Association of Anaemia and Anthropometric Indices Among Chinese Adults: Based on the Sixth China Chronic Disease and Risk Factor Surveillance
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Survey Design and Populations
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Diagnostic Criteria for Anaemia and Definition of Study Variables
2.4. Associated Factors
2.5. Statistical Analysis Methods
3. Results
3.1. Study Population
3.2. Summary
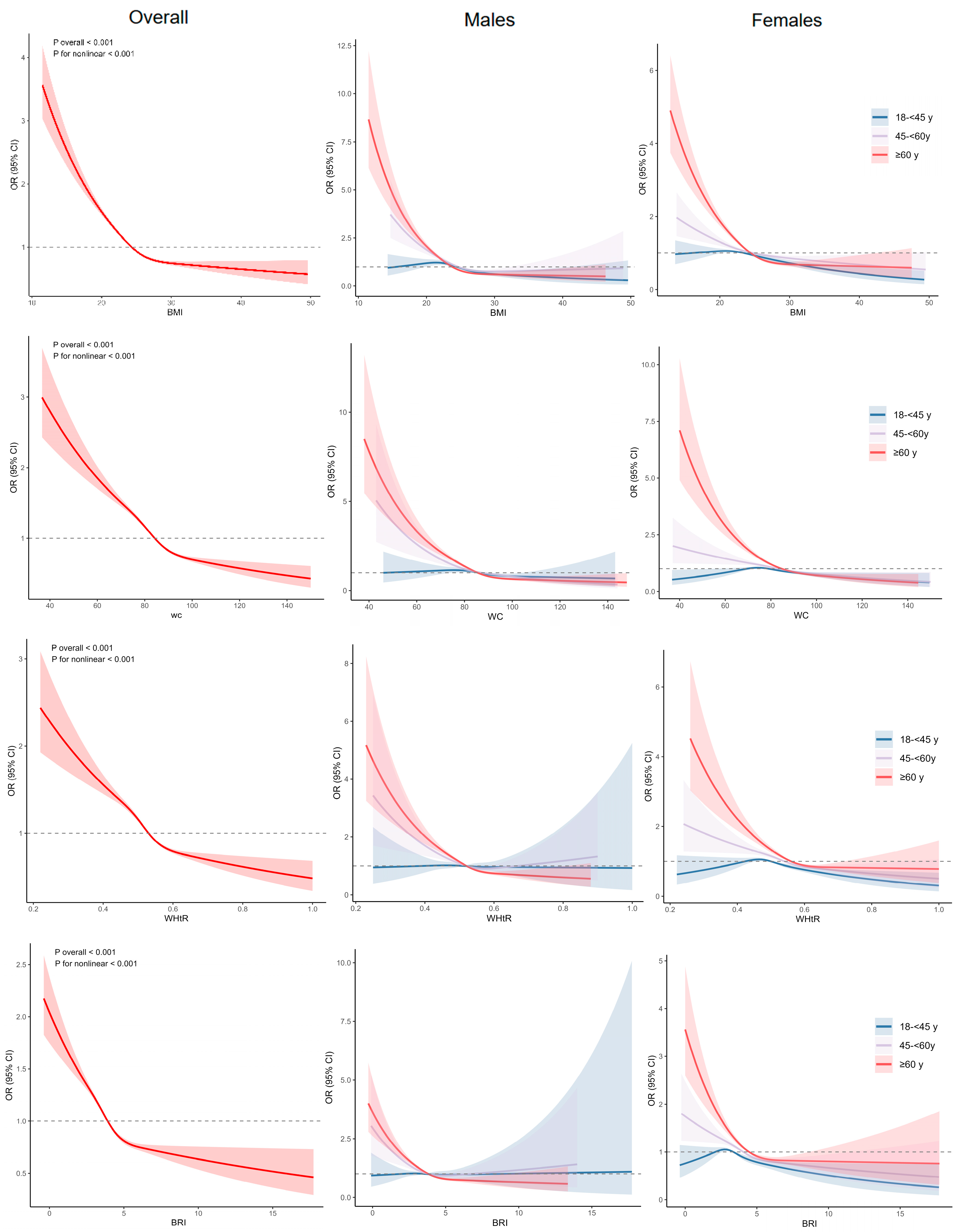
3.3. Factors Related to Anaemia
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| WC | Waist circumference |
| WHtR | Waist-to-height ratio |
| BRI | Body roundness index |
| CCDRFS | China Chronic Disease and Risk Factor Surveillance |
| NCNCD | Noncommunicable Diseases Control and Prevention |
| HbA1c | Haemoglobin A1c |
| HDL-C | High-density lipoprotein cholesterol |
| LDL-C | Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol |
| Scr | Serum creatinine |
| eGFR | Estimated glomerular filtration rate |
| RCS | Restricted cubic spline |
| CI | Confidence interval |
| OR | Odds ratio |
References
- Safiri, S.; Kolahi, A.-A.; Noori, M.; Nejadghaderi, S.A.; Karamzad, N.; Bragazzi, N.L.; Sullman, M.J.M.; Abdollahi, M.; Collins, G.S.; Kaufman, J.S.; et al. Burden of Anemia and Its Underlying Causes in 204 Countries and Territories, 1990–2019: Results from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 14, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization (Ed.) Guideline on Haemoglobin Cutoffs to Define Anaemia in Individuals and Populations; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2024; ISBN 978-92-4-008854-2. [Google Scholar]
- Haas, J.D.; Brownlie, T. Iron Deficiency and Reduced Work Capacity: A Critical Review of the Research to Determine a Causal Relationship. J. Nutr. 2001, 131, 676S–688S, discussion 688S–690S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoccali, C.; Mallamaci, F.; Adamczak, M.; de Oliveira, R.B.; Massy, Z.A.; Sarafidis, P.; Agarwal, R.; Mark, P.B.; Kotanko, P.; Ferro, C.J.; et al. Cardiovascular Complications in Chronic Kidney Disease: A Review from the European Renal and Cardiovascular Medicine Working Group of the European Renal Association. Cardiovasc. Res. 2023, 119, 2017–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, B.; Venketasubramanian, N.; Vrooman, H.; Cheng, C.-Y.; Wong, T.Y.; Chen, C.; Hilal, S. Haemoglobin, Magnetic Resonance Imaging Markers and Cognition: A Subsample of Population-Based Study. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 2018, 10, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gelaw, Y.; Getaneh, Z.; Melku, M. Anemia as a Risk Factor for Tuberculosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Environ. Health Prev. Med. 2021, 26, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinsson, A.; Andersson, C.; Andell, P.; Koul, S.; Engström, G.; Smith, J.G. Anemia in the General Population: Prevalence, Clinical Correlates and Prognostic Impact. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2014, 29, 489–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GBD 2021 Anaemia Collaborators. Prevalence, Years Lived with Disability, and Trends in Anaemia Burden by Severity and Cause, 1990–2021: Findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet Haematol. 2023, 10, e713–e734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balarajan, Y.; Ramakrishnan, U.; Özaltin, E.; Shankar, A.H.; Subramanian, S.V. Anaemia in Low-Income and Middle-Income Countries. Lancet 2011, 378, 2123–2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaparro, C.M.; Suchdev, P.S. Anemia Epidemiology, Pathophysiology, and Etiology in Low- and Middle-Income Countries. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2019, 1450, 15–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global Nutrition Target Collaborators. Global, Regional, and National Progress towards the 2030 Global Nutrition Targets and Forecasts to 2050: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet 2024, 404, 2543–2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, G.A.; Paciorek, C.J.; Flores-Urrutia, M.C.; Borghi, E.; Namaste, S.; Wirth, J.P.; Suchdev, P.S.; Ezzati, M.; Rohner, F.; Flaxman, S.R.; et al. National, Regional, and Global Estimates of Anaemia by Severity in Women and Children for 2000–19: A Pooled Analysis of Population-Representative Data. Lancet Glob. Health 2022, 10, e627–e639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daru, J.; Zamora, J.; Fernández-Félix, B.M.; Vogel, J.; Oladapo, O.T.; Morisaki, N.; Tunçalp, Ö.; Torloni, M.R.; Mittal, S.; Jayaratne, K.; et al. Risk of Maternal Mortality in Women with Severe Anaemia during Pregnancy and Post Partum: A Multilevel Analysis. Lancet Glob. Health 2018, 6, e548–e554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Cheng, X.; Guo, Q.; He, L.; Ju, L.; Xu, X.; Gong, W.; Li, S.; Zhao, L.; Fang, H. Analysis of Prevalence, Years Lived with Disability, and Trends of Anemia Burden and Main Causes in China. Front. Public Health 2025, 13, 1564756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinyoki, D.; Osgood-Zimmerman, A.E.; Bhattacharjee, N.V.; Kassebaum, N.J.; Hay, S.I. Anemia Prevalence in Women of Reproductive Age in Low- and Middle-Income Countries between 2000 and 2018. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 1761–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Bo, Y.; Ren, H.; Zhou, C.; Lao, X.; Zhao, L.; Yu, D. Regional Differences in the Prevalence of Anaemia and Associated Risk Factors among Infants Aged 0–23 Months in China: China Nutrition and Health Surveillance. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, J.; Huang, Y.; Sun, J.; Huang, J.; Dong, J.; Sun, Y.; Feng, X.L. Malnutrition in Infants Aged 6–23 Months in China’s Poorest Rural Counties from 2016 to 2021: Cross Sectional Study. BMJ 2024, 387, e079499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, A.N.M.S.; Sultana, H.; Refat, M.N.H.; Farhana, Z.; Kamil, A.A.; Rahman, M.M. The Global Burden of Overweight-Obesity and Its Association with Economic Status, Benefiting from STEPs Survey of WHO Member States: A Meta-Analysis. Prev. Med. Rep. 2024, 46, 102882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhou, B.; Zhao, Z.; Yang, L.; Zhang, M.; Jiang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhou, M.; Wang, L.; Huang, Z.; et al. Trends in Body-Mass Index and Obesity in Urban and Rural China: Findings from Consecutive Nationally Representative Surveys during 2004–2018. Lancet 2021, 398, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ausk, K.J.; Ioannou, G.N. Is Obesity Associated with Anemia of Chronic Disease? A Population-Based Study. Obesity 2008, 16, 2356–2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saltiel, A.R.; Olefsky, J.M. Inflammatory Mechanisms Linking Obesity and Metabolic Disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, G.; Ganz, T.; Goodnough, L.T. Anemia of Inflammation. Blood 2019, 133, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Melse-Boonstra, A.; Pan, X.; Yuan, B.; Dai, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zimmermann, M.B.; Kok, F.J.; Zhou, M.; Shi, Z. Anemia in Relation to Body Mass Index and Waist Circumference among Chinese Women. Nutr. J. 2013, 12, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Wei, Y.; Zhu, W.; Wang, C.; Su, R.; Feng, H.; Yang, H. Prevalence, Risk Factors and Associated Adverse Pregnancy Outcomes of Anaemia in Chinese Pregnant Women: A Multicentre Retrospective Study. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2018, 18, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhu, X.; Dai, Q.; Hong, X.; Zhang, H.; Huang, K.; Wang, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Peng, Z.; et al. The Prevalence and Influencing Factors of Anaemia among Pre-Pregnant Women in Mainland China: A Large Population-Based, Cross-Sectional Study. Br. J. Nutr. 2022, 127, 439–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okorodudu, D.O.; Jumean, M.F.; Montori, V.M.; Romero-Corral, A.; Somers, V.K.; Erwin, P.J.; Lopez-Jimenez, F. Diagnostic Performance of Body Mass Index to Identify Obesity as Defined by Body Adiposity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Obes. 2010, 34, 791–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardinha, L.B.; Santos, D.A.; Silva, A.M.; Grøntved, A.; Andersen, L.B.; Ekelund, U. A Comparison between BMI, Waist Circumference, and Waist-To-Height Ratio for Identifying Cardio-Metabolic Risk in Children and Adolescents. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0149351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rico-Martín, S.; Calderón-García, J.F.; Sánchez-Rey, P.; Franco-Antonio, C.; Martínez Alvarez, M.; Sánchez Muñoz-Torrero, J.F. Effectiveness of Body Roundness Index in Predicting Metabolic Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Obes. Rev. Off. J. Int. Assoc. Study Obes. 2020, 21, e13023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Chen, S.; Hu, G.; Chen, P.; Wu, J.; Ma, X.; Yang, Z.; Yang, W.; Jia, W.; China National Diabetes, Metabolic Disorders Study Group. Stronger Associations of Waist Circumference and Waist-to-Height Ratio with Diabetes than BMI in Chinese Adults. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2019, 147, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Morales, I.; Colin-Ramirez, E.; Rivera-Mancía, S.; Vallejo, M.; Vázquez-Antona, C. Performance of Waist-To-Height Ratio, Waist Circumference, and Body Mass Index in Discriminating Cardio-Metabolic Risk Factors in a Sample of School-Aged Mexican Children. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, H.X.; Min, W.L.; Yu, C.S.; Bei, L.Y.; Mei, Z.; Jing, H.Z.; Li, C.H.; Zhu, W.J.; Jing, W.U.; Ping, J.W. Data Resource Profile: A Protocol of China National Diabetic Chronic Complications Study. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2022, 35, 633–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Xu, X.; Zhang, M.; Hu, C.; Zhang, X.; Li, C.; Nie, S.; Huang, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Hou, F.F.; et al. Prevalence of Chronic Kidney Disease in China: Results from the Sixth China Chronic Disease and Risk Factor Surveillance. JAMA Intern. Med. 2023, 183, 298–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levey, A.S.; Stevens, L.A.; Schmid, C.H.; Zhang, Y.L.; Castro, A.F.; Feldman, H.I.; Kusek, J.W.; Eggers, P.; Van Lente, F.; Greene, T.; et al. A New Equation to Estimate Glomerular Filtration Rate. Ann. Intern. Med. 2009, 150, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Obesity and Overweight. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight (accessed on 14 September 2025).
- Thomas, D.M.; Bredlau, C.; Bosy-Westphal, A.; Mueller, M.; Shen, W.; Gallagher, D.; Maeda, Y.; McDougall, A.; Peterson, C.M.; Ravussin, E.; et al. Relationships between Body Roundness with Body Fat and Visceral Adipose Tissue Emerging from a New Geometrical Model. Obesity 2013, 21, 2264–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. 2. Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes: Standards of Care in Diabetes—2024. Diabetes Care 2024, 47, S20–S42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echouffo-Tcheugui, J.B.; Perreault, L.; Ji, L.; Dagogo-Jack, S. Diagnosis and Management of Prediabetes: A Review. JAMA 2023, 329, 1206–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults. Executive Summary of the Third Report of the National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III). JAMA 2001, 285, 2486–2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Li, M.; Wu, J.; Wang, R.; Mao, D.; Chen, J.; Li, W.; Yang, Y.; Piao, J.; Yang, L.; et al. Prevalence and Risk Factors for Anemia in Non-Pregnant Childbearing Women from the Chinese Fifth National Health and Nutrition Survey. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalal, C.S.; De-Regil, L.M.; Pike, V.; Mithra, P. Fortification of Condiments and Seasonings with Iron for Preventing Anaemia and Improving Health. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2023, 2023, CD009604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, B.; Man, S.; Bao, H.; Huang, Y.; Yu, C.; Lyu, J.; Wang, L.; Li, L.; Liu, H. Variations in the Prevalence of Anemia of Varying Severity Among Urban Non-Pregnant Women—China, 2021. China CDC Wkly. 2024, 6, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ping, Y.-J.; Jin, H.-Y.; Ge, N.; Wu, C. Prevalence and Health Correlates of Anaemia among Community-Dwelling Chinese Older Adults: The China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e038147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, T.; Yan, M.; Fu, Z.; Song, Y.; Lu, W.; Fu, A.; Yin, P. Association between Anemia and Cognitive Decline among Chinese Middle-Aged and Elderly: Evidence from the China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study. BMC Geriatr. 2019, 19, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munro, M.G.; Critchley, H.O.D.; Fraser, I.S.; FIGO Menstrual Disorders Committee. The Two FIGO Systems for Normal and Abnormal Uterine Bleeding Symptoms and Classification of Causes of Abnormal Uterine Bleeding in the Reproductive Years: 2018 Revisions. Int. J. Gynaecol. Obstet. Off. Organ. Int. Fed. Gynaecol. Obstet. 2018, 143, 393–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, I.S.; Mansour, D.; Breymann, C.; Hoffman, C.; Mezzacasa, A.; Petraglia, F. Prevalence of Heavy Menstrual Bleeding and Experiences of Affected Women in a European Patient Survey. Int. J. Gynecol. Obstet. 2015, 128, 196–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Critchley, H.O.D.; Munro, M.G.; Shakur-Still, H.; Roberts, I. Menstruation Should Not Be Overlooked in Control of Anaemia. Lancet 2021, 397, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, C.H.H. The Prevalence of Anemia and Moderate-Severe Anemia in the US Population (NHANES 2003–2012). PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0166635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Nutritional Anaemias: Tools for Effective Prevention and Control; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017; ISBN 978-92-4-151306-7. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, D.; Jin, Y.; Shao, X.; Xu, Y.; Ma, G.; Jiang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Hu, D. Global, Regional, and National Burden of Inflammatory Bowel Disease, 1990–2021: Insights from the Global Burden of Disease 2021. Int. J. Color. Dis. 2024, 39, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Firquet, A.; Kirschner, W.; Bitzer, J. Forty to Fifty-Five-Year-Old Women and Iron Deficiency: Clinical Considerations and Quality of Life. Gynecol. Endocrinol. 2017, 33, 503–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, T.-Y.; Strong, C.; Yu, T. Age at Menopause and Mortality in Taiwan: A Cohort Analysis. Maturitas 2020, 136, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, K.V. Epidemiology of Anemia in Older Adults. Semin. Hematol. 2008, 45, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seitz, A.E.; Eberhardt, M.S.; Lukacs, S.L. Anemia Prevalence and Trends in Adults Aged 65 and Older: U.S. National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey: 2001–2004 to 2013–2016. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2018, 66, 2431–2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.-Y.; McCulloch, C.E.; Curhan, G.C. Epidemiology of Anemia Associated with Chronic Renal Insufficiency among Adults in the United States: Results from the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. JASN 2002, 13, 504–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson-Ehle, H.; Jagenburg, R.; Landahl, S.; Svanborg, A. Blood Haemoglobin Declines in the Elderly: Implications for Reference Intervals from Age 70 to 88. Eur. J. Haematol. 2000, 65, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Yin, W.; Huang, D.; Sun, K.; Chen, Z.; Guo, H.; Wu, D. Trend and Equity of General Practitioners’ Allocation in China Based on the Data from 2012–2017. Hum. Resour. Health 2021, 19, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, P.; Dong, S.; Xiao, J.; Liu, C.; Feng, X.; Wang, Y. Regional Inequality in Health and Its Determinants: Evidence from China. Health Policy 2010, 94, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Li, Q.; Song, Y.; Fang, L.; Huang, L.; Sun, Y. Nutritional Factors for Anemia in Pregnancy: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 1041136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, M.-B.; Chen, J.; Bergquist, R.; Li, Z.-J.; Li, S.-Z.; Xiao, N.; Utzinger, J.; Zhou, X.-N. Neglected Tropical Diseases in the People’s Republic of China: Progress towards Elimination. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2019, 8, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, J.; Dong, X.; Fu, C.; Jiang, Q. Increased Prevalence and Incidence of Anemia among Adults in Transforming Rural China: Two Cross-Sectional Surveys. BMC Public Health 2015, 15, 1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Song, Z.; Zhao, L.; Gonzalez, S.C.; Wang, E.; Hou, X. The Temporal Trends of Prevalence and Years Lived with Disability of Anaemia in China, Japan, and South Korea, from 1990 to 2021: Results from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. J. Glob. Health 2024, 14, 04073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rachmah, Q.; Mondal, P.; Phung, H.; Ahmed, F. Association between Overweight/Obesity and Iron Deficiency Anaemia among Women of Reproductive Age: A Systematic Review. Public Health Nutr. 2024, 27, e176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, P.; Li, L.; Man, Q.; Wang, C.; Meng, L.; Zhang, J. Case–Control Study of Anaemia among Middle-Aged and Elderly Women in Three Rural Areas of China. BMJ Open 2014, 4, e004751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, W.; Yuan, X.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, J. Anaemia and Associated Factors among Older Adults in an Urban District in China: A Large-Scale Cross-Sectional Study. BMJ Open 2022, 12, e056100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cepeda-Lopez, A.C.; Osendarp, S.J.; Melse-Boonstra, A.; Aeberli, I.; Gonzalez-Salazar, F.; Feskens, E.; Villalpando, S.; Zimmermann, M.B. Sharply Higher Rates of Iron Deficiency in Obese Mexican Women and Children Are Predicted by Obesity-Related Inflammation Rather than by Differences in Dietary Iron Intake. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 93, 975–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corcoran, C.; Murphy, C.; Culligan, E.P.; Walton, J.; Sleator, R.D. Malnutrition in the Elderly. Sci. Prog. 2019, 102, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ja’afar, M.H.; Mat Nasir, N.; Md Isa, Z.; Ismail, R.; Mohd Tamil, A.; Ismail, N.H.; Ariffin, F.; Ab Razak, N.H.; Zainol Abidin, N.; Yusof, K.H. Dietary Nutrient Intake Study among Older Adults: Baseline Malaysian Pure Study. BMC Geriatr. 2024, 24, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.M.Y.; Huxley, R.R.; Wildman, R.P.; Woodward, M. Indices of Abdominal Obesity Are Better Discriminators of Cardiovascular Risk Factors than BMI: A Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2008, 61, 646–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Başıbüyük, G.Ö.; Ayremlou, P.; Saeidlou, S.N.; Ay, F.; Dalkıran, A.; Simzari, W.; Vitályos, G.Á.; Bektaş, Y. A Comparison of the Different Anthropometric Indices for Assessing Malnutrition among Older People in Turkey: A Large Population-Based Screening. J. Health Popul. Nutr. 2021, 40, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Long, Z.; Long, Z. Epidemiology of Dietary Iron Deficiency in China from 1990 to 2021: Findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. BMC Public Health 2025, 25, 596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haase, V.H. Hypoxic Regulation of Erythropoiesis and Iron Metabolism. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2010, 299, F1–F13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordenberg, D.; Yip, R.; Binkin, N.J. The Effect of Cigarette Smoking on Hemoglobin Levels and Anemia Screening. JAMA 1990, 264, 1556–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.J.; Addo, O.Y.; Mei, Z.; Suchdev, P.S. Reexamination of Hemoglobin Adjustments to Define Anemia: Altitude and Smoking. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2019, 1450, 190–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristics | Total | No Anaemia | Anaemia | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | 159,468 | 142,691 | 16,777 | |
| n (%) | ||||
| Gender | <0.001 | |||
| Male | 70,477 (44.2) | 64,896 (45.5) | 5581 (33.3) | |
| Female | 88,991 (55.8) | 77,795 (54.5) | 11,196 (66.7) | |
| Township | <0.001 | |||
| Urban | 65,311 (41.0) | 59,167 (41.5) | 6144 (36.6) | |
| Rural | 94,157 (59.0) | 83,524 (58.5) | 10,633 (63.4) | |
| Location in China | <0.001 | |||
| South | 16,780 (10.5) | 14,644 (10.3) | 2136 (12.7) | |
| East | 41,548 (26.1) | 37,506 (26.3) | 4042 (24.1) | |
| Central | 19,966 (12.5) | 17,900 (12.5) | 2066 (12.3) | |
| North | 22,308 (14.0) | 20,512 (14.4) | 1796 (10.7) | |
| Northeast | 15,050 (9.4) | 13,830 (9.7) | 1220 (7.3) | |
| Southwest | 23,359 (14.6) | 19,671 (13.8) | 3688 (22.0) | |
| Northwest | 20,457 (12.8) | 18,628 (13.1) | 1829 (10.9) | |
| Education | <0.001 | |||
| Primary school or lower | 78,924 (49.5) | 69,262 (48.5) | 9662 (57.6) | |
| Secondary school | 48,660 (30.5) | 44,188 (31.0) | 4472 (26.7) | |
| High school | 20,889 (13.1) | 19,192 (13.5) | 1697 (10.1) | |
| College or above | 10,995 (6.9) | 10,049 (7.0) | 946 (5.6) | |
| Ethnicity | <0.001 | |||
| Han | 140,436 (88.1) | 126,485 (88.6) | 13,951 (83.2) | |
| Other | 19,032 (11.9) | 16,206 (11.4) | 2826 (16.8) | |
| Annual household income, CNY | <0.001 | |||
| <6000 | 9132 (5.7) | 8044 (5.6) | 1088 (6.5) | |
| 6000–11,999 | 13,625 (8.5) | 12,146 (8.5) | 1479 (8.8) | |
| 12,000–23,999 | 20,490 (12.8) | 18,312 (12.8) | 2178 (13.0) | |
| ≥24,000 | 81,796 (51.3) | 73,823 (51.7) | 7973 (47.5) | |
| Refused/do not know | 34,425 (21.6) | 30,366 (21.3) | 4059 (24.2) | |
| Cigarette smoking | <0.001 | |||
| Never | 110,873 (69.5) | 98,179 (68.8) | 12,694 (75.7) | |
| Former | 10,110 (6.3) | 9245 (6.5) | 865 (5.2) | |
| Current | 38,485 (24.1) | 35,267 (24.7) | 3218 (19.2) | |
| Alcohol drinking, | <0.001 | |||
| No | 105,268 (66.0) | 93,109 (65.3) | 12,159 (72.5) | |
| Yes | 54,200 (34.0) | 49,582 (34.7) | 4618 (27.5) | |
| Hypertension | <0.001 | |||
| No hypertension | 94,983 (59.6) | 84,060 (58.9) | 10,923 (65.1) | |
| Previously diagnosed | 28,413 (17.8) | 25,893 (18.1) | 2520 (15.0) | |
| Newly detected | 36,072 (22.6) | 32,738 (22.9) | 3334 (19.9) | |
| Diabetes | <0.001 | |||
| No diabetes | 60,728 (38.1) | 53,537 (37.5) | 7191 (42.9) | |
| Prediabetes | 71,469 (44.8) | 64,280 (45.0) | 7189 (42.9) | |
| Newly detected | 15,773 (9.9) | 14,522 (10.2) | 1251 (7.5) | |
| Previously diagnosed | 11,498 (7.2) | 10,352 (7.3) | 1146 (6.8) | |
| Dyslipidaemia | 65,351 (41.0) | 60,033 (42.1) | 5318 (31.7) | <0.001 |
| Hyperuricemia | 17,283 (10.8) | 15,628 (11.0) | 1655 (9.9) | <0.001 |
| Chronic kidney disease | 18,946 (11.9) | 16,071 (11.3) | 2875 (17.1) | <0.001 |
| Fruit/vegetable intake < 400 g/d | 74,694 (46.8) | 66,476 (46.6) | 8218 (49.0) | <0.001 |
| Red meat intake ≥ 100 g/d | 57,634 (36.1) | 51,683 (36.2) | 5951 (35.5) | 0.057 |
| Median [IQR] | ||||
| Age, years | 55.7 (18.7) | 55.8 (18.2) | 55.3 (22.5) | 0.001 |
| Fasting glucose, mg/dL | 100.3 (17.5) | 100.6 (17.6) | 97.9 (15.8) | <0.001 |
| Glycated haemoglobin A1c, % | 5.4 (0.6) | 5.4 (0.6) | 5.3 (0.5) | <0.001 |
| Total cholesterol, mmol/L | 4.9 (1.3) | 4.9 (1.3) | 4.6 (1.3) | <0.001 |
| HDL-C, mmol/L | 1.3 (0.5) | 1.3 (0.5) | 1.4 (0.6) | <0.001 |
| LDL-C, mmol/L | 2.9 (1.1) | 3.0 (1.2) | 2.7 (1.2) | <0.001 |
| Triglyceride, mg/dL | 120.5 (89.4) | 123.1 (92.1) | 104.5 (70.8) | <0.001 |
| Scr, μmol/L | 71.0 (22.0) | 71.0 (22.0) | 67.0 (23.0) | <0.001 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 24.3 (4.8) | 24.4 (4.8) | 23.1 (4.7) | <0.001 |
| WC, cm | 84.2 (13.8) | 84.7 (13.7) | 81.0 (13.6) | <0.001 |
| WHtR | 0.5 (0.1) | 0.5 (0.1) | 0.5 (0.1) | <0.001 |
| BRI | 3.9 (1.7) | 4.0 (1.7) | 3.6 (1.6) | <0.001 |
| Characteristics | b | SE | Wald χ2 | OR | 95% CI | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BMI | ||||||
| Underweight (<18.5) | 0.01 | 0.096 | 0.004 | 1.01 | (0.83, 1.22) | 0.956 |
| Normal (18.5–) | 1(Ref) | |||||
| Overweight (24–) | −0.24 | 0.037 | 41.8 | 0.79 | (0.73, 0.86) | <0.001 |
| Obesity (≥28) | −0.44 | 0.063 | 48.8 | 0.64 | (0.57, 0.73) | <0.001 |
| Central obesity | ||||||
| No | 1(Ref) | |||||
| Yes | −0.34 | 0.047 | 51.7 | 0.71 | (0.66, 0.78) | <0.001 |
| WHtR | ||||||
| <0.5 | 1(Ref) | |||||
| ≥0.5 | −0.21 | 0.454 | 21.3 | 0.81 | (0.74, 0.89) | <0.001 |
| BRI Quartile a | ||||||
| Q1 | 1(Ref) | |||||
| Q2 | −0.04 | 0.054 | 0.5 | 0.96 | (0.87, 1.07) | 0.469 |
| Q3 | −0.23 | 0.051 | 20.6 | 0.79 | (0.71, 0.89) | <0.001 |
| Q4 | −0.42 | 0.062 | 45.4 | 0.66 | (0.59, 0.73) | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Du, C.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, X.; Li, C.; Zhao, Z.; Guo, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, X. Association of Anaemia and Anthropometric Indices Among Chinese Adults: Based on the Sixth China Chronic Disease and Risk Factor Surveillance. Nutrients 2025, 17, 3045. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17193045
Du C, Zhang M, Zhang X, Zhu X, Li C, Zhao Z, Guo Y, Wang L, Li X. Association of Anaemia and Anthropometric Indices Among Chinese Adults: Based on the Sixth China Chronic Disease and Risk Factor Surveillance. Nutrients. 2025; 17(19):3045. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17193045
Chicago/Turabian StyleDu, Chuangjia, Mei Zhang, Xiao Zhang, Xiaolei Zhu, Chun Li, Zhenping Zhao, Yu Guo, Limin Wang, and Xiuyang Li. 2025. "Association of Anaemia and Anthropometric Indices Among Chinese Adults: Based on the Sixth China Chronic Disease and Risk Factor Surveillance" Nutrients 17, no. 19: 3045. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17193045
APA StyleDu, C., Zhang, M., Zhang, X., Zhu, X., Li, C., Zhao, Z., Guo, Y., Wang, L., & Li, X. (2025). Association of Anaemia and Anthropometric Indices Among Chinese Adults: Based on the Sixth China Chronic Disease and Risk Factor Surveillance. Nutrients, 17(19), 3045. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17193045






