Clinical Phenotypes of Severe Cow’s Milk Protein Allergy with Various Responses to Amino Acid-Based Formula
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Statistical Methods
3. Results
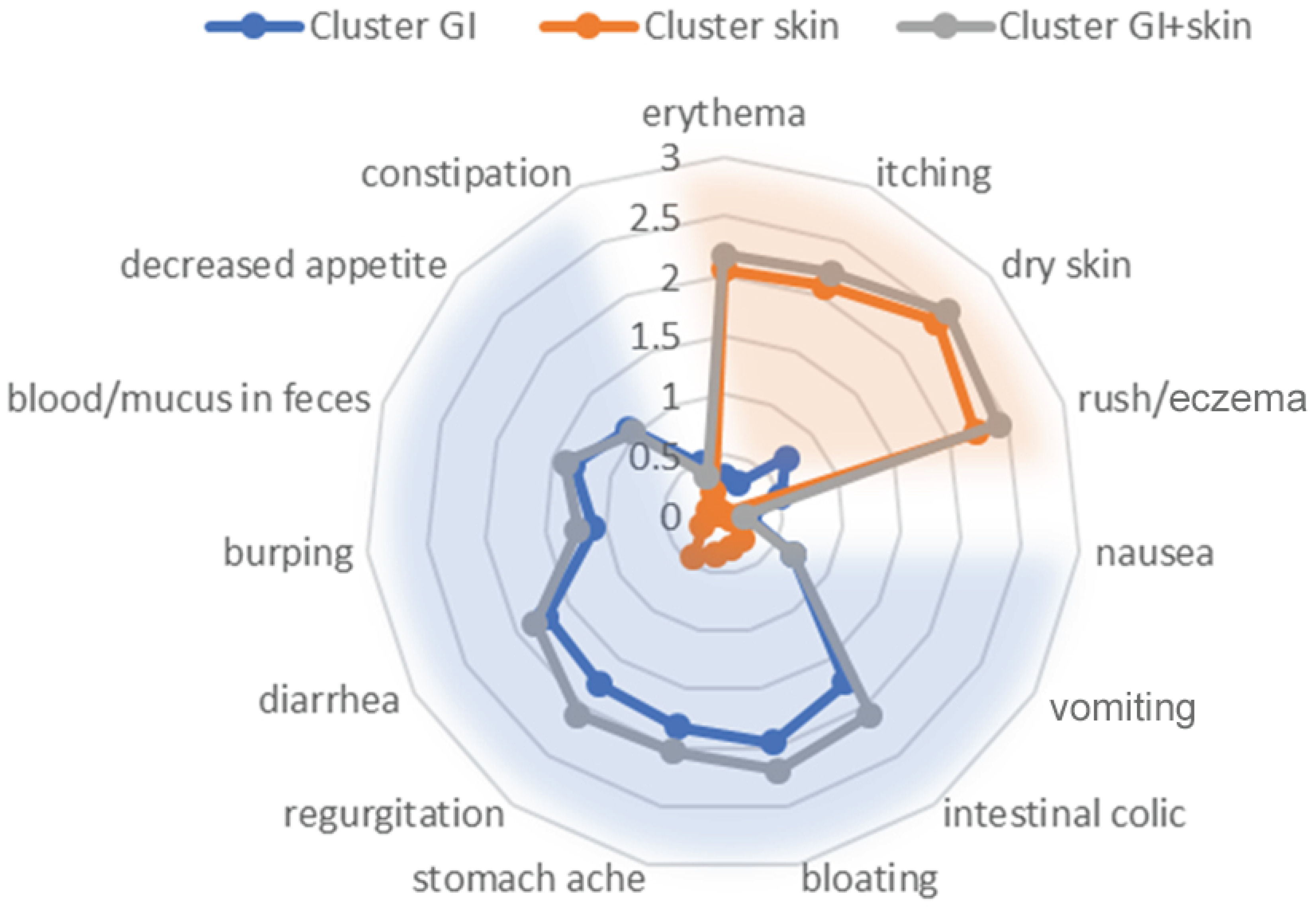
3.1. Baseline Characteristics and Cluster Analysis
3.2. Validation of Clustering
3.3. The Effect of the Intervention by Cluster
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AAF | amino-acid based formula |
| CMA | cow’s milk protein allergy |
| EAACI | European Academy of Allergy and Clinical Immunology |
| EHF | extensively hydrolized formula |
| EHCF | extensively hydrolized casein formula |
| EHWF | extensively hydrolized whey formula |
| ESPGHAN | European Society for Paediatric Gastroenterology Hepatology and Nutrition |
| FPIES | Food Protein-Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome |
| GERD | Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease |
| GI | gastrointestinal |
| IgE | immunoglobulin E |
| OFC | Oral Food challenge |
References
- Sampath, V.; Abrams, E.M.; Adlou, B.; Akdis, C.; Akdis, M.; Brough, H.A.; Chan, S.; Chatchatee, P.; Chinthrajah, R.S.; Cocco, R.R.; et al. Food allergy across the globe. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2021, 148, 1347–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golden, D.B.K.; Wang, J.; Waserman, S.; Akin, C.; Campbell, R.L.; Ellis, A.K.; Greenhawt, M.; Lang, D.M.; Ledford, D.K.; Lieberman, J.; et al. Anaphylaxis: A 2023 practice parameter update. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2024, 132, 124–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonasson, K.; Clausen, M.; Bjornsdottir, K.L.; Sigurdardottir, S.E.; Roberts, G.; Grimshaw, K.; Papadopoulos, N.G.; Xepapadaki, P.; Fiandor, A.; Quirce, S.; et al. Prevalence and early-life risk factors of school-age allergic multimorbidity: The EuroPrevall-iFAAM birth cohort. Allergy 2021, 76, 2855–2865. [Google Scholar]
- Lyons, S.A.; Clausen, M.; Knulst, A.C.; Ballmer-Weber, B.K.; Fernandez-Rivas, M.; Barreales, L.; Bieli, C.; Dubakiene, R.; Fernandez-Perez, C.; Jedrzejczak-Czechowicz, M.; et al. Prevalence of Food Sensitization and Food Allergy in Children Across Europe. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pr. 2020, 8, 2736–2746.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, R.; Venter, C.; Bognanni, A.; Szajewska, H.; Shamir, R.; Nowak-Wegrzyn, A.; Fiocchi, A.; Vandenplas, Y. World Allergy Organization (WAO) Diagnosis and Rationale for Action against Cow’s Milk Allergy (DRACMA) Guideline update—VII—Milk elimination and reintroduction in the diagnostic process of cow’s milk allergy. WAO J. 2023, 16, 100785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riggioni, C.; Ricci, C.; Moya, B.; Wong, D.; van Goor, E.; Bartha, I.; Buyuktiryaki, B.; Giovannini, M.; Jayasinghe, S.; Jaumdally, H.; et al. Systematic review and meta-analyses on the accuracy of diagnostic tests for IgE-mediated food allergy. Allergy 2024, 79, 324–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nocerino, R.; Bedogni, G.; Carucci, L.; Cosenza, L.; Cozzolino, T.; Paparo, L.; Palazzo, S.; Riva, L.; Verduci, E.; Canani, R.B. The Impact of Formula Choice for the Management of Pediatric Cow’s Milk Allergy on the Occurrence of Other Allergic Manifestations: The Atopic March Cohort Study. J. Pediatr. 2021, 232, 183–191.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alduraywish, S.A.; Standl, M.; Lodge, C.J.; Abramson, M.J.; Allen, K.J.; Erbas, B.; von Berg, A.; Heinrich, J.; Lowe, A.J.; Dharmage, S.C. Is there a march from early food sensitization to later childhood allergic airway disease? Results from two prospective birth cohort studies. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2017, 28, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, M.M.; Nissen, S.P.; Halken, S.; Høst, A. The natural course of cow’s milk allergy and the development of atopic diseases into adulthood. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2021, 32, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, S.A.; Fiocchi, A.; Baars, T.; Jordakieva, G.; Nowak-Wegrzyn, A.; Pali-Schöll, I.; Passanisi, S.; Pranger, C.L.; Roth-Walter, F.; Takkinen, K.; et al. Diagnosis and Rationale for Action against Cow’s Milk Allergy (DRACMA) Guidelines update—III—Cow’s milk allergens and mechanisms triggering immune activation. WAO J. 2022, 15, 100668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venter, C.; Roth-Walter, F.; Vassilopoulos, E.; Hicks, A. Dietary management of IgE and non-IgE-mediated food allergies in pediatric patients. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2024, 35, e14100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bognanni, A.; Fiocchi, A.; Arasi, S.; Chu, D.K.; Ansotegui, I.; Assa’Ad, A.H.; Bahna, S.L.; Canani, R.B.; Bozzola, M.; Dahdah, L.; et al. World Allergy Organization (WAO) Diagnosis and Rationale for Action against Cow’s Milk Allergy (DRACMA) guideline update—XII—Recommendations on milk formula supplements with and without probiotics for infants and toddlers with CMA. WAO J. 2024, 17, 100888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venter, C.; Meyer, R.; Groetch, M.; Nowak-Wegrzyn, A.; Mennini, M.; Pawankar, R.; Kamenwa, R.; Assa’Ad, A.; Amara, S.; Fiocchi, A.; et al. World Allergy Organization (WAO) Diagnosis and Rationale for Action against Cow’s Milk Allergy (DRACMA) guidelines update—XVI—Nutritional management of cow’s milk allergy. WAO J. 2024, 17, 100931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobrakowski, Ł.; Błażowski, J.; Boligłowa, M.; Majak, P. The clinical presentation, diagnostic approach, dietary treatment, and effectiveness of Nutramigen PURAMINO amino acid-based formula in the management of severe cow’s milk allergy. Stand. Med. Pediatr. 2023, 20, 642–650. [Google Scholar]
- Biernacki, C.; Jacques, J. Model-based clustering of multivariate ordinal data relying on a stochastic binary search algorithm. Stat. Comput. 2016, 26, 929–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muraro, A.; Werfel, T.; Hoffmann-Sommergruber, K.; Roberts, G.; Beyer, K.; Bindslev-Jensen, C.; Cardona, V.; Dubois, A.; Dutoit, G.; Eigenmann, P.; et al. EAACI food allergy and anaphylaxis guidelines: Diagnosis and management of food allergy. Allergy 2014, 69, 1008–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiocchi, A.; Brozek, J.; Schünemann, H.; Bahna, S.L.; von Berg, A.; Beyer, K.; Bozzola, M.; Bradsher, J.; Compalati, E.; Ebisawa, M.; et al. World Allergy Organization (WAO) Diagnosis and Rationale for Action against Cow’s Milk Allergy (DRACMA) Guidelines. World Allergy Organ. J. 2010, 3, 57–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, D.J.; Murch, S.H.; Rafferty, K.; Wallis, P.; Green, C.J. The efficacy of amino acid-based formulas in relieving the symptoms of cow’s milk allergy: A systematic review. Clin. Exp. Allergy. 2007, 37, 808–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isolauri, E.; Sutas, Y.; Makinen-Kiljunen, S.; Oja, S.S.; Isosomppi, R.; Turjanmaa, K. Efficacy and safety of hydrolyzed cow milk and amino acid-derived formulae in infants with cow milk allergy. J. Pediatr. 1995, 127, 550–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gold, M.S.; Quinn, P.J.; Campbell, D.E.; Peake, J.; Smart, J.; Robinson, M.; O’Sullivan, M.; Vogt, J.K.; Pedersen, H.K.; Liu, X.; et al. Effects of an Amino Acid-Based Formula Supplemented with Two Human Milk Oligosaccharides on Growth, Tolerability, Safety, and Gut Microbiome in Infants with Cow’s Milk Protein Allergy. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koletzko, S.; Niggemann, B.; Arató, A.; Dias, J.A.; Heuschkel, R.; Husby, S.; Mearin, M.L.; Papadopoulou, A.; Ruemmele, F.M.; Staiano, A.; et al. European Society of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition. Diagnostic approach and management of cow’s-milk protein allergy in infants and children: ESPGHAN GI Committee practical guidelines. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2012, 55, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venter, C.; Brown, T.; Meyer, R.; Walsh, J.; Shah, N.; Nowak-Węgrzyn, A.; Chen, T.X.; Fleischer, D.M.; Heine, R.G.; Levin, M.; et al. Better recognition, diagnosis and management of non-IgE-mediated cow’s milk allergy in infancy: iMAP-an international interpretation of the MAP (Milk Allergy in Primary Care) guideline. Clin. Transl. Allergy 2017, 7, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, R.; Groetch, M.; Venter, C. When Should Infants with Cow’s Milk Protein Allergy Use an Amino Acid Formula? A Practical Guide. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2018, 6, 383–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Variable | n (% of Group) |
|---|---|
| Female | 95 (40.9) |
| Male | 137 (59.1) |
| Age, days * (mean ± SD) | 142.02 ± 82.69 |
| Age, months * (mean ± SD) | 4.67 ± 2.72 |
| Height, cm ** (mean ± SD) | 64.13 ± 7.18 |
| Weight, kg (mean ± SD) | 6.53 ± 1.93 |
| Height—percentile *** | |
| <3 | 3 (1.3) |
| 3–10 | 27 (11.6) |
| 10–25 | 57 (24.6) |
| 25–50 | 58 (25.0) |
| 50–75 | 52 (22.4) |
| 75–90 | 25 (10.8) |
| 90–97 | 7 (3.0) |
| >97 | 3 (1.3) |
| Weight—percentile *** | |
| <3 | 13 (5.6) |
| 3–10 | 46 (19.8) |
| 10–25 | 53 (22.8) |
| 25–50 | 50 (21.6) |
| 50–75 | 52 (22.4) |
| 75–90 | 14 (6.0) |
| 90–97 | 4 (1.7) |
| >97 | 0 (0.0) |
| Allergic diseases in family | 156 (67.2) |
| mother | 82 (35.3) |
| father | 62 (26.7) |
| siblings | 61 (26.3) |
| Variable: | Cluster A (GI) n = 90 | Cluster B (Skin) n = 79 | Cluster C (GI + Skin) n = 60 | p | Post Hoc Test *** |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, days * | 128.12 ± 85.31 | 160.48 ± 80.39 | 137.60 ± 79.15 | 0.038 1 | AB 2 |
| Height, cm ** | 62.80 ± 8.45 | 65.49 ± 5.87 | 63.68 ± 5.72 | 0.003 | AB |
| Weight, kg | 6.15 ± 2.10 | 7.01 ± 1.91 | 6.50 ± 1.60 | 0.003 | AB |
| Variables: | Cluster A (GI) n = 89 | Cluster B (Skin) n = 76 | Cluster C (GI + Skin) n = 58 | p | Hoc Test * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total symptom scores (sum of all symptom severity scores) >0 on visit I | −14.28 ± 7.04 | −9.62 ± 4.46 | −20.72 ± 6.59 | <0.001 3 | AB, AC, BC 2 |
| Skin | |||||
| Erythema | −0.19 ± 0.67 | −1.47 ± 0.89 | −1.53 ± 0.80 | <0.001 | AB, AC |
| Itching | −0.19 ± 0.58 | −1.59 ± 0.98 | −1.67 ± 0.80 | <0.001 | AB, AC |
| Dry skin | −0.36 ± 0.77 | −1.43 ± 0.91 | −1.64 ± 0.77 | <0.001 1 | AB, AC 2 |
| Rush/edema | −0.37 ± 0.73 | −1.75 ± 0.91 | −1.91 ± 0.82 | <0.001 | AB, AC |
| Urticaria | −0.12 ± 0.52 | −0.26 ± 0.64 | −0.22 ± 0.65 | 0.190 | − |
| Angioedema | 0.00 ± 0.15 | −0.01 ± 0.50 | −0.07 ± 0.37 | 0.420 | − |
| Gastrointestinal | |||||
| Stomach ache ** | −1.51 ± 0.99 | −0.17 ± 0.82 | −1.50 ± 0.82 | <0.001 | AB, BC |
| Diarrhea | −1.54 ± 1.06 | −0.17 ± 0.50 | −1.66 ± 0.89 | <0.001 | AB, BC |
| Nausea | −0.15 ± 0.55 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | −0.16 ± 0.41 | 0.024 | BC |
| Vomiting | −0.62 ± 0.98 | −0.07 ± 0.30 | −0.60 ± 0.84 | <0.001 | AB, BC |
| Regurgitation | −1.26 ± 1.02 | −0.24 ± 0.86 | −1.57 ± 0.75 | <0.001 | AB, BC |
| Burping | −0.89 ± 1.02 | −0.01 ± 0.31 | −1.05 ± 0.98 | <0.001 | AB, BC |
| Bloating | −1.48 ± 0.99 | −0.20 ± 0.71 | −1.72 ± 0.79 | <0.001 | AB, BC |
| Decreased appetite | −0.93 ± 1.12 | 0.00 ± 0.40 | −0.98 ± 1.02 | <0.001 | AB, BC |
| Blood/mucus in feces | −1.26 ± 1.12 | −0.14 ± 0.45 | −1.29 ± 0.94 | <0.001 | AB, BC |
| Intestinal colic *** | −1.43 ± 1.09 | −0.18 ± 0.60 | −1.83 ± 0.92 | <0.001 | AB, BC, AC |
| Constipation | −0.34 ± 0.77 | −0.17 ± 0.62 | −0.29 ± 0.75 | 0.129 | − |
| Respiratory | |||||
| Restricted nasal passage | −0.07 ± 0.47 | −0.14 ± 0.48 | −0.12 ± 0.65 | 0.517 | − |
| Running nose | −0.06 ± 0.31 | −0.14 ± 0.56 | −0.10 ± 0.52 | 0.549 | − |
| Chronic cough | −0.09 ± 0.42 | −0.03 ± 0.16 | −0.02 ± 0.35 | 0.677 | − |
| Wheezing breath | −0.12 ± 0.52 | −0.13 ± 0.44 | −0.14 ± 0.63 | 0.801 | − |
| Laryngeal edema | −0.02 ± 0.26 | −0.03 ± 0.23 | 0.03 ± 0.32 | 0.549 | − |
| Dyspnea | −0.10 ± 0.48 | −0.14 ± 0.51 | 0.03 ± 0.32 | 0.068 | − |
| Other symptoms | |||||
| Tearing eyes | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.00 ± 0.16 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | >0.999 | − |
| Itching eyes | −0.01 ± 0.11 | −0.01 ± 0.11 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.697 | − |
| Eye redness | 0.00 ± 0.00 | −0.04 ± 0.26 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.143 | − |
| Anxiety | −0.13 ± 0.53 | −0.11 ± 0.42 | −0.05 ± 0.39 | 0.434 | − |
| Sleep disorders | −0.09 ± 0.47 | −0.08 ± 0.36 | 0.00 ± 0.26 | 0.378 | − |
| Apathy | −0.02 ± 0.21 | −0.03 ± 0.16 | −0.03 ± 0.26 | 0.777 | − |
| Paleness | −0.02 ± 0.34 | −0.08 ± 0.42 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.177 | − |
| Heavy sweating after a meal | −0.02 ± 0.21 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.471 | − |
| Growing disorders | −0.13 ± 0.63 | −0.08 ± 0.42 | −0.03 ± 0.18 | 0.940 | − |
| Variable | β | 95% CI for β | Std. β | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cluster | ||||
| A (vs. B) | −4.67 | −6.52 to −2.81 | −0.62 | <0.001 |
| A (vs. C) | 6.44 | 4.15 to 8.73 | 0.86 | <0.001 |
| B (vs. C) | 11.11 | 9.21 to 13.00 | 1.49 | <0.001 |
| Sex, male | 0.45 | −1.56 to 2.45 | 0.06 | 0.660 |
| Age at baseline days | 0.01 | 0.00 to 0.02 | 0.13 | 0.058 |
| Height at baseline, cm | 0.17 | 0.03 to 0.31 | 0.16 | 0.020 |
| Weight at baseline, kg | 0.68 | 0.16 to 1.20 | 0.17 | 0.010 |
| Allergic diseases in family | −1.73 | −3.83 to 0.36 | −0.23 | 0.104 |
| Mother | −4.15 | −6.15 to −2.14 | −0.56 | <0.001 |
| Father | −2.64 | −4.85 to −0.42 | −0.35 | 0.020 |
| Siblings | 0.00 | −2.23 to 2.23 | 0.00 | 0.997 |
| Additional intervention * | ||||
| Antihistamine | −1.30 | −3.92 to 1.32 | −0.17 | 0.330 |
| Emollients | −1.17 | −3.17 to 0.83 | −0.16 | 0.251 |
| Probiotics | −3.05 | −5.10 to −0.99 | −0.41 | 0.004 |
| Breastfeeding | 0.58 | −1.66 to 2.82 | 0.08 | 0.609 |
| Reason for introducing AAF: | ||||
| Symptoms did not resolve after extensively hydrolyzed formula (EHF) | 0.58 | −1.74 to 2.90 | 0.08 | 0.623 |
| Severe gastrointestinal symptoms | −4.67 | −6.58 to −2.77 | −0.63 | <0.001 |
| Severe atopic dermatitis | −1.73 | −3.74 to 0.27 | −0.23 | 0.090 |
| Food allergy to multiple ingredients | −1.08 | −5.29 to 3.14 | −0.14 | 0.615 |
| Lack of recovery after mother’s elimination diet | −1.59 | −3.80 to 0.62 | −0.21 | 0.157 |
| Growth retardation | −5.72 | −8.27 to −3.17 | −0.77 | <0.001 |
| Anaphylaxis | −2.64 | −17.43 to 12.14 | −0.35 | 0.725 |
| Other | −0.95 | −5.51 to 3.61 | −0.13 | 0.682 |
| Variable | β | 95% CI for β | Std. β | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cluster | ||||
| A (GI) | 4.18 | 2.02 to 6.33 | −0.56 | <0.001 |
| B (skin) | 9.73 | 7.70 to 11.75 | 0.74 | <0.001 |
| C (GI + skin) (reference) | - | - | - | - |
| Allergic diseases—mother | −2.14 | −3.79 to −0.49 | −0.29 | 0.011 |
| Allergic diseases—father | −1.88 | −3.62 to −0.15 | −0.25 | 0.034 |
| Reason for AAF implementation—growth retardation | −3.08 | −5.16 to −1.00 | −0.41 | 0.004 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Błażowski, Ł.; Podlecka, D.; Brzozowska, A.; Jerzyńska, J.; Seweryn, M.; Błażowski, M.; Majak, P. Clinical Phenotypes of Severe Cow’s Milk Protein Allergy with Various Responses to Amino Acid-Based Formula. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1809. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17111809
Błażowski Ł, Podlecka D, Brzozowska A, Jerzyńska J, Seweryn M, Błażowski M, Majak P. Clinical Phenotypes of Severe Cow’s Milk Protein Allergy with Various Responses to Amino Acid-Based Formula. Nutrients. 2025; 17(11):1809. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17111809
Chicago/Turabian StyleBłażowski, Łukasz, Daniela Podlecka, Agnieszka Brzozowska, Joanna Jerzyńska, Michał Seweryn, Marcin Błażowski, and Paweł Majak. 2025. "Clinical Phenotypes of Severe Cow’s Milk Protein Allergy with Various Responses to Amino Acid-Based Formula" Nutrients 17, no. 11: 1809. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17111809
APA StyleBłażowski, Ł., Podlecka, D., Brzozowska, A., Jerzyńska, J., Seweryn, M., Błażowski, M., & Majak, P. (2025). Clinical Phenotypes of Severe Cow’s Milk Protein Allergy with Various Responses to Amino Acid-Based Formula. Nutrients, 17(11), 1809. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17111809





