The Gut Microbiota in Young Adults with High-Functioning Autism Spectrum Disorder and Its Performance as Diagnostic Biomarkers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Participants
2.2. Sample Size
2.3. Questionnaires
2.4. Sample Collection, DNA Extraction and Sequencing
2.5. Bioinformatics and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographics and Clinical Characteristics of the Participants
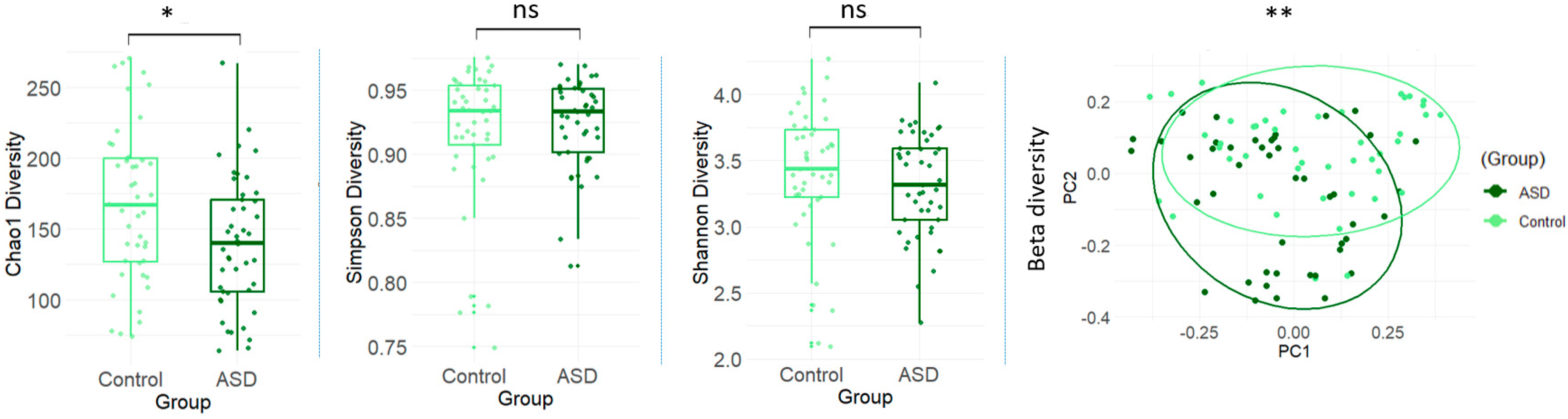
3.2. Gut Microbial Diversity Between ASD and Control Groups
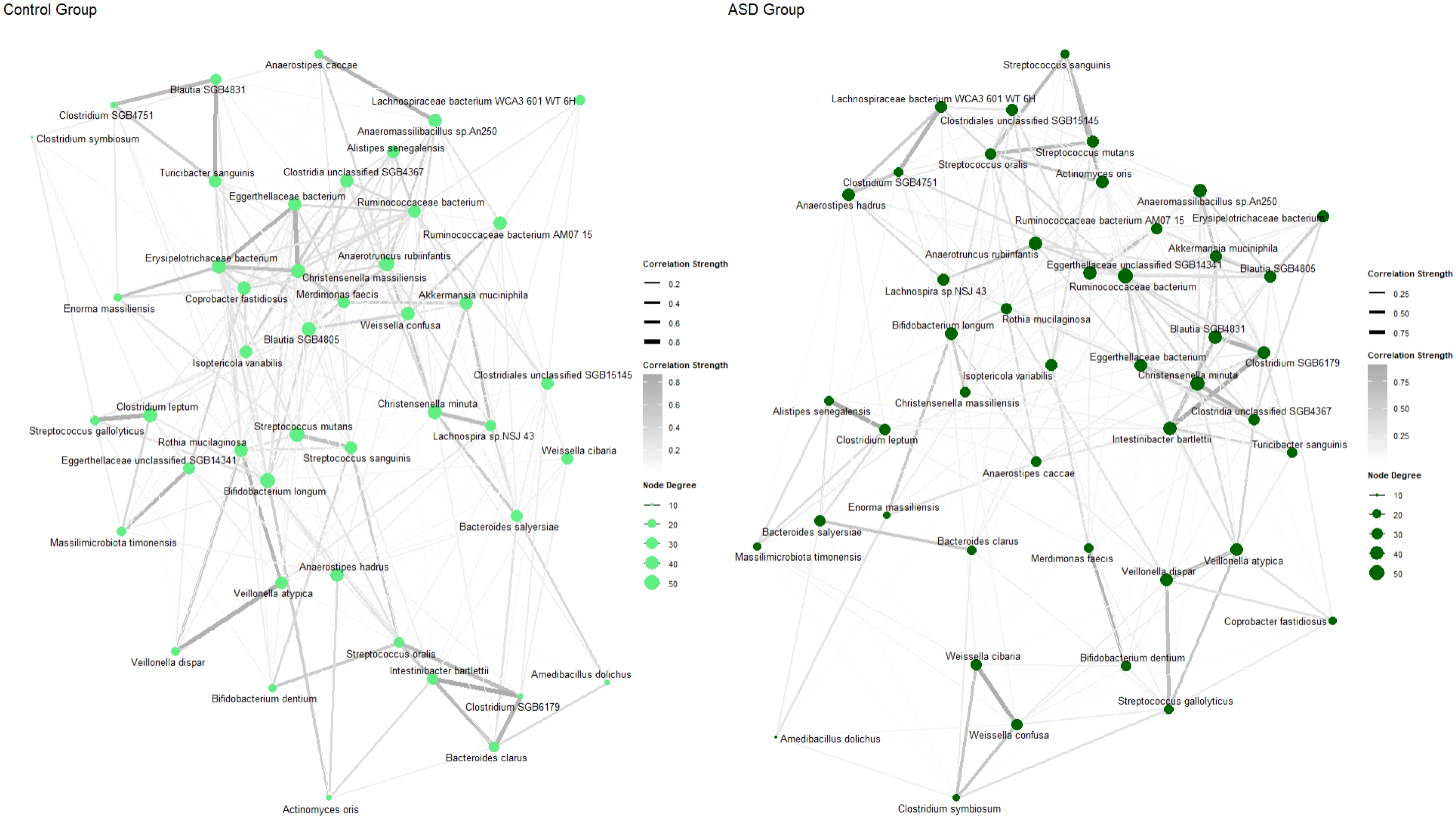
3.3. Abundance of Microbial Species Between ASD and Control Groups
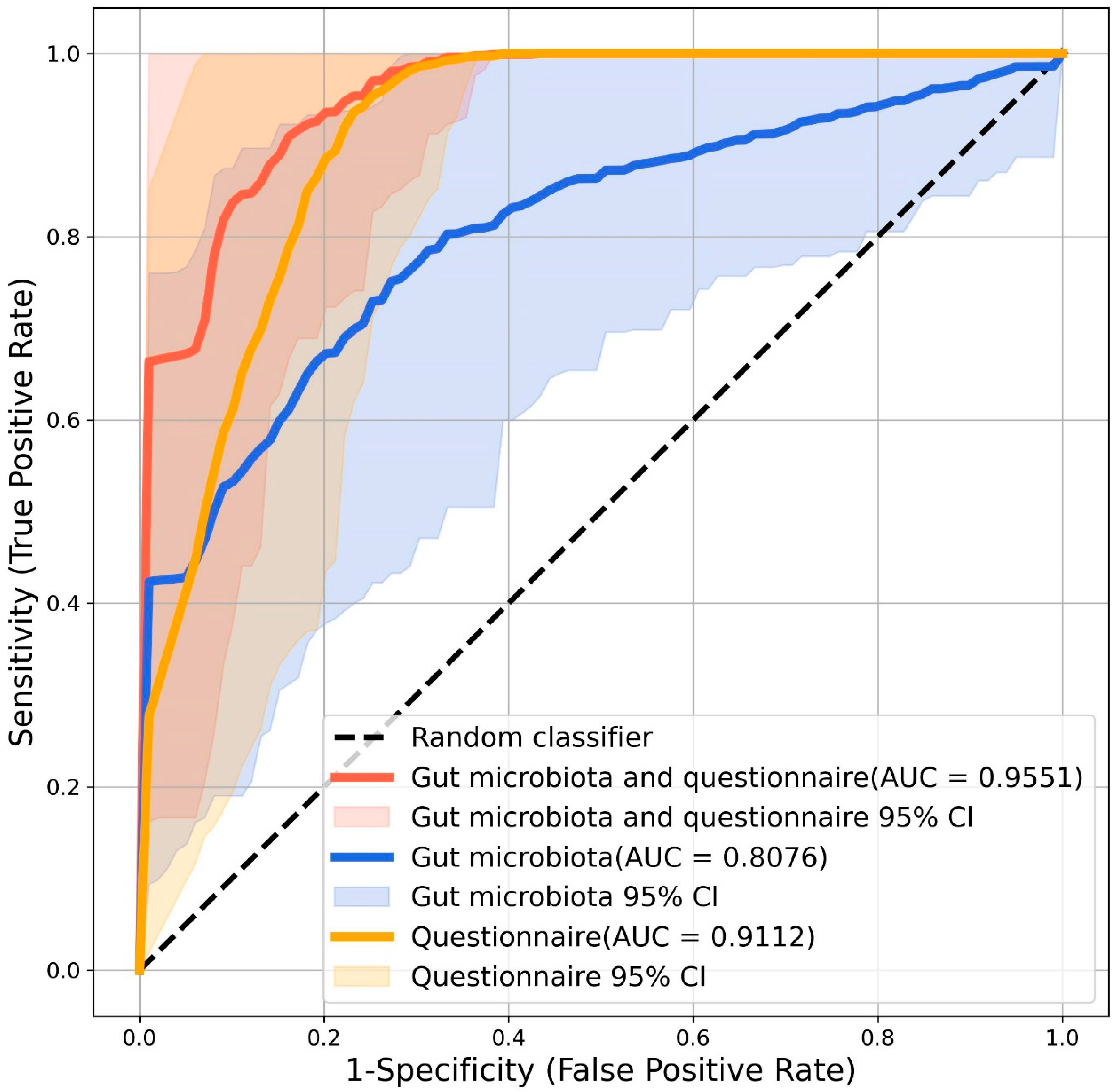
3.4. Microbial Biomarkers for ASD Diagnosis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ASD | Autism spectrum disorder |
| ID | Intellectual disability |
| AND | Adult Neurodevelopmental Service |
| IMH | Institute of Mental Health |
| DSM-5 | Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| FGI | Functional Gastrointestinal |
| DASH | Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension |
| CPM | Copies per million |
| FDR | False discovery rate |
| ROC | Receiver operating characteristic |
| AUC | Area under the curve |
| IQR | Interquartile range |
| PCoA | Principal coordinate analysis |
| SCFA | Short-chain fatty acids |
References
- Diagnostic and Statistical Mannual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition, Text Revision; American Psychiatric Association: Washington DC, USA, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Zeidan, J.; Fombonne, E.; Scorah, J.; Ibrahim, A.; Durkin, M.S.; Saxena, S.; Yusuf, A.; Shih, A.; Elsabbagh, M. Global prevalence of autism: A systematic review update. Autism Res. 2022, 15, 778–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maenner, M.J.; Warren, Z.; Williams, A.R.; Amoakohene, E.; Bakian, A.V.; Bilder, D.A.; Durkin, M.S.; Fitzgerald, R.T.; Furnier, S.M.; Hughes, M.M.; et al. Prevalence and Characteristics of Autism Spectrum Disorder Among Children Aged 8 Years—Autism and Developmental Disabilities Monitoring Network, 11 Sites, United States, 2020. MMWR Surveill. Summ. 2023, 72, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Lu, F.; Wang, X.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, R.; He, P.; Zheng, X. The economic burden of autism spectrum disorder with and without intellectual disability in China: A nationwide cost-of-illness study. Asian J. Psychiatr. 2024, 92, 103877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheroni, C.; Caporale, N.; Testa, G. Autism spectrum disorder at the crossroad between genes and environment: Contributions, convergences, and interactions in ASD developmental pathophysiology. Mol. Autism 2020, 11, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rylaarsdam, L.; Guemez-Gamboa, A. Genetic Causes and Modifiers of Autism Spectrum Disorder. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2019, 13, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Geng, H.; Liu, W.; Zhang, G. Prenatal, perinatal, and postnatal factors associated with autism: A meta-analysis. Medicine 2017, 96, e6696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cryan, J.F.; Dinan, T.G. Mind-altering microorganisms: The impact of the gut microbiota on brain and behaviour. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2012, 13, 701–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Xiao, H.; Zhu, H.; Du, Y.; Wang, L. Revealing the gut microbiome mystery: A meta-analysis revealing differences between individuals with autism spectrum disorder and neurotypical children. Biosci. Trends 2024, 18, 233–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, O.W.H.; Lam, A.M.W.; Or, B.P.N.; Mo, F.Y.M.; Shea, C.K.S.; Lai, K.Y.C.; Ma, S.L.; Hung, S.F.; Chan, S.; Kwong, T.N.Y.; et al. Disentangling the relationship of gut microbiota, functional gastrointestinal disorders and autism: A case-control study on prepubertal Chinese boys. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 10659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.C.; Lin, H.Y.; Chien, Y.; Tung, Y.H.; Ni, Y.H.; Gau, S.S. Altered gut microbiota correlates with behavioral problems but not gastrointestinal symptoms in individuals with autism. Brain Behav. Immun. 2022, 106, 161–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharon, G.; Cruz, N.J.; Kang, D.W.; Gandal, M.J.; Wang, B.; Kim, Y.M.; Zink, E.M.; Casey, C.P.; Taylor, B.C.; Lane, C.J.; et al. Human Gut Microbiota from Autism Spectrum Disorder Promote Behavioral Symptoms in Mice. Cell 2019, 177, 1600–1618.e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, D.W.; Adams, J.B.; Coleman, D.M.; Pollard, E.L.; Maldonado, J.; McDonough-Means, S.; Caporaso, J.G.; Krajmalnik-Brown, R. Long-term benefit of Microbiota Transfer Therapy on autism symptoms and gut microbiota. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yu, L.; Liu, Z.; Che, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, M.; Yang, G.; Cao, A. FMT intervention decreases urine 5-HIAA levels: A randomized double-blind controlled study. Front Med. 2024, 11, 1411089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Q.; Wong, O.W.H.; Lu, W.; Wan, Y.; Zhang, L.; Xu, W.; Li, M.K.T.; Liu, C.; Cheung, C.P.; Ching, J.Y.L.; et al. Multikingdom and functional gut microbiota markers for autism spectrum disorder. Nat. Microbiol. 2024, 9, 2344–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinninella, E.; Raoul, P.; Cintoni, M.; Franceschi, F.; Miggiano, G.A.D.; Gasbarrini, A.; Mele, M.C. What is the Healthy Gut Microbiota Composition? A Changing Ecosystem across Age, Environment, Diet, and Diseases. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.Y.; Berg, C. Participation of young adults with high-functioning autism in Taiwan: A pilot study. OTJR Occup. Particip. Health 2014, 34, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieting, J.; Baumann, M.V.; Deest-Gaubatz, S.; Bleich, S.; Eberlein, C.K.; Frieling, H.; Deest, M. Structured neurological soft signs examination reveals motor coordination deficits in adults diagnosed with high-functioning autism. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 16123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, M.C.; Baron-Cohen, S. Identifying the lost generation of adults with autism spectrum conditions. Lancet Psychiatry 2015, 2, 1013–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, J.; Zhang, M.W.; Sajith, S.G.; Tan, G.M.; Wei, K.C. Misdiagnosis of Psychosis and Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder in a Young Patient with Autism Spectrum Disorder. Case Rep. Psychiatry 2023, 2023, 7705913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, J.P.; Tan, H.T.; Lam, K.F.; Lim, J.M.; Cheak, C.C.; Wei, K.C.; Sajith, S.G.; Chai, S.B.; Tan, G.M.Y. Adult neurodevelopmental services in Singapore: A sociodemographic and clinical profile at a tertiary psychiatric hospital. Asia Pac. Psychiatry 2020, 12, e12388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faul, F.; Erdfelder, E.; Lang, A.G.; Buchner, A. G*Power 3: A flexible statistical power analysis program for the social, behavioral, and biomedical sciences. Behav. Res. Methods 2007, 39, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruzich, E.; Allison, C.; Smith, P.; Watson, P.; Auyeung, B.; Ring, H.; Baron-Cohen, S. Measuring autistic traits in the general population: A systematic review of the Autism-Spectrum Quotient (AQ) in a nonclinical population sample of 6,900 typical adult males and females. Mol. Autism 2015, 6, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodbury-Smith, M.R.; Robinson, J.; Wheelwright, S.; Baron-Cohen, S. Screening adults for Asperger Syndrome using the AQ: A preliminary study of its diagnostic validity in clinical practice. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2005, 35, 331–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, Y.; Kitada, R.; Miyahara, M.; Kochiyama, T.; Naruse, H.; Sadato, N.; Okazawa, H.; Kosaka, H. Altered perspective-dependent brain activation while viewing hands and associated imitation difficulties in individuals with autism spectrum disorder. Neuroimage Clin. 2018, 19, 384–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, Y.; Cheong, P.K.; Fang, F.F.; Cheung, C.K.Y.; Lan, L.L.; Yuen, K.W.K.; Ching, J.Y.L.; Mak, A.D.P.; Wu, J.C. A symptom severity questionnaire for patients suffering from functional gastrointestinal disorder: FGI-Checklist. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 35, 1130–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitton, C.; Ho, J.C.Y.; Rebello, S.A.; van Dam, R.M. Relative validity and reproducibility of dietary quality scores from a short diet screener in a multi-ethnic Asian population. Public Health Nutr. 2018, 21, 2735–2743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fung, T.T.; Chiuve, S.E.; McCullough, M.L.; Rexrode, K.M.; Logroscino, G.; Hu, F.B. Adherence to a DASH-style diet and risk of coronary heart disease and stroke in women. Arch. Intern. Med. 2008, 168, 713–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco-Miguez, A.; Beghini, F.; Cumbo, F.; McIver, L.J.; Thompson, K.N.; Zolfo, M.; Manghi, P.; Dubois, L.; Huang, K.D.; Thomas, A.M.; et al. Extending and improving metagenomic taxonomic profiling with uncharacterized species using MetaPhlAn 4. Nat. Biotechnol. 2023, 41, 1633–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beghini, F.; McIver, L.J.; Blanco-Miguez, A.; Dubois, L.; Asnicar, F.; Maharjan, S.; Mailyan, A.; Manghi, P.; Scholz, M.; Thomas, A.M.; et al. Integrating taxonomic, functional, and strain-level profiling of diverse microbial communities with bioBakery 3. Elife 2021, 10, e65088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, D.E.; Lu, J.; Langmead, B. Improved metagenomic analysis with Kraken 2. Genome Biol. 2019, 20, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, A.; Nayfach, S.; Boland, M.; Strozzi, F.; Beracochea, M.; Shi, Z.J.; Pollard, K.S.; Sakharova, E.; Parks, D.H.; Hugenholtz, P.; et al. A unified catalog of 204,938 reference genomes from the human gut microbiome. Nat. Biotechnol. 2021, 39, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksanen, J.S.G.; Blanchet, F.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; Minchin, P.; O’Hara, R.; Solymos, P.; Stevens, M.; Szoecs, E.; Wagner, H.; et al. vegan: Community Ecology Package, R package version 2.6-6.1; R Core Team: Vienna, Austria, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- McMurdie, P.J.; Holmes, S. phyloseq: An R package for reproducible interactive analysis and graphics of microbiome census data. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Zuo, T.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, F.; Zhan, H.; Chan, D.; Leung, T.F.; Yeoh, Y.K.; Chan, F.K.L.; Chan, R.; et al. Underdevelopment of the gut microbiota and bacteria species as non-invasive markers of prediction in children with autism spectrum disorder. Gut 2022, 71, 910–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Chu, Y.; Meng, Q.; Ding, R.; Shi, X.; Wang, Z.; He, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liu, J.; Zhang, J.; et al. A quasi-paired cohort strategy reveals the impaired detoxifying function of microbes in the gut of autistic children. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaba3760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelsalam, N.A.; Hegazy, S.M.; Aziz, R.K. The curious case of Prevotella copri. Gut Microbes 2023, 15, 2249152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedarf, J.R.; Hildebrand, F.; Coelho, L.P.; Sunagawa, S.; Bahram, M.; Goeser, F.; Bork, P.; Wullner, U. Functional implications of microbial and viral gut metagenome changes in early stage L-DOPA-naive Parkinson’s disease patients. Genome Med. 2017, 9, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanauchi, O.; Fukuda, M.; Matsumoto, Y.; Ishii, S.; Ozawa, T.; Shimizu, M.; Mitsuyama, K.; Andoh, A. Eubacterium limosum ameliorates experimental colitis and metabolite of microbe attenuates colonic inflammatory action with increase of mucosal integrity. World J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 12, 1071–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Li, E.; Sun, Z.; Fu, D.; Duan, G.; Jiang, M.; Yu, Y.; Mei, L.; Yang, P.; Tang, Y.; et al. Altered gut microbiota and short chain fatty acids in Chinese children with autism spectrum disorder. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goralczyk-Binkowska, A.; Szmajda-Krygier, D.; Kozlowska, E. The Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis in Psychiatric Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrison, D.J.; Preston, T. Formation of short chain fatty acids by the gut microbiota and their impact on human metabolism. Gut Microbes 2016, 7, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrio, C.; Arias-Sanchez, S.; Martin-Monzon, I. The gut microbiota-brain axis, psychobiotics and its influence on brain and behaviour: A systematic review. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2022, 137, 105640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandhu, K.V.; Sherwin, E.; Schellekens, H.; Stanton, C.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. Feeding the microbiota-gut-brain axis: Diet, microbiome, and neuropsychiatry. Transl. Res. 2017, 179, 223–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cocean, A.M.; Vodnar, D.C. Exploring the gut-brain Axis: Potential therapeutic impact of Psychobiotics on mental health. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2024, 134, 111073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, B.; Yao, J.H.; Lin, X.; Lv, W.Q.; Jiang, L.D.; Wang, Z.Q.; Shen, J.; Xiao, H.M.; Xu, H.; Xu, L.L.; et al. Metagenomic study of the gut microbiota associated with cow milk consumption in Chinese peri-/postmenopausal women. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 957885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Li, H.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, R.; Liu, H.; Sun, Y.; Fan, Y.; Shi, Y.; Qiao, S.; Liu, S.; et al. Multi-omics study reveals that statin therapy is associated with restoration of gut microbiota homeostasis and improvement in outcomes in patients with acute coronary syndrome. Theranostics 2021, 11, 5778–5793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, R.O.; Quinn, G.M.; Umarova, R.; Haddad, J.A.; Zhang, G.Y.; Townsend, E.C.; Scheuing, L.; Hill, K.L.; Gewirtz, M.; Rampertaap, S.; et al. Longitudinal multi-omics analyses of the gut-liver axis reveals metabolic dysregulation in hepatitis C infection and cirrhosis. Nat. Microbiol. 2023, 8, 12–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayeni, F.A.; Sanchez, B.; Adeniyi, B.A.; de Los Reyes-Gavilan, C.G.; Margolles, A.; Ruas-Madiedo, P. Evaluation of the functional potential of Weissella and Lactobacillus isolates obtained from Nigerian traditional fermented foods and cow’s intestine. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2011, 147, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.W.; Park, J.Y.; Jeong, H.R.; Heo, H.J.; Han, N.S.; Kim, J.H. Probiotic properties of Weissella strains isolated from human faeces. Anaerobe 2012, 18, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selle, K.; Klaenhammer, T.R. Genomic and phenotypic evidence for probiotic influences of Lactobacillus gasseri on human health. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 37, 915–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vellanki, S.; Navarro-Mendoza, M.I.; Garcia, A.; Murcia, L.; Perez-Arques, C.; Garre, V.; Nicolas, F.E.; Lee, S.C. Mucor circinelloides: Growth, Maintenance, and Genetic Manipulation. Curr. Protoc. Microbiol. 2018, 49, e53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Ma, Z.; Jiao, M.; Wang, Y.; Li, A.; Ding, S. Effects of Smoking on Inflammatory Markers in a Healthy Population as Analyzed via the Gut Microbiota. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 633242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Meng, F.; Chen, X.; Chang, T.; Huang, H.; He, F.; Zheng, Y. Altered Gut Microbiota as Potential Biomarkers for Autism Spectrum Disorder in Early Childhood. Neuroscience 2023, 523, 118–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernocchi, P.; Del Chierico, F.; Putignani, L. Gut Microbiota Metabolism and Interaction with Food Components. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socala, K.; Doboszewska, U.; Szopa, A.; Serefko, A.; Wlodarczyk, M.; Zielinska, A.; Poleszak, E.; Fichna, J.; Wlaz, P. The role of microbiota-gut-brain axis in neuropsychiatric and neurological disorders. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 172, 105840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomaszek, N.; Urbaniak, A.D.; Baldyga, D.; Chwesiuk, K.; Modzelewski, S.; Waszkiewicz, N. Unraveling the Connections: Eating Issues, Microbiome, and Gastrointestinal Symptoms in Autism Spectrum Disorder. Nutrients 2025, 17, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozcan, E.; Hsiao, E.Y. Are changes in the gut microbiome a contributor or consequence of autism-why not both? Cell Rep. Med. 2022, 3, 100505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Song, B.; Wang, C.; Tang, D.; Li, K.; He, X.; Cao, Y. Diet, microbe, and autism: Cause or consequence? Cell Host Microbe 2022, 30, 5–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yap, C.X.; Henders, A.K.; Alvares, G.A.; Wood, D.L.A.; Krause, L.; Tyson, G.W.; Restuadi, R.; Wallace, L.; McLaren, T.; Hansell, N.K.; et al. Autism-related dietary preferences mediate autism-gut microbiome associations. Cell 2021, 184, 5916–5931.e5917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, L.; Wang, H.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yao, X.; Zhu, G.; Cai, J.; Liu, G.; Liu, X.; Niu, Q.; et al. Effect of oral faecal microbiota transplantation intervention for children with autism spectrum disorder: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Clin. Transl. Med. 2024, 14, e70006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howlin, P.; Moss, P. Adults with autism spectrum disorders. Can. J. Psychiatry 2012, 57, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fusar-Poli, L.; Brondino, N.; Rocchetti, M.; Panisi, C.; Provenzani, U.; Damiani, S.; Politi, P. Diagnosing ASD in Adults Without ID: Accuracy of the ADOS-2 and the ADI-R. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2017, 47, 3370–3379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron-Cohen, S.; Wheelwright, S.; Skinner, R.; Martin, J.; Clubley, E. The autism-spectrum quotient (AQ): Evidence from Asperger syndrome/high-functioning autism, males and females, scientists and mathematicians. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2001, 31, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.; Zhang, Q.; Sun, J.; Li, Q.; Li, D.; Zhu, M.; Fu, X.; Zhao, L.; Wang, M.; Lou, X.; et al. A comparison between children and adolescents with autism spectrum disorders and healthy controls in biomedical factors, trace elements, and microbiota biomarkers: A meta-analysis. Front. Psychiatry 2023, 14, 1318637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| ASD Group (n = 45) | Control Group (n = 45) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | |||
| Median (IQR) | 23 (4) | 25 (4) | 0.004 |
| Gender | |||
| Male | 41 | 40 | 1.000 |
| Female | 4 | 5 | |
| Race | |||
| Chinese | 42 | 37 | 0.268 |
| Malay | 1 | 4 | |
| Indian | 2 | 2 | |
| Others | 0 | 2 | |
| BMI (kg/m2) | |||
| Mean (SD) | 26.0 (8.77) | 24.5 (6.23) | 0.696 |
| Housing type | |||
| 1–3 room government flat | 5 | 2 | 0.466 |
| 4–5 room government flat | 25 | 29 | |
| private flat or landed property | 15 | 14 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ying, J.; Xu, X.; Zhou, R.; Chung, A.C.K.; Ng, S.K.; Fan, X.; Subramaniam, M.; Wong, S.H. The Gut Microbiota in Young Adults with High-Functioning Autism Spectrum Disorder and Its Performance as Diagnostic Biomarkers. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1748. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17111748
Ying J, Xu X, Zhou R, Chung ACK, Ng SK, Fan X, Subramaniam M, Wong SH. The Gut Microbiota in Young Adults with High-Functioning Autism Spectrum Disorder and Its Performance as Diagnostic Biomarkers. Nutrients. 2025; 17(11):1748. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17111748
Chicago/Turabian StyleYing, Jiangbo, Xinran Xu, Ruwen Zhou, Arthur C. K. Chung, Siu Kin Ng, Xiuyi Fan, Mythily Subramaniam, and Sunny H. Wong. 2025. "The Gut Microbiota in Young Adults with High-Functioning Autism Spectrum Disorder and Its Performance as Diagnostic Biomarkers" Nutrients 17, no. 11: 1748. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17111748
APA StyleYing, J., Xu, X., Zhou, R., Chung, A. C. K., Ng, S. K., Fan, X., Subramaniam, M., & Wong, S. H. (2025). The Gut Microbiota in Young Adults with High-Functioning Autism Spectrum Disorder and Its Performance as Diagnostic Biomarkers. Nutrients, 17(11), 1748. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17111748






