Evaluation of the Reliability and Validity of a Food Frequency Questionnaire Using Three-Day 24-Hour Dietary Recalls: A Study in Fujian, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Participants and Design
2.2. Questionnaire Instruments
2.2.1. Sociodemographic Information
2.2.2. Food Frequency Questionnaire (FFQ)
2.3. Three-Day 24-Hour Dietary Recall (3d-24HDR)
2.4. Calculation of Food Group and Nutrient Intake
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.5.1. Reliability Analysis
2.5.2. Validity Analysis
2.6. Sample Size Calculation
2.7. Ethical Considerations
3. Results
3.1. General Characteristics of Participants
3.2. Reliability Analysis
3.2.1. Reliability of Food Group Intake from FFQs
3.2.2. Reliability of Energy and Nutrient Intakes from FFQs
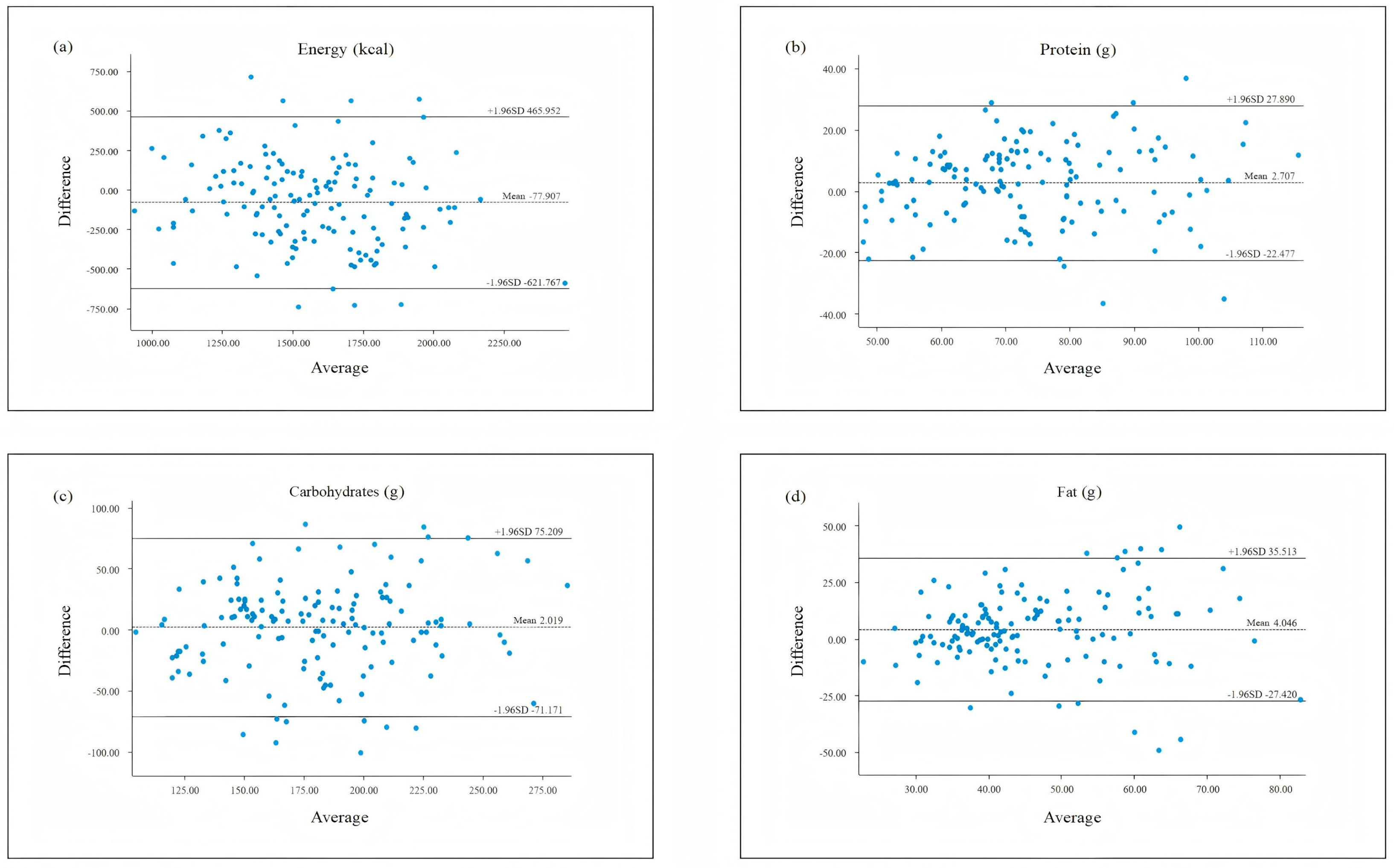
3.3. Validity Analysis
3.3.1. Validity of Food Group Intake
3.3.2. Validity of Energy and Nutrient Intake
4. Discussion
4.1. Reliability Evaluation of the FFQ
4.2. Validity Evaluation of the FFQ
4.2.1. Choice of Validation Method
4.2.2. FFQ Validity Analysis
4.3. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Murray, C.J.; Lopez, A.D. Measuring the Global Burden of Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 448–457. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nugent, R. Preventing and Managing Chronic Diseases. BMJ 2019, 364, l459. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dominguez, L.J.; Di Bella, G.; Veronese, N.; Barbagallo, M. Impact of Mediterranean Diet on Chronic Non-Communicable Diseases and Longevity. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khemka, S.; Reddy, A.; Garcia, R.I.; Jacobs, M.; Reddy, R.P.; Roghani, A.K.; Pattoor, V.; Basu, T.; Sehar, U.; Reddy, P.H. Role of Diet and Exercise in Aging, Alzheimer’s Disease, and Other Chronic Diseases. Ageing Res. Rev. 2023, 91, 102091. [Google Scholar]
- Mills, K.T.; Stefanescu, A.; He, J. The Global Epidemiology of Hypertension. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2020, 16, 223–237. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, A.; Mirzaei, H.; Guidi, N.; Vinciguerra, M.; Mouton, A.; Linardic, M.; Rappa, F.; Barone, R.; Navarrete, G.; Wei, M.; et al. Fasting-Mimicking Diet Prevents High-Fat Diet Effect on Cardiometabolic Risk and Lifespan. Nat. Metab. 2021, 3, 1342–1356. [Google Scholar]
- Mititelu, M.; Licu, M.; Neacșu, S.M.; Călin, M.F.; Matei, S.R.; Scafa-Udriște, A.; Stanciu, T.I.; Busnatu, Ș.S.; Olteanu, G.; Măru, N.; et al. An Assessment of Behavioral Risk Factors in Oncology Patients. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajani, J.A.; D’Amico, T.A.; Bentrem, D.J.; Chao, J.; Cooke, D.; Corvera, C.; Das, P.; Enzinger, P.C.; Enzler, T.; Fanta, P.; et al. Gastric Cancer, Version 2.2022, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2022, 20, 167–192. [Google Scholar]
- Shim, J.S.; Oh, K.; Kim, H.C. Dietary Assessment Methods in Epidemiologic Studies. Epidemiol. Health 2014, 36, e2014009. [Google Scholar]
- Willett, W. Nutritional Epidemiology, 3rd ed.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, W.; Sun, C.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Wu, L. Reproducibility and Relative Validity of a Food Frequency Questionnaire Developed for Female Adolescents in Suihua, North China. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e19656. [Google Scholar]
- Nusser, S.M.; Carriquiry, A.L.; Dodd, K.W.; Fuller, W.A. A Semiparametric Transformation Approach to Estimating Usual Daily Intake Distributions. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1996, 91, 1440–1449. [Google Scholar]
- Brouwer-Brolsma, E.M.; Perenboom, C.; Sluik, D.; van de Wiel, A.; Geelen, A.; Feskens, E.J.; Vries, J.H. Development and External Validation of the ‘Flower-FFQ’: A FFQ Designed for the Lifelines Cohort Study. Public Health Nutr. 2022, 25, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cui, Q.; Xia, Y.; Wu, Q.; Chang, Q.; Niu, K.; Zhao, Y. Validity of the Food Frequency Questionnaire for Adults in Nutritional Epidemiological Studies: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 1670–1688. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bueno de Mesquita, H.B.; Smeets, F.W.; Runia, S.; Hulshof, K.F. The Reproducibility of a Food Frequency Questionnaire Among Controls Participating in a Case-Control Study on Cancer. Nutr. Cancer 1992, 18, 143–156. [Google Scholar]
- Engle, A.; Lynn, L.L.; Koury, K.; Boyar, A.P. Reproducibility and Comparability of a Computerized, Self-Administered Food Frequency Questionnaire. Nutr. Cancer 1990, 13, 281–292. [Google Scholar]
- Moridpour, A.H.; Rafraf, M.; Sarbakhsh, P.; Asghari, S.; Molani-Gol, R.; Asghari-Jafarabadi, M. Validity and Reliability of a Semi-Quantitative Food Frequency Questionnaire for Assessing Dietary Vitamin D and Calcium Intakes in Iranian Childbearing Age Women. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 1028265. [Google Scholar]
- Seidelmann, S.B.; Claggett, B.; Cheng, S.; Henglin, M.; Shah, A.; Steffen, L.M.; Folsom, A.R.; Rimm, E.B.; Willett, W.C.; Solomon, S.D.; et al. Dietary Carbohydrate Intake and Mortality: A Prospective Cohort Study and Meta-Analysis. Lancet Public Health 2018, 3, e419–e428. [Google Scholar]
- Willett, W.C.; Howe, G.R.; Kushi, L.H. Adjustment for Total Energy Intake in Epidemiologic Studies. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1997, 65, 1220S–1228S. [Google Scholar]
- Fleiss, J.L.; Cohen, J. The Equivalence of Weighted Kappa and the Intraclass Correlation Coefficient As Measures of Reliability. Educ. Psychol. Meas. 2016, 33, 613–619. [Google Scholar]
- Syauqy, A.; Afifah, D.N.; Purwanti, R.; Nissa, C.; Fitranti, D.Y.; Chao, J.C. Reproducibility and Validity of a Food Frequency Questionnaire (FFQ) Developed for Middle-Aged and Older Adults in Semarang, Indonesia. Nutrients 2021, 13, 4163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Q.; Hong, X.; Wang, Z.; Yang, H.; Chen, X.; Zhou, H.; Wang, C.; Lai, Y.; Sun, L.; Xu, F.; et al. Reproducibility and Validity of an FFQ Developed for Adults in Nanjing, China. Br. J. Nutr. 2016, 115, 887–894. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Qin, C.; Guo, Y.; Pei, P.; Du, H.; Yang, L.; Chen, Y.; Shen, X.; Shi, Z.; Qi, L.; Chen, J.; et al. The Relative Validity and Reproducibility of Food Frequency Questionnaires in the China Kadoorie Biobank Study. Nutrients 2022, 14, 794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Q.; Xia, Y.; Wu, Q.; Chang, Q.; Niu, K.; Zhao, Y. A Meta-Analysis of the Reproducibility of Food Frequency Questionnaires in Nutritional Epidemiological Studies. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2021, 18, 12. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Whitton, C.; Ho, J.C.Y.; Tay, Z.; Rebello, S.A.; Lu, Y.; Ong, C.N.; van Dam, R.M. Relative Validity and Reproducibility of a Food Frequency Questionnaire for Assessing Dietary Intakes in a Multi-Ethnic Asian Population Using 24-h Dietary Recalls and Biomarkers. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Xie, R.; Ni, C.; Yang, M.; Wang, Z.; Ding, G.; Yuan, C. A Meta-Analysis on the Reliability and Validity of Food Frequency Questionnaires Among Chinese Adults. Acta Nutr. Sin. 2022, 44, 293–300. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hebden, L.; Kostan, E.; O’Leary, F.; Hodge, A.; Allman-Farinelli, M. Validity and Reproducibility of a Food Frequency Questionnaire as a Measure of Recent Dietary Intake in Young Adults. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e75156. [Google Scholar]
- Rendo-Urteaga, T.; Saravia, L.; Sadalla Collese, T.; Monsalve-Alvarez, J.M.; González-Zapata, L.I.; Tello, F.; Martínez-Oliván, B.; Torres-Leal, F.L.; Moreno, L.A.; De Moraes, A.C.F.; et al. Reliability and Validity of an FFQ for South American Children and Adolescents from the SAYCARE Study. Public Health Nutr. 2020, 23, 13–21. [Google Scholar]
- Flood, V.M.; Wen, L.M.; Hardy, L.L.; Rissel, C.; Simpson, J.M.; Baur, L.A. Reliability and Validity of a Short FFQ for Assessing the Dietary Habits of 2-5-Year-Old Children, Sydney, Australia. Public Health Nutr. 2014, 17, 498–509. [Google Scholar]
- Silva-Jaramillo, K.M.; Neutzling, M.B.; Drehmer, M. FFQ for the Adult Population of the Capital of Ecuador (FFQ-Quito): Development, Reliability and Validity. Public Health Nutr. 2015, 18, 2540–2549. [Google Scholar]
- Noor Hafizah, Y.; Ang, L.C.; Yap, F.; Nurul Najwa, W.; Cheah, W.L.; Ruzita, A.T.; Jumuddin, F.A.; Koh, D.; Lee, J.A.C.; Essau, C.A.; et al. Validity and Reliability of a Food Frequency Questionnaire (FFQ) to Assess Dietary Intake of Preschool Children. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4722. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, Y.; Yang, K.; Wang, B.; Liu, C.; Mao, Z.; Yu, S.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Sun, H.; Wang, C. Reproducibility and Validity of an FFQ in the Henan Rural Cohort Study. Public Health Nutr. 2020, 23, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- El Kinany, K.; Garcia-Larsen, V.; Khalis, M.; Deoula, M.M.S.; Benslimane, A.; Ibrahim, A.; Benjelloun, M.C.; El Rhazi, K. Adaptation and Validation of a Food Frequency Questionnaire (FFQ) to Assess Dietary Intake in Moroccan Adults. Nutr. J. 2018, 17, 61. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bahreynian, M.; Feizi, A.; Kelishadi, R. The First Semi-Quantitative Toddler’s Food Frequency Questionnaire (T-FFQ) in Iran. Int. J. Vitam. Nutr. Res. 2023, 93, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhai, L.; Pan, H.; Cao, H.; Zhao, S.; Yao, P. Reliability and Validity of a Semi-Quantitative Food Frequency Questionnaire: Dietary Intake Assessment Among Multi-Ethnic Populations in Northwest China. J. Health Popul. Nutr. 2023, 42, 111. [Google Scholar]
- Sam, C.H.; Skeaff, S.; Skidmore, P.M. A Comprehensive FFQ Developed for Use in New Zealand Adults: Reliability and Validity for Nutrient Intakes. Public Health Nutr. 2014, 17, 287–296. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, Y.; Yuan, C.; Wang, D.D.; Wang, M.; Song, M.; Shan, Z.; Hu, F.; Rosner, B.; Smith-Warner, S.A.; Willett, W.C. Reproducibility and Validity of Diet Quality Scores Derived from Food-Frequency Questionnaires. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 115, 843–853. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Sa, R.; Yan, H. Validity and Reproducibility of a Food Frequency Questionnaire Designed for Residents in North China. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 17, 629–634. [Google Scholar]
- Takachi, R.; Ishihara, J.; Iwasaki, M.; Hosoi, S.; Ishii, Y.; Sasazuki, S.; Sawada, N.; Yamaji, T.; Shimazu, T.; Inoue, M.; et al. Validity of a Self-Administered Food Frequency Questionnaire for Middle-Aged Urban Cancer Screenees: Comparison with 4-Day Weighed Dietary Records. J. Epidemiol. 2011, 21, 447–458. [Google Scholar]
- Cade, J.E.; Burley, V.J.; Warm, D.L.; Thompson, R.L.; Margetts, B.M. Food-Frequency Questionnaires: A Review of Their Design, Validation and Utilisation. Nutr. Res. Rev. 2004, 17, 5–22. [Google Scholar]
- Cade, J.; Thompson, R.; Burley, V.; Warm, D. Development, Validation and Utilisation of Food-Frequency Questionnaires-A Review. Public Health Nutr. 2002, 5, 567–587. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Huang, W. Development of a Food Frequency Questionnaire for College Students and Its Reliability and Validity Evaluation. Chin. J. Public Health 2011, 27, 1611–1612. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Lyu, L.C.; Lin, C.F.; Chang, F.H.; Chen, H.F.; Lo, C.C.; Ho, H.F. Meal Distribution, Relative Validity and Reproducibility of a Meal-Based Food Frequency Questionnaire in Taiwan. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 16, 766–776. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Marques-Vidal, P.; Ross, A.; Wynn, E.; Rezzi, S.; Paccaud, F.; Decarli, B. Reproducibility and Relative Validity of a Food-Frequency Questionnaire for French-Speaking Swiss Adults. Food Nutr. Res. 2011, 55, 5905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sierra-Ruelas, É.; Bernal-Orozco, M.F.; Macedo-Ojeda, G.; Márquez-Sandoval, Y.F.; Altamirano-Martínez, M.B.; Vizmanos, B. Validation of Semiquantitative FFQ Administered to Adults: A Systematic Review. Public Health Nutr. 2021, 24, 3399–3418. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, M.; Yuan, Z.; Lin, L.; Hu, B.; Wang, X.; Yang, Y.; Chen, X.; Jin, L.; Lu, M.; Ye, W. Reproducibility and Relative Validity of a Food Frequency Questionnaire Developed for Adults in Taizhou, China. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e48341. [Google Scholar]
- Eghtesad, S.; Hekmatdoost, A.; Faramarzi, E.; Homayounfar, R.; Sharafkhah, M.; Hakimi, H.; Dehghani, A.; Moosazadeh, M.; Mortazavi, Z.; Pasdar, Y.; et al. Validity and Reproducibility of a Food Frequency Questionnaire Assessing Food Group Intake in the PERSIAN Cohort Study. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1059870. [Google Scholar]
- De Keyzer, W.; Huybrechts, I.; De Vriendt, V.; Vandevijvere, S.; Slimani, N.; Van Oyen, H.; De Henauw, S. Repeated 24-Hour Recalls Versus Dietary Records for Estimating Nutrient Intakes in a National Food Consumption Survey. Food Nutr. Res. 2011, 55, 7307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghan, M.; Martinez, S.; Zhang, X.; Seron, P.; Lanas, F.; Islam, S.; Merchant, A.T. Relative Validity of an FFQ to Estimate Daily Food and Nutrient Intakes for Chilean Adults. Public Health Nutr. 2013, 16, 1782–1788. [Google Scholar]
- Molina, M.d.C.; Benseñor, I.M.; Cardoso, L.d.O.; Velasquez-Melendez, G.; Drehmer, M.; Pereira, T.S.; Faria, C.P.; Melere, C.; Manato, L.; Gomes, A.L.; et al. Reproducibility and Relative Validity of the Food Frequency Questionnaire Used in the ELSA-Brasil. Cad. Saude Publica 2013, 29, 379–389. [Google Scholar]
- Ahluwalia, N.; Dwyer, J.; Terry, A.; Moshfegh, A.; Johnson, C. Update on NHANES dietary data: Focus on collection, release, analytical considerations, and uses to inform public policy. Adv. Nutr. 2016, 7, 121–134. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, K.; Xie, C.; Li, Z.; Zeng, H.; Zhao, Y.; Shi, Z. Selenium intake and its interaction with iron intake are associated with cognitive functions in Chinese adults: A longitudinal study. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malekshah, A.F.; Kimiagar, M.; Saadatian-Elahi, M.; Pourshams, A.; Nouraie, M.; Goglani, G.; Hoshiarrad, A.; Sadatsafavi, M.; Golestan, B.; Yoonesi, A.; et al. Validity and Reliability of a New Food Frequency Questionnaire Compared to 24 h Recalls and Biochemical Measurements: Pilot Phase of Golestan Cohort Study of Esophageal Cancer. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 60, 971–977. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zang, J.; Luo, B.; Chang, S.; Jin, S.; Shan, C.; Ma, L.; Zhu, Z.; Guo, C.; Zou, S.; Jia, X.; et al. Validity and Reliability of a Food Frequency Questionnaire for Assessing Dietary Intake Among Shanghai Residents. Nutr. J. 2019, 18, 30. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Flegal, K.M.; Graubard, B.; Ioannidis, J.P.A. Use and Reporting of Bland-Altman Analyses in Studies of Self-Reported Versus Measured Weight and Height. Int. J. Obes. 2020, 44, 1311–1318. [Google Scholar]
- Vila-Real, C.; Pimenta-Martins, A.; Magu, J.S.; Kunyanga, C.; Mbugua, S.; Katina, K.; Maina, N.H.; Gomes, A.M.; Pinto, E. A Culture-Sensitive Semi-Quantitative FFQ for Use Among the Adult Population in Nairobi, Kenya: Development, Validity and Reproducibility. Public Health Nutr. 2021, 24, 834–844. [Google Scholar]
- Zack, R.M.; Irema, K.; Kazonda, P.; Leyna, G.H.; Liu, E.; Gilbert, S.; Lukmanji, Z.; Spiegelman, D.; Fawzi, W.; Njelekela, M.; et al. Validity of an FFQ to Measure Nutrient and Food Intakes in Tanzania. Public Health Nutr. 2018, 21, 2211–2220. [Google Scholar]
| Frequency | Rarely/Never | 1–3 Times/Month | 1 Time/Week | 2–3 Times/Week | 4–6 Times/week | 1 Time/Day | 2–3 Times/Day | 4 Times/Day |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weight | 0.00 | 0.07 | 0.14 | 0.36 | 0.71 | 1.00 | 2.50 | 4.00 |
| Variables | Reliability Study (N = 152) | Validity Study (N = 142) |
|---|---|---|
| Age (years), mean ± std | 42.38 ± 11.92 | 42.67 ± 11.87 |
| Age group (years) | ||
| <30 | 19 (12.5) | 17 (12.0) |
| 30–40 | 55 (36.2) | 50 (35.2) |
| >40 | 78 (51.3) | 75 (52.8) |
| Sex | ||
| Male | 69 (45.4) | 60 (42.3) |
| Female | 83 (54.6) | 82 (57.7) |
| BMI, kg/m2, mean ± std | 22.66 ± 3.03 | 22.35 ± 2.79 |
| BMI group (kg/m2) | ||
| <25.0 | 109 (71.7) | 108 (76.1) |
| 25.0–29.9 | 35 (23.0) | 29 (20.4) |
| ≥30.0 | 8 (5.3) | 5 (3.5) |
| Education level | ||
| Primary school or below | 18 (11.8) | 18 (12.7) |
| Middle/high school | 46 (30.3) | 41 (28.9) |
| College or above | 88 (57.9) | 83 (58.5) |
| Marital status | ||
| Unmarried | 34 (22.4) | 31 (21.8) |
| Married | 114 (75.0) | 107 (75.4) |
| Divorced/Widowed | 4 (2.6) | 4 (2.8) |
| Average monthly household income (RMB) | ||
| <6000 | 45 (29.6) | 44 (31.0) |
| 6000–12,000 | 73 (48.0) | 70 (49.3) |
| >12,000 | 34 (22.4) | 28 (19.7) |
| Smoking | ||
| Yes | 29 (19.1) | 23 (16.2) |
| No | 123 (80.9) | 119 (83.8) |
| Alcohol drinking | ||
| Yes | 49 (32.2) | 43 (30.3) |
| No | 103 (67.8) | 99 (69.7) |
| History of chronic disease | ||
| Yes | 20 (13.2) | 19 (13.4) |
| No | 132 (86.8) | 123 (86.6) |
| Family cancer history | ||
| Yes | 37 (24.3) | 35 (24.6) |
| No | 116 (76.3) | 107 (75.4) |
| Food (g/d) | FFQ-1 | FFQ-2 | p a | SCC b | ICC c | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M (P25–P75) | M (P25–P75) | Crude | Adjusted d | Crude | Adjusted d | ||
| Refined rice and related products | 325.00 (185.00–437.50) | 274.25 (185.50–437.50) | 0.043 | 0.63 * | 0.60 * | 0.57 | 0.55 |
| Wheat products (e.g., noodles, bread) | 93.60 (47.20–141.70) | 80.70 (37.80–120.58) | 0.135 | 0.73 * | 0.69 * | 0.67 | 0.64 |
| Whole grains | 0.00 (0.00–10.85) | 0.00 (0.00–10.50) | 0.261 | 0.80 * | 0.30 * | 0.91 | 0.39 |
| Root and tuber vegetables | 14.00 (0.00–36.00) | 7.00 (0.00–24.50) | 0.265 | 0.67 * | 0.66 * | 0.55 | 0.53 |
| Processed meat | 0.00 (0.00–11.20) | 0.00 (0.00–5.60) | 0.447 | 0.60 * | 0.58 * | 0.80 | 0.78 |
| Eggs | 50.00 (35.50–50.00) | 40.40 (35.50–50.00) | 0.335 | 0.69 * | 0.59 * | 0.60 | 0.50 |
| Red meat | 125.00 (88.75–125.00) | 88.75 (45.00–125.00) | 0.045 | 0.63 * | 0.46 * | 0.61 | 0.44 |
| Poultry | 36.00 (0.00–71.00) | 14.00 (0.00–36.00) | 0.201 | 0.82 * | 0.80 * | 0.65 | 0.63 |
| Organ meat | 0.00 (0.00–0.00) | 0.00 (0.00–5.60) | 0.209 | 0.72 * | 0.64 * | 0.78 | 0.70 |
| Seafood | 85.00 (43.20–120.68) | 56.63 (28.35–87.35) | <0.001 | 0.77 * | 0.72 * | 0.70 | 0.64 |
| Dairy products | 90.00 (90.00–177.50) | 64.35 (17.50–169.70) | 0.549 | 0.75 * | 0.78 * | 0.71 | 0.75 |
| Snacks and nuts | 6.30 (0.00–28.05) | 5.60 (0.00–14.39) | 0.828 | 0.67 * | 0.64 * | 0.65 | 0.62 |
| Soybeans and soybean products | 54.40 (26.89–98.85) | 31.50 (15.75–52.50) | <0.001 | 0.69 * | 0.67 * | 0.53 | 0.54 |
| Vegetables | 297.91 (222.59–388.43) | 256.08 (191.89–321.70) | <0.001 | 0.73 * | 0.70 * | 0.68 | 0.64 |
| Fruits | 107.09 (54.30–150.83) | 107.09 (54.30–150.83) | 0.338 | 0.73 * | 0.65 * | 0.64 | 0.56 |
| Beverages | 0.00 (0.00–42.00) | 0.00 (0.00–35.00) | 0.464 | 0.70 * | 0.69 * | 0.56 | 0.54 |
| Nutrients | FFQ-1 | FFQ-2 | p a | SCC b | ICC c | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M (P25–P75) | M (P25–P75) | Crude | Adjusted d | Crude | Adjusted d | ||
| Energy (kcal) | 1572.04 (1426.76–1757.33) | 1469.67 (1222.87–1734.55) | 0.004 | 0.66 * | 0.67 | ||
| Protein (g) | 75.44 (62.96–90.45) | 68.64 (62.96–83.70) | 0.046 | 0.77 * | 0.41 * | 0.75 | 0.38 |
| Fat (g) | 46.51 (38.26–58.60) | 43.88 (37.21–53.31) | 0.082 | 0.78 * | 0.48 * | 0.74 | 0.46 |
| Carbohydrates (g) | 180.93 (154.54–216.97) | 175.33 (158.59–204.90) | 0.369 | 0.83 * | 0.67 * | 0.88 | 0.65 |
| Dietary fiber (g) | 8.61 (6.70–10.98) | 7.44 (6.30–9.21) | 0.002 | 0.78 * | 0.61 * | 0.67 | 0.48 |
| Cholesterol (mg) | 507.84 (409.64–595.22) | 518.50 (430.56–595.24) | 0.629 | 0.77 * | 0.65 * | 0.74 | 0.63 |
| Folate (mg) | 104.61 (75.33–138.53) | 105.76 (84.71–132.86) | 0.844 | 0.96 * | 0.94 * | 0.97 | 0.93 |
| Vitamin A (μg) | 424.73 (350.54–553.15) | 416.10 (349.33–516.51) | 0.454 | 0.83 * | 0.77 * | 0.83 | 0.77 |
| Vitamin B1 (mg) | 0.64 (0.53–0.78) | 0.62 (0.53–0.72) | 0.166 | 0.69 * | 0.34 * | 0.71 | 0.31 |
| Vitamin B2 (mg) | 0.96 (0.77–1.13) | 0.87 (0.72–1.06) | 0.022 | 0.79 * | 0.61 * | 0.78 | 0.59 |
| Vitamin B3 (mg) | 17.69 (14.18–21.53) | 16.31 (14.59–19.68) | 0.133 | 0.77 * | 0.48 * | 0.74 | 0.46 |
| Vitamin B6 (mg) | 0.23 (0.15–0.29) | 0.20 (0.15–0.26) | 0.103 | 0.85 * | 0.76 * | 0.86 | 0.75 |
| Vitamin C (mg) | 84.06 (62.23–113.57) | 81.38 (62.37–103.28) | 0.237 | 0.81 * | 0.75 * | 0.76 | 0.70 |
| Vitamin E (mg) | 8.76 (6.57–10.97) | 7.94 (6.54–9.65) | 0.075 | 0.68 * | 0.48 * | 0.57 | 0.46 |
| Calcium (mg) | 553.26 (418.85–689.63) | 482.75 (370.01–616.66) | 0.014 | 0.85 * | 0.75 * | 0.78 | 0.68 |
| Phosphorus (mg) | 1072.02 (878.17–1221.47) | 1028.42 (873.99–1146.06) | 0.284 | 0.82 * | 0.42 * | 0.87 | 0.46 |
| Potassium (mg) | 1863.56 (1491.40–2190.27) | 1825.29 (1512.76–2085.62) | 0.178 | 0.84 * | 0.60 * | 0.82 | 0.58 |
| Sodium (mg) | 701.86 (567.13–858.22) | 693.98 (605.33–802.53) | 0.677 | 0.85 * | 0.68 * | 0.87 | 0.66 |
| Magnesium (mg) | 269.66 (218.81–308.70) | 262.91 (215.92–308.67) | 0.660 | 0.89 * | 0.62 * | 0.92 | 0.63 |
| Iron (mg) | 17.97 (15.03–21.07) | 16.92 (15.47–20.26) | 0.158 | 0.78 * | 0.33 * | 0.77 | 0.30 |
| Zinc (mg) | 13.45 (10.79–15.85) | 13.45 (11.24–15.35) | 0.850 | 0.78 * | 0.51 * | 0.78 | 0.49 |
| Selenium (μg) | 68.56 (52.33–80.24) | 65.50 (54.28–75.34) | 0.219 | 0.76 * | 0.49 * | 0.74 | 0.47 |
| Copper (mg) | 1.62 (1.28–2.15) | 1.54 (1.24–1.93) | 0.087 | 0.79 * | 0.36 * | 0.33 | 0.34 |
| Manganese (mg) | 4.18 (3.37–5.25) | 3.89 (3.26–4.61) | 0.020 | 0.76 * | 0.55 * | 0.73 | 0.54 |
| Food (g/d) | (FFQ-1 + FFQ-2)/2 | 3d-24HDR | p a | SCC b | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M (P25–P75) | M (P25–P75) | Crude | Adjusted c | ||
| Refined rice and related products | 311.50 (202.75–437.50) | 333.33 (245.83–400.00) | 0.391 | 0.51 * | 0.52 * |
| Wheat products (e.g., noodles, bread) | 90.95 (43.09–126.68) | 100.00 (56.67–163.33) | 0.032 | 0.61 * | 0.64 * |
| Whole grains | 0.00 (0.00–10.68) | 0.00 (0.00–34.17) | 0.868 | 0.59 * | 0.50 * |
| Root and tuber vegetables | 14.00 (2.63–35.91) | 16.67 (0.00–33.33) | 0.079 | 0.58 * | 0.48 * |
| Processed meat | 0.00 (0.00–1.40) | 0.00 (0.00–0.00) | 0.069 | 0.64 * | 0.27 * |
| Eggs | 42.75 (34.00–50.00) | 33.33 (16.67–50.00) | 0.040 | 0.41 * | 0.40 * |
| Red meat | 106.88 (85.00–125.00) | 130.00(80.00–180.00) | 0.146 | 0.44 * | 0.41 * |
| Poultry | 18.00 (0.00–40.88) | 16.67 (0.00–47.50) | 0.207 | 0.54 * | 0.56 * |
| Organ meat | 0.00 (0.00–2.80) | 0.00 (0.00–0.00) | 0.071 | 0.57 * | 0.55 * |
| Seafood | 74.70 (42.43–102.41) | 60.00 (24.58–103.33) | 0.036 | 0.56 * | 0.46 * |
| Dairy products | 76.45 (8.75–177.50) | 50.00 (0.00–133.33) | <0.001 | 0.63 * | 0.62 * |
| Snacks and nuts | 5.43 (0.88–21.54) | 4.17 (0.00–30.83) | 0.305 | 0.69 * | 0.51 * |
| Soybeans and soybean products | 48.11 (21.23–75.73) | 35.84 (16.67–83.33) | 0.117 | 0.55 * | 0.53 * |
| Vegetables | 275.83 (208.55–352.49) | 266.67 (199.17–367.50) | 0.740 | 0.45 * | 0.41 * |
| Fruits | 107.09 (50.15–150.83) | 100.00 (33.33–141.25) | 0.035 | 0.72 * | 0.66 * |
| Beverages | 0.00 (0.00–24.50) | 0.00 (0.00–10.00) | 0.008 | 0.54 * | 0.50 * |
| Nutrients | (MFFQ-1 + MFFQ-2)/2 | 3d-24HDR | p a | SCC b | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M (P25–P75) | M (P25–P75) | Crude | Adjusted c | ||
| Energy (kcal) | 1519.94 (1344.21–1720.80) | 1608.70 (1370.50–1841.75) | 0.084 | 0.66 * | |
| Protein (g) | 73.82 (64.82–84.34) | 72.16 (60.33–82.75) | 0.098 | 0.77 * | 0.41 * |
| Fat (g) | 44.30 (38.53–56.26) | 44.07 (34.78–50.48) | 0.008 | 0.78 * | 0.48 * |
| Carbohydrates (g) | 179.29 (158.47–211.41) | 180.74 (145.83–207.38) | 0.759 | 0.83 * | 0.67 * |
| Dietary fiber (g) | 8.10 (6.78–10.08) | 8.70 (6.90–10.90) | 0.111 | 0.78 * | 0.61 * |
| Cholesterol (mg) | 504.80 (406.97–595.31) | 494.00 (395.5–658.5) | 0.862 | 0.77 * | 0.65 * |
| Folate (mg) | 104.06 (79.10–134.01) | 66.60 (49.68–97.38) | <0.001 | 0.96 * | 0.94 * |
| Vitamin A (μg) | 418.71 (344.00–523.23) | 406.00 (333.25–509.50) | 0.180 | 0.83 * | 0.77 * |
| Vitamin B1 (mg) | 0.63 (0.53–0.74) | 0.61 (0.52–0.72) | 0.241 | 0.69 * | 0.34 * |
| Vitamin B2 (mg) | 0.89 (0.75–1.09) | 0.82 (0.67–1.02) | 0.014 | 0.79 * | 0.61 * |
| Vitamin B3 (mg) | 17.18 (14.27–20.17) | 16.57 (13.63–18.45) | 0.034 | 0.77 * | 0.48 * |
| Vitamin B6 (mg) | 0.20 (0.15–0.27) | 0.31 (0.20–0.42) | 0.144 | 0.85 * | 0.76 * |
| Vitamin C (mg) | 81.00 (60.28–107.45) | 58.60 (36.88–82.30) | <0.001 | 0.81 * | 0.75 * |
| Vitamin E (mg) | 8.51 (6.70–10.23) | 8.60 (6.79–11.58) | 0.192 | 0.68 * | 0.48 * |
| Calcium (mg) | 529.84 (394.52–645.50) | 526.50 (414.75–710.00) | 0.241 | 0.85 * | 0.75 * |
| Phosphorus (mg) | 1054.32 (888.11–1167.37) | 973.00 (822.50–1148.00) | 0.039 | 0.82 * | 0.42 * |
| Potassium (mg) | 1833.73 (1500.44–2128.20) | 1708.50 (1349.25–2023.75) | 0.045 | 0.84 * | 0.60 * |
| Sodium (mg) | 717.07 (568.00–841.36) | 605.05 (475.78–772.75) | <0.001 | 0.85 * | 0.68 * |
| Magnesium (mg) | 267.24 (218.13–310.92) | 241.00 (202–283.25) | 0.660 | 0.89 * | 0.62 * |
| Iron (mg) | 17.57 (15.07–20.43) | 17.00 (13.8–19.63) | 0.158 | 0.78 * | 0.33 * |
| Zinc (mg) | 13.44 (11.14–15.86) | 13.86 (10.85–16.33) | 0.850 | 0.78 * | 0.51 * |
| Selenium (μg) | 66.21 (53.51–77.73) | 54.57 (44.92–68.37) | 0.219 | 0.76 * | 0.49 * |
| Copper (mg) | 1.58 (1.29–2.05) | 1.80 (1.43–2.17) | 0.087 | 0.79 * | 0.36 * |
| Manganese (mg) | 3.99 (3.31–5.00) | 4.02 (3.43–4.81) | 0.020 | 0.76 * | 0.55 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, L.; Chen, Y.; Luo, Z.; Wang, Q.; Zou, F.; Lin, Y. Evaluation of the Reliability and Validity of a Food Frequency Questionnaire Using Three-Day 24-Hour Dietary Recalls: A Study in Fujian, China. Nutrients 2025, 17, 2270. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17142270
Cheng L, Chen Y, Luo Z, Wang Q, Zou F, Lin Y. Evaluation of the Reliability and Validity of a Food Frequency Questionnaire Using Three-Day 24-Hour Dietary Recalls: A Study in Fujian, China. Nutrients. 2025; 17(14):2270. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17142270
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Lu, Yuhang Chen, Zhijie Luo, Qingying Wang, Fengqin Zou, and Yulan Lin. 2025. "Evaluation of the Reliability and Validity of a Food Frequency Questionnaire Using Three-Day 24-Hour Dietary Recalls: A Study in Fujian, China" Nutrients 17, no. 14: 2270. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17142270
APA StyleCheng, L., Chen, Y., Luo, Z., Wang, Q., Zou, F., & Lin, Y. (2025). Evaluation of the Reliability and Validity of a Food Frequency Questionnaire Using Three-Day 24-Hour Dietary Recalls: A Study in Fujian, China. Nutrients, 17(14), 2270. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17142270







