The Impact of Frailty, Activity of Daily Living, and Malnutrition on Mortality in Older Adults with Cognitive Impairment and Dementia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Method
2.1. Study Setting and Cohort of Analysis
2.2. Data Collection and Definition of Key Variables
2.3. Outcomes
2.4. Statistics Methods
3. Results
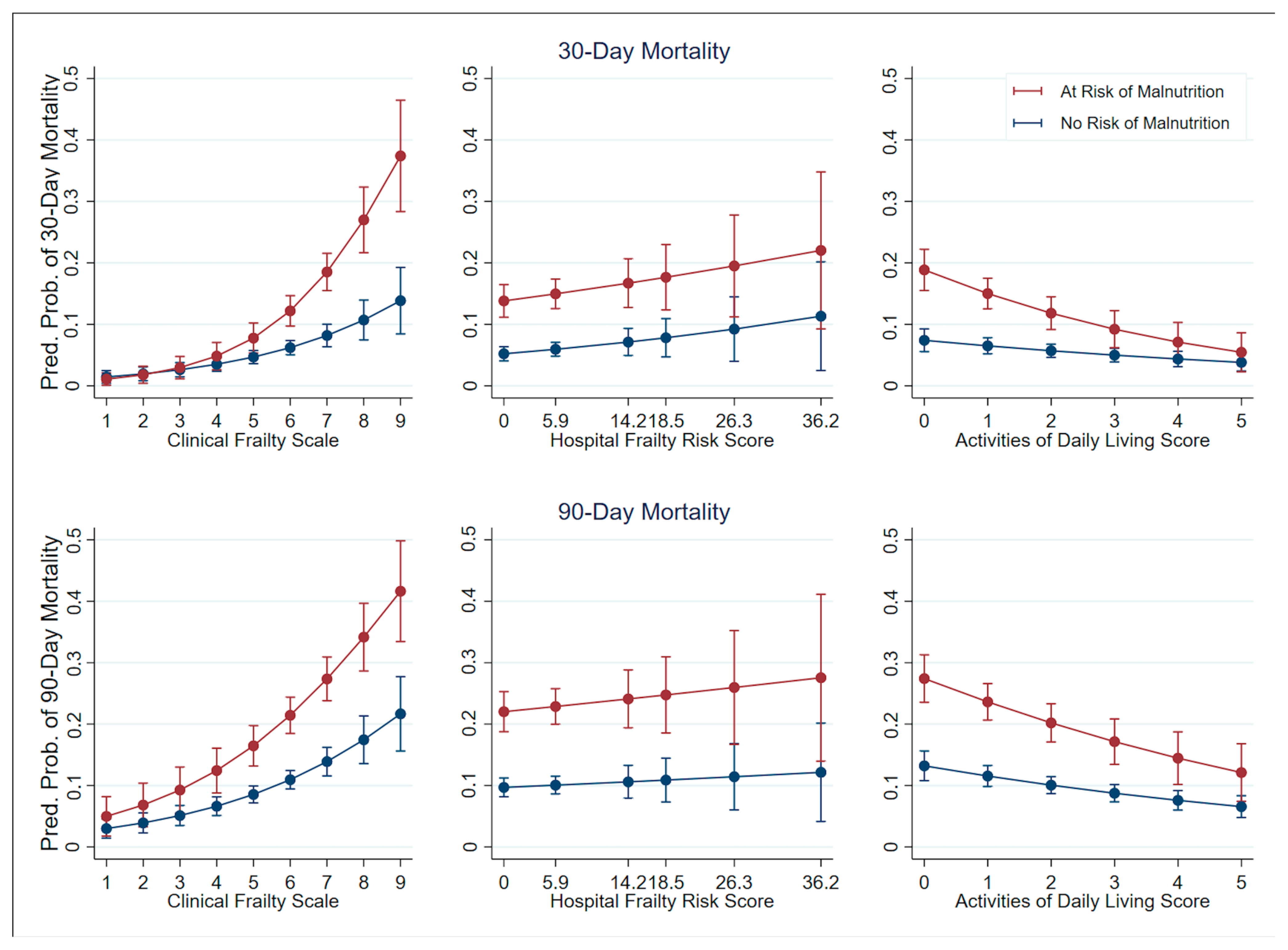
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Garmany, A.; Terzic, A. Global Healthspan-Lifespan Gaps Among 183 World Health Organization Member States. JAMA Netw. Open 2024, 7, e2450241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramaniam, M.; Abdin, E.; Asharani, P.; Roystonn, K.; Devi, F.; Peizhi, W.; Shafie, S.; Sagayadevan, V.; Jeyagurunathan, A.; Chua, B.Y.; et al. Prevalence of dementia in Singapore: Changes across a decade. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2025, 21, e14485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nichols, E.; Steinmetz, J.D.; Vollset, S.E.; Fukutaki, K.; Chalek, J.; Abd-Allah, F.; Abdoli, A.; Abualhasan, A.; Abu-Gharbieh, E.; Akram, T.T.; et al. Estimation of the global prevalence of dementia in 2019 and forecasted prevalence in 2050: An analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet Public Health 2022, 7, e105–e125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Wang, P.; Gong, J.; Sun, W.; Han, X.; Xu, C.; Shan, A.; Wang, X.; Luan, H.; Li, S.; et al. The disease burden, risk factors and future predictions of Alzheimer’s disease and other types of dementia in Asia from 1990 to 2021. J. Prev. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2025, 12, 100122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Lancet Public Health. Reinvigorating the public health response to dementia. Lancet Public Health 2021, 6, e696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, J.G.; Dent, E.; Morley, J.E.; Merchant, R.A.; Beilby, J.; Beard, J.; Tripathy, C.; Sorin, M.; Andrieu, S.; Aprahamian, I.; et al. Screening for and Managing the Person with Frailty in Primary Care: ICFSR Consensus Guidelines. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2020, 24, 920–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merchant, R.A.; Chen, M.Z.; Tan, L.W.L.; Lim, M.Y.; Ho, H.K.; van Dam, R.M. Singapore Healthy Older People Everyday (HOPE) Study: Prevalence of Frailty and Associated Factors in Older Adults. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2017, 18, 734.e9–734.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, F.; Zhou, W.; Pu, J.; Chen, H.; Wang, X.; Lee, J.J. Association of Longitudinal Trajectories of Physical Frailty With Dementia Status in Older Adults: A National Cohort Study. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2025, 40, e70051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Q.-L.; Bandeen-Roche, K.; Tian, J.; Kasper, J.D.; Fried, L.P. Progression of Physical Frailty and the Risk of All-Cause Mortality: Is There a Point of No Return? J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2021, 69, 908–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petermann-Rocha, F.; Lyall, D.M.; Gray, S.R.; Esteban-Cornejo, I.; Quinn, T.J.; Ho, F.K.; Pell, J.P.; Celis-Morales, C. Associations between physical frailty and dementia incidence: A prospective study from UK Biobank. Lancet Healthy Longev. 2020, 1, e58–e68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, D.D.; Flint, J.P.; Littlejohns, T.J.; Foote, I.F.; Canevelli, M.; Wallace, L.M.K.; Gordon, E.H.; Llewellyn, D.J.; Ranson, J.M.; Hubbard, R.E.; et al. Frailty Trajectories Preceding Dementia in the US and UK. JAMA Neurol. 2024, 82, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howlett, S.E.; Rutenberg, A.D.; Rockwood, K. The degree of frailty as a translational measure of health in aging. Nat. Aging 2021, 1, 651–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maxwell, C.J.; Mondor, L.; Hogan, D.B.; Campitelli, M.A.; Bronskill, S.E.; Seitz, D.P.; Wodchis, W.P. Joint impact of dementia and frailty on healthcare utilisation and outcomes: A retrospective cohort study of long-stay home care recipients. BMJ Open 2019, 9, e029523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Røsvik, J.; Rokstad, A.M.M. What are the needs of people with dementia in acute hospital settings, and what interventions are made to meet these needs? A systematic integrative review of the literature. BMC Health Serv. Res. 2020, 20, 723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stineman, M.G.; Xie, D.; Pan, Q.; Kurichi, J.E.; Zhang, Z.; Saliba, D.; Henry-Sánchez, J.T.; Streim, J. All-Cause 1-, 5-, and 10-Year Mortality in Elderly People According to Activities of Daily Living Stage. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2012, 60, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Lubetkin, E.I.; DeMichele, K.; Stark, D.S.; Zack, M.M.; Thompson, W.W. Quality-adjusted life years (QALYs) associated with limitations in activities of daily living (ADL) in a large longitudinal sample of the U.S. community-dwelling older population. Disabil. Health J. 2019, 12, 699–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hugo, J.; Ganguli, M. Dementia and Cognitive Impairment. Clin. Geriatr. Med. 2014, 30, 421–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolz, E.; Gill, T.M.; Mayerl, H.; Rásky, É.; Freidl, W. Trajectories of Late-Life Disability Vary by the Condition Leading to Death. J. Gerontol. Ser. A 2021, 76, 1260–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yassine, H.N.; Samieri, C.; Livingston, G.; Glass, K.; Wagner, M.; Tangney, C.; Plassman, B.L.; Ikram, M.A.; Voigt, R.M.; Gu, Y.; et al. Nutrition state of science and dementia prevention: Recommendations of the Nutrition for Dementia Prevention Working Group. Lancet Healthy Longev. 2022, 3, e501–e512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ligthart-Melis, G.C.; Luiking, Y.C.; Kakourou, A.; Cederholm, T.; Maier, A.B.; de van der Schueren, M.A.E. Frailty, Sarcopenia, and Malnutrition Frequently (Co-)occur in Hospitalized Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2020, 21, 1216–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseer, M.; Forssell, H.; Fagerström, C. Malnutrition, functional ability and mortality among older people aged ≥60 years: A 7-year longitudinal study. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 70, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, C.L.; Wengreen, H.J.; Schwartz, S.; Behrens, S.J.; Corcoran, C.; Lyketsos, C.G.; Tschanz, J.T. Nutritional Status is Associated With Severe Dementia and Mortality: The Cache County Dementia Progression Study. Alzheimer Dis. Assoc. Disord. 2018, 32, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suma, S.; Watanabe, Y.; Hirano, H.; Kimura, A.; Edahiro, A.; Awata, S.; Yamashita, Y.; Matsushita, K.; Arai, H.; Sakurai, T. Factors affecting the appetites of persons with Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2018, 18, 1236–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, R.M.; Irish, M.; Kam, J.; van Keizerswaard, J.; Bartley, L.; Samaras, K.; Hodges, J.R.; Piguet, O. Quantifying the Eating Abnormalities in Frontotemporal Dementia. JAMA Neurol. 2014, 71, 1540–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; Hu, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y. Dual Challenges in the Context of Healthy Aging: A Comprehensive Exploration of the Association Between Malnutrition and Cognitive Decline in Disabled Elderly. Aging Dis. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.Y.; Liu, L.k.; Hwang, A.; Lin, M.h.; Peng, L.n.; Chen, L.k.; Lan, C.; Chang, P. Impact of Malnutrition on Physical, Cognitive Function and Mortality among Older Men Living in Veteran Homes by Minimum Data Set: A Prospective Cohort Study in Taiwan. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2015, 20, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseng, H.-K.; Cheng, Y.-J.; Yu, H.-K.; Chou, K.-T.; Pang, C.-Y.; Hu, G.-C. Malnutrition and Frailty Are Associated with a Higher Risk of Prolonged Hospitalization and Mortality in Hospitalized Older Adults. Nutrients 2025, 17, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Yu, Q.; Shen, S.; Chen, L.; Lei, X. The activity of daily living (ADL) subgroups and health impairment among Chinese elderly: A latent profile analysis. BMC Geriatr. 2021, 21, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, K.; Nyunt, M.-S.-Z.; Gao, Q.; Wee, S.-L.; Yap, K.-B.; Ng, T.-P. Association of Frailty and Malnutrition With Long-term Functional and Mortality Outcomes Among Community-Dwelling Older Adults: Results From the Singapore Longitudinal Aging Study 1. JAMA Netw. Open 2018, 1, e180650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laura, T.; Melvin, C.; Yoong, D.Y. Depressive symptoms and malnutrition are associated with other geriatric syndromes and increase risk for 30-Day readmission in hospitalized older adults: A prospective cohort study. BMC Geriatr. 2022, 22, 634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gingrich, A.; Volkert, D.; Kiesswetter, E.; Thomanek, M.; Bach, S.; Sieber, C.C.; Zopf, Y. Prevalence and overlap of sarcopenia, frailty, cachexia and malnutrition in older medical inpatients. BMC Geriatr. 2019, 19, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merchant, R.A.; Dong, Y.Q.; Kumari, S.; Murphy, D. Frailty, malnutrition, healthcare utilization, and mortality in patients with dementia and cognitive impairment obtained from hospital administrative data. Front. Med. 2025, 12, 1540050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laurila, J.V.; Strandberg, T.E.; Tilvis, R.S.; Pitkala, K.H. Detecting Delirium Using Different Diagnostic Criteria Among Long-Term Care Residents. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2009, 10, 511–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rockwood, K.; Song, X.; MacKnight, C.; Bergman, H.; Hogan, D.B.; McDowell, I.; Mitnitski, A. A global clinical measure of fitness and frailty in elderly people. Can. Med. Assoc. J. 2005, 173, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, T.; Neuburger, J.; Kraindler, J.; Keeble, E.; Smith, P.; Ariti, C.; Arora, S.; Street, A.; Parker, S.; Roberts, H.C. Development and validation of a Hospital Frailty Risk Score focusing on older people in acute care settings using electronic hospital records: An observational study. Lancet 2018, 391, 1775–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imam, T.; Konstant-Hambling, R.; Fluck, R.; Hall, N.; Palmer, J.; Conroy, S. The Hospital Frailty Risk Score—Outcomes in specialised services. Age Ageing 2020, 50, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilmer, S.; Hubbard, R.E. Where next with frailty risk scores in hospital populations? Age Ageing 2021, 51, afab203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mlinac, M.E.; Feng, M.C. Assessment of Activities of Daily Living, Self-Care, and Independence. Arch. Clin. Neuropsychol. 2016, 31, 506–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.-L.; Tong, C.-Y.; Ang, E.; Lee, E.J.-C.; Loke, W.-C.; Chen, Y.; Ferguson, M.; Daniels, L. Development and validation of 3-Minute Nutrition Screening (3-MinNS) tool for acute hospital patients in Singapore. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 18, 395–403. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Health. Action Plan for Successful Aging. Available online: https://www.moh.gov.sg (accessed on 23 March 2025).
- Wang, S.; Li, Q.; Wang, S.; Huang, C.; Xue, Q.-L.; Szanton, S.L.; Liu, M. Sustained frailty remission and dementia risk in older adults: A longitudinal study. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2024, 20, 6268–6277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carey, S.; Deng, J.; Ferrie, S. The impact of malnutrition on cognition in older adults: A systematic review. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2024, 63, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dent, E.; Wright, O.R.; Woo, J.; Hoogendijk, E.O. Malnutrition in older adults. Lancet 2023, 401, 951–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arifin, H.; Chen, R.; Banda, K.J.; Kustanti, C.Y.; Chang, C.-Y.; Lin, H.-C.; Liu, D.; Lee, T.-Y.; Chou, K.-R. Meta-analysis and moderator analysis of the prevalence of malnutrition and malnutrition risk among older adults with dementia. Int. J. Nurs. Stud. 2024, 150, 104648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perry, E.; Walton, K.; Lambert, K. Prevalence of Malnutrition in People with Dementia in Long-Term Care: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukundan, M.; Dhar, M.; Saxena, V.; Panda, P.K.; Bhat, N.K. Nutritional assessment in hospitalized elderly patients, its sociodemographic determinants and co-relation with activities of daily life. J. Fam. Med. Prim. Care 2022, 11, 5082–5086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matusik, P.; Tomaszewski, K.; Chmielowska, K.; Nowak, J.; Nowak, W.; Parnicka, A.; Dubiel, M.; Gąsowski, J.; Grodzicki, T. Severe frailty and cognitive impairment are related to higher mortality in 12-month follow-up of nursing home residents. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2012, 55, 22–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Ortuno, R.; Wallis, S.; Biram, R.; Keevil, V. Clinical frailty adds to acute illness severity in predicting mortality in hospitalized older adults: An observational study. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2016, 35, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omura, T.; Tamura, Y.; Sakurai, T.; Umegaki, H.; Iimuro, S.; Ohashi, Y.; Ito, H.; Araki, A.; the Japanese Elderly Diabetes Intervention Trial Research Group. Functional categories based on cognition and activities of daily living predict all-cause mortality in older adults with diabetes mellitus: The Japanese Elderly Diabetes Intervention Trial. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2021, 21, 512–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millán-Calenti, J.C.; Tubío, J.; Pita-Fernández, S.; González-Abraldes, I.; Lorenzo, T.; Fernández-Arruty, T.; Maseda, A. Prevalence of functional disability in activities of daily living (ADL), instrumental activities of daily living (IADL) and associated factors, as predictors of morbidity and mortality. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2010, 50, 306–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramaniam, A.; Ueno, R.; Tiruvoipati, R.; Srikanth, V.; Bailey, M.; Pilcher, D. Comparison of the predictive ability of clinical frailty scale and hospital frailty risk score to determine long-term survival in critically ill patients: A multicentre retrospective cohort study. Crit. Care 2022, 26, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocyigit, S.E.; Ates Bulut, E.; Aydin, A.E.; Dost, F.S.; Kaya, D.; Isik, A.T. The relationship between cognitive frailty, physical frailty and malnutrition in Turkish older adults. Nutrition 2024, 126, 112504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bianchi, V.E.; Herrera, P.F.; Laura, R. Effect of nutrition on neurodegenerative diseases. A systematic review. Nutr. Neurosci. 2021, 24, 810–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noale, M.; Prinelli, F.; Conti, S.; Sergi, G.; Maggi, S.; Brennan, L.; de Groot, L.C.; Volkert, D.; McEvoy, C.T.; Trevisan, C.; et al. Undernutrition, cognitive decline and dementia: The collaborative PROMED-COG pooled cohorts study. Clin. Nutr. 2024, 43, 2372–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liquori, G.; De Leo, A.; De Nuzzo, D.; D’Inzeo, V.; Arancio, R.M.; Di Simone, E.; Dionisi, S.; Giannetta, N.; Ricciardi, F.; Fabbian, F. Management Strategies and Nursing Activities for Nutritional Care in Hospitalized Patients with Cognitive Decline: A Scoping Review. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loda, I.; D’Angelo, E.; Marzetti, E.; Kerminen, H. Prevention, assessment, and management of malnutrition in older adults with early stages of cognitive disorders. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa Khalid, N.; Haron, H.; Shahar, S.; Fenech, M. Current Evidence on the Association of Micronutrient Malnutrition with Mild Cognitive Impairment, Frailty, and Cognitive Frailty among Older Adults: A Scoping Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 15722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cederholm, T.; Jensen, G.L.; Correia, M.I.T.D.; Gonzalez, M.C.; Fukushima, R.; Higashiguchi, T.; Baptista, G.; Barazzoni, R.; Blaauw, R.; Coats, A.J.S.; et al. GLIM criteria for the diagnosis of malnutrition—A consensus report from the global clinical nutrition community. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2019, 10, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| 65–84 Years Old 1587 (59.3) | ≥85 Years Old 1090 (40.7) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Malnutrition Risk | |||||||
| No | Yes | No | Yes | ||||
| N = 2677 | 1209 (76.2) | 378 (23.8) | p Value | 686 (62.9) | 404 (37.1) | p Value | |
| Sex | 0.410 | 0.710 | |||||
| Male | 1253 (46.8) | 637 (52.7) | 190 (50.3) | 271 (39.5) | 155 (38.4) | ||
| Female | 1424 (53.2) | 572 (47.3) | 188 (49.7) | 415 (60.5) | 249 (61.6) | ||
| Race | 0.282 | 0.424 | |||||
| Chinese | 2180 (81.4) | 945 (78.2) | 304 (80.4) | 591 (86.2) | 340 (84.2) | ||
| Indian | 159 (5.9) | 81 (6.7) | 21 (5.6) | 35 (5.1) | 22 (5.5) | ||
| Malay | 204 (7.6) | 117 (9.9) | 27 (7.1) | 32 (4.7) | 28 (6.9) | ||
| Others | 134 (5.0) | 66 (5.5) | 26 (6.9) | 28 (4.1) | 14 (3.5) | ||
| Comorbidities | |||||||
| Diabetes Mellitus | 1129 (42.2) | 605 (50.0) | 150 (39.7) | <0.001 | 243 (35.4) | 131 (32.4) | 0.314 |
| Hypertension | 1479 (55.3) | 750 (62.0) | 181 (47.9) | <0.001 | 356 (51.9) | 192 (47.5) | 0.163 |
| Hyperlipidemia | 1108 (41.4) | 600 (49.6) | 138 (36.5) | <0.001 | 257 (37.5) | 113 (28.0) | 0.001 |
| Discharge Diagnosis | |||||||
| Delirium | 723 (27.0) | 292 (24.2) | 106 (28.0) | 0.128 | 183 (26.7) | 142 (35.2) | 0.003 |
| Pneumonia | 764 (28.5) | 285 (23.6) | 129 (34.1) | <0.001 | 200 (29.2) | 150 (37.1) | 0.006 |
| UTI | 771 (28.8) | 321 (26.6) | 117 (31.0) | 0.095 | 207 (30.2) | 126 (31.2) | 0.726 |
| Constipation | 151 (5.6) | 72 (6.0) | 19 (5.0) | 0.498 | 42 (6.1) | 18 (4.5) | 0.244 |
| Hyponatremia | 455 (17.0) | 157 (13.0) | 76 (20.1) | 0.001 | 111 (16.2) | 111 (27.5) | <0.001 |
| Ischemic Stroke | 220 (8.2) | 119 (9.8) | 23 (6.1) | 0.025 | 52 (7.6) | 26 (6.4) | 0.479 |
| Intracranial Bleed | 115 (4.3) | 66 (5.5) | 10 (2.7) | 0.025 | 20 (2.9) | 19 (4.7) | 0.125 |
| Acute Myocardial Infarction | 257 (9.6) | 114 (9.4) | 27 (7.1) | 0.173 | 56 (8.2) | 60 (14.9) | 0.001 |
| Heart failure | 186 (7.0) | 88 (7.3) | 15 (4.0) | 0.023 | 63 (9.2) | 20 (5.0) | 0.011 |
| Orthostatic Hypotension | 174 (6.5) | 86 (7.1) | 32 (8.5) | 0.382 | 37 (5.4) | 19 (4.7) | 0.618 |
| Osteoporosis Fractures | 140 (5.2) | 53 (4.4) | 15 (4.0) | 0.728 | 56 (8.2) | 16 (4.0) | 0.007 |
| Parkinson’s Disease | 120 (4.5) | 60 (5.0) | 24 (6.4) | 0.293 | 23 (3.4) | 13 (3.2) | 0.904 |
| Sepsis | 327 (12.2) | 139 (11.5) | 57 (15.1) | 0.065 | 72 (10.5) | 59 (14.6) | 0.044 |
| CCI, median (IQR) | 6 (4–7) | 6 (4–8) | 5.5 (4–7) | 0.442 | 5 (4–7) | 5 (4–7) | 0.216 |
| CFS | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||||
| 1–4 | 758 (28.3) | 434 (35.9) | 83 (22.0) | 183 (26.7) | 58 (14.4) | ||
| 5–6 | 1134 (42.4) | 536 (44.3) | 156 (41.3) | 304 (44.3) | 138 (34.2) | ||
| 7–9 | 785 (29.3) | 239 (19.8) | 139 (36.8) | 199 (29.0) | 208 (51.5) | ||
| HFRS | 0.609 | 0.024 | |||||
| 0–4 | 1963 (73.3) | 898 (74.3) | 271 (71.7) | 516 (75.2) | 278 (68.8) | ||
| 5–15 | 487 (18.2) | 221 (18.3) | 76 (20.1) | 115 (16.8) | 75 (18.6) | ||
| 16- | 227 (8.5) | 90 (7.4) | 31 (8.2) | 55 (8.0) | 51 (12.6) | ||
| ADL | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||||
| 0 | 927 (34.6) | 264 (21.8) | 178 (47.1) | 244 (35.6) | 241 (59.7) | ||
| 1 | 364 (13.6) | 144 (11.9) | 51 (13.5) | 118 (17.2) | 51 (12.) | ||
| 2 | 317 (11.8) | 151 (12.5) | 37 (9.8) | 88 (12.8) | 41 (10.2) | ||
| 3 | 137 (5.1) | 70 (5.8) | 20 (5.3) | 36 (5.3) | 11 (2.7) | ||
| 4 | 139 (5.2) | 84 (7.0) | 11 (2.9) | 34 (5.0) | 10 (2.5) | ||
| 5 | 793 (29.6) | 496 (41.0) | 81 (21.4) | 166 (24.2) | 50 (12.4) | ||
| Mortality (30 day and 90 day) | |||||||
| 30-day mortality | 231 (8.6) | 46 (3.8) | 43 (11.4) | <0.001 | 55 (8.0) | 87 (21.5) | <0.001 |
| 90-day mortality | 372 (13.9) | 91 (7.5) | 74 (19.6) | <0.001 | 89 (13.0) | 118 (29.2) | <0.001 |
| (A) Clinical Frailty Score (CFS) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30-Day Mortality | 90-Day Mortality | |||||
| Variable | aOR (95% CI) | SE | p-Value | OR (95% CI) | SE | p-Value |
| CFS score | 1.498 (1.349, 1.664) | 0.080 | <0.001 | 1.361 (1.255, 1.475) | 0.056 | <0.001 |
| Malnutrition | 2.348 (1.748, 3.156) | 0.034 | <0.001 | 2.320 (1.824, 2.951) | 0.029 | <0.001 |
| (B) Hospital Frailty Risk Score (HFRS) | ||||||
| HFRS score | 1.020 (1.001, 1.040) | 0.010 | 0.038 | 1.008 (0.992, 1.025) | 0.008 | 0.333 |
| Malnutrition | 2.944 (2.210, 3.922) | 0.431 | <0.001 | 2.770 (2.192, 3.500) | 0.331 | <0.001 |
| (C) Activity of Daily Living (ADL) | ||||||
| ADL (number) | 0.819 (0.753, 0.890) | 0.035 | <0.001 | 0.837 (0.785, 0.892) | 0.027 | <0.001 |
| Malnutrition | 2.573 (1.922, 3.443) | 0.383 | <0.001 | 2.422 (1.908, 3.075) | 0.295 | <0.001 |
| (A) Clinical Frailty Score (CFS) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30-Day Mortality | 90-Day Mortality | |||||
| Variable | aOR (95% CI) | SE | p-Value | OR (95% CI) | SE | p-Value |
| CFS score | 1.359 (1.181, 1.564) | 0.097 | <0.001 | 1.326 (1.191, 1.476) | 0.072 | <0.001 |
| Malnutrition risk | 0.603 (0.148, 2.451) | 0.431 | 0.479 | 1.613 (0.576, 4.519) | 0.848 | 0.363 |
| CFS × Malnutrition | 1.236 (0.999, 1.530) | 0.134 | 0.051 | 1.061 (0.902, 1.247) | 0.088 | 0.476 |
| (B) Hospital Frailty Risk Score (HFRS) | ||||||
| HFRS score | 1.024 (0.996, 1.054) | 0.015 | 0.095 | 1.007 (0.984, 1.031) | 0.012 | 0.548 |
| Malnutrition risk | 3.048 (2.177, 4.267) | 0.523 | <0.001 | 2.752 (2.099, 3.609) | 0.381 | <0.001 |
| HFRS × Malnutrition | 0.993 (0.956, 1.031) | 0.019 | 0.699 | 1.002 (0.969, 1.035) | 0.017 | 0.927 |
| (C) Activity of Daily Living (ADL) | ||||||
| ADL score | 0.866 (0.780, 0.962) | 0.046 | 0.007 | 0.853 (0.787, 0.924) | 0.035 | <0.001 |
| Malnutrition risk | 3.053 (2.134, 4.369) | 0.558 | <0.001 | 2.597 (1.930, 3.493) | 0.393 | <0.001 |
| ADL × Malnutrition | 0.864 (0.725, 1.029) | 0.077 | 0.101 | 0.949 (0.832, 1.083) | 0.064 | 0.437 |
| (A) Clinical Frailty Score (CFS) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30-Day Mortality | 90-Day Mortality | |||||
| Variable | aOR (95% CI) | SE | p Value | OR (95% CI) | SE | p Value |
| CFS score | 1.239 (1.027, 1.493) | 0.118 | 0.025 | 1.238 (1.064, 1.440) | 0.096 | 0.006 |
| Malnutrition risk | 0.217 (0.033, 1.416) | 0.208 | 0.110 | 0.483 (0.109, 2.145) | 0.367 | 0.339 |
| CFS × Malnutrition * | 1.435 (1.082, 1.902) | 0.206 | 0.012 | 1.263 (1.005, 1.588) | 0.148 | 0.045 |
| (B) Hospital Frailty Risk Score (HFRS) | ||||||
| HFRS score | 1.019 (0.979, 1.061) | 0.021 | 0.362 | 1.007 (0.972, 1.042) | 0.018 | 0.702 |
| Malnutrition risk | 2.965 (1.915, 4.589) | 0.661 | <0.001 | 2.564 (1.772, 3.712) | 0.484 | <0.001 |
| HFRS × Malnutrition * | 0.992 (0.943, 1.044) | 0.026 | 0.753 | 1.003 (0.959, 1.049) | 0.023 | 0.904 |
| (C) Activity of Daily Living (ADL) | ||||||
| ADL score | 0.791 (0.670, 0.935) | 0.067 | 0.006 | 0.775 (0.678, 0.887) | 0.053 | <0.001 |
| Malnutrition risk | 2.633 (1.686, 4.110) | 0.598 | <0.001 | 2.330 (1.588, 3.419) | 0.456 | <0.001 |
| ADL × Malnutrition * | 0.946 (0.736, 1.217) | 0.122 | 0.669 | 0.961 (0.779, 1.185) | 0.103 | 0.708 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Z.; Dong, Y.-Q.; Kumari, S.; Murphy, D.; Merchant, R.A. The Impact of Frailty, Activity of Daily Living, and Malnutrition on Mortality in Older Adults with Cognitive Impairment and Dementia. Nutrients 2025, 17, 2612. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17162612
Wang Z, Dong Y-Q, Kumari S, Murphy D, Merchant RA. The Impact of Frailty, Activity of Daily Living, and Malnutrition on Mortality in Older Adults with Cognitive Impairment and Dementia. Nutrients. 2025; 17(16):2612. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17162612
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Zitong, Ying-Qiu Dong, Shikha Kumari, Diarmuid Murphy, and Reshma Aziz Merchant. 2025. "The Impact of Frailty, Activity of Daily Living, and Malnutrition on Mortality in Older Adults with Cognitive Impairment and Dementia" Nutrients 17, no. 16: 2612. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17162612
APA StyleWang, Z., Dong, Y.-Q., Kumari, S., Murphy, D., & Merchant, R. A. (2025). The Impact of Frailty, Activity of Daily Living, and Malnutrition on Mortality in Older Adults with Cognitive Impairment and Dementia. Nutrients, 17(16), 2612. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17162612






