland, T.; Bohov, P.; et al. Low fibre intake is associated with gut microbiota alterations in chronic heart failure. ESC Heart Fail. 2020, 7, 456–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinakis, E.; O’Donnell, J.A.; Marques, F.Z. The gut-immune axis during hypertension and cardiovascular diseases. Acta Physiol. 2024, 240, e14193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Tontonoz, P. Liver X receptors in lipid signalling and membrane homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2018, 14, 452–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chávez-Talavera, O.; Tailleux, A.; Lefebvre, P.; Staels, B. Bile Acid Control of Metabolism and Inflammation in Obesity, Type 2 Diabetes, Dyslipidemia, and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, 1679–1694.e1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choucair, I.; Nemet, I.; Li, L.; Cole, M.A.; Skye, S.M.; Kirsop, J.D.; Fischbach, M.A.; Gogonea, V.; Brown, J.M.; Tang, W.H.W.; et al. Quantification of bile acids: A mass spectrometry platform for studying gut microbe connection to metabolic diseases. J. Lipid Res. 2020, 61, 159–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hug, H.; Mohajeri, M.H.; La Fata, G. Toll-Like Receptors: Regulators of the Immune Response in the Human Gut. Nutrients 2018, 10, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastori, D.; Carnevale, R.; Nocella, C.; Novo, M.; Santulli, M.; Cammisotto, V.; Menichelli, D.; Pignatelli, P.; Violi, F. Gut-Derived Serum Lipopolysaccharide is Associated with Enhanced Risk of Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events in Atrial Fibrillation: Effect of Adherence to Mediterranean Diet. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2017, 6, e005784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidary Moghaddam, R.; Samimi, Z.; Asgary, S.; Mohammadi, P.; Hozeifi, S.; Hoseinzadeh-Chahkandak, F.; Xu, S.; Farzaei, M.H. Natural AMPK Activators in Cardiovascular Disease Prevention. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 738420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, J.Y.; Choi, H.M.; Yang, H.I.; Kim, K.S. Dysregulated Autophagy Mediates Sarcopenic Obesity and Its Complications via AMPK and PGC1α Signaling Pathways: Potential Involvement of Gut Dysbiosis as a Pathological Link. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, A.; Krieg, R.; Massey, H.D.; Carl, D.; Ghosh, S.; Gehr, T.W.B.; Ghosh, S.S. Sodium butyrate ameliorates insulin resistance and renal failure in CKD rats by modulating intestinal permeability and mucin expression. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. Off. Publ. Eur. Dial. Transpl. Assoc.-Eur. Ren. Assoc. 2019, 34, 783–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Yang, X.; Jiang, Q.; Chen, L.; Gu, S.; Shen, G.; Liu, S.; Xiang, X. Effect of mussel polysaccharide on glucolipid metabolism and intestinal flora in type 2 diabetic mice. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2023, 103, 3353–3366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Du, Y.; Wei, L.; Tan, Z.; Zhou, T.; Wang, L.; Yang, X.; Zhao, Y. Preventive effects of turmeric against HFD/STZ-induced type 2 diabetes in mice by activating IRS1/PI3K/Akt signaling in association with gut microbiota metabolism. Food Funct. 2025, 16, 3613–3626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, G.; Du, Y.; Guan, H.; Jia, J.; Zhu, N.; Shi, Y.; Rong, S.; Yuan, W. Butyrate ameliorates skeletal muscle atrophy in diabetic nephropathy by enhancing gut barrier function and FFA2-mediated PI3K/Akt/mTOR signals. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2022, 179, 159–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, S.S.; Yang, X.Y.; Zheng, T.; Li, W.J.; Wu, D.; Chi, J.Y.; Bian, F.; Bai, X.L.; Wu, G.J.; Zhang, Y.Z.; et al. Salidroside improves endothelial function and alleviates atherosclerosis by activating a mitochondria-related AMPK/PI3K/Akt/eNOS pathway. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2015, 72, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Characteristics | LDII (n = 101) | MDII (n = 101) | HDII (n = 99) | p-Value b |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DII score | −0.32 ± 0.86 | 1.30 ± 0.37 | 2.56 ± 0.43 | <0.001 *** |
| Age | 65.58 ± 2.75 | 65.70 ± 2.59 | 65.70 ± 2.70 | 0.939 |
| Male | 33 (32.7%) | 29 (28.7%) | 31 (31.3%) | 0.826 |
| History of diabetes mellitus | 6 (5.9%) | 15 (14.9%) | 8 (8.1%) | 0.082 |
| History of cardiovascular disease | 14 (13.9%) | 23 (22.8%) | 26 (26.3%) | 0.084 |
| CVH Indicators | LDII (n = 101) | MDII (n = 101) | HDII (n = 99) | p-Value b |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LE8 score | 67.61 ± 11.08 | 65.54 ± 9.57 | 62.89 ± 11.76 | 0.009 ** |
| Diet score | 37.97 ± 13.81 | 32.18 ± 11.37 | 26.77 ± 6.44 | <0.001 *** |
| PA score | 45.15 ± 41.99 | 41.58 ± 38.72 | 32.83 ± 40.00 | 0.086 |
| Smoke score | 88.37 ± 29.49 | 91.09 ± 26.36 | 85.86 ± 32.17 | 0.454 |
| Sleep score | 81.88 ± 24.73 | 82.08 ± 25.66 | 81.21 ± 28.79 | 0.971 |
| BMI score | 83.86 ± 21.43 | 85.79 ± 18.90 | 83.23 ± 22.58 | 0.668 |
| Blood Lipids score | 66.14 ± 29.09 | 63.37 ± 27.29 | 64.04 ± 28.85 | 0.770 |
| Blood Glucose score | 79.50 ± 22.02 | 76.93 ± 24.57 | 76.57 ± 25.40 | 0.640 |
| BP score | 57.97 ± 31.44 | 51.29 ± 31.22 | 52.63 ± 29.30 | 0.264 |
| CVH level | 0.042 * | |||
| Low CVH | 7 (6.9%) | 4 (4.0%) | 14 (14.1%) | |
| Moderate CVH | 81 (80.2%) | 89 (88.1%) | 79 (79.8%) | |
| High CVH | 13 (12.9%) | 8 (7.9%) | 6 (6.1%) | |
| Skin AGEs | 2.34 ± 0.38 | 2.42 ± 0.45 | 2.52 ± 0.56 | 0.029 * |
| Gut Microbiota at the Genus Level | DII Score | LE8 Score | LE8-Diet | LE8-PA | LE8-Smoke | LE8-Sleep | LE8-BMI | LE8-BloodLipids | LE8-BloodGlucose | LE8-BP | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| g_Allobaculum | ρ | −0.167 | 0.033 | 0.026 | 0.01 | 0.069 | −0.033 | −0.014 | 0.049 | 0.024 | 0.016 |
| p | 0.004 ** | 0.573 | 0.655 | 0.871 | 0.242 | 0.581 | 0.817 | 0.408 | 0.683 | 0.785 | |
| g_Atopostipes | ρ | −0.182 | 0.058 | −0.014 | 0.043 | 0.095 | −0.007 | 0.036 | 0.033 | −0.013 | 0.004 |
| p | 0.002 ** | 0.327 | 0.818 | 0.468 | 0.106 | 0.906 | 0.546 | 0.578 | 0.830 | 0.949 | |
| g_Barnesiella | ρ | −0.13 | 0.03 | 0.031 | −0.036 | 0.026 | −0.012 | 0.019 | 0.029 | 0.04 | 0.066 |
| p | 0.027 * | 0.612 | 0.597 | 0.546 | 0.656 | 0.839 | 0.752 | 0.622 | 0.499 | 0.265 | |
| g_Coprobacter | ρ | −0.133 | 0.078 | 0.036 | 0.03 | −0.011 | −0.014 | −0.026 | 0.005 | 0.108 | 0.128 |
| p | 0.023 * | 0.187 | 0.538 | 0.616 | 0.856 | 0.810 | 0.657 | 0.939 | 0.066 | 0.029 * | |
| g_Eisenbergiella | ρ | 0.129 | −0.051 | −0.059 | −0.109 | 0.014 | −0.029 | 0.158 | 0.014 | −0.036 | 0.002 |
| p | 0.028 * | 0.390 | 0.319 | 0.064 | 0.814 | 0.625 | 0.007 ** | 0.819 | 0.546 | 0.978 | |
| g_Intestinimonas | ρ | −0.143 | 0.087 | 0.02 | −0.023 | 0.092 | 0.034 | 0.105 | 0.088 | 0.029 | 0.042 |
| p | 0.015 * | 0.141 | 0.731 | 0.701 | 0.119 | 0.559 | 0.074 | 0.133 | 0.626 | 0.481 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, Y.; Chen, Q.; Fan, R.; Song, L.; Wang, S.; You, M.; Cai, M.; Li, Y.; Xu, M. Association Between the Dietary Inflammatory Index and Life’s Essential 8 in Older Adults Based on Gut Microbiota Profiles. Nutrients 2025, 17, 3050. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17193050
Wu Y, Chen Q, Fan R, Song L, Wang S, You M, Cai M, Li Y, Xu M. Association Between the Dietary Inflammatory Index and Life’s Essential 8 in Older Adults Based on Gut Microbiota Profiles. Nutrients. 2025; 17(19):3050. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17193050
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Yuxiao, Qianqian Chen, Rui Fan, Lixia Song, Shuyue Wang, Mei You, Meng Cai, Yong Li, and Meihong Xu. 2025. "Association Between the Dietary Inflammatory Index and Life’s Essential 8 in Older Adults Based on Gut Microbiota Profiles" Nutrients 17, no. 19: 3050. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17193050
APA StyleWu, Y., Chen, Q., Fan, R., Song, L., Wang, S., You, M., Cai, M., Li, Y., & Xu, M. (2025). Association Between the Dietary Inflammatory Index and Life’s Essential 8 in Older Adults Based on Gut Microbiota Profiles. Nutrients, 17(19), 3050. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17193050







