The Fourth Survey on the Activity of Human Milk Banks in Italy
Abstract
1. Background
1.1. Benefits of Human Milk
1.2. The Situation of Human Milk Banks (HMBs)
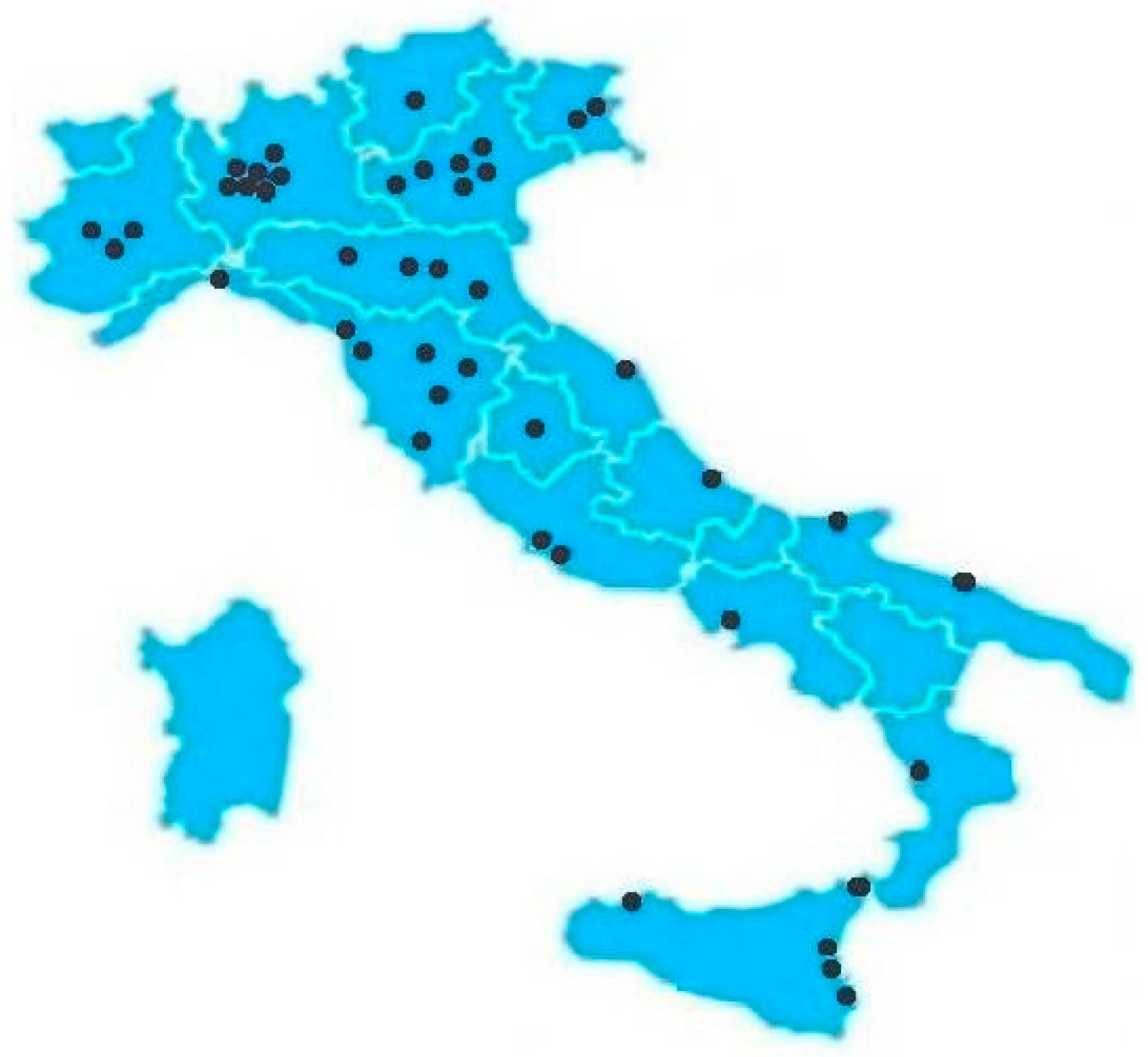
1.3. The Italian Context
2. Research Aim
3. Methods
3.1. Research Design
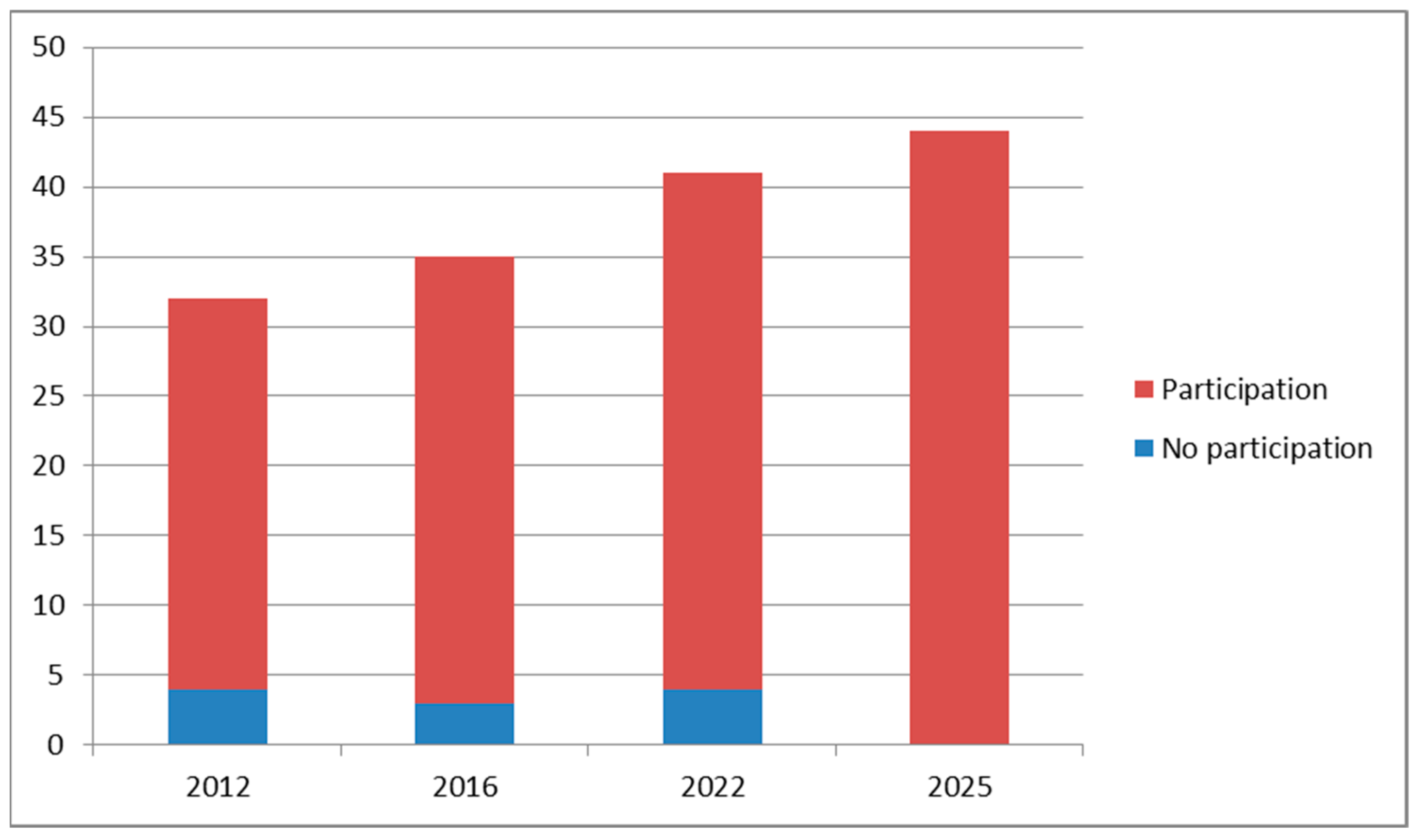
3.2. Sample
3.3. Data Collection
3.4. Data Analysis
4. Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Davanzo, R.; Maffeis, C.; Silano, M.; Bertino, E.; Cazzato, C.A.; Tonetto, P.; Staiano, A.; Vitiello, R.; Natale, F. Allattamento Al Seno E Uso Del Latte Materno/Umano. Position Statement 2015 di Società Italiana di Pediatria (SIP), Società Italiana di Neonatologia (SIN), Società Italiana delle Cure Primarie Pediatriche (SICuPP), Società Italiana di Gastroenterologia Epatologia e Nutrizione Pediatrica (SIGENP) e Società Italiana di Medicina Perinatale (SIMP). Available online: https://www.salute.gov.it/imgs/C_17_pubblicazioni_2415_allegato.pdf (accessed on 21 June 2021).
- World Health Organization/United Nations International Children’s Emergency Fund (WHO/UNICEF). Global Strategy for Infant and Young Child Feeding; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2003; Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/42590 (accessed on 21 June 2021).
- World Health Organization. Guidelines on Optimal Feeding of Low Birth-Weight Infants in Low- and Middle-Income Countries; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011; Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/85670?searchresult=true&query=Guidelines+on+optimal+feeding+of+low+birth-weight (accessed on 21 June 2021).
- World Health Organization. Donor Human Milk for Low-Birth-Weight Infants. Available online: https://www.who.int/tools/elena/interventions/donormilk-infants (accessed on 9 August 2021).
- American Academy of Pediatrics. Section on Breastfeeding. Breastfeeding and the use of human milk. Pediatrics 2012, 129, e827–e841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Committee on Nutrition; Section on Breastfeeding; Committee on Fetus and Newborn. Donor human milk for the high-risk infant: Preparation, safety, and usage options in the United States. Pediatrics 2017, 139, e20163440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ESPGHAN Committee on Nutrition; Arslanoglu, S.; Corpeleijn, W.; Moro, G.; Braegger, C.; Campoy, C.; Colomb, V.; Decsi, T.; Domellöf, M.; Fewtrell, M.; et al. Donor human milk for preterm infants: Current evidence and research directions. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2013, 57, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haiden, N.; Ziegler, E.E. Human milk banking. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2016, 69 (Suppl. S2), 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bode, L. The functional biology of human milk oligosaccharides. Early Hum. Dev. 2015, 91, 619–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bode, L.; McGuire, M.; Rodriguez, J.M.; Geddes, D.T.; Hassiotou, F.; Hartmann, P.E.; McGuire, M.K. It’s alive: Microbes and cells in human milk and their potential benefits to mother and infant. Adv. Nutr. 2014, 5, 571–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koletzko, B. Human Milk Lipids. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2016, 69 (Suppl. S2), 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagström, H.; Rautava, S.; Ollila, H.; Kaljonen, A.; Turta, O.; Mäkelä, J.; Yonemitsu, C.; Gupta, J.; Bode, L. Associations between human milk oligosaccharides and growth in infancy and early childhood. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 111, 769–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz, L.; García-Carral, C.; Rodriguez, J.M. Unfolding the Human Milk Microbiome Landscape in the Omics Era. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wada, Y.; Lönnerdal, B. Bioactive peptides derived from human milk proteins: An update. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2020, 23, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Nisi, G.; Ambruzzi, A.M.; Arslanoglu, S.; Bertino, E.; Biasini, A.; Gagliardi, L.; Moro, G.E.; Mosca, F.; Profeti, C.; Salvatori, G.; et al. Raccomandazioni Per La Costituzione E L’organizzazione Di Una Banca Del Latte Umano Donato; New Magazine Edizioni: Trento, Italy, 2021; ISBN 978-88-8041-133-8. [Google Scholar]
- De Nisi, G.; Moro, G.E.; Arslanoglu, S.; Ambruzzi, A.M.; Biasini, A.; Profeti, C.; Tonetto, P.; Bertino, E.; the members of AIBLUD (Italian Association of Donor Human Milk Banks). The Third Survey on the Activity of Human Milk Banks in Italy and the Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic. Int. J. Nutr. 2022, 7, 31–41. Available online: https://openaccesspub.org/international-journal-of-nutrition/article/1862 (accessed on 30 May 2025).
- Gazzetta Ufficiale della Repubblica Italiana. Linee Di Indirizzo Nazionale Per L’organizzazione E La Gestione Delle Banche Del Latte Umano Donato Nell’ambito Della Protezione, Promozione E Sostegno Dell’allattamento Al Seno. 13 March 2014. Available online: https://www.salute.gov.it/imgs/C_17_pubblicazioni_2127_allegato.pdf (accessed on 25 April 2025).
- Food and Drug Administration. Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point (HACCP). February 2022. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/food/guidance-regulation-food-and-dietary-supplements/hazard-analysis-critical-control-point-haccp (accessed on 15 April 2025).
- Kontopodi, E.; Arslanoglu, S.; Bernatowicz-Lojko, U.; Bertino, E.; Bettinelli, M.E.; Buffin, R.; Cassidy, T.; van Elburg, R.M.; Gebauer, C.; Grovslien, A.; et al. Donor milk banking: Improving the future. A survey on the operation of the European donor human milk banks. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0256435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz, F.O. Rede Global De Ban-Cos De Leite Humano. A Rede BLH–História. Available online: https://rblh.fiocruz.br/historia (accessed on 29 April 2025).
- da Saude, M. Rede Brasileira De Bancos De Leite Humano. Banco De Leite Humano-FIOCRUZ. Available online: https://portal.fiocruz.br/banco-de-leite-humano (accessed on 29 April 2025).
- Oda, A.; Mizuno, K. Questionnaire survey on donor human milk programs targeting NICUs in Japan. Pediatr. Int. 2022, 64, e15344. Available online: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/ped.15344 (accessed on 29 April 2025). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brownell, E.A.; Lussier, M.M.; Herson, V.C.; Hagadorn, J.I.; Marinelli, K.A. Donor human milk bank data collection in North America: An assessment of current status and future needs. J. Hum. Lact 2014, 30, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| NAME OF PERSON COMPLETING THIS QUESTIONNAIRE MILK BANK NAME and ADDRESS NAME OF RESPONSIBLE PERSONS (Manager and Clinical) |
| STATISTICS Number of pasteurizers and freezers Use of pool of donor milk Donor’s screening and microbiological checks on donor milk Number of donors in years 2023 and 2024 Volume of donor milk collected in years 2023 and 2024 Average length of donation in years 2023 and 2024 Number of infants fed with donor milk in years 2023 and 2024 |
| HOME COLLECTION SERVICE Transport service for home collection of donor milk and provision of material |
| HACCP (HAZARD ANALYSIS AND CRITICAL CONTROL POINT) Application of the principles of the HACCP system |
| REGIONALIZATION OF THE SERVICE Human milk bank with regional activity as a “hub” center |
| General Management | No. Banks | % |
|---|---|---|
| Pasteurizers No. > 1 | 16 | 36 |
| Utilization of Holder pasteurization | 44 | 100 |
| Freezers No. > 2 | 18 | 41 |
| Temperature of storage ≤ 20 °C | 44 | 100 |
| Use of pools of milk from single donors | 29 | 66 |
| Use of pools of milk from multiple donors | 18 | 41 |
| System data collection with paper | 22 | 50 |
| System data collection with spreadsheet | 6 | 14 |
| System data collection with specific software | 16 | 36 |
| Milk supplied to other hospitals | 14 | 32 |
| Tracking from donor to recipient | 44 | 100 |
| Home collection service | 28 | 64 |
| Provision of material for milk collection at home | 43 | 98 |
| Use of HACCP * system | 42 | 96 |
| Screening and Microbiological Tests | N. Banks | % |
|---|---|---|
| Infectious tests on prospective donor performed at the beginning of donation | 40 | 91 |
| Infectious tests on the prospective donor accepted if they have been performed no later than three months before the beginning of donation | 41 | 93 |
| Type of infectious tests performed on the donor: serology only | 34 | 77 |
| Type of infectious tests performed on the donor: serology + NAT * | 10 | 23 |
| Bacteriological analysis on donor milk: only at the beginning of donation on unpasteurized milk | 37 | 84 |
| Bacteriological analysis on donor milk: at beginning of donation on unpasteurized milk, and random after pasteurization | 13 | 30 |
| Bacteriological analysis on donor milk: only random after pasteurization | 30 | 68 |
| Bacillus Cereus search on donor milk | 29 | 66 |
| Discarding donor milk if it tests positive for Bacillus Cereus | 44 | 100 |
| Year | 2016 | 2023 | 2024 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of donors | 1336 | 1431 | 1520 |
| Volume of donor milk collected (L) | 9181 | 9120 | 9631 |
| Average volume of milk collected per donor (L) | 6.9 | 6.4 | 6.3 |
| Average length of donation (days) | 142 | 114 | 117 |
| Birth Weight | 2016 | 2023 | 2024 |
|---|---|---|---|
| <1500 g | 1299 | 1239 | 1139 |
| 1500–2499 g | 1447 | 1729 | 1813 |
| >2499 g (in NICU *) | 1049 | 1034 | 1198 |
| Healthy term infants ** | 1192 | 693 | 585 |
| Total | 4987 | 4695 | 4735 |
| Year | Total Number of Live Births in Italy | N. of Infants Fed with Donor Milk | Total Number of VLBW * Infants Born in Italy | N. of VLBW * Infants Fed with Donor Milk |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2016 | 474,925 | 4987 (1.05%) | 4749 | 1299 (29.3%) |
| 2018 | 442,676 | 3984 (0.90%) | 4427 | 1014 (26.7%) |
| 2019 | 421,913 | 4180 (0.99%) | 3797 | 993 (27.3%) |
| 2020 | 404,260 | 3936 (0.97%) | 3638 | 946 (19.9%) |
| 2023 | 379,890 | 4695 (1.24%) | 3419 | 1239 (36.2%) |
| 2024 | 370,000 | 4735 (1.28%) | 3330 | 1139 (34.2%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
De Nisi, G.; Moro, G.E.; Arslanoglu, S.; Ambruzzi, A.M.; Bertino, E.; Biasini, A.; Profeti, C.; Salvatori, G.; Tonetto, P.; Quitadamo, P.A.; et al. The Fourth Survey on the Activity of Human Milk Banks in Italy. Nutrients 2025, 17, 2663. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17162663
De Nisi G, Moro GE, Arslanoglu S, Ambruzzi AM, Bertino E, Biasini A, Profeti C, Salvatori G, Tonetto P, Quitadamo PA, et al. The Fourth Survey on the Activity of Human Milk Banks in Italy. Nutrients. 2025; 17(16):2663. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17162663
Chicago/Turabian StyleDe Nisi, Giuseppe, Guido E. Moro, Sertac Arslanoglu, Amalia M. Ambruzzi, Enrico Bertino, Augusto Biasini, Claudio Profeti, Guglielmo Salvatori, Paola Tonetto, Pasqua Anna Quitadamo, and et al. 2025. "The Fourth Survey on the Activity of Human Milk Banks in Italy" Nutrients 17, no. 16: 2663. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17162663
APA StyleDe Nisi, G., Moro, G. E., Arslanoglu, S., Ambruzzi, A. M., Bertino, E., Biasini, A., Profeti, C., Salvatori, G., Tonetto, P., Quitadamo, P. A., Danese, N., & the members of AIBLUD (Italian Association of Donor Human Milk Banks). (2025). The Fourth Survey on the Activity of Human Milk Banks in Italy. Nutrients, 17(16), 2663. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17162663






